Interpreting the evolution of SARS-CoV-2
Jesse Bloom
Fred Hutch Cancer Center / HHMI
These slides at https://slides.com/jbloom/grc-2023

The Faroe Islands


"Measles had not prevailed on the Faroes since 1781, then it broke out early in April 1846."
"Of the 7782 inhabitants, about 6000 were taken with measles."
"Of the many aged people still living in the Faroes who had measles in 1781, not one was attacked the second time."
Panum is describing immune memory, which provides lifelong protection from measles.

CoV-229E causes common colds and has been circulating in humans for a long time.
The typical person is infected every ~3 to 5 years.
How do other human coronaviruses evolve?
Evolution of CoV-229E spike

We experimentally generated CoV-229E spikes at ~8 year intervals so we could study them in the lab:
- 1984
- 1992
- 2001
- 2008
- 2016
Evolution of CoV-229E spike erodes neutralization by human serum antibodies
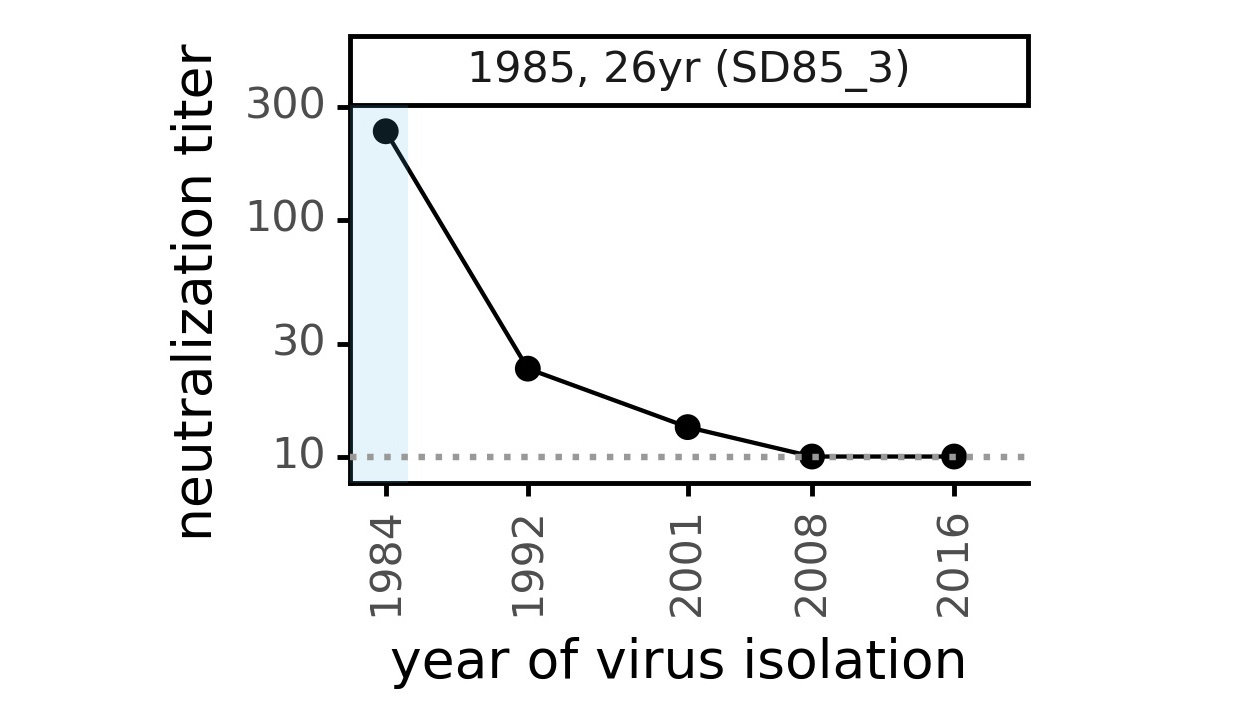
Evolution erodes CoV-229E neutralization by different sera at different rates

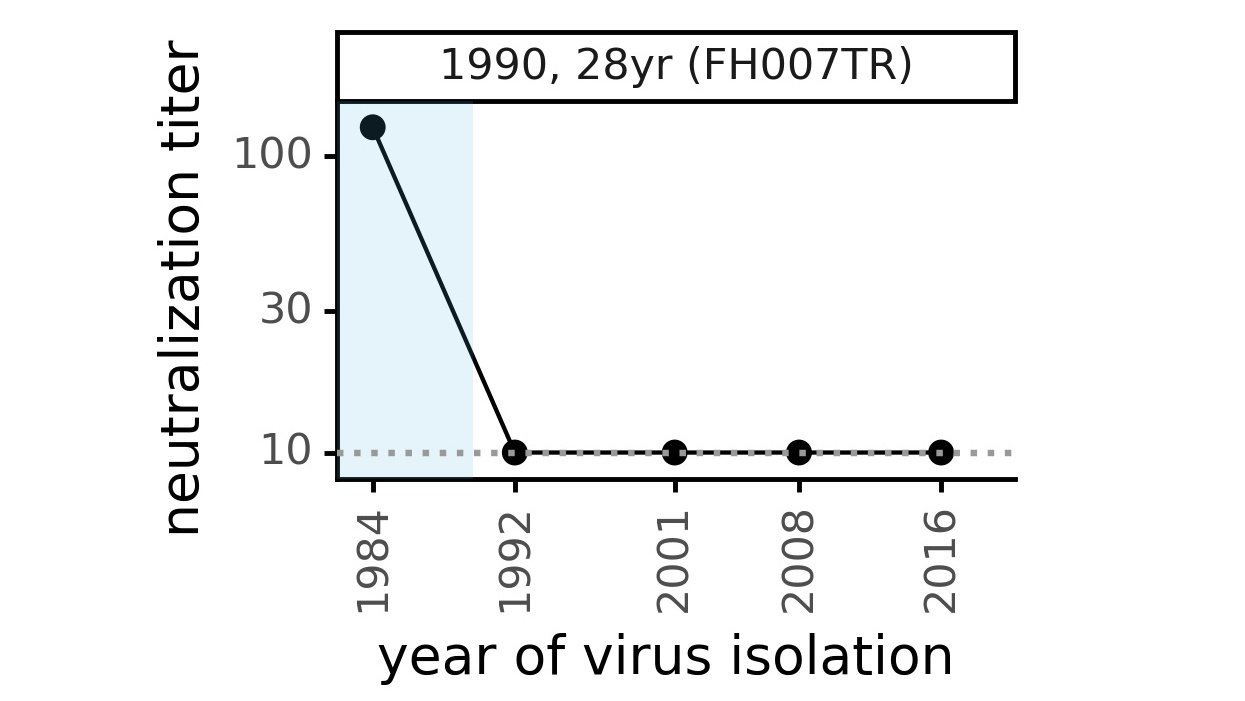
Ideally vaccines would elicit evolution-resistant neutralizing antibodies (like those naturally made by person at right) rather than evolution-sensitive antibodies (like those naturally made by person at left)
Strongest evolutionary selection is in RBD
Sites of evolutionary change in the spike of CoV-229E over the last four decades
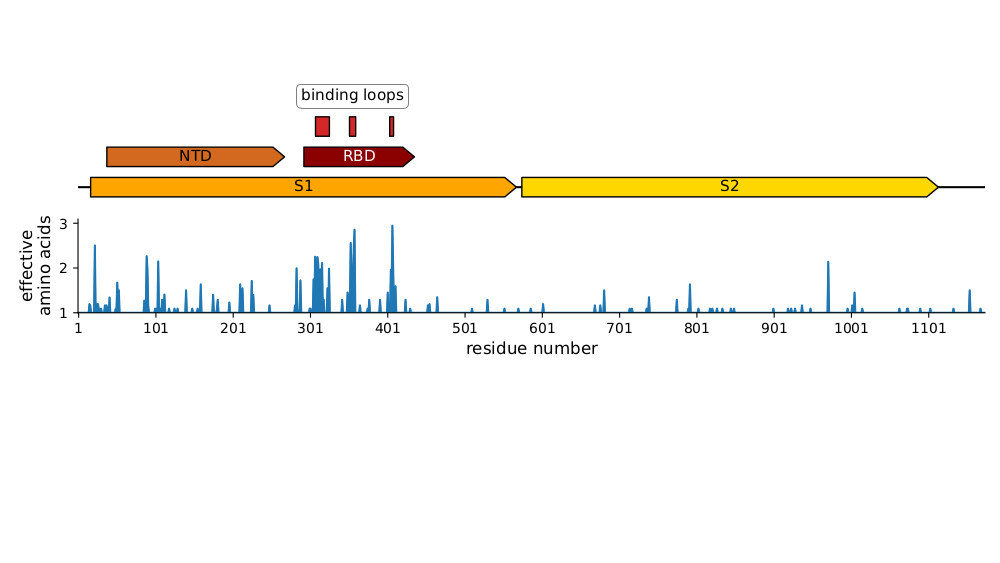
Strongest evolutionary selection is in RBD
Sites of evolutionary change in the spike of CoV-229E over the last four decades

Sites of mutations in SARS-CoV-2 Omicron BQ.1.1 spike relative to Wuhan-Hu-1
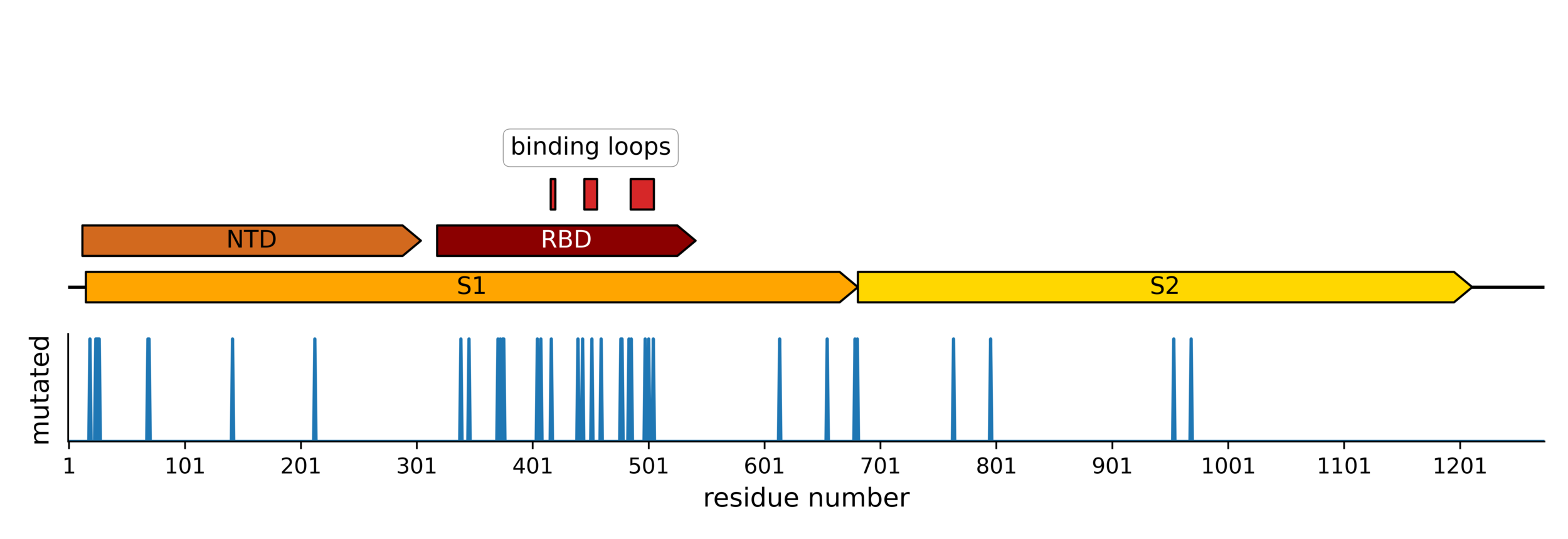
RBD does not run out of evolutionary space
25 of 31 residues in CoV-229E RBD that contact receptor varied during virus's evolution in humans over last ~50 years (Li et al, 2019)
How did Omicron acquire so many mutations with no sampled evolutionary intermediates?
The molecular clock identifies unusual patterns in Omicron evolution
Excess antibody-escape mutations in spike are characteristic of viruses that evolve in chronic human infections
During typical acute infections, random transmission bottlenecks disrupt selection
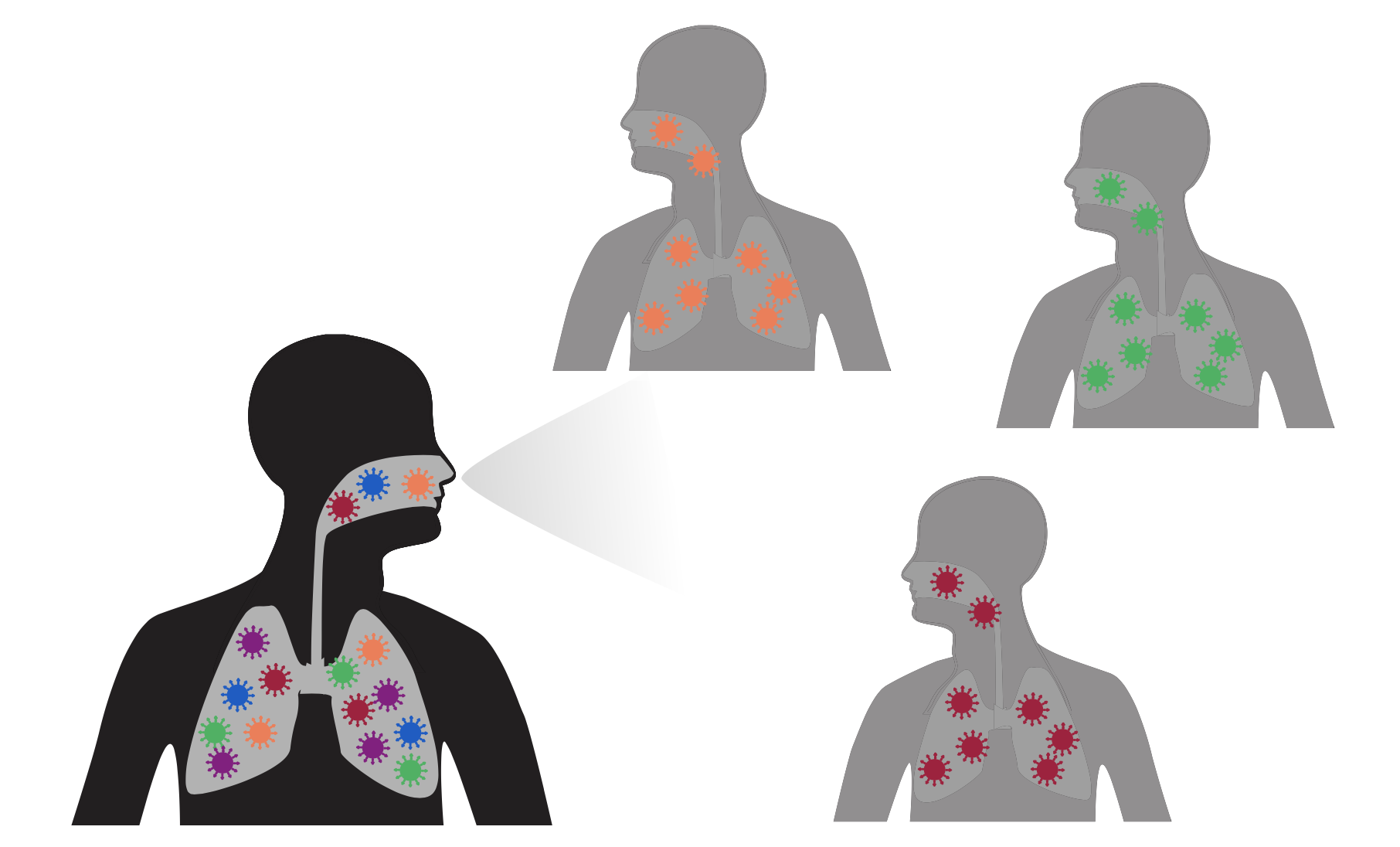
But in chronic infections of 100+ days, selection can fix antibody-escape mutations without bottlenecks
If evolution is being driven by neutralizing antibody escape, what might be next?
Deep mutational scanning to map RBD mutations that escape antibody binding
RBD
fluorescently labeled antibody
yeast
fluorescent tag on RBD
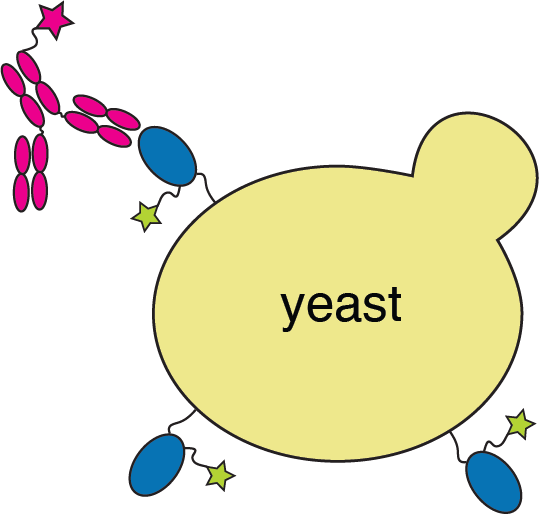
Experiments combine flow cytometry and deep sequencing of a library of yeast expressing all RBD mutants
These measurements can be made on ~10,000 to ~100,000 mutants all at once

Escape map from one antibody (LY-CoV555, ie bamlanivimab)
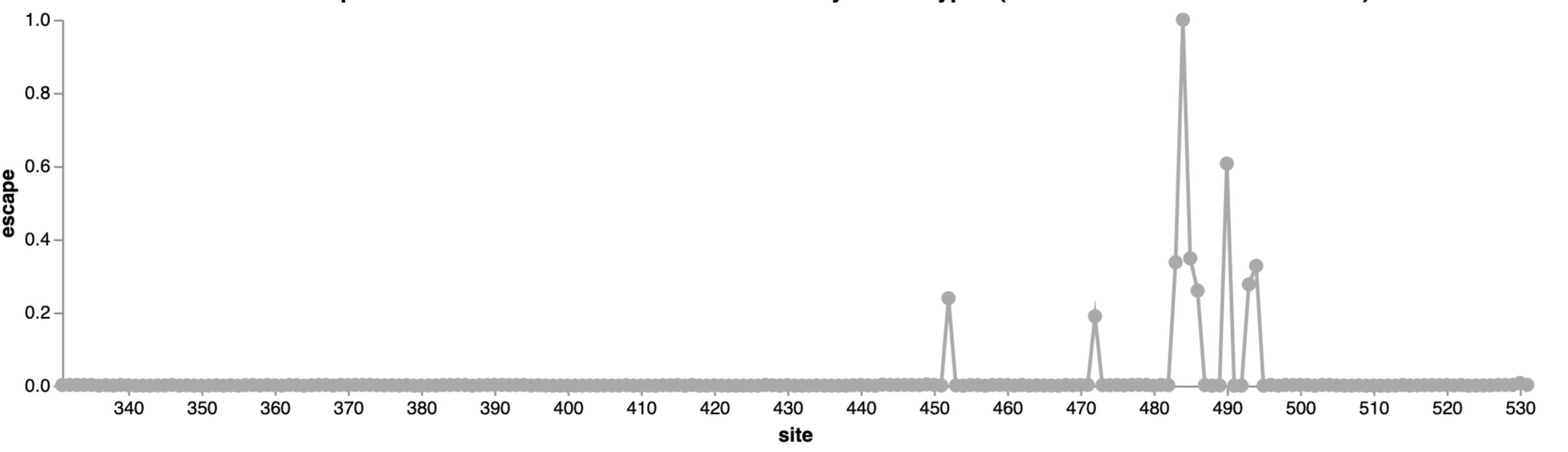
484
452
490
This turned out be an unfortunate choice of an antibody for Eli Lilly to develop as drug, as mutations at sites 484 and 452 were prevalent by early to mid 2021
Infection / vaccination elicit polyclonal antibodies
Deep mutational scanning has now been applied to many antibodies
36 antibodies mapped by Tyler Starr & Allie Greaney in Bloom lab.
36 antibodies mapped by Tyler Starr & Allie Greaney in Bloom lab.
>4,000 (!) antibodies mapped by Yunlong Cao et al at Peking University. See here and here.
Deep mutational scanning has now been applied to many antibodies
Sites of likely future escape in XBB
Interactive escape calculator: https://jbloomlab.github.io/SARS2-RBD-escape-calc/
ACE2 affinity from: https://jbloomlab.github.io/SARS-CoV-2-RBD_DMS_Omicron/RBD-heatmaps/
Fitness effects from: https://jbloomlab.github.io/SARS2-mut-fitness/S.html
We can integrate these experimental data to track antigenic evolution in real time
Bloom lab
Tyler Starr
Allie Greaney
Kate Crawford
Rachel Eguia
Peking University
Yunlong Cao
Fanchong Jian
University of Washington
Helen Chu and HAARVI cohort
Alex Greninger and UW Lab Medicine
Nextstrain
Cornelius Roemer
Richard Neher
Trevor Bedford



