Blockchain Technolgy in Finance: DeFi Lending. Staking.
Instructor: Katya Malinova
Course : F741 Fall 2023

Application: DeFi lending
Prerequistes
Key Components for Defi
borrowing/lending
on-chain ability to exchange arbitrary value


Borrowing/Lending & Unit of Account creation

Idea:
- create fiat money on chain with borrowing
- mechanism
- a collateralized loan with ETH in escrow
- DAO-managed monetary policy (=creation or destruction of tokens)
Sidebar: what is a DAO?
- DAO=decentralized autonomous organization
- \(\to\) entity without management
- governance decided by token holders essentially by vote
user perspective

1 ETH
(1 ETH = $1,577)
(Feb 15, 2023)
\(\approx\) $1,500










\(\vdots\)
1,500 DAI
(1 DAI = $1)
formally: this smart contract is a collateralized debt position (CDP)
user perspective
fractional collateral \(\to\) collateralization factor \(=\) 150%
total collateral = $1,500
maximum loan = $1000
overcollateralization = $500
actual loan (example) = $500
buffer = $500
user perspective: what happens if the price of ETH rises?
ETH \(\nearrow\) $2,000
value of ETH collateral = $2,000
maximum loan = $2,000/150%=$1,333
total collateral = $2,000
maximum loan = $1,333
overcollateralization = $667
actual loan (example) = $500
buffer = $500
overcollateralization = $667
new loan capacity= $333
user perspective: what happens if the price of ETH falls?
ETH \(\searrow\) $750
value of ETH collateral = $750
maximum loan = $750/150%=$500
total collateral = $750
maximum loan = $500
overcollateralization = $250
actual loan (example) = $500
buffer = $0
for reference: former value of collateral
user perspective: what happens if the price falls & max loan is exceeded?
Maker DAO
ETH \(\searrow\) $600
value of ETH collateral = $600
maximum loan = $600/150%=$400
total collateral = $600
maximum loan = $400
required overcollateralization = $200
actual loan (example) = $500
buffer = -$100
for reference: former value of collateral
\(\Rightarrow\) triggering of liquidation auction by "keeper"
sell 3.33 ETH=$500=500 DAI
repay $500=500 DAI loan
retain incentive
return remainding ETH to vault owner
Maintaining the Peg: monetary policy
Maker DAO
- How works:
- 1 DAI = 1.01 USDC
- use USDC to mint new DAI
- supply (DAI) \(\nearrow\)
- price (DAI) \(\searrow\)
- use USDC to mint new DAI
- 1 DAI = 0.99 USDC
- Swap Dai for USDC (more below)
- demand (DAI) \(\nearrow\)
- price (DAI) \(\nearrow\)
- 1 DAI = 1.01 USDC
\(\Rightarrow\) all relies on behavioral assumptions
\(\Rightarrow\) But: there are also real incentives & mechanisms
Maintaining the Peg: monetary policy (warning: may be slightly outdated)
Maker DAO
- stability fee
- DAI savings rate (DSR)
- debt ceiling
borrowers of DAI need to pay interest \(\to\) stability fee
- if too much minting (=too much DAI) then
- \(\to\) interest \(\nearrow\) \(\to\) cost of DAI \(\nearrow\)
- \(\to\) minting \(\searrow\) \(\to\) supply DAI \(\searrow\)
DSR paid on "locked" DAI
- DAI deposited to specific contract (demand \(\nearrow\))
- funded by stability fees (SF)
- \(\to\) SF > DSR
total amount of debt (or DAI) outstanding is limited
Sidebar: how is this decided?
\(\to\) special "governance" token MKR
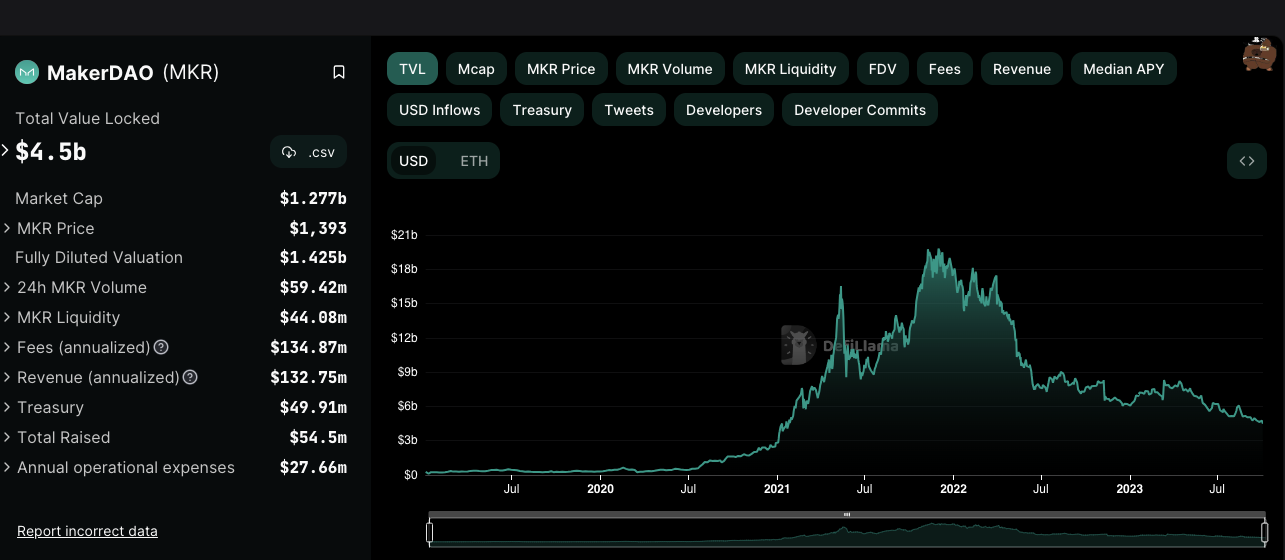
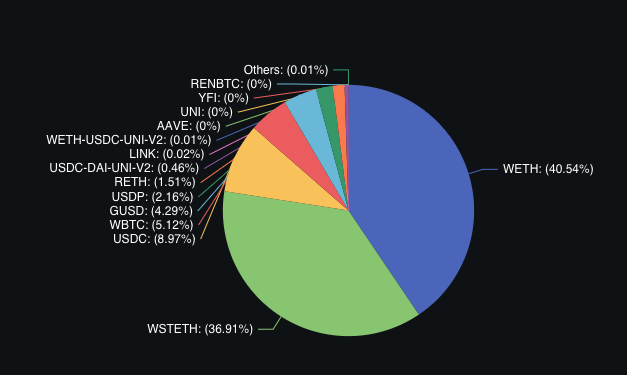
Value locked Oct 03, 2023: USD 4.5 Bln
Maker DAO
Source: daistats.com (Oct 27, 2021)
Source: daistats.com (Oct 26, 2022)
The March 12, 2020 "Black Thursday" Drama
Maker DAO
- some crypto prices dropped more than 50%
- cascading liquidations in leveraging platforms
- network congestion: some liquidations done at near-zero prices
- collateral shortfall in DAI
- MakerDAO sold new DAO tokens to collect collateral
- odd: DAI became riskier but high demand for DAI to trigger liquidations!
PEG stability module (PSM) (has been further updated over time)
Maker DAO
The Problem:
- in extreme bull/bear runs, the peg may no longer work
- example: March 2020
- ETH dropped significantly and suddenly
- a rush occurred to (a) get out of ETH into safe assets and (b) to collect DAI to get keeper fee
- upward pressure on price of DAI
The Solution:
- Peg stability module
- swap a given collateral type directly for DAI at a fixed rate (no minting/borrowing)
- like regular vault type with a zero stability fee and a liquidation ratio of 100%
- accessed through a user-facing smart contract containing the relevant swap functions (no ownership, just straight swap)
Note: In May 2021, ETH prices dropped again by >30% but no drama in DAI
categories and assessment for defi
TradeFi vs Makerdao
Interest rates influenced by the FED, access to loan products controlled by regulation and institutional policies
MakerDAO platform is openly controlled by the MKR holders.
Difficulty of obtaining loans for large majority of population
Open ability to take out DAI liquidity against an overcollateralized position in any supported token.
Costs of time and money to acquire a loan
Instant liquidity with minimal transaction costs.
Can't seamlessly use the same USD (esp. outside the US)
DAI, a permissionless USD-tracking stablecoin backed by cryptocurrency. DAI can be used in any smart contract or DeFi application.
interoperability
inefficiency
centralized control
limited access
opacity
Unclear collateralization of lending institutions.
Transparent collateralization ratios of vaults visible to entire ecosystem
TradFi
MakerDAO
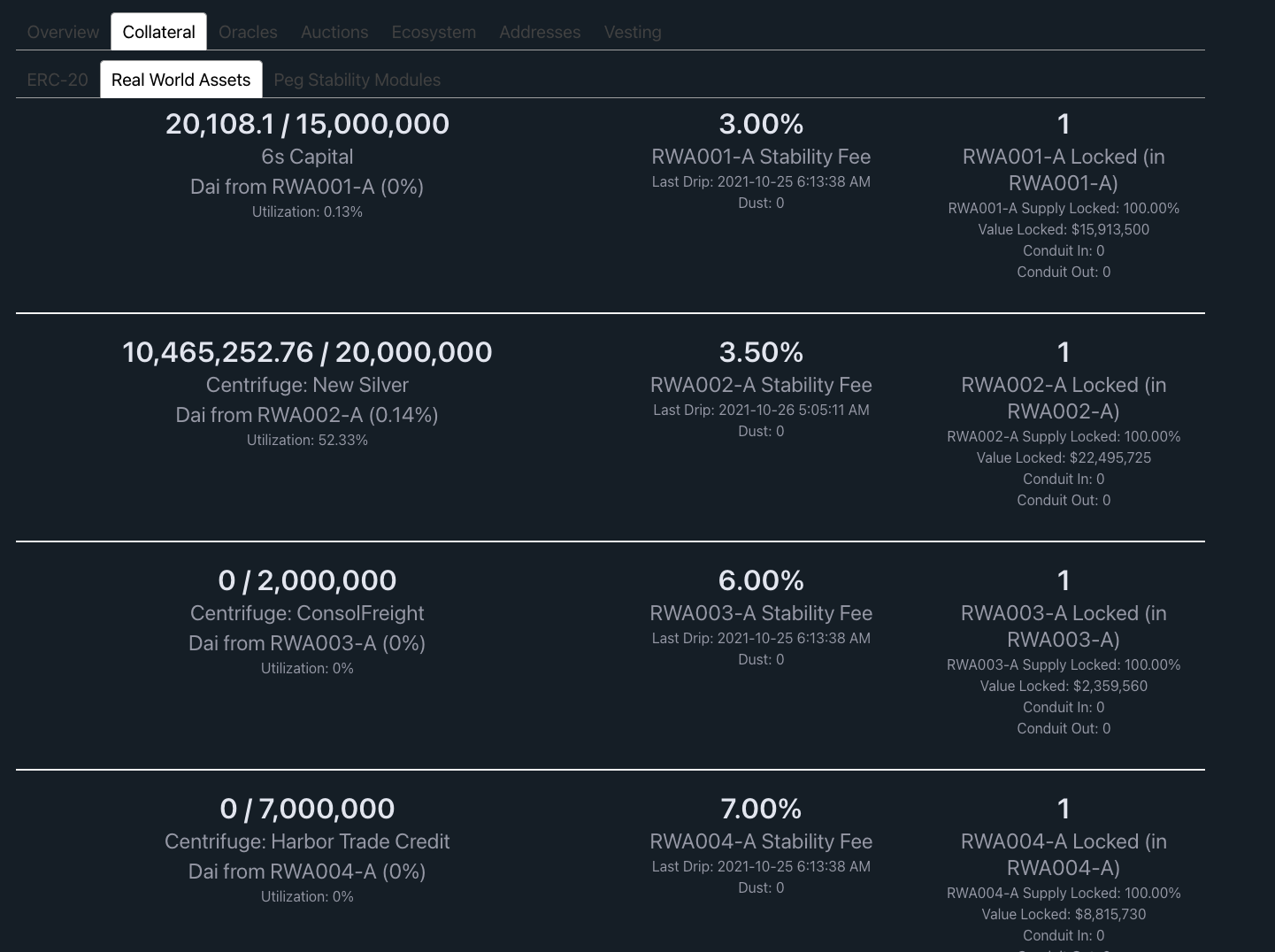
The frontier: DAI loans for real-world assets
Maker DAO
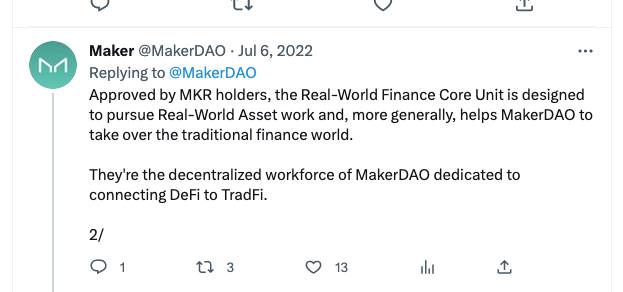
The next steps: DAI loans for real-world assets

MakerDAO bought another $700 million U.S. Treasurys, taking the total to $1.2 billion [...]
[... ]to diversify the assets backing the $4.5 billion dollar-pegged stablecoin
The next steps: DAI loans for real-world assets
Application: DeFi lending:
Compound (and Aave)
How does compound finance work?
Lending

Fundamentally, what does a bank do?
- size intermediation
- term intermediation
- risk intermediation
And how is this done?
- pooling deposits
- issuing loans based on deposits
- loan rates based on collateral or credit rating
on blockchain
- short-term loans
- pseudo-anonymous
Nothing new is minted
collateral
compound Finance
- Collateral ratio \(\in[0,90]\)
- =0 \(\to\) not usable
- =90 \(\to\) stablecoin
- post 100 DAI
- factor 90
- \(\to\) for each $1 borrow, deposit $100/90=$1.11
- can borrow up to $90
- post 1 ETH=$300
- factor 60
- \(\to\) for each $1 borrowed, deposit $100/60=$1.67
- can borrow up to $180
Example 1
Example 2
Example 3
- post 1 ETH=$300 and 100 DAI \(\to\) $400
- factor 60 and 90
- \(\to\) for each $1 borrowed, deposit
$100/(.75\(\cdot\)60+.25\(\cdot\) 90)=$1.48 - can borrow up to $270
compound Finance
- Compound escrows tokens
- must account for % ownership
- \(\to\) tokenized user share
- \(\to\) use the c-token
- cDAI
- cETH
- c-tokens are "minted" ("burned") based on the funds that are added (removed) to (from) Compound
- ability to use the ctokens in other protocols
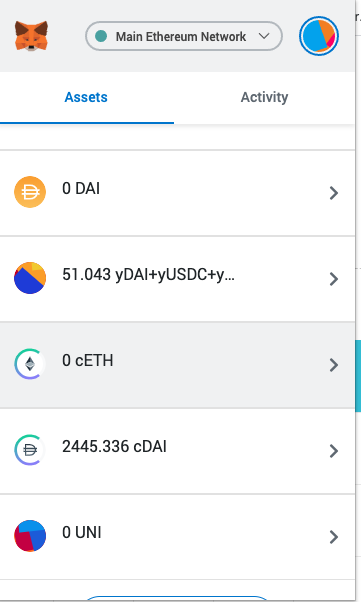
Tracking ownership - How do you reclaim a deposit?
Tracking ownership - Example
compound Finance
In Compound
translated to c-tokens (example, can be different conversion)
new deposit
1,000 DAI
100 cDAI
500 DAI
add 50 new cDAI
Tracking ownership - Example
compound Finance
In Compound
translated to c-tokens
new deposit
1,000 DAI
150 cDAI
500 DAI
1 year later: 10% interest on compound
150 DAI
(same cDAI, each cDAI is worth more)
interest
Some (minor) differences across protocols & receipt tokens
-
Compound : share of the pool
- deposit 100 USDT to a pool with 900 USDT
- If, say, 100 cUSDT tokens total in circulation, the user gets 10
- signifies 10% of the pool total
- say, 5% interest => value of the pool increases to 1050 USDT
- user: still has 10 cUSDT tokens at the end, but exchanges them for 10% of the pool = 105 USDT
-
Aave: receipt for your tokens
- deposit 100 USDT to a pool with 900 USDT
- get 100 aUSDT tokens, no matter the pool value
- say, 5% interest
- => have 105 aUSDT tokens and can collect 105 from Aave

common theme in DeFi: jumping between dApps
-
Assume
- 1 ETH = 200 DAI
- supplied 100 ETH in Compound
- borrowed 10,000 DAI to lever up and purchase an additional 50 ETH
- \(\to\) also supplied to Compound
-
Borrow interest rate in DAI
- Compound: 15%
- Aave: 5%.
- Can you refinance your borrowing?
dapp-linking
Defi is like real "high" finance
Source: Harvey, Ramachandran, and Santoro (2020)
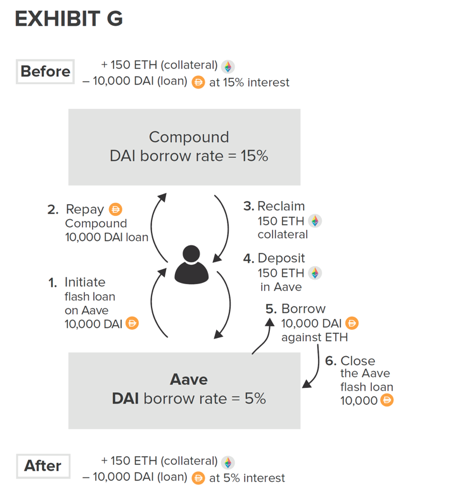
Revisit the flash loan example from the previous slides for a more complex DeFi Lego build.
The Flow of Event: Normal Times
The Flow of Event: Collateral Liquidation
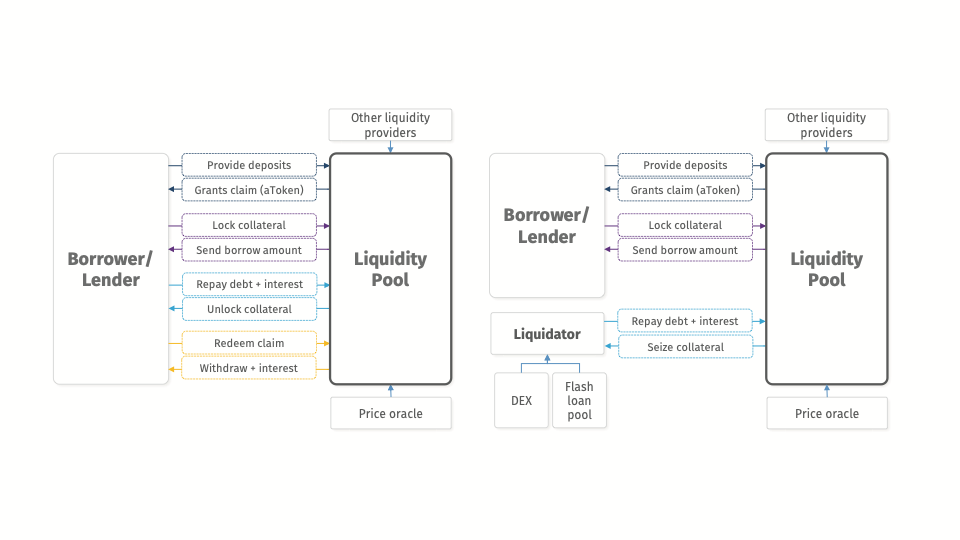

Dapp composability & Flash loans


1. flash-borrow DAI

5. repay DAI


3. receive the collateral (ETH) at a discount

4. convert ETH to DAI

2. liquidate ETH-collaterilized loan with DAI

Loan liquidation opportunity
either all of these execute or none -> true arbitrage
- no capital commitment
- zero risk
Stopped here in lecture 4
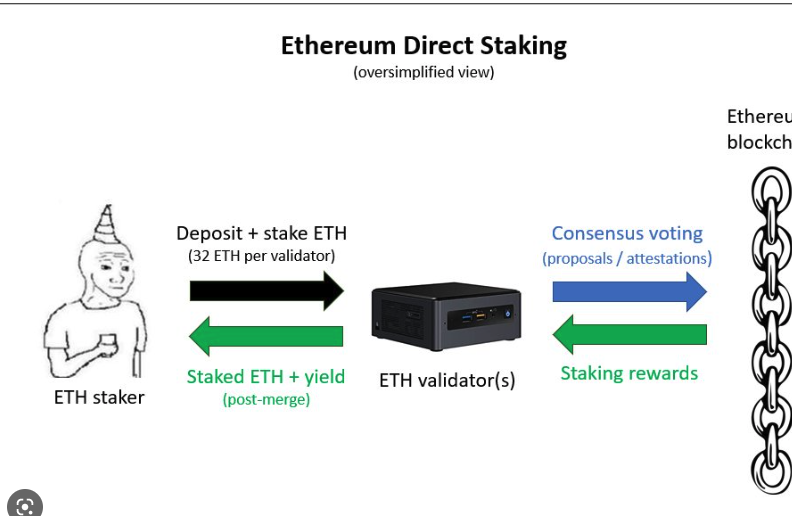
Staking: One word, multiple meanings
Very loosely: locking in the funds
Staking as a Validator







Similar rule in Canada: look up "Pacific Coin test"
When is it a security (SEC point of view)?
In the case of Howey, the buyers of the Florida citrus groves saw the transactions as valuable primarily because the labor and expertise were provided by others. Buyers only needed to invest capital to access an income stream.
Staking More Broadly & Yield Farming
- "Staking" : commonly used in decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols.
- DeFi staking often refers to locking up tokens within a protocol to achieve a specific goal or result.
- Could be considered a misnomer but it is a common phrase.
- Typically receive: a portion of the protocol fees. Examples:
- trading fees (Uniswap)
- protocol-issued tokens (e.g., governance tokens)
- liquidity mining fees (rewards for providing liquidity on the platform)
Staking in DeFi
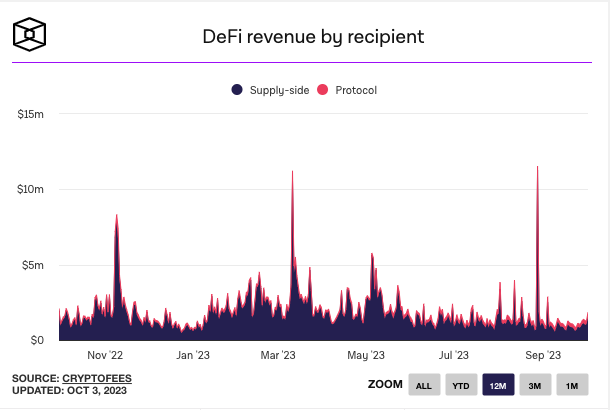
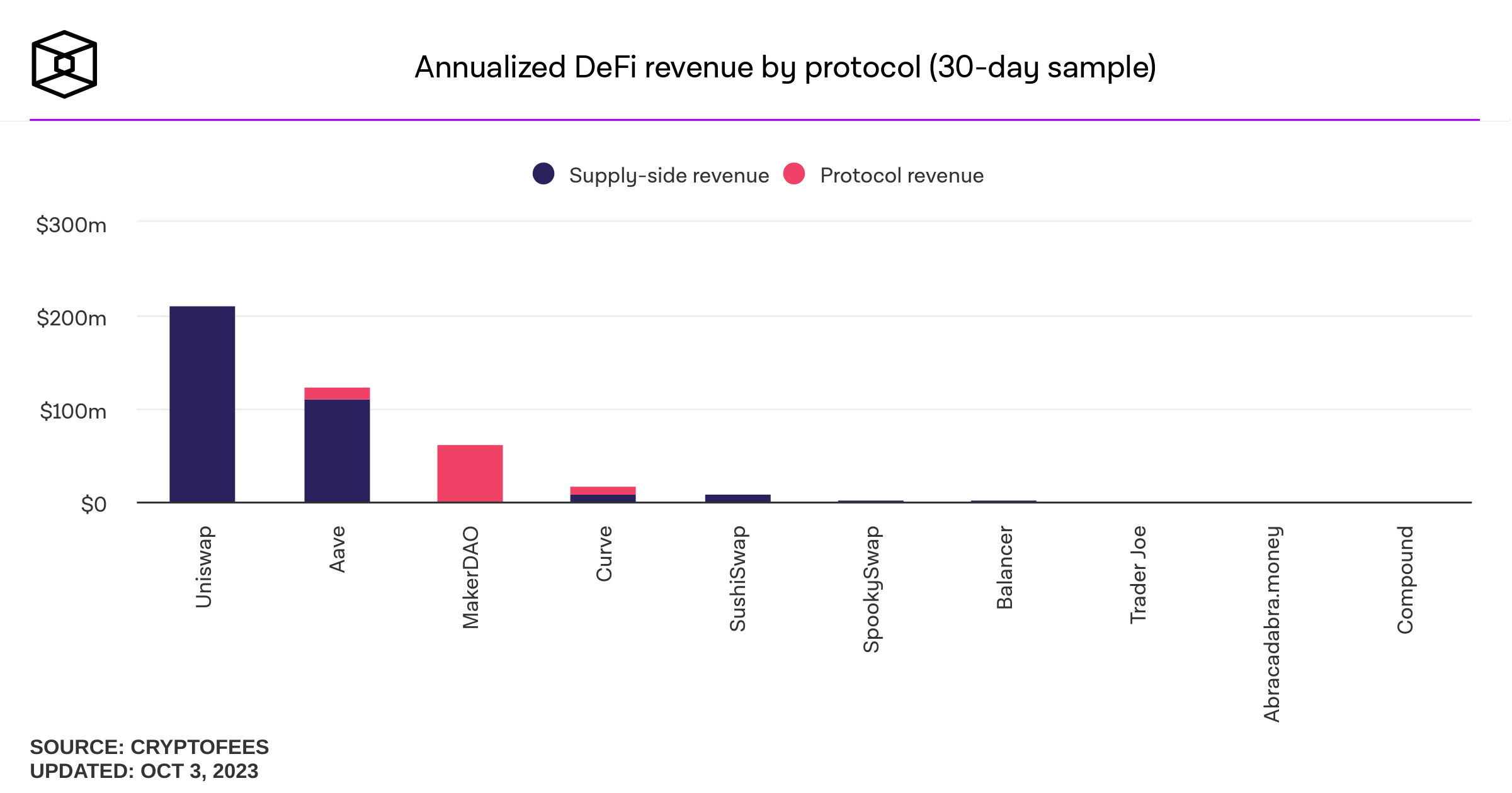
- Protocol Insurance (liquidity to be used as a backstop)
- Governance (e.g., Curve) -- only have this right if the tokens are staked
- Liquidity Provision
- Synthetix: staking as a way to supply collateral for the creation of synthetic assets
- Token distribution
- only get rewards ("dividends" in tradfi) when/if your tokens are staked -- e.g., because the ownership is easily defined (and also as a reward for facilitating the protocol)
Staking in DeFi: Why?
- Very broadly and very loosely:
- Yield farming refers to any effort to put crypto assets to work to generate the highest returns possible on those assets.
- E.g.,
- staking
- lending in a DeFi lending protocol
- supplying liquidity on a decentralized exchange
"Yield farming"
Many automated DeFi products are emerging


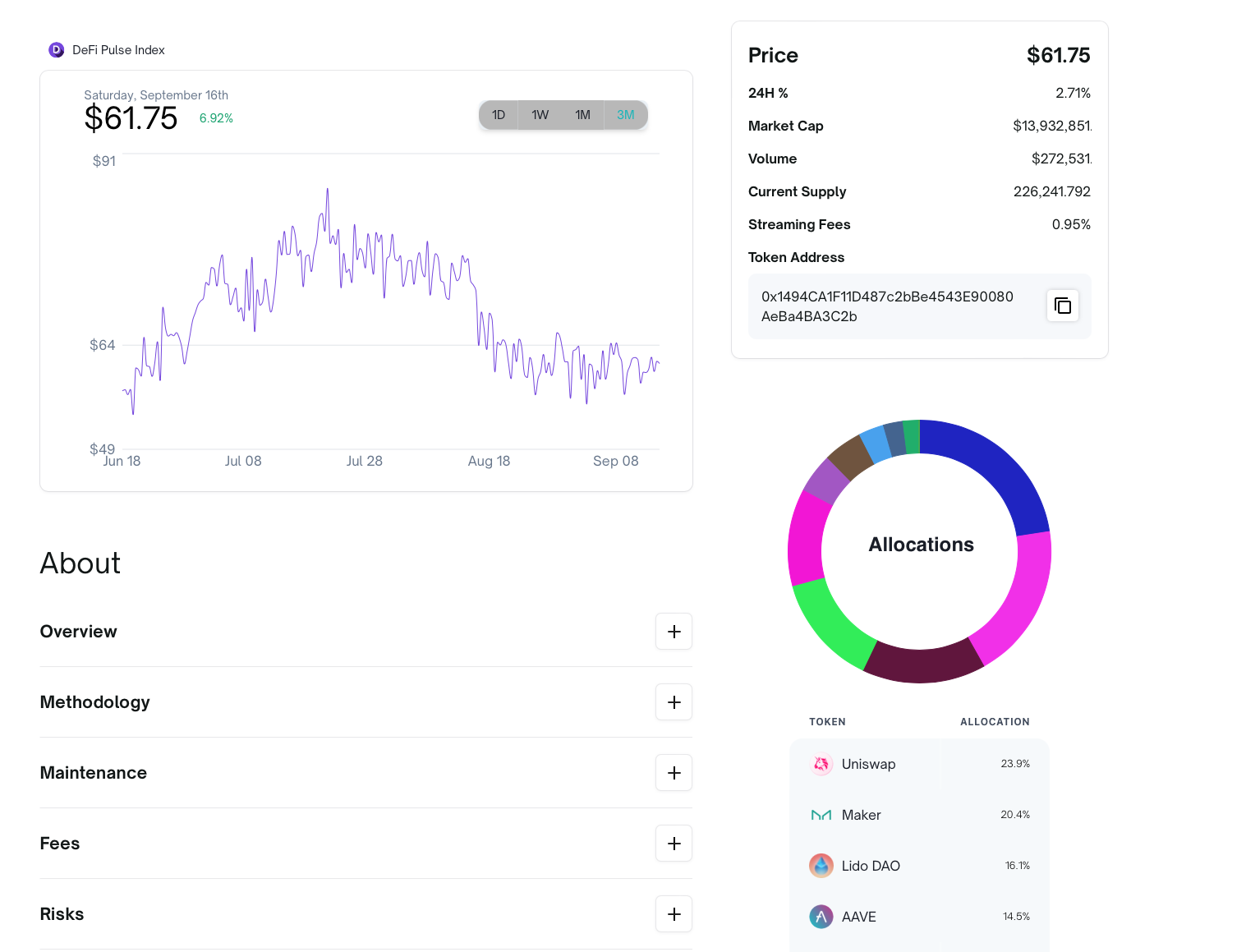
Obvious Smart Contract Application: Automate Investment Strategies

"yield aggregator:" push capital where rate of return is highest
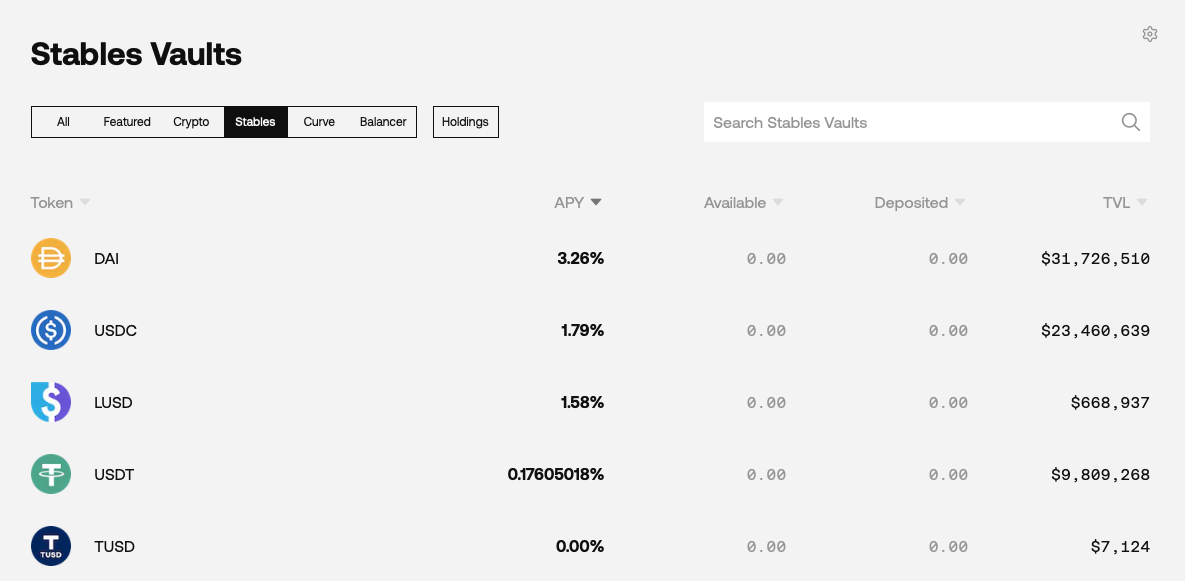

Caution: "yield farming" has its risks ....
Odd Lots: SBF and Matt Levine on How to Make Money in Crypto (podcast, April 25, 2022)
If too pressed for time to listen, start at minute 21:17, or check out:
And yet: staking, lending, and supplying liquidity on DEXes - at least in theory - allows (non-expert) investors to passivley participate in and benefit from the promise/growth of cryptoassets
For a more rigorous analysis (not for F741), see Augustin, Chen-Zhang, and Shin, Donghwa, "Reaching for Yield in Decentralized Financial Markets"
https://ssrn.com/abstract=4063228
"investors chase farms with high yields and that [...] farms with the highest headline rates record the most negative risk-adjusted returns"
@katyamalinova
malinovk@mcmaster.ca

slides.com/kmalinova
https://sites.google.com/site/katyamalinova/