Let's Talk about

Javascript

Johan Esteban Higuita
Software Developer at Talent.com
Bioengineer - Universidad de Antioquia
Session 1
Let's Talk about Javascript

Why Javascript?





















Let's Talk about Javascript

Why Javascript?
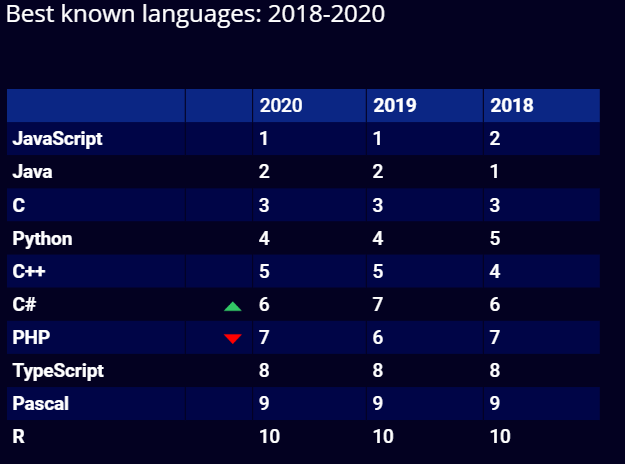
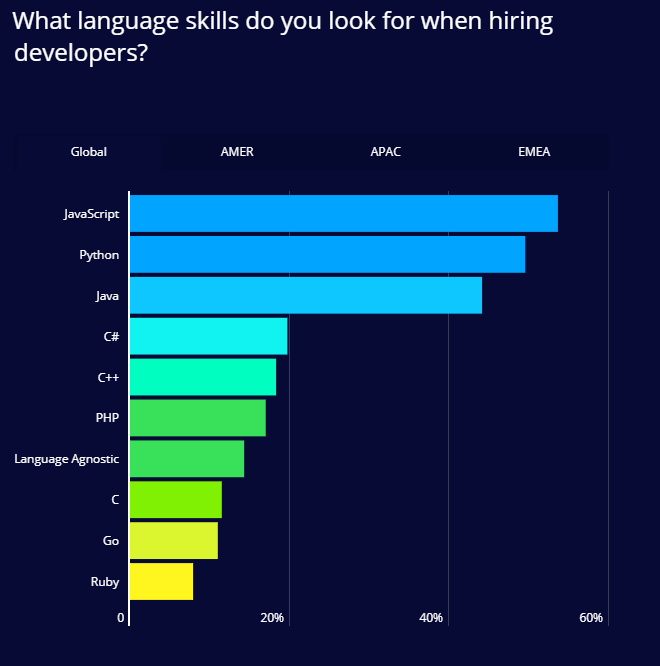
HackerRank Survey
Let's Talk about Javascript

Why Javascript?
Stack Overflow Survey
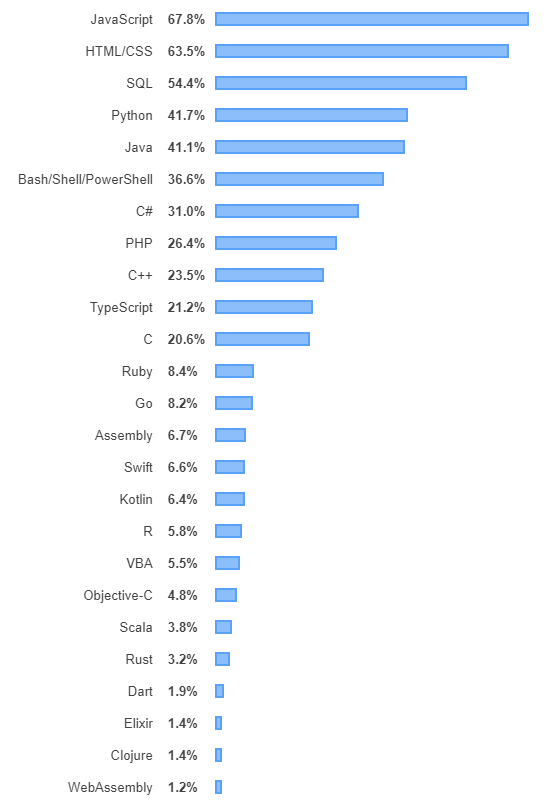
Most popular technologies
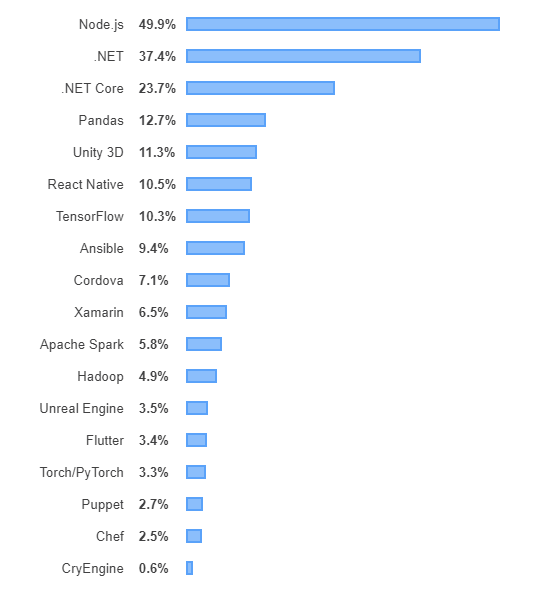
Most used tecnology
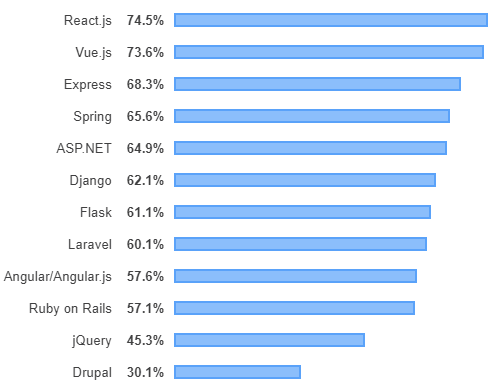
Most loved web framework
Let's Talk about Javascript

Main Features
Dynamic
Weakly Typed
Just-in-time compiled
Multiparadigm
High level
Single-threaded
Non-blocking
Asynchronous

Prototype-based
Cross-platform
Let's Talk about Javascript

Weakly Typed
You do not have to tell Javascript what type of variable you are going to store
const name = "Juan";
const age = 21;
const languages = ["Javascript", "Ruby", "C++"];
public static void main(String[] args) {
String name = "Juan";
int age = 21;
String[] languages = {"Javascript", "PHP", "C++"};
}Weakly typed language:
Javascript
Strong typed language:
Java
Let's Talk about Javascript

Dynamic
You are allowed to dynamically switch the type of data
let name = "Juan";
console.log(name); //Juan
name = 10;
console.log(name); //10 public static void main(String[] args) {
String name = "Juan";
System.out.print(name); //Juan
name = 10;
//error: incompatible types: int cannot be converted to String
}Dynamic Language:
Javascript
Works
Error
Static Language:
Java
Let's Talk about Javascript

Concurrency and Parallelism
Concurrency: Multiple tasks progress simultaneously.
Parallelism: Multiple tasks are executed at the same time.
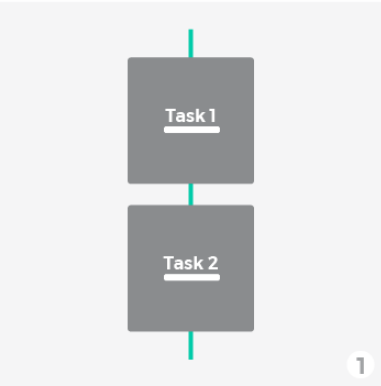
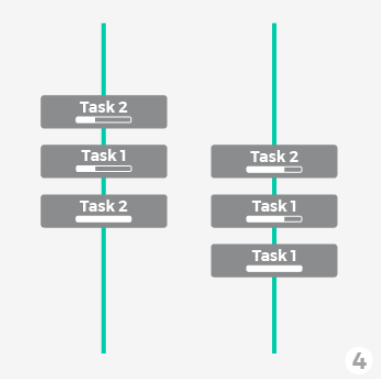
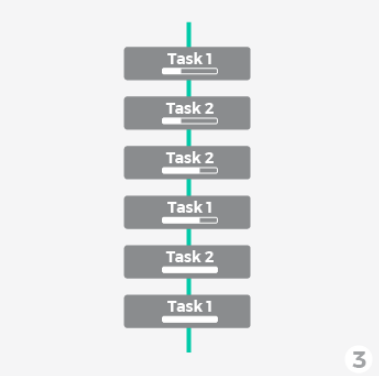
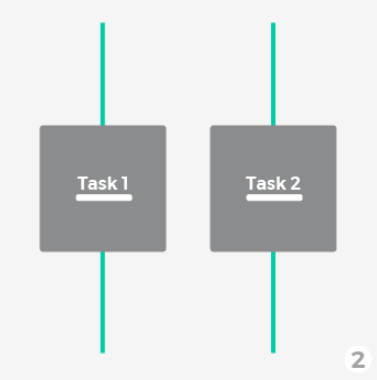
Single Thread
Multiple Thread
concurrent
parallel
no concurrent
no parallel
concurrent
parallel
concurrent
no parallel


parallel
concurrent
concurrent
Let's Talk about Javascript

Asynchronous and Non-blocking
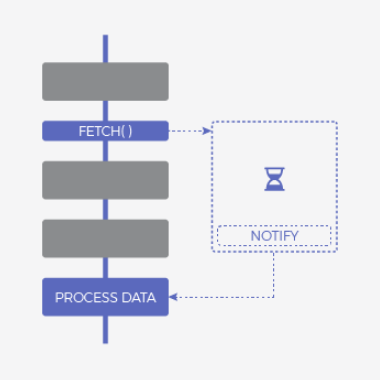
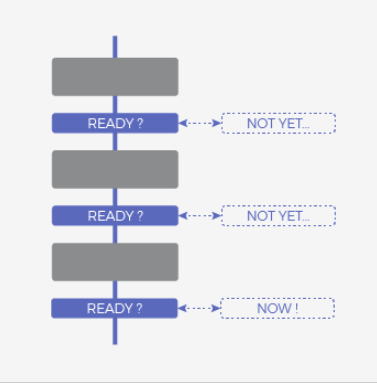
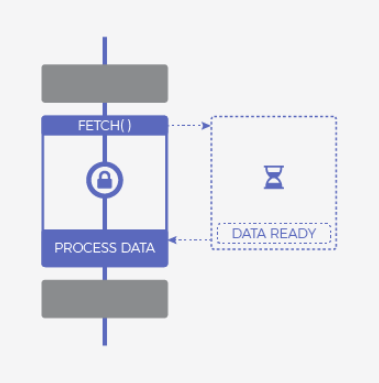
Synchronous and blocking
Synchronous and non-blocking
Asynchronous and non-blocking
How can JavaScript be asynchronous and single threaded at the same time?
Javascript Model
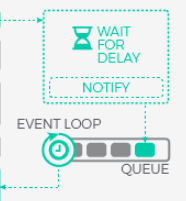
(Polling)
Let's Talk about Javascript

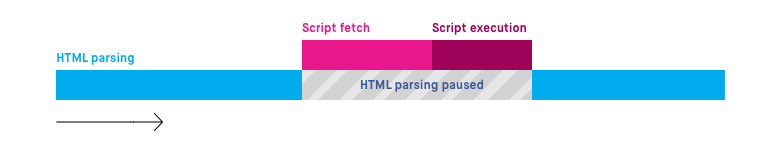
Import scripts: async vs defer
How it works?
1. Stops HTML parsing and rendering.
2. Load JS file
3. Execute JS file
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>App Title</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="style.css">
<script src="main.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<header>
<h1>App Header</h1>
</header>
<main>
<h4>Lorem</h4>
<p>Lorem ipsum dolor sit, amet consectetur adipisicing elit.
Reprehenderit consequuntur et autem nam placeat impedit dicta.
</p>
</main>
<button id="btn">Click me!</button>
</body>
</html>// Javascript
const btn = document.getElementById("btn");
btn.addEventListener("click", () => alert("You clicked on me"))index.html
main.js
!
?
Let's Talk about Javascript

Import scripts: async vs defer
<html>
<head> ... </head>
<body>
...
<script src="script.js">
....
</body>
</html><script src="script.js" defer>
<script src="script.js" async>
normal execution
defer execution
async execution


Code Time!

Let's Talk about Javascript

Web workers
A web worker is a JavaScript program running on a different thread, in parallel with main thread.

- The browser creates one thread per tab
- The main thread can spawn an unlimited number of web workers.
- moving computationally intensive tasks to web workers.
Let's Talk about Javascript

Web workers
How it works?
- Create a Worker Object.
- Send a message using postMessage() (from worker to browser).
- Receive the message using the event onmessage()
- Close the worker using terminate()
// Create Worker
worker = new Worker("workerFile.js");
// Receive data from the worker
worker.onmessage = function (event) {
const incommingData = event.data;
//do Something...
}
worker.terminate(); // Kill the worker
Browser
//Send data to the browser
const dataToSend = "Testing Web Workers";
postMessage(dataToSend);workerFile.js
Code Time!

Let's Talk about Javascript

More topics...
- Functional programming
- ES6
- Immutability
- Data types
- Node
- Scope, hoisting, closures
- Asynchronous programming
- Referenced values
- Web workers
- Iterators
- Memory managment
- Functions
- Promises & Callbacks
- IA APIs
Thank you!