Introduction
to
Kubernetes
Before we begin
Organizational stuff
Contract
- Ask about anything!
- Make notes!
- Do your exercises, and we can guarantee you will gain understanding of how things works
- If you feel you need a break, tell us!
Introduction
Goal of the workshop
Big bang theory






If you can’t feed a team with two pizzas, it’s too large. That limits a task force to five to seven people, depending on their appetites
Jeff Bezos
A bit lasagna and ravioli
Modern one





Deployment
Kubernetes
- From Greek, meaning helmsman or pilot
- Does not limit the types of applications supported
- Does not deploy source code and does not build your application
- Does not provide application-level services
- Does not dictate logging, monitoring, or alerting solutions
- Does not provide nor mandate a configuration language/system
- Does not provide nor adopt any comprehensive machine configuration, maintenance, management, or self-healing systems
K8s
- What's k8s?
K8s
- Where do you know it is used?
- Where can you use it?
- Who uses it?
- ...
WHY not K8s?
K8S - main concepts
Ubiquitous Language
Birds-eye view
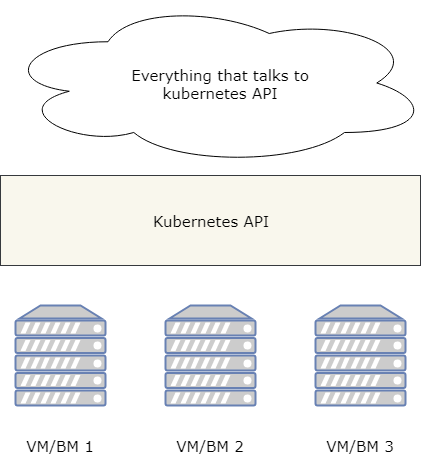
Main blocks of K8S
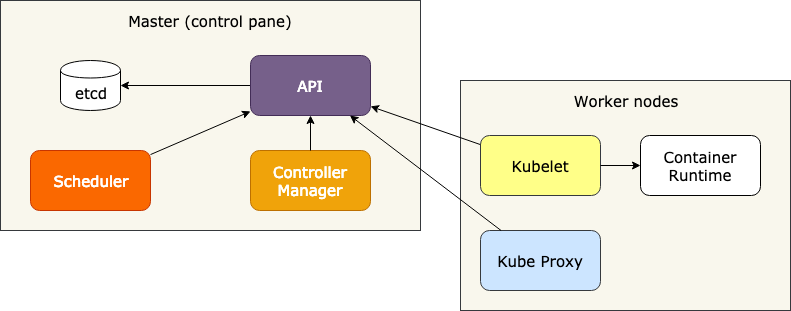
Master Node
- API - RESTful API used by all components to communicate
- Scheduler - assign nodes to deployable components
- Controller Manager - performs cluster-wide operations like, registering new nodes, or replicating components
-
etcd - key-value store keeping the current state of the application and configuration. Only API talks toetcd .
Worker Node
- Kubelet - is responsible for everything that runs on worker node, this is the only component that needs to be executed as binary on node, all others might be deployed over kubernetes as part of kubernetes (🤯)
- Kube Proxy - responsible for providing network access to containers in the cluster
- Container Runtime - shim over different container technologies like Docker or rkt
One API to rule them all
- Core of K8S is REST API
- This API is consumed by
- Dashboard (UI) - clickable
- kubectl (CLI) - imperative
- and all k8s main components and more
K8S - dictionary
Quick guide to awesomnes
Pod
- Smallest unit in kubernetes
- Pod is a running application but with a twist
- Name pod comes from word play - docker whale in logo used to be in a pod... so something that have a "whale" is a pod
- One Pod can have one ore many containers
- Containers are not limited to Docker
Pods are ephemeral
this is a twist

Pods are cattle
pets vs cattle (another twist)


Pod
what exactly happens when execute create?
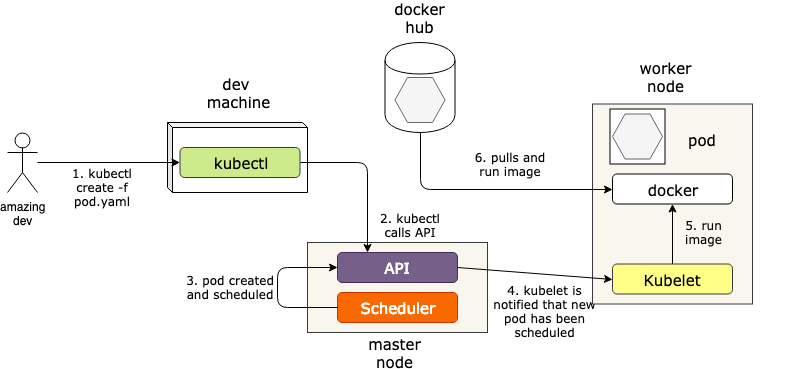
ReplicaSet
- Manage instances of Pods
- Ensures that X number of Pods are up and running
- Its not responsible for updating Pods or issuing new version of the Pods
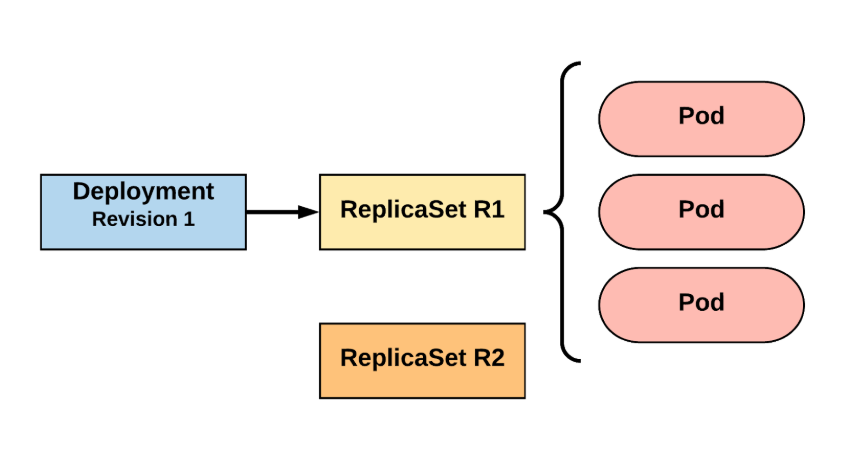
Deployment
- Manage instances of ReplicaSet
- Ensures that ReplicaSet is up and running
- When Pod definition changes, its responsible for roll new Pod definition using ReplicaSet
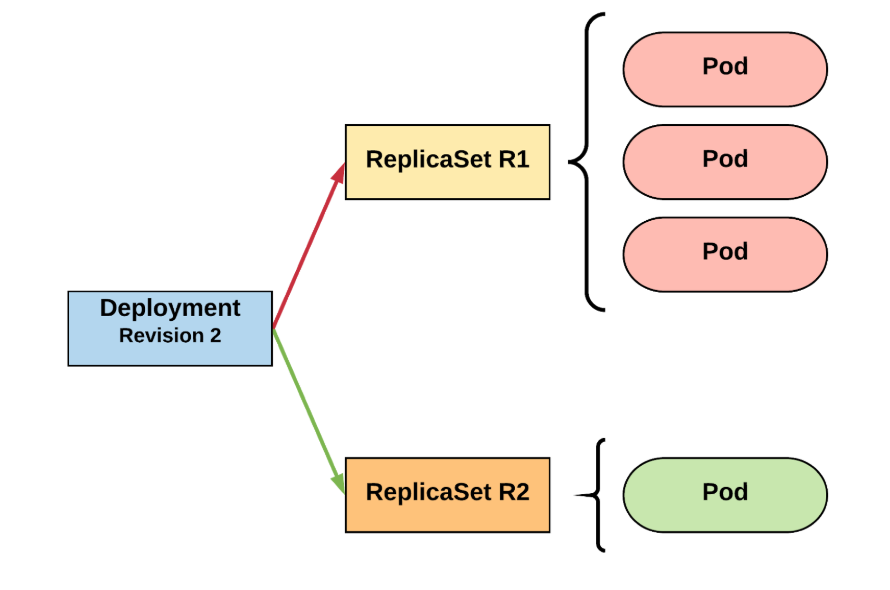
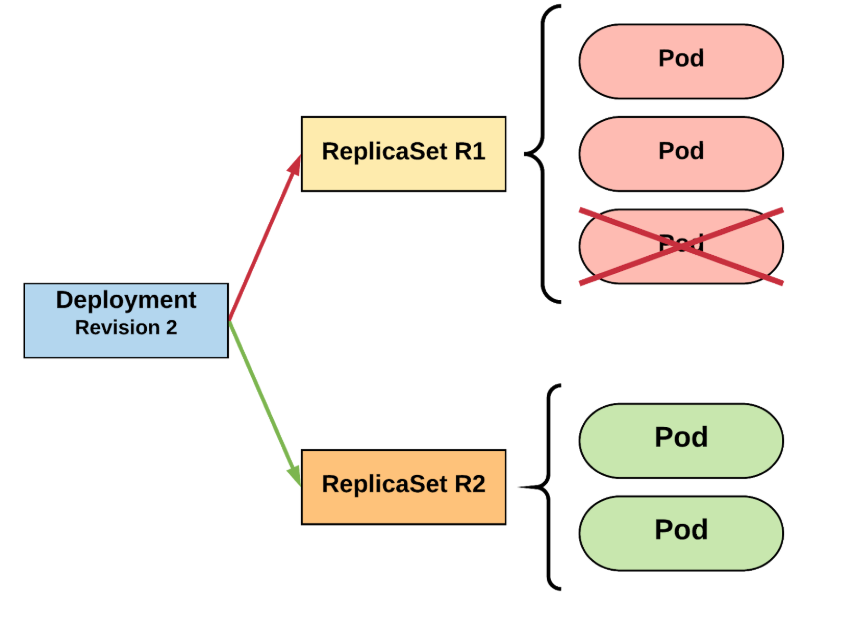
- By default, to deployments are possible (:
- recreate - delete all and create everything again
- rolling update - granularity deletes one pod and creates new one
- this is achieved by manipulating ReplicaSet parameters
RollingUpdate
RollingUpdate
RollingUpdate
RollingUpdate
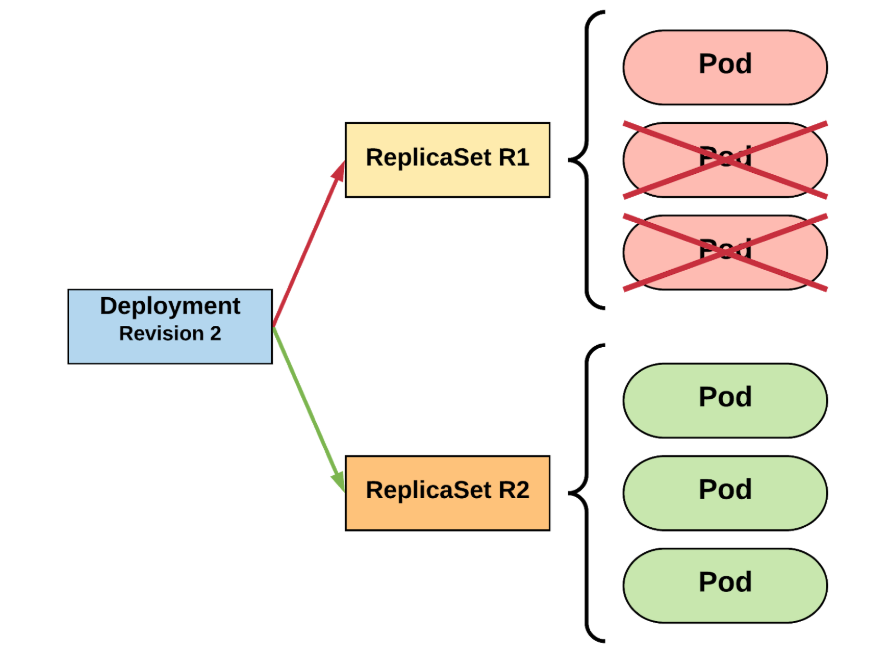
RollingUpdate
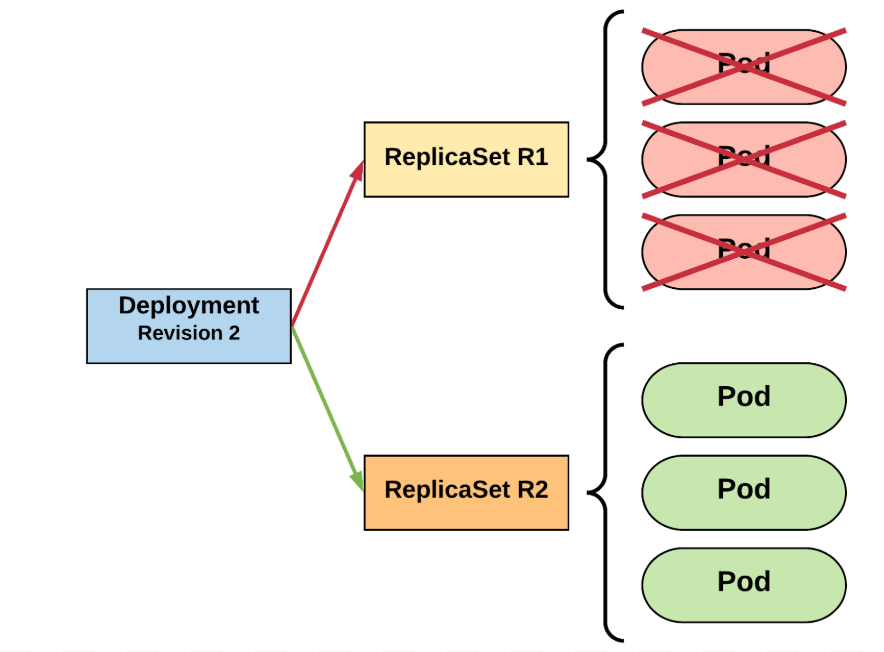
RollingUpdate
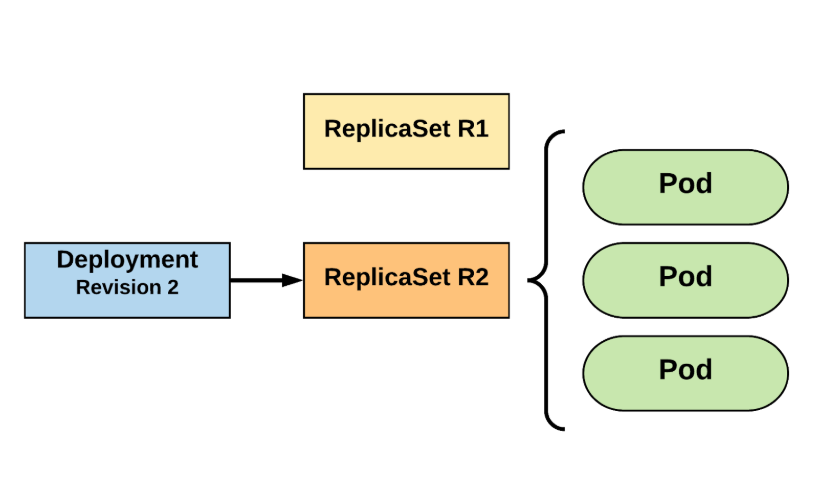
Services
- Abstract thing that expose group of Pods to internal or external network
- Pods are selected based on Label selection
- It creates DNS name for group of Pods that we can use, i.e. like in good old times we did on IIS, this app.name.corp will be used to access this app
- It creates virtual IP for group of Pods - its quite important, we can't ping virtual IP!
Services
- There are three types of services, each another one builds on top of previous one:
- ClusterIP - add's internal virtual IP address so Pods can be access inside cluster
- NodePort - extends ClusterIP with opening external port on each VM/BM, so application is accessible externally by going to VM/BM IP adress:OPENED_PORT
- LoadBalancer - extends NodePort and connects to external Load Balancer
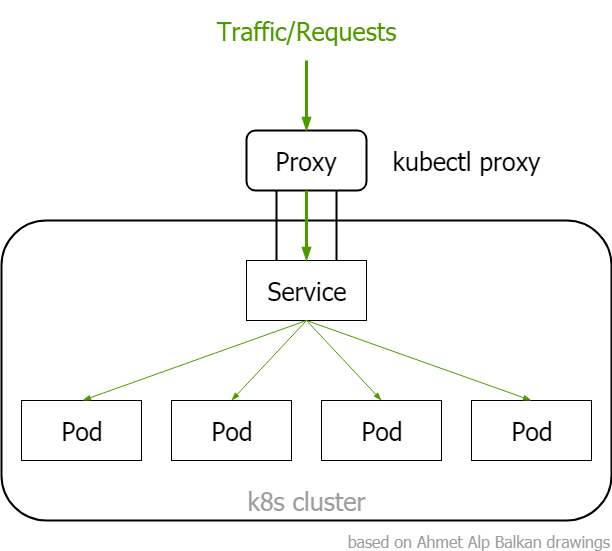
Services
ClusterIP
Services
ClusterIP (how it works)
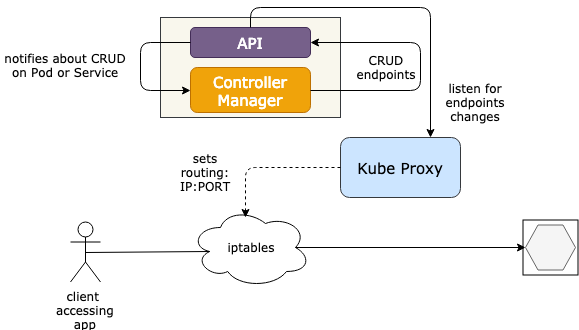
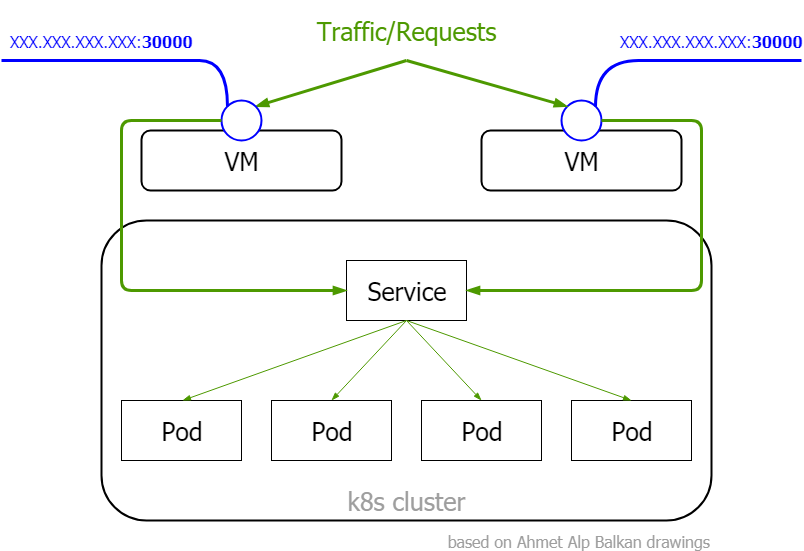
Services
NodePort
Services
LoadBalancer
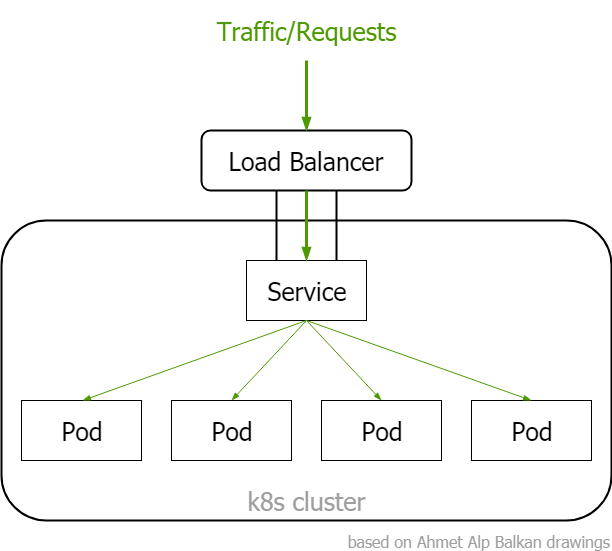
Services
LoadBalancer
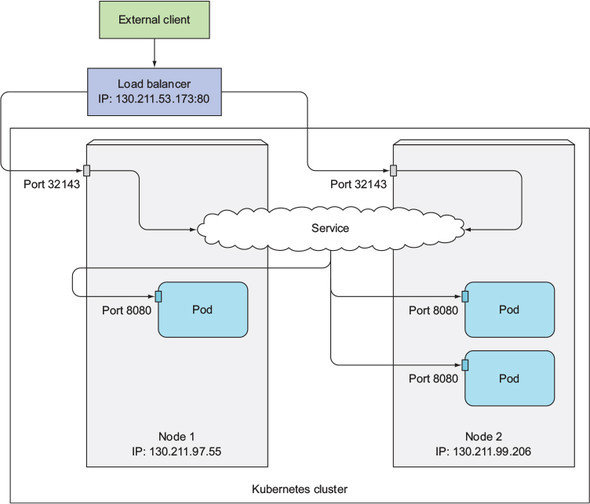
k8s in action, manning
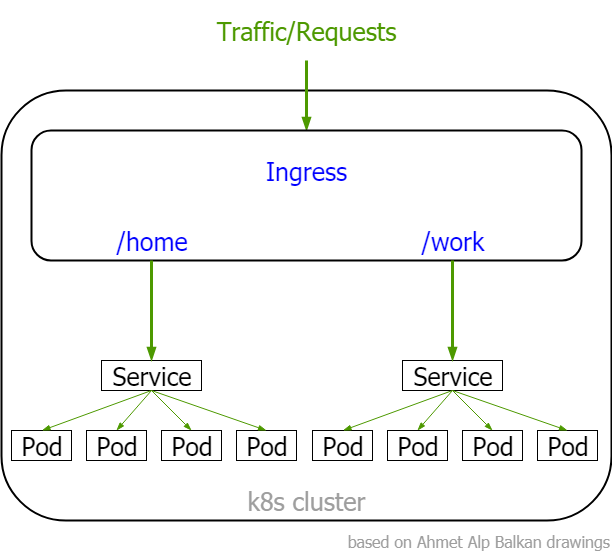
Services
Ingress - special type, needs to be installed
Other (not all) resources
- Namespaces - groups Pods, Services, Deployments etc. Can be used for dev, test, prod or per user basis so my user will only see my pods.
- Endpoints - mapping between IP's and ports
- ConfigMap - key/value configuration
- Secret - key/value configuration base64 encoded
Common commands
kubectl
kubectl explain
- explain what specific resource is
- nice help, not really useful later on
# what is node
kubectl explain node
# what is pod
kubectl explain pod
kubectl explain pod.spec
kubectl explain pod.spec.containers
kubectl explain pod.spec.containers.command
# what is service
kubectl explain service
# what is RESOURCE_NAME
kubectl explain RESOURCE_NAME
kubectl get|describe
- display details of resource
# get status information about all nodes
$ kubectl get node
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
NODE_NAME-0 Ready agent 25d v1.11.3
NODE_NAME-1 Ready agent 25d v1.11.3
NODE_NAME-3 Ready agent 25d v1.11.3
# get status information about single node
$ kubectl get node NODE_NAME
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
NODE_NAME Ready agent 25d v1.11.3
# get status information about single RESOURCE (pod, service...)
$ kubectl get RESOURCE RESOURCE_NAME
# get details about node
$ kubectl describe node NAME
# get node yaml representation
$ kubectl get node NAME -o yamlPod
deployment
# create pod from file
kubectl create -f pod.yaml
# create pod and save base configuration so it can be used later by apply
kubectl create -f pod.yaml --save-config=true
# create pod or update if exists
kubectl apply -f pod.yaml
# replace pod
kubectl replace -f pod.yaml
# get the current pod definition
kubectl get pod NAME -o yaml|json
Pod
delete
# deletes pod described in file
$ kubectl delete -f pod.yaml
# delete pod of name
$ kubectl delete pod POD_NAMEPod
how to access pod from the command line
# allowing access to the pod by url http://127.0.0.1:8888
kubectl port-forward pod/NAME 8888:pod_container_port
# accessing container in pod/running app in container
kubectl exec -it POD_NAME bash
kubectl exec -it POD_NAME -c container_name bash
kubectl exec POD_NAME -- cmd -p1 -p2
kubectl exec POD_NAME cmd
# and
kubectl proxyLabels
# adding
kubectl label pod NAME key1=value1 key2=value2
# changing
kubectl label pod NAME key1=newValue --overwriteServices
kubectl
# get services
kubectl get service
kubectl get services
kubectl get svc
NAMESPACE NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
default kubernetes ClusterIP 10.0.0.1 <none> 443/TCP 97d
default my-svc NodePort 10.0.18.147 <none> 8080:31238/TCP 97d
default my-second-svc NodePort 10.0.45.201 <none> 8080:32245/TCP 97d
# removes service
kubectl delete svc NAME
# create/update service
kubectl apply -f service.yamlDeployments
kubectl
# create/update deployment
kubectl apply -f deployment.yaml
# create/update deployment and keep track of operations
kubectl apply -f deployment.yaml --record=true
# get all deployments
kubectl get deployments
kubectl get deployment
kubectl get deploy
# get replica sets
kubectl get rsDeployments
managing deployments from kubectl
# return status of current deployment
# this waits if the status is not finished
$ kubectl rollout status deployment/NAME
# get a history of rollout's
$ kubectl rollout history deployment/NAME
# get history details of rollout N
$ kubectl rollout history deployment/NAME --revision=N
# undo rollout
$ kubectl rollout undo deployment/NAMEkubectl run
- runs particular images (pod)
- creates deployment for for managing pod
- will be removed in next versions of K8S
# create deployment with pod and one replicaset
kubectl run NAME --image gutek/dumpster:v1
# create 5 replicas
kubectl run NAME --image gutek/dumpster:v2 --replicas=5
# run pod that will be removed once done
kubectl run -it NAME --image=some/img --rm --restart=Never -- curl http://onet
# we can use different generators
# only pod
kubectl run NAME --image=some/img --generator=run-pod/v1
# deployment
kubectl run NAME --image=some/img --generator=extensions/v1beta1- good for quick demos
kubectl set
- updates particular property of the resource
# List the environment variables defined on all pods
kubectl set env pods --all --list
# Update all containers in all replication controllers in the project to have ENV=prod
kubectl set env deploy --all ENV_VAR=VALUE_1
# Set a deployment's container image to 'nginx:1.9.1'
kubectl set image deployment/DEPLOYMENT_NAME CONTAINER_NAME=nginx:1.9.1- whenever you do this, always! update yaml to have that changes included
- rule: don't do it on production... unless your boss asks you to do this ;)
kubectl scale
- manually scale instances of pod manage by ReplicaSet and/or deployment
# scale to 3 replicas deployment of name DEPLOYMENT_NAME
$ kubectl scale --replicas=3 deployment/DEPLOYMENT_NAME
# scale to 3 replicas ReplicaSet of name RS_NAME
$ kubectl scale --replicas=3 rs/RS_NAME- when needed can save ass
- always analyze why you needed to use scale manually
kubectl expose
- expose resource (pod, deployment, replicates etc.) as new service
# create service of type NodePort
# for deployment hello-minikube
# and name it front-minikube
kubectl expose deployment hello-minikube --type=NodePort --name=front-minikube
# create service of type NodePort
# for pod POD_NAME
# and name it POD_NAME_svc
kubectl expose pod POD_NAME --type=NodePort --name=POD_NAME_svc
helm
helm
- Package manager for k8s
- Allows installing packages as well as packaging our own solution as "deployable package"
- helm installation is simple as kubectl - binary file
# check
$ helm version
# linux
$ sudo snap install helm --classic
# mac
brew install kubernetes-helm
# win
choco install kubernetes-helm
# or by visual studio code kubernetes pluginhelm
basic commands
# initialize helm usage
$ helm init
# refresh repo
$ helm repo update
# list all installed packages
$ helm list
# list all even deleted pacakges
$ helm list --all
# uninstall package but keep it locally
$ help delete NAME
# remove deleted pacakges completly
$ helm del --purge NAME
# install package
$ help install channel/package-nameDesign Patterns
multi container systems
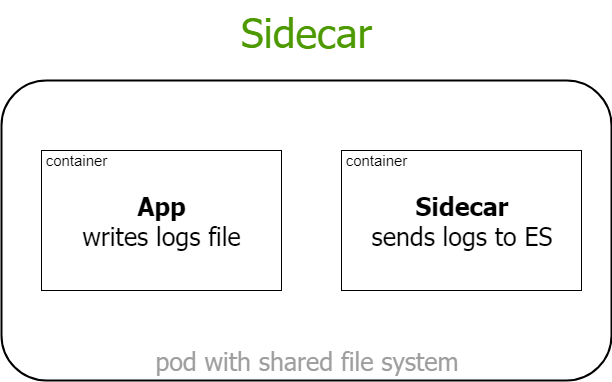
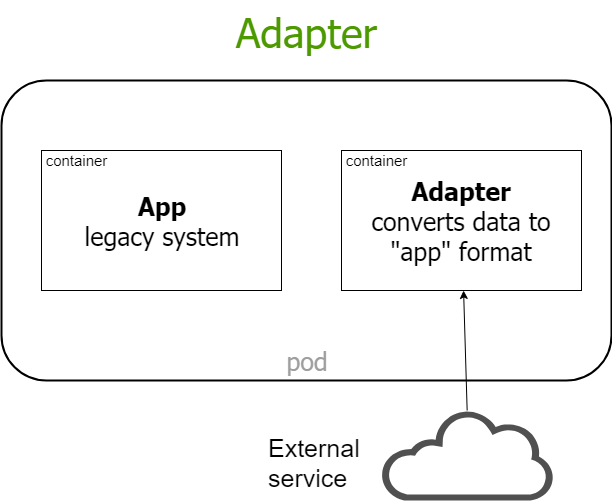
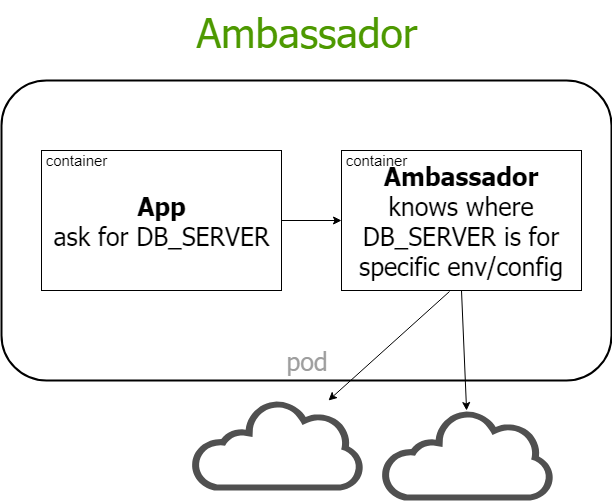

Jeszcze nie koniec
Do domu