Biology Department, StFX (Apr 4th, 2022)
Jesse McNichol (he/him) : PhD, Biological Oceanography
Postdoctoral Scholar, University of Southern California
Mechanisms of DNA Transfer in Prokaryotes
(Biology 112, Diversity of Life)

Roadmap
- Group discussion activity to set stage
- Vertical vs. horizontal gene transfer (HGT)
- HGT is a process
- Long versus short-range HGT
- HGT, human health, and the environment
- Group debate - tree vs. web of life
- Clicker questions / short discussions
Roadmap
- Group discussion activity to set stage
- Vertical vs. horizontal gene transfer (HGT)
- HGT is a process
- Long versus short-range HGT
- HGT, human health, and the environment
- Group debate - tree vs. web of life
- Clicker questions / short discussions
-
You are part of a colonization mission to Mars and need food crops adapted to low light, radiation, Martian soil, etc
- How to do this?

Discussion

Discuss with your neighbors (2-3 people; 3 min):
- What limits speed & effectiveness of natural plant breeding?
- How could you improve / speed it up?
Discussion



Discuss with your neighbors (2-3 people; 3 min):
- What limits speed & effectiveness of natural plant breeding?
- Full life cycle is slow
- Existing crop diversity may not be enough
- How could you improve / speed it up?
- Genetic engineering (larger selection of genetic material, speed up by "skipping" full life cycle)
Discussion
An analogy for horizontal gene transfer in prokaryotes


Vertical vs. horizontal

Transfer from parent/ancestor = vertical DNA transfer
Transfer between organisms = horizontal DNA transfer (HGT / LGT)

HGT, vertical inheritance, and natural selection
D) 2 & 3
E) 1 & 3
C) 2
B) 1 & 2
A) All of the above
- Horizontally-transferred genes by definition cannot be transferred vertically from ancestors
- Once incorporated into a cell, genes that arrived from HGT can then be transmitted vertically
- Horizontally-transferred genes are often purged through natural selection


HGT, vertical inheritance, and natural selection
D) 2 & 3
E) 1 & 3
C) 2
B) 1 & 2
A) All of the above

- Horizontally-transferred genes by definition cannot be transferred vertically from ancestors
- Once incorporated into a cell, genes that arrived from HGT can then be transmitted vertically
- Horizontally-transferred genes are often purged through natural selection
HGT, vertical inheritance, and natural selection
HGT is a process
1. Transfer
2. Entry
3. Incorporation
4. Persistence
Donor genome
Recipient genome


HGT is a process

1. Transfer
2. Entry
3. Incorporation
4. Persistence
Donor genome
Recipient genome
In pairs, discuss for 3 minutes:
- What factors might promote or stop HGT at each step?
- Why that would be advantageous?
HGT is a process

1. Transfer
(+) Active production
(+) Mobile elements
2. Entry
(+) Stress induction
(-) Viral resistance
3. Incorporation
(-) DNA degradation
(+) HGT "hot spots"
4. Persistence
(+/-) Natural selection
Donor genome
Recipient genome
In pairs, discuss for 3 minutes:
- What factors might promote or stop HGT at each step?
- Why that would be advantageous?
Short vs. long-range HGT

short range
long range
In pairs, discuss for 2 minutes:
Do you think long or short-range HGT is more common, and why?
DNA similarity and HGT

- As evolutionary distance increases, HGT is less likely
- Homologous recombination = mixing based on DNA similarity
- Results in gene "shuffling"
(log10 scale, i.e. 10-fold differences)
Implications of HGT


Evolution, biogeochemistry

Human health, environment
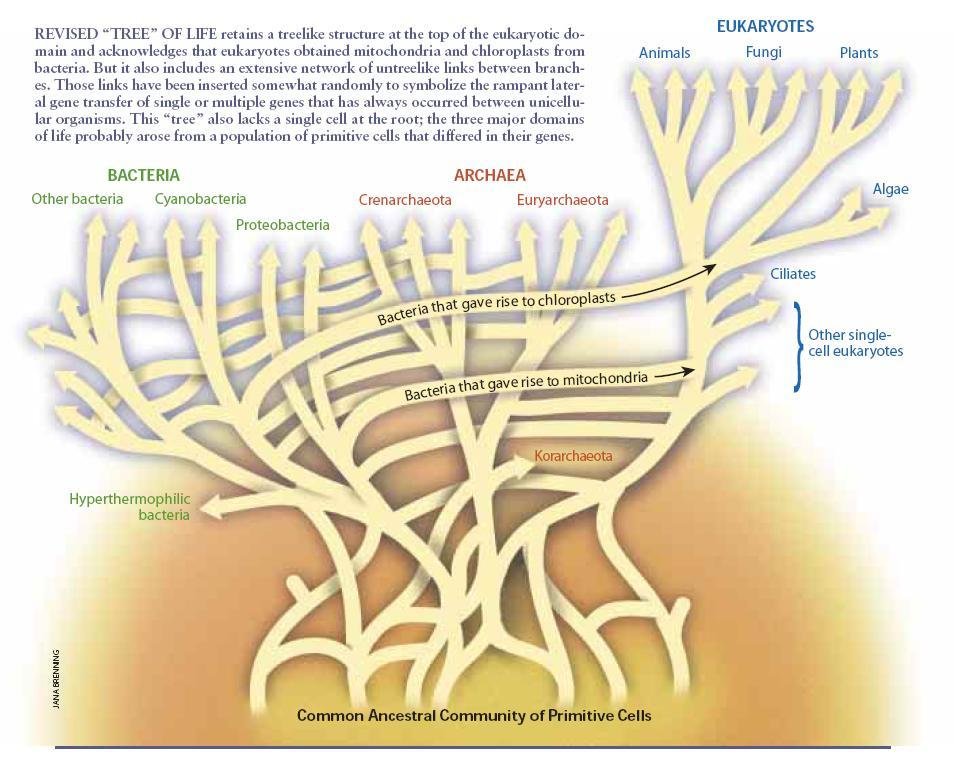
Debate
-
In groups of 4+, using today's content, debate for 5 minutes whether microbial species exist:
- No: The tree of life is a web, and it doesn't make sense to think about microbial species
- Yes: HGT is rare enough and biased towards transfers from relatives so species still exist

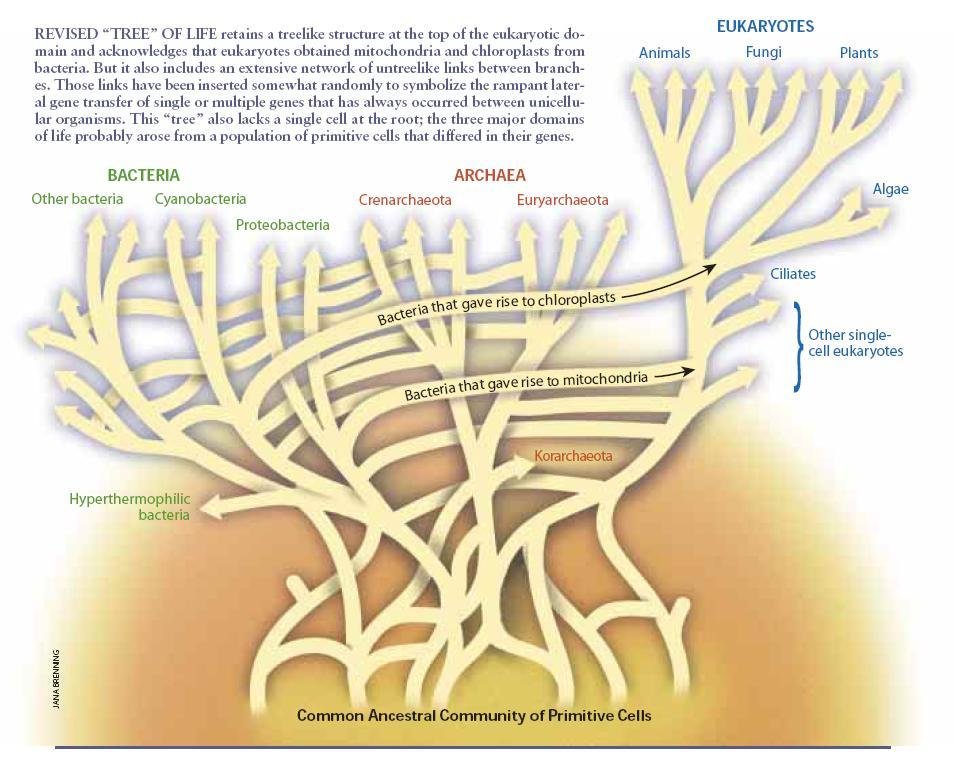

Conclusion



-
Do microbial species exist?
- It's debatable!
- Life has both tree and web-like structure
Review: Learning objectives
-
Describe the difference between vertical DNA inheritance and horizontal/lateral DNA transfer and the 3 major mechanisms of HGT
-
Differentiate between “short-range” genome-shuffling and “long-range” HGT between distantly-related donor/recipients and explain which of the 3 mechanisms could cause short and/or long-range HGT
-
Explain how HGT is modulated by natural stress responses, mechanisms to degrade foreign DNA, and natural selection
-
Describe at least two specific examples of HGT and the functional implications for microbial evolution and/or human health / society / the environment
Next time: HGT and evolution
Cheap DNA sequencing => direct quantification of HGT:

Prokaryotes:
- Evolution of novel lineages
- Pangenomes


Eukaryotes:
- HGT in symbioses
- Origin and diversification

Closing thought
Vital physiological processes... do not map simply to the [tree of life]* but are patchily distributed along its branches... We have in fact, ...come to accept that many ... genes have been transferred across species, phylum, or even domain boundaries.” —Boucher et al 2003

*i.e. Woese's universal SSU rRNA tree
References:
Speciation diagram:
- Andrew Z. Colvin (en.wikipedia.org/wiki/User:Azcolvin429)
Genome size diagram:
- T. R. Gregory, “CHAPTER 1 - Genome Size Evolution in Animals” in The Evolution of the Genome, T. R. Gregory, Ed. (Academic Press, 2005), pp. 3–87.
Other references:
-
A. Spang, T. J. G. Ettema, Microbial diversity: The tree of life comes of age. Nat Microbiol 1, 16056 (2016).
-
H. Imachi, et al., Isolation of an archaeon at the prokaryote–eukaryote interface. Nature, 1–7 (2020).
-
S. J. Sibbald, J. M. Archibald, More protist genomes needed. Nature Ecology & Evolution 1, 1–3 (2017).
-
D. Hutchins, Plastic plankton prosper. Nature Climate Change 3, 183–184 (2013).
Other images: Own work / Wikimedia commons / Duckduckgo image search
Similarities to speciation in eukaryotes
Prokaryote gene flow:
- Horizontal gene transfer
- Direct exchange of DNA between cells
Eukaryote gene flow:
- Sexual reproduction
- Two organisms merge gametes

- Barriers to gene flow stop genetic "shuffling"
- Without "shuffling", genomes accumulate changes and diverge
- "Lowly" salamanders and liverworts with huge genomes:
- Explain answers
- Highlight student responses
-
Gnome genome: Tiny symbiotic bacteria in sap-feeding insects:
- Explain answers
- Highlight student responses
Review: Quickwrite responses


Bishop lab, StFX