PHYS 207.013
Chapter 3
vectors
Instructor: Dr. Bianco
TAs: Joey Betz; Lily Padlow
University of Delaware - Spring 2021



H&R CH3 vectors
0. demo
vectors and scalars
F
H&R CH3 vectors
vectors and scalars
we live in a 3D physical space so quantities that describe how we move within it are typically vectors (but not only!)
1. definition
a vector is a physical quantity with 2 properties: magnitude and direction
H&R CH3 vectors
vectors and scalars
a vector is a physical quantity with 2 properties: magnitude and direction
2. notation
- We draw vectors as arrows with appropriate length and direction specified with respect to a coordinate system
- The length of a vector when drawn corresponds to its magnitude
H&R CH3 vectors
vectors and scalars
a vector is a physical quantity with 2 properties: magnitude and direction
2. notation
- We draw an arrow above a symbol to indicate its a vector
- We sometimes (the book does) use bold font to indicate a symbols refers to a vector
- To refer to the magnitude of the vector we use the absolute value notation
- We sometimes just drop the arrow to refer to the magnitude of the vector
vectors and scalars
a vector is a physical quantity with 2 properties: magnitude and direction
2. notation
- We draw an arrow above a symbol to indicate its a vector
- We sometimes (the book does) use bold font to indicate a symbols refers to a vector
- To refer to the magnitude of the vector we use the absolute value notation
- We sometimes just drop the arrow to refer to the magnitude of the vector
- The direction of the vector is quantified by the angle it makes with the coordinates' axis
- Angles are usually referred to by a greek letter
vectors and scalars

length
time
displacement
mass
pressure
acceleration
acceleration
density
temperature
force
velocity
momentum
H&R CH3 vectors
speed
energy
vectors and scalars

length
time
displacement
mass
pressure
density
temperature
force
velocity
momentum
H&R CH3 vectors
speed
acceleration
energy
vector operations



H&R CH3 vectors



vector sum: the resultant vector from a sum of a series of vectors is the vector that joins the starting point with the ending point
y
the point may be in displacement space, or in velocity space, or in any other vector space

vector operations
H&R CH3 vectors
vy
vx
x
vector sum: the resultant vector from a sum of a series of vectors is the vector that joins the starting point with the ending point
If two vectors start at the same point their sum is the vector resulting by drawing a parallelogram and joining the opposite corners of it
x
y

vector operations
H&R CH3 vectors
vector sum: the resultant vector from a sum of a series of vectors is the vector that joins the starting point with the ending point
vector operations
H&R CH3 vectors
x
y
Properties
Commutative:
vector sum: the resultant vector from a sum of a series of vectors is the vector that joins the starting point with the ending point
Properties
Commutative:
Associative
vector operations
H&R CH3 vectors
x
y
vector sum: the resultant vector from a sum of a series of vectors is the vector that joins the starting point with the ending point
vector subtraction: the sign of a vector relates to its direction
vector operations
H&R CH3 vectors
x
y
Properties
Commutative:
Associative
vector sum: the resultant vector from a sum of a series of vectors is the vector that joins the starting point with the ending point
vector operations
vector sum: the resultant vector from a sum of a series of vectors is the vector that joins the starting point with the ending point
x
y
vector subtraction: the sign of a vector relates to its direction
Properties
Commutative:
Associative
H&R CH3 vectors
x
y
vector component: the component of a vector is its projection along an axis
vector component: the component of a vector is its projection along an axis
vector operations
H&R CH3 vectors
MATH REVIEW:
vector math
vector sum: the sum of 2 vectors reduces to the sum of 2 scalars for each component of the vector
x
x
vector component: the component of a vector is its projection along an axis
H&R CH3 vectors



MATH REVIEW:
vector math
vector sum: the sum of 2 vectors reduces to the sum of 2 scalars for each component of the vector
x
y
vector component: the component of a vector is its projection along an axis
H&R CH3 vectors
MATH REVIEW:
trigonometry
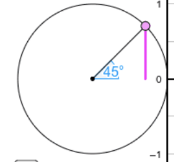
vector component: the component of a vector is its projection along an axis which you can derive using trigonometry
H&R CH3 vectors
https://www.geogebra.org/m/aavMVjyK
MATH REVIEW:
trigonometry
vector component: the component of a vector is its projection along an axis which you can derive using trigonometry
H&R CH3 vectors
things to notice:
the cosine is measure along the x axis
the sine is measure along the y axis
the angles repeat identically after you go 360 degrees around
MATH REVIEW:
trigonometry
vector component: the component of a vector is its projection along an axis which you can derive using trigonometry
H&R CH3 vectors
https://www.geogebra.org/m/aavMVjyK
things to notice:
the cosine is measure along the x axis
the sine is measure along the y axis
the angles repeat identically after you go 360 degrees around
each quadrant has a specific sign for the cosine/sine
Top Right
Bottom Right
Bottom Left
Top Left
MATH REVIEW:
trigonometry

H&R CH3 vectors
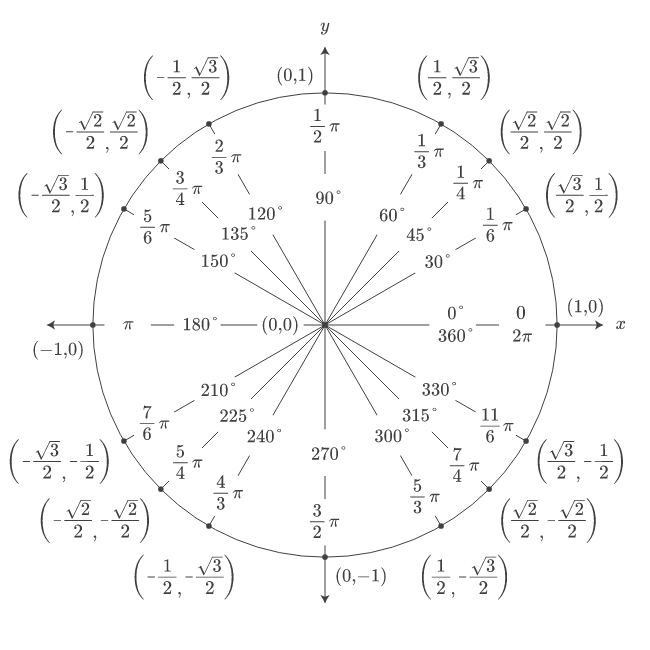
the sine and cosine of some common angles
}
}
H&R CH1 measuring things - including length
MATH REVIEW:
trigonometry


3
MATH REVIEW:
trigonometry
H&R CH3 vectors
useful trig tricks!
MATH REVIEW:
trigonometry
H&R CH3 vectors
useful trig tricks!
MATH REVIEW:
vector math
vector sum: the sum of 2 vectors reduces to the sum of 2 scalars for each component of the vector
x
x
vector component: the component of a vector is its projection along an axis
H&R CH3 vectors



MATH REVIEW:
vector math
vector sum: the sum of 2 vectors reduces to the sum of 2 scalars for each component of the vector
vector component: the component of a vector is its projection along an axis
what sign does cx have?
what sign does cy have?
vector products
- Multiply vector by scalar
- Multiply vector by vector
2.1- Dot product
2.2- Vector product
H&R CH3 vectors
there are 3 kinds of products that involve vectors
vector products
- Multiply vector by scalar
the magnitude of changes by a factor c.
the direction is unchanged
H&R CH3 vectors
the result is a vector
vector products
- Multiply vector by vector : Dot product
the result is a scalar
x
y
H&R CH3 vectors
results is the product of the magnitudes times the product of the cosine of the angle between the vectors
vector products
2. Multiply vector by vector : Dot product
the result is a scalar
x
y
H&R CH3 vectors
results is the product of the magnitudes times the product of the cosine of the angle between the vectors
the result is a scalar
vector products
- Multiply vector by vector : Cross product
the result is a vector
y
x
result is a vector
whose magnitude is the product of the magnitudes times the sin of the angle between the vectors
whose direction is given by the right hand rule
H&R CH3 vectors
vector products
- Multiply vector by vector : Cross product
the result is a vector
y
x
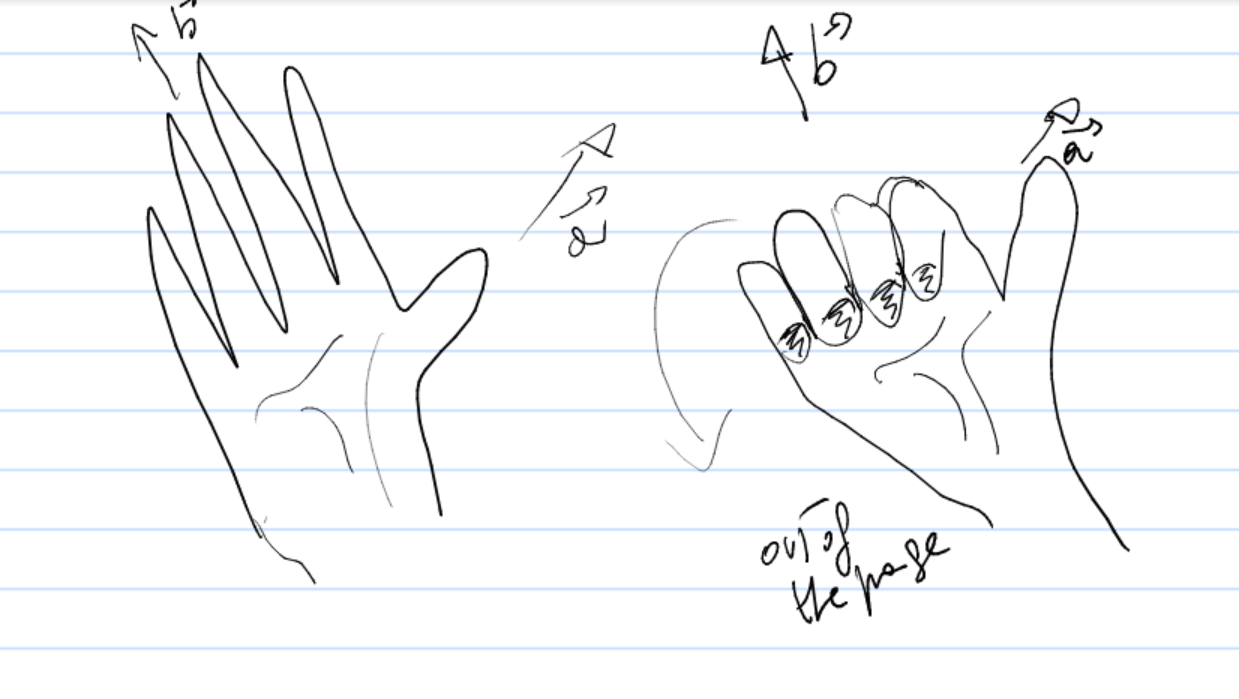
direction perpendicular to the plane of the 2 vectors, following the right hand rule
H&R CH3 vectors
the result is a vector
vector products
- Multiply vector by vector : Cross product
the result is a vector
y
x

direction perpendicular to the plane of the 2 vectors, following the right hand rule
H&R CH3 vectors
the result is a vector
vector products
- Multiply vector by vector : Cross product
the result is a vector
y
x

direction perpendicular to the plane of the 2 vectors, following the right hand rule
let's look at the components:
H&R CH3 vectors



H&R CH3 vectors
demo

vectors and scalars
F
F
F1
F2
}

}
KEY POINTS:


- vectors can be summed geometrically with the parallelogram rule
- vectors can be summed algebraically by splitting them into their components
- the components of a vector are its projections on the coordinate axes


- vectors have 2 properties: magnitude and direction
- the direction of a vector ie measured as the angle it makes counterclockwise with the x axis


- the projections are found with trigonometry
H&R CH3 vectors
KEY POINTS:


- cross product of 2 vectors produces a vector with magnitude that points perpendicularly to the plane of the 2 vectors according to the right hand rule
- vector multiplication with a scalar changes the magnitude of the vector
- dot product of vectors produces a scalar with magnitude

H&R CH3 vectors
KEY POINTS:


- the tangent of an angle is the ration of sin/cosin and this relation can be inverted to measure angles

- the cosine of an angle is its projection on the x axis for a vector of unit magnitude
- the sine of an angle is its projection on the y axis for a vector of unit magnitude

- the tangent of an angle is the ration of sin/cosin and this relation can be inverted to measure angles
- the sum of the square of cosine and sine is equal to 1
H&R CH3 vectors