<info 343/>
Accessible HTML
Joel Ross
Autumn 2016
View of the Day
-
Review & Warmup
-
Standards and Accessibility
-
Screen Readers
-
<br/>
-
Accessible HTML
-
Forms


(command + space, search for "Terminal")
Command Shell
Fork My Repo!

# configure git (lab machines)
git config --global user.email "your-email-address"
git config --global user.name "your-full-name"
# change to desktop
cd Desktop
# clone the repo
git clone https://github.com/github-user-name/02-accessibility
# change into the repo
cd lecture02-accessibilityCreate a Dev Branch
# create a development branch called 'classwork'
git branch classwork
# remember to switch to that branch!
git checkout classwork
# (or create and switch at once)
git checkout -b classwork
# check branch status
git branchWarmup Exercise
-
Open the
warmup.htmlandcss/warmup.cssfiles from the repo.
-
Modify the HTML and CSS following the instructions in the comments.
Stuck? Can look at the completed branch!

Commit Changes
# add changed files to staging area
git add .
# commit the changes. REMEMBER THE COMMIT MESSAGE!
# "If applied, this commit will {your message}"
git commit -m "Complete the warmup"
# when in doubt, check the status!
git statusPush to GitHub
# check you're on the correct branch
git branch
# push development branch to GitHub
git push -u origin classwork
Check the browser to confirm you pushed the branch!
Need Help?
-
Check the notes
-
e.g., your notes, lecture slides, etc
-
-
Check the documentation
-
e.g., MDN, w3schools, Resources page
-
-
Check Google/StackOverflow
- remember to evaluate the answer
-
Ask on Slack! We don't bite!
- but don't share code please
or come to
office hours!
What factors might contribute to whether a person can use your web page?
Web Browsers


Web Standards
Agreed-upon specification for how web pages should be rendered by a browser (and thus written by the developer)
| 1990 | HTML original specification (Tim Berners-Lee) |
| Nov 1995 | HTML 2.0 (Internet Engineering Task Force) |
| Jan 1997 | HTML 3.2 (World Wide Web Consortium [W3C]) |
| Dec 1997 | HTML 4.0 (W3C) |
| Jan 2008 | HTML 5 draft (W3C) |
| Oct 2014 | HTML 5 (W3C) |
HTML Standard History
Browsers may or may not follow the standard!

Markup Validation
Check if your HTML conforms to the standard.
Note that in some browsers pages may still seem to "work" (look correct) even if they are not compliant.
Develop for other people's browsers,
not your own!
Some people who may want to use our web page...

Tracy Young
Tracy is a 19-year-old college student and was born blind. In high school she did well as she could rely on audio tapes and books and the support of tutors, so she never bothered to really learn Braille. She is interested in English literature and is very fond of short stories; her dream is to become an audiobook author.
Tracy uses the Internet to share her writing and to connect with other writers. She owns a laptops and uses a screen reader called JAWS: a computer program which reads her screen out loud to her in an artificial voice.
persona adapted from
http://scidok.sulb.uni-saarland.de/volltexte/2007/1098/pdf/personas_access.pdf

Gerald Oldman
Gerald is 68-years-old, and recently retired from his position as an investment banker for an international bank. Although retired, he still is
interested in business, economics, and banking; he uses the Internet to do research and manage his personal investments and pension funds.
Gerald has stage 2 Rheumatoid arthritis, that primarily affects his wrists, hands, and fingers. He has trouble manipulating a computer mouse, clicking on content on the computer screen, or doing any complex/fine motor movement that requires his hands. Gerald has voice-recognition software that he utilizes when his pain makes typing difficult or impossible.
persona adapted from https://wiki.jasig.org/display/UPC/Disabled+Personas
Accessibility
Need to make sure a web page supports all users, even if they have disabilities or other impairments.
-
Vision Impairments
- blind (2% of population), farsighted, colorblind
-
Motor Impairments
- arthritis (1% of population), tremors, motor neuron conditions, paralysis
-
Cognitive Impairments
- autism, dyslexia, language barriers
-
and more
Accessibility Tech
Users may access a web page using specialized technologies:




VoiceOver
Screen reader built into Mac OS X.

Open with
command + F5 (cmd-f5)
VoiceOver Task
- Turn on VoiceOver (plug in your headphones)
- With a mouse, open a browser and navigate to Google.com
- Using the keyboard only, search for the Wikipedia page on Web Accessibility, and navigate to that.
- Close your eyes / hide the browser / etc.
- Using the screen reader, navigate through the page to find information on accessibility standards and guidelines.
- In that section, find a link to an article on the guidelines themselves. Navigate to that.
- Hint: Use the "web roto"!
- On that page, find the number (e.g., 1.0) of the current standard and what are the main principles behind those guidelines.
BREAK

A screen reader is just a web browser without a visual display!
This means they rely only on the semantic meaning of the document, not the visual appearance.
Screen Readers

Designing for accessibility benefits everyone, whether or not they have a disability.
Example: Curb Cuts

Universal Usability
If you improving page accessibility and structure to help those with disabilities, you can help those with without disabilities as well.
Accessibility and HTML
Supporting Screen Readers
We'll make web pages support screen readers in two parts:
-
Supporting Navigation
-
Describing Visual Content
WAI-ARIA
Web Accessibility Initiative - Accessible Rich Internet Applications
A standard that provides an extension to HTML supporting screen readers.
-
Provides extra attributes
-
Primarily intended for Rich interactive applications
Where HTML falls short, ARIA steps in!
Consider the
blog.html file...
How can we easily navigate through this page with a Screen Reader?
Heading Navigation
We can use the
Web Item rotor to skip through
headings (
h1,
h2, etc).
Headings should be
-
meaningful (don't use for appearance!)
-
hierarchical (don't skip levels!)
ARIA Landmark Roles
Give non-semantic elements (e.g.,
<div>) a
role attribute to provide semantic meaning about the purpose of that element.
| "banner" | site-oriented content; not page-specific |
| "main" | main content of the page |
| "contentinfo" | visible information about the document (author, etc). |
| "navigation" | collection of site links |
| "region" | a "section" of a web page. Not technically a landmark! |
| "progressbar" | a widget role for an element (e.g., a stylized div) that acts as a progress bar. Not a landmark! |
Roles
HTML5 Semantic Tags
HTML5 introduced new tags that provide similar semantic meanings (also keep landmark roles for compatibility).

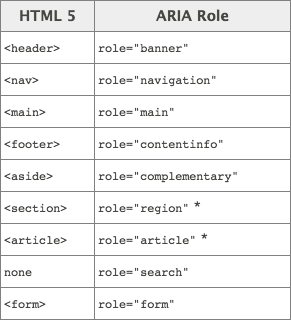
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>...</head>
<body>
<header>
header information (title, etc)
<nav>navigation bar</nav>
</header>
<main>
<article>
<section>article 1, section 1</section>
<section>
article 1, section 2
<aside>an aside</aside>
</section>
</article>
<article>article 2</article>
</main>
<footer>
footer information (copyright, etc)
</footer>
</body>
</html>Adding Navigation
-
Add a navigation section at an appropriate point in the page.
-
The navigation section should include an unordered list of links to the blog posts
- The content of the links is the title of the post
- Leave the href blank ("") for now
Internal Links
We can refer to a specific element in a page by giving that element a
unique
id attribute.
We can then refer to the element from a link using
#element-id.
<section id="first">
...
</section><a href="#first">
Describing Images
Help screen readers understand images by including alternate text.
<!-- an image -->
<img src="baby_picture.jpg" alt="a cute baby">leave off "picture of"
ARIA Labels
ARIA include additional attributes that can be used to describe visual elements.
- alt tags for any element
<!-- aria-label provides descriptions for
arbitrary elements -->
<div class="green-rect"
aria-label="a giant green rectangle"></div>
<!-- aria-describedby refers to an element that
contains the description -->
<div class="green-rect"
aria-describedby="#rectDetail"></div>
<p id="rectDetail">
The above rectangle is giant and green.</p>
replaces read description
added after read description
Other Semantic Tags
Structural Semantics:
-
figureSpecifies self-contained content, like illustrations, diagrams, photos, code listings, etc.
-
asideDefines content aside from the page content.
-
details(demo) Defines additional details that the user can view or hide. Not supported by all browsers!
Formatting Semantics:
-
mark,abbr,cite,address,time,code, etc.
Look up details at http://www.w3schools.com/tags/
One more example...
Forms
Represents a form that the user can fill out, providing a way to get information from the user.
<form role="form">
<label for="commentbox">Leave a comment:</label>
<input type="text" name="comment" id="commentbox">
</form> <input type="text" name="comment">
landmark role!
no content so no closing tag
Forms contain
fields (usually
input tags).
Input Types
More Form Fields
We create dropdown lists ("combo-boxes") with the
<select> and
<option> elements. Note that
<option>'s value can be different than the displayed text.
<form id="signup">
<select name="birthMonth">
<option value="01">January</option>
<option value="02">February</option>
<option value="03">March</option>
...
</select>
</form>And other elements as well!
http://www.w3schools.com/html/html_form_elements.asp
Buttons
<button> elements also have a type!
<form id="signup">
<label for="nameField">
<input type="text" name="name" id="nameField">
<button type="button">I'm a button!</button>
<button type="submit">Submit Form</button>
<button type="reset">Clear Form</button>
</form>Questions on making semantically detailed forms?
What we did...
- git review
- Accessibility & Screen Readers
- ARIA and Semantic Elements
Action Items!
- Git Challenge due "tonight"
- Accessibility Challenge due next week.
Monday: Getting stylish with CSS!