Balancing stars and dust at different redshift ranges
Katarzyna (Kasia) Małek



National Centre for Nuclear Research, Warsaw, Poland / Laboratoire d’Astrophysique de Marseille, France

With a collaboration of Mahmoud Hamed, Gabriele Riccio, Veronique Buat, Yannick Roehlly, Raphael Shirley, Denis Burgarella, and Ambra Nanni
From the very beginning of the
we can learn how complex is the interaction between dust and stars..
only the panchromatic view on the galaxy can give full information about the physical properties of galaxies.

The main components
(but not all of them):
- old and young star,
- stellar remnants,
- interstellar medium,
- metallicity,
- dust emission/geometry,
- supermassive black holes ....
only the panchromatic view on the galaxy can give full information about the physical properties of galaxies.


CIGALE, Boquien+19

But how to deal with the photometric measurements?
Spectral Energy Distribution fitting
i.e. A. Nanni, V. Buat, L. Barrufet, M. Hamed, J.Alvarez-Marquez, D. Donevski, G. Riccio talks
the link between
stellar (complex)
&
dust (complex)
Aλ/AV
λ [μm]
Attenuation laws



V. Buat talk
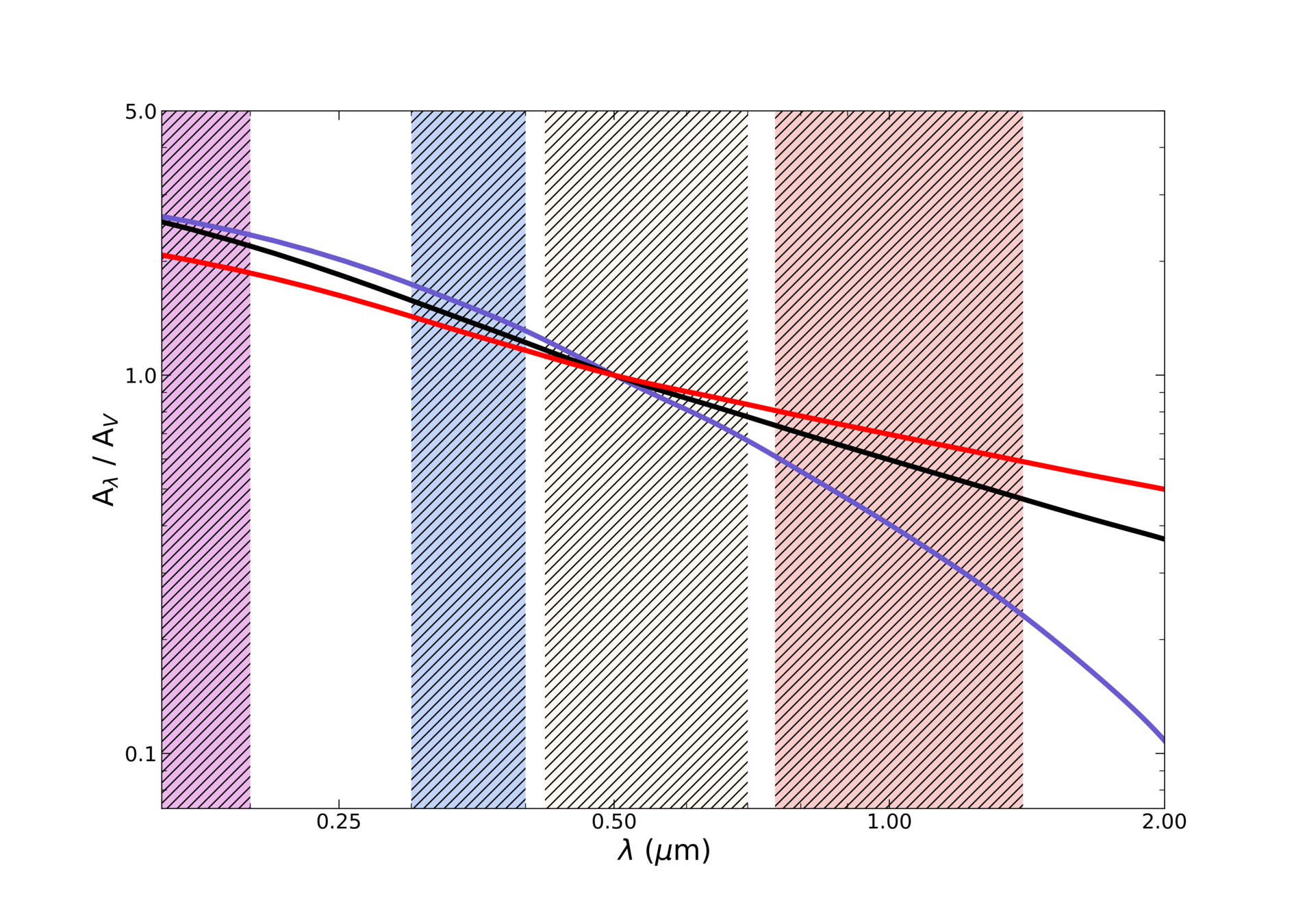
Calzetti 2000
Chalrot&Fall 2000
Lo Faro+2017
Credit: M. Hamed
Are all attenuation laws interchangeable?



To reply to that question we need a statistically important, unique sample of galaxies with reach photometrical measurements, with farIR data, spread out in a wide redshift range.
HELP (Oliver et al., in prep)
aims to collate and homogenize photometric observations from many astronomical observatories

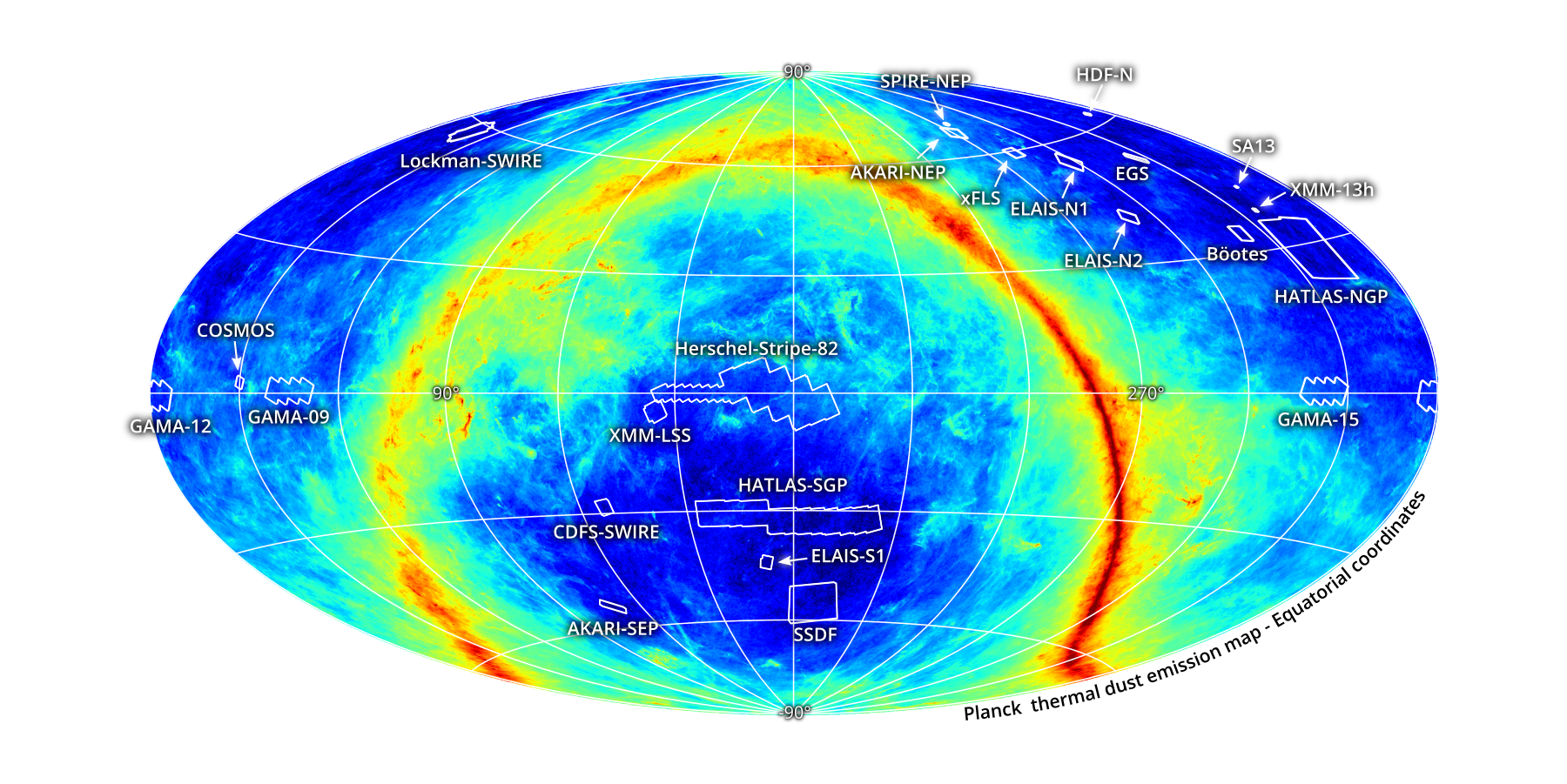
XID+ deblending tool for Herschel maps (Hurley+17)

HELP
aims to collate and homogenize photometric observations from many astronomical observatories,


ELAIS N1
CDFS SWIRE

Based on the HELP data and SED fitting we found that:



Charlot&Fall 2000
Lo Faro 2017
Calzetti 2000
Małek et al., 2018
But why?
see also V. Buat & M. Hamed talks based on the ALMA selected galaxies
Mstar (basic physical parameter) changes with dust attenuation


~45 000 galaxies
For sure not due to the attenuation in the FUV regime ...
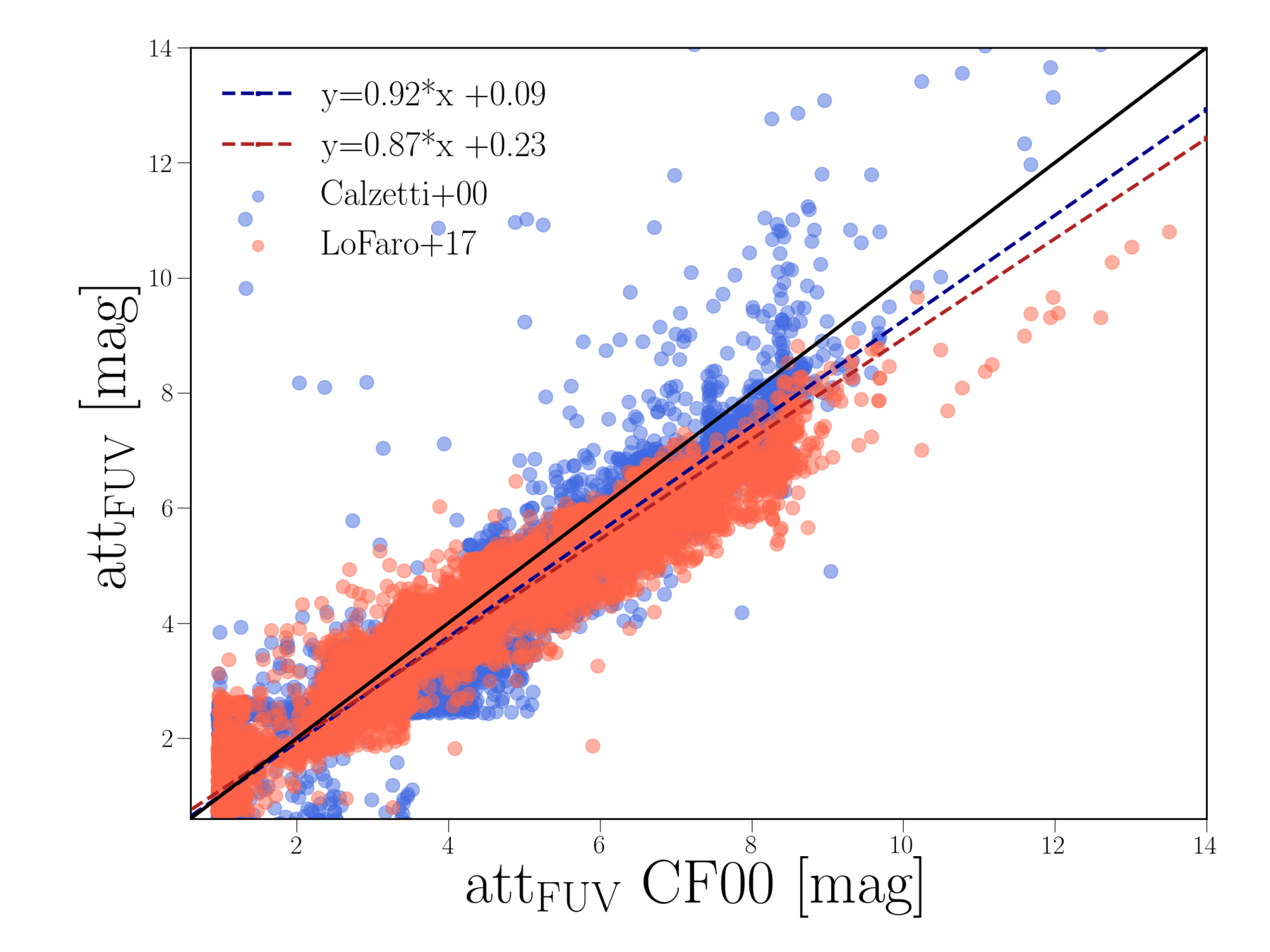
... but because of the changes in the NIR wavelenghts.
Att. NIR
Att. FUV
Małek et al., 2020

Lo Faro+2017
Charlot&Fall 2000
Calzetti 2000





Małek et al., 2018
... and taking into account changes with SFR (i.e. M. Figueira, poster):
we can change for example Main Sequance (not that "Main" anymore?)
Figueira et al., in prep.

GALEX-SDSS-WISE (z < 0.3)
VIPERS (z ~ 0.7)
Hamed, KM et al., in preparation
Mahmoud HAMED talk ("Dust attenuation in ALMA-detected dusty star-forming galaxies in the COSMOS field "

The difference in specific dust mass over redshifts with different attenuation laws.

Mdust/Mstar
redshift
Calzetti 2000
Charlot&Fall 2000
Lo Faro+2017
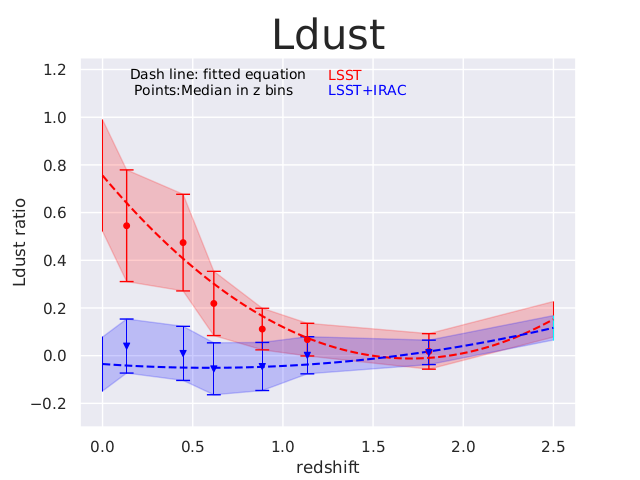
Riccio, KM et al., in preparation
Gabriele RICCIO talk (Friday, "How reliable are galaxies physical parameters estimations for LSST main sequence sample?"
Overestimation of the FUV attenuation for the LSST-like data (ugrizy).

Summary
- a universal attenuation law doesn't exist (yet),
- a flatter attenuation curve at longer λ results in the larger estimation of Mstar,
- the geometry of the galaxy plays an important role in the selection of proper attenuation law (Buat+19, M.Hamed talk), but what else?
- the set of photometric data (G.Riccio talk) and metallicity is also important.
we have a unique photometric data set:
the Herschel Extragalactic Legacy Project
(~ 1300 deg2 of the Herschel Space Observatory)

Our main conclusion is that we need to work on the possible new dust attenuation law or we should find a boundary condition for the application of different laws.
and we are working on that




ASTROdust team
Mahmoud (Misha) Hamed

Gabriele Riccio

Kasia Małek
Ambra Nanni
Krzysztof Lisiecki






