How do genomes evolve?
Biology 112, Diversity of Life
StFX Biology department, March 31st, 2021
Jesse McNichol, Postdoctoral Scholar, USC

Genome evolution and progress
- What are some assumptions we have about the narrative of evolution?
- Do these ideas reflect how evolution really happens?

Today's questions
By the end of class, you should be able to answer to the following:
- How do different species emerge and develop new genomes?
- What led to the evolution of large genomes and complex life from small genomes and what processes reverse this trend?
Genomes evolve due to speciation
- Changes are "shuffled" or removed by selection
- Genomes diverge by random changes after shuffling blocked
- Future shuffling likely impossible
- Natural selection may be involved but not necessary


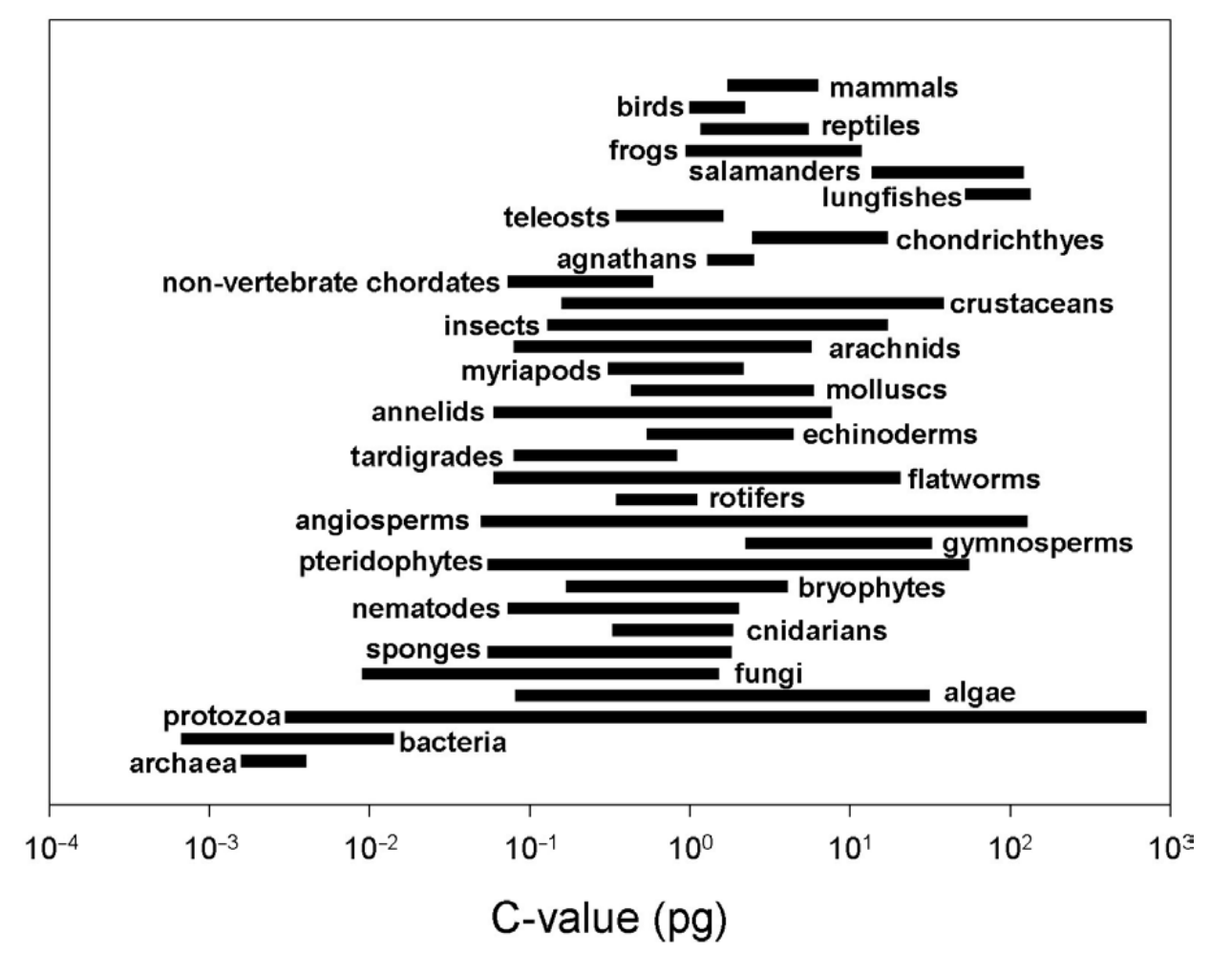
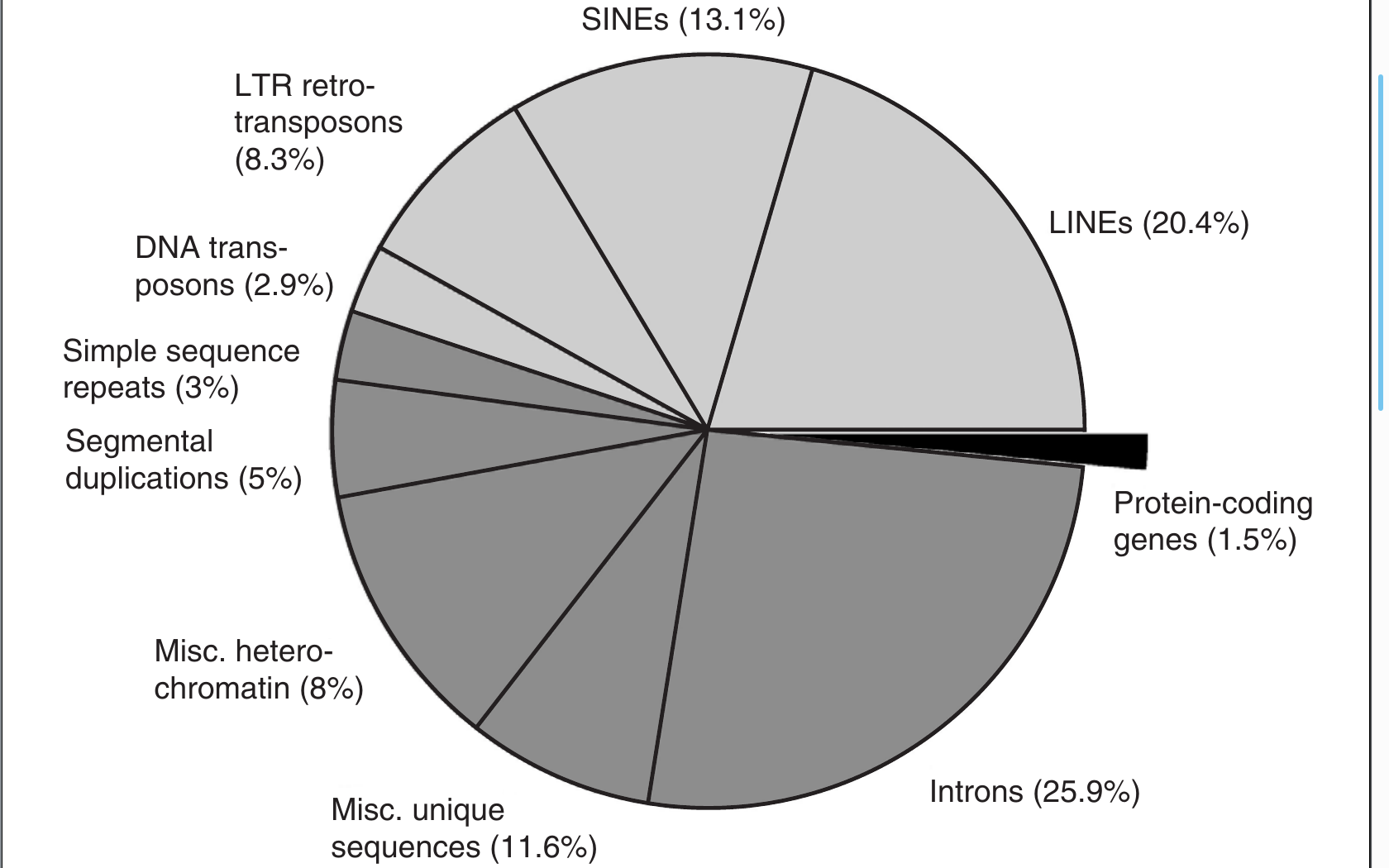
Genome size is decoupled from complexity
Note logarithmic scale
Humans
Genome size: bigger ≠ more complex

The case of dinoflagellates:
- A group of single-celled algae with genomes 1 - 80x bigger than the human genome!
- Is all this extra DNA just filling up space to make the cell bigger?
Genome size: A quantum leap

Simple prokaryotic genomes
Complex eukaryotic genomes
Genome size evolution




- Bacterial and Archaeal genomes stay within a narrow range
- Endosymbiosis provides power to support genomes at larger scale
Smallest free-living Eukaryote Ostreococcus

Birds have reduced non-coding DNA
Conclusions
- In a species, individuals "shuffle" genes; new species emerge when "shuffling" is blocked and genomes diverge
- Bacteria / Archaea merger broke "genome size barrier"
- Size could then increase, but is decoupled from complexity
- Streamlining reduces genome size and complexity









References:
Speciation diagram:
- Andrew Z. Colvin (en.wikipedia.org/wiki/User:Azcolvin429)
Genome size diagram:
- T. R. Gregory, “CHAPTER 1 - Genome Size Evolution in Animals” in The Evolution of the Genome, T. R. Gregory, Ed. (Academic Press, 2005), pp. 3–87.
Quickwrites:
- I. J. Leitch, Genome sizes through the ages. Heredity 99, 121–122 (2007).
- P. Ball, Smallest genome clocks in at 182 genes. Nature, news061009-10 (2006).
Other references:
- S. J. Gould, Full House: The Spread of Excellence from Plato to Darwin, Reprint edition (Three Rivers Press, 1997).
-
A. Spang, T. J. G. Ettema, Microbial diversity: The tree of life comes of age. Nat Microbiol 1, 16056 (2016).
-
H. Imachi, et al., Isolation of an archaeon at the prokaryote–eukaryote interface. Nature, 1–7 (2020).
-
S. J. Sibbald, J. M. Archibald, More protist genomes needed. Nature Ecology & Evolution 1, 1–3 (2017).
-
D. Hutchins, Plastic plankton prosper. Nature Climate Change 3, 183–184 (2013).
Other images: Own work / Wikimedia commons / Duckduckgo image search
Next time: Active research
Cheap DNA sequencing => new areas in genome evolution:

Prokaryotes:
- Novel lineages
- Pangenomes


Eukaryotes:
- Huge unsampled diversity
- Non-coding DNA & "function"

Group discussion + worksheet (2o minutes)
In groups of 3-5, discuss the following scenario, fill out the worksheet (2-3 sentences per question in your own words), and hand in by the end of class.
- During fieldwork, you discover two new species that have diverged from a common ancestor. Assuming you have their genomes and can identify coding / non-coding DNA, answer the following questions:
- What other processes other than geographic separation might be responsible?
- One of the two organisms' genomes is much smaller than the other. Assuming their common ancestor had a large genome, what potential factors could explain this difference?
Slides: https://tinyurl.com/genome-evo
- "Lowly" salamanders and liverworts with huge genomes:
- Explain answers
- Highlight student responses
-
Gnome genome: Tiny symbiotic bacteria in sap-feeding insects:
- Explain answers
- Highlight student responses
Review: Quickwrite responses


Bishop lab, StFX
References:
Speciation diagram:
- Andrew Z. Colvin (en.wikipedia.org/wiki/User:Azcolvin429)
Genome size diagram:
- T. R. Gregory, “CHAPTER 1 - Genome Size Evolution in Animals” in The Evolution of the Genome, T. R. Gregory, Ed. (Academic Press, 2005), pp. 3–87.
Other references:
-
A. Spang, T. J. G. Ettema, Microbial diversity: The tree of life comes of age. Nat Microbiol 1, 16056 (2016).
-
H. Imachi, et al., Isolation of an archaeon at the prokaryote–eukaryote interface. Nature, 1–7 (2020).
-
S. J. Sibbald, J. M. Archibald, More protist genomes needed. Nature Ecology & Evolution 1, 1–3 (2017).
-
D. Hutchins, Plastic plankton prosper. Nature Climate Change 3, 183–184 (2013).
Other images: Own work / Wikimedia commons / Duckduckgo image search
- A "recipe book" for a cell
- Language of DNA
- Genes code for proteins
- Coding and non-coding DNA
- Genome size varies hugely, even within groups
- Viruses: Tiny - small
- Prokaryotes: Small
- Eukaryotes: Small - gigantic





Review: Genome basics
Review: Factors causing genomic change
- Random processes are "raw material" for evolution:
-
Mutation alters DNA sequence
- Neutral, deleterious, or (rarely) advantageous
-
Shuffling mixes gene content:
- "Recombination" between similar sequences
-
Bulking up increases size:
- Duplication (gene / genome)
- Selfish genetic elements
-
Mutation alters DNA sequence
-
Natural selection "acts" on this raw material:
- Either remove or keep changes


Focus on consequences,
don't worry about exact
mechanisms
Genome evolution and progress

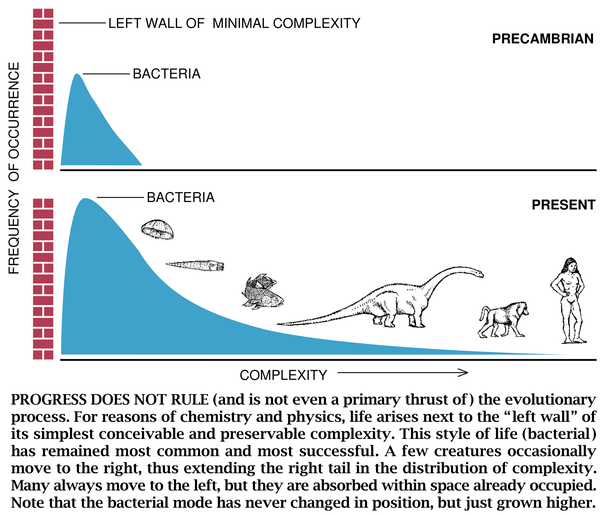
Image credit: Stephen Jay Gould: "Full House"
A two-way street
"quantum leap"

Review: Genome properties
Prokaryotes (small):
- Huge collective metabolic diversity
- High coding density


Eukaryotes (small to huge):
- High morphological diversity
- Low coding density


The process of speciation

- Divergence occurs due to factors such as:
- Different resource use (e.g. Darwin's finches)
- Geographic separation
- These are barriers to gene flow, causing species to diverge
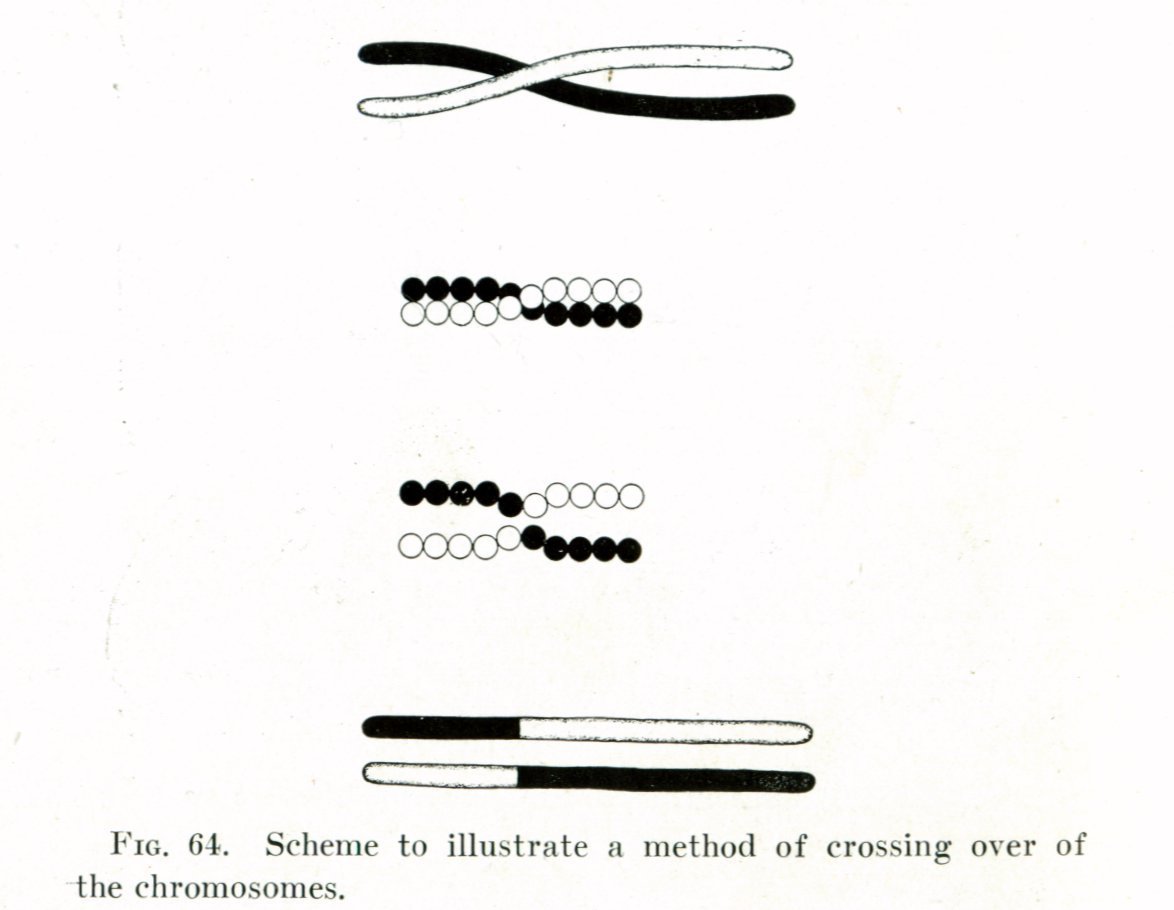
Genome evolution at species level
- In a species, individuals "shuffle" genes; new species emerge when "shuffling" is blocked
1. Common ancestor:
- Changes are "shuffled" or removed by selection

Time (millions of years)
Difference
Modern
Ancient
2. Barrier to gene flow
3. Speciation:
- "Shuffling" blocked
- Genomes diverge by random changes & selection
- Future shuffling impossible
- Natural selection may be involved (not necessarily)
The process of speciation
Prokaryote gene flow:
- Horizontal gene transfer
- Direct exchange of DNA between cells
Eukaryote gene flow:
- Sexual reproduction
- Two organisms merge gametes

- Barriers to gene flow stop genetic "shuffling"
- Without "shuffling", genomes accumulate changes and diverge
Do bigger genomes have more functions?



The case of dinoflagellates:
- Single-celled algae; genome size = 3-245 Gb (1 - 80x bigger than the human genome!)
- Just filling up space? Perhaps quite literally...
Oxygen, Ne, and genome size

1. Rise of oxygen
2. Endosymbiosis
3. Animal evolution
O2

| < 0.001 % current | ~ 1 % current | ~ 100 % current | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ************ | **** | ** | |
| drift | ** | ******** | ************ |
|
size |
* | **** | ********** |
[O2]
Ne
Why did Eukaryote genomes get so big?
- Two general theories:
- Energy: Mitochondria provide more power to support large genomes
- Drift: "Relaxed" selection, allowing expansion through random processes


Evolution "acts" on changes
- If advantageous, may be selected for
- If deleterious, may be "purified"
- If neutral, may be retained
- Function of "effective population size" (Ne)
- High Ne = selection acts efficiently
- Low Ne = selection acts ineffciently
- Neutral / weakly deleterious changes retained
- Leads to "genetic drift"
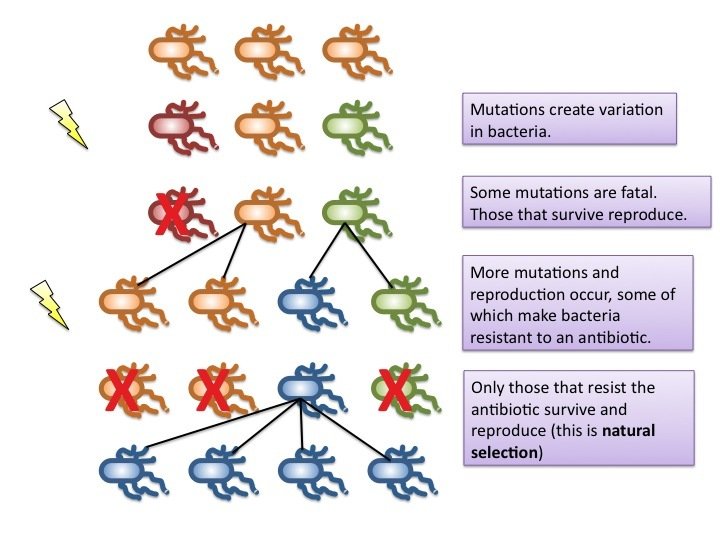
Abdundant, high Ne =
Drift is weak,
selection strong
Rare, low Ne =
Drift is strong, selection weak

Ne (relative scale)
But... this depends on strength of selection:
Evolution "acts" on changes
At the gene level:
- If advantageous, may be selected for
- If deleterious, may be "purified"
- If neutral, may be retained
- Leads to "genetic drift"
At the species level:

