Cutting Edge STEM
Professional Learning Day, 26 Nov, 2025
How to use free-online digital technologies to enhance student understanding of key concepts from the Specialist Maths syllabus
Juan Carlos Ponce Campuzano
Workshop

Gold Coast Campus

Linear regression: Residuals
Code:
GTXF J8AA

Let's get ready to explore maths in GeoGebra

GeoGebra calculator
1. Exploring systems of linear equations in 3D
Consider the system corresponding to three planes
\(\lambda\) is a parameter.
- Use Gaussian elimination to determine the value of \(\lambda\) for which this system has infinitely many solution.
- Use part a) to determine the infinitely many solutions. Express your answer in the form of a vector equation
1. Exploring systems of linear equations in 3D
the system is consistent with \(\infty\) solutions
1. Exploring systems of linear equations in 3D
lambda = Slider(-10, 10, 0.1)
eq1: x + 5y = 1 + 2z
eq2: x + z= 3y + 3
eq3: 8y - lambda = 3z
Solve({eq1, eq2, eq3})
line: X = (9/4, -1/4, 0) + t * (1/8, 3/8, 1)
🔗 Solve
🔗 Slider
2. Differential equations and slope fields
The slope fied for the differential equation \(\dfrac{dy}{dx}=\dfrac{-0.5(y-4)}{x},\) with \(x\neq 0,\) where \(-6\leq x\leq 6\) and \(-6\leq y \leq 6\) is shown below.
- Determine the value of the slope at point \(A=(-4,-2)\).
- Use the slope field to sketch the solution curve given \(x=-6,\) \(y=3.5\)

2. Differential equations and slope fields
n = Slider(10, 30, 1)
s = Slider(0.1, 1, 0.1)
F(x, y) = -0.5 * (y - 4)/x
SlopeField(F, n, s, -6, -6, 6, 6)
A = (0, 0)
SolveODE(F, x(A), y(A), 6, 0.01)
SolveODE(F, x(A), y(A), -6, 0.01) 🔗 SolveODE
3. Roots of complex numbers
Represent in the Argand diagram the solutions of
3. Roots of complex numbers
Represent in the Argand diagram the solutions of

3. Roots of complex numbers
z_1 = i
u = Vector(z_1)
r = abs(z_1)
theta = arg(z_1)
n = Slider(2, 10, 1)
L = Sequence(r^(1/n) * exp(i * ( theta + 2pi * k )/n ), k, 0, n-1)
Sequence(Vector(Element(L, k)), k, 1, Length(L))
# Alternatively
Zip(Vector(Point), Point, L)🔗 Sequence
🔗 Vector
🔗 Zip (advance)
- assign interactive and engaging tasks
- view live updated progress of students
- ask questions and see all student answers instantly
- facilitate rich, interactive discussions
GeoGebra Classroom is a virtual platform through which teachers can
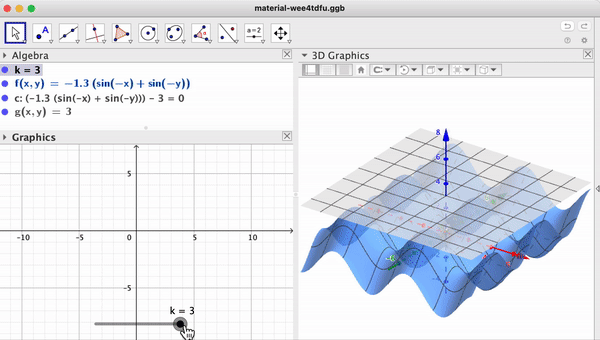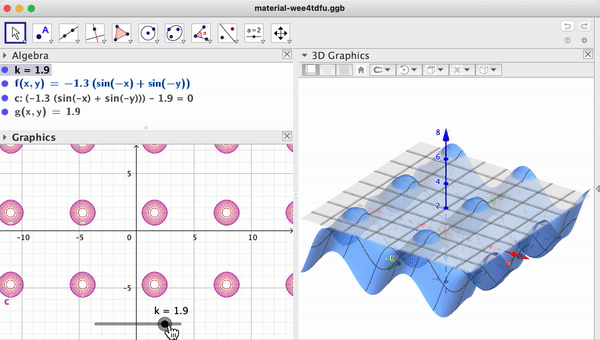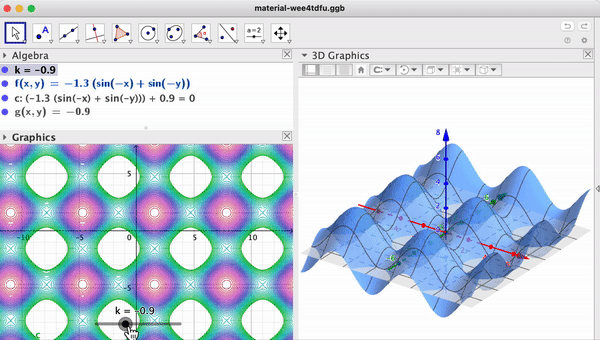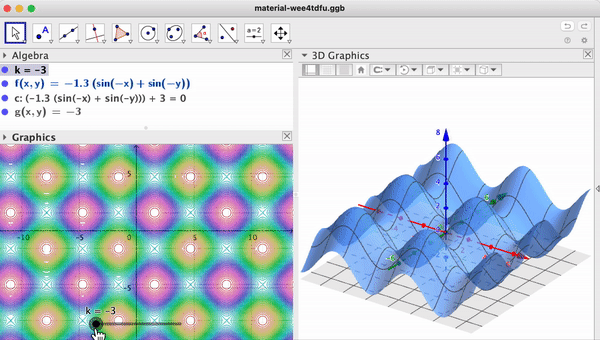
Support / Help
If you want to go far, go together.
If you want to go fast, go alone.

GeoGebra

🔗 Applied Mathematics, Statistics and Physics
School of Environment and Science
Thank you!