Assignment 2
Tuesday 9/23
Wednesday 9/24

Field Trips




Manning College of Nursing
10/9
10/14
Thursday
Tuesday
by Tuesday 9/30!
CS460 Computer Graphics - University of Massachusetts Boston
Assignment 3
Due 10/2!


var geometry = new THREE.Geometry();
geometry.vertices.push(
new THREE.Vector3(-10, 10, 0),
new THREE.Vector3(-10, -10, 0),
new THREE.Vector3(10, -10, 0)
);
geometry.faces.push( new THREE.Face3(0, 1, 2));


GPU

Vertex Shader
Fragment Shader

Viewport
From 3D..
..to 2D
vertex coordinates X Y Z
screenspace coordinates X Y
Vertices
Face
Rasterization
The Rendering Pipeline


it will be more clear later!!
From 3D to 2D
From 2D to 3D?
Unprojecting...



0, 0
width, height

renderer.domElement.onclick = function(e) {
pixel_coords = new THREE.Vector2(e.clientX, e.clientY);
};400, 200
400 , 200
Screen Space Coordinates

-1, -1

renderer.domElement.onclick = function(e) {
pixel_coords = new THREE.Vector2( e.clientX, e.clientY );
vp_coords = new THREE.Vector2(
( pixel_coords.x / window.innerWidth ) * 2 - 1, // X
- ( pixel_coords.y / window.innerHeight ) * 2 + 1 ); // Y
};-0.2, 0.3
-0.2
Viewport Coordinates
1, 1
0, 0
0.3

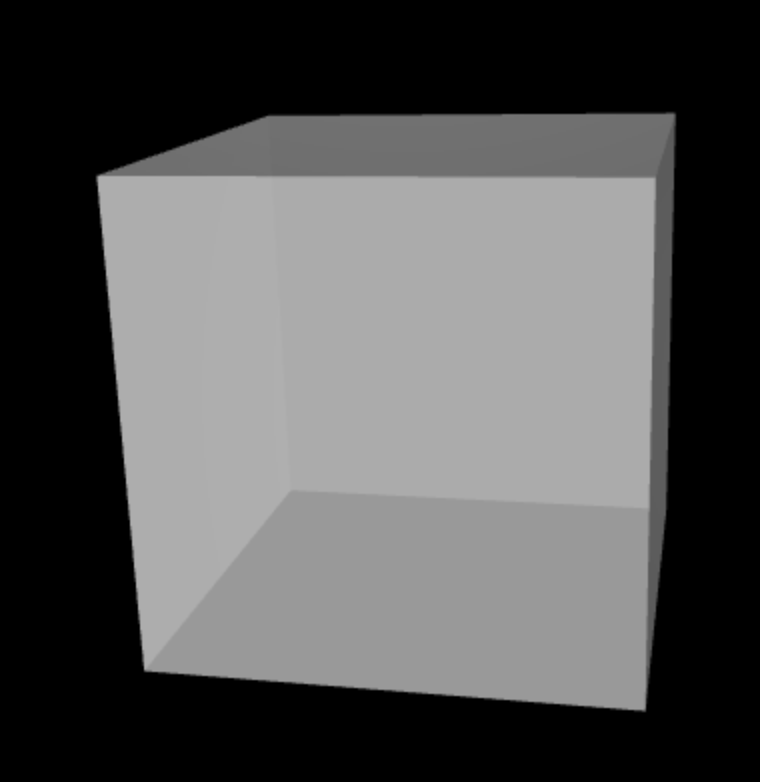
zNear
zFar

Ray
2D Click can be mapped to any
point on the 3D Ray


zNear
zFar

Ray
2D Click can be mapped to any
point on the 3D Ray
But we know the exact
position on zNear!
renderer.domElement.onclick = function(e) {
pixel_coords = new THREE.Vector2( e.clientX, e.clientY );
vp_coords = new THREE.Vector2(
( pixel_coords.x / window.innerWidth ) * 2 - 1, // X
- ( pixel_coords.y / window.innerHeight ) * 2 + 1 ); // Y
vp_coords_3d_near = new THREE.Vector3(vp_coords.x,
vp_coords.y,
0); // for zNear
};Towards 3D Coordinates
This is not 3D yet!
THREE.Raycaster


zNear
zFar

Ray
Position (x,y,z)

needs 2 points to define Ray
raycaster = new THREE.Raycaster();
raycaster.setFromCamera(vp_coords_near, camera);
zNear

Ray
Position (x,y,z)

Invisible Plane
intersects = raycaster.intersectObject( );
zNear

Ray
Position (x,y,z)

Invisible Plane
intersects = raycaster.intersectObject( );geometry = new THREE.PlaneBufferGeometry( 10000, 10000 );
material = new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial( {
visible: false
});
invisible_plane = new THREE.Mesh( geometry, material );
scene.add( invisible_plane );intersects = raycaster.intersectObject( invisible_plane );
console.log( intersects[0].point.x, intersects[0].point.y, intersects[0].point.z );( 0, 0, 0 )
Ray + Object
<html>
<head>
<style>
html, body {
background-color:#000;
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
height: 100%;
overflow: hidden !important;
}
</style>
<script async src="https://unpkg.com/es-module-shims@1.6.3/dist/es-module-shims.js"></script>
<script type="importmap">
{
"imports": {
"three": "https://unpkg.com/three@latest/build/three.module.js",
"three/addons/": "https://unpkg.com/three@latest/examples/jsm/"
}
}
</script>
<script type="module">
import * as THREE from 'three';
import { OrbitControls } from 'three/addons/controls/OrbitControls.js';
var renderer, controls, scene, camera;
window.onload = function() {
// Three.js code goes here
scene = new THREE.Scene();
// setup the camera
var fov = 75;
var ratio = window.innerWidth / window.innerHeight;
var zNear = 1;
var zFar = 10000;
camera = new THREE.PerspectiveCamera( fov, ratio, zNear, zFar );
camera.position.set(0, 0, 100);
// create renderer and setup the canvas
renderer = new THREE.WebGLRenderer({ antialias: true });
renderer.setSize( window.innerWidth, window.innerHeight );
document.body.appendChild( renderer.domElement );
renderer.domElement.onclick = function( e ){
console.log('Yay! We clicked!');
var pixel_coords = new THREE.Vector2( e.clientX, e.clientY );
console.log('Pixel coords', pixel_coords);
var vp_coords = new THREE.Vector2(
( pixel_coords.x / window.innerWidth ) * 2 - 1, //X
-( pixel_coords.y / window.innerHeight ) * 2 + 1) // Y
console.log('Viewport coords', vp_coords);
var vp_coords_near = new THREE.Vector3( vp_coords.x, vp_coords.y, 0);
var raycaster = new THREE.Raycaster();
raycaster.setFromCamera(vp_coords_near, camera);
var intersects = raycaster.intersectObject(invisible_plane);
console.log('Ray to Invisible Plane', intersects[0].point);
// update cube position
cube.position.set(intersects[0].point.x, intersects[0].point.y, intersects[0].point.z);
};
// setup lights
var ambientLight = new THREE.AmbientLight();
scene.add( ambientLight );
var light = new THREE.DirectionalLight( 0xffffff, 5.0 );
light.position.set( 10, 100, 10 );
scene.add( light );
// configure cube
var geometry = new THREE.BoxGeometry( 20, 20, 20 );
var material = new THREE.MeshStandardMaterial({ color: 0xffffff, wireframe: true });
var cube = new THREE.Mesh( geometry, material );
scene.add( cube );
//
// The invisible plane
//
geometry = new THREE.PlaneGeometry( 10000, 10000 );
material = new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial( {
visible: false
});
var invisible_plane = new THREE.Mesh( geometry, material );
scene.add( invisible_plane );
//
//
//
// interaction
controls = new OrbitControls( camera, renderer.domElement );
// call animation/rendering loop
animate();
};
function animate() {
requestAnimationFrame( animate );
// and here..
controls.update();
renderer.render( scene, camera );
};
</script>
</head>
<body></body>
</html>
This is also Assignment 03 starter code!
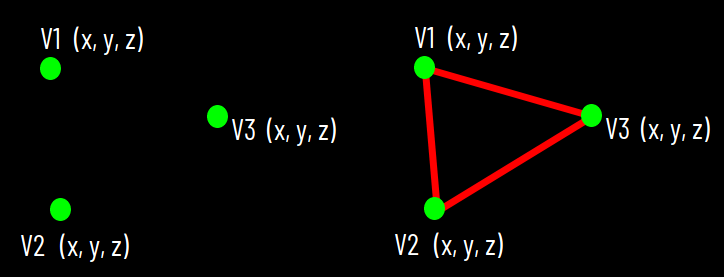
V1
V2
(x, y, z)
(x, y, z)
V3
(x, y, z)
V1
V2
(x, y, z)
(x, y, z)
V3
(x, y, z)




var geometry = new THREE.Geometry();
geometry.vertices.push(
new THREE.Vector3(-10, 10, 0),
new THREE.Vector3(-10, -10, 0),
new THREE.Vector3(10, -10, 0)
);
geometry.faces.push( new THREE.Face3(0, 1, 2));Graphics Processing Unit (GPU)
Vertex Shader
3D World
Shape Assembly
Perspective Projection
V1
V2
V3




var geometry = new THREE.Geometry();
geometry.vertices.push(
new THREE.Vector3(-10, 10, 0),
new THREE.Vector3(-10, -10, 0),
new THREE.Vector3(10, -10, 0)
);
geometry.faces.push( new THREE.Face3(0, 1, 2));Graphics Processing Unit (GPU)
Vertex Shader
Fragment Shader

3D World
2D Space
Rasterization

Colorization



Blending
Frame Buffer / Viewport


var geometry = new THREE.Geometry();
geometry.vertices.push(
new THREE.Vector3(-10, 10, 0),
new THREE.Vector3(-10, -10, 0),
new THREE.Vector3(10, -10, 0)
);
geometry.faces.push( new THREE.Face3(0, 1, 2));


GPU

Vertex Shader
Fragment Shader

Viewport
From 3D..
..to 2D
vertex coordinates X Y Z
screenspace coordinates X Y
Shaders
GLSL

A rather complex example of shaders:
Vertex Shader
Fragment Shader


Vertex Shader

attribute vec4 a_position;
void main() {
gl_Position = a_position;
}This shader does nothing besides passing through positions.
Vertex Shader

attribute vec4 a_position;
void main() {
gl_Position = a_position;
}This shader does nothing besides passing through positions.
data is different for each vertex!
(x, y, z, w)
(x, y, z, 1.)
name
Vertex Shader

attribute vec4 a_position;
void main() {
gl_Position = a_position;
}This shader does nothing besides passing through positions.
gl_Position is the output of any vertex shader
Fragment Shader
precision mediump float;
void main() {
gl_FragColor = vec4(1., 1., 1., 1.);
}This shader colors every fragment (pixel) white.

Fragment Shader
precision mediump float;
void main() {
gl_FragColor = vec4(1., 1., 1., 1.);
}This shader colors every fragment (pixel) white.

defines the number of decimals for every value
Fragment Shader
precision mediump float;
void main() {
gl_FragColor = vec4(1., 1., 1., 1.);
}This shader colors every fragment (pixel) white.

every fragment shader outputs a color for
the current fragment / pixel.
Fragment Shader

Vertex Shader

gl_Position
gl_FragColor
for every vertex
for every pixel
gl_PointSize
Shader Input Types
attribute: changes per vertex
uniform: changes per draw call
varying: transfer info to fragment shader
Fragment Shader

Shader Art



easy
hard
XTK
Three.js
WebGL
limited
freedom
Complexity
Functionality
XTK
X.renderer3D
X.cube
Three.js
THREE.WebGLRenderer
THREE.Scene
THREE.TrackballControls
THREE.PerspectiveCamera
THREE.AmbientLight
THREE.DirectionalLight
WebGL
gl.viewport
gl.createShader
gl.shaderSource
gl.compileShader
gl.getShaderInfoLog
gl.createProgram
gl.attachShader
gl.linkProgram
gl.useProgram
gl.createBuffer
gl.bindBuffer
gl.BufferData
gl.getAttribLocation
gl.vertexAttribPointer
gl.enableVertexAttribArray
gl.clearColor
gl.clear
gl.drawArrays
THREE.Geometry
THREE.Material
THREE.Mesh



1. Initialize WebGL
2. Shaders
3. Create Geometry
4. Connect Shader with Geometry
5. Draw!
1. Initialize WebGL
setup Canvas
setup GL Context
gl = c.getContext( 'webgl' );c = document.getElementById( 'c' ); // setup canvas
c.width = window.innerWidth;
c.height = window.innerHeight;
gl = c.getContext( 'webgl' ); // setup GL context
gl.viewport(0, 0, c.width, c.height );1. Initialize WebGL
2. Shaders
setup Canvas
setup GL Context
compile vertex shader
compile fragment shader
attach and link shaders
<script id="vertexshader" type="glsl">
attribute vec3 position;
void main(void) {
gl_Position = vec4( position, 1.);
}
</script> <script id="fragmentshader" type="glsl">
precision mediump float;
void main(void) {
gl_FragColor = vec4(1., 1., 1., 1.);
}
</script>1. Initialize WebGL
2. Shaders
setup Canvas
setup GL Context
compile vertex shader
compile fragment shader
attach and link shaders
v_shader = gl.createShader( gl.VERTEX_SHADER );
f_shader = gl.createShader( gl.FRAGMENT_SHADER );
// compile vertex shader
gl.shaderSource( v_shader, document.getElementById( 'vertexshader' ).innerText );
gl.compileShader( v_shader );
if (!gl.getShaderParameter( v_shader, gl.COMPILE_STATUS)) {
console.log(gl.getShaderInfoLog( v_shader ));
}
1. Initialize WebGL
2. Shaders
setup Canvas
setup GL Context
compile vertex shader
compile fragment shader
attach and link shaders
v_shader = gl.createShader( gl.VERTEX_SHADER );
f_shader = gl.createShader( gl.FRAGMENT_SHADER );
// compile vertex shader
gl.shaderSource( v_shader, document.getElementById( 'vertexshader' ).innerText );
gl.compileShader( v_shader );
if (!gl.getShaderParameter( v_shader, gl.COMPILE_STATUS)) {
console.log(gl.getShaderInfoLog( v_shader ));
}
// compile fragment shader
gl.shaderSource( f_shader, document.getElementById( 'fragmentshader' ).innerText );
gl.compileShader( f_shader );
if (!gl.getShaderParameter( f_shader, gl.COMPILE_STATUS)) {
console.log(gl.getShaderInfoLog( f_shader ));
}
1. Initialize WebGL
2. Shaders
setup Canvas
setup GL Context
compile vertex shader
compile fragment shader
attach and link shaders
// attach and link the shaders
shaderprogram = gl.createProgram();
gl.attachShader( shaderprogram, v_shader );
gl.attachShader( shaderprogram, f_shader );
gl.linkProgram( shaderprogram );
gl.useProgram( shaderprogram );1. Initialize WebGL
2. Shaders
setup Canvas
setup GL Context
compile vertex shader
compile fragment shader
attach and link shaders
v_shader = gl.createShader( gl.VERTEX_SHADER );
f_shader = gl.createShader( gl.FRAGMENT_SHADER );
// compile vertex shader
gl.shaderSource( v_shader, document.getElementById( 'vertexshader' ).innerText );
gl.compileShader( v_shader );
if (!gl.getShaderParameter( v_shader, gl.COMPILE_STATUS)) {
console.log(gl.getShaderInfoLog( v_shader ));
}
// compile fragment shader
gl.shaderSource( f_shader, document.getElementById( 'fragmentshader' ).innerText );
gl.compileShader( f_shader );
if (!gl.getShaderParameter( f_shader, gl.COMPILE_STATUS)) {
console.log(gl.getShaderInfoLog( f_shader ));
}
// attach and link the shaders
shaderprogram = gl.createProgram();
gl.attachShader( shaderprogram, v_shader );
gl.attachShader( shaderprogram, f_shader );
gl.linkProgram( shaderprogram );
gl.useProgram( shaderprogram );1. Initialize WebGL
2. Shaders
3. Create Geometry
setup Canvas
setup GL Context
compile vertex shader
compile fragment shader
attach and link shaders
create vertices
create and bind buffer
put data in
unbind buffer



V0
V1
V2

V0
V1
V2

V0
V1
V2
V3
V4
V5

V0
V1
V2
V3
V4
V5
Viewport Coordinates
-1, -1
1, 1
-0.5, -0.5
-0.5, 0.5
0.5, 0.5
0.5, -0.5
vertices = new Float32Array( [
-0.5, 0.5, 0.0, // V0
-0.5, -0.5, 0.0, // V1
0.5, 0.5, 0.0, // V2
0.5, 0.5, 0.0, // V3
-0.5, -0.5, 0.0, // V4
0.5, -0.5, 0.0 // V5
] );
V0
V1
V2
V3
V4
V5
vertices = new Float32Array( [
-0.5, 0.5, 0.0, // V0
-0.5, -0.5, 0.0, // V1
0.5, 0.5, 0.0, // V2
0.5, 0.5, 0.0, // V3
-0.5, -0.5, 0.0, // V4
0.5, -0.5, 0.0 // V5
] ); vertices = new Float32Array( [
-0.5, 0.5, 0.0, // V0
-0.5, -0.5, 0.0, // V1, V4
0.5, 0.5, 0.0, // V2, V3
0.5, -0.5, 0.0 // V5
] );18 * 32 bit == 18 * 4 bytes == 72 bytes
12 * 32 bit == 12 * 4 bytes == 48 bytes

V0
V1
V2
V3
V4
V5
vertices = new Float32Array( [
-0.5, 0.5, 0.0, // V0 // 0
-0.5, -0.5, 0.0, // V1, V4 // 1
0.5, 0.5, 0.0, // V2, V3 // 2
0.5, -0.5, 0.0 // V5 // 3
] );var indices = new Uint8Array( [ 0, 1, 2, // Triangle 1
2, 1, 3 ] ); // Triangle 20
1
2
3
Indexed Geometry
48 bytes
6 * 8 bit == 6 bytes
we now use 48 + 6 == 54 bytes instead of 72 bytes!
1. Initialize WebGL
2. Shaders
3. Create Geometry
setup Canvas
setup GL Context
compile vertex shader
compile fragment shader
attach and link shaders
create vertices
create and bind buffer
put data in
unbind buffer
v_buffer = gl.createBuffer(); // create
gl.bindBuffer( gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, v_buffer ); // bind
gl.bufferData( gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, vertices, gl.STATIC_DRAW ); // put data in
gl.bindBuffer( gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, null ); // unbind1. Initialize WebGL
2. Shaders
3. Create Geometry
4. Connect Shader with Geometry
setup Canvas
setup GL Context
compile vertex shader
compile fragment shader
attach and link shaders
create vertices
create and bind buffer
put data in
unbind buffer
bind buffer
find vertex attribute in shader source
configure vertex attribute
enable vertex attribute array
gl.bindBuffer( gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, v_buffer );
// find the attribute in the shader source
var a_position = gl.getAttribLocation( shaderprogram, 'position' );
gl.vertexAttribPointer( a_position, 3, gl.FLOAT, false, 0, 0 );
gl.enableVertexAttribArray ( a_position );1. Initialize WebGL
2. Shaders
3. Create Geometry
4. Connect Shader with Geometry
5. Draw!
setup Canvas
setup GL Context
compile vertex shader
compile fragment shader
attach and link shaders
create vertices
create and bind buffer
put data in
unbind buffer
bind buffer
find vertex attribute in shader source
configure vertex attribute
enable vertex attribute array
clear viewport
clear color buffer
draw vertex arrays
gl.clearColor( 0., 0., 0., 0.)
gl.clear( gl.COLOR_BUFFER_BIT );
gl.drawArrays( gl.TRIANGLES, 0, 6 );1. Initialize WebGL
2. Shaders
3. Create Geometry
4. Connect Shader with Geometry
5. Draw!
setup Canvas
setup GL Context
compile vertex shader
compile fragment shader
attach and link shaders
create vertices
create and bind buffer
put data in
unbind buffer
bind buffer
find vertex attribute in shader source
configure vertex attribute
enable vertex attribute array
clear viewport
clear color buffer
draw vertex arrays

What the...
but don't worry!
you will understand it when you work on assignment 4!
<html>
<head>
<meta content="text/html;charset=utf-8" http-equiv="Content-Type">
<meta content="utf-8" http-equiv="encoding">
<title>Default WebGL!</title>
<style>
html, body {
background-color:#000;
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
height: 100%;
overflow: hidden !important;
}
#c {
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
}
</style>
</head>
<script id="vertexshader" type="glsl">
attribute vec3 position;
void main(void) {
gl_Position = vec4( position, 1.);
}
</script>
<script id="fragmentshader" type="glsl">
precision mediump float;
void main(void) {
gl_FragColor = vec4(1., 1., 1., 1.);
}
</script>
<script>
var c, gl;
var v_shader, f_shader, shaderprogram;
var vertices, v_buffer;
window.onload = function() {
//************************************************************//
//
// INITIALIZE WEBGL
//
c = document.getElementById( 'c' ); // setup canvas
c.width = window.innerWidth;
c.height = window.innerHeight;
gl = c.getContext( 'webgl' ); // setup GL context
gl.viewport(0, 0, c.width, c.height );
//************************************************************//
//
// SHADERS
//
v_shader = gl.createShader( gl.VERTEX_SHADER );
f_shader = gl.createShader( gl.FRAGMENT_SHADER );
// compile vertex shader
gl.shaderSource( v_shader, document.getElementById( 'vertexshader' ).innerText );
gl.compileShader( v_shader );
if (!gl.getShaderParameter( v_shader, gl.COMPILE_STATUS)) {
console.log(gl.getShaderInfoLog( v_shader ));
}
// compile fragment shader
gl.shaderSource( f_shader, document.getElementById( 'fragmentshader' ).innerText );
gl.compileShader( f_shader );
if (!gl.getShaderParameter( f_shader, gl.COMPILE_STATUS)) {
console.log(gl.getShaderInfoLog( f_shader ));
}
// attach and link the shaders
shaderprogram = gl.createProgram();
gl.attachShader( shaderprogram, v_shader );
gl.attachShader( shaderprogram, f_shader );
gl.linkProgram( shaderprogram );
gl.useProgram( shaderprogram );
//************************************************************//
//
// CREATE GEOMETRY
//
vertices = new Float32Array( [
-0.5, 0.5, 0.0, // V0
-0.5, -0.5, 0.0, // V1
0.5, 0.5, 0.0, // V2
0.5, 0.5, 0.0, // V3
-0.5, -0.5, 0.0, // V4
0.5, -0.5, 0.0 // V5
] );
v_buffer = gl.createBuffer(); // create
gl.bindBuffer( gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, v_buffer ); // bind
gl.bufferData( gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, vertices, gl.STATIC_DRAW ); // put data in
gl.bindBuffer( gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, null ); // unbind
//************************************************************//
//
// CONNECT SHADER WITH GEOMETRY
//
gl.bindBuffer( gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, v_buffer );
// find the attribute in the shader source
var a_position = gl.getAttribLocation( shaderprogram, 'position' );
gl.vertexAttribPointer( a_position, 3, gl.FLOAT, false, 0, 0 );
gl.enableVertexAttribArray ( a_position );
//************************************************************//
//
// DRAW!
//
gl.clearColor( 0., 0., 0., 0.)
gl.clear( gl.COLOR_BUFFER_BIT );
gl.drawArrays( gl.TRIANGLES, 0, 6 );
};
</script>
<body>
<canvas id="c"></canvas>
</body>
</html>

Uniforms
createRectangle()
Rendering Loop
And, they move!
Quiz 4 due today!!
submit your music!