Blockchain Technolgy in Finance: DeFi Intro and Crypto Trading
Instructor: Katya Malinova
Course : F741 Fall 2023

A quick recap
blockchain=
an infrastructure for digital resource transfers
software protocols that allow multiple parties to operate under shared assumptions and data
without trusting each other.
Updates are packaged into “blocks” and are “chained” together cryptographically to allow an audit of the prior history
cryptocurrency =
internal payment mechanism to pay for operation of a blockchain
Consensus Protocol =
a set of rules that determine what kinds of blocks can become part of the chain and become the “truth”.
Transaction
Execution



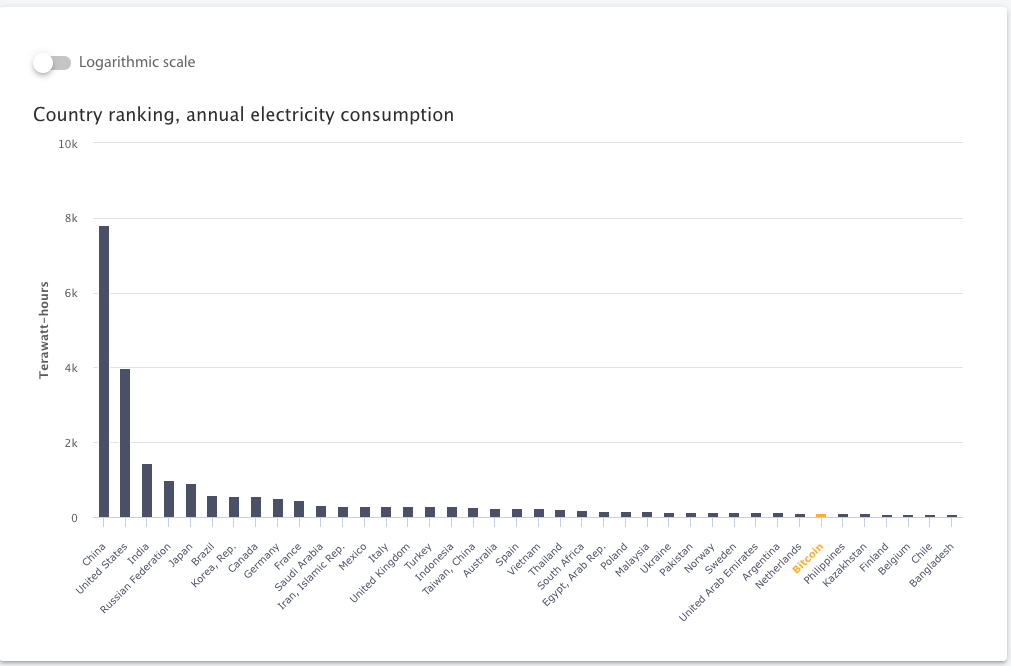
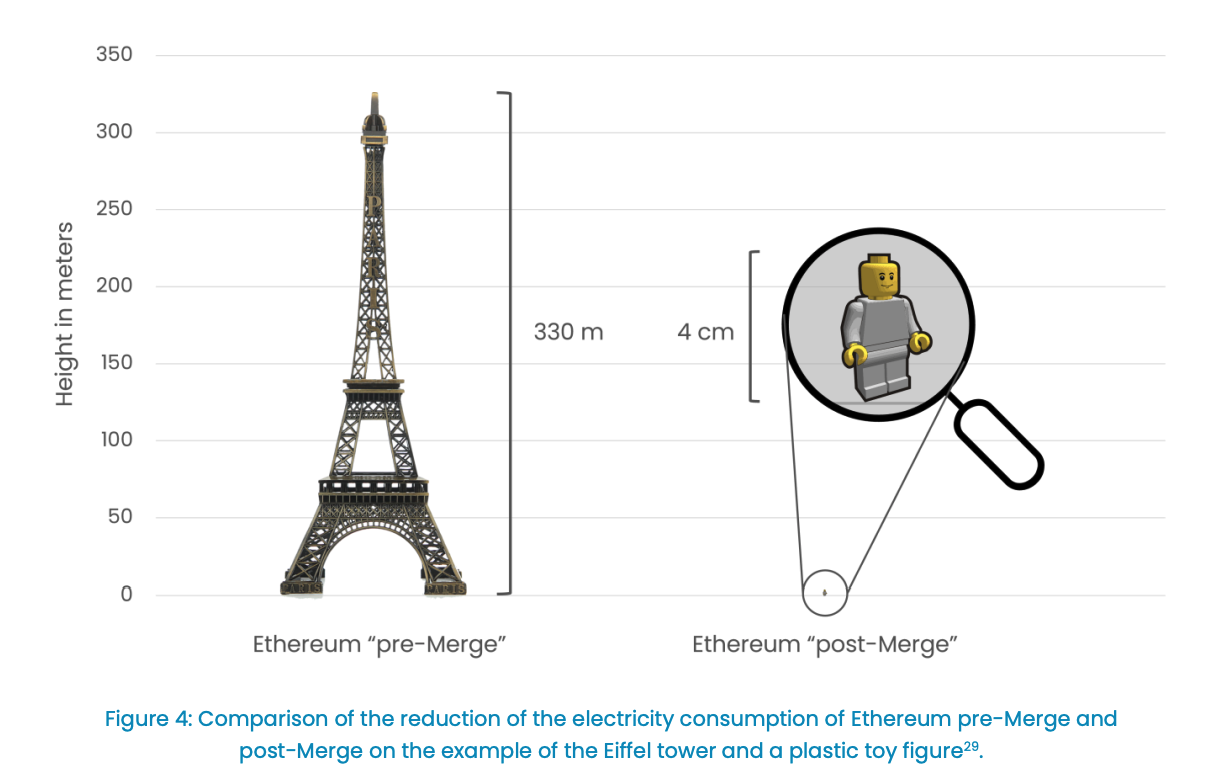
Source: Cambridge Bitcoin Energy Consumption Index https://cbeci.org/

Proof of work protocol: unsustainable amount of energy


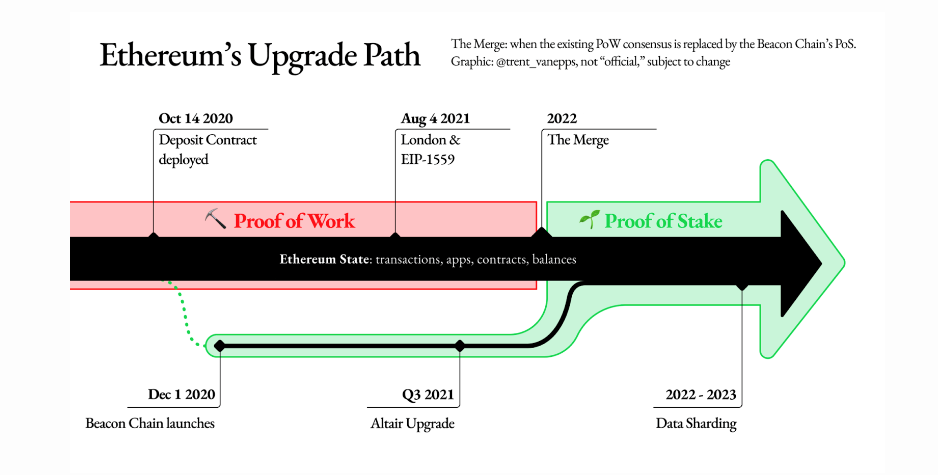
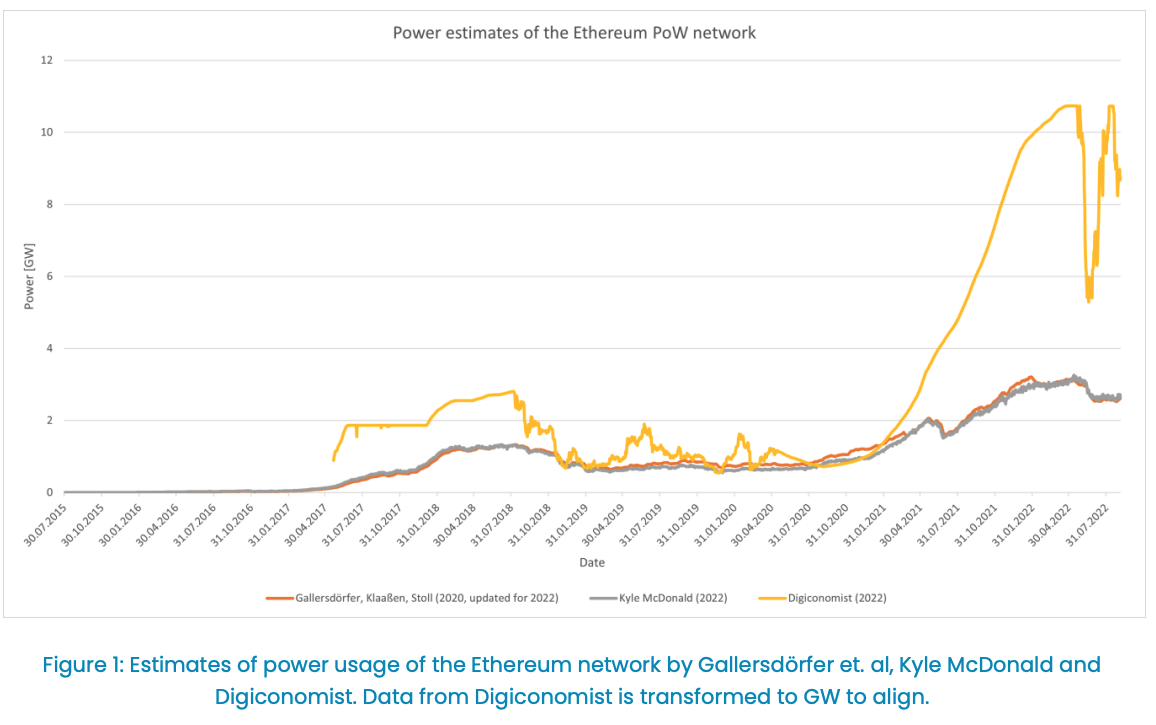
Ethereum power usage before the Sept 15, 2022 Merge
Why is this idea powerful?

payments
stocks, bonds, and options
swaps, CDS, MBS, CDOs
insurance contracts

A blockchain is a
- general purpose
- open access
- value management
- infrastructure
- that is communally run
What makes DeFi different from TradFi
decentralized finance =
provision of financial service functionality without the necessary involvement of a traditional financial intermediary like a bank or broker-dealer*
digital media =
provision of information service functionality without the necessary involvement of a traditional information intermediary like a publisher, library, or newagency
*my take: applies to only commoditizable services
trading Infrastructure
payments network
Stock Exchange
Clearing House
custodian
custodian
beneficial ownership record
seller
buyer
Broker
Broker










Application: decentralized trading with automated market makers













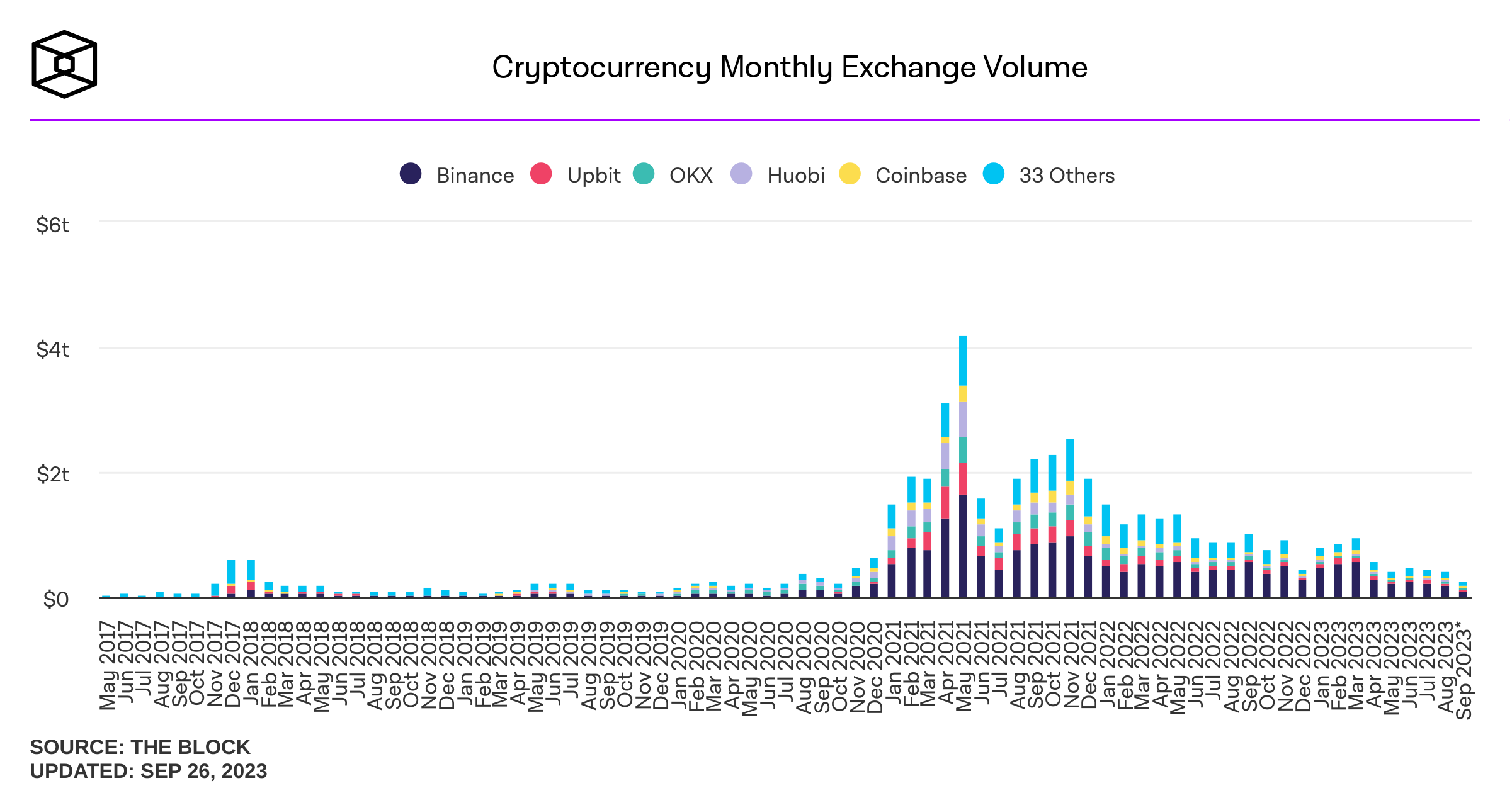
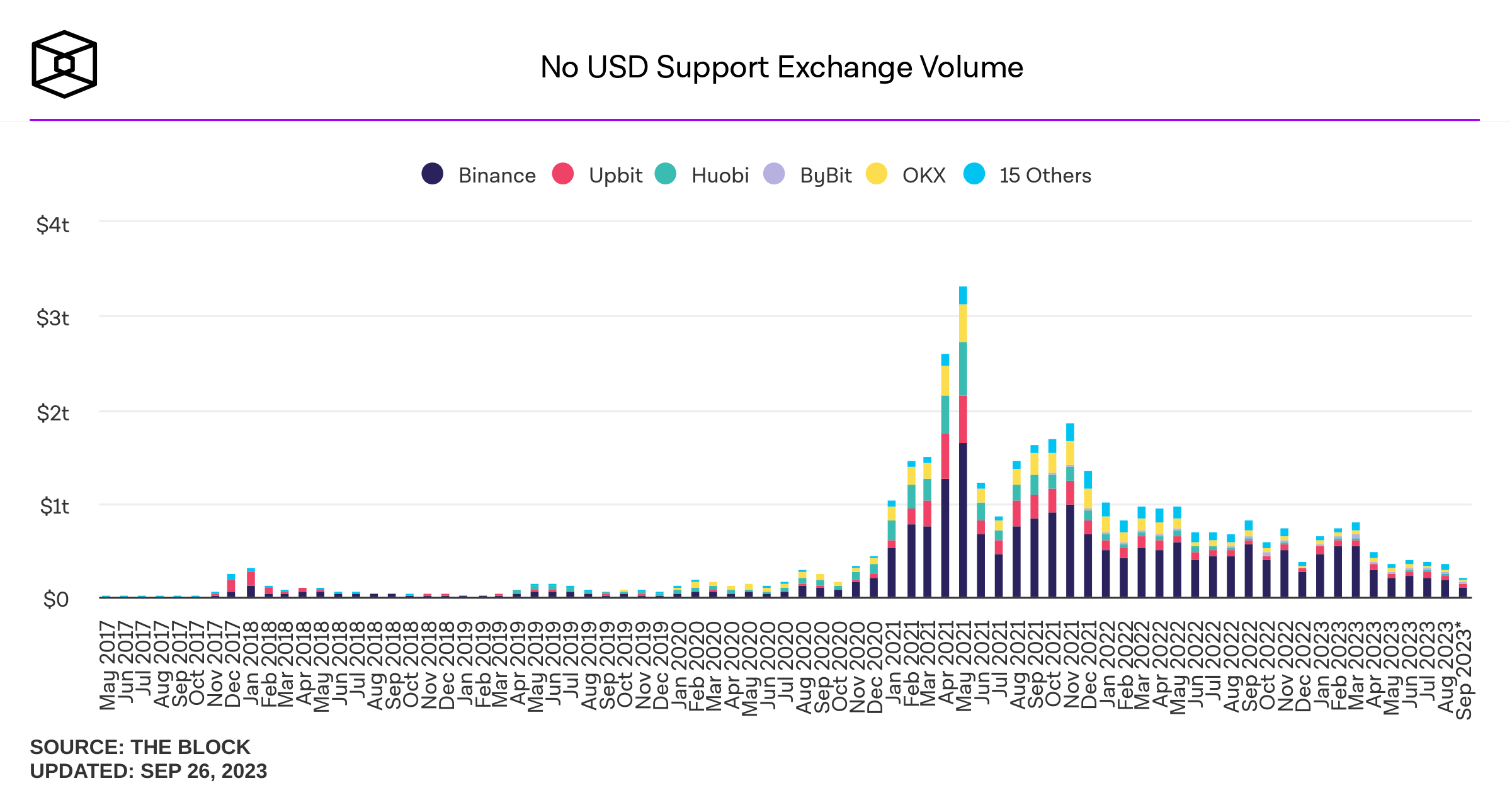
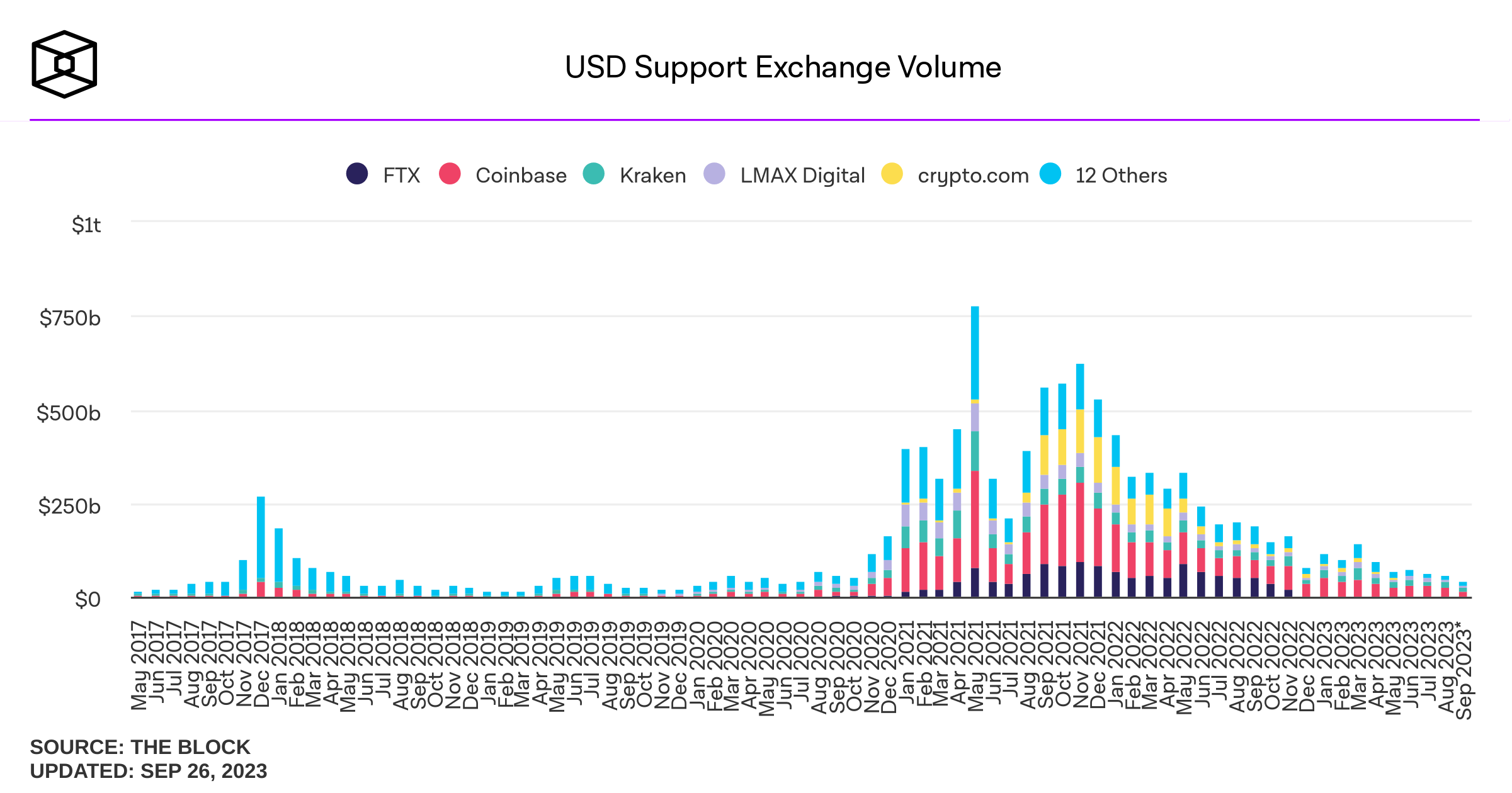
Some background stats on DEcentralized Exchanges (DEX)
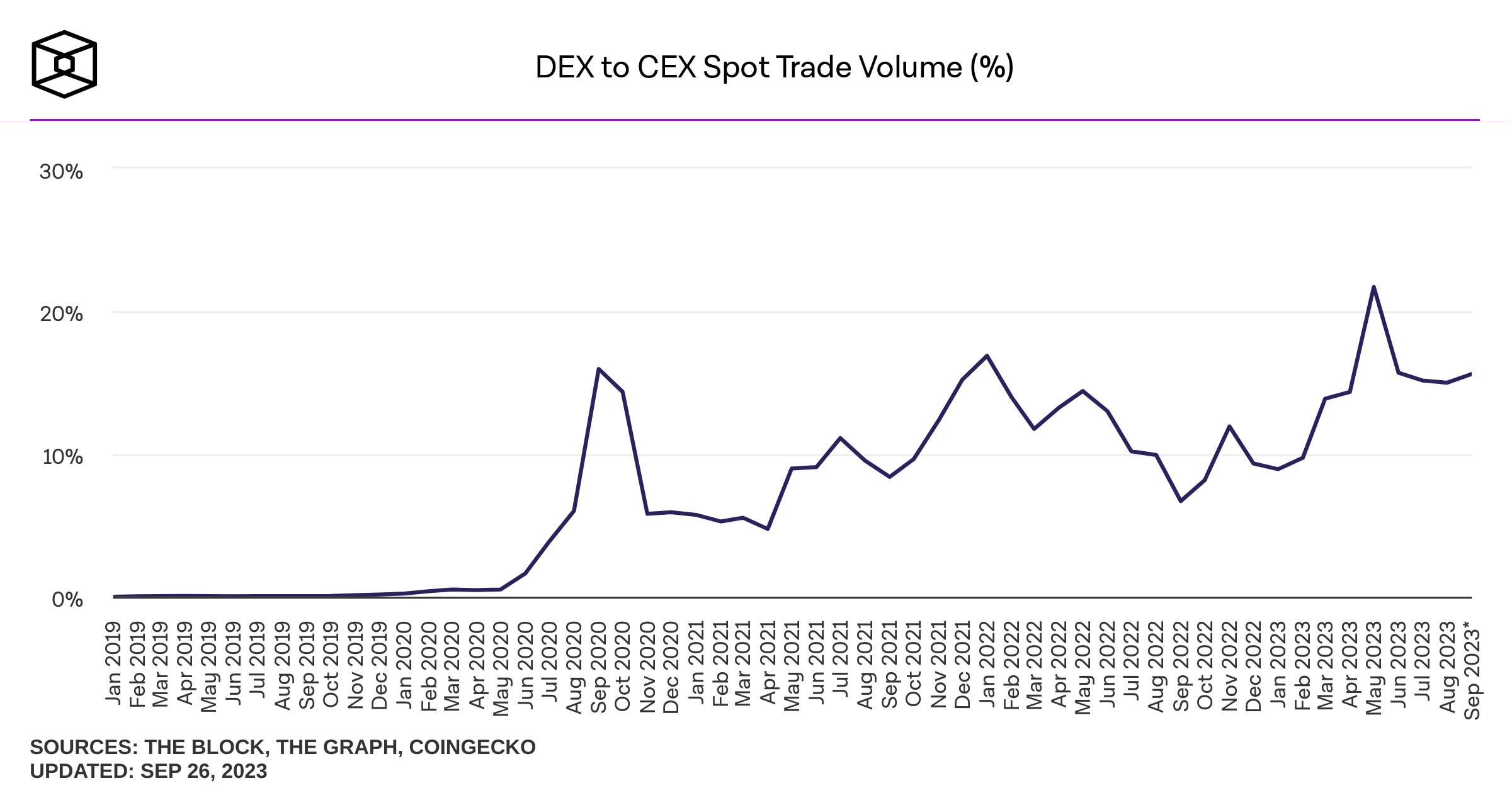
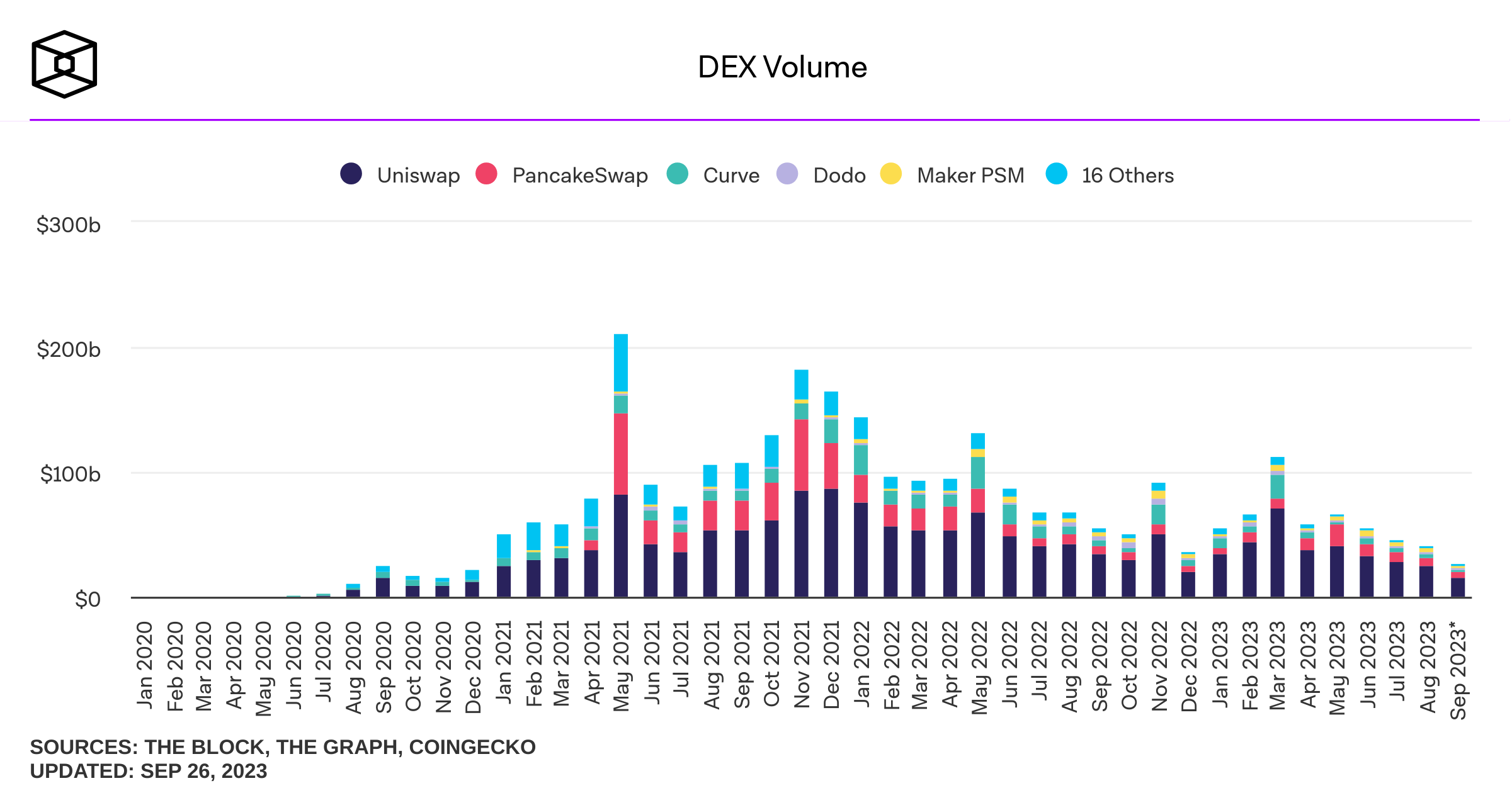
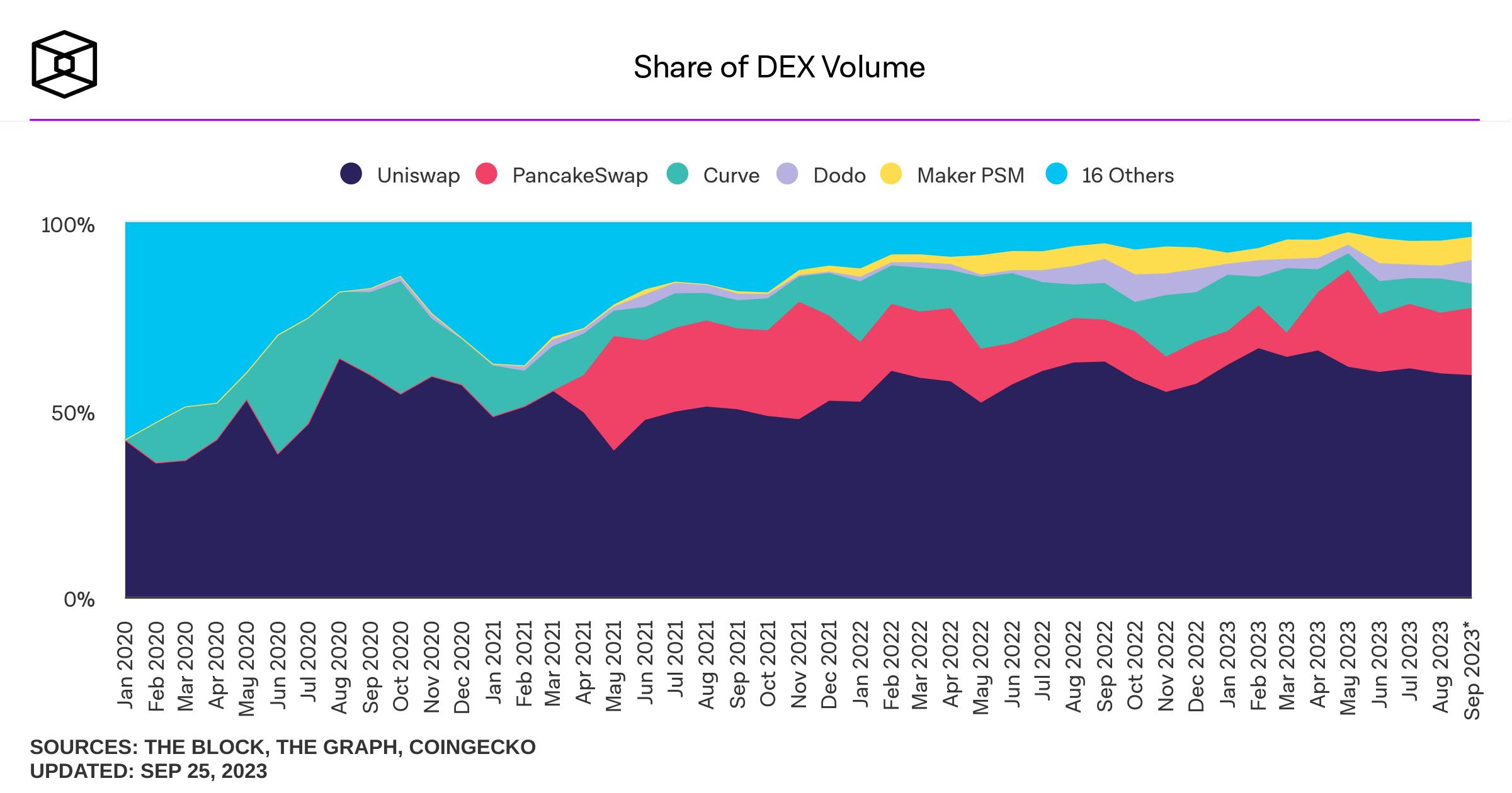
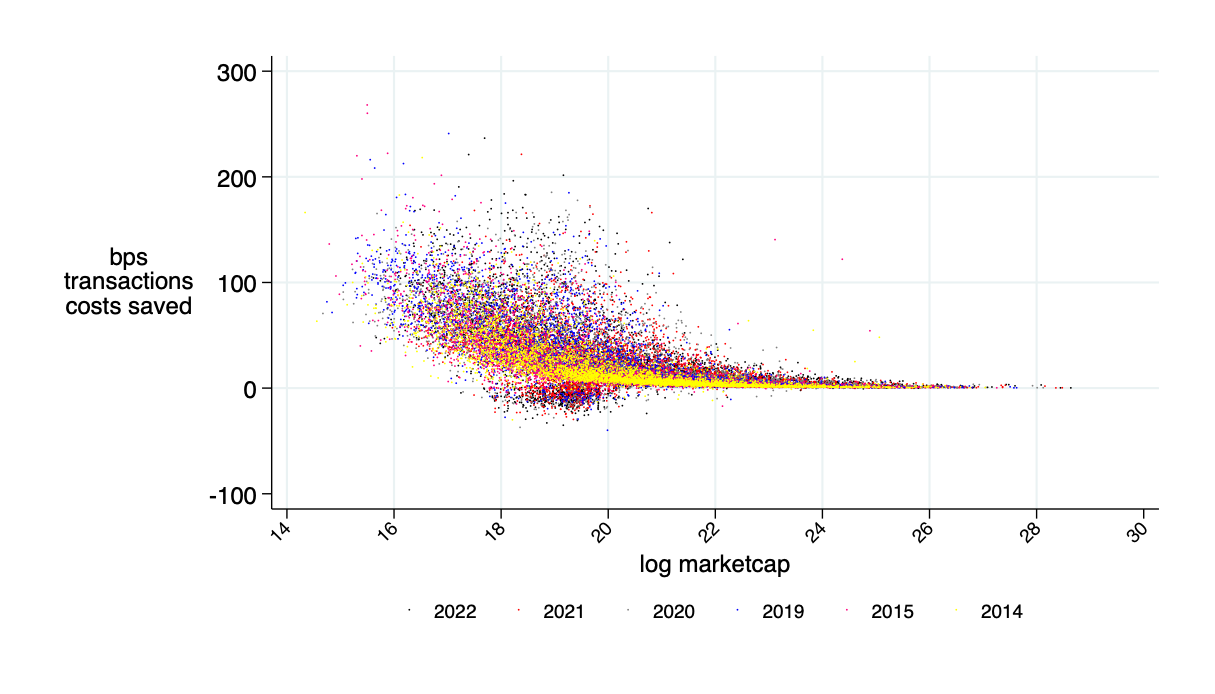
Sources of savings:
- better risk sharing among liquidity providers
- better use of capital
Possible transaction cost savings in cash equities: \(\approx\) 30%
Source: "Learning from DeFi: Would Automated Market Makers Improve Equity Trading?" working paper, Malinova & Park 2023
Who controls the Projects? Decentralized Autonomous organizations

UniSwap Lab supports development
a website app accesses the code

token holders control contact features
don't own the code
operation = decentral
control = decentral
anyone can use the baseline code


core code runs on the blockchain

tokens used as rewards
Application: Decentralized Borrowing & Lending











borrow
provide collateral
The Flow of Event: Normal Times
The Flow of Event: Collateral Liquidation
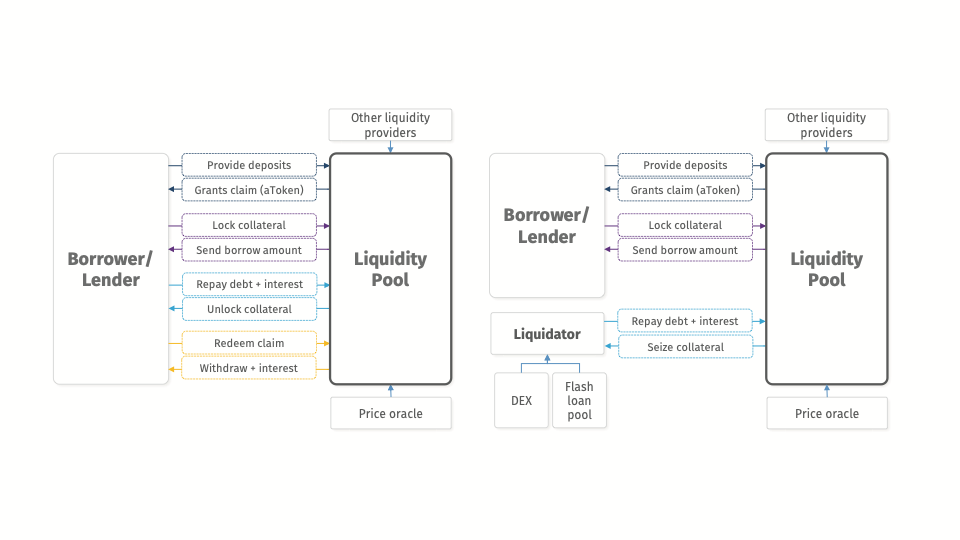

Dapp composability & Flash loans


1. flash-borrow DAI

5. repay DAI


3. receive the collateral (ETH) at a discount

4. convert ETH to DAI

2. liquidate ETH-collaterilized loan with DAI

Loan liquidation opportunity
New tools: flash loan
- either all of these execute or none -> arbitrage!
- can be used more traditionally -- e.g. to refinance a loan at a better rate
UNI governance token holders: control rights, but no cash flows
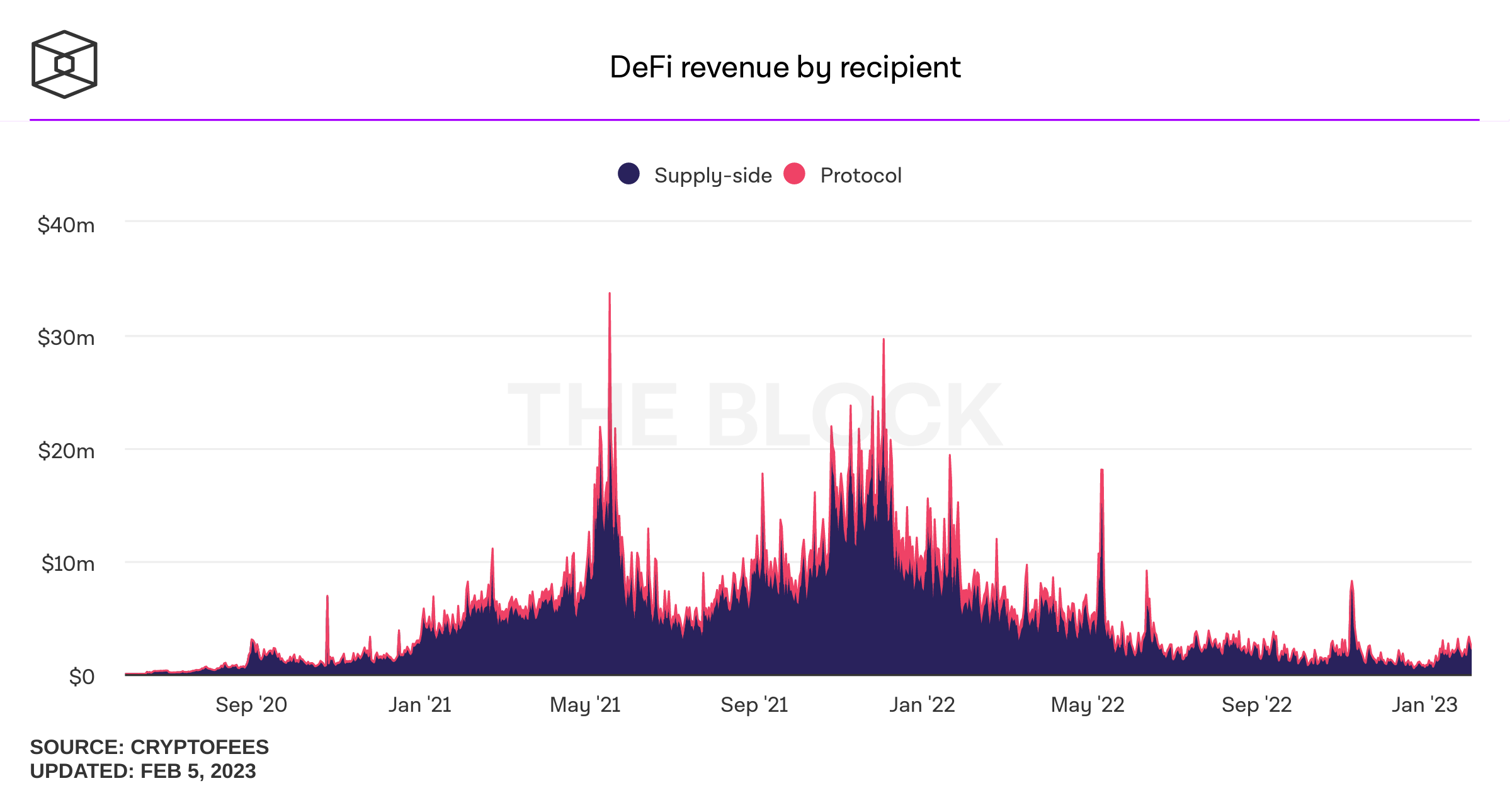
Many automated DeFi products are emerging


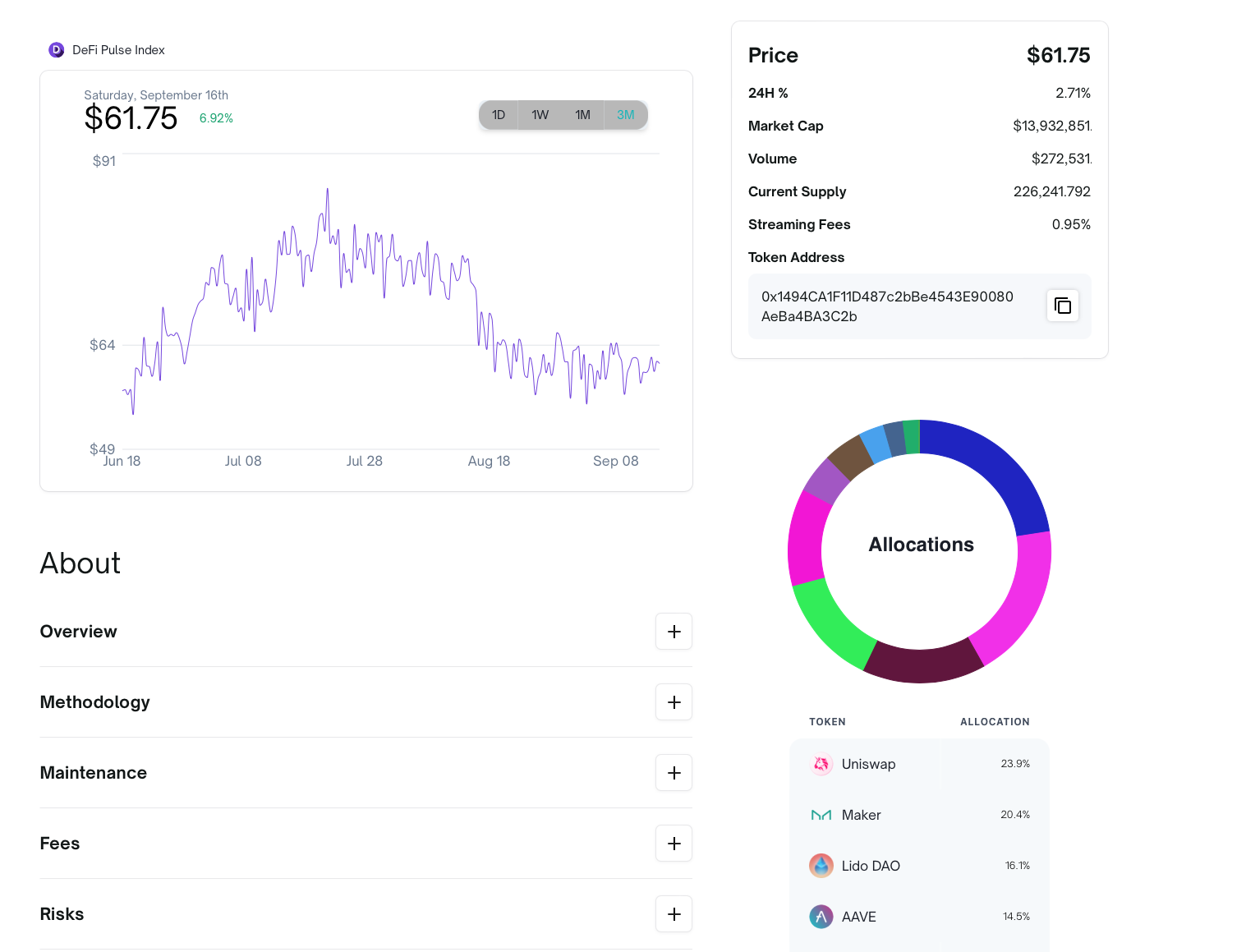
Obvious Smart Contract Application: Automate Investment Strategies

"yield aggregator:" push capital where rate of return is highest

Crypto Trading



















Broker


Exchange
Internalizer
Wholeseller
Darkpool


Venue



Settlement
Centralized Trading

















Issues and concerns with CEX trading
- No shortage of drama!
- A short list of issues
- expensive arbitrage
- price manipulation
- volume manipulation
- security risk
- Google "Lazarus Group"
- Are they unlicensed securities exchanges?
Costly Arbitrage
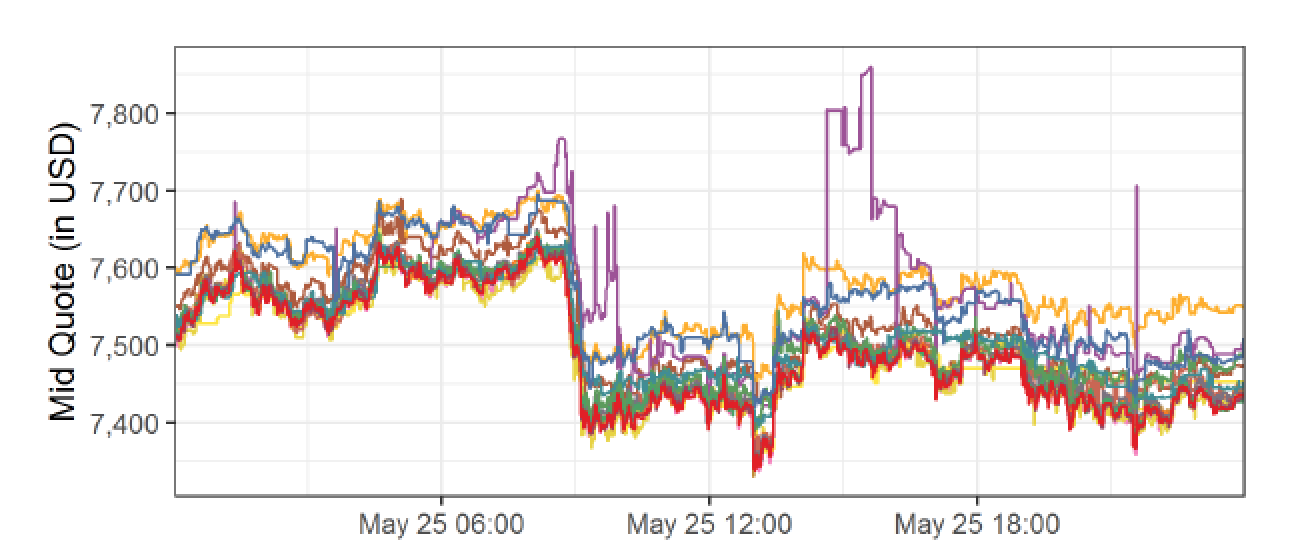

BTC/USD
ask: 7,600
bid: 7,550
BTC/USD
ask: 7,500
bid: 7,450

buy BTC
sell BTC
move BTC to Kraken



=> arbitrage = commit capital on multiple exchanges
Crypto Wash Trading, Lin William Cong, Xi Li, Ke Tang, Yang Yang
- systematic tests:
- robust statistical and behavioral patterns in trading to detect fake transactions on 29 cryptocurrency exchanges.
- Regulated exchanges are OK
- unregulated exchanges: rampant manipulations
- wash trading on each unregulated exchange:
- on average over 70% of the reported volume
- improve exchange ranking
- temporarily distort prices
Volume Manipulation
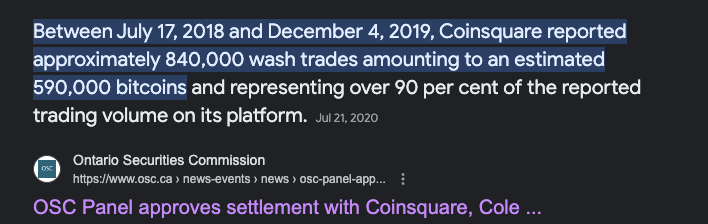
Cryptocurrency Pump-and-Dump Schemes
Tao Li, Donghwa Shin, and Baolian Wang, 2020

What is pump and dump?
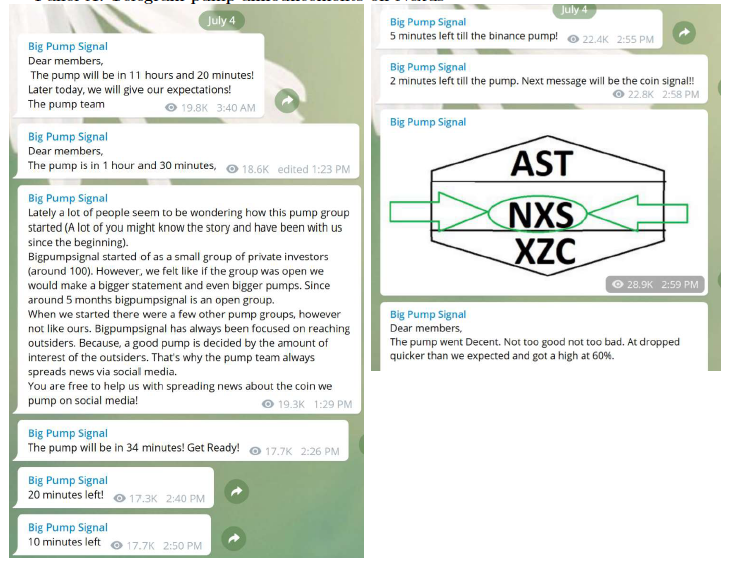
arranged via Telegram Channels
Price Manipulation: Pump & Dump
IS BITCOIN REALLY UN-TETHERED? JOHN M. GRIFFIN and AMIN SHAMS
Journal of Finance 2020
- Tether = ‘pushed’
- print an unbacked digital dollar to purchase Bitcoin.
- \(\to\) additional supply of Tether creates unwarranted inflation in Bitcoin price


vs.
- Tether = ‘pulled’
- driven by legitimate demand from investors who use Tether as a medium of exchange
- \(\to\) the price impact of Tether reflects natural market demand
Price Manipulation: Pumping Bitcoin
Price Manipulation: Pumping Bitcoin
Figure 1. Aggregate Flow of Tether between Major Addresses



August 2016




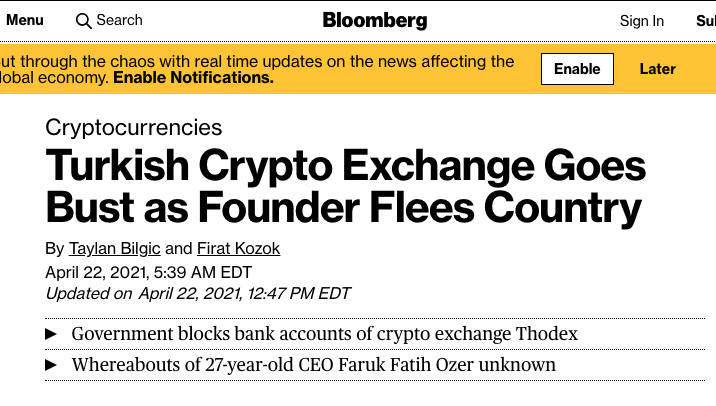
Security Risk


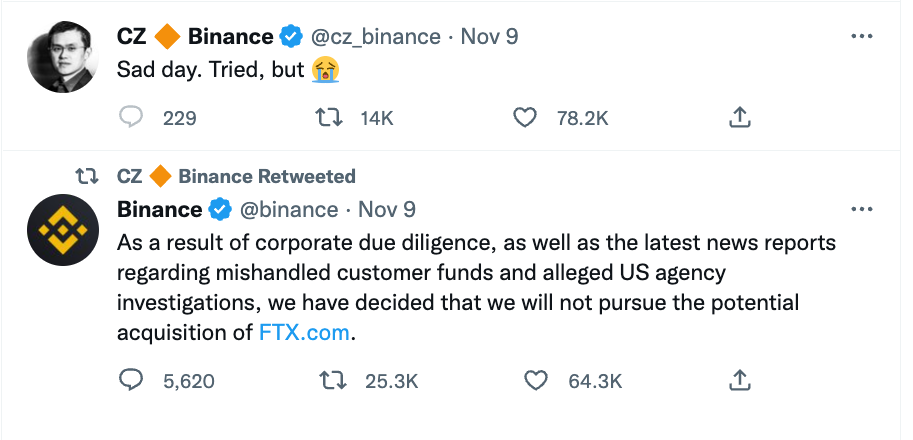
Nov 8

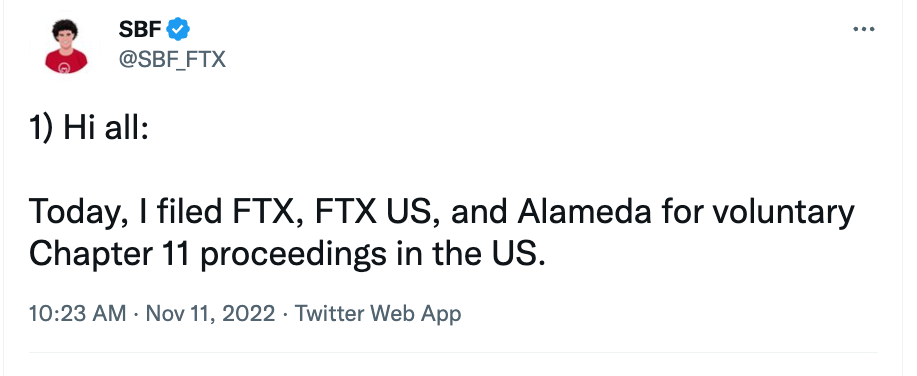
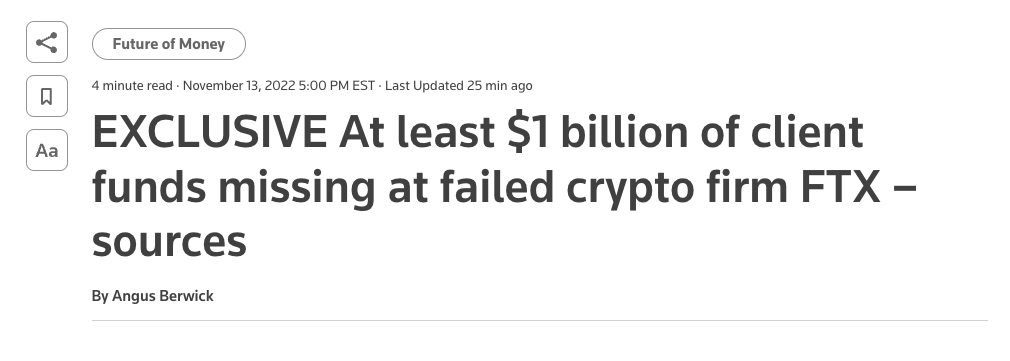

The FTX Implosion
Recurring Core problem
-
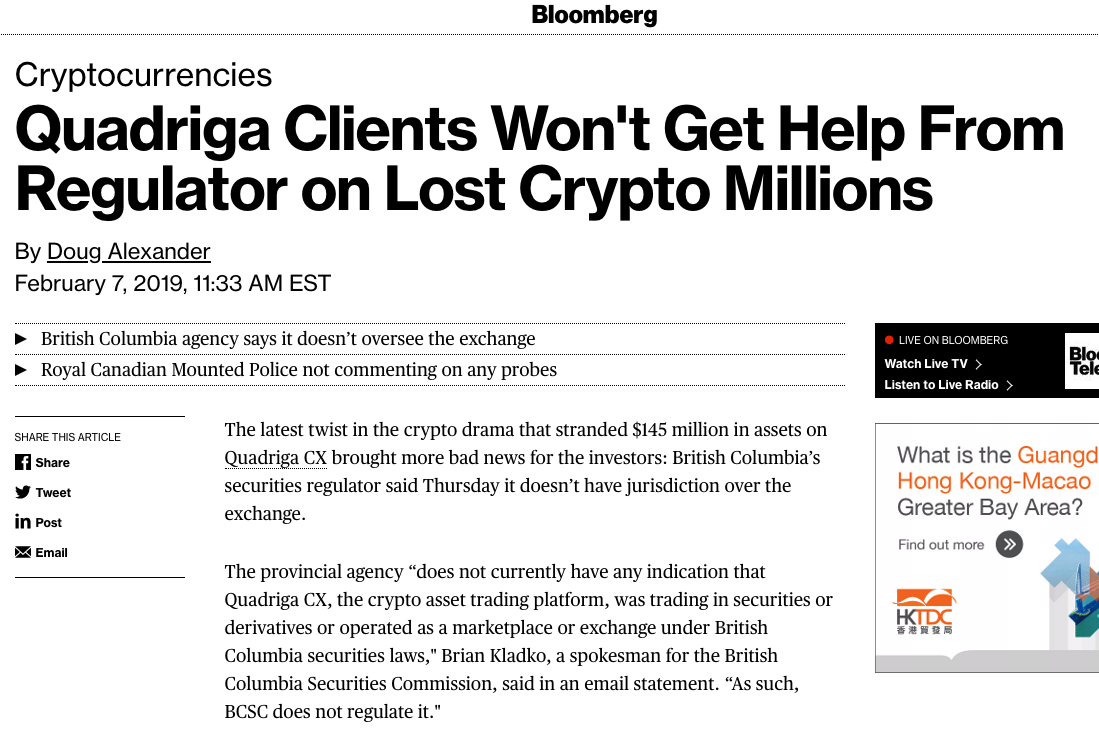
QuadrigaCX (Jan/Feb 2019) (OSC report):
- Co-founder and CEO Gerry Cotten sold people crypto he did not have
- "like a Ponzi scheme"
- => Clients collectively lost $169 million
-
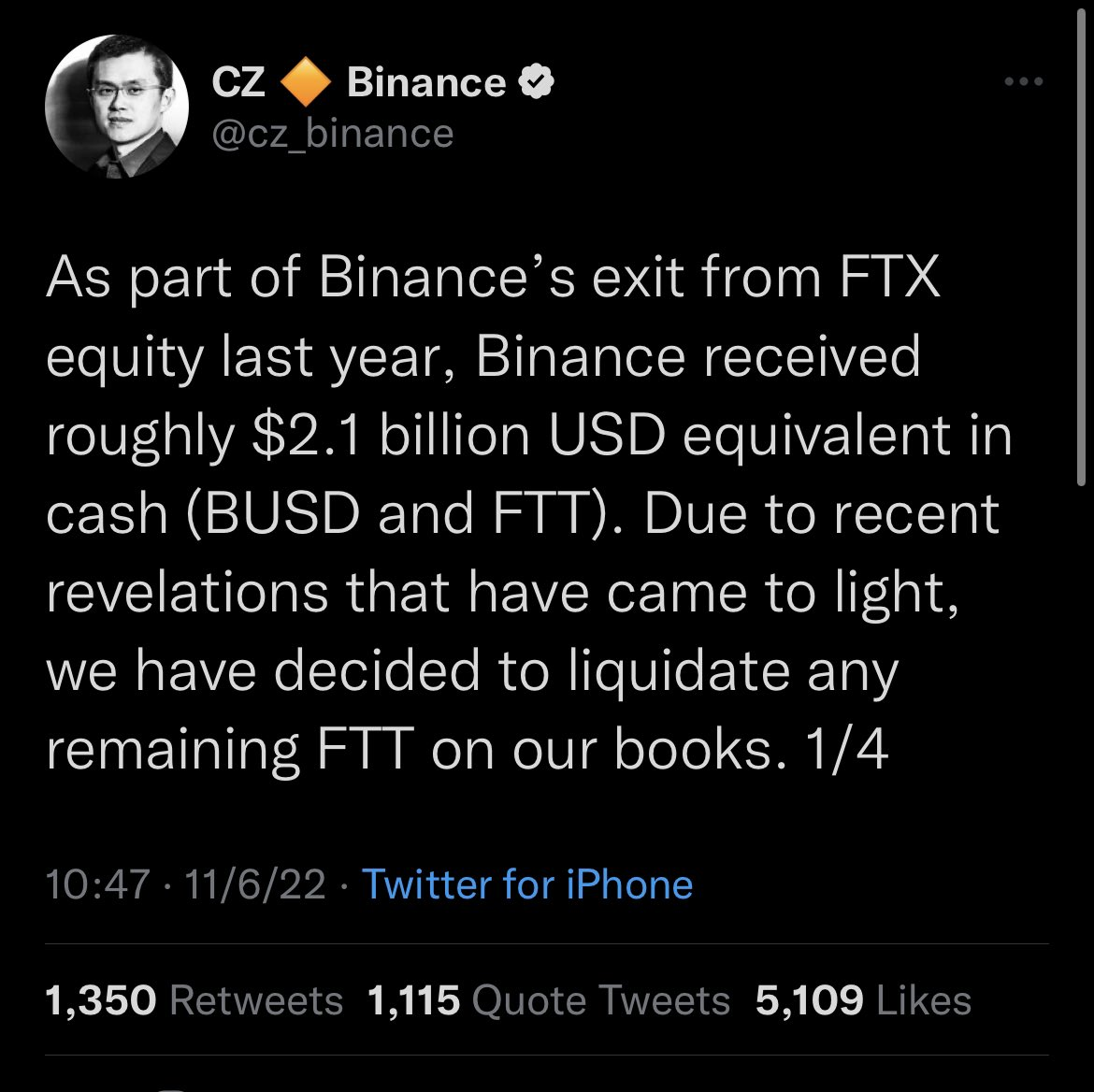
FTX (Nov 2022) (according to the CFTC allegations):
- SBF controls both FTX.com and Alameda Research
- "features in the code underlying the FTX trading platform that allowed Alameda to maintain an essentially unlimited line of credit on FTX"
- Allowed Alameda research to bypass the auto-liquidation risk-management process
- => $8 billion of customer funds siphoned via Alameda
In a regulatory vaccum re: custody
Decentralized Trading

















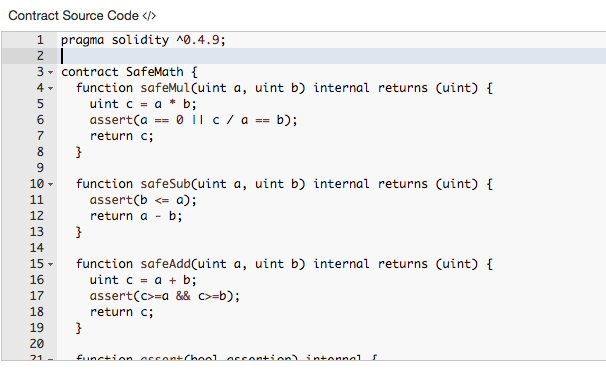
... 300 lines of code ...

First approaches: de-centralized limit order book
Turns out ...
- bad idea
- Why?
- Data-intensive, computation intensive, costly, inefficient
- re-pricing of limit orders is very costly!
Decentralized Exchanges (DEX)
Some background stats on DEcentralized Exchanges (DEX)



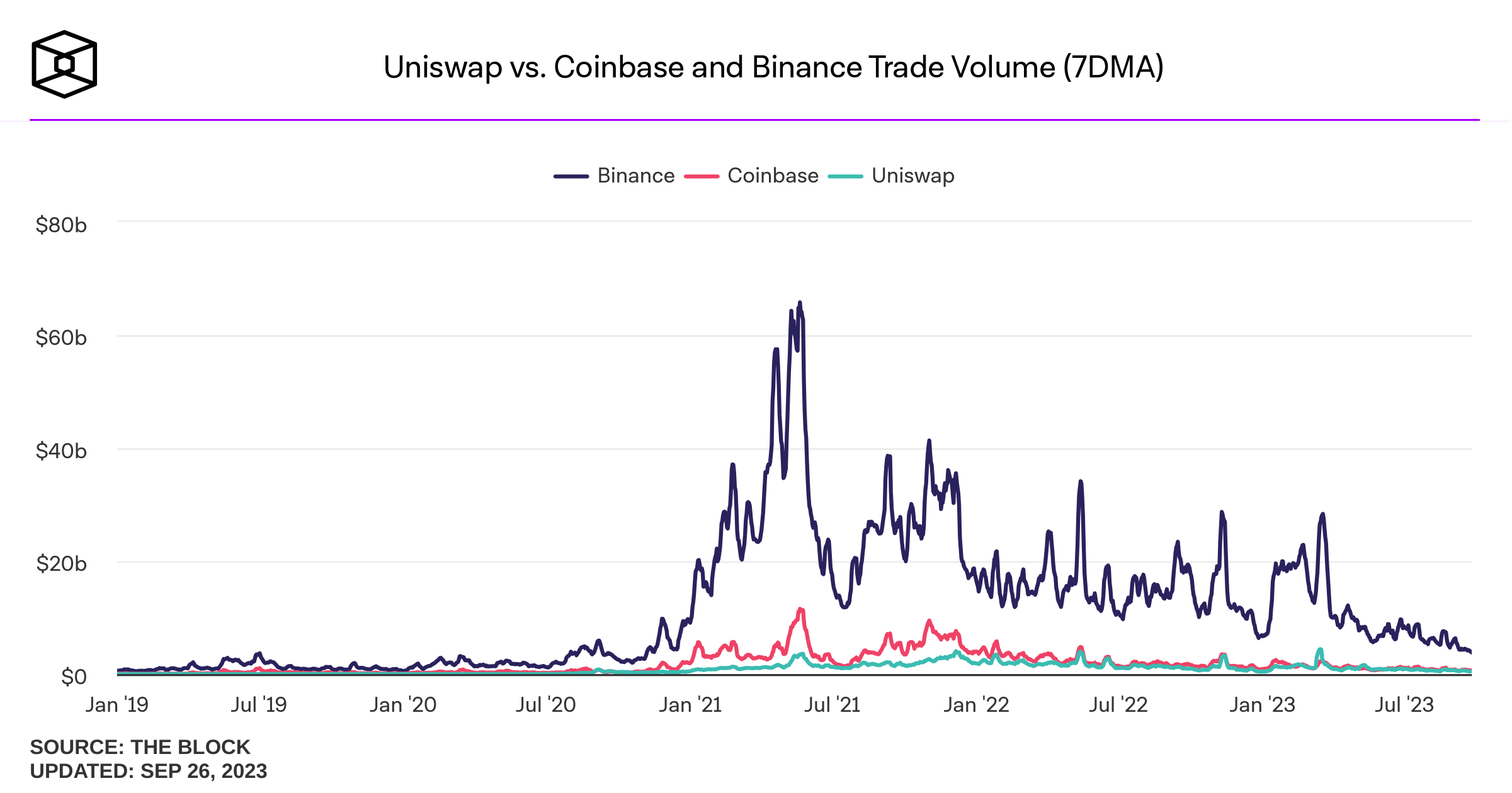
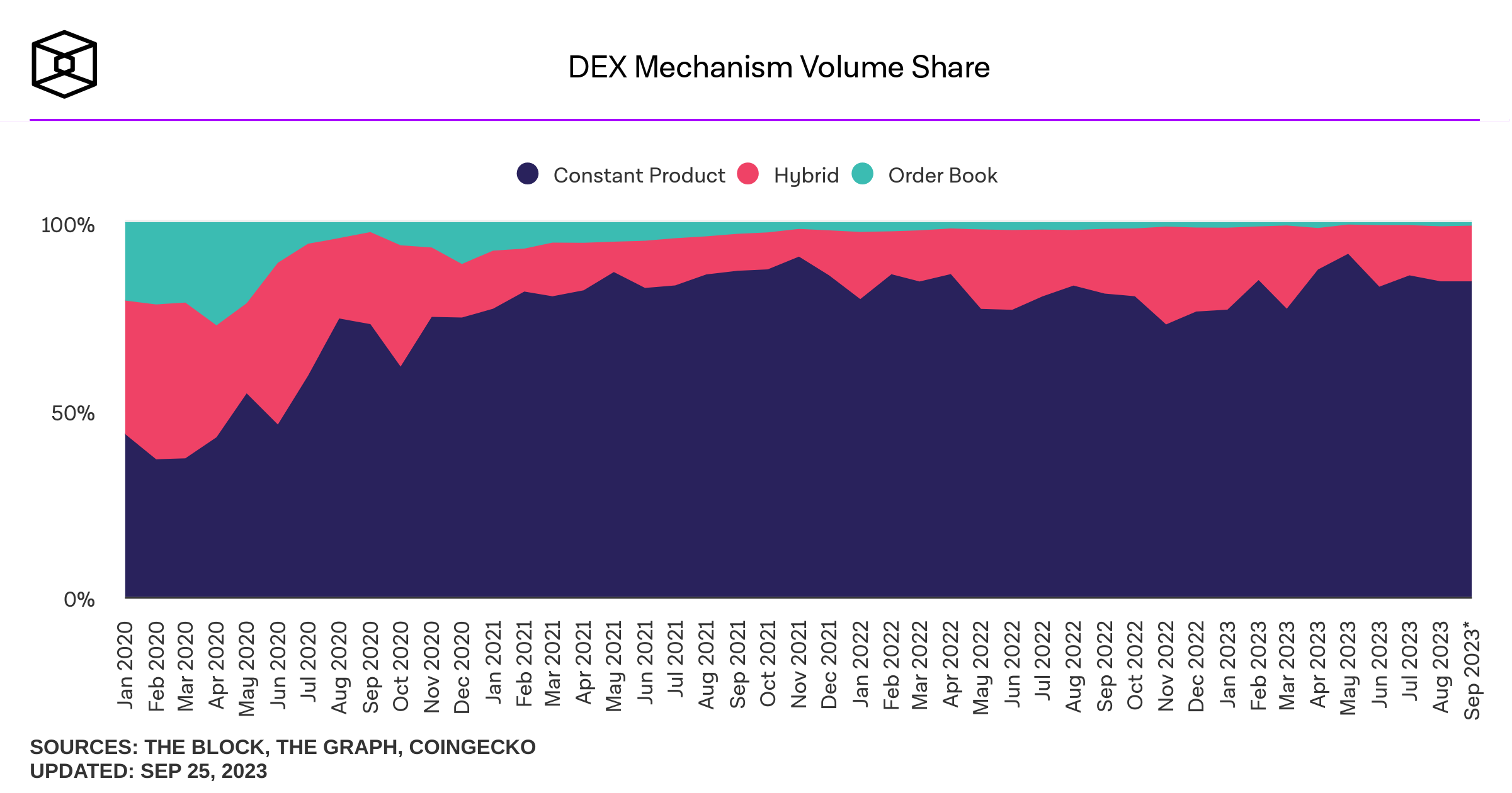
decentralized exchange
Key Components

Idea:
- create a way to exchange items on-chain
- fully decentralized
- \(\to\) no single controlling entity, or location, everything runs with smart contracts
How does it look?
automated market maker


\(\to\) simply connect with MetaMask (or similar wallet)
Application: decentralized trading with automated market makers













New institutions!
- passive "shared" liquidity provision
- new pricing function
AMM Pricing
- AMMs require liquidity deposits
- Deposits:
- \(a\) units of an asset (e.g. a stock)
- \(c\) units of cash
Key Components
- pooling of liquidity
- pro-rated (for liquidity providers)
- fee income
- risk
- Liquidity providers:
- use existing assets to earn passive income
- Liquidity demanders:
- predicatable price
- continuous trading
- ample liquidity
\(X-Q\)
\(X\)
\(Y+P(Q))\)
\(Y\)
\(c=X\cdot Y\)
automated market makers Pricing Function
- remove \(Q\) of one token
- must add \(P(Q)\) of other token
- so that liquidity stays invariant \[L(X,Y)=L(X-Q,Y+P(Q))\]
- Common rule: constant product \[X\cdot Y=(X-Q)\cdot (Y+P(Q))\]
How do you organize DEX trading?
automated market maker

Price mechanism:
- risk-neutral "invariance" pricing
- at price, contract (AMM) is indifferent between buying and selling
- \(X=\) contract balance of asset \(A\)
- \(Y=\) contract balance of asset \(B\)
- \(k=\) invariance factor
- key relation \(k=X\times\ Y\)
Prices
- when you want to sell \(x\le X\) you receive \(y\) that maintains invariance.
How do you organize DEX trading? EXAMPLE
automated market maker

invariant \(k=4\times4=16\)
Instantaneous exchange rate:


1 = 1

Contract deposit:








How do you organize DEX trading? EXAMPLE
automated market maker






sell 4 DAI for how many USDC?














1
0.5
=

How do you organize DEX trading? EXAMPLE
automated market maker

invariant \(k=100\times100=10,000\)
Contract deposit:


Problem: large "slippage" (or price impact)
"Deep liquidity" helps minimize this.
\(100\times\)
\(100\times\)
How do you organize DEX trading? EXAMPLE
automated market maker



sell 4 DAI for how many USDC?









\(100\times\)

\(100\times\)
\(3.85\times\)
\(-3.85\times\)

1
0.9625
=

How do you organize DEX trading? EXAMPLE
automated market maker

\(\to\) the more money is in the contracts, the lower the price impact
-
Increase the deposit to 10,000 DAI & USDC:
- \(k=10,000\times10,000=100,000,000\)
- \(~\to\) for \(4\) DAI you get \(10,000-100,000,000/10,004=3.998\) USDC
How do you organize DEX trading? other mechanisms
automated market maker

- anyone can become a liquidity provider when supplying both sides of a pair
- can also establish a new pair
- including creating a brand-new token \(\to\) establish a starting price!
- trades carry a fee \(\to\) paid to liquidity providers (pooled)
- liquidity providers face adverse selection and opportunity costs relative to all other assets \(\to\) fee income must be sufficient
superannoying feature
automated market maker

-
front-running
-
transactions enter mem-pool
-
\(\to\) all visible there
-
arbitrageur make instant-swap trade at higher gas price
-
\(\to\) trade instead of original trade
-
"fix" (not a proper solution): set a max slippage (a range of prices that willing to trade at)
-
Uniswap V3
-
-
Stopped here in lecture 3
DEX: Quick Recap
Decentralized trading using automated market makers (AMM)













Liquidity providers
Liquidity demander
Liquidity Pool

AMM pricing is mechanical:
- determined by the amounts of deposits
- most common:
- constant product
- #USDC \(\times\) #ETH = const
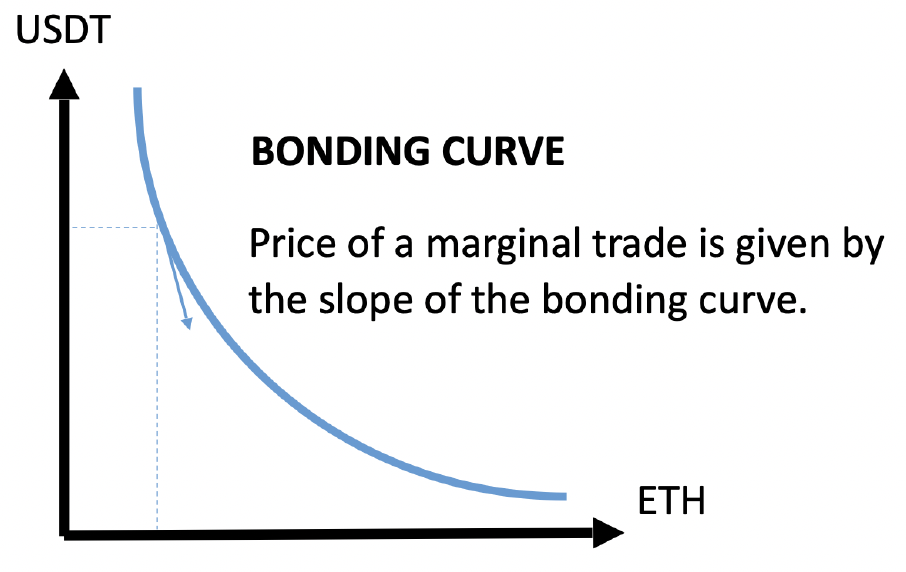
USDC
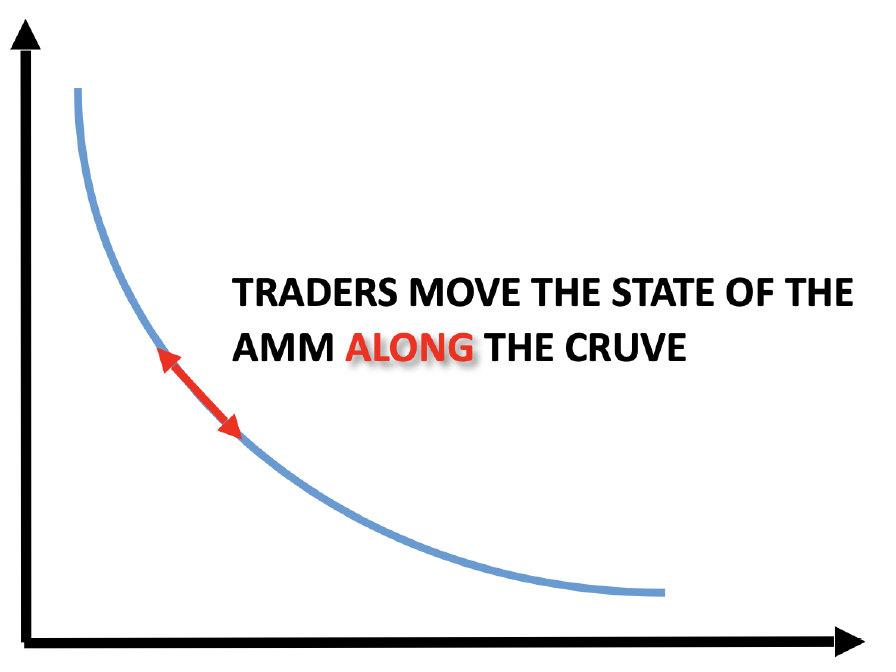
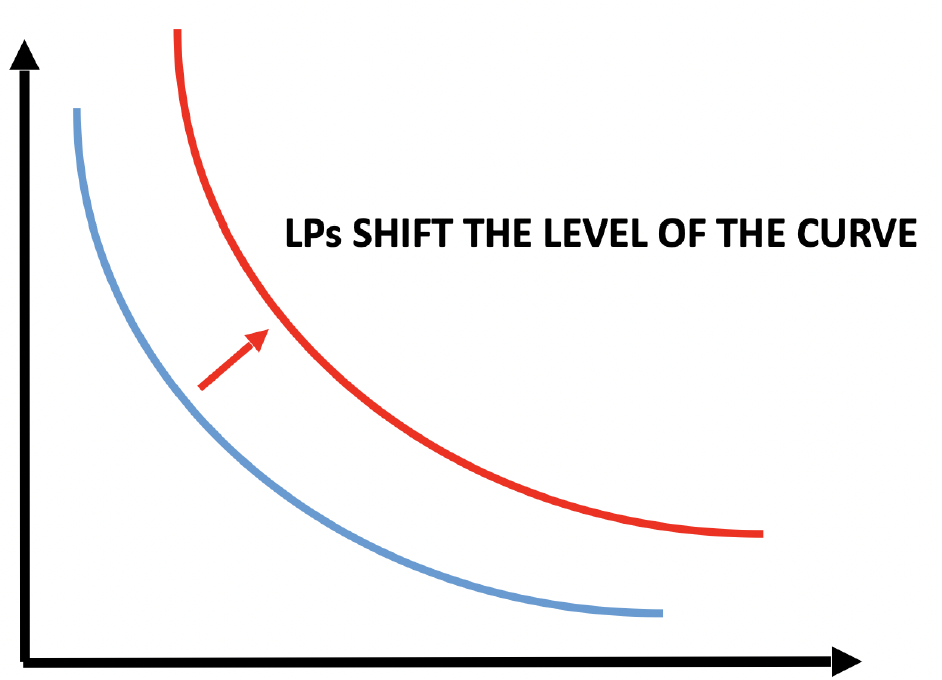
Quiz: Quick Recap
Consider a DEX (decentralized exchange) that prices securities according to the constant product rule discussed in lecture. The initial deposits in the liquidity pool are 200 ETH and 300,000 USDC. You want to buy ETH.
Note: buy ETH = sell USDC
After you buy 1 ETH in exchange for y USDC, the pool will have
- 200-1 = 199 ETH
- 300,000 + y USDC
\(\Rightarrow 200 \times 300,000= (300,000 + y) \times (200-1) \)
\(\to y = 1,508\)
Quiz: Quick Recap
After you buy 10 ETH and sell y USDC, the pool will have
- 200-10 = 190 ETH
- 300,000 + y USDC
\(\Rightarrow 200 \times 300,000= (300,000 + y) \times (200-10) \)
\(\to y = 15,789\) -- cost of 10 ETH!
\(\to 1,578.9\) per 1 ETH
Some facts about DEXes
automated market maker

- anyone can become a liquidity provider when supplying both sides of a pair
- can also establish a new pair
- including creating a brand-new token \(\to\) establish a starting price!
- trades carry a fee \(\to\) paid to liquidity providers (pooled)
- liquidity providers face adverse selection and opportunity costs relative to all other assets \(\to\) fee income must be sufficient
superannoying feature
automated market maker

-
front-running
-
transactions enter mem-pool
-
\(\to\) all visible there
-
arbitrageur make instant-swap trade at higher gas price
-
\(\to\) trade instead of original trade
-
"fix" (not a proper solution): set a max slippage (a range of prices that willing to trade at)
-
Uniswap V3
-
-
Transaction Processing in DeFi
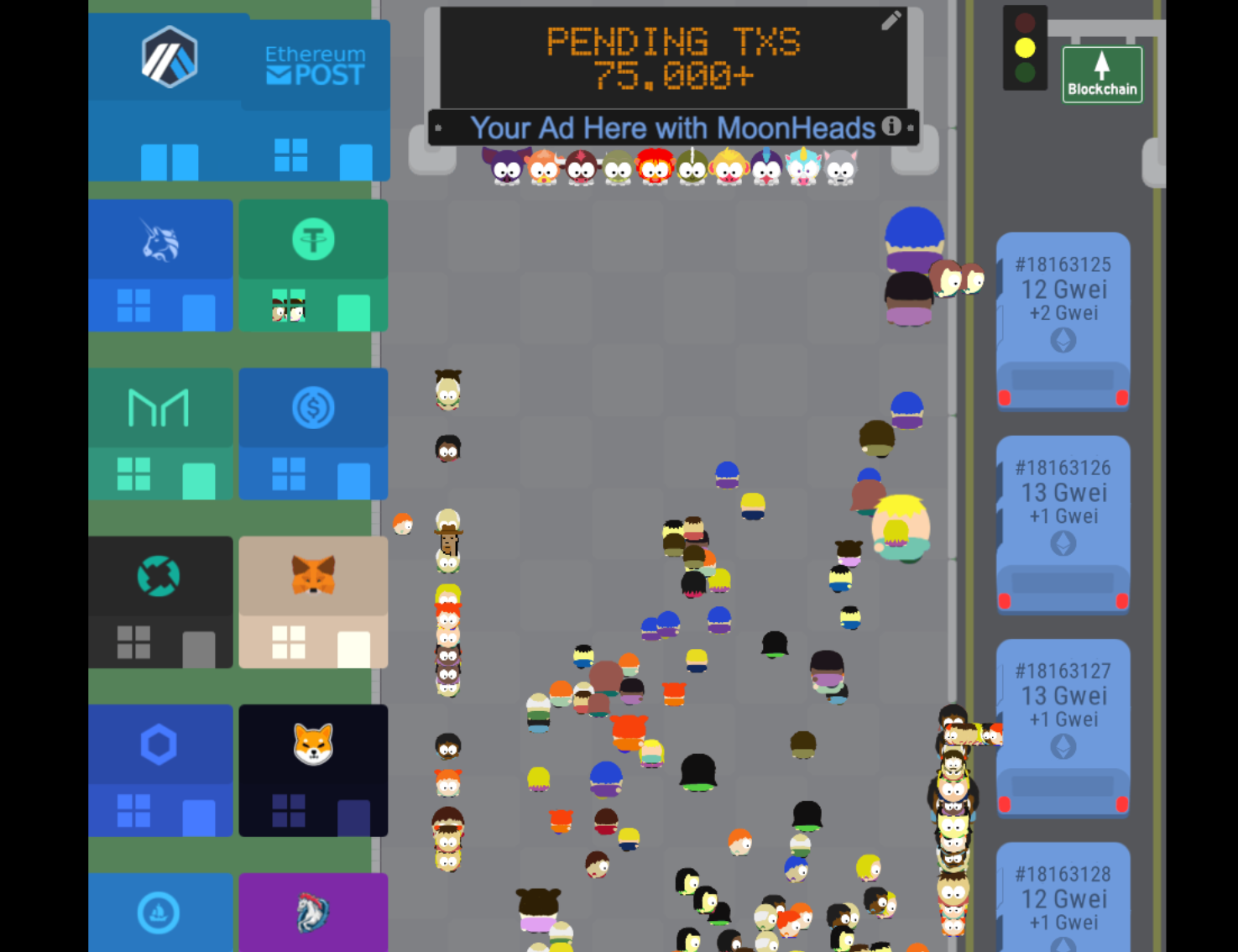
Transaction Visualization
transactions
decentralized applications
tokens
The
"Mem-Pool"

















a
b
c
d
e
f
g






A Simple Overview





































a
b
c
d
e
f
g






The reality is more complicated
Consequence 1: Extract Value from Users

"Ethereum is a Dark Forest"
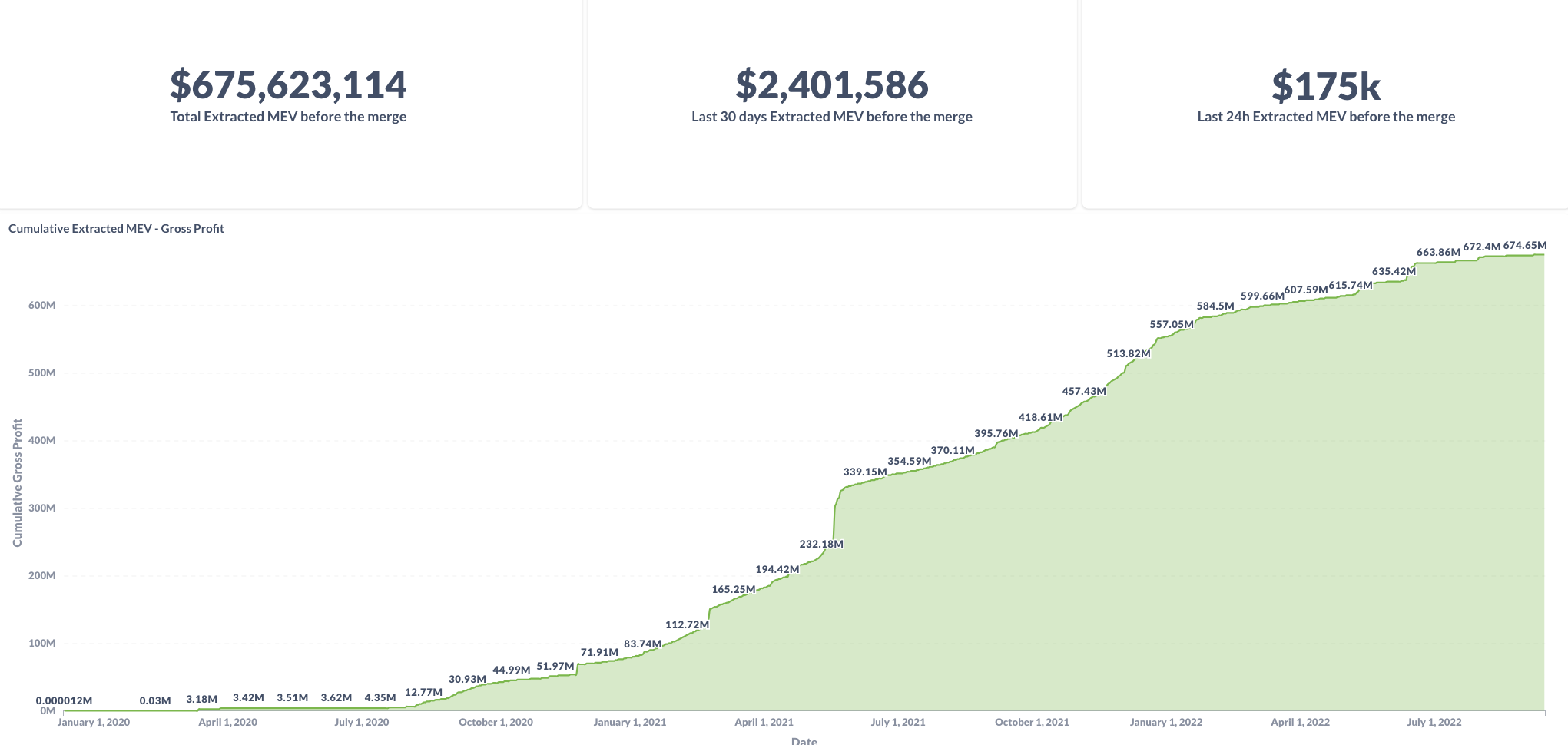
The "dark side": MEV = maximum (formally: miner) extractable value
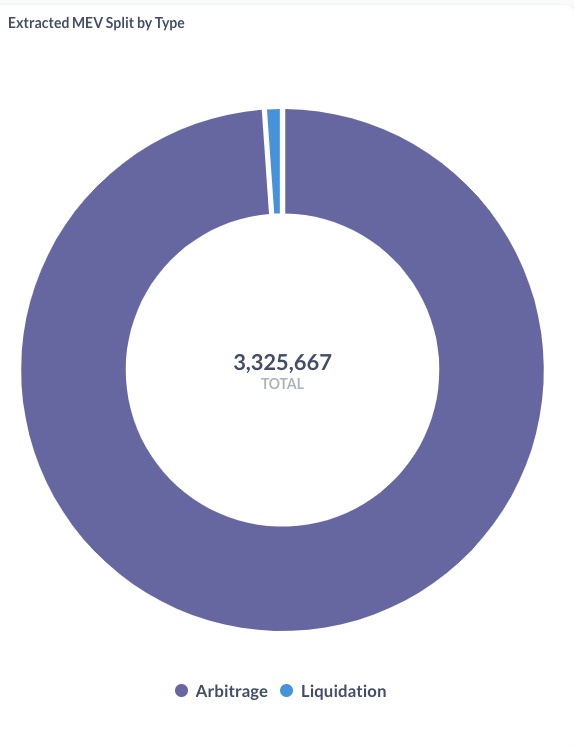
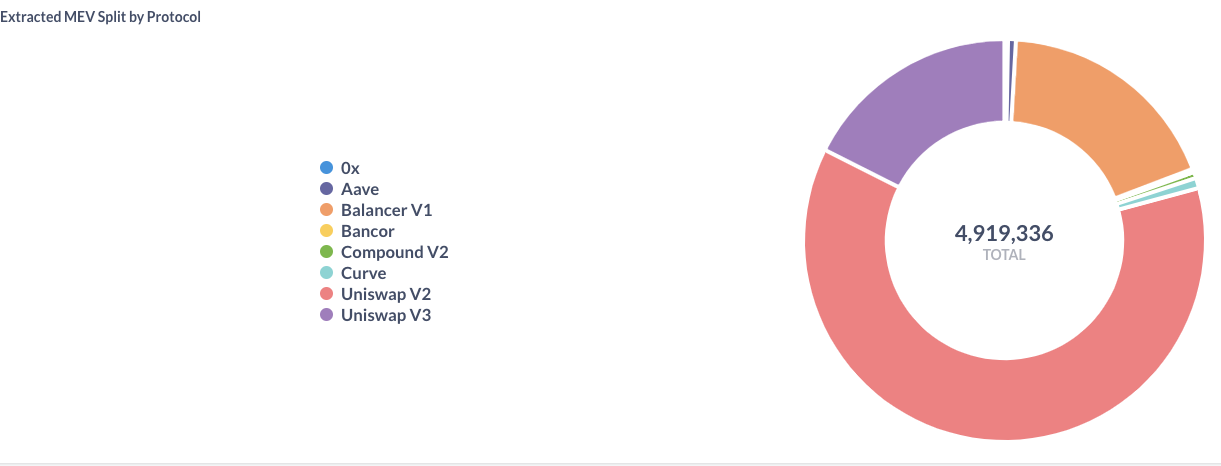
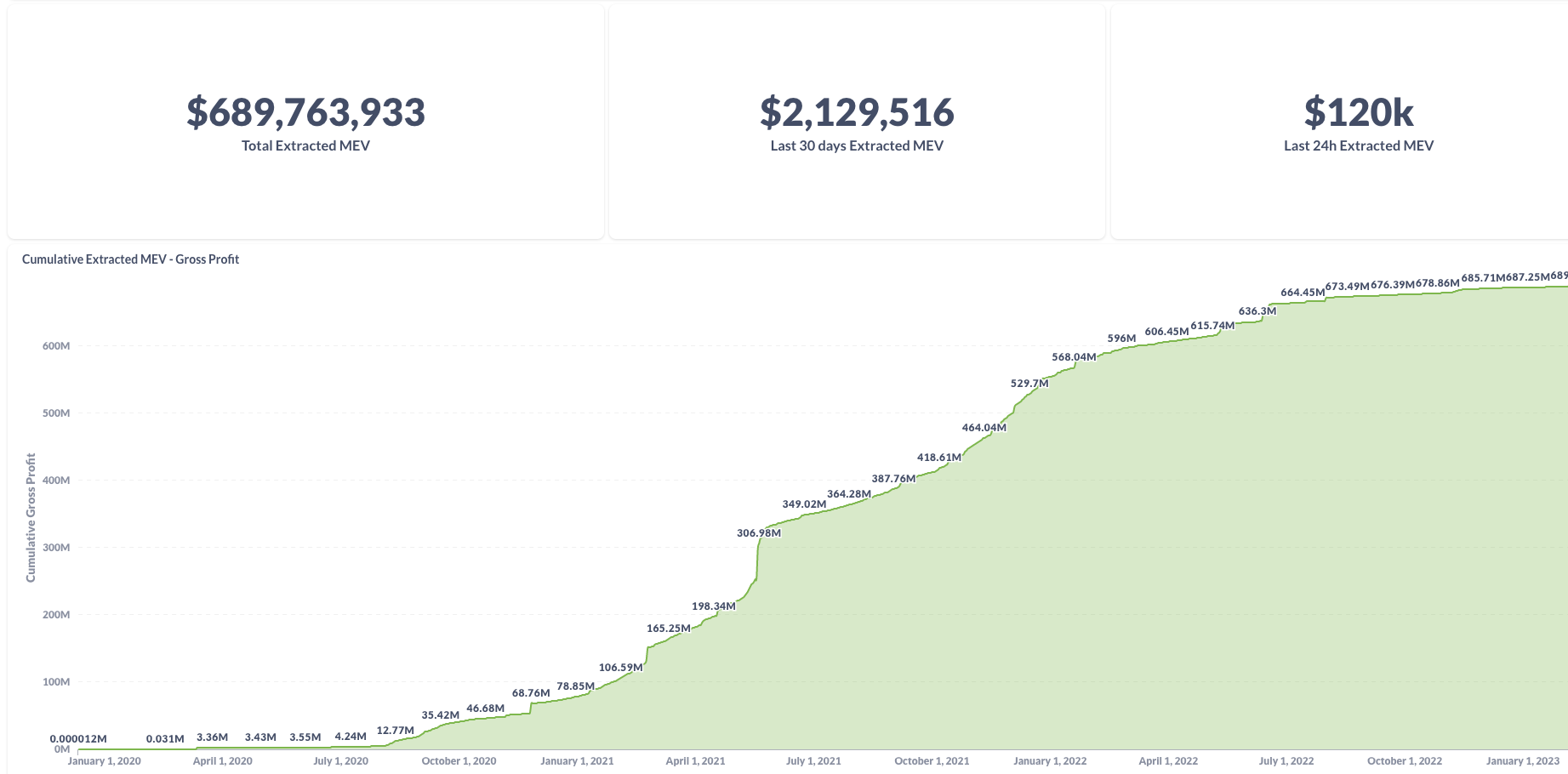
The charts are for pre-merge, see https://transparency.flashbots.net for post-merge stats
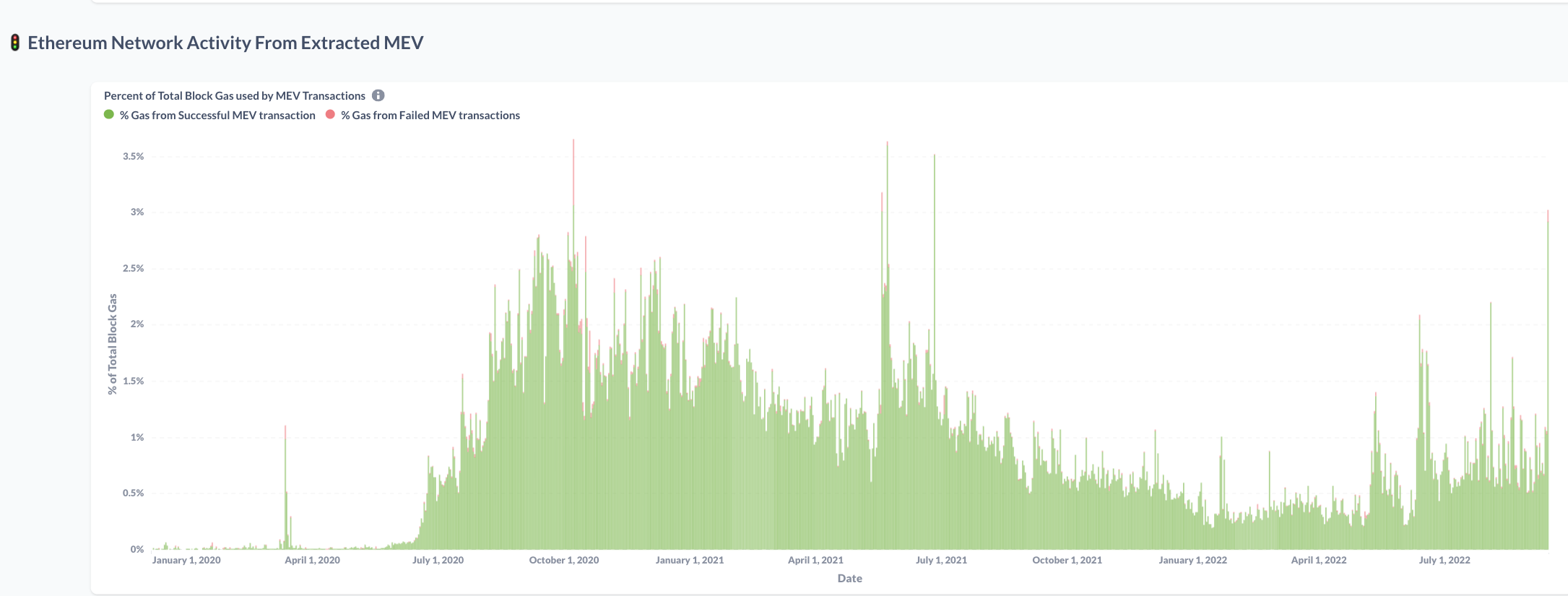
Consequence 2: Excess Gas Prices ("Priority Gas Auctions")
- may raise costs for all users without economic benefit
- wastes blockspace
- slows down processing
One resolution:
Flashbots Protocol


Idea of Flashbots
- separate user roles
- builders/seekers
- relay
- miners/validators
- eliminate public mempool
- reserve top of blockspace for privately submitted transactions
Flashbots does not prevent MEV!
- "democratize" the access
- the structure helps prevent gas auctions
@katyamalinova
malinovk@mcmaster.ca

slides.com/kmalinova
https://sites.google.com/site/katyamalinova/
Illustration
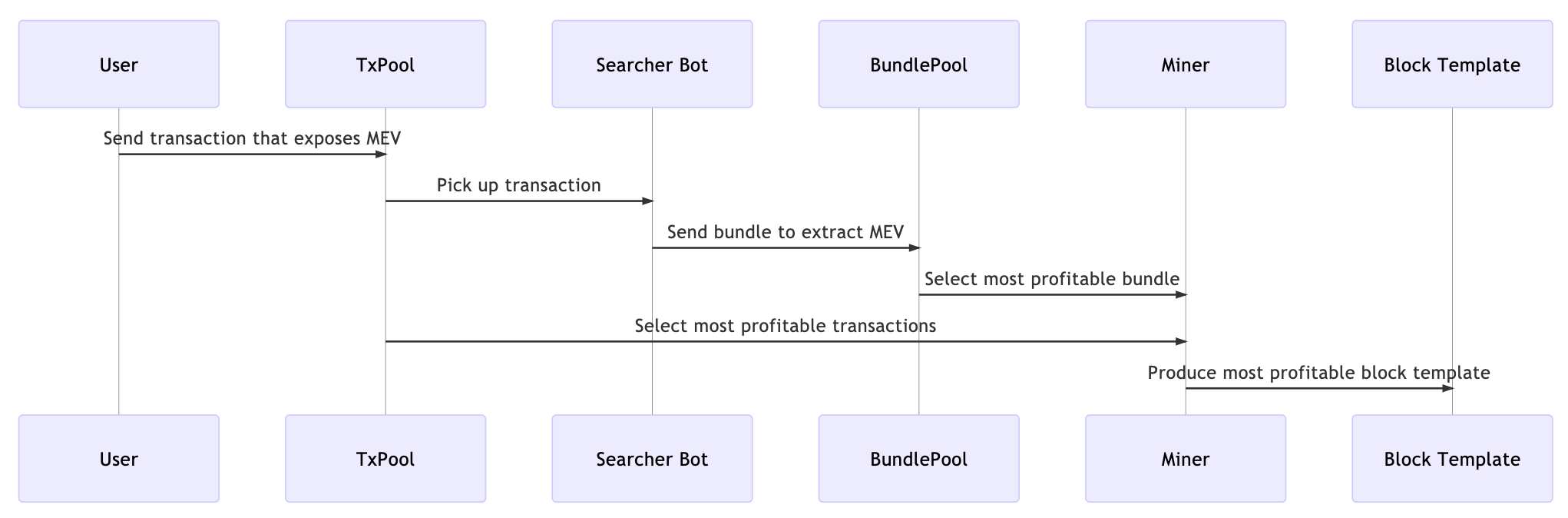
Transactions Send to Searchers
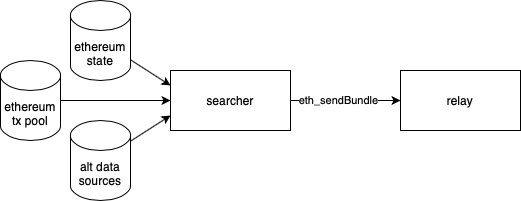
NB: the relay is a security measure: it has high capacity and can distinguish garbage from real transactions
Bundles come to Miners
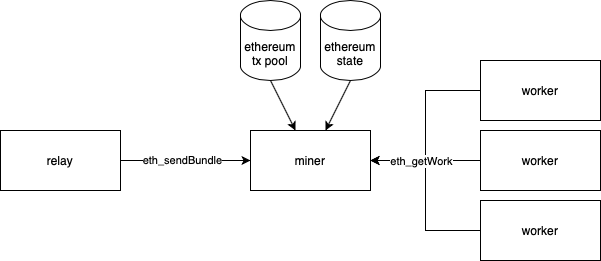
NB: miners could still manipulate, front-run etc, but Flashbots monitors them and would cut them off if they misbehave
Is it used?
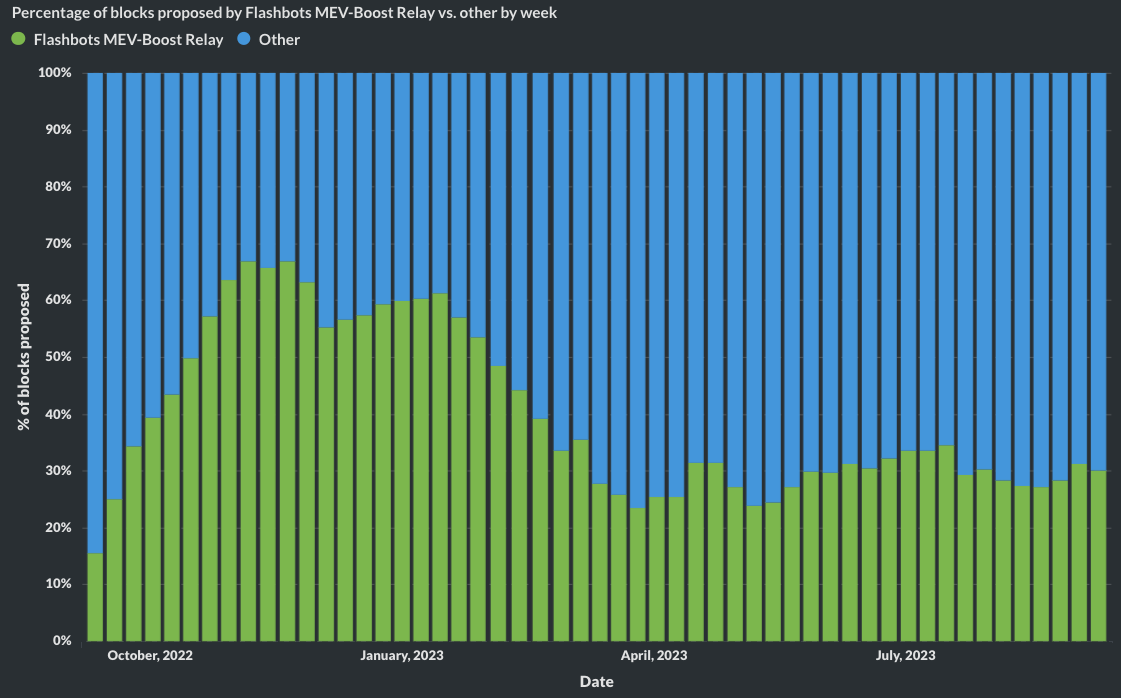
81% of validators have signed on with Flashbots (>880,000 total)
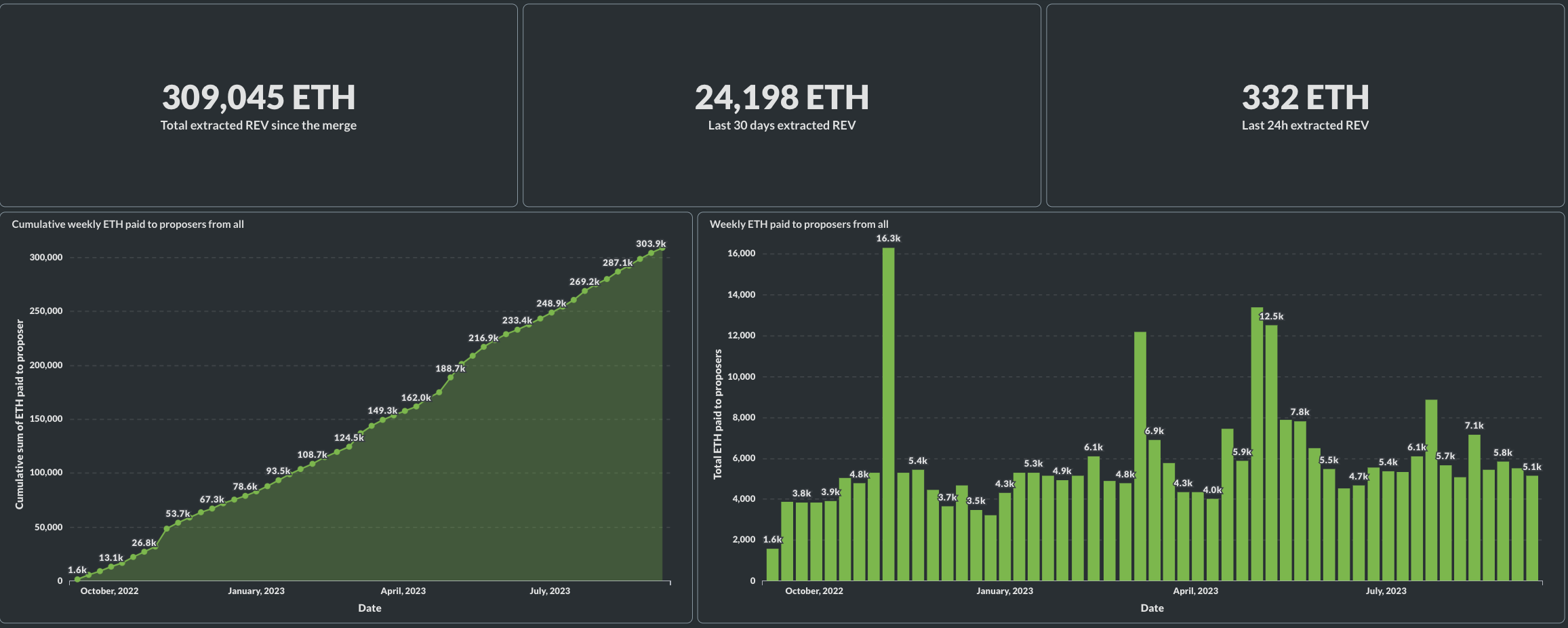
Does Flashbots Prevent MEV? No!
Does Flashbots Prevent MEV?
- Flashbots "democratizes" MEV
- prevents priority gas auctions
Flashbot 3.0 Transaction Privacy
- under development (as of 2023)
- Idea:
- submit encrypted transactions
- block building based on gas but not content
- decryption only occurs at processing
- But: very tricky problem in a trustless world