Cluster Patterns in Tensors Data
Peter A. Brooksbank, Bucknell University
Martin D. Kassabov, Cornell University
& James B. Wilson, Colorado State University
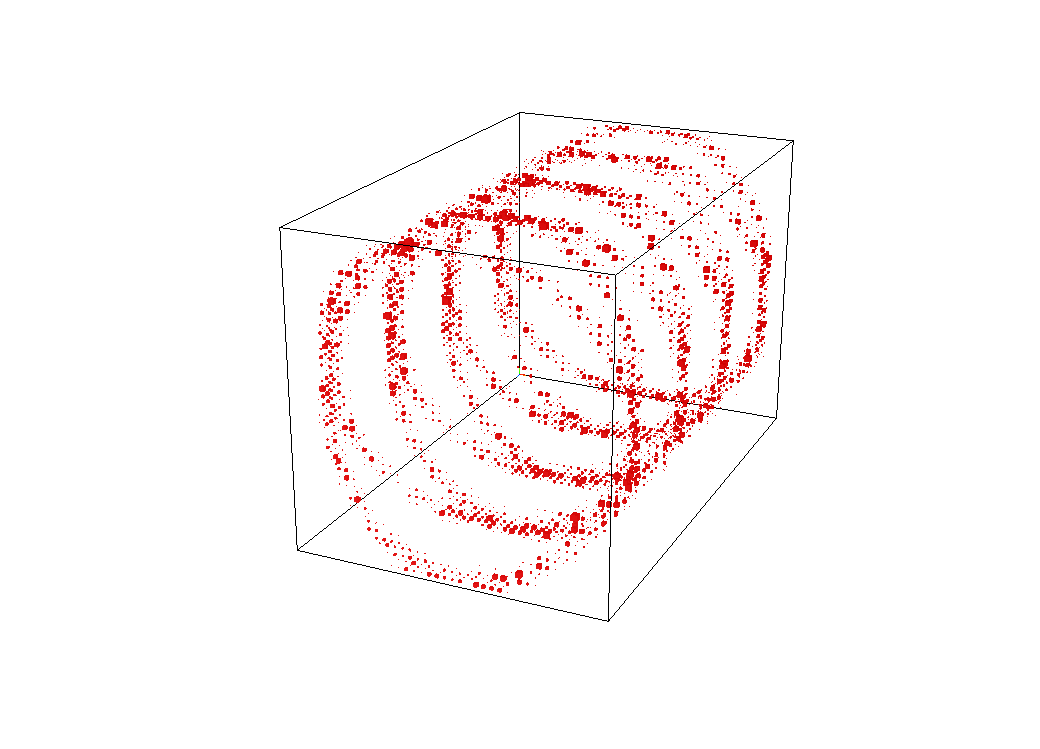
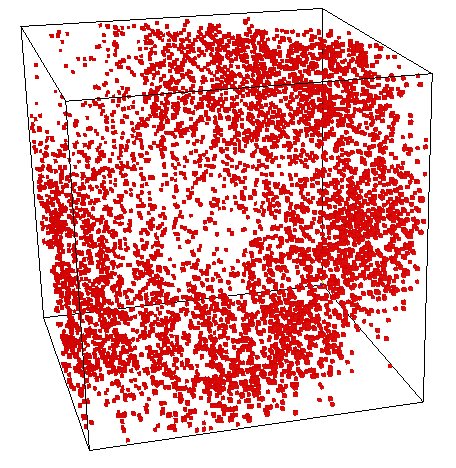
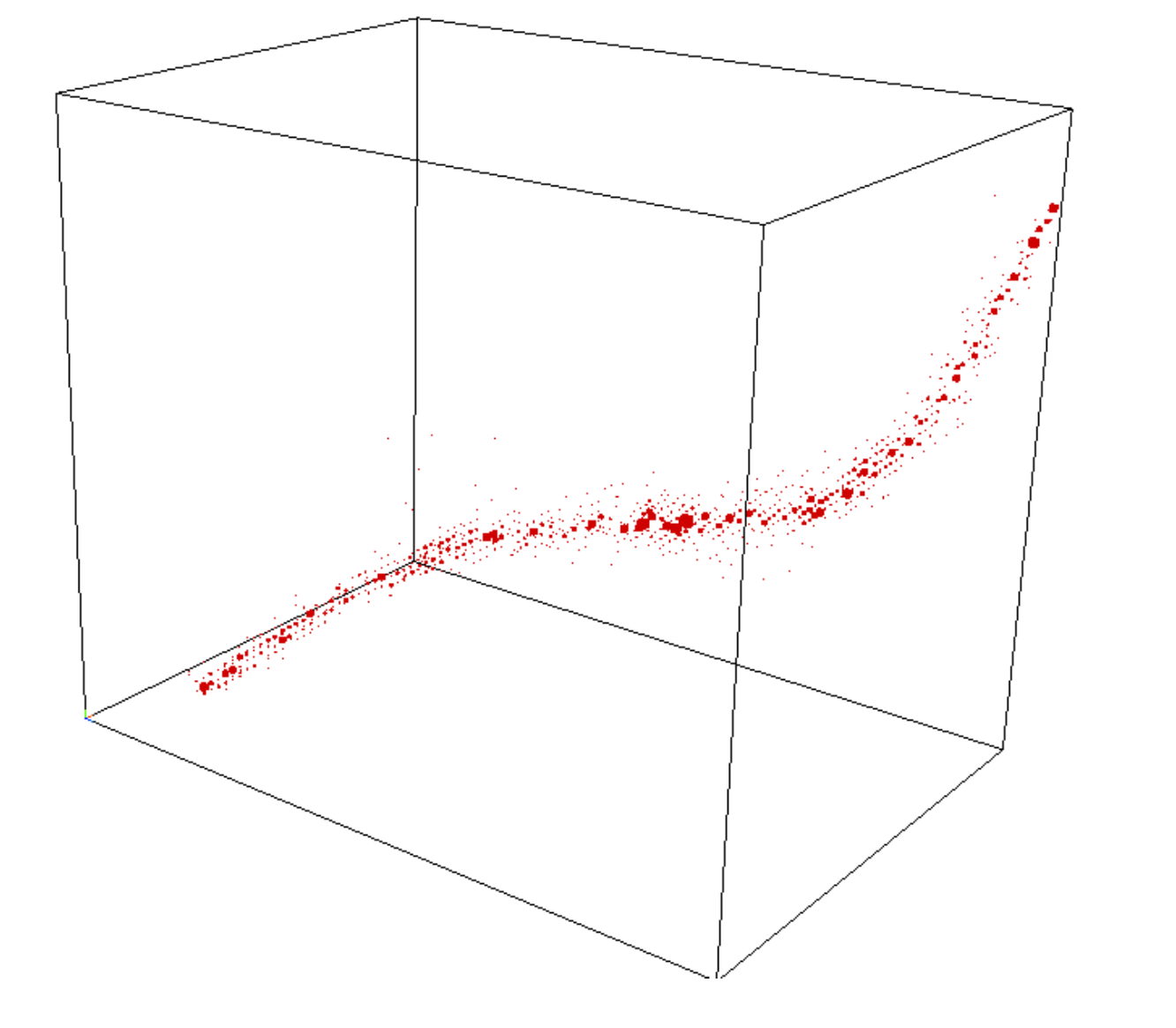
What do you see here?
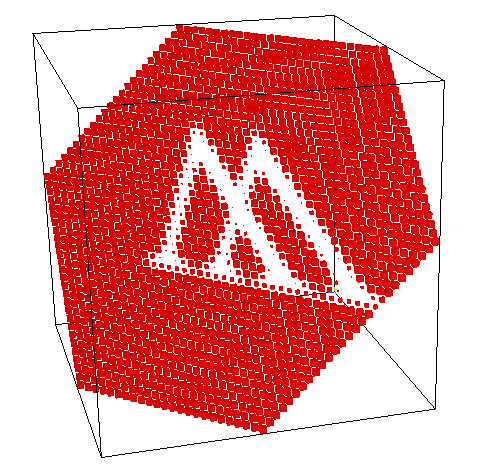
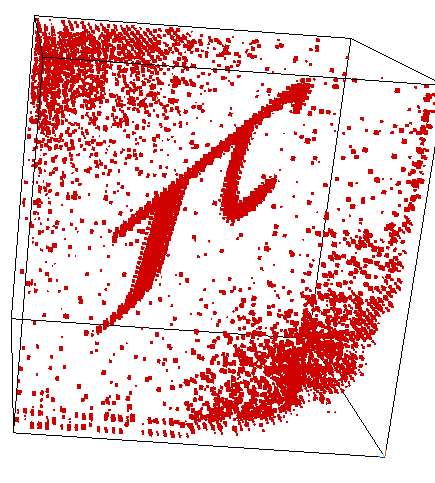




"Random" Basis Change
Cluster Patterns in Tensors Data
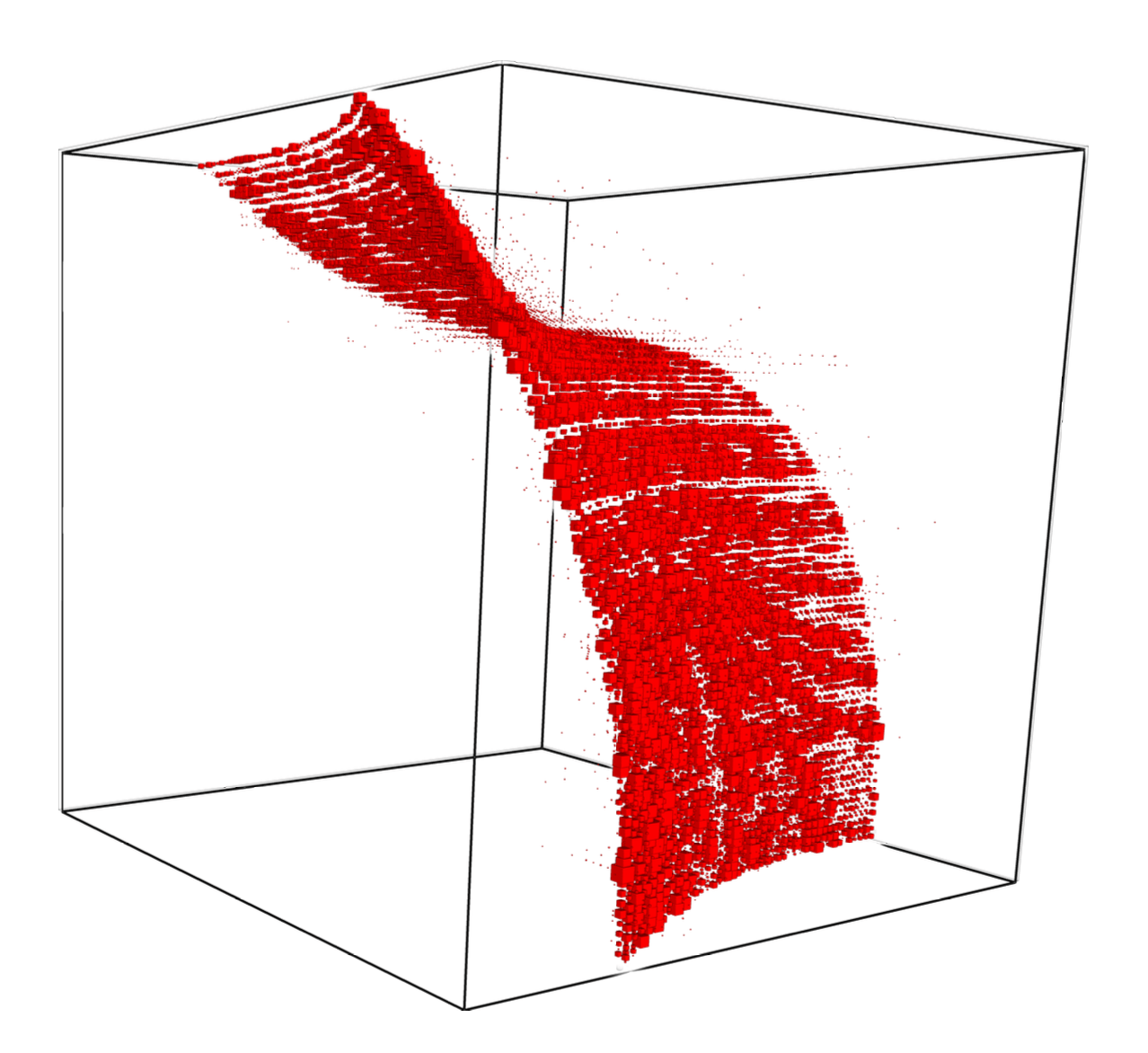
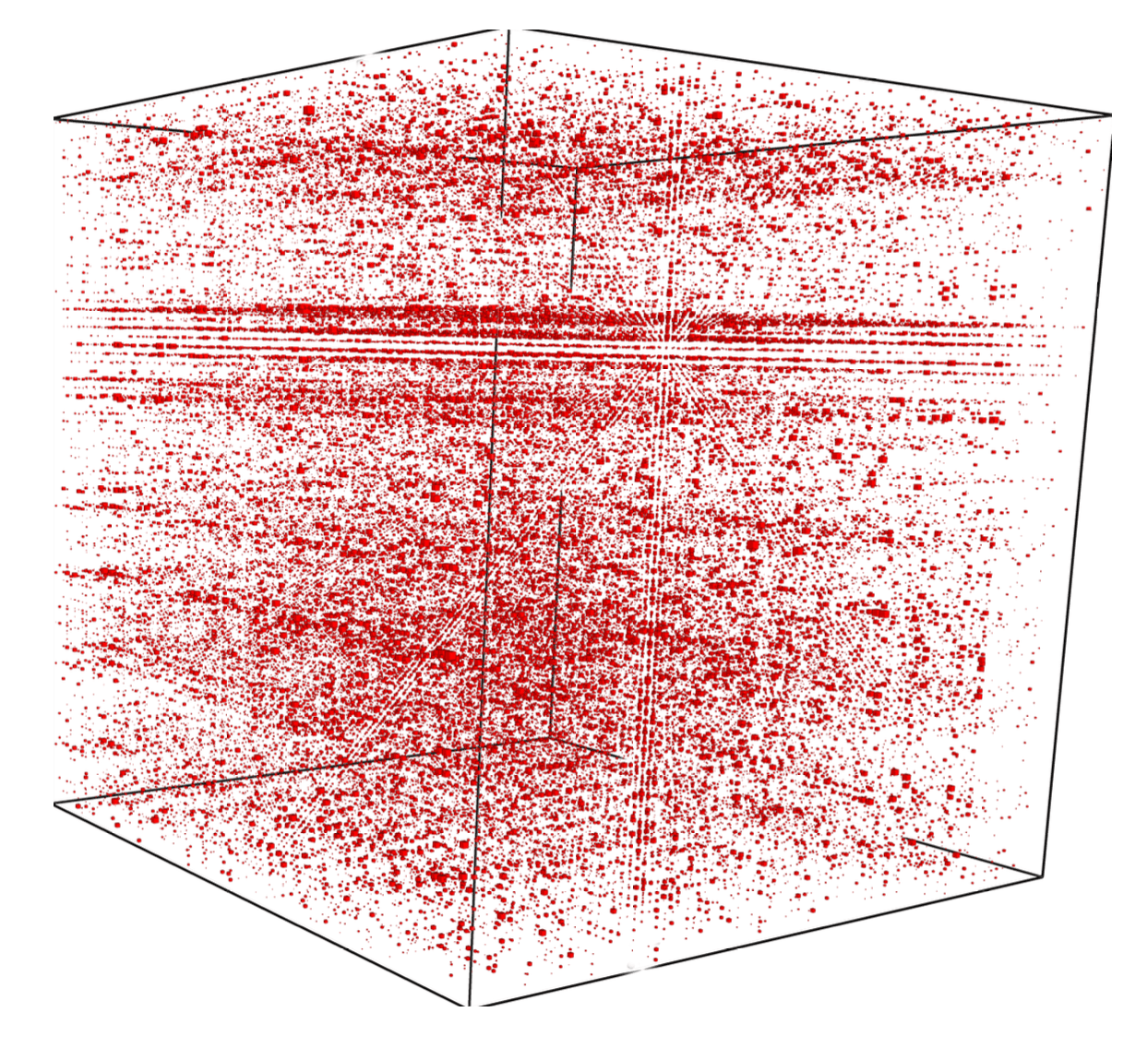
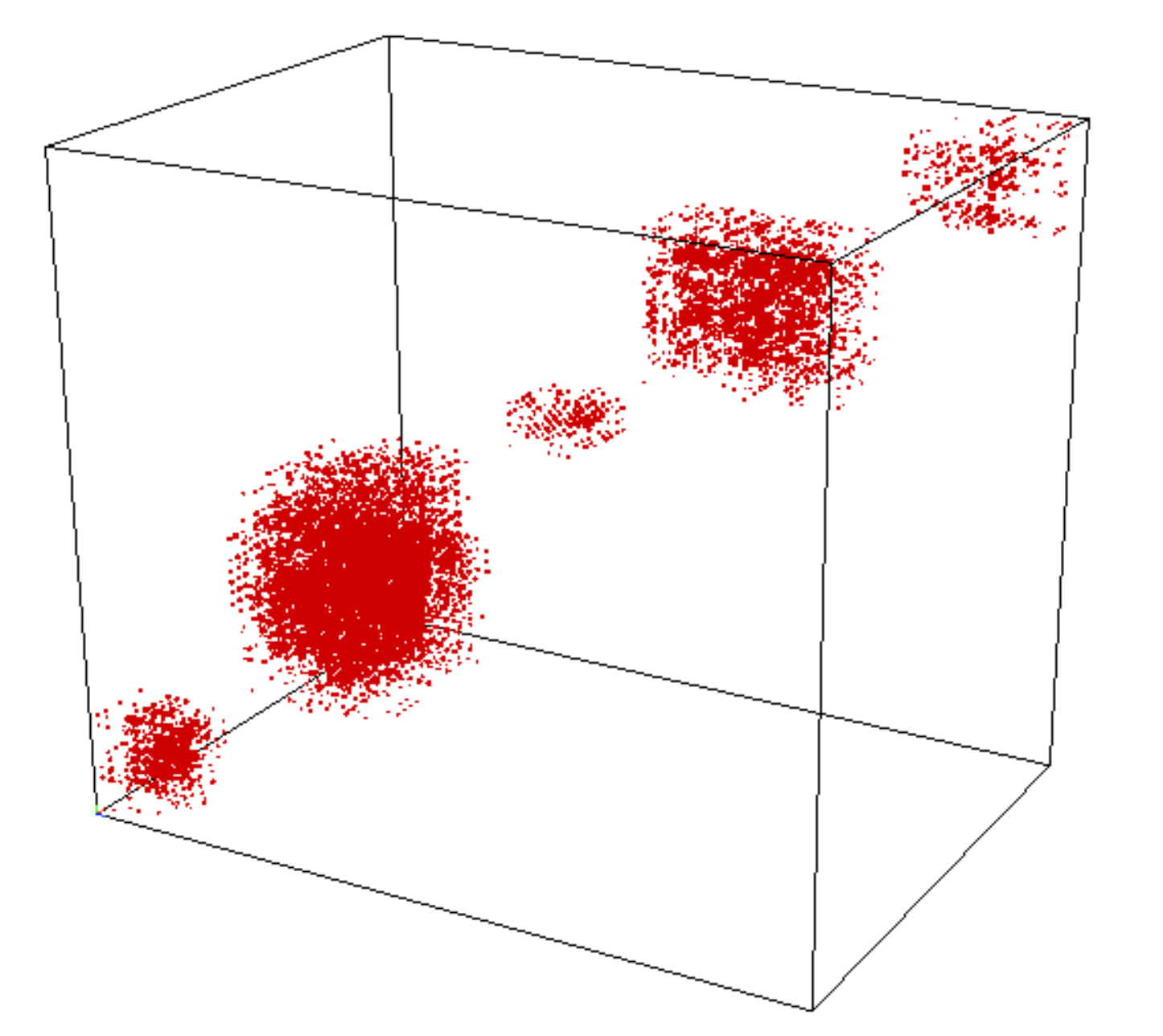
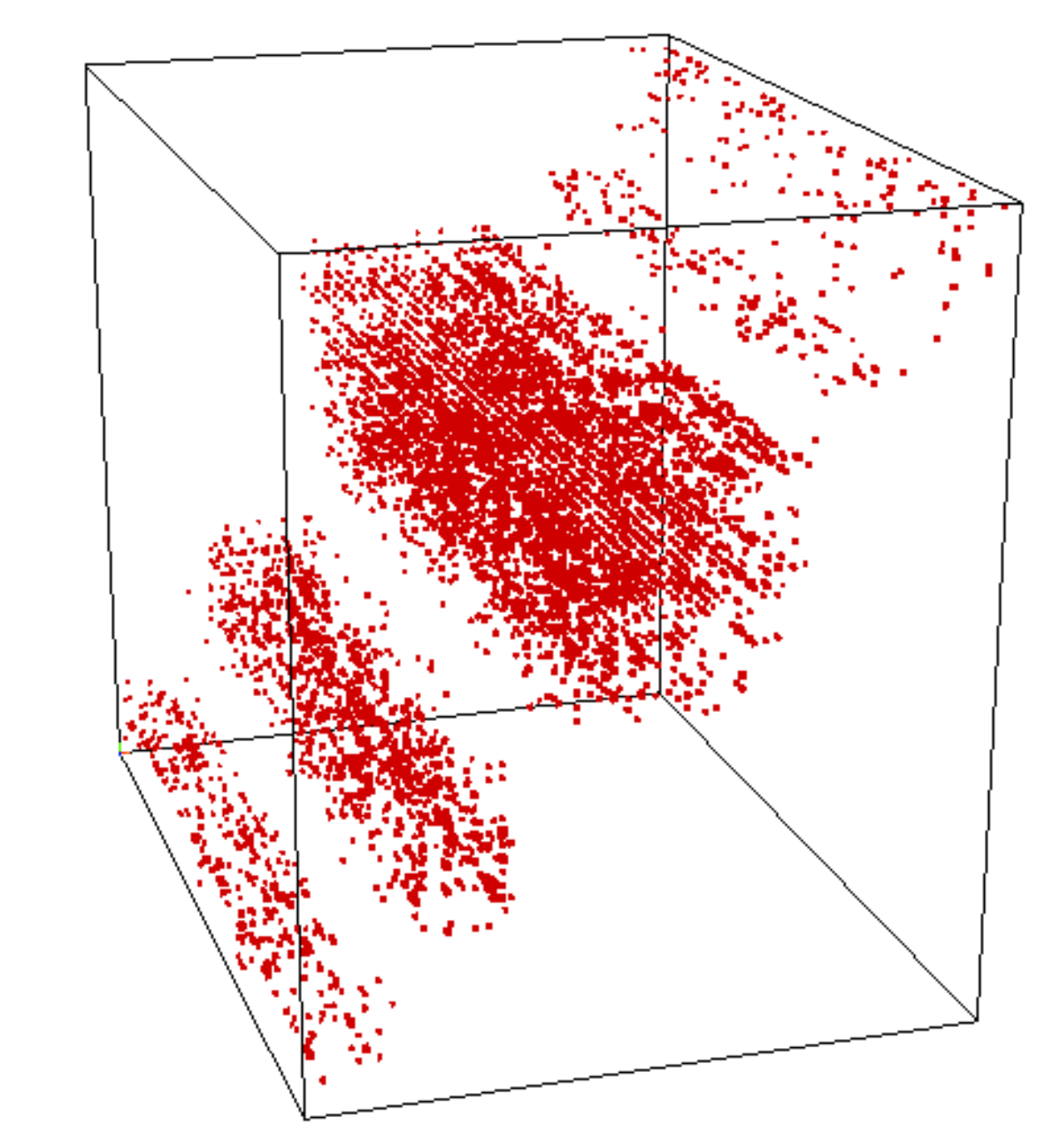
Who cares about these things?
Tensors as area & volume

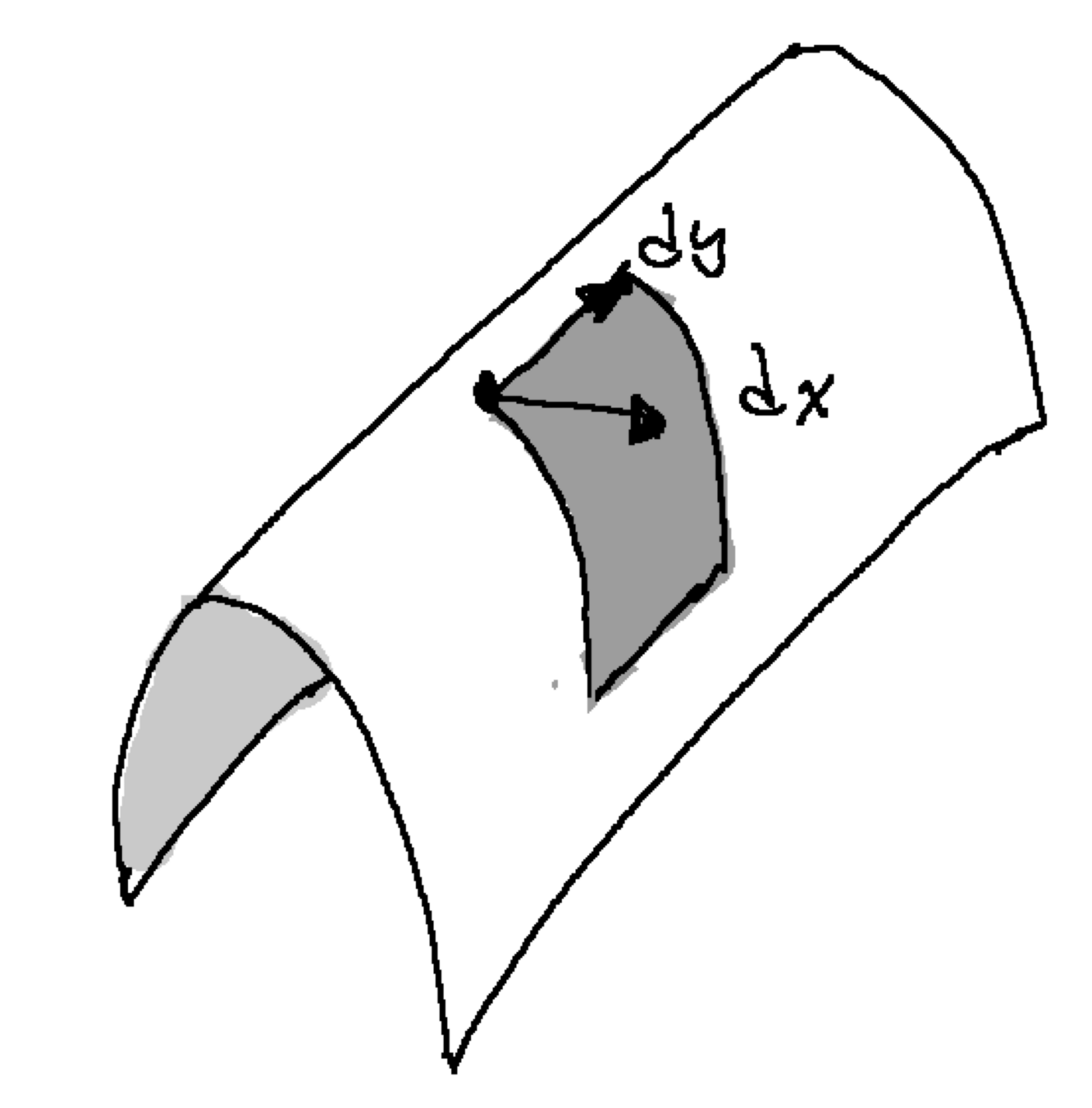
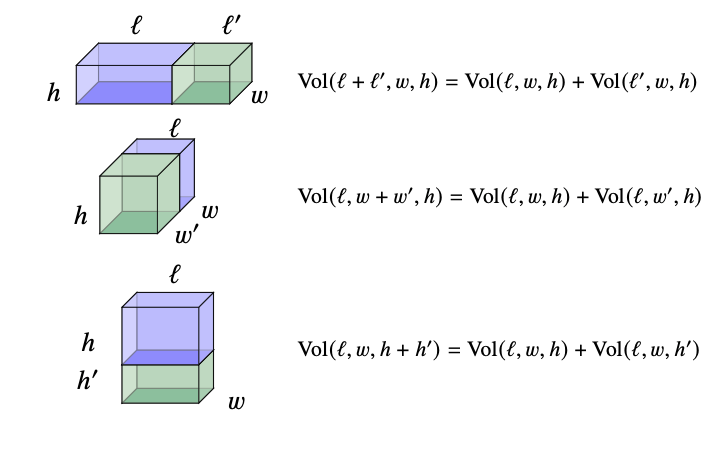
Volume basics
\[Vol(\ell, w,h)= \ell\times w\times h\]


Volume reality
\[Vol(t\mid \ell, w,h)= t\times \ell\times w\times h\] where \(t\) converts miles/meters/gallons/etc.
tensor conversion
Miles
Yards
Feet
Gallons
Area...easy
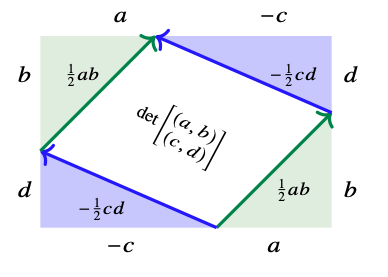
Area...not so easy

\[det\left(\begin{array}{c} (a,b)\\ (c,d)\end{array}\right) = ad-bc\]
\[= \begin{bmatrix} a & b\end{bmatrix}\begin{bmatrix} 0 & 1 \\ -1 & 0 \end{bmatrix}\begin{bmatrix} c\\ d \end{bmatrix}\]
tensor
Area...getting worse

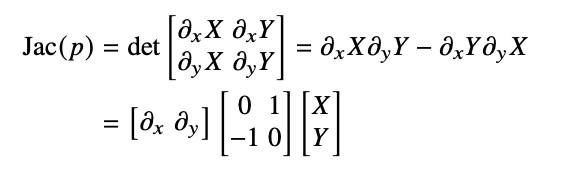
New uses? Make up new measurements

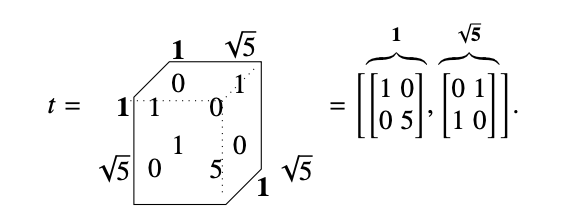
New uses? Sales Volume?
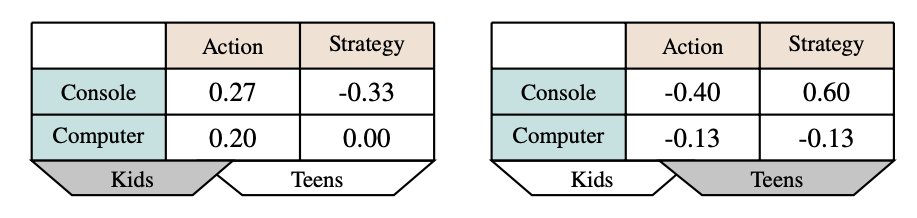
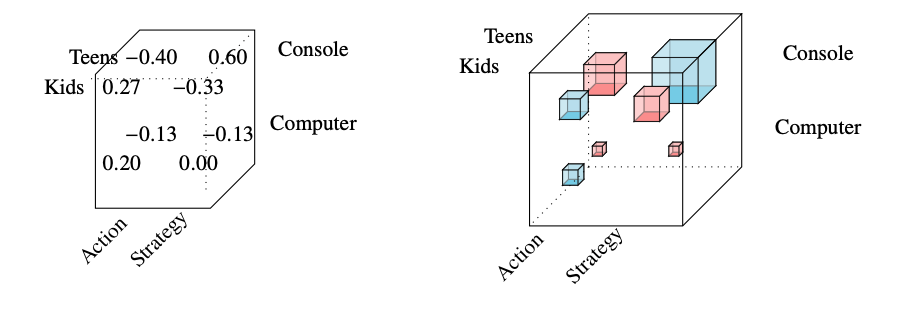
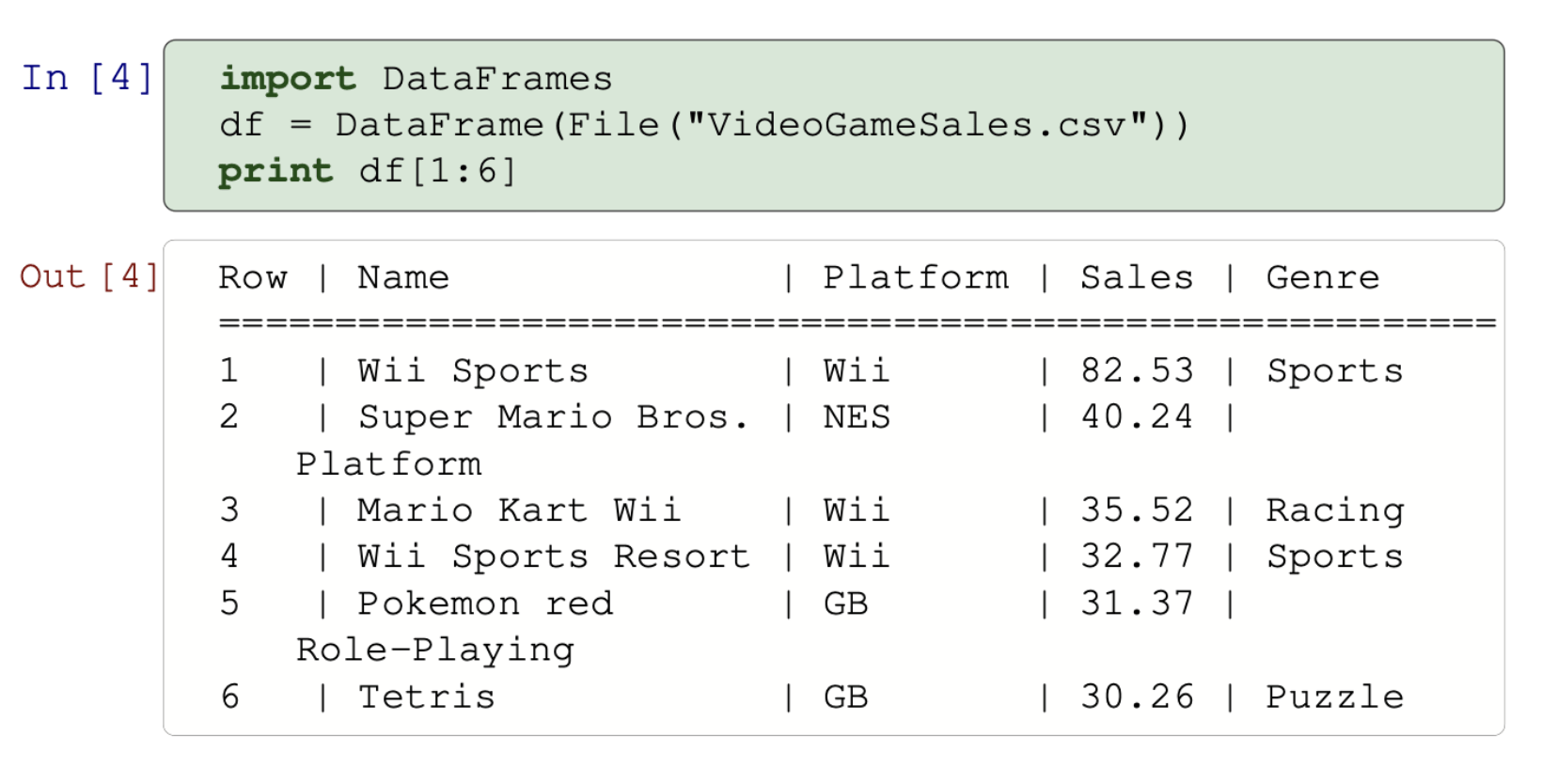
Slightly more honest

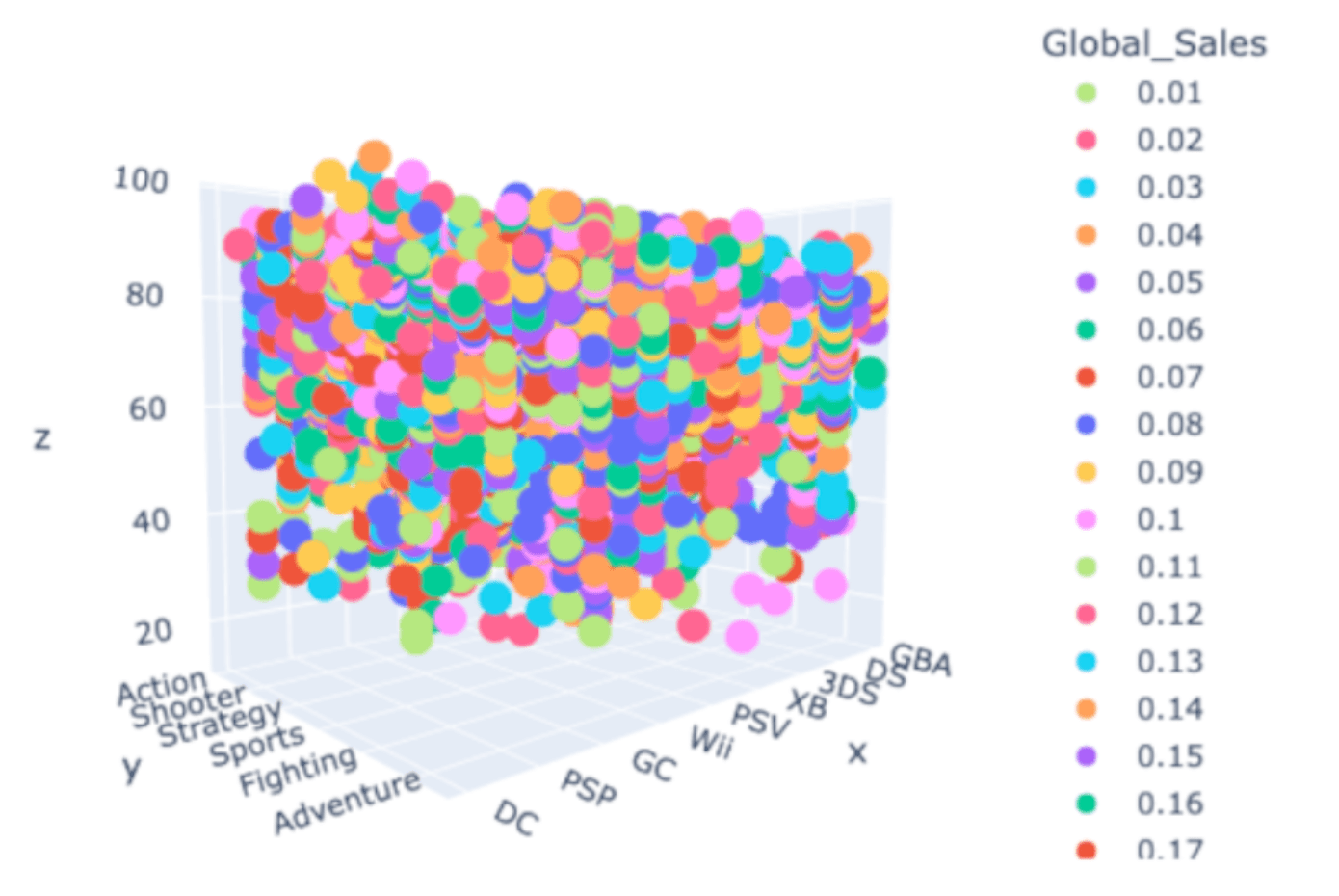
Histogram Visualization
New uses? interactions probabilities and quantum information
Tensors algebra
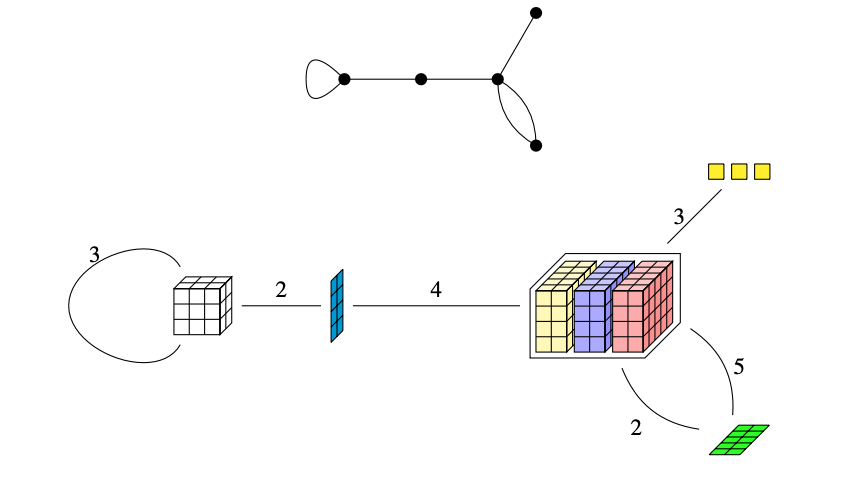
Facts?

Facts?
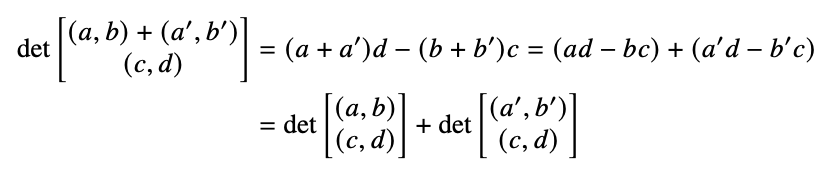
Consequences?

Consequences?

Real Consequences?

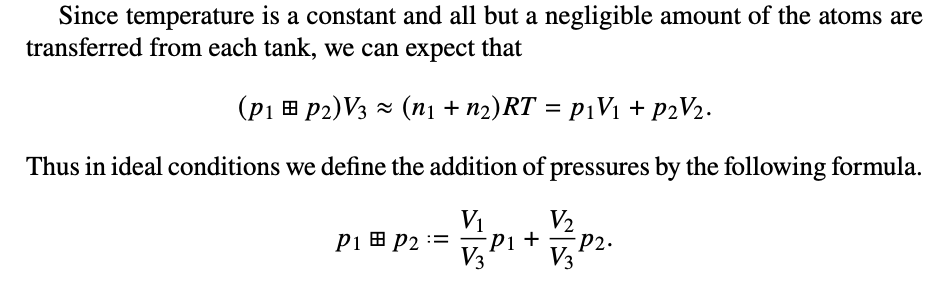
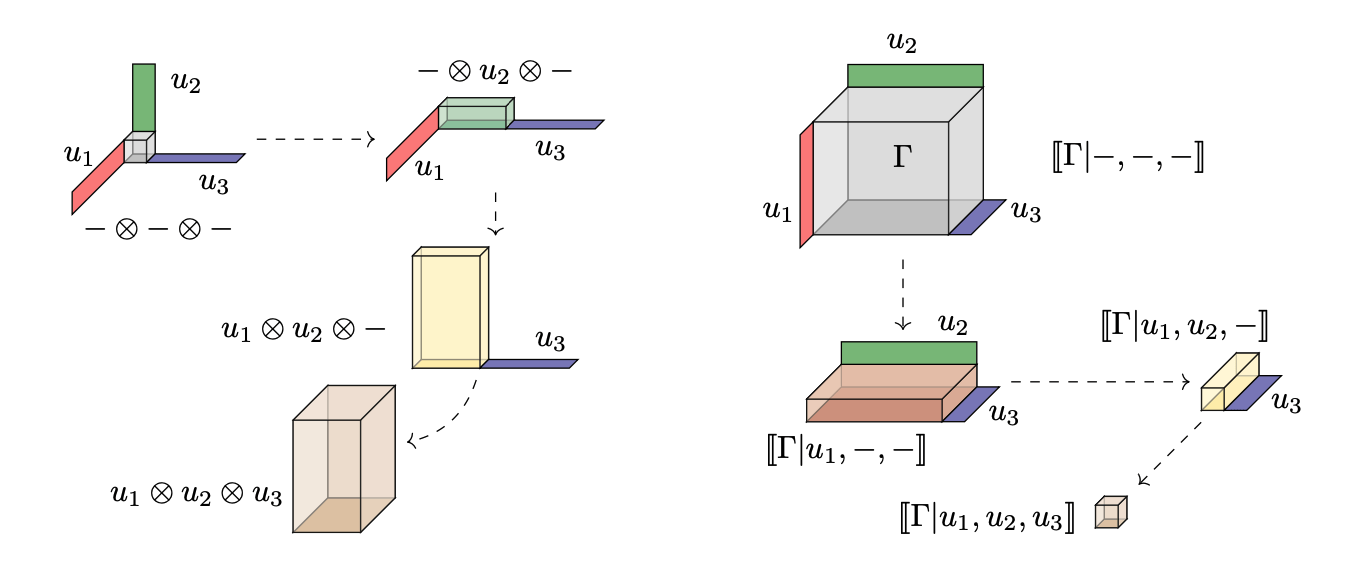
Building blocks
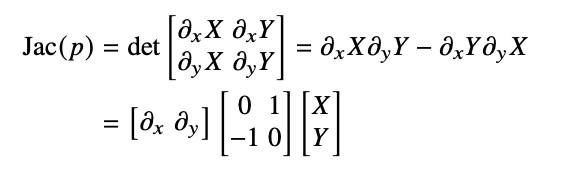
- Some parts expand up: \[a*b\qquad \partial_x X\partial_y Y\]
- Some parts accumulate: \[a*d-b*c\qquad \partial_x X\partial_y Y-\partial_x Y\partial_y X\]
- One version of decomposition focusses on this separation: "sums of products"

Products can grow bigger (inflation)
or get smaller (contraction)
\[\begin{array}{c|ccc|} * & 1 & 2 & 3 \\ \hline 1 & 1 & 2 & 3 \\ 2 & 2 & 4 & 6 \\ \hline\end{array}\]
\[\begin{bmatrix} 1 & 2 \end{bmatrix}\begin{bmatrix} 1 & 3 \\ 2 & 4 \end{bmatrix}=\begin{bmatrix} 5 & 10 \end{bmatrix}\]
\[\begin{aligned}\begin{bmatrix} 1 \\ 2 \end{bmatrix}&\begin{bmatrix} 1 & 3 \\ 2 & 4 \end{bmatrix}\\ \hline &\begin{bmatrix} 5 & 10 \end{bmatrix}\end{aligned}\]
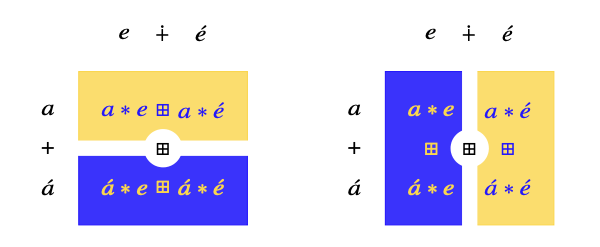
Math convention
Computation convention
Distributive dicta
\[a*e*\cdots *u\] \[a\otimes e\otimes \cdots \otimes u\] \[\langle a,e,\ldots, u\rangle\]
\[\langle v_1,\ldots, v_{\ell}\rangle= \langle v_a,v_{\bar{a}}\rangle\qquad \{1,\ldots,\ell\}=\{a\}\sqcup\bar{a}\]
Choose a heterogenous product notation
Choose a sums
\(\displaystyle \int_I v_a(i) d\mu\) short for code "sum(vs[a],method54)"
For \(\{v_a(i)\mid i\in I\}\)
\[\int_I \langle v_a(i),v_{\bar{a}}\rangle\,d\mu = \left\langle \int_I v_a(i)\,d\mu,v_{\bar{a}}\right\rangle\]
Entropic Edict / Fubini Formula
\[=\int_J\int_I \langle v_a(i), v_b(j),v_{\overline{ab}}\rangle d\nu d\mu\]
\[\int_I \int_J \langle v_a(i), v_b(j),v_{\overline{ab}}\rangle d\mu d\nu = \left\langle \int_I v_a(i) \,d\mu, \int_J v_b(j)\, d\nu,v_{\overline{ab}}\right\rangle\]
\[\int_I \int_J f\, d\mu d\nu=\int_J\int_I f \, d\nu d\mu\]
Theory
Murdoch-Toyoda Bruck
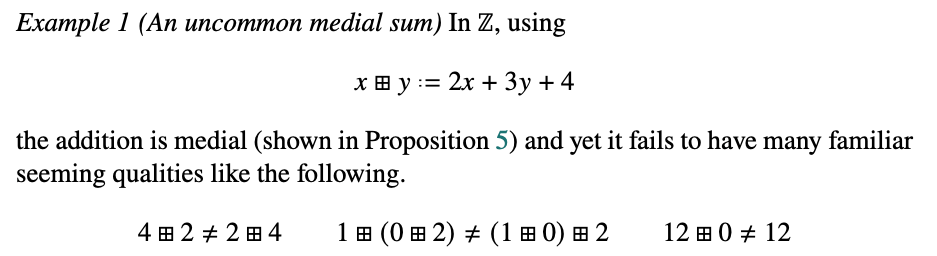
All entropic sums that can solve equations \(a+x=b\) are affine.
Eckmann-Hilton
Entropic sums with 0 are associative & commutative.
Grothendieck
You can add negatives.
Mal'cev, Miyasnikov
You can enrich distributive products with universal scalars.
Davey-Davies
Tensor algebra is ideal determined precisely for affine.
First-Maglione-Wilson
Full classification of algebraic enrichment:
- If 3 or more positions must be Lie
- 2 can be associative or Jordan.
Summary:
- data tables,
- arrays,
- hypermatrices
- functions on several variables....
All these examples have coordinates.
We could change the coordinates!
What do we expect?
Echelon
Jordan
Diagonal
What are the markets?


Data table --> Multiplication table

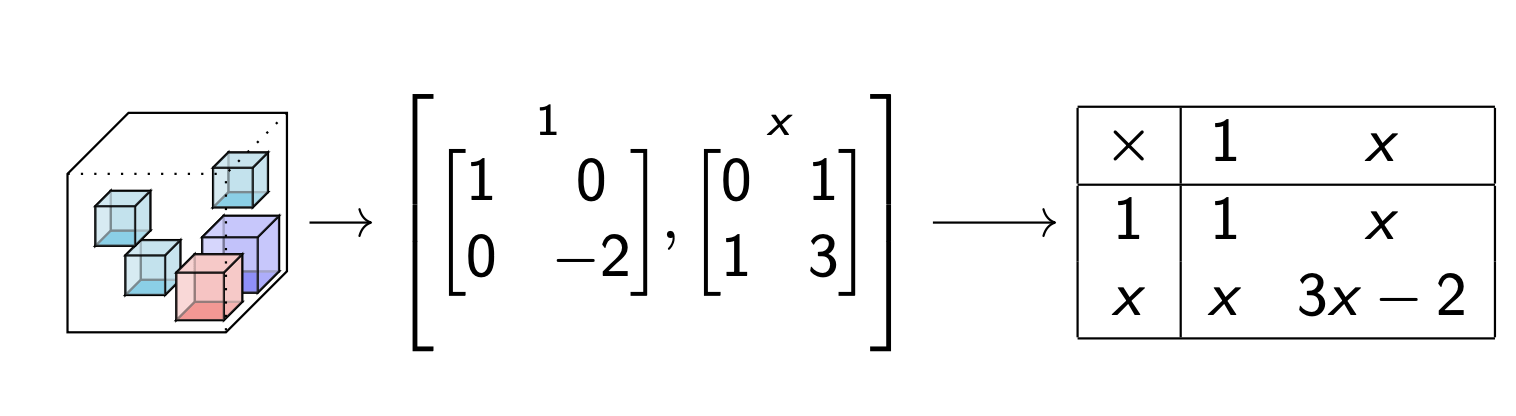
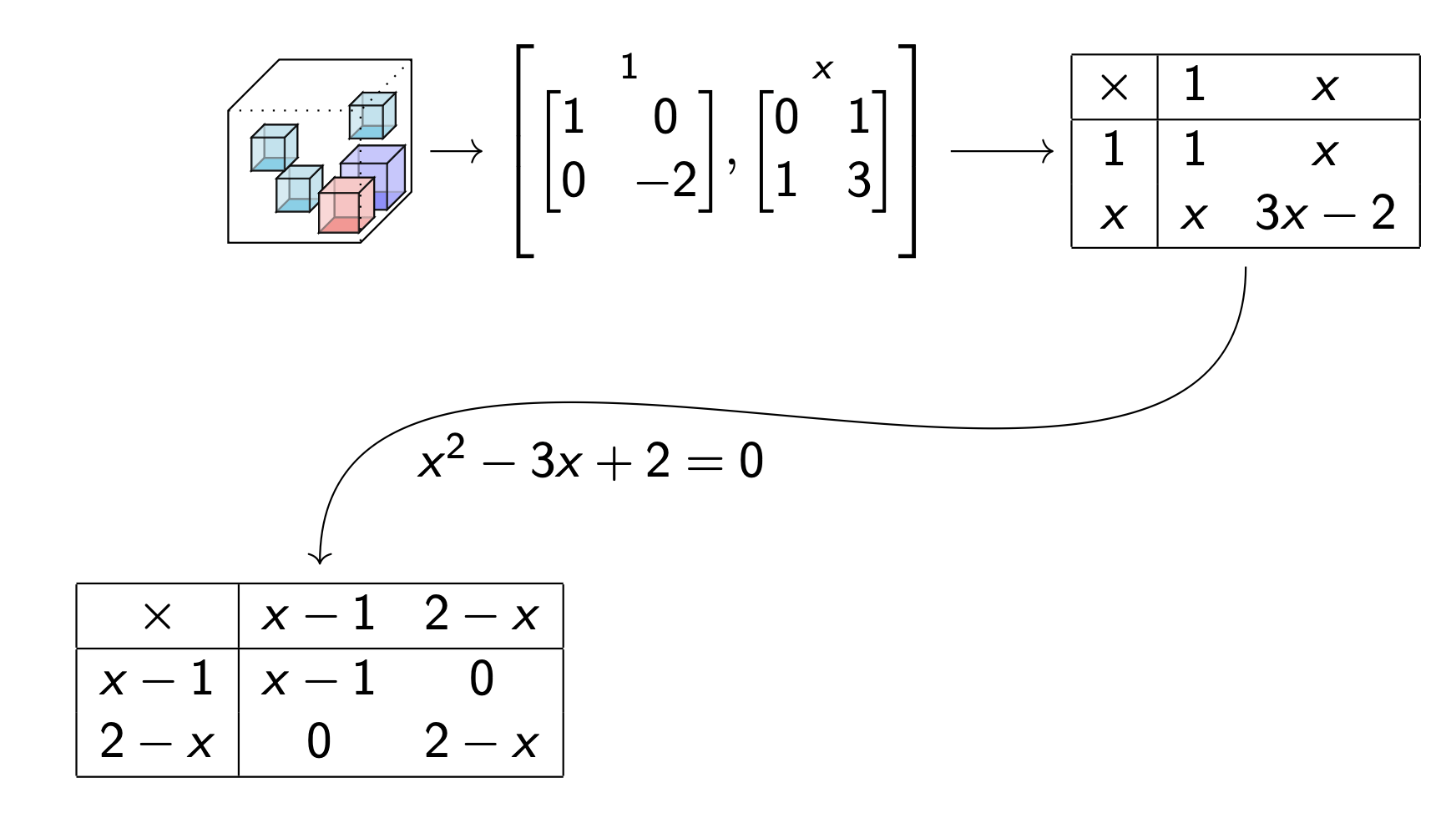
Use algebra to factor
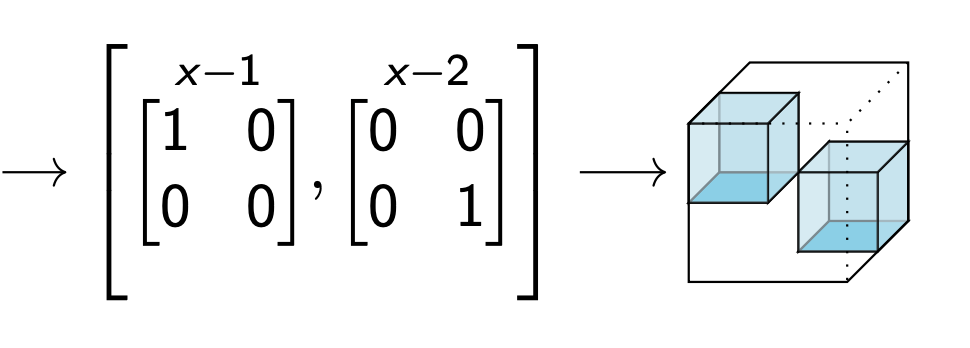
Moral: seeing a tensor as a distributive multiplication has uses for decomposition.
Forcing Good Algebra in Real Life
Toy Problem
Get to 100's 1000's of dimensions and you have no chance to know this algebra.
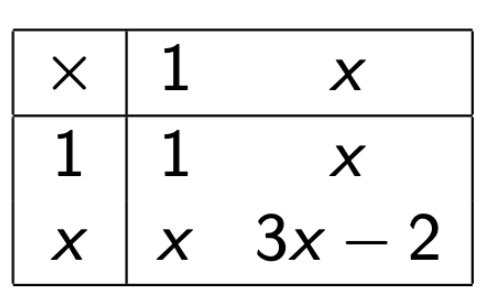

"Real" Problem


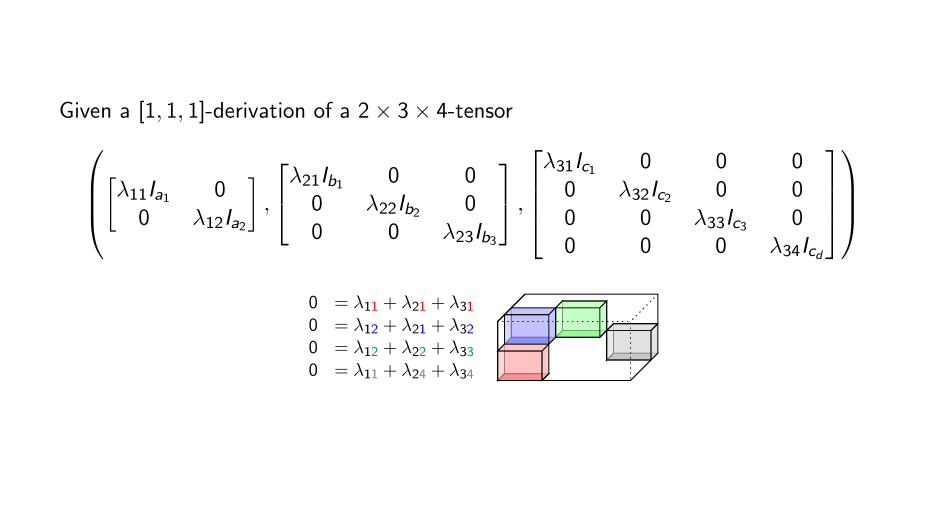
Theorem. (U. First-J. Maglione-J. Wilson) Every tensor has attached to it an algebra of derivations (a Lie algebra) which encodes the symmetries of a tensor. It can be computed from a system of linear equations.
Study a function by its changes, i.e. derivatives.
Study multiplication by derivatives:
\[\partial (f·g ) = (\partial f )·g + f·(\partial g ).\]
In our context discretized. I.e. ∂ is a matrix D.
\[D(f ∗g ) = D(f ) ∗g + f ∗D(g )\]
And it is heterogeneous, so many D's
\[D_0(f*g) = D_1(f)*g + f * D_2(g).\]
Years of this guy's life went
into tensor software
StarAlge MatrixAlge TameGenus (w/ J. Maglione) TensorSpace (w/ J. Maglione)

For general tensors \[\langle t| : U_{1}\times \cdots \times U_{\ell}\to U_0\] there are many generalizations.
E.g.
Or \[ D_0\langle t |u_1,u_2, u_3\rangle = \langle t| D_1 u_1, u_2,u_3\rangle + \langle t| u_1, D_2 u_2, u_3\rangle + \langle t|u_1, u_2, D_3 u_3\rangle.\]

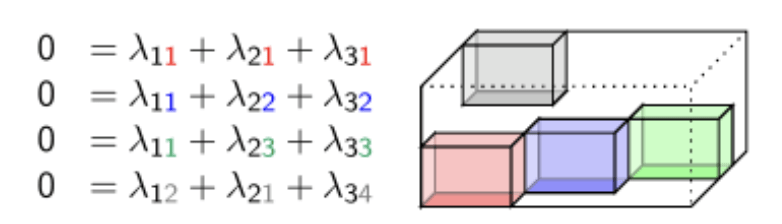
Theorem (Brooksbank-Kassabov-Wilson)
Generically non-trivial derivations encode decomposition.
A derivation of a tensor
Postion (1,1,1): 1 + 1 + -2 = 0
Postion (1,2,2): 1 + 5 -6 = 0
Postion (1,3,3): 1 -6 + 5 = 0
Postion (2,1,4): 2 + 1 -3 = 0
Postion (2,1,1):
2 + 1 -2 \(\neq\) 0
This observation leads to a proof of the main theorem.
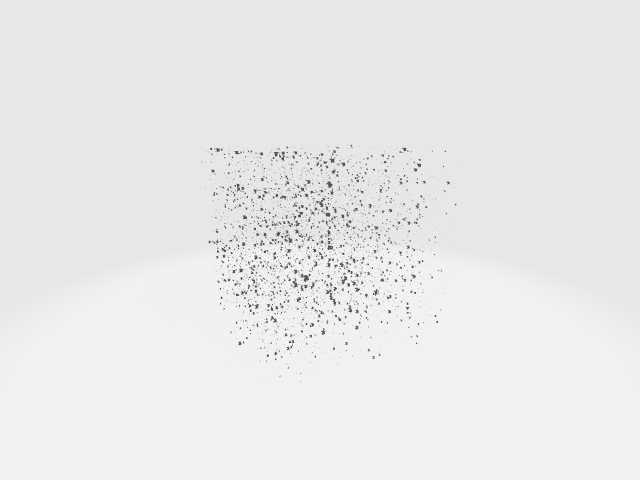
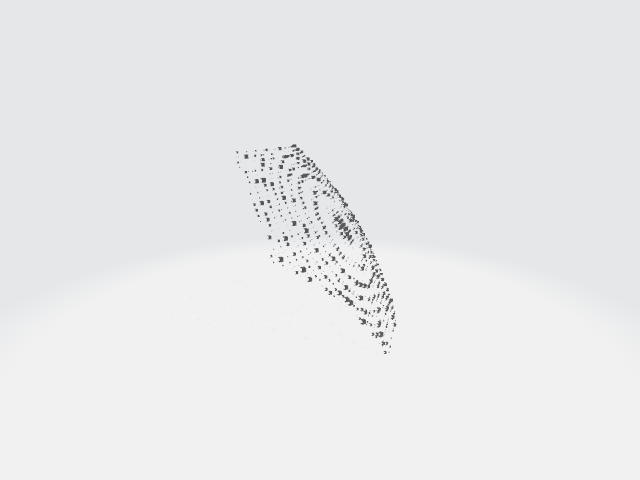
First ever stratification
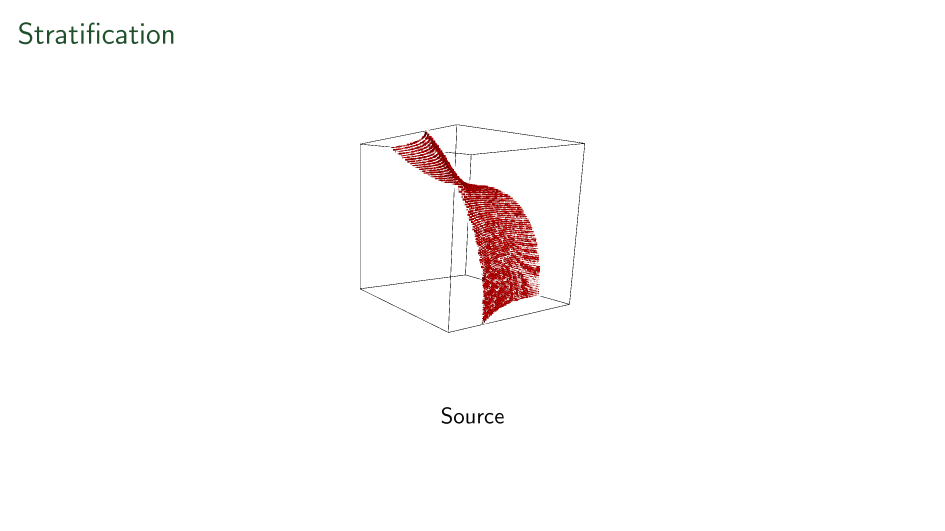
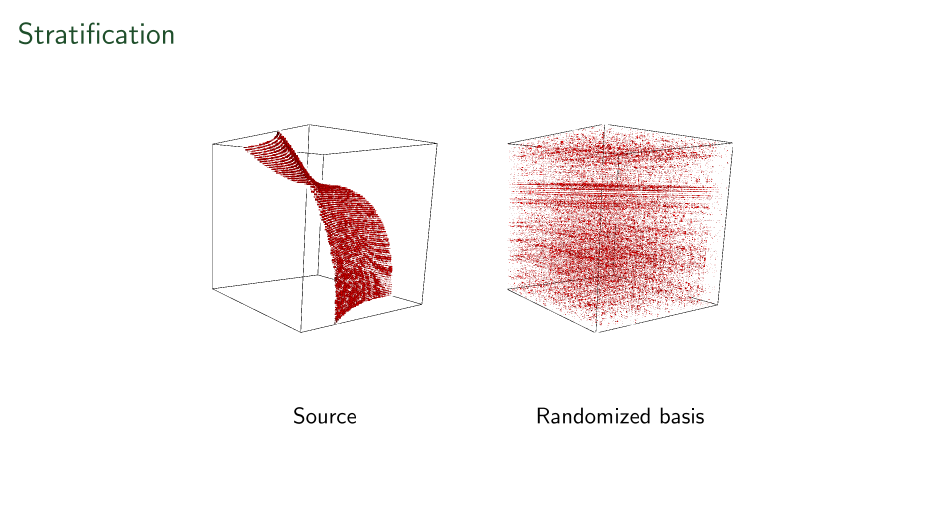
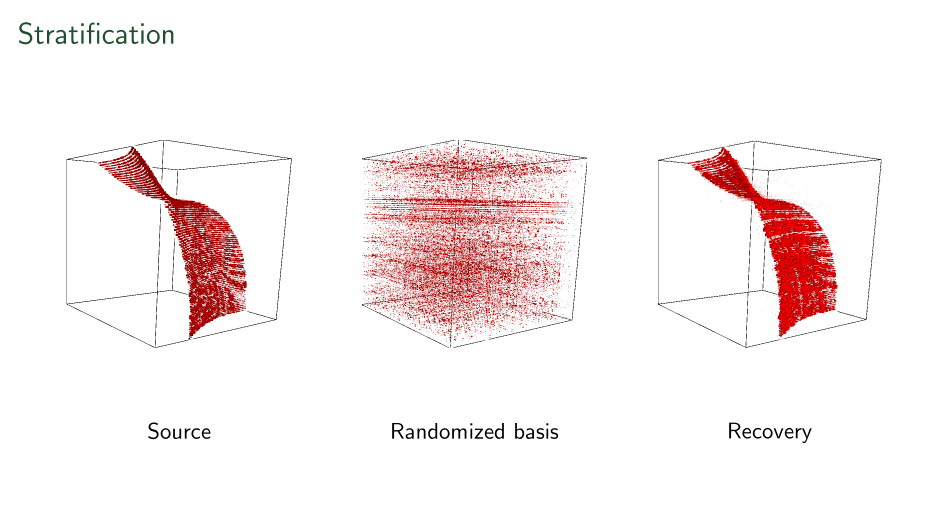


Variations
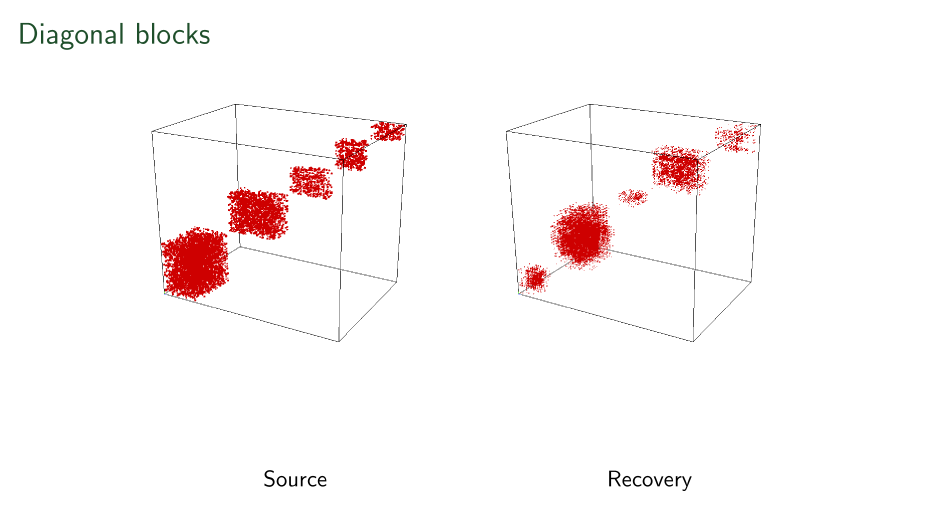
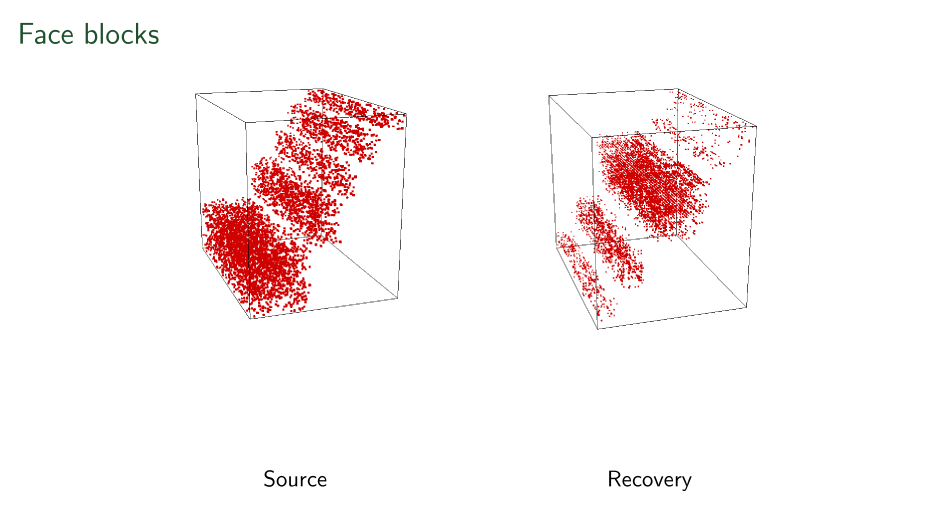
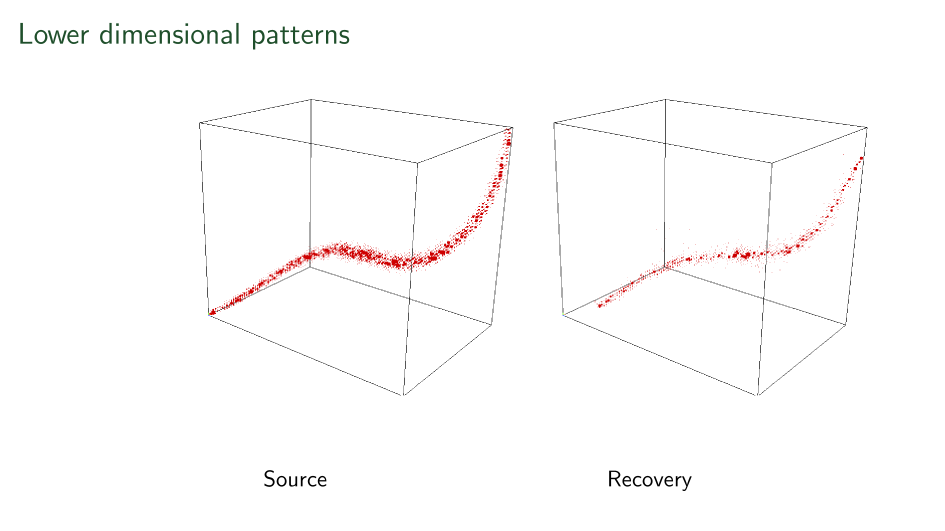
Things are not perfect
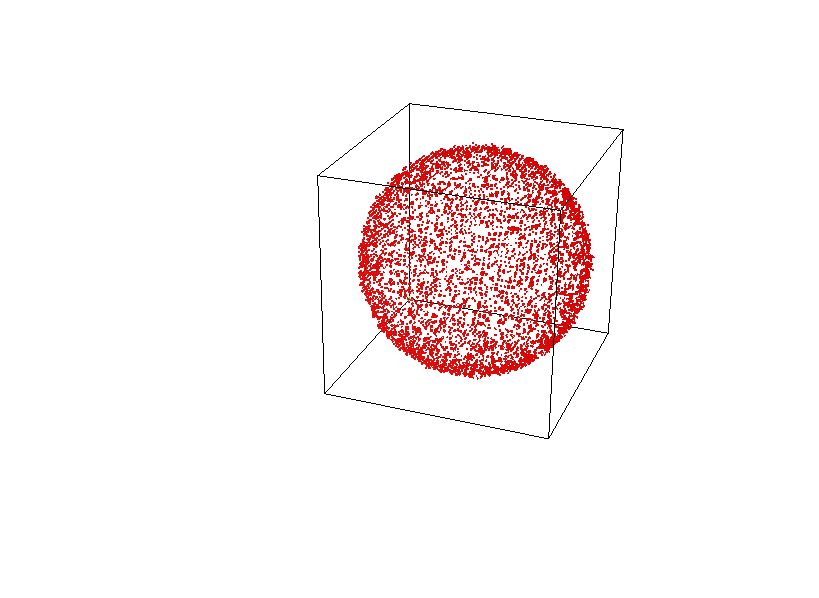
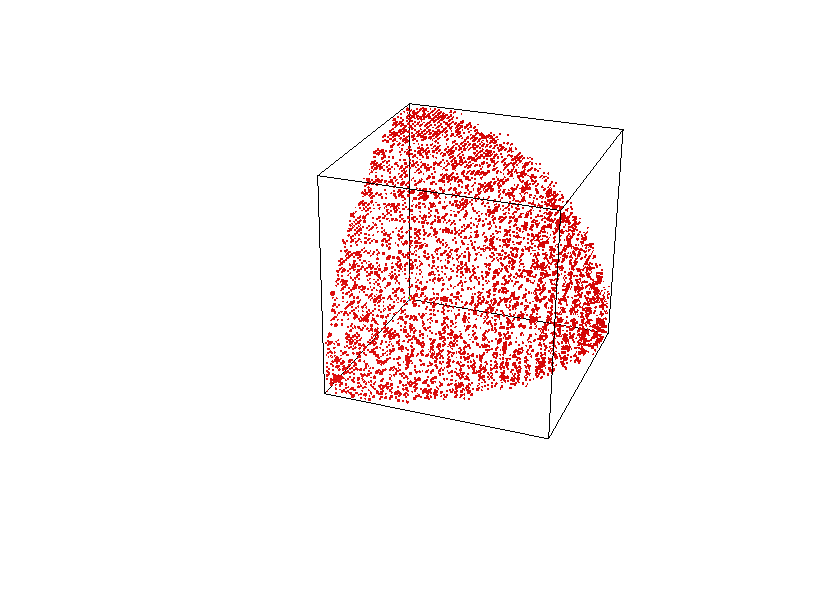

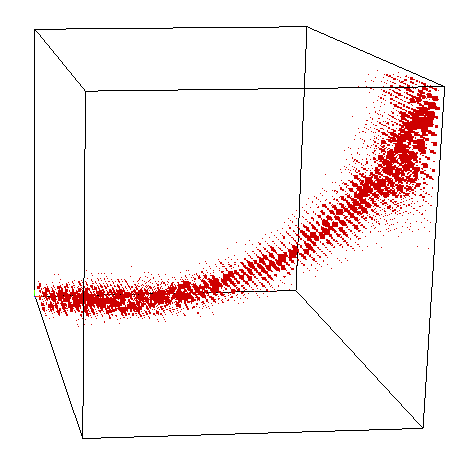
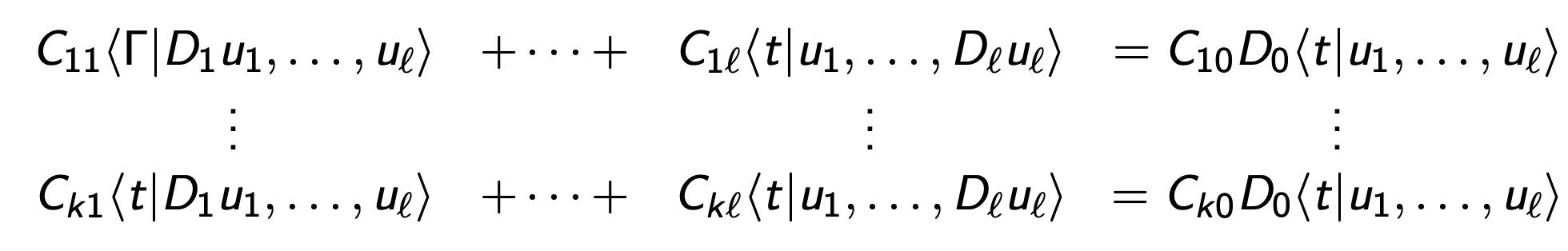
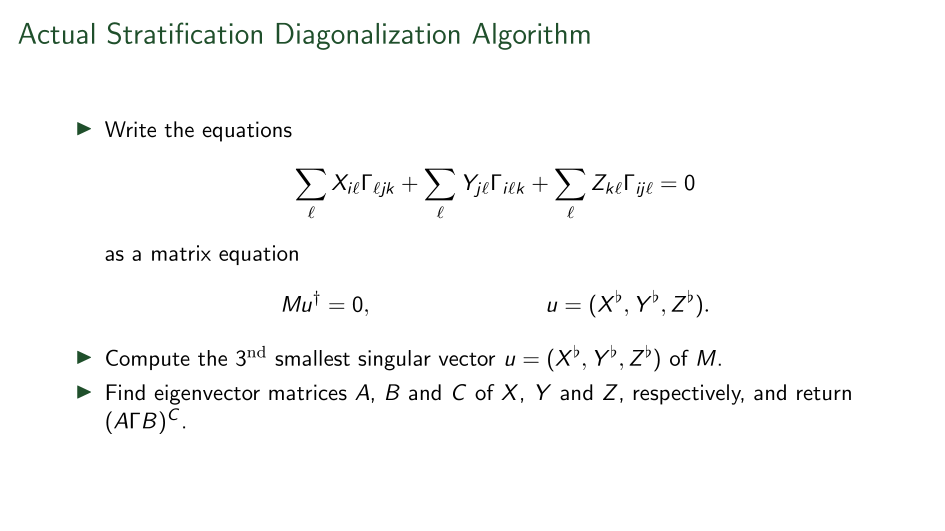
For general tensors \[\langle t|u_1,\ldots, u_{\ell}\rangle \]
Choose a "chisel" (dleto) an augmented matrix C.
Write \[\langle \Gamma | C(D)|u\rangle =0\] to mean:
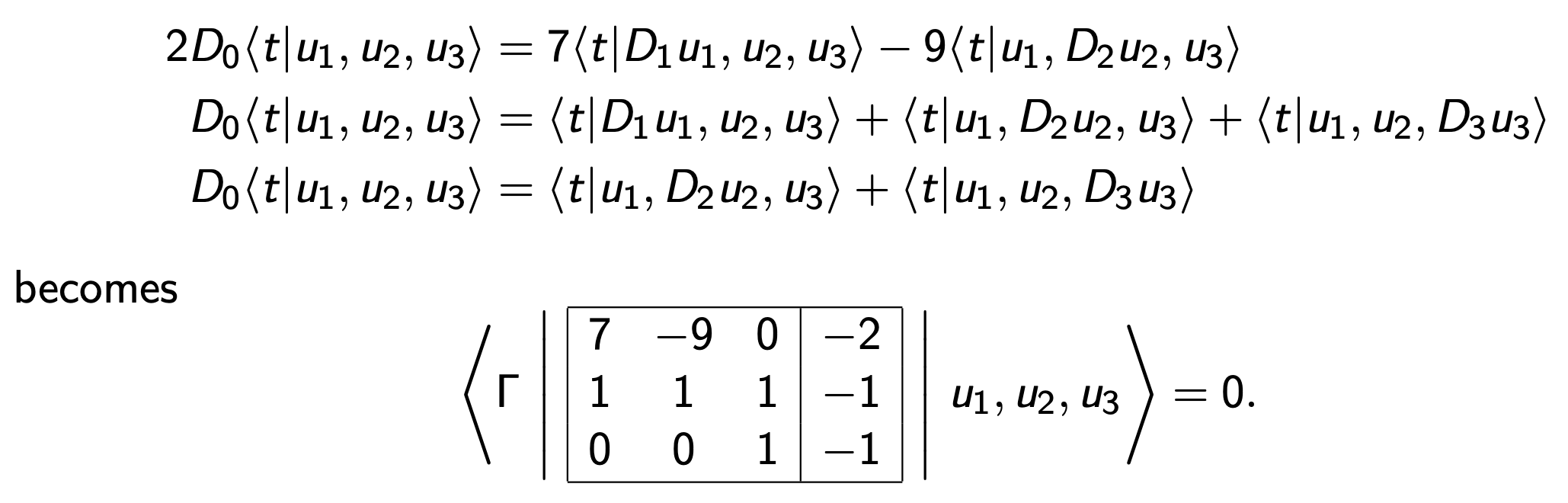
means chisel
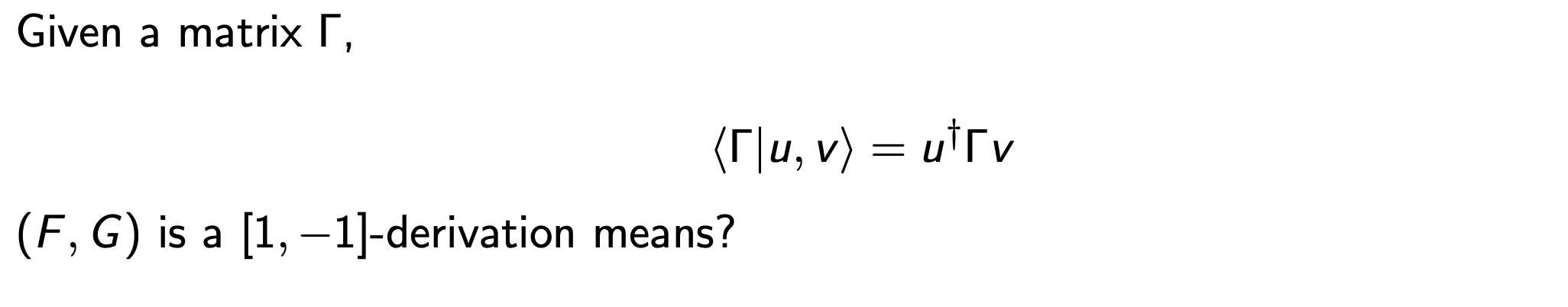
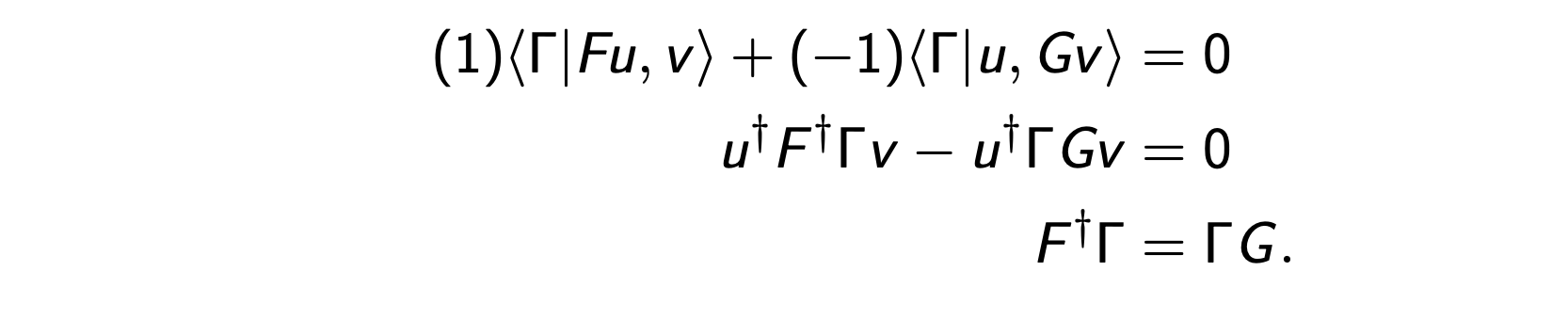
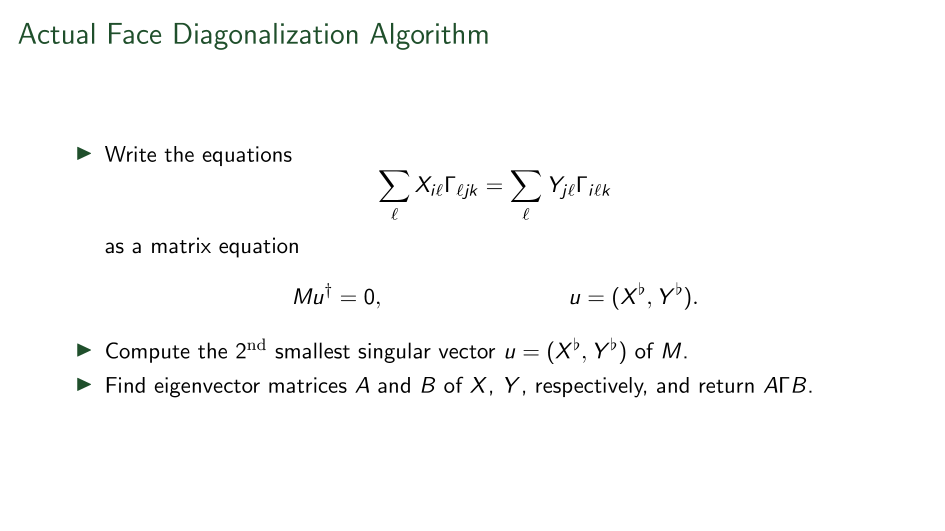
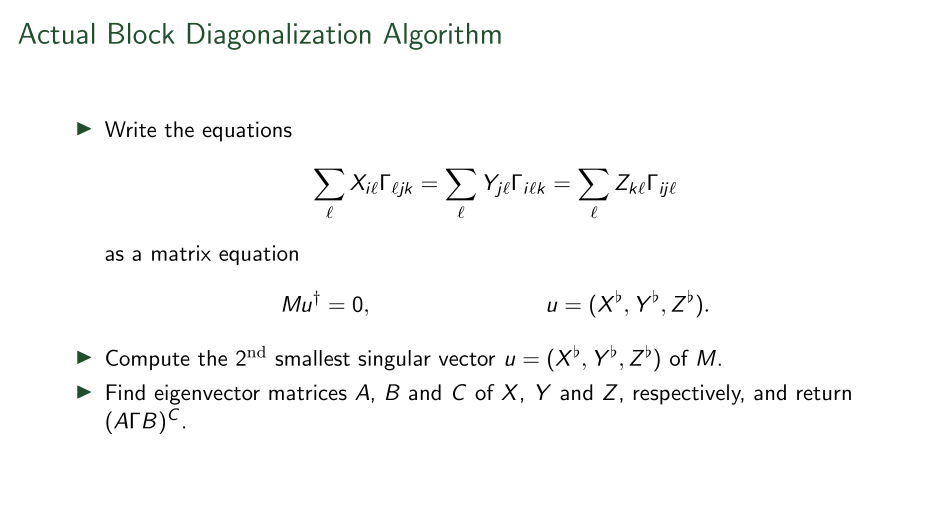
Summary
-
Not tested.
-
Suboptimal implementation
-
We don't understand all the outcomes.
-
But it is unsupervised.
-
Seems to tolerate noise.
-
Does something new, hopefully useful.