Using deep mutational scanning to identify possible next steps in SARS-CoV-2 antigenic evolution
These slides: https://slides.com/jbloom/escape-calc
Data shown here from:
Allie Greaney, Tyler Starr, Jesse Bloom (Fred Hutch)
Sunney Xie, Richard Cao, Fanchong Jian, et al (Peking University)
Background: deep mutational scanning antibody-escape calculator
Deep mutational scanning maps how all mutations to SARS-CoV-2 receptor-binding domain (RBD) affect antibody binding
RBD
fluorescently labeled antibody
yeast
fluorescent tag on RBD
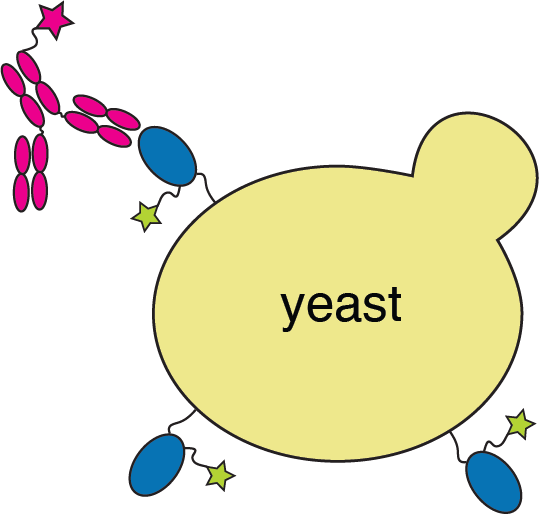
Experiments combine flow cytometry and deep sequencing of a library of yeast expressing all RBD mutants
For an interactive version of this escape map, see:
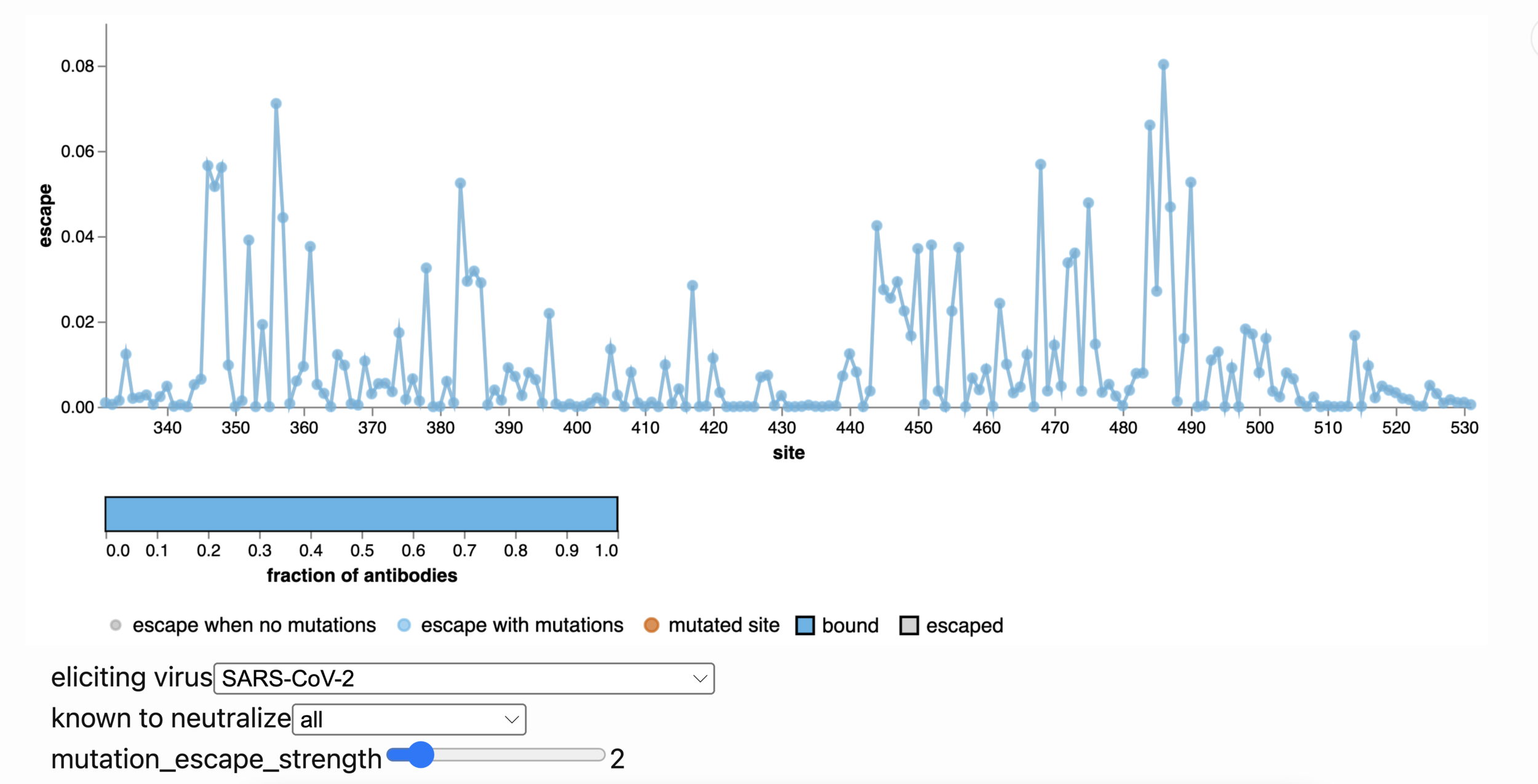
Escape map from one antibody (LY-CoV555, ie bamlanivimab). Peaks indicate sites where mutations escape binding.
484
452
490
Infection / vaccination elicit polyclonal antibodies
How do mutations affect polyclonal antibodies? First, consider an equal mix of three monoclonal antibodies.

Interactive version of this mini example is at https://jbloomlab.github.io/SARS2_RBD_Ab_escape_maps/mini-example-escape-calc/
LY-CoV555 is escaped at both sites 484 and 490, so mutating either site has same overall effect
Average escape across all antibodies

Mutating site 484 or 490 eliminates neutralization by antibody LY-CoV555, as reflected in thick black line showing average
Interactive version of this mini example is at https://jbloomlab.github.io/SARS2_RBD_Ab_escape_maps/mini-example-escape-calc/
Antibody-escape calculator extends this principle to deep mutational scanning data for ~1,500 different human antibodies
Escape calculator is described in Greaney et al (2022), and is available at https://jbloomlab.github.io/SARS2_RBD_Ab_escape_maps/escape-calc/
36 antibodies mapped by Tyler Starr & Allie Greaney in Bloom lab, from early SARS-CoV-2 strains
Antibody-escape calculator extends this principle to deep mutational scanning data for ~1,500 different human antibodies
Escape calculator is described in Greaney et al (2022), and is available at https://jbloomlab.github.io/SARS2_RBD_Ab_escape_maps/escape-calc/
36 antibodies mapped by Tyler Starr & Allie Greaney in Bloom lab, from early SARS-CoV-2 strains
1,522 (!) antibodies mapped by Sunney Xie, Richard Cao, Fanchong Jian, et al at Peking University. From early strains, BA.1, & patients with prior SARS-CoV-1 infection. See here.
What does escape calculator using these data tell us about evolution that has already happened?
Antibodies elicited by early SARS-CoV-2 that neutralize Wuhan-Hu-1 heavily focus on sites like 484, 417, 446

417
446
484
417
446
484
490 not mutated, but antibodies that bind there are escaped by mutation at 484 which is in same epitope.

Note Omicron has additional escape not modeled here due to mutations that put RBD more in down conformation and cause N343 glycan displacement: Cao et al (2022), Gobeil et al (2022), and explanation here.
Omicron BA.1 is mutated at many of these sites, which is why it is neutralized substantially less well by current vaccines
Omicron BA.2 has some different RBD mutations than BA.1, but similar overall escape from antibodies from early SARS-CoV-2

Note Omicron has additional escape not modeled here due to mutations that put RBD more in down conformation and cause N343 glycan displacement: Cao et al (2022), Gobeil et al (2022), and explanation here.
Can identify mutations that mediate further escape. In Dec 2021 we predicted 486 as likely site of future evolution--in April 2022, mutation F486V was identified in Omicron BA.4 and BA.5.

486 is largest site of escape for antibodies not already escaped by mutations in BA.2
What are likely next steps in antigenic evolution of SARS-CoV-2?

Sites of escape from antibodies elicited by early (pre-Omicron) infection/vaccination that still neutralize Omicron BA.2
346
356
444-446
452
450
462
468
486
499
mutated in BA.4/BA.5 or BA.2.12.1
Sites of escape are somewhat different for antibodies from people who had an Omicron BA.1 breakthrough infection

346-348
444-446
452
486
468
mutated in BA.4/BA.5 or BA.2.12.1
356
490
The differences in antibody-escape mutations between people who have / have-not had BA.1 breakthrough infections is consistent with prior studies on other viruses showing that serum antibodies from people with different exposure histories have different viral escape mutations.
Averaging across early SARS-CoV-2 & BA.1 breakthrough exposures, sites of escape in BA.2. Watch these sites!
346-348
444-446
452
486
468
mutated in BA.4/BA.5 or BA.2.12.1
356