BUILDING OF A MULTILEVEL SECURITY PLATFORM [PMN]


SUMMARY:
- Companies presentation: DGA & DGA Missile Tests
- Mission context
- Methodology
- Resources
- Production
- Conclusion
GENERAL
DIRECTORATE
FOR
ARMAMENT

DGA - EM : MISSILE TESTING


R&D
Military training
Testing new armaments
Context


ANSSI
Context


ANSSI

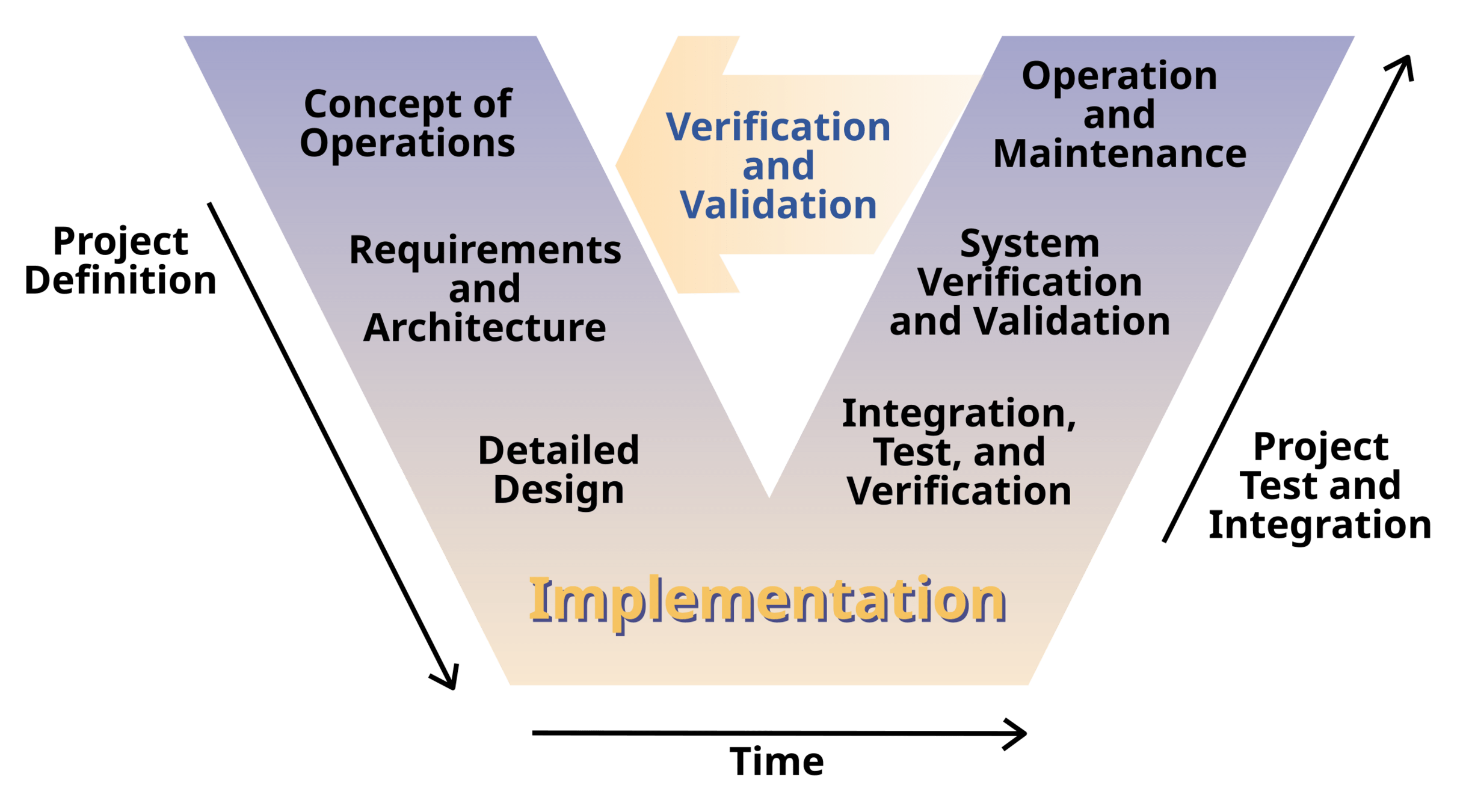
Definition: Multilevel Security
A set of practices, technologies, and policies to protect systems at different classification levels (e.g., Confidential, Secret, Top Secret), relying on compartmentalization and strict access control.
Objective
Develop a functional prototype of the multilevel platform to confirm scalability without loss of functionality.
(Context: a full build would take several years—for example, the Thales Smart Digital Platform took 3+ years.)


Methodology
Milestones
-
Assessment: documentation and state of the art
-
Architecture diagrams
-
Miscellaneous documents: resources, bill of materials, procedures, functional documentation
-
Unit tests
-
Prototype


Resources
People:
-
Technical lead
-
Developer(s)
-
Cybersecurity expert
-
Testers



Resources
Software:
-
GitLab
-
SonarQube
-
Rust / Python
-
Repositories



Resources
Hardware:
-
Secure development environments
-
Servers for multilevel testing


Resources
Hardware:
-
Secure development environments
-
Servers for multilevel testing
Software:
-
GitLab
-
SonarQube
-
Rust / Python
-
Repositories
People:
-
Technical lead
-
Developer(s)
-
Cybersecurity expert
-
Testers
Risks
-
Technical complexity (standards / Rust / cybersecurity scope)
-
Time constraints
-
Real-time constraints
-
Limited resources (single person assigned)
Mitigation strategies: documentation, code reviews, security testing, regular consultations.
Definition: REAL TIME
Real-time constraints: time-bounded requirements where a system’s correctness depends on when results are produced, not only on what they are.
-
Hard: any missed deadline = system failure (e.g., braking control).
-
Firm: late results have zero value; rare misses tolerated.
-
Soft: occasional misses degrade quality only (e.g., video).
Key metrics: deadlines, worst-case execution time (WCET), latency, jitter, determinism/schedulability.
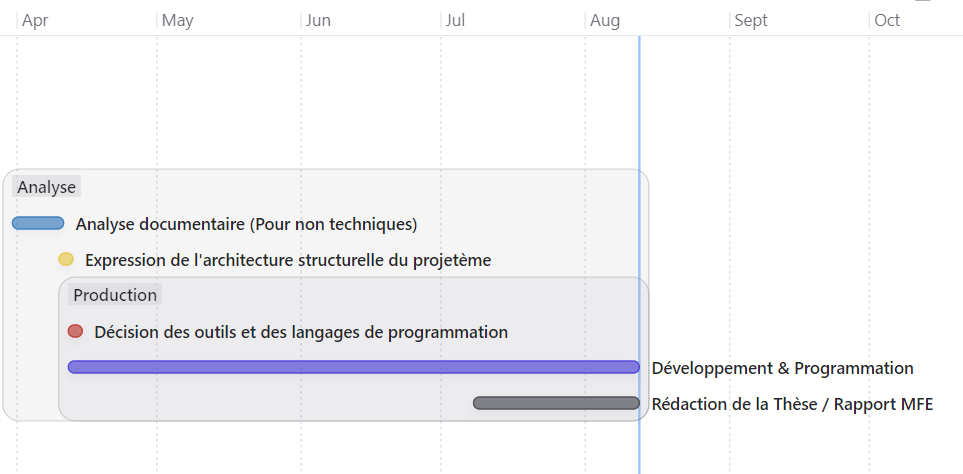
Calendar & Milestones
- Weeks 1-2 : Initialization (analysis & confirmation of the needs)
- Weeks 3-8 : Conception (diagrams, planning)
- Weeks 9-20 : Implementation & Unit tests
- Weeks 21-26 : Assembly
- Weeks 27-30 : Security audit & showcase
- Weeks 31-32 : Final review
Deliverables
-
Assessment: documentation & state of the art
-
Architecture diagrams
-
Supporting documents: resources/infrastructure, bill of materials (BOM), procedures, functional documentation
-
Unit tests
-
Prototype
Objective
Develop a functional prototype of the multilevel platform as a proof of concept.
(Context: a full-scale build would take several years—for example, Thales’s Smart Digital Platform.)
REQUIREMENTS
| 🆔 | 📋 Requirement |
|---|---|
| E1 | Filter non-compliant packets |
| E2 | Inspect packet content |
| EA1 | Passively and centrally log application activity |
| EA2 | Verify the authenticity of packets |
| EA3 | Verify the integrity of packets |
| EM1 | Ensure real-time performance (< 10 ms response time) |
| EI1 | Adhere to secure development standards (state of the art) |
What
have
been done
Calendar & Milestones
- Weeks 1-2 : Initialization (analysis & confirmation of the needs)
- Weeks 3-8 : Conception (diagrams, planning)
- Weeks 9-20 : Implementation & Unit tests
- Weeks 21-26 : Assembly
- Weeks 27-30 : Security audit & showcase
- Weeks 31-32 : Final review
Calendar & Milestones
Documentary ANALYSIS
Documents studied :
- The ANSSI guide on the development of a multilevel architecture
- NATO's metadata system standard
- DO-178C on securing critical systems
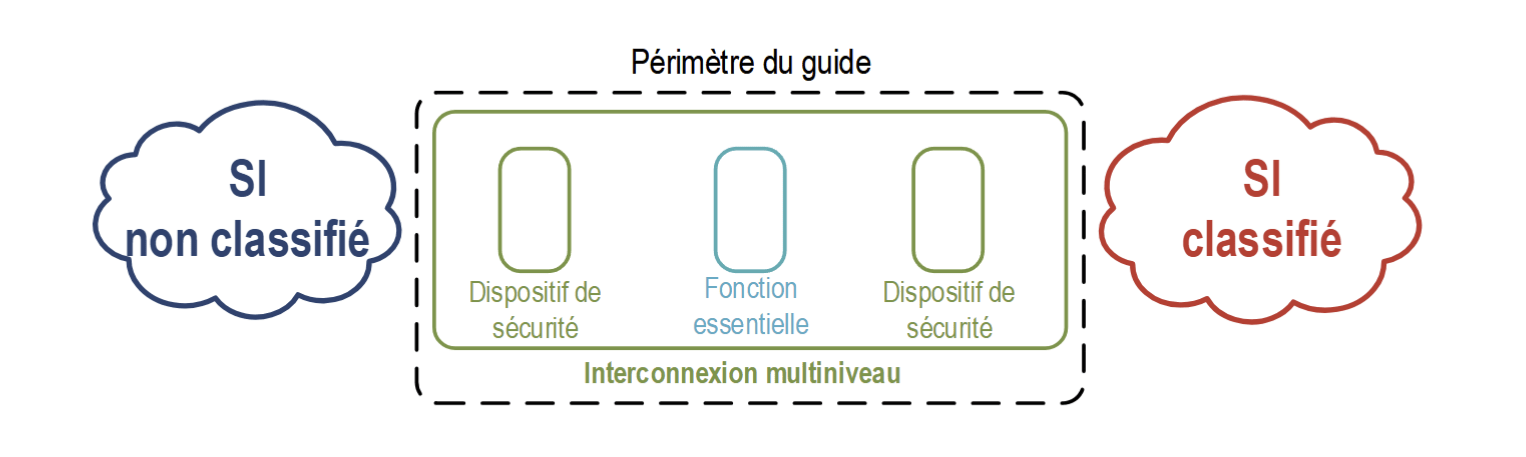
Document ANALysis: GUIDE ON THE DEVELOPMENT OF A MULTILEVEL ARCHITECTURE
Note:
The National Cybersecurity Agency is the national authority for cybersecurity and cyber defense in France. The purpose of ANSSI is to build and organize, in an inter-ministerial manner, the protection of the Nation against cyberattacks, and to contribute to the stability of cyberspace.

ANSSI
Document ANALysis: GUIDE ON THE DEVELOPMENT OF A MULTILEVEL ARCHITECTURE
Definitions :
- IS : Information System, a group of organized resources (software / hardware / HR)
- Metadata : Metadata is data that describes other data like author, date, format, and keywords to enable organization, discovery, and management.
Document ANALysis: GUIDE ON THE DEVELOPMENT OF A MULTILEVEL ARCHITECTURE
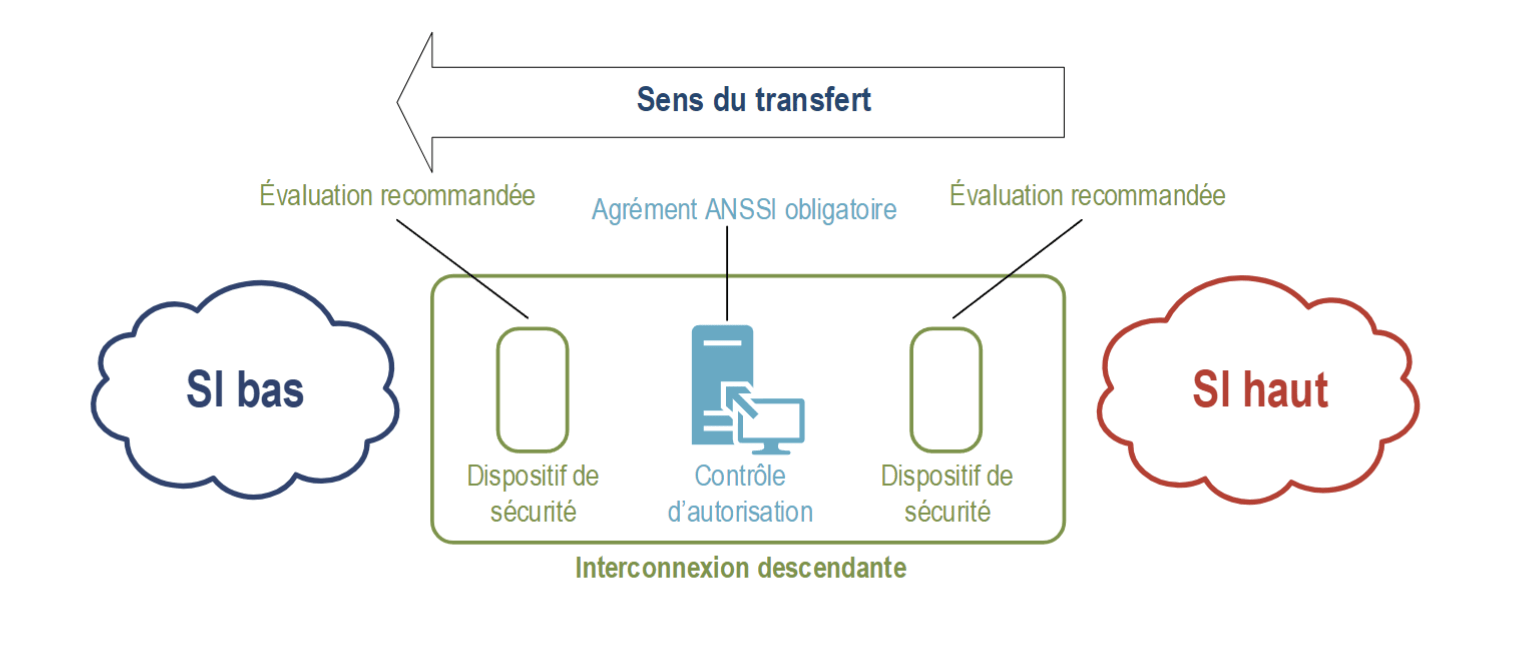
Document ANALysis: GUIDE ON THE DEVELOPMENT OF A MULTILEVEL ARCHITECTURE
Document ANALysis: GUIDE ON THE DEVELOPMENT OF A MULTILEVEL ARCHITECTURE

Document ANALysis: GUIDE ON THE DEVELOPMENT OF A MULTILEVEL ARCHITECTURE

??


??

OK
Document ANALysis: GUIDE ON THE DEVELOPMENT OF A MULTILEVEL ARCHITECTURE




Document ANALysis: GUIDE ON THE DEVELOPMENT OF A MULTILEVEL ARCHITECTURE

Document ANALysis: NATO's metadata system standard



[]
Document ANALysis: NATO's metadata system standard
[]
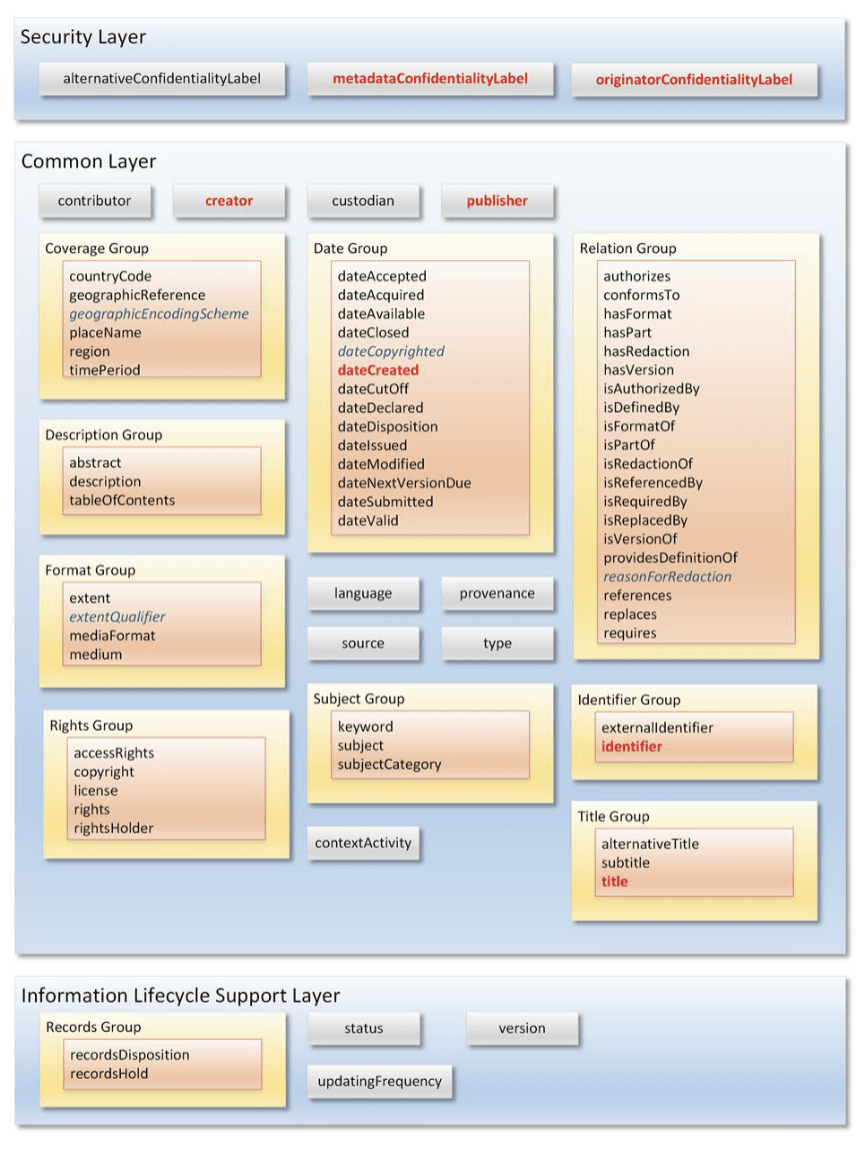
SPIF
Document ANALysis: NATO's metadata system standard
[]

Document ANALysis: NATO's metadata system standard
[]
MetaConfidentiality => confidentiality level Hash
originatorConfidentiality => Launch & Context Hash
Document ANALysis: NATO's metadata system standard
[]
1
2
Document ANALysis: NATO's metadata system standard
[]



Private
1
2
Public
Document ANALysis: NATO's metadata system standard
[]

1
2

Public

Private


Public

Public

Private

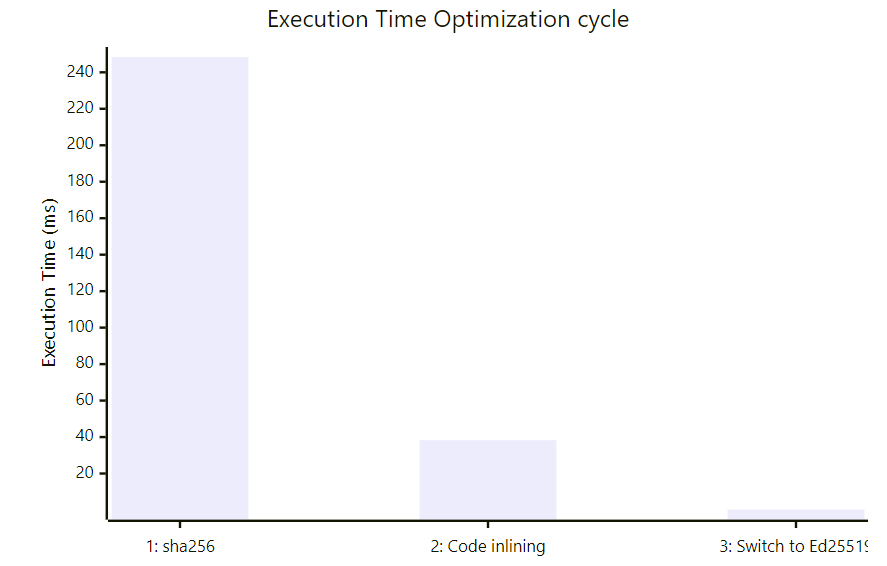
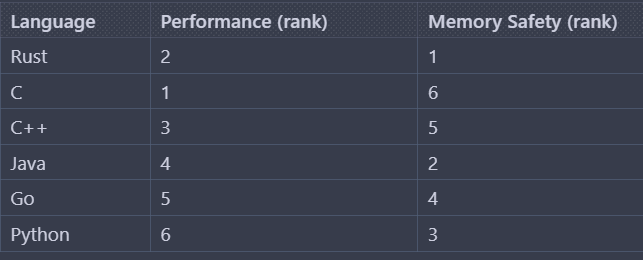
Choice of PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE

The SIMULATOR


The SIMULATOR

- Customizable data layout
- Include simulation data ( Time / position ...)
- Easy to use
the encapsulator & THE PMN
DATA


Metadata
BENCHMARKING