Applications of fractional diffusion in option pricing
Jan Korbel
CCS Satelite on Econophysics, 27th October, Lyon

slides available at: slides.com/jankorbel
Option pricing
- First option pricing model (Black and Scholes 1973)
- based on ordinary Brownian motion
- Nobel prize in economics (Scholes, Merton) - 1997
-
In financial crises or in complex markets, the model cannot catch
realistic market dynamics- large drops, sudden shocks, memory effects
- Finite moment log-stable model (Carr and Wu 2003)
- based on Lévy-stable fractional diffusion
- enables large drops
- We generalize the models by using space-time fractional diffusion equation
Space-time fractional diffusion
The STFD equation is defined as
$$ \left({}^*_0 \mathcal{D}^\gamma_t - \mu \ {}^\theta \mathcal{D}_x^{\alpha}\right) g(x,t) = 0$$
Caputo derivative: \( {}^*_{t_0} \mathcal{D}^\gamma_t f(t) = \frac{1}{\Gamma(\lceil \gamma \rceil - \gamma)} \int_{t_0}^t \mathrm{d} \tau \frac{f^{\lceil \gamma \rceil}(\tau)}{(t-\tau)^{\gamma + 1 - \lceil \gamma \rceil}}\)
Riesz-Feller derivative: \(\mathcal{F}[{}^{\theta} \mathcal{D}^\alpha_x f(x)](k) = -|k|^\alpha e^{i \, \mathrm{sign}(k) \theta \pi/2} \mathcal{F}[f(x)](k) \)
Solution can be defined in terms of Mellin-Barnes transform
$$g_{\alpha,\theta,\gamma}(x,t) = \frac{1}{2 \pi i} \frac{1}{\alpha x} \int_{c-i \infty}^{c+i \infty} \frac{\Gamma(\frac{y}{\alpha}) \Gamma(1-\frac{y}{\alpha})\Gamma(1-y)}{\Gamma(1-\frac{\gamma}{\alpha} y)\Gamma(\frac{\alpha-\theta}{2 \alpha} y) \Gamma(1- \frac{\alpha-\theta}{2 \alpha} y)} \left(\frac{x}{-\mu t}\right)^y \mathrm{d} y$$
[1] Physica A 449 (2016) 200-214
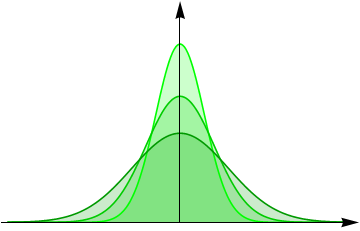
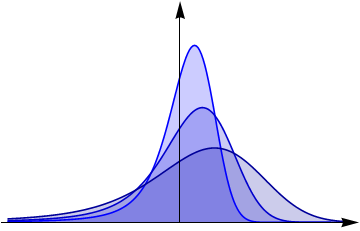
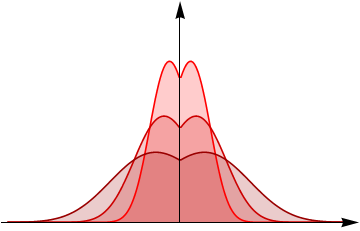
Space-time fractional diffusion
- \(\gamma=1, \alpha=2\) - ordinary Gaussian diffusion
- \(\gamma=1, \alpha<2\) - Lévy-stable diffusion
- \(\gamma \neq 1, \alpha=2\) - diffusion with memory
- \(\gamma \neq 1, \alpha<2\) - space-time fractional diffusion

[6] Mathematics 7 (9) (2019) 796
Space-time fractional option pricing
Price of European call option: $$C(S,K,\tau) = \int_{-\infty}^\infty \max\{S e^{(r+\mu) \tau + x}-K,0\} g_{\alpha,\theta,\gamma}(x,\tau) \mathrm{d} x$$
Interpretation of parameters:
- \(\theta = \max\{-\alpha, \alpha-2\}\)
- maximally asymmetric distribution
- power-law probability of drops (negative Lévy tail)
- Gaussian probability of rises (positive exponential tail
- \(\alpha < 2\) - risk redistribution to large drops
- \(\gamma \) - risk redistribution in time
- \(\gamma < 1\) shorter contracts are more risky
- \(\gamma > 1\) longer contracts are more risky
[1] Physica A 449 (2016) 200-214; [3] Fractal Fract. 2 (1) (2018) 15
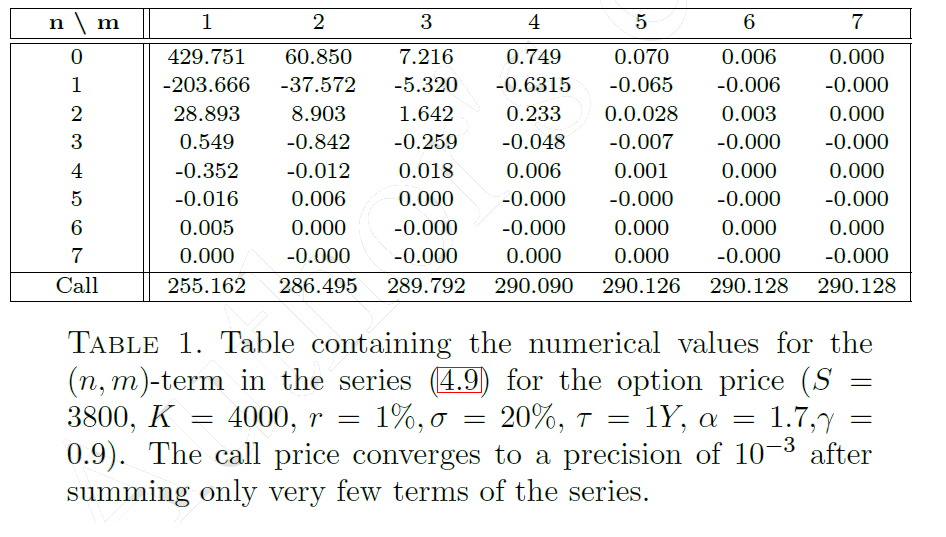
Double-series representation
By using residue summation in \(\mathbb{C}^2\) it is possible to express the price in terms of rapidly-convergent double series ( \(\mathcal{L} = \log \frac{S}{K} + r \tau\) )
$$C(S,K,\tau) = \frac{K e^{-r \tau}}{\alpha} \sum_{n=0}^\infty \sum_{m=1}^\infty \frac{1}{n! \Gamma\left(1 + \frac{m-n}{\alpha}\right)}(\mathcal{L}+\mu \tau)^{n}(-\mu \tau)^{\frac{m-n}{2}}$$
[4] Fract. Calc. Appl. Anal. 21 (4) (2018) 981-1004
Subordinator representation
\(g_{\alpha,\theta,\gamma}(x,t)\) can be represented as a subordinated process
$$g_{\alpha,\theta,\gamma}(x,t) = \int_0^\infty \mathrm{d} l K_\gamma(t,l) L_{\alpha}^\theta(l,x)$$
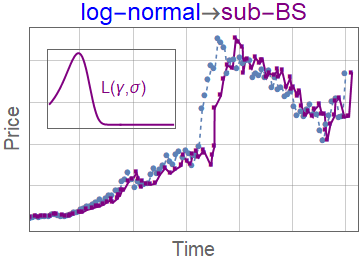
- \(L_{\alpha}^\theta(l,x)\) - Lévy-stable distribution with scaling parameter \(l\)
- \(K_\gamma(t,l\) - subordinator (smearing kernel)
- \(K_\gamma(t,l) = \frac{t}{l^{1+1/\gamma} \gamma} L_\gamma^{\gamma}\left(\frac{t}{l^{1/\gamma}}\right)\)
- We compare with other subordinated models
- Variance gamma \(K_\lambda(t,l) = \lambda e^{\lambda (-t/l)}\)
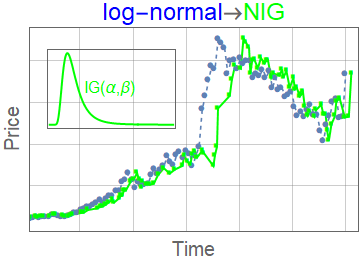
- Negative inverse-gamma \(K_{\alpha,\beta}(t,l) = \frac{e^{-\frac{\beta }{t/l}} \left(\frac{\beta }{t/l}\right)^{\alpha }}{t/l \Gamma (\alpha )}\)
[1] Physica A 449 (2016) 200-214; [8] Risks 8 (4) (2020) 124
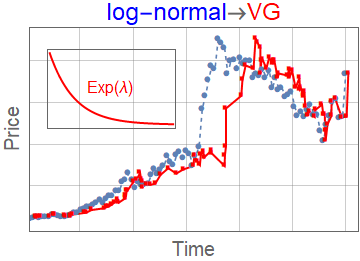
Subordinator representation
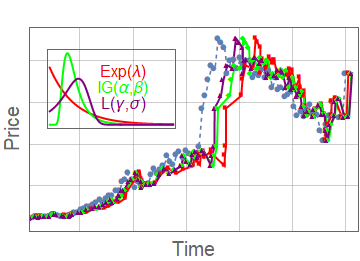
Other results
- Space-time fractional option pricing with varying order of fractional derivatives
- [3] FCAA 19 (6) (2016) 1414-1433
- Pricing of more exotic types of options (American, digital,...) under the space-time fractional diffusion model and formulas for the risk sensitives ("the Greeks" - Gamma, Delta, Rho,...)
- [5] Risks 7 (2) (2019) 36; 10.3390/risks7020036
- [6] Mathematics 7 (9) (2019) 796; 10.3390/math7090796
-
Option pricing with more complicated fractional diffusion equation based on Hilfer-Prabhakar fractional derivative
- [7] Fract. Calc. Appl. Anal. 23 (4) (2020) 996-1012


Thank you!

Keywords: option pricing, Black–Scholes model, fractional calculus, fractional diffusion, long-term memory, Lévy stable processes, jump processes, fractional Brownian motion, subordinated models, Bergomi model, rough volatility models