Karl Ho
School of Economic, Political and Policy Sciences
University of Texas at Dallas
Social Data Computing: Mining and Modeling Social Media Data
Presentation prepared for International Virtual Conference on Innovations and Research in Marine Electrical and Electronics Engineering hosted at Academy of Maritime Education and Training (AMET), Chennai, India, June 17, 2021
-
Karl Ho is:
- Associate Professor of Instruction at University of Texas at Dallas (UTD) School of Economic, Political and Policy Sciences (EPPS)
- Co-founder of the UTD Social Data Analytics and Research program (SDAR)
- Director of Academic Computing, EPPS (2002-2018)
- Founder of DataGeneration.org
- Author of Data Programming
- Co-Principal Investigator of the Hong Kong Election Study project
- Website: karlho.com (talks, lecture, publications)
Speaker bio.
-
What is social data? Why it matters?
-
Social data: collection and models
-
Illustrations:
-
Political behavior
-
Leaders
-
Parliamentary members
-
-
Military monitoring
-
Disaster monitoring
-
News
-
Data collection
-
-
Strategy for collecting and modeling social data
Overview
Illustration: Go
Go is:
- One on one
- Two-dimensional
- Limited board (19 x 19, 361 nodes)
- \(10^{360}\) possible moves.

With its breadth of 250 possible moves each turn (go is played on a 19 by 19 board compared to the much smaller eight by eight chess field) and a typical game depth of 150 moves, there are about \(250^{150}\), or \(10^{360}\) possible moves. (Koch, Christof. 2016. How the Computer Beat the Go Master)
Imagine a game that is:
- Many on many
- multi-dimensional
- Expanded board (n x n x n ..., \(n^k\) nodes)
- how many possible moves?
What is Social Data?
Social data refer to data generated via human social inter-activities. With the advent of smart mobile devices, social media become the fastest and most voluminous source of big data among other data kinds.
Social data involves text, image data and meta data associated with the social network communications.
What is Social Data?
Social data is by nature:
-
Time-series data
-
Social network data
-
Geospatial data
Social data is by substance:
-
public opinion data
-
positional data
-
political data
What is Social Data?
Social data is by type:
-
text data (communication, posting)
-
spatial-temporal data (meta data)
-
behavioral data (game, experiments)
-
Images, audio, video
What is Social Data?
Social data is by collection:
-
solicitation initiated by data consumers, i.e. companies in need of data for marketing.
Social data is by production:
-
contribution by owners to reap benefit by better data (e.g. Amazon customer reviews, Spotify playlist, Netflix movie suggestions)
By enabling users to actively contribute such explicit data, Amazon.com succeeded in leveraging knowledge dormant in its large customer base to help customers with their purchasing decisions.
- Andreas Weigend. 2009. The Social Data Revolution(s)
Crowdsourcing process of data
Applications using social data:
Political behaviors (leaders)
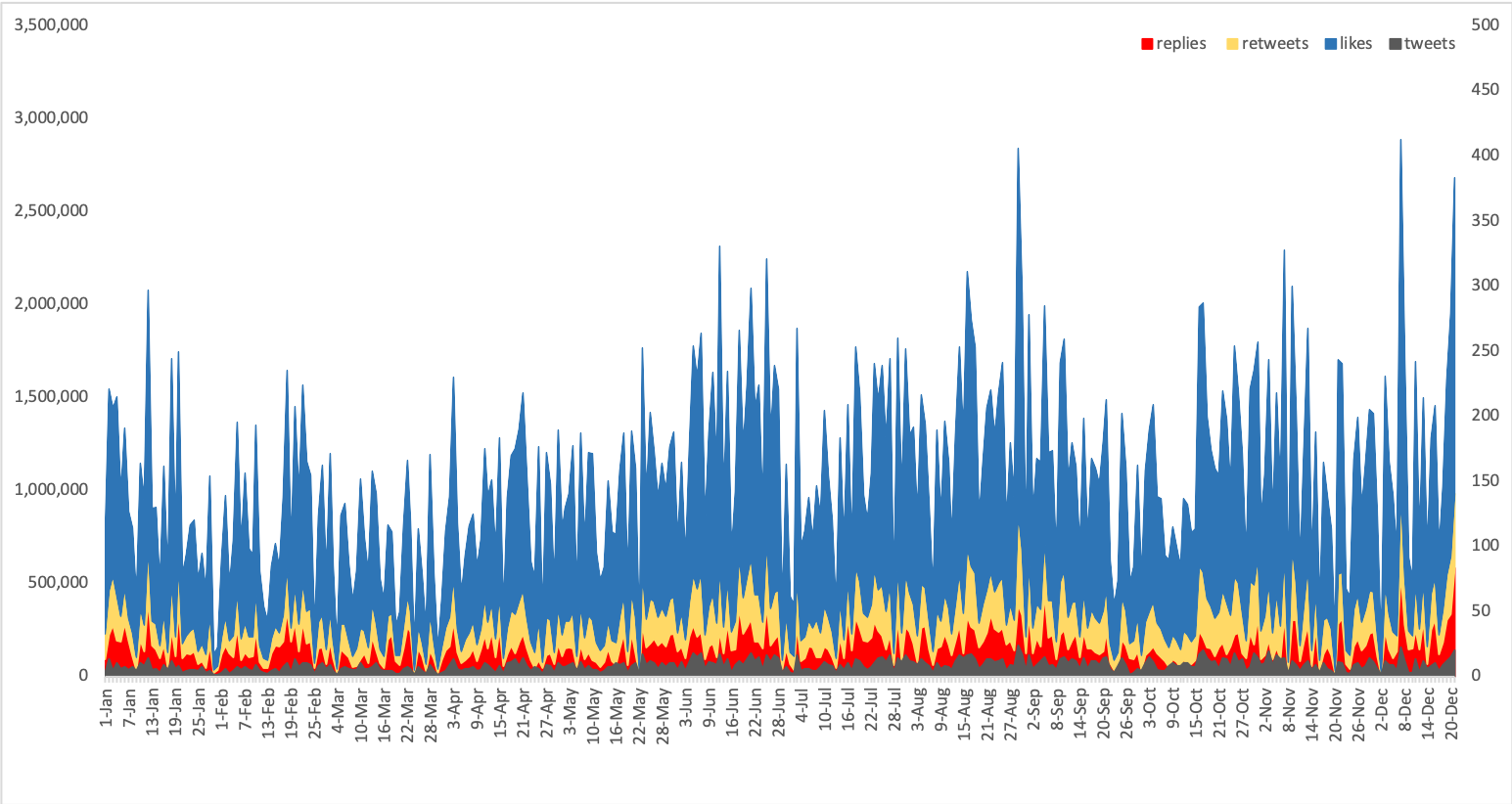
Retweet daily sums and counts
July 27, 2018-September 8, 2018
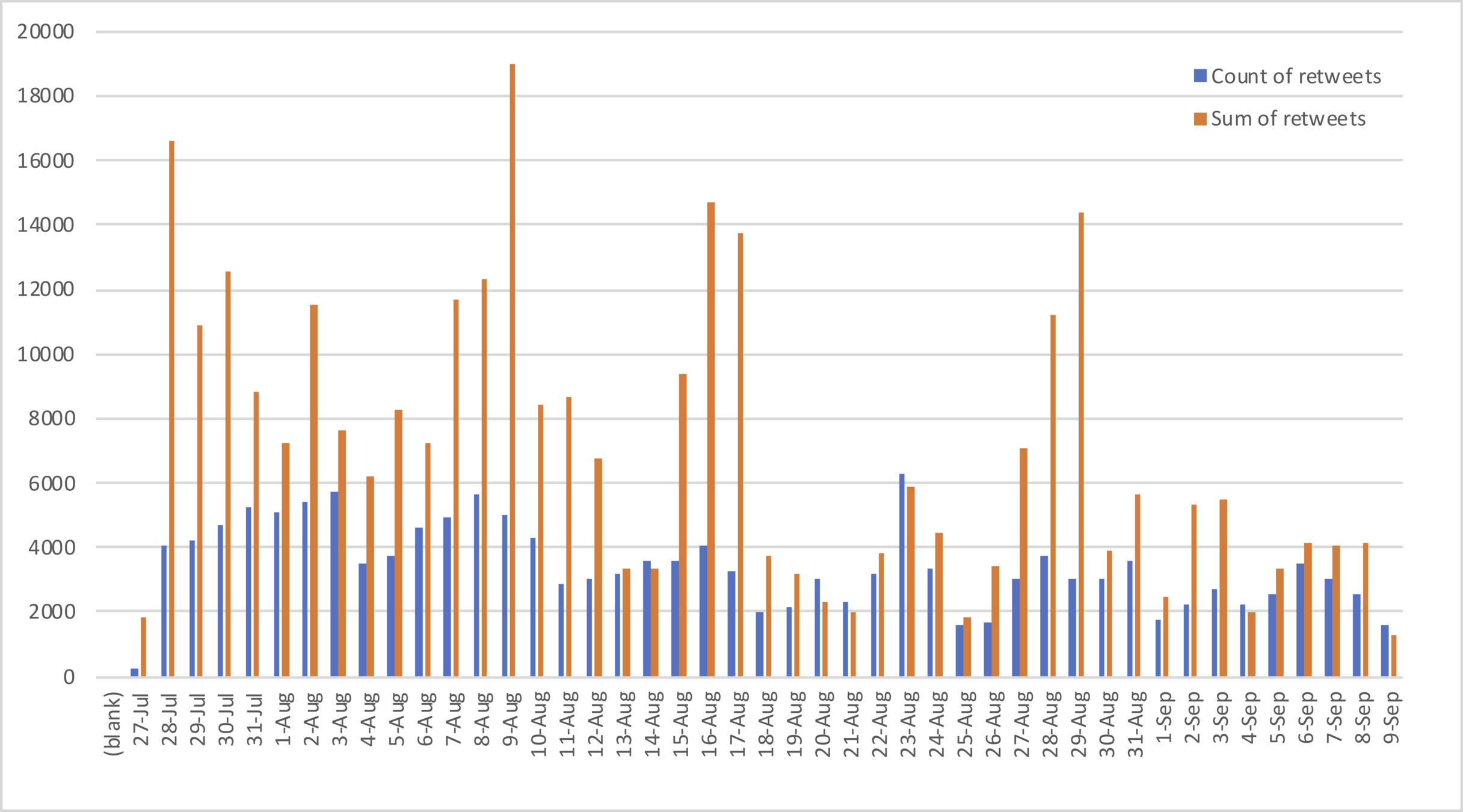
"realDonaldTrump" tweets
Applications using social data:
Political behaviors (leaders)
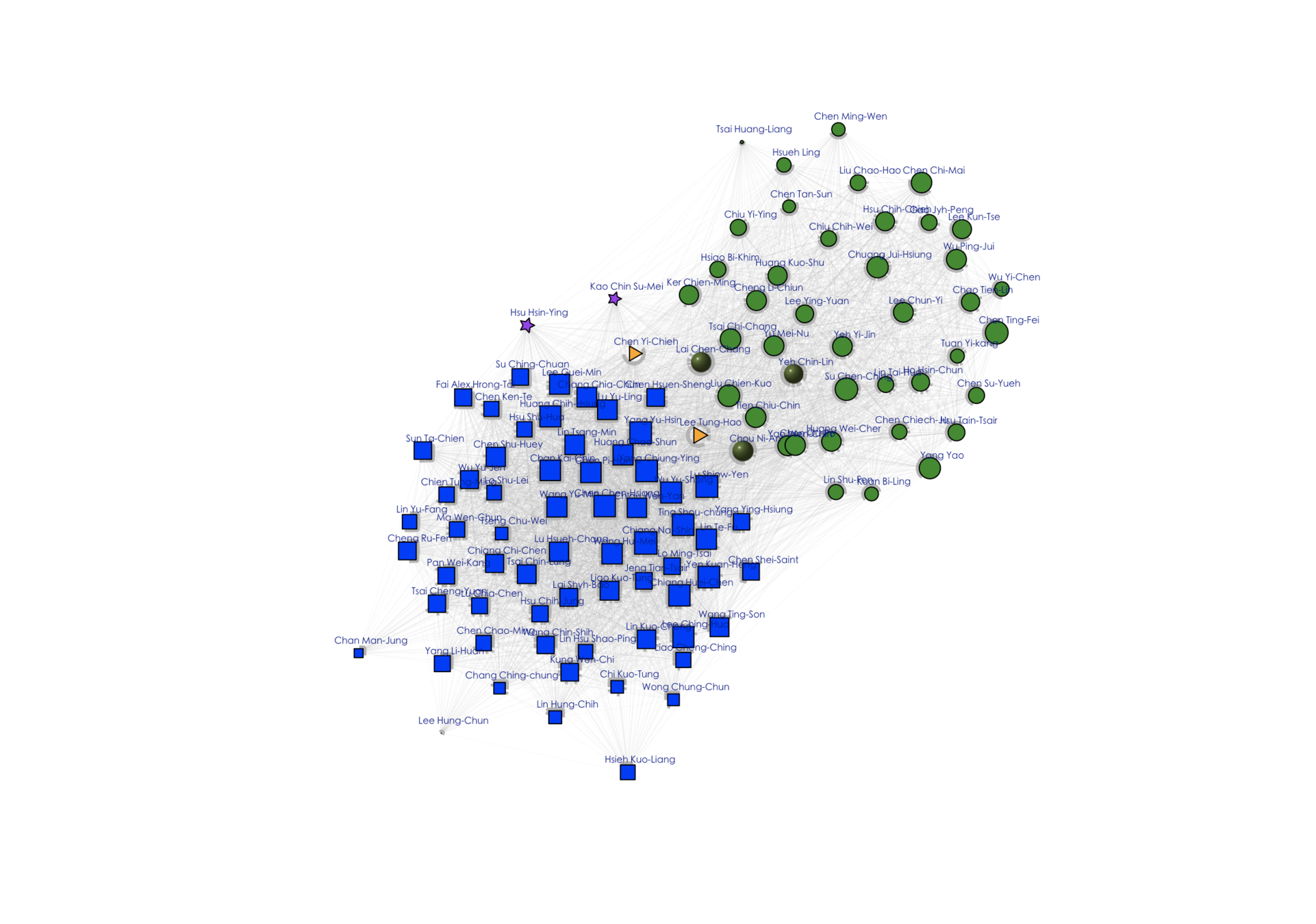
Applications using social data:
Network structure in parliaments

Applications using social data:
Network structure in parliaments
- Colors and shapes represent members of parties.
- Size indicates importance in terms of number of bills and mobilization of cosigners
- Positions indicate distances from other networks and within own network.
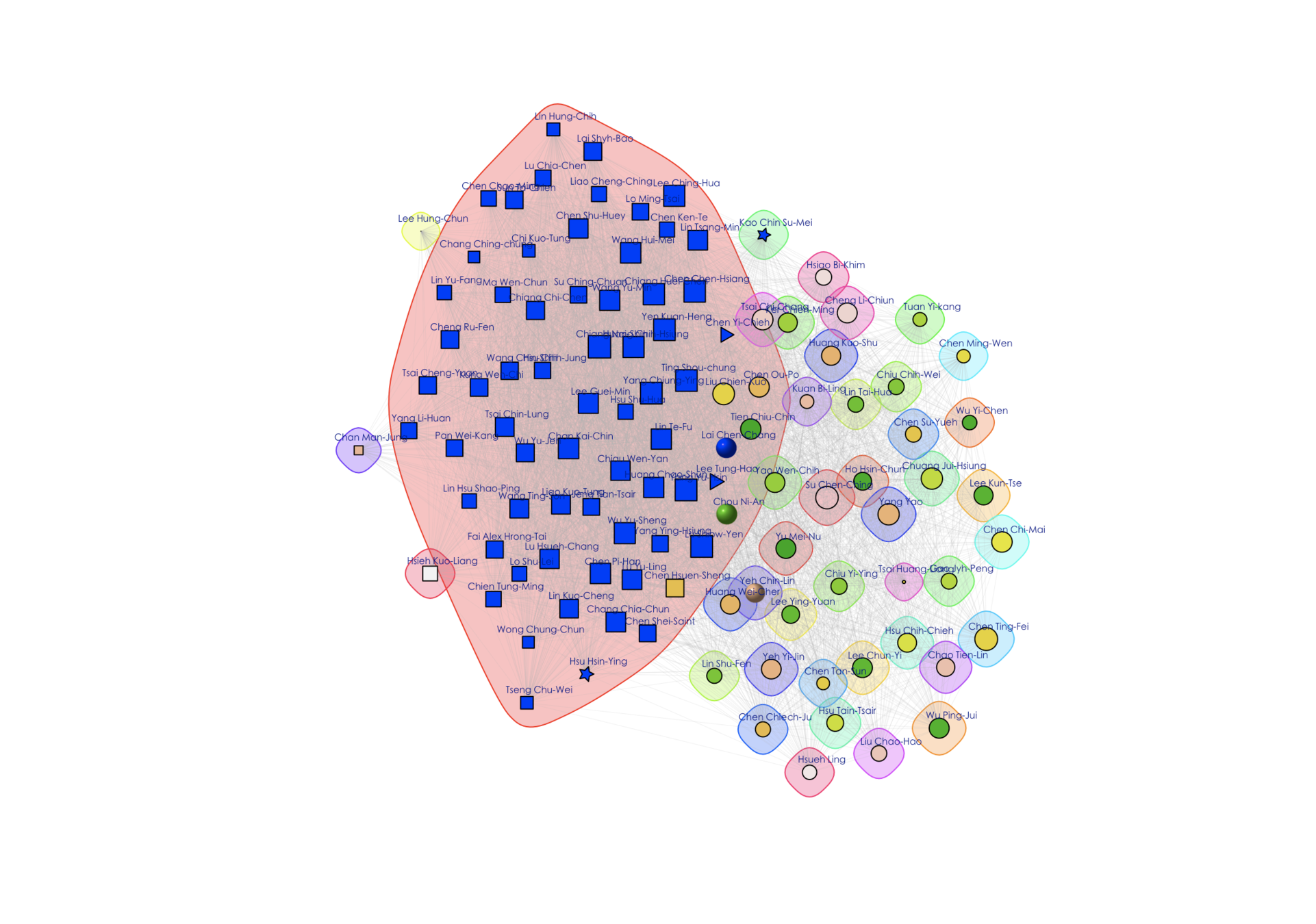
Applications using social data:
Network structure in parliaments
(Communality)

Applications using social data:
Network structure in parliaments
(Communality)
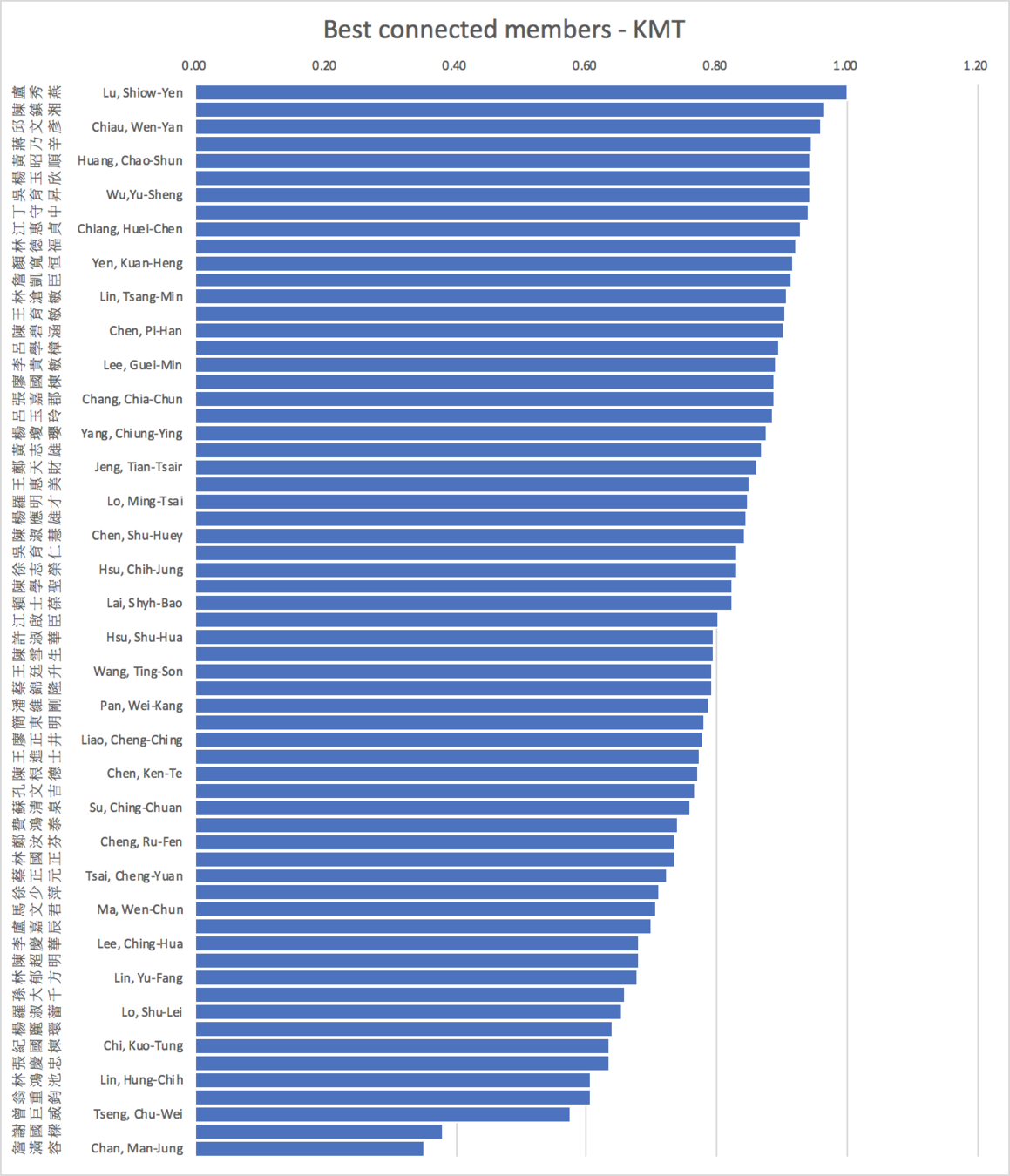
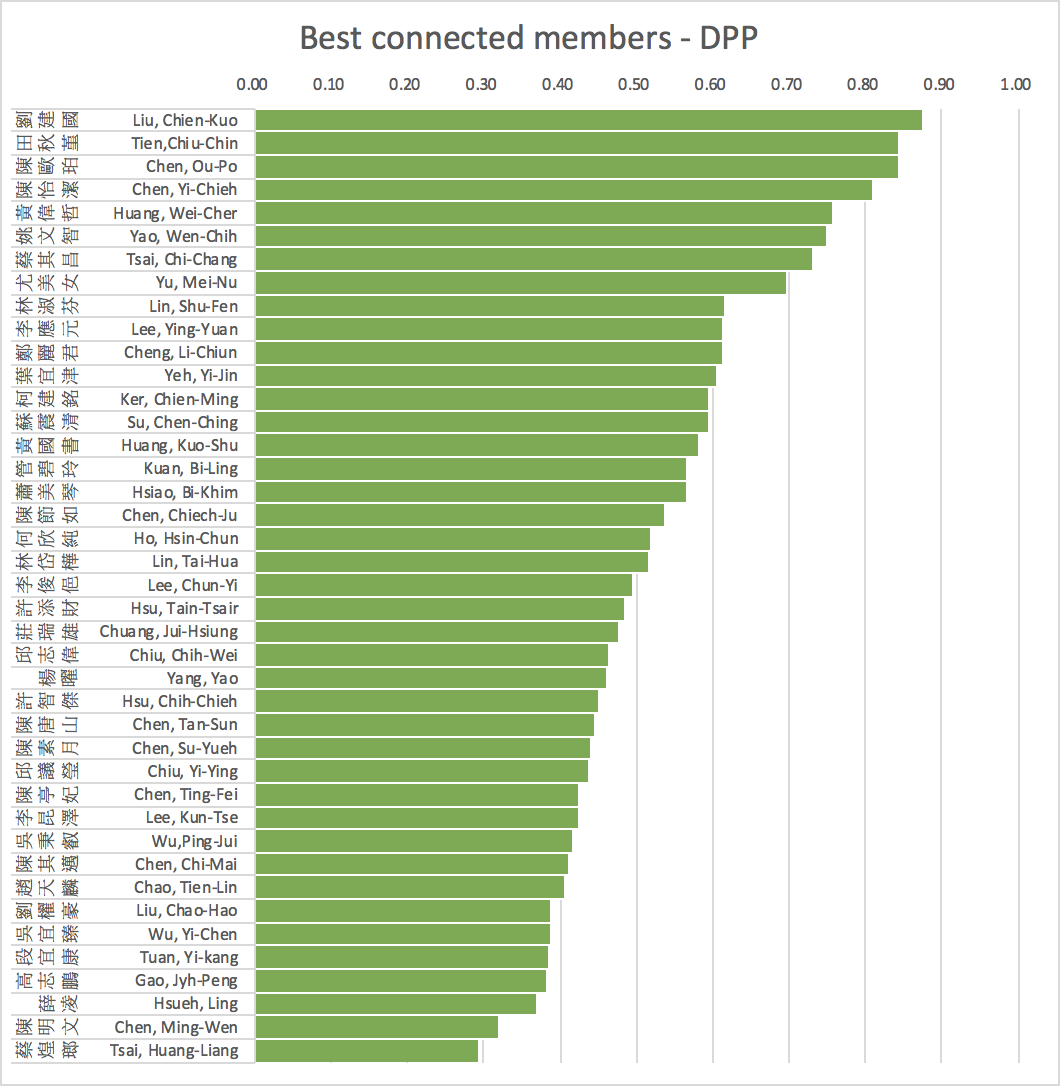
average=0.79 s.d.=0.13 skewness= -1.12
average=0.54 s.d.=0.15 skewness=0.72
Applications using social data:
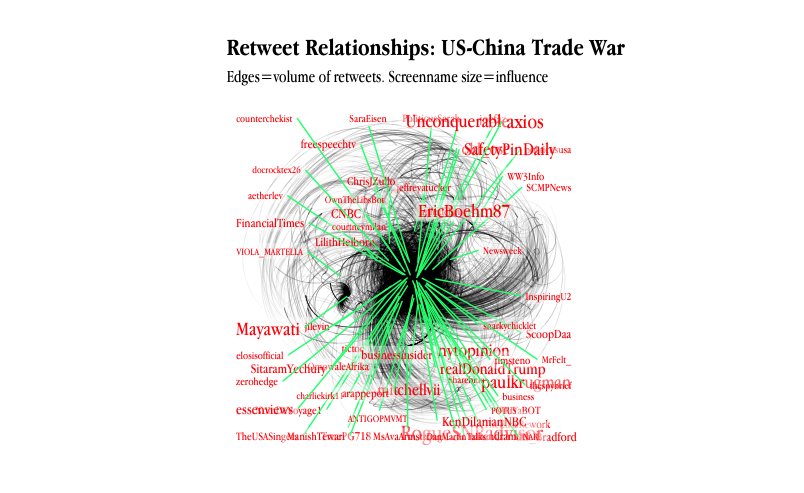
Political network structure based on tweets
"China tariff" tweets
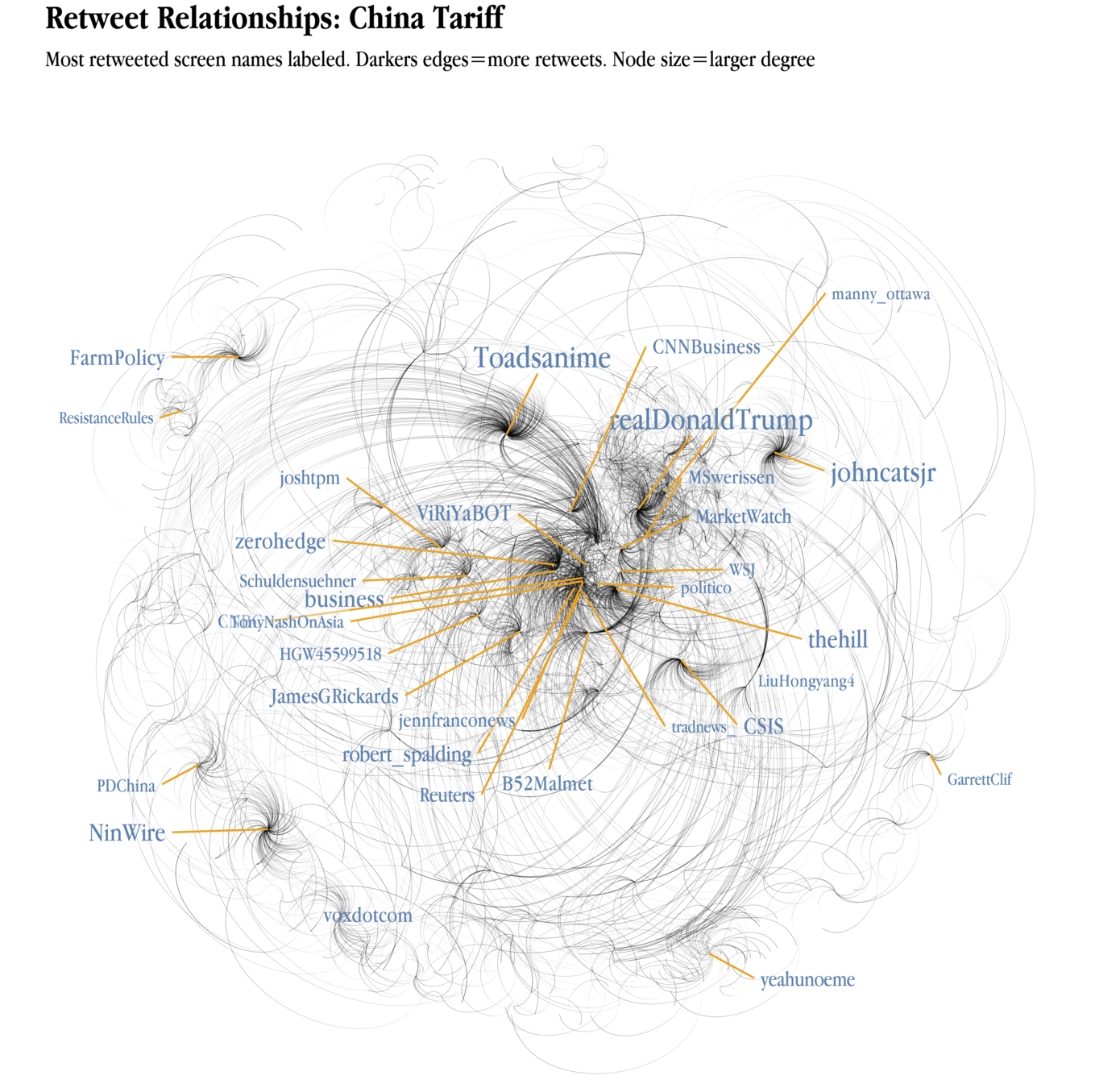


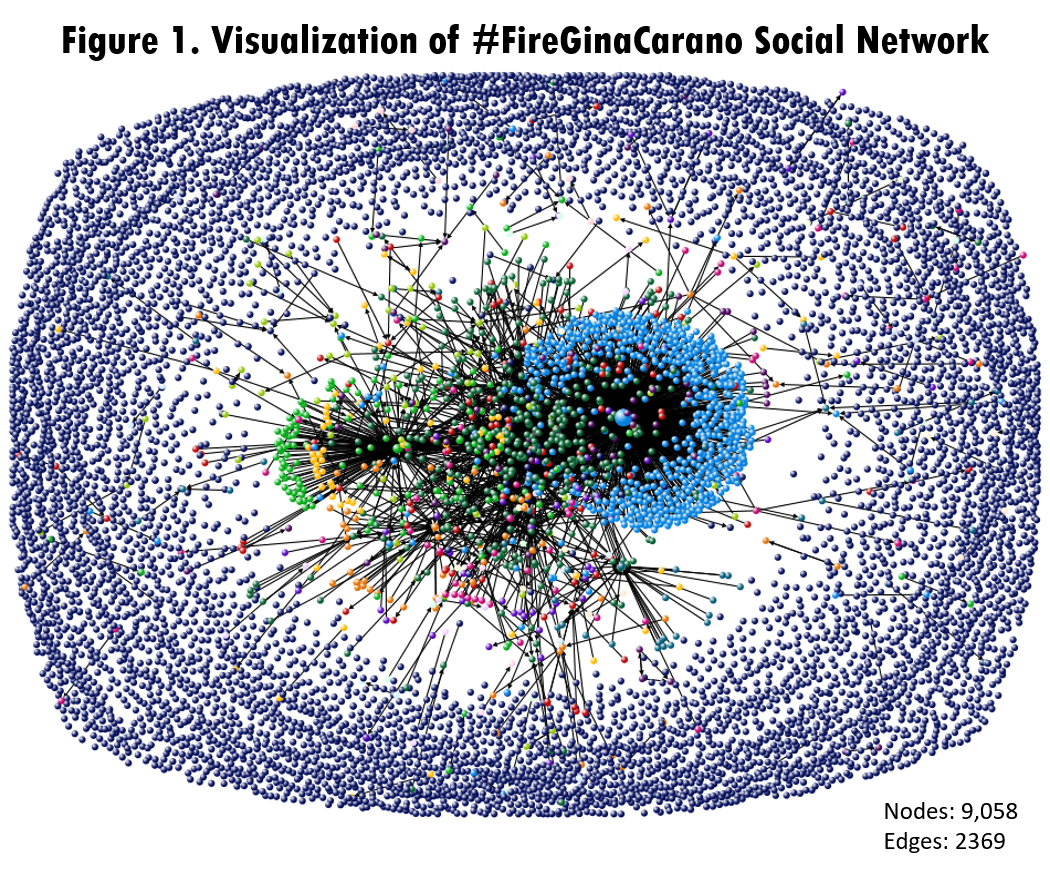
Applications using social data:
Mapping disasters using tweets
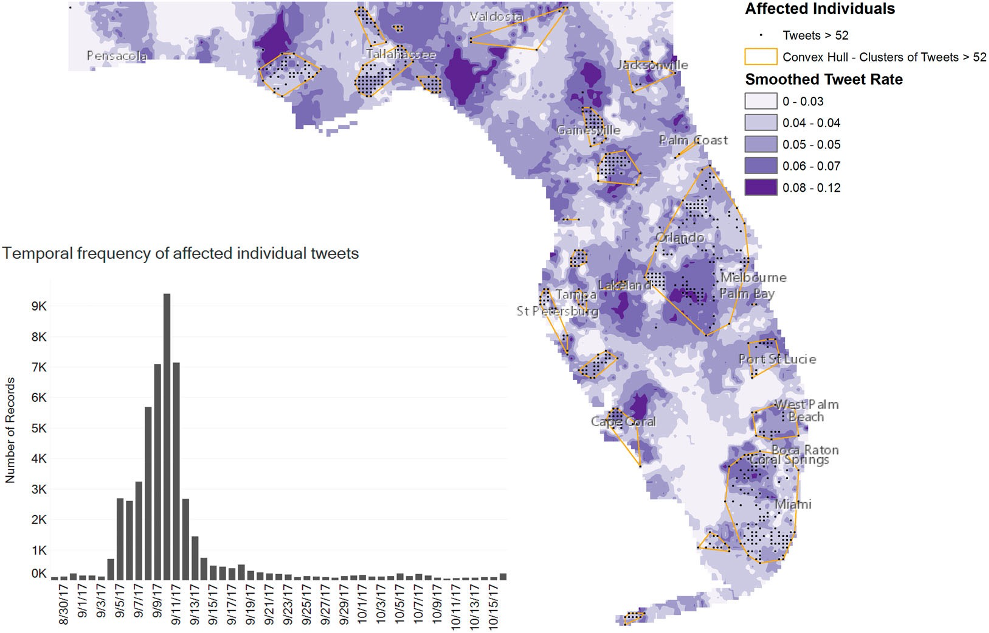
Sit, Muhammed Ali, Caglar Koylu, and Ibrahim Demir. 2019. "Identifying disaster-related tweets and their semantic, spatial and temporal context using deep learning, natural language processing and spatial analysis: a case study of Hurricane Irma." International Journal of Digital Earth.
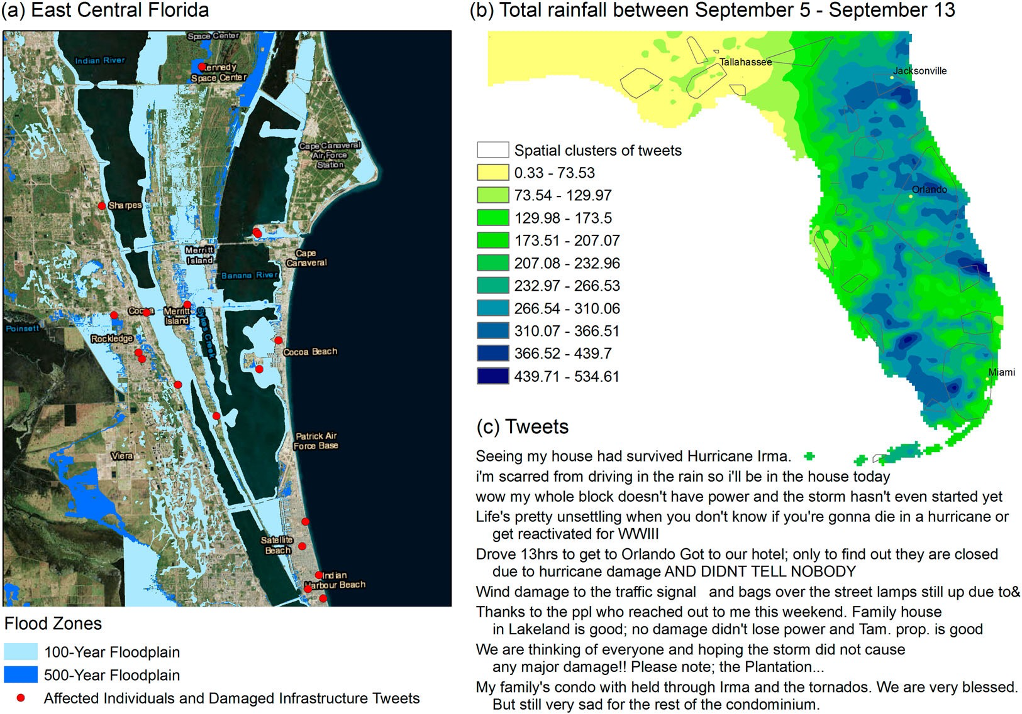
Applications using social data:
Mapping disasters using tweets
Sit, Muhammed Ali, Caglar Koylu, and Ibrahim Demir. 2019. "Identifying disaster-related tweets and their semantic, spatial and temporal context using deep learning, natural language processing and spatial analysis: a case study of Hurricane Irma." International Journal of Digital Earth.

Applications using social data:
Track military actions and hostility
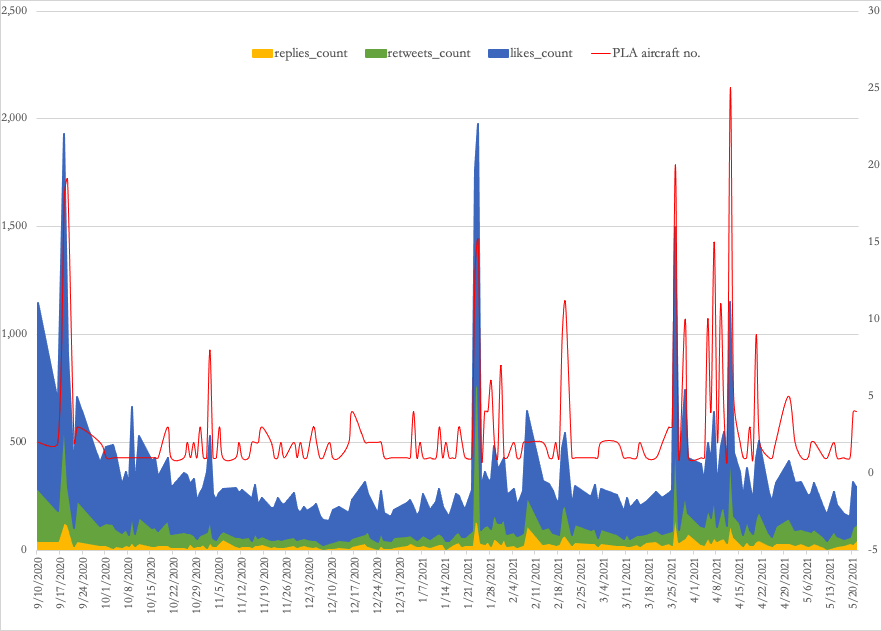
Applications using social data:
Track military actions and hostility
Twitter news example
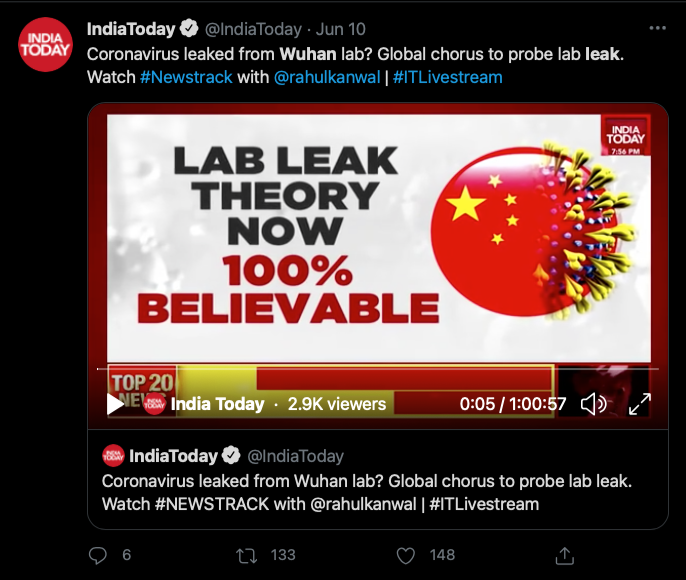
Twitter news example:
Collect data using twint
New strategy for social media sampling:
-
Focus on the network structure
-
Build samples over time
-
Collect data by influential networks and nodes
-
State-space models
-
Twitter data are time series data
-
Twitter data are social network data
-
Community identification
-
Future developments:
-
Network-driven sampling vs. Respondent-driven sampling (Heckathorn 1997, 2009)
-
Exponential random graph models (ERGM)
-
Markov chain models
-
Conclusion and Discussions
Little understanding of data collection process.....
"might lead to the collection of incomplete or biased data sets, which in turn might negatively influence the inferences drawn based on the data.”
- Jungherr (2016)
With some Data Science knowledge at your fingertips, you and your colleagues will begin asking the right questions instead of assuming the wrong answers.
- Luke Posey 2019
Engineering + Data Science: The Missing Duo.
https://towardsdatascience.com/engineering-data-science-the-ultimate-yet-somehow-missing-duo-597eb21dda98
Why Engineering and Data Science?
Engineers can avoid wasting the massive data sets piling up in manufacturing plants, processing plants, and other data heavy areas when they find the data scientists among themselves.
Two solutions:
- Hire data scientists to help engineer with mounting complex data
- Train engineers data science to deal with data themselves
Which one is more expensive?
Again, wrong question!
What is the question?
Next generation of engineers should equip themselves with data science skills, just like typing.
Precision
Precision
Precision
Prediction
Prediction
Prediction
Engineers
Data Scientists
X
To students in India, your comparative and absolute advantages:
Global Value Chain Restructuring
India's new role in the Indo-Pacific
"Democracy" club membership
Global partnership with Taiwan, Singapore, US and Europe
Illustration: Go
Go is:
- One on one
- Two-dimensional
- Limited board (19 x 19, 361 nodes)
- \(10^{360}\) possible moves.

With its breadth of 250 possible moves each turn (go is played on a 19 by 19 board compared to the much smaller eight by eight chess field) and a typical game depth of 150 moves, there are about \(250^{150}\), or \(10^{360}\) possible moves. (Koch, Christof. 2016. How the Computer Beat the Go Master)
Imagine a game that is:
- Many on many
- multi-dimensional
- Expanded board (n x n x n ..., \(n^k\) nodes)
- how many possible moves?
Thank you!
Wait... are you sure you have no questions?

