Ecosystem-centered microbial
ecology & biogeochemistry
DPES, University of Toronto-Scarborough (March 15th, 2022)
Jesse McNichol (he/him) : PhD, Biological Oceanography
Postdoctoral Scholar, University of Southern California





How do microbial communities* influence the Earth System**, and vice-versa***?

*whole community methods

**primary productivity, elemental cycling

***effect of anthropogenic pressure on ecosystems
Microbe art: @claudia_traboni
Core research question
Microbiology
Bioinformatics

Pillars support core research question
Environmental science
A lab that links microbial diversity & biogeochemical function in the context of global ecosystem change with modern 'omics-enabled techniques

(In)organic chemistry
Ecosystem modelling
Biogeochemistry
Climate & physics


My scientific training
Local systems
Getting there from here...
|
|
Years 1-2 |
|---|---|
|
|
Years 3-4 |
|
|
Year 5 onwards |
Getting there from here...
|
|
Years 1-2 |
|---|---|
|
|
Years 3-4 |
|
|
Year 5 onwards |


- Begin "shovel-ready" projects
- In silico primer optimization
- Explore local systems
Y1-2: Ecophysiology of vent Campylobacteria
-
Addresses basic questions about oxygen and carbon dioxide metabolism
- Biogeochemical, Earth Systems History implications
- Constrained projects with samples, data, and clear goals
- International collaborations
- NSERC Discovery Grant (GS12/13/16)



?




Y1-2: Ecophysiology of vent chemoautotrophs (1)
- What is the genetic basis of differential oxygen tolerance in hydrothermal vent microbes?
Advantages for mentees:
- Clear environmental context, data available
- Unique publication
- Implications for evolution over geological time scales
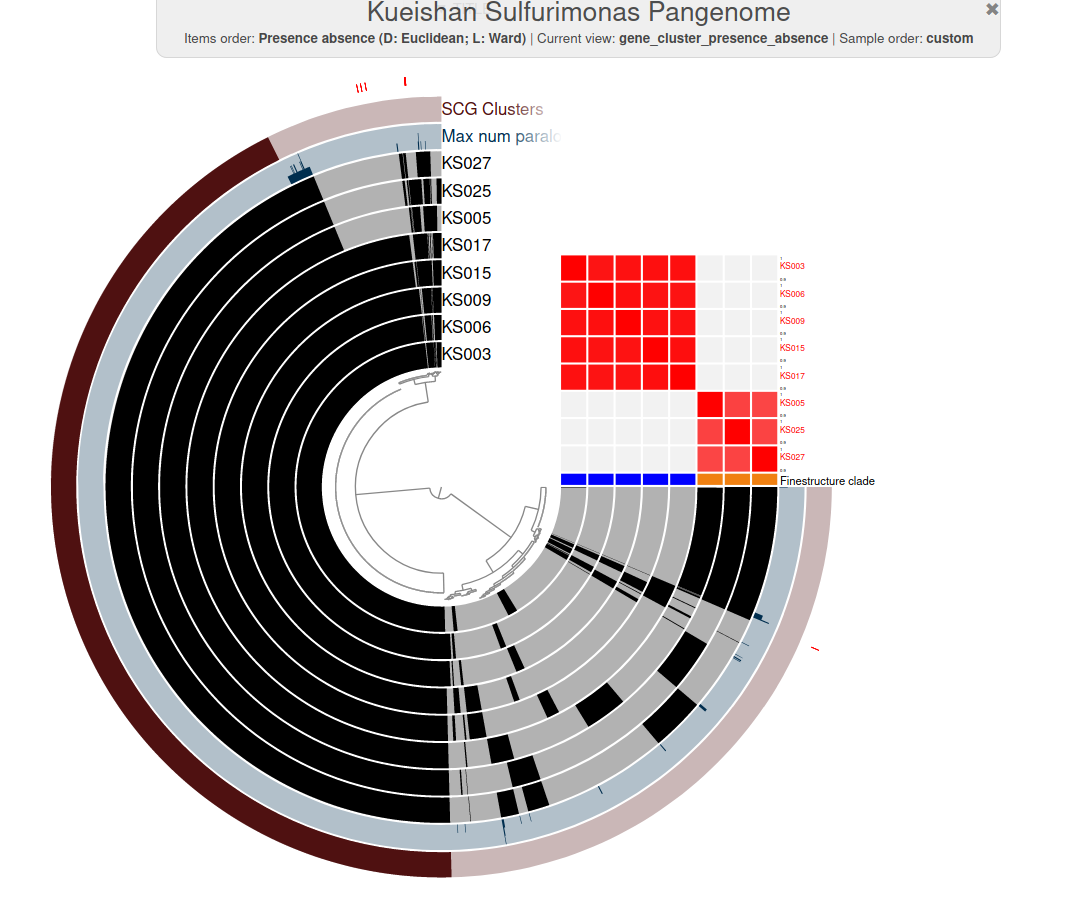
O2 caused major shift in community over ~ 24 h

Use single-cell genomes to investigate genetic basis of this response

Y1-2: Ecophysiology of vent chemoautotrophs (2)
- What characterizes a new genus of chemoautotrophs isolated from shallow-water vents in Taiwan?
Advantages for mentees:
- Fun, hands-on introduction to microbiology
- Impactful publication
- Could be extended with lab experiments, metagenomics, or possibly field work in Taiwan



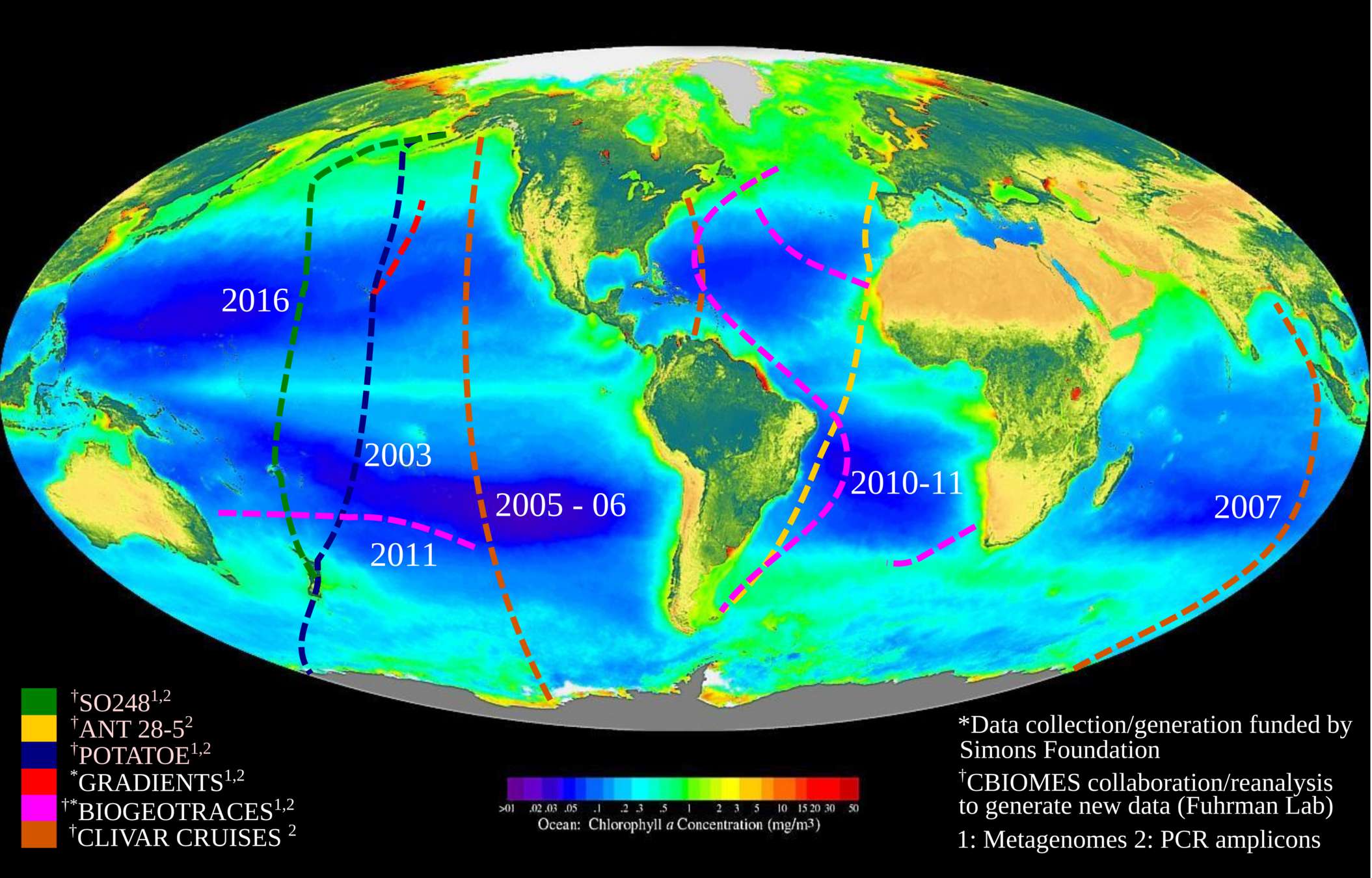
Y1-2: Biogeography of global-scale transects
-
Address major gaps in our understanding of whole ecosystems
- International, interdisciplinary collaboration
- Potential funding from Simons Foundation International
- Access sample material from collaborators





Y1-2: Biogeography of global-scale transects (1)
- How well do imaging-based methods (flow cytometry, imaging flow cytobot) align with 3-domain metabarcoding?
Advantages for mentees:
- Simple but impactful
- Simons CMAP database makes possible
- Extend by mining global distribution data


Kalmbach et al. (2017), arXiv:1703.07309v1

Y1-2: Biogeography of global-scale transects (2)
- How can we infer changes in microbial community composition change across decadal time-scales using barcoding data from different regions of SSU rRNA?
Advantages for mentees:
- "Rosetta stone" allows intercomparisons, FISH probe design from barcodes
- Address previously impossible questions
- "Data science" project experience



Dueholm et al. (2020) mBio, e01557-20
Database of full-length 16S rRNA

Model-data intercomparison (Yubin Raut, USC)


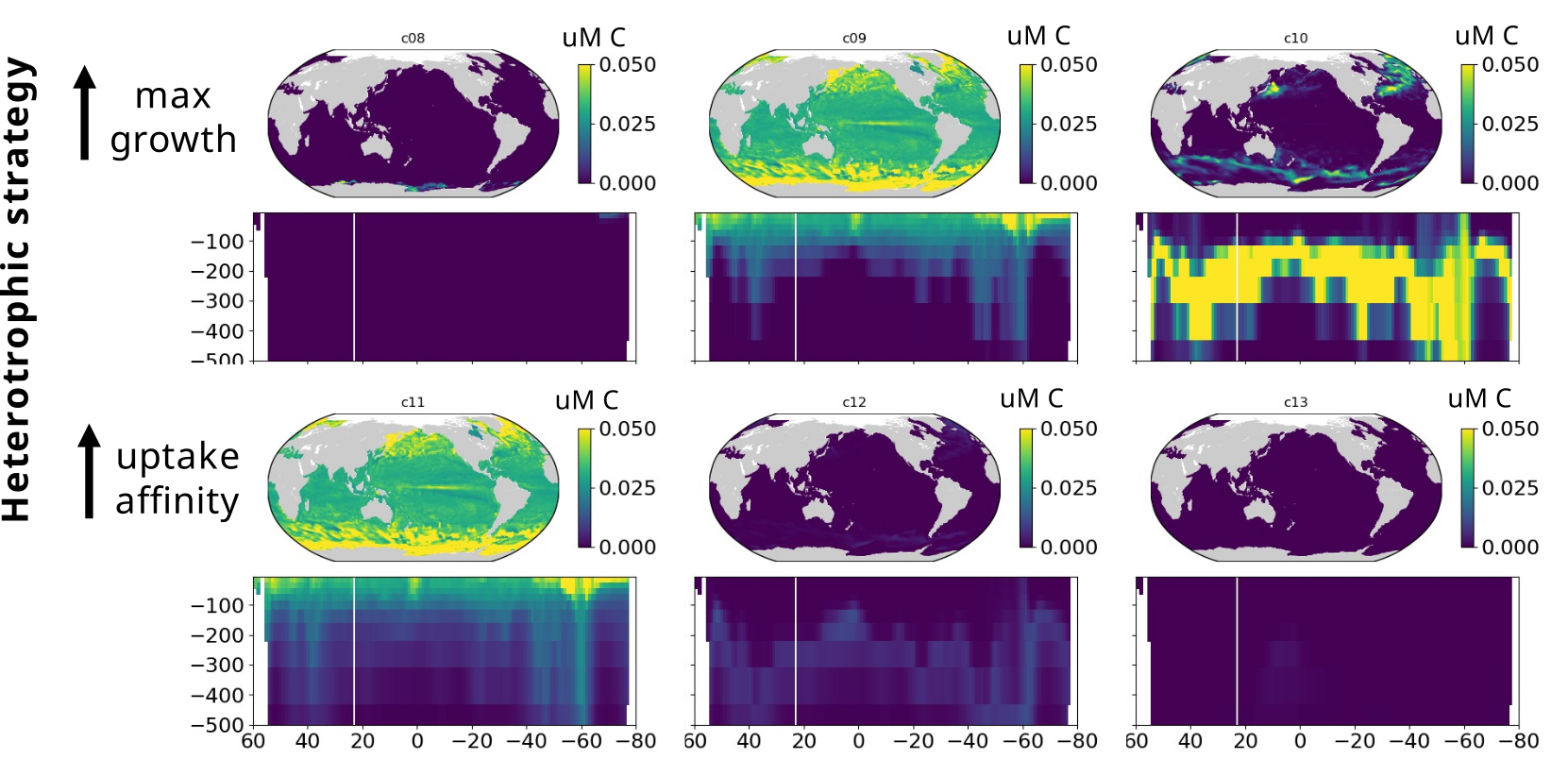
Modelling marine heterotrophs (Emily Zakem, Carnegie Inst.)
- Play key intermediate role between data and modelling worlds
- Basis of application for Simons Foundation "Early Career Investigator in Marine Microbial Ecology and Evolution Awards"
- Contingent on successful NSERC application or other federal award
Y1-2: Biogeography, modelling, and funding

Y1-2: Equipment needs
|
|
Years 1-2 |
|---|---|
|
|
Years 3-4 |
|
|
Year 5 onwards |

Epifluorescence microscope

Microoxic cultivation equipment
A small computer lab for open-source bioinformatics software (qiime2, anvi'o) and databases (PR2, SILVA, GTDB)
Integrating disciplinary pillars = holistic research
Holistic, process studies require a "model system"
Ecology & environmental science

Microbiology
Bioinformatics


One great need is to expand upon the existing monitoring programs ... to address other cycles including organic carbon, seasonality of all parameters, fine-grained vertical profile information, and biogeochemical transformation rates of many kinds."
Y1-2: Develop local freshwater "model system"
Y1-2: Develop local freshwater "model system"
- Very few microbial observations in Laurentian Great Lakes; it's time to bridge the "salty divide"!


...the differences between fresh and salt water [are] trivial, when compared to the common principles with which limnologists and oceanographers alike are concerned” —Redfield (1956)
Y1-2: Find collaborators to obtain samples
- Reach out to CCIW scientists to discuss collaboration
- Contact "eDNA" researchers, other microbial ecologists
- Explore small-scale local sampling to capture blooms

Alice Dove (2009), AEHMS.

Image: Harrison Fornasier
Seek longer term funding sources:
Great Lakes Protection Initiative?
Cooperative Science and Monitoring Initiative (CSMI)?

CCIW, Burlington, ON

Needham & Fuhrman (2016), 10.1038/nmicrobiol.2016.5

Microbe art: @claudia_traboni
Y1-2: Develop a solid foundation for "model system"
- "3-domain metabarcoding" is a powerful tool






3-domain metabarcoding as a foundation

FISH
SIP
Identity + Activity

Microbe art: @claudia_traboni
- 3-domain metabarcoding is a powerful tool
-
"3 for the price of one" assay:
- Eukaryotic 18S, e(ukaryotic)16S, p(rokaryotic)16S
-
"3 for the price of one" assay:
Y1-2: Develop a solid foundation for "model system"
p16S
e16S
18S

Microbe art: @claudia_traboni
18S
p16S
e16S
- 3-domain metabarcoding is a powerful tool
-
"3 for the price of one" assay:
- Eukaryotic 18S, e(ukaryotic)16S, p(rokaryotic)16S
-
"3 for the price of one" assay:
Y1-2: Develop a solid foundation for "model system"
- 3-domain metabarcoding is a powerful tool
-
"3 for the price of one" assay:
- Eukaryotic 18S, e(ukaryotic)16S, p(rokaryotic)16S
- A step towards Analytical 'omics
-
"3 for the price of one" assay:

18S
p16S
e16S

Chavez et al (2021), Oceanography
Y1-2: Develop a solid foundation for "model system"
- 3-domain metabarcoding is a powerful tool
- Primer bias can distort results
- Optimization for freshwater needed

Primer bias
Microbe art: @claudia_traboni
Y1-2: Optimize foundation
Y1-2: Optimize foundation
-
Goal: Optimize 3-domain metabarcoding for freshwater systems
- Obtain metagenomes from range of trophic status, depth, season
- Using in silico pipeline, develop metabarcoding primers for freshwater covering as much cellular life as possible

Y 3-4
|
|
Years 1-2 |
|---|---|
|
|
Years 3-4 |
|
|
Year 5 onwards |



- Link Campylobacteria work to Earth History
- Begin holistic experimental work
- Start local sampling, publish results

- Begin "shovel-ready" projects
- In silico primer optimization
- Explore local systems

- Developed theoretical metabolic model of chemoautotrophic Campylobacteria during PhD
Y 3-4: Campylobacteria, physiology, and evolution

Targets for physiological / evolutionary studies
- Campylobacteria are oxygen-sensitive and capnophiles (CO2-loving), existing in an "intermediate evolutionary state"
-
How does the emergence of genomic traits/clades relate to the development of a more oxic, lower CO2 atmosphere?
- Method: Molecular dating using genome phylogeny
- Japanese collaborator has agreed to contribute genomes








Y 3-4: Campylobacteria, physiology, and evolution

Models
Microbe art: @claudia_traboni
Ecosystem
Kalmbach et al. (2017), arXiv:1703.07309v1



Physics
Biology
Chemistry

Y3-4: Begin holistic studies
Y3-4: Begin holistic studies






Identity + Activity


Sebastián & Gasol (2019), 10.1098/rstb.2019.0083
Y3-4: Develop single-cell activity methods
- Taxonomy (CARD/HCR-FISH) / transcription (FISH-TAMB)
- Respiration, cell viability (RSG); Polyphosphate content (DAPI)
Automatic cell-sorting + environmental databases = taxon-specific activity or genetic potential measurements
Many uses for sorted cells:
- Taxon-specific isotope uptake
- Mini-metagenomes with few cells
- Single-cell genomics
- Cell isolation for cultivation
Pjevac et al (2019) 10.1111/1462-2920.14739
Multiple sorting axes now possible

Y3-4: Develop single-cell activity methods

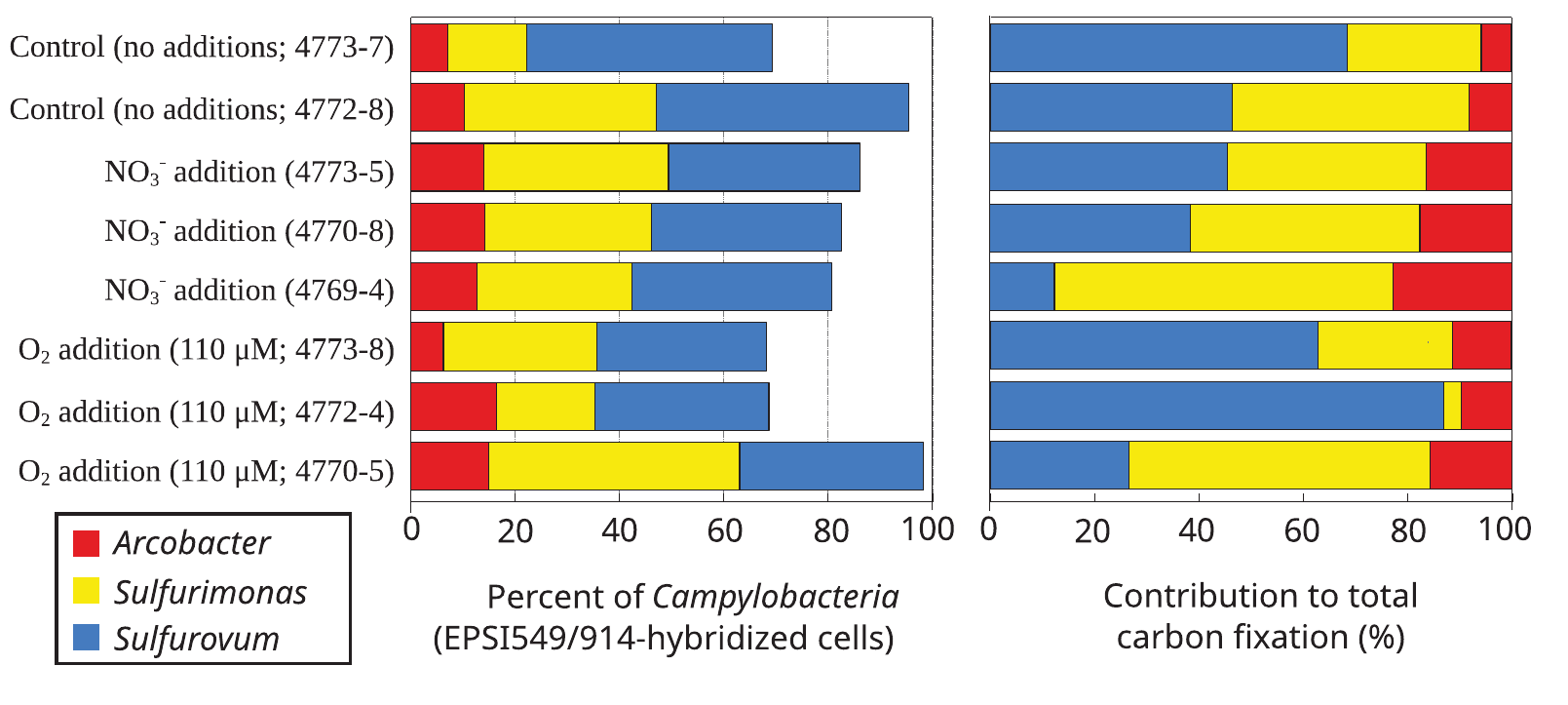
Experience with holistic studies
Specific FISH labeling + radiocarbon incubations = Carbon fixation rates were measured at the genus level and across different conditions
- Developed novel high-pressure incubations
- Quantified bulk and single-cell CO2 fixation
- Used DNA to measure community change

FISH
SIP


Experience with holistic studies

'omics data in an experimental, biogeochemical context
Y3-4: Apply holistic techniques "at sea"
-
"Rosetta stone" => FISH probes:
- Cell enrichment for mini-metagenomes
- Visualize predicted symbioses / other ecological interactions
- Measure cell-specific traits such as biovolume
-
Attempt cultivation of "microbial dark matter":
- Flow cytometry with "live stains"
- Enrichment experiments


Y3-4: Begin freshwater monitoring
-
Begin sampling campaigns:
- Validate performance of 3-domain metabarcoding across nutrient gradients, seasons
- Publish descriptions of whole-community structure and dynamics, compare with (phyto/zoo)plankton records
- Automate wet lab techniques
Image: Warren Currie

- Intercalibration, intercomparison
- Methods development
- Interdisciplinary by nature
- Lots of room for young scientists!


Y3-4: Become involved in BioGeoSCAPES*
*Depending on funding, availability of reference material
Y3-4: Equipment needs
|
|
Years 1-2 |
|---|---|
|
|
Years 3-4 |
|
|
Year 5 onwards |




Robotic automation for high-throughput DNA prep

Automatic cell sorter to measure in situ activity, sort cells for sequencing
|
|
Years 1-2 |
|---|---|
|
|
Years 3-4 |
|
|
Year 5 onwards |




- Begin "shovel-ready" projects
- In silico primer optimization
- Explore local collaborations
Y5 - onwards
A lab that links microbial diversity & biogeochemical function in the context of global ecosystem change with modern 'omics-enabled techniques
- Link Campylobacteria work to Earth History
- Begin holistic experimental work
- Start local sampling, publish results
Y5 - onwards: Scientific questions
Great Lakes work:
- What can spatiotemporal abundance patterns and interaction networks from 3-domain metabarcoding contribute to models?
- What biogeochemical functions do the prokaryotes catalyze?
- What are the biogeochemical consequences of extreme phosphorus / iron limitation in oligotrophic lake waters?
Global work:
- Can targeted mini-metagenomes improve databases & models?
- Can we cultivate microbial dark matter?
Vent work:
- What proportion of organisms are active?
- How abundant are oxygen-sensitive / tolerant types in situ?
Y5 - onwards: Outside the box
Departmental / interdepartmental collaborations:
- Who are polyphosphate-accumulating & nitrogen-fixing organisms?
- Link DOM transformations to microbial metabolism quantitatively?
- What are the consequences of persistent organic pollutants on microbial community structure and biogeochemistry?
- Centre for Global Change Science
Access work:
- How to make microbiome profiling more accessible, affordable, reliable?
- How can diverse students be nurtured?
Natural history:
- What unique projects can students of Native Microbiota devise?
- A "SEA-PHAGES"-like project?
Potential for training HQP
-
Data Science
- Genomics, amplicon sequencing, FAIR principles
- conda, snakemake, github, bash/python
-
Microbiology
- High-throughput cultivation approaches
-
Environmental science
- Oceanography, limnology, water quality
- Holistic ecosystem measurements
Ecosystem-driven research

Motivated by desire to understand the Earth System

We anticipate that as trait-based biogeography continues to evolve, micro- and macroorganisms will be studied in concert, establishing a science that is informed by and relevant to all domains of life.” -Green, Bohannan, and Whitaker, Science (2008)
Acknowledgements
WHOI / UFZ: Stefan Sievert, Jeff Seewald, François Thomas, Niculina Musat, Craig Taylor
CUHK / Academia Sinica: Haiwei Luo, Annie Wing-Yi Lo, Benny Chan
USC/MIT/UCSB/Dalhousie/Carnegie: Jed Fuhrman, Yubin Raut, Enrico Ser-Giacomi, Paul Berube, Steven Biller, Mick Follows, Stephanie Dutkiewicz, Craig Carlson, Zoe Finkel, Emily Zakem







Mentoring philosophy & DEI
Instrumental
- Real data, skills
- Student-driven research
- Important questions, diverse collaborations
Psychosocial
Evidence-based approaches
- Building "soft skills"
- Foster emotional belonging
- Student-centered mentoring philosophy
- Modern pedagogy
- Scaffolding approaches
- Culturally-aware mentoring
Y5 - onwards: Other potential collaborators
- Niculina Musat, Leipzig, Germany
- ProVis: Single-cell techniques including NanoSIMS
- Jeff Seewald, WHOI, USA
- Hydrocarbon chemistry
- Irene Wagner-Döbler / Meinhard Simon, Germany
- Plymouth Marine Laboratory, UK
- Camila Signori, Brazil
- Shengwei Hou, SUSTech, China
- Grad student community
The dearth of direct measurements of PP is an obstacle for ground truthing remotely sensed PP."
Near total absence of
winter measurements of OC cycling and virtually all other biogeochemical parameters also is an important gap in knowledge."
Methane exchange with the atmosphere has seldom been examined in the Great Lakes.
There have been only a few measurements of N2O, but both oligotrophic and eutrophic waters are a source to the atmosphere..."
There have been only a few measurements of anammox in the Great Lakes..."
Nitrogen fixation has seldom been measured in the Great Lakes but is usually considered mi-
nor. Nevertheless, some studies suggest fixation may be more important than normally realized."
Y1-2: Develop local freshwater "model system"
Clade 1:
+ denit, + N2'ase
N source & sink
Clade 2:
- denit, + N2'ase
N source



Diagram = Li et al., 2018.

N2
Campylobacteria and biogeochemistry
- Use metagenomics to assess impact in natural system
Craig Carlson, Elisa Halewood, UCSB
P16S/N
Fraction of 18S amplicon sequences

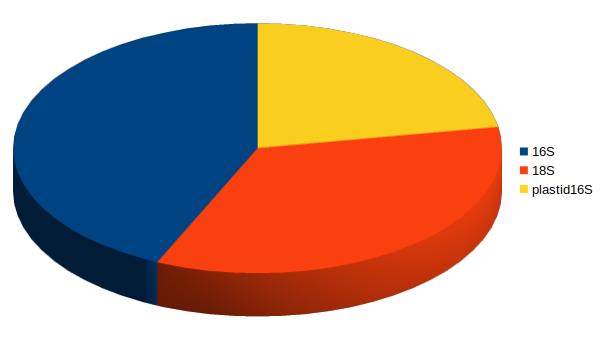
16S
plastid 16S
18S




Jan-Feb 2005
Feb-Mar 2006
With deep sequencing, good coverage for all 3 domains
Looking for interactions
plastid
16S
mito 16S
nuclear 18S
Space / time
Abundance
A eukaryotic phytoplankter
Complementary to existing techniques
"eDNA"




Jan-Feb 2005
Feb-Mar 2006
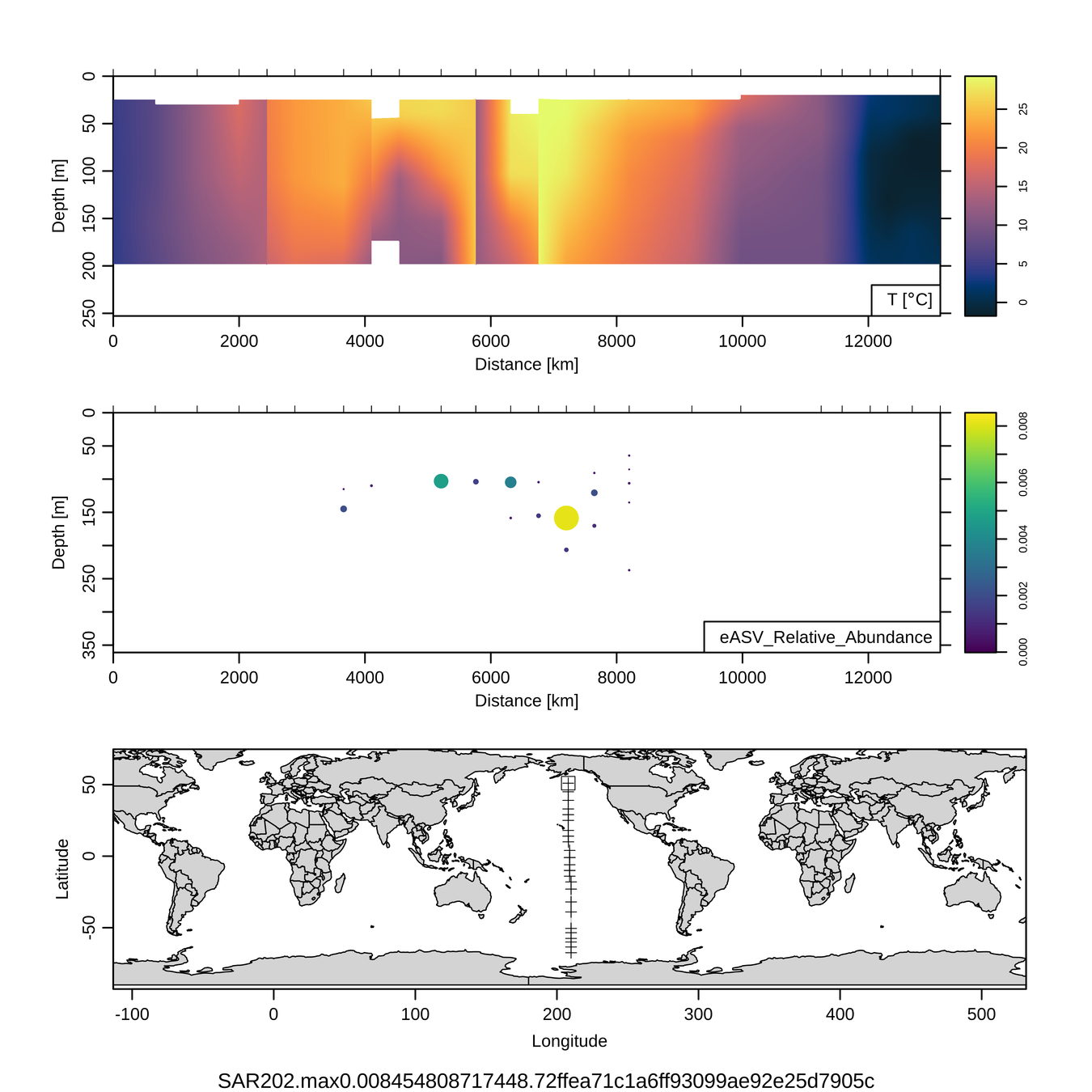
Craig Carlson, Elisa Halewood, UCSB
P16S/N - Biogeography of top 10 SAR202 "species"




Jan-Feb 2005
Feb-Mar 2006
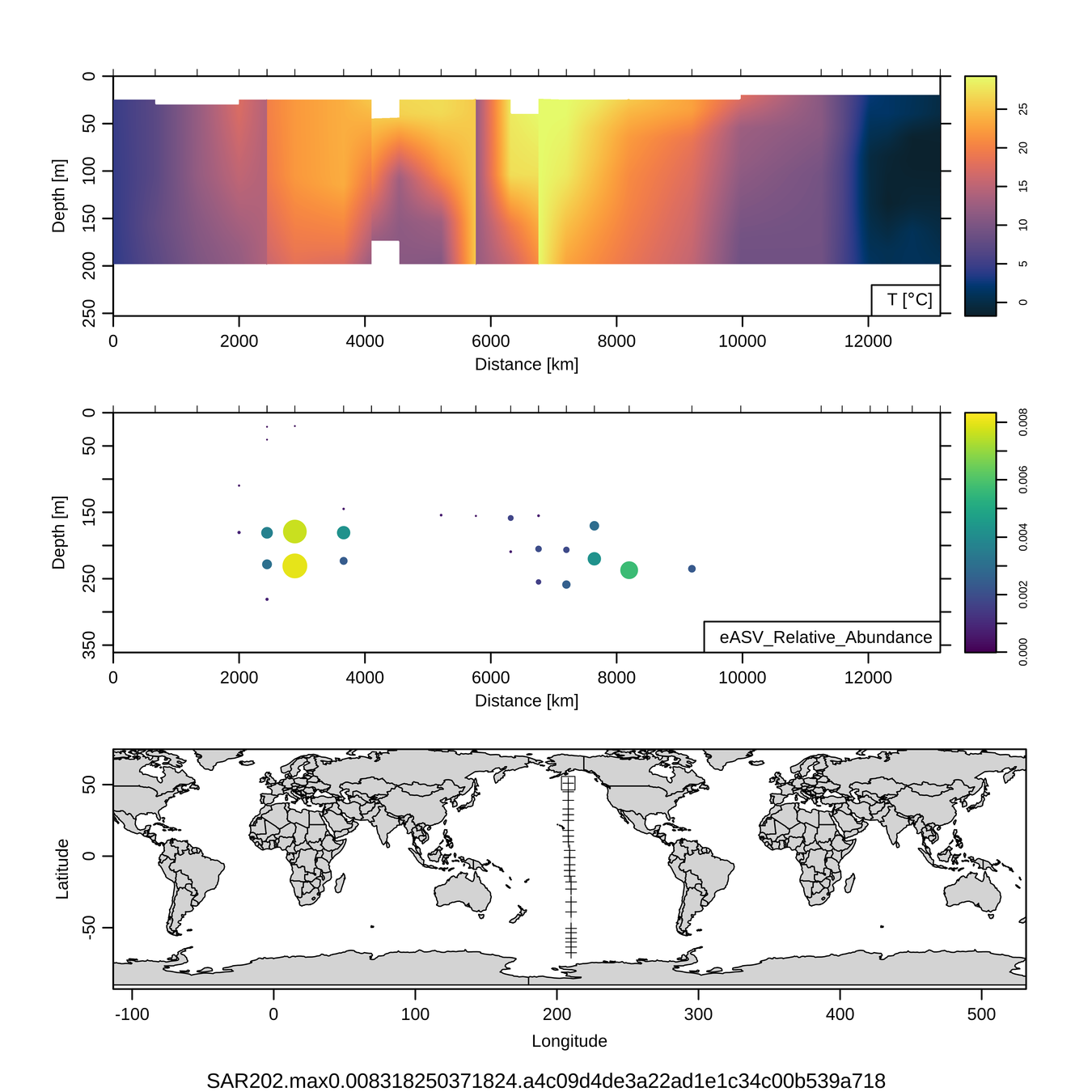
Craig Carlson, Elisa Halewood, UCSB
P16S/N - Biogeography of top 10 SAR202 "species"




Jan-Feb 2005
Feb-Mar 2006
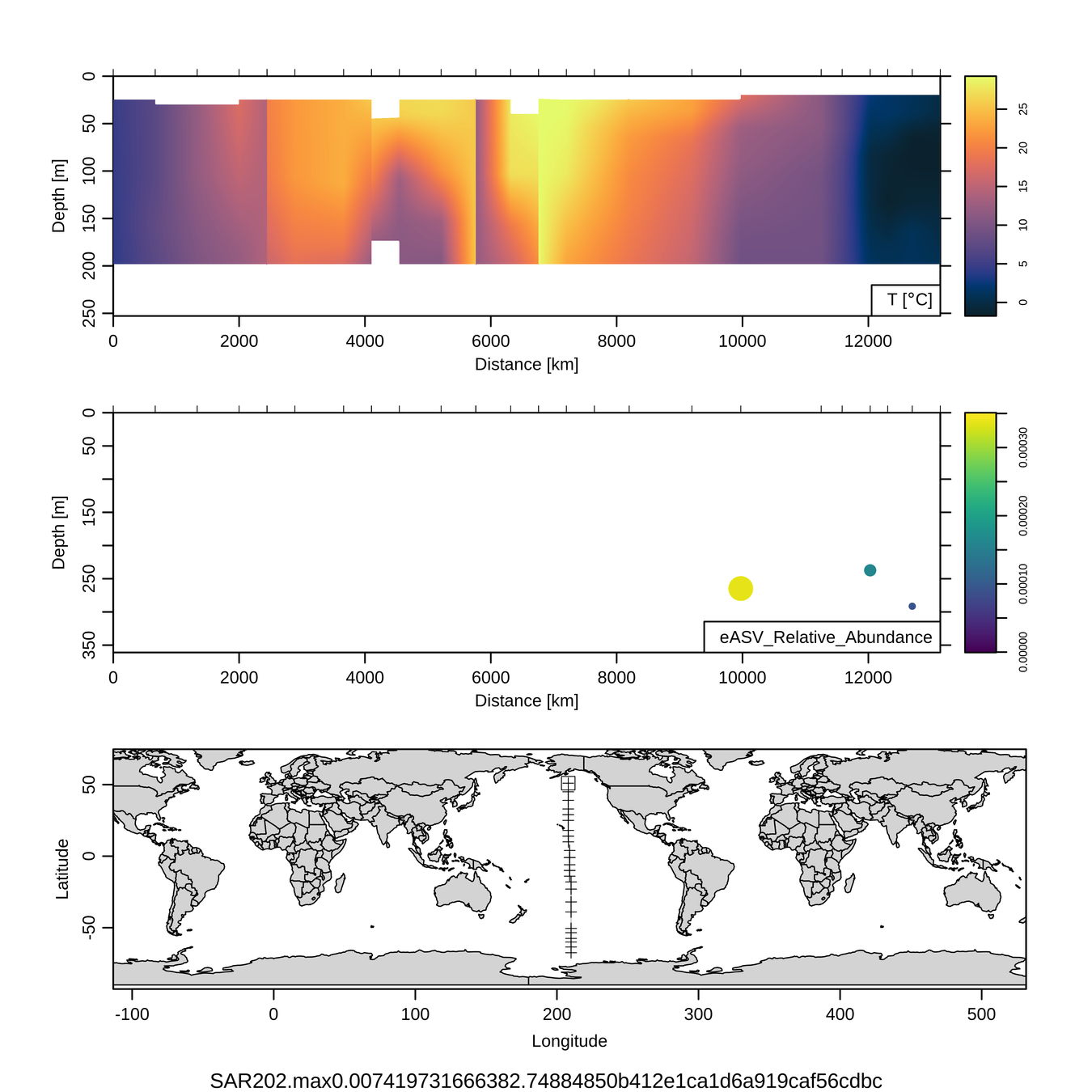
Craig Carlson, Elisa Halewood, UCSB
P16S/N - Biogeography of top 10 SAR202 "species"




Jan-Feb 2005
Feb-Mar 2006
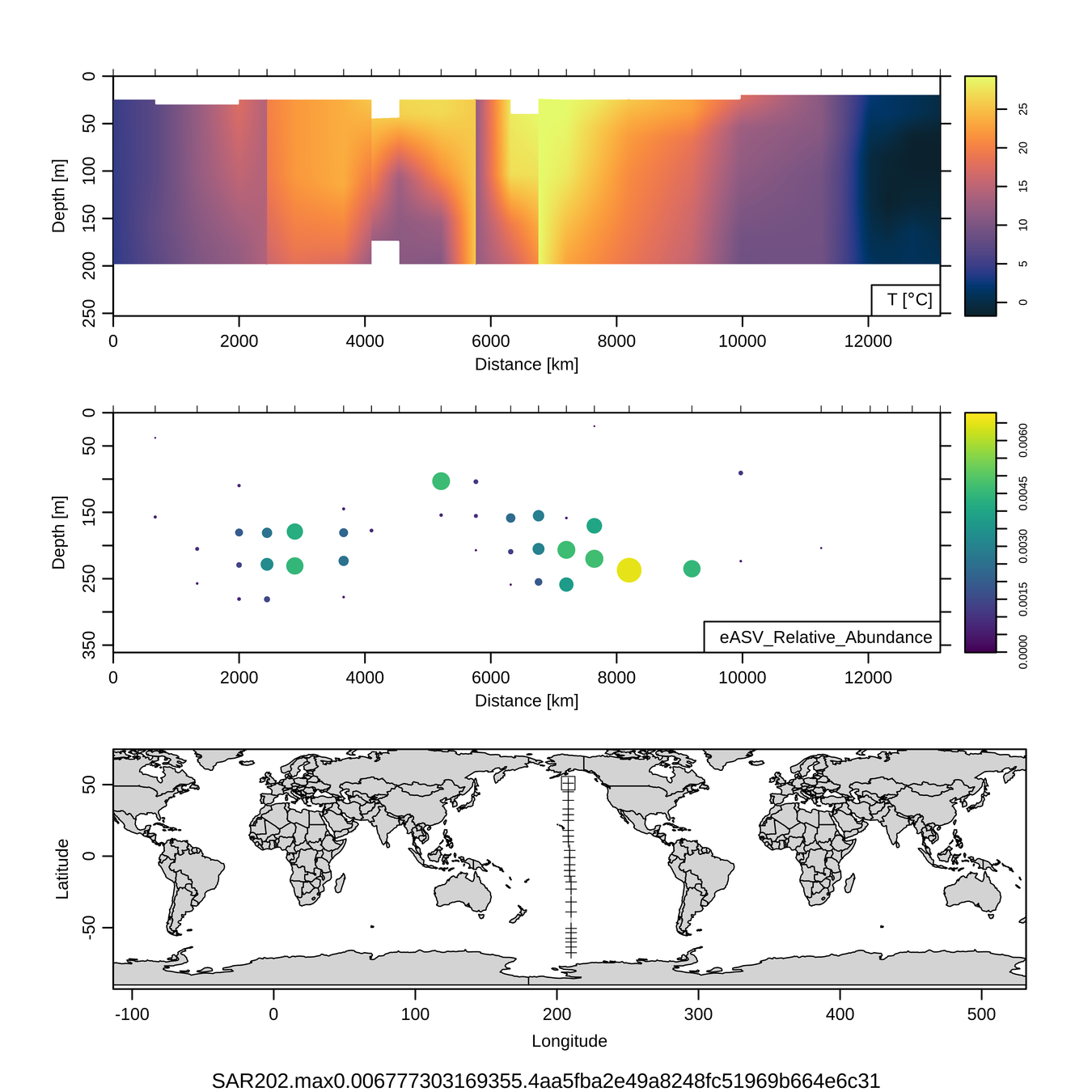
Craig Carlson, Elisa Halewood, UCSB
P16S/N - Biogeography of top 10 SAR202 "species"




Jan-Feb 2005
Feb-Mar 2006
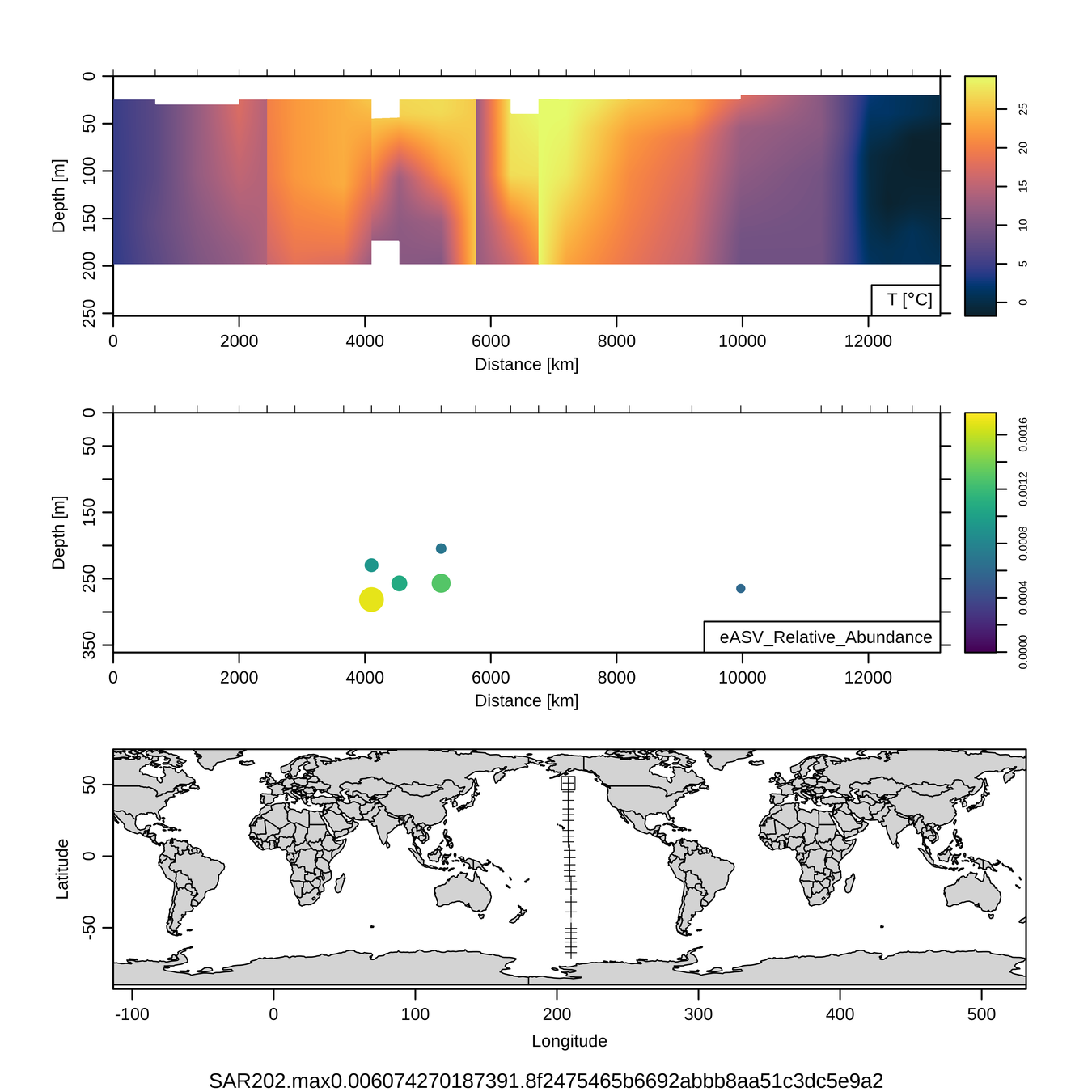
Craig Carlson, Elisa Halewood, UCSB
P16S/N - Biogeography of top 10 SAR202 "species"




Jan-Feb 2005
Feb-Mar 2006
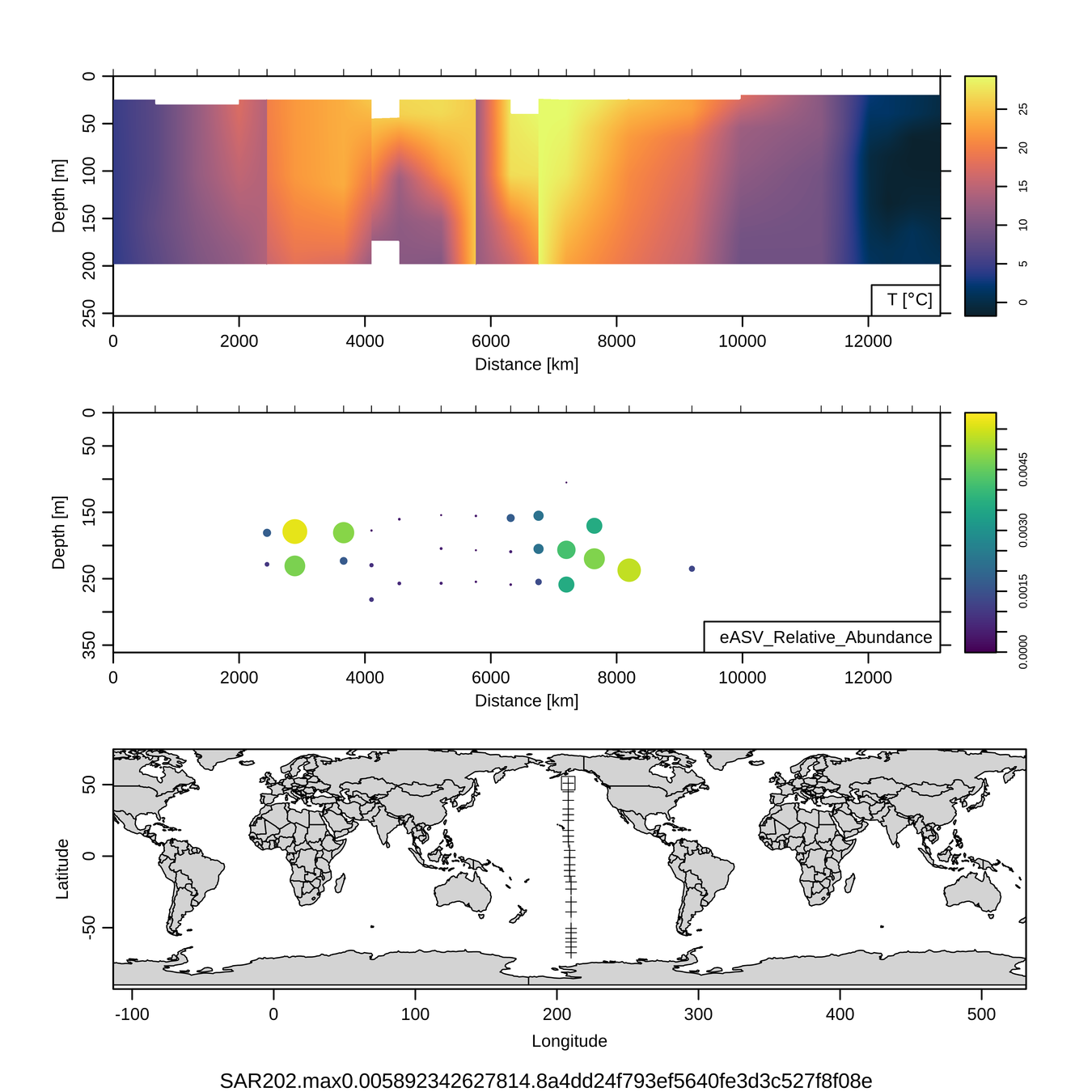
Craig Carlson, Elisa Halewood, UCSB
P16S/N - Biogeography of top 10 SAR202 "species"




Jan-Feb 2005
Feb-Mar 2006
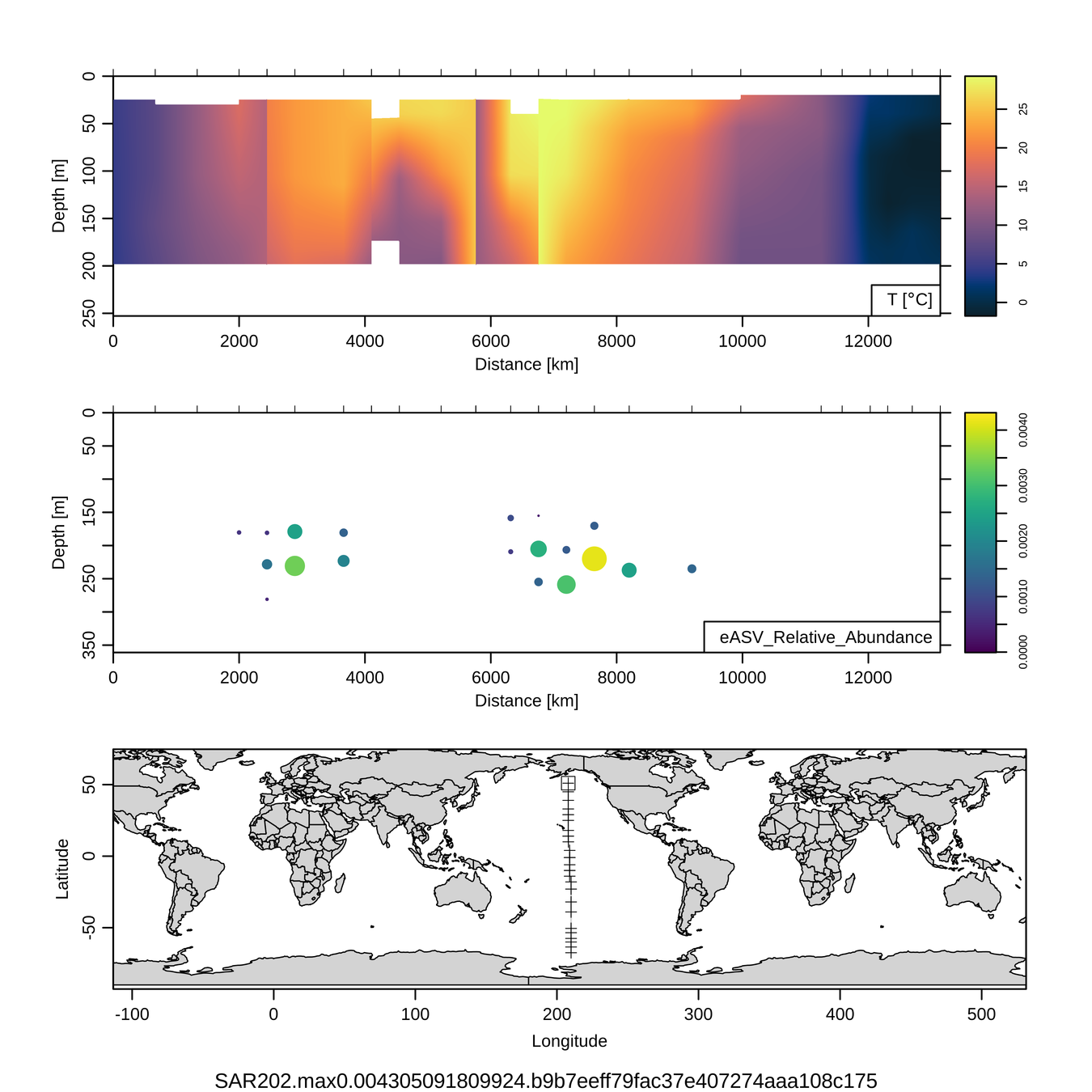
Craig Carlson, Elisa Halewood, UCSB
P16S/N - Biogeography of top 10 SAR202 "species"




Jan-Feb 2005
Feb-Mar 2006
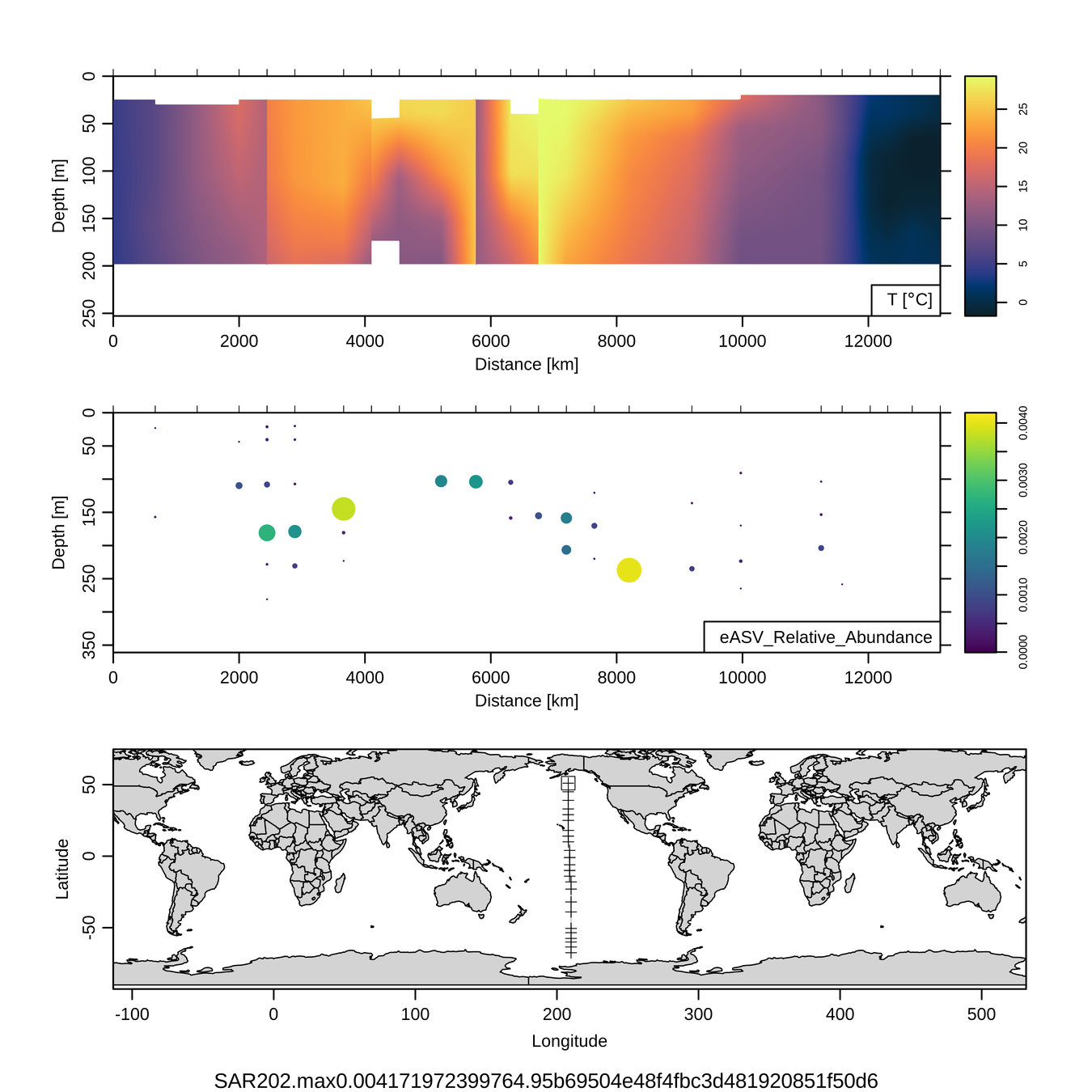
Craig Carlson, Elisa Halewood, UCSB
P16S/N - Biogeography of top 10 SAR202 "species"




Jan-Feb 2005
Feb-Mar 2006
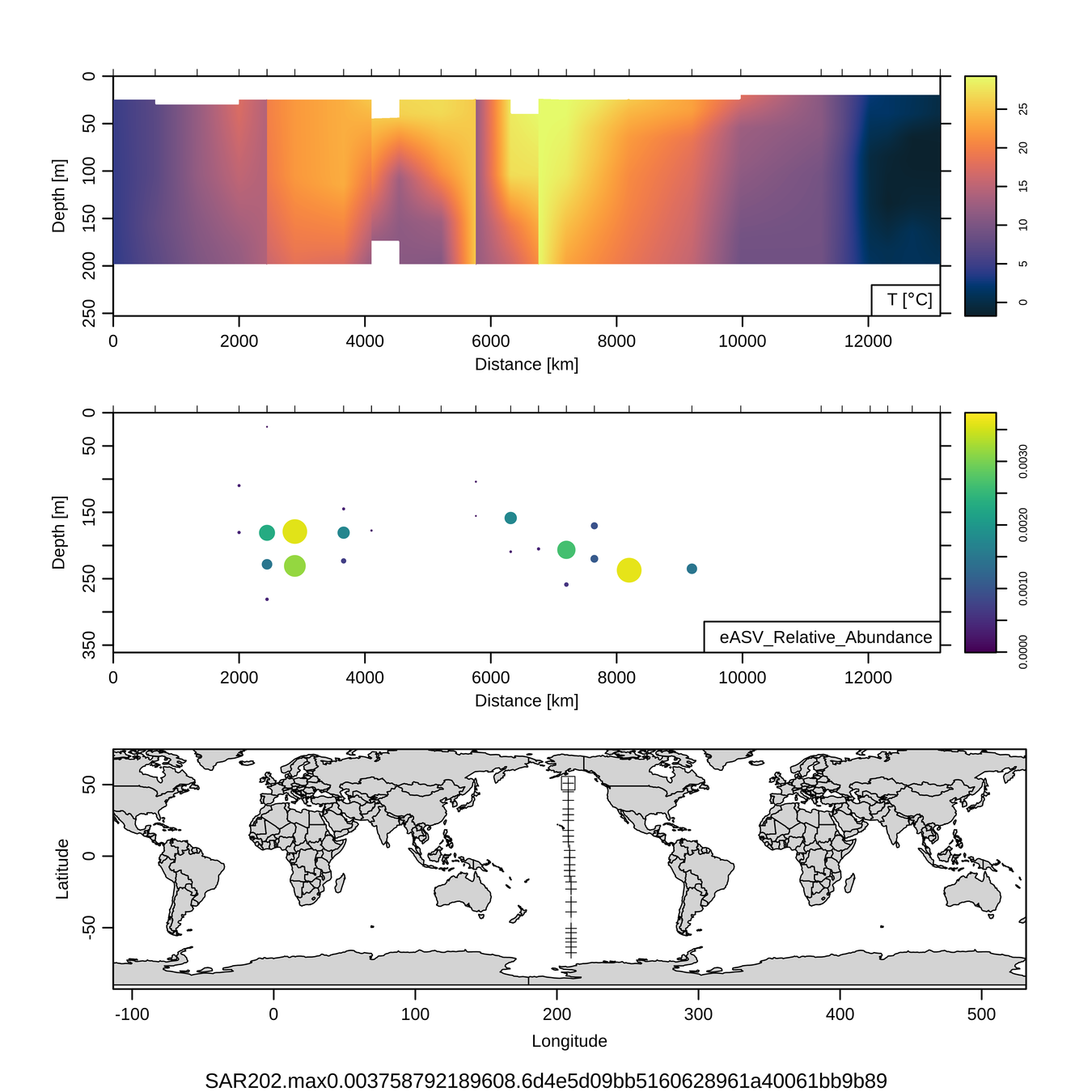
This is only the top 10 from one bacterial taxon!
Similar patterns for phytoplankton (and even some Metazoa)
Craig Carlson, Elisa Halewood, UCSB
P16S/N - Biogeography of top 10 SAR202 "species"
Sources
| Images used in presentation were adapted from: |
|---|
|
Line diagram (slide 9): J. A. Fuhrman, J. A. Cram, D. M. Needham, Marine microbial community dynamics and their ecological interpretation. Nature Reviews Microbiology 13, 133–146 (2015). Metagenome image (slide 19): V.A. Iverson et al., Untangling genomes from metagenomes: revealing an uncultured class of marine Euryarchaeota. Science, 335(6068): 587-590 (2012). Anvi'o used to make image on slide 20: https://merenlab.org/software/anvio/; https://peerj.com/articles/1319/ Shallow-water vent image (slides 20, 22): Y. Li et al., Coupled Carbon, Sulfur, and Nitrogen Cycles Mediated by Microorganisms in the Water Column of a Shallow-Water Hydrothermal Ecosystem. Frontiers in Microbiology. 9:2718 (2018). Speciation image (slides 20, 22): R. Stepanauskas et al., Gene exchange networks define species-like units in marine prokaryotes. bioRxiv, 2020.09.10.291518 (2020). Oxygen diagram (slide 25): L.R. Kump, The Rise of Atmospheric Oxygen. Nature, 451(7176): 277-8 (2008). Water column image on slide 30 adapted from: M. Hügler, S. M. Sievert, Beyond the Calvin Cycle: Autotrophic Carbon Fixation in the Ocean. Annu. Rev. Marine. Sci. 3, 261–289 (2011). |
Unless otherwise noted, other images are either my own (un)published work, ⓒWHOI, or public domain images from Wikimedia Commons
Notes
- Center for Global Change Science
- Explain how techniques could apply to soil, host-associated microbiomes, etc
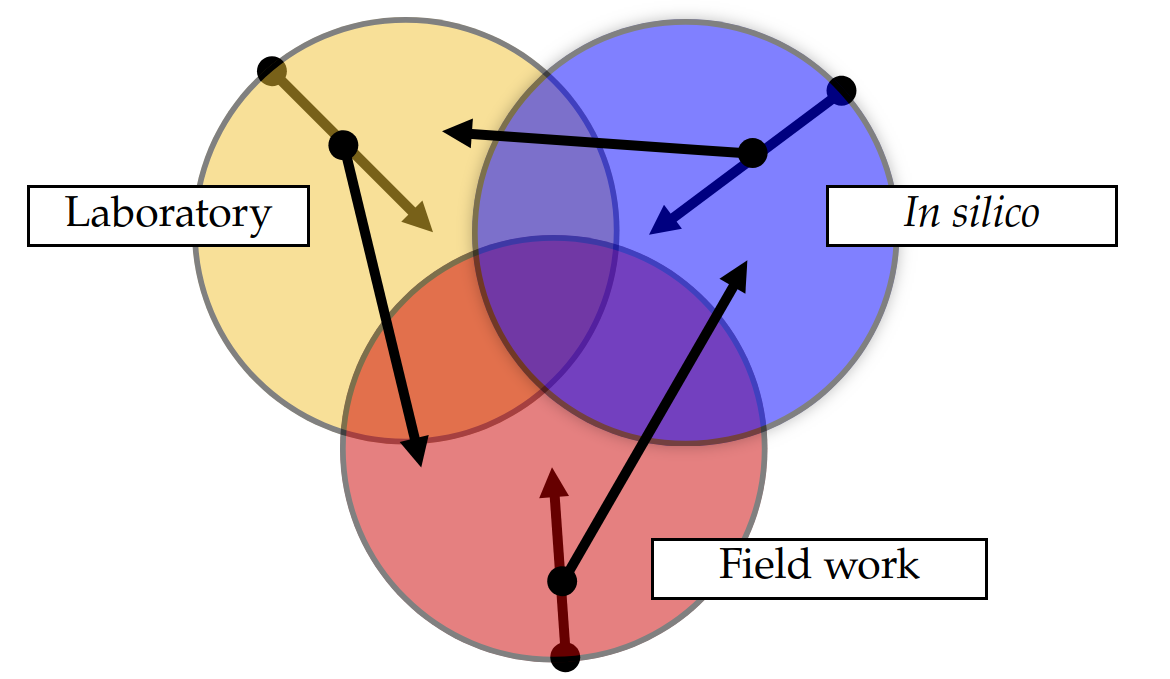
In silico
- Collaboration with modellers
Laboratory
- Method optimization / intercalibration
Field work
- New data collection
Pathways for mentees





In silico
- Study evolution and explore new genomes
Laboratory
- Describe novel taxa, study their physiology
Field work
- Explore new ecosystems
Pathways for mentees





Annie Wing-Yi Lo, CUHK
Microbiology
Environmental science
Bioinformatics
Evolution, population genetics
Ecosystem modelling, global change biology
Microbial ecology, biogeochemistry
3 "pillars"
What I would bring to your department
Microbiology
Ecology & environmental science
Bioinformatics
- > 10 years experience in marine microbial ecology
- Can train mentees in lab, computational, field techniques
- Diverse interests: oceanography, modelling, analytical method development, natural history, evolution
- Passionate about integrating cutting-edge "microbiome" research techniques into my teaching (CURE)
- Track record of successful interdisciplinary collaborations, and excited to build connections at DPES / UofT
- Set up equipment for O2-sensitive microbes
- Retrieve cultures / samples / data
- Train students in cultivation, genomic analysis
- Medium term: Develop methods to identify essential genes (Tn-Seq)
- Long term: Conduct isolation campaigns in model systems, do biochemical assays


Cultivation and genomics at DPES





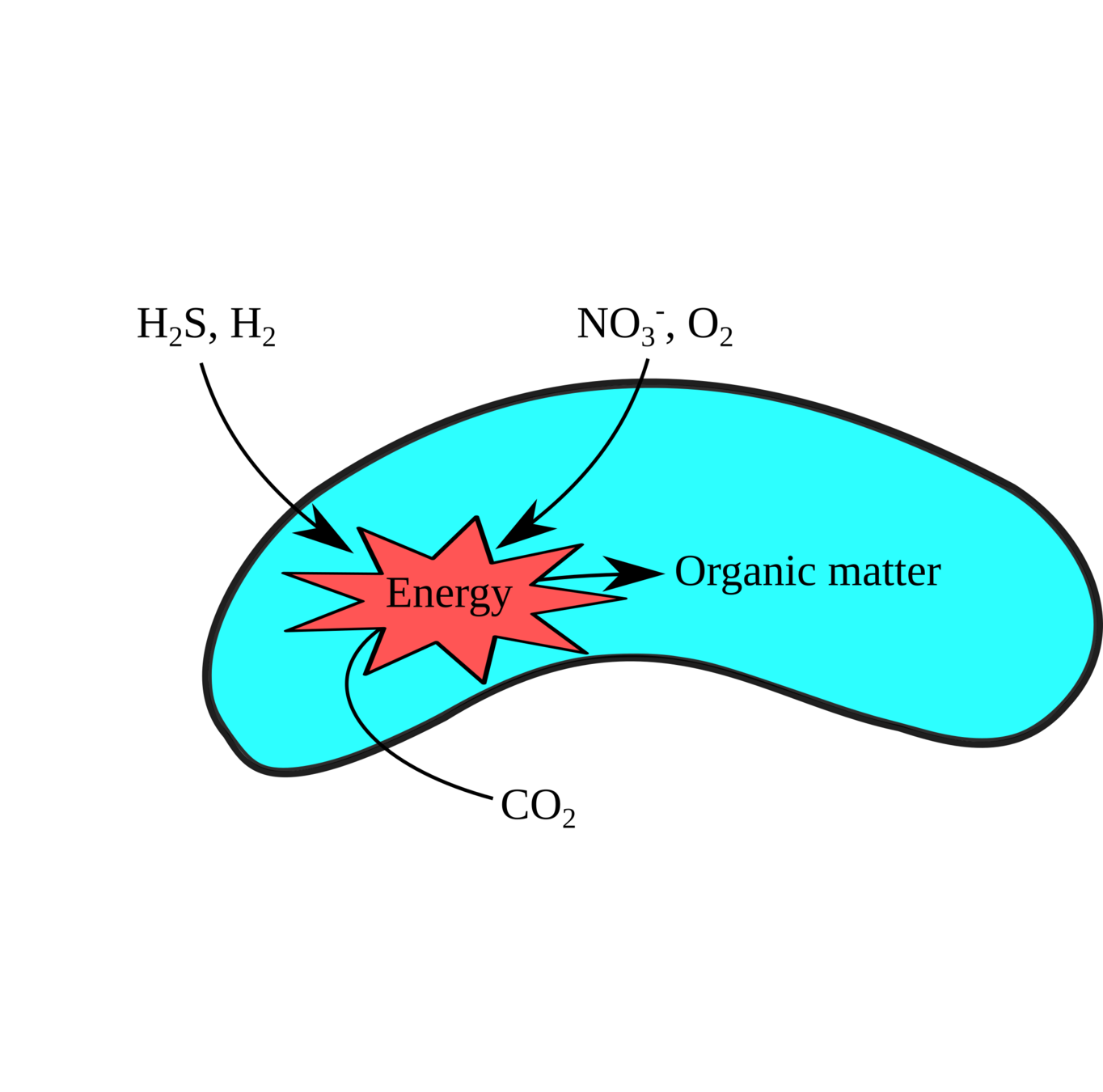
Pure culture physiology / genetics
Integrative techniques: A Microbe's Eye View


Metabolic enzyme function