PROPERTY TESTING?
WHAT IS
property
? counter-example ?
something always true
λ> quickCheck $ \(x :: Integer) -> x === 1
*** Failed! Falsified (after 1 test):
x: 0
0 /= 1λ> quickCheck $ \(xs :: [Char]) -> length xs === 0
*** Failed! Falsified (after 3 tests and 2 shrinks):
xs: "a"
1 /= 0λ> quickCheck $ \(x :: Integer) (y :: Integer) -> x /= 0 ==> y+x =/= y*x
+++ OK, passed 100 tests; 12 discarded.λ> quickCheck $ \(x :: Integer) (y :: Integer) -> x /= 0 ==> y+x =/= y*x
*** Failed! Falsified (after 3 tests):
x: 2
y: 2
4 == 4sort :: [x] -> [x]
!
assert (sort [] == [])
assert (sort [2,1] == [1,2])
assert (sort [1,2,1] == [1,1,2])Generating
Labelling
Simplifying
Generating...
(random) data from composable primitives.
Simplifying...
complex data structures down to "minimal" counter-examples.
Labelling...
properties to measure coverage and efficiency.
GREAT TEST RUNNER
HOW TO
FIND PROPERTIES
Idempotence
Oracles
?
Labyrinth
Roundtrips
SMART
CONTRACTS
state 0
state 1
state 2



validator
redeemer
O.K.
K.O.

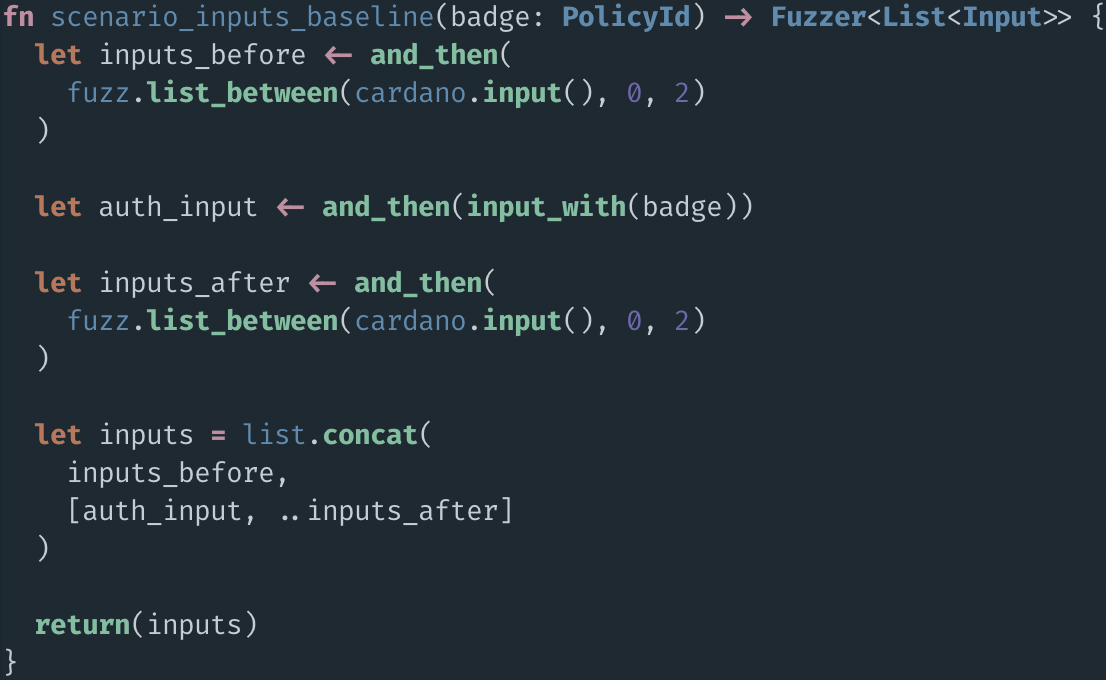
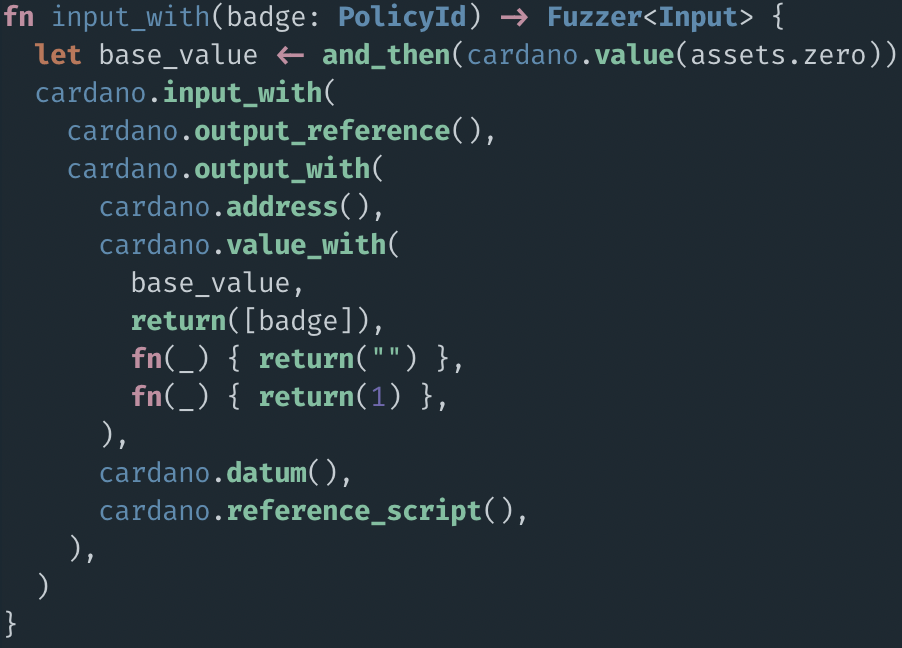
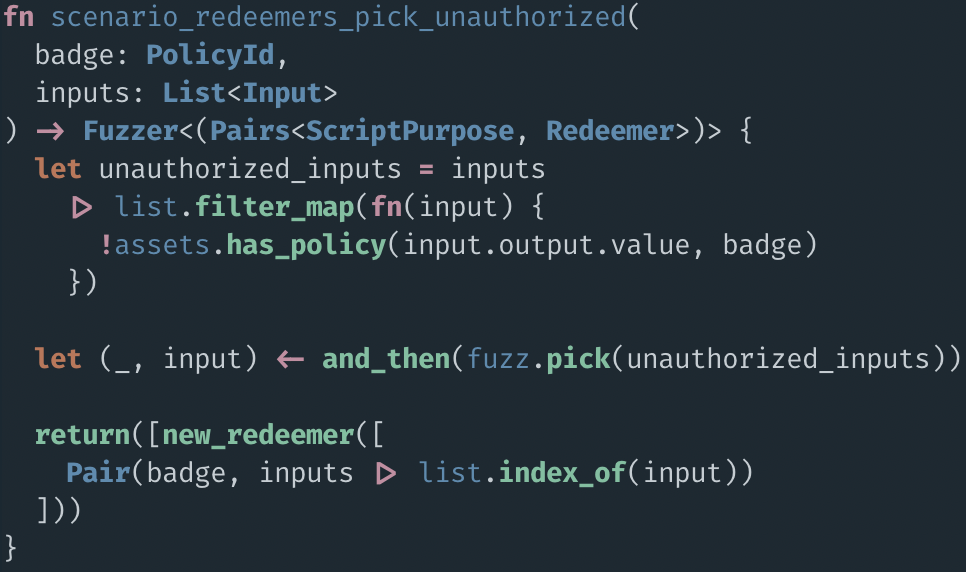
Example: Authentication Badges



$A, $B, ...
main redeemer
42 ₳, 1 $A
14 ₳, 1M $HOSKY, 1 $B


CHAOS
ENGINEERING
Chaos engineering is the discipline of experimenting on a system in order to build confidence in the system's capability to withstand turbulent conditions in production.
inputs
reference inputs
redeemers
witnesses
transaction

??
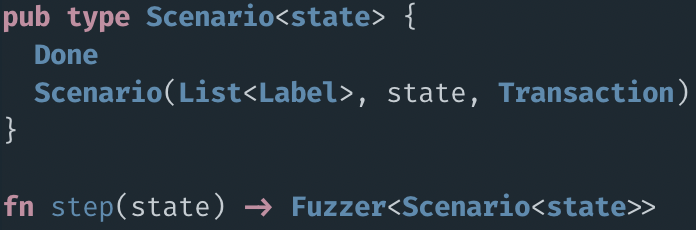
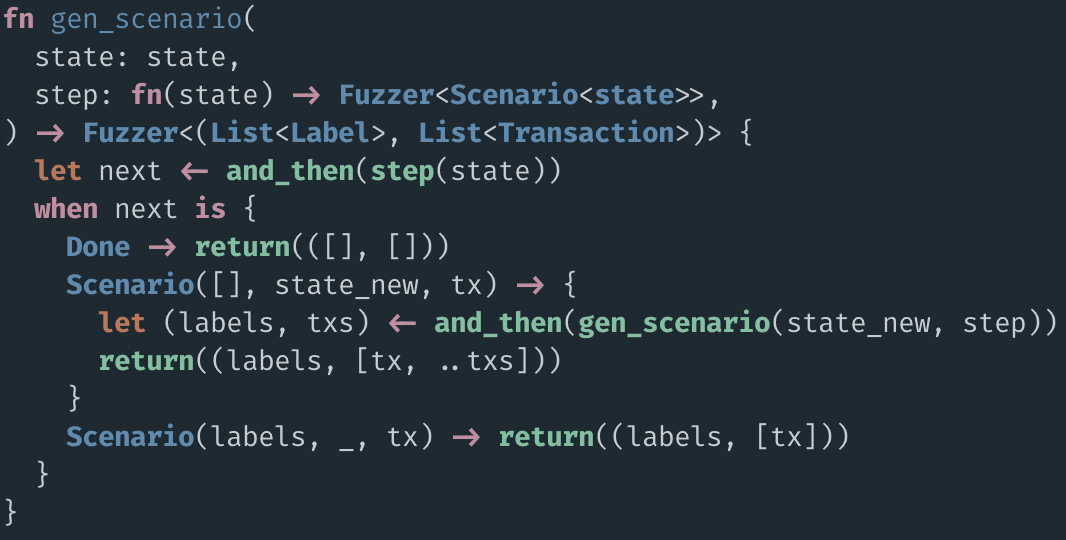
Bespoke to the contract
Allow for building
sequences of transactions
Classify failures

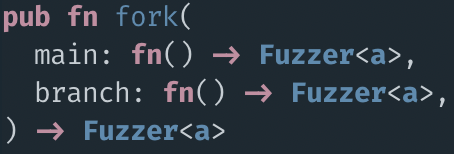
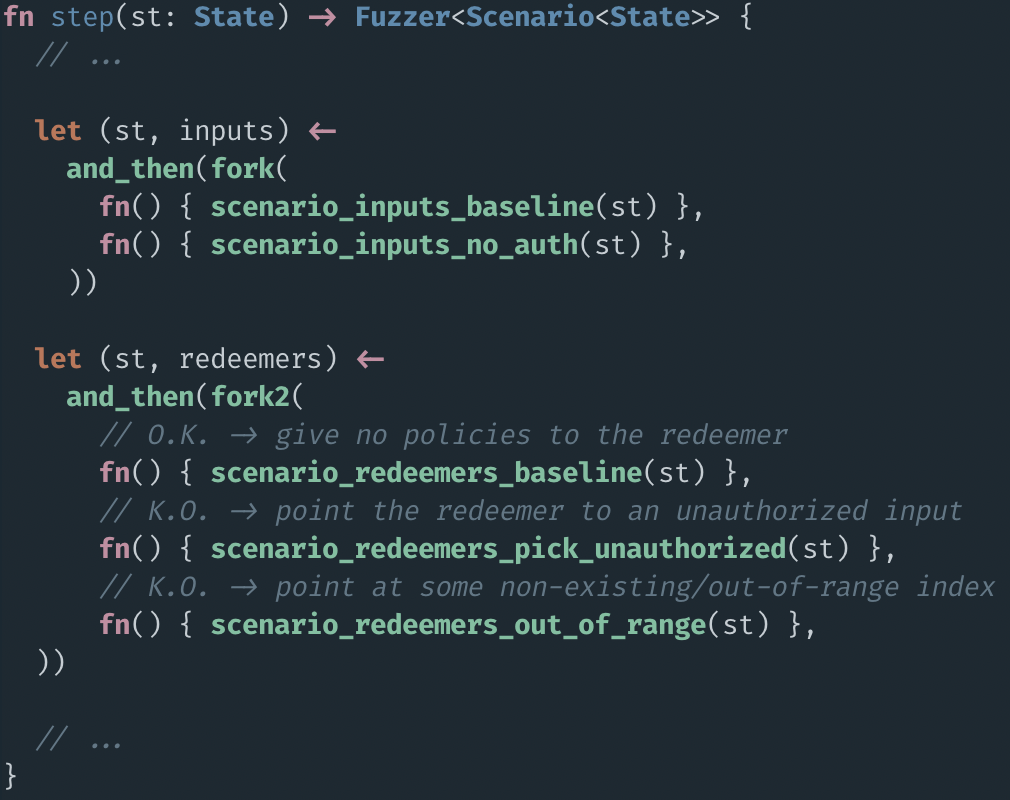
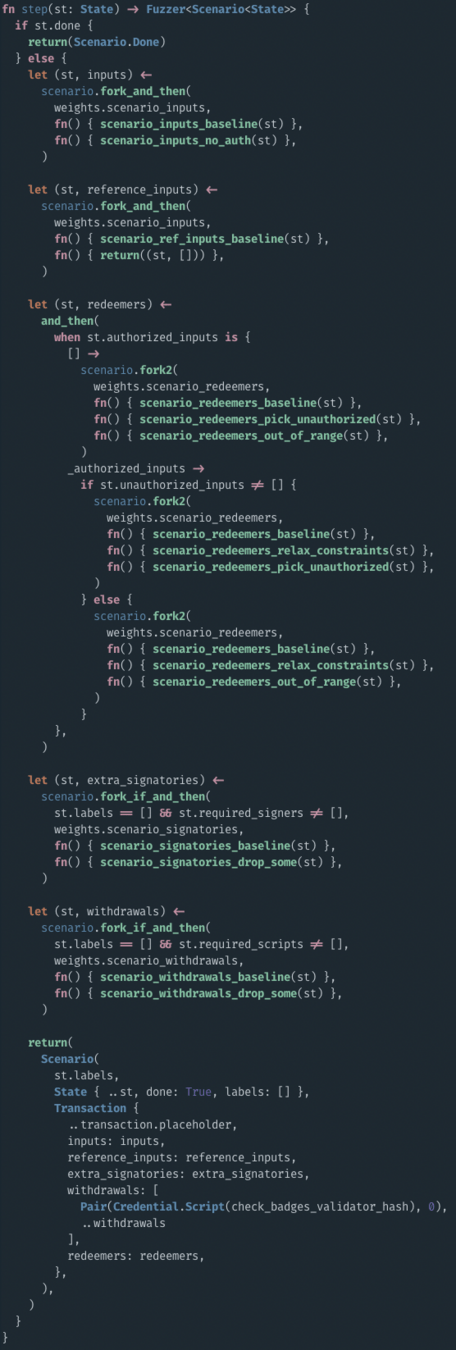

validator logic

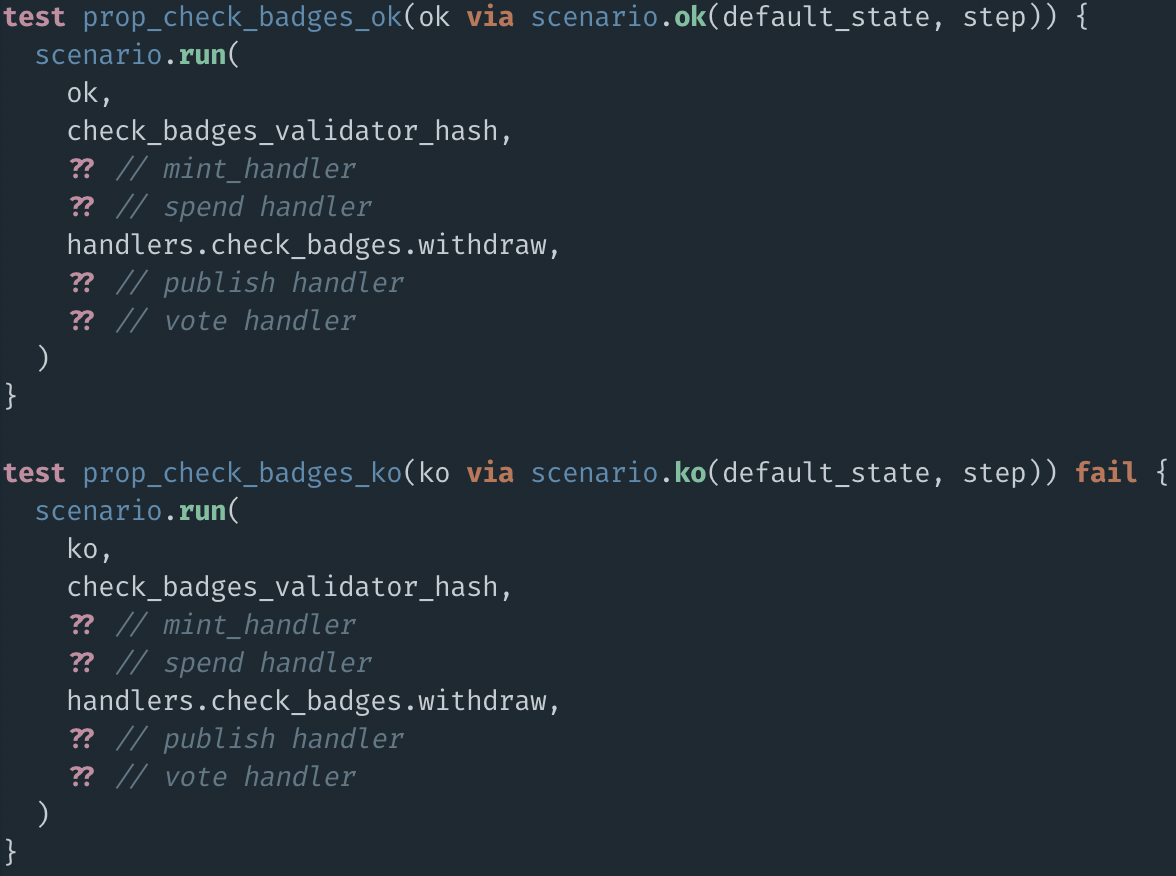
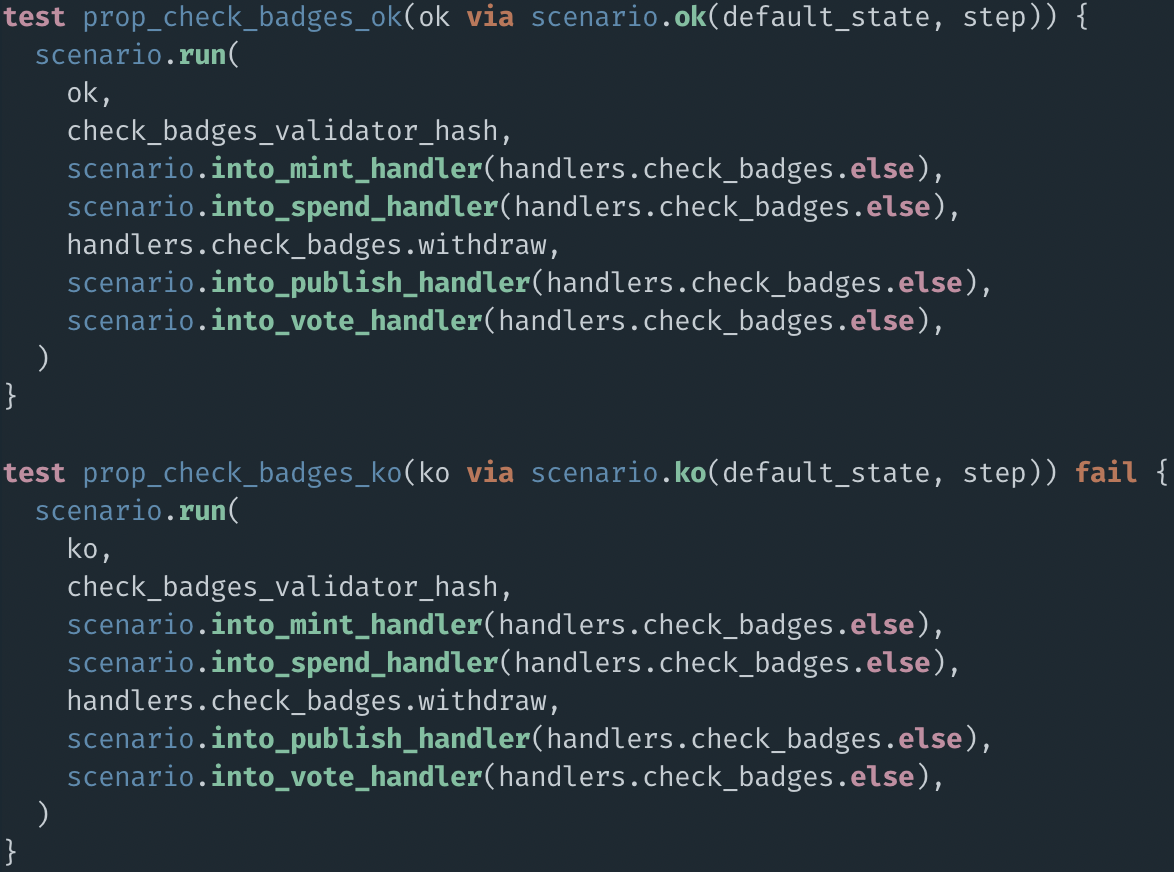
FIRST BUG
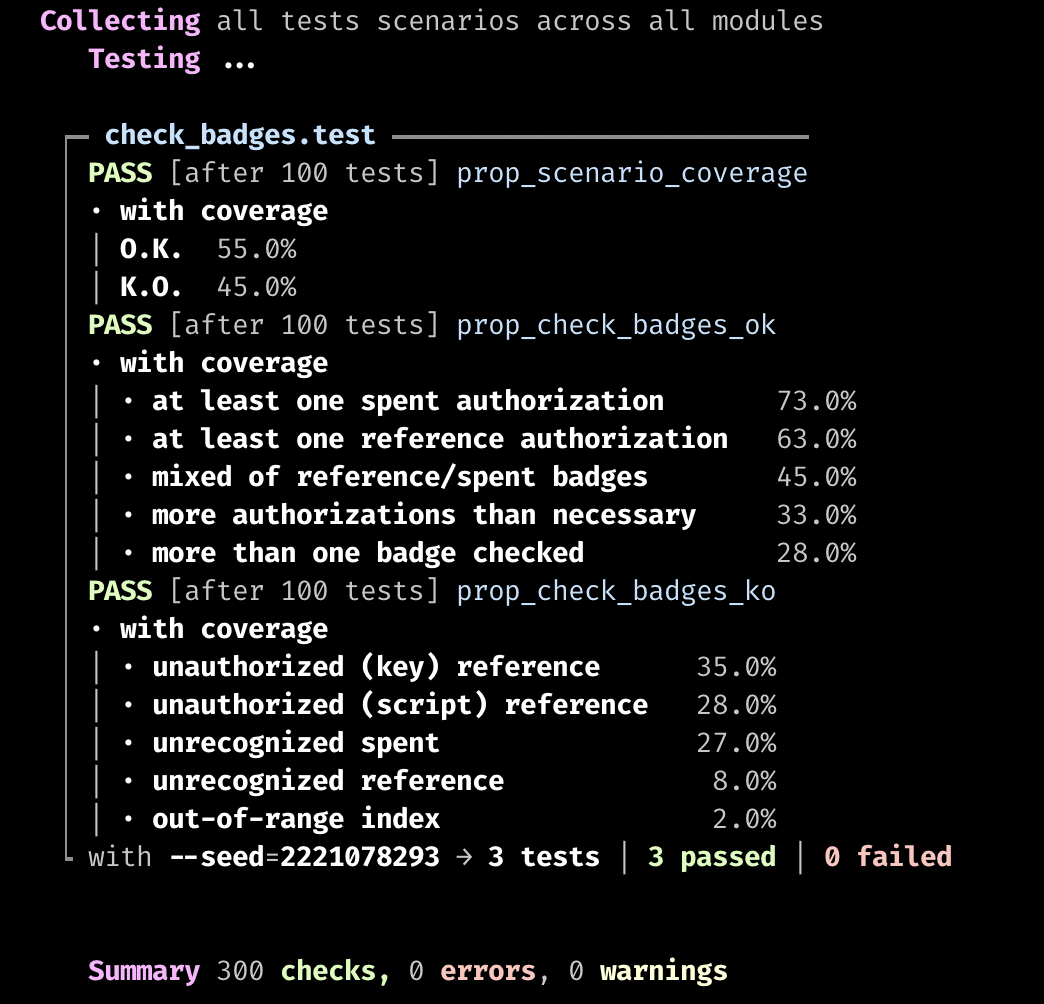
prop_check_badges_ok

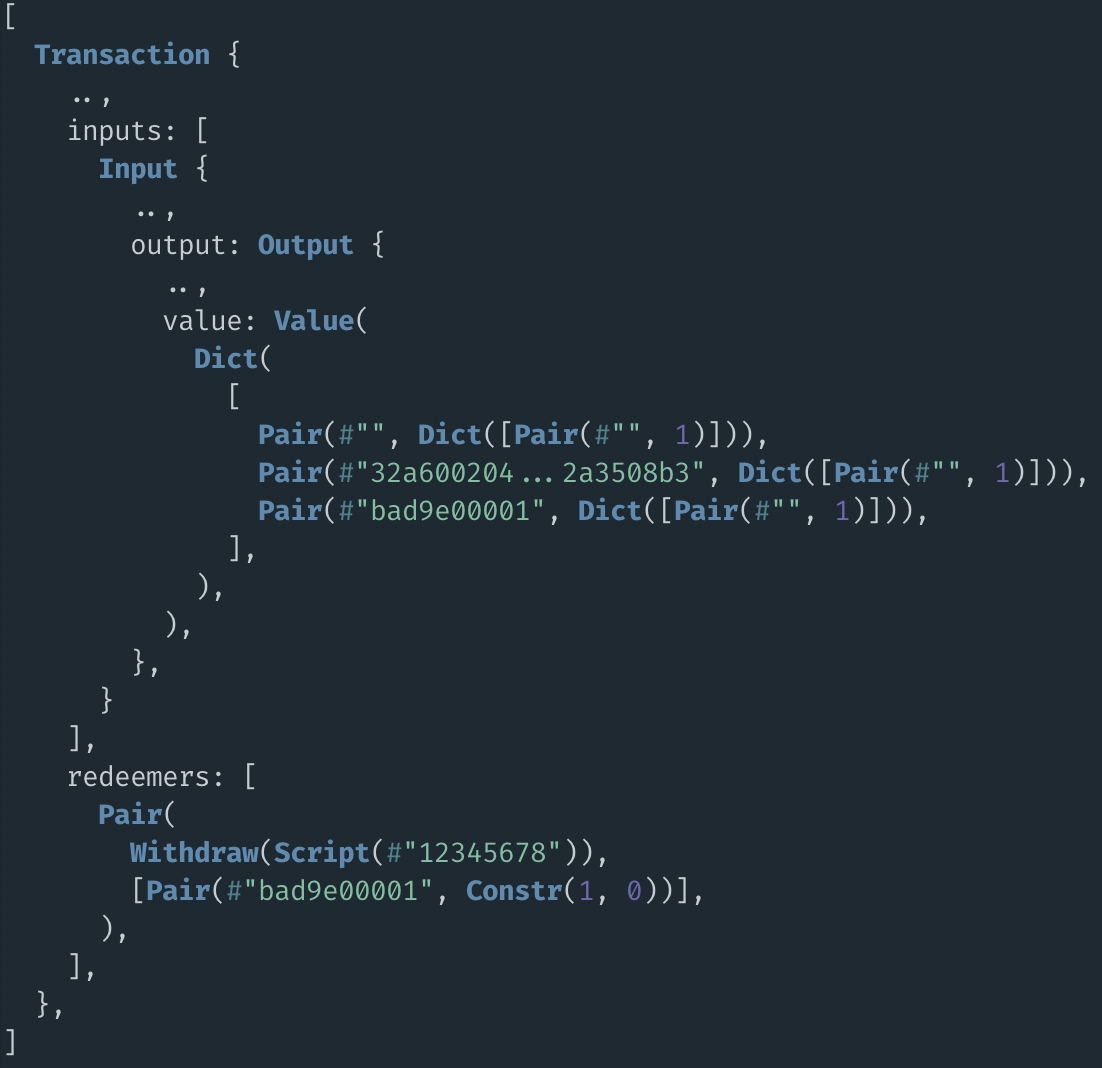
_ada
badge
..
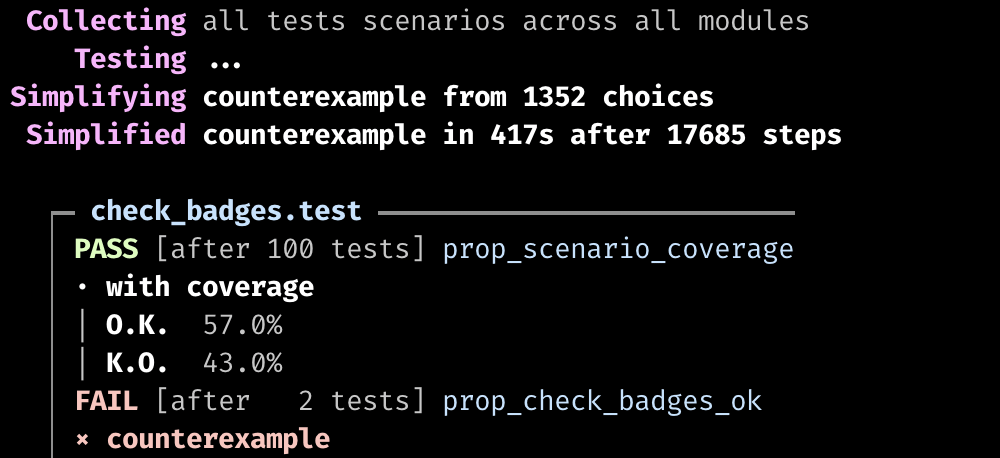


counterexample

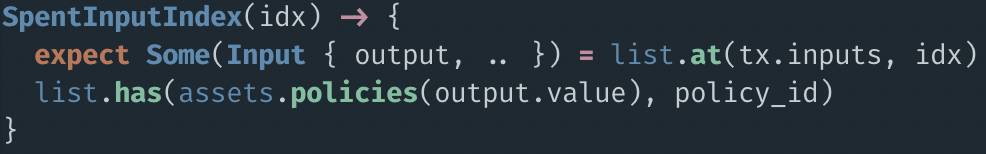
SECOND BUG
prop_check_badges_ko
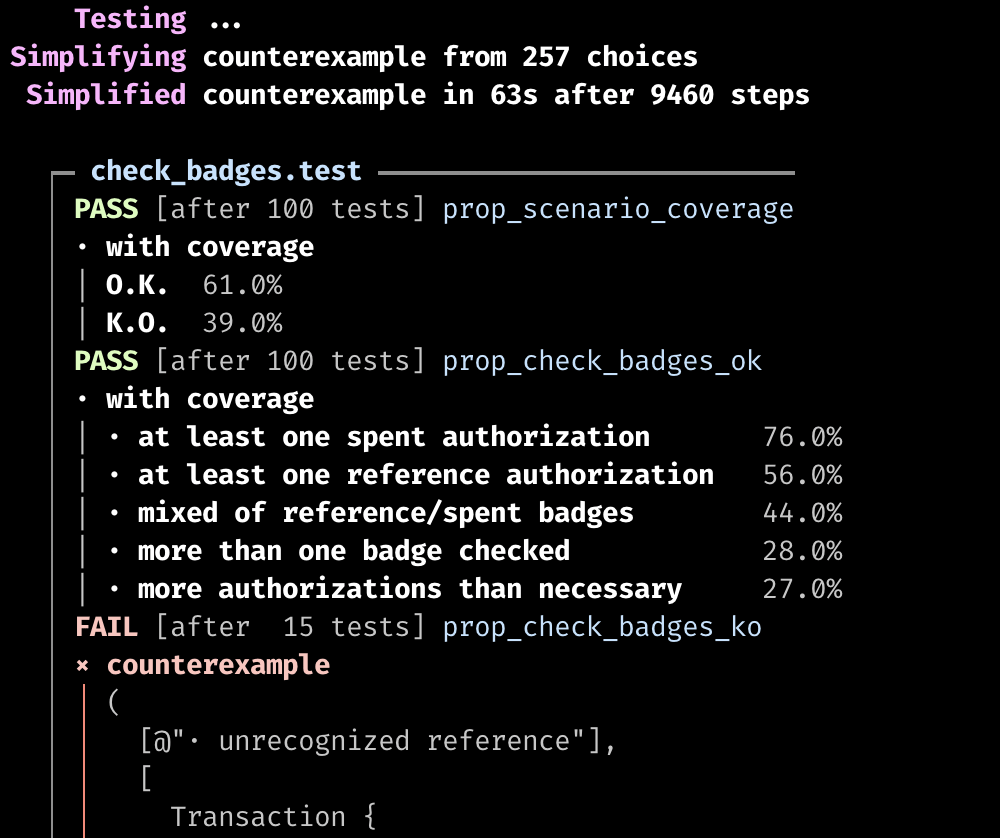


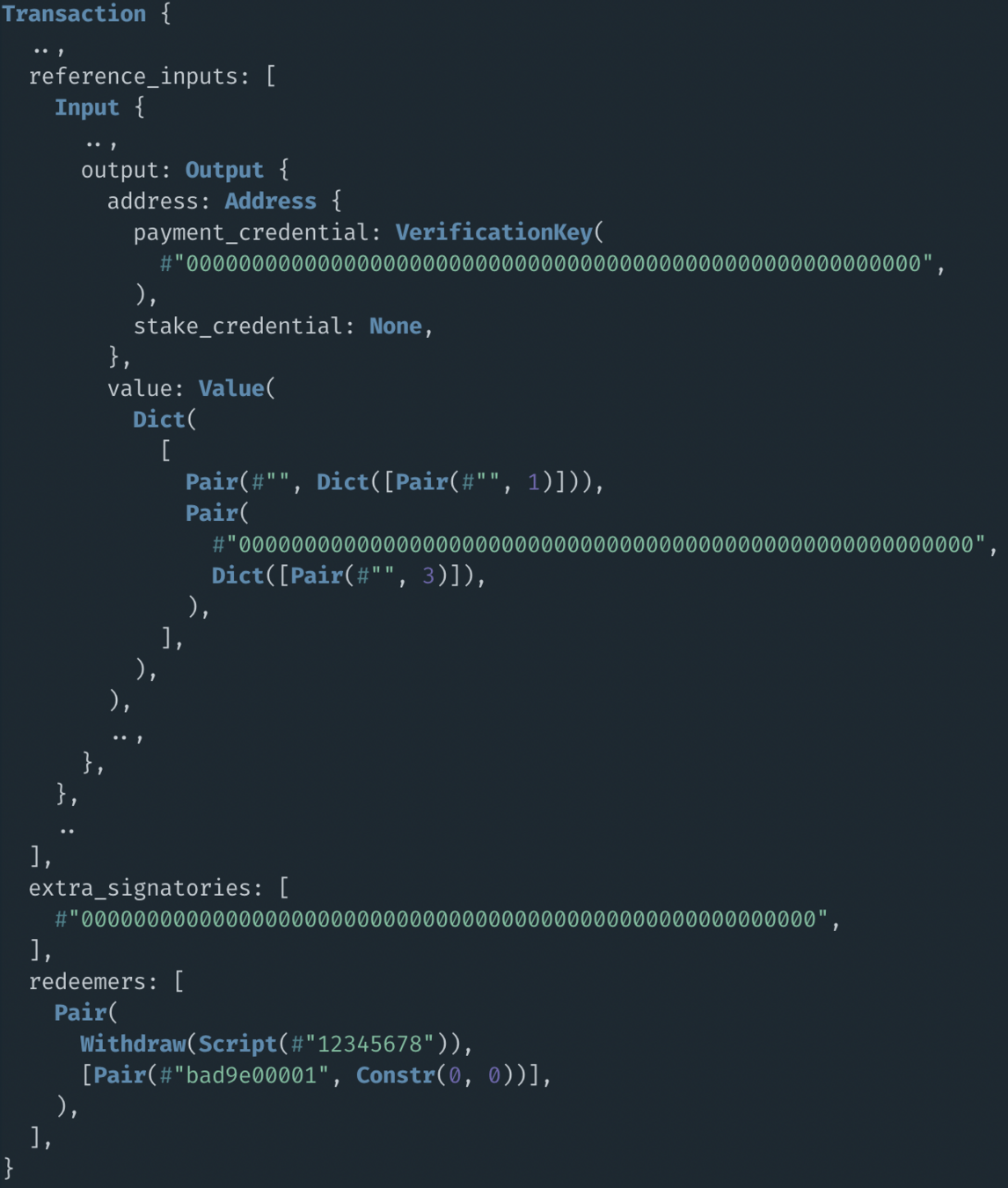
badge??



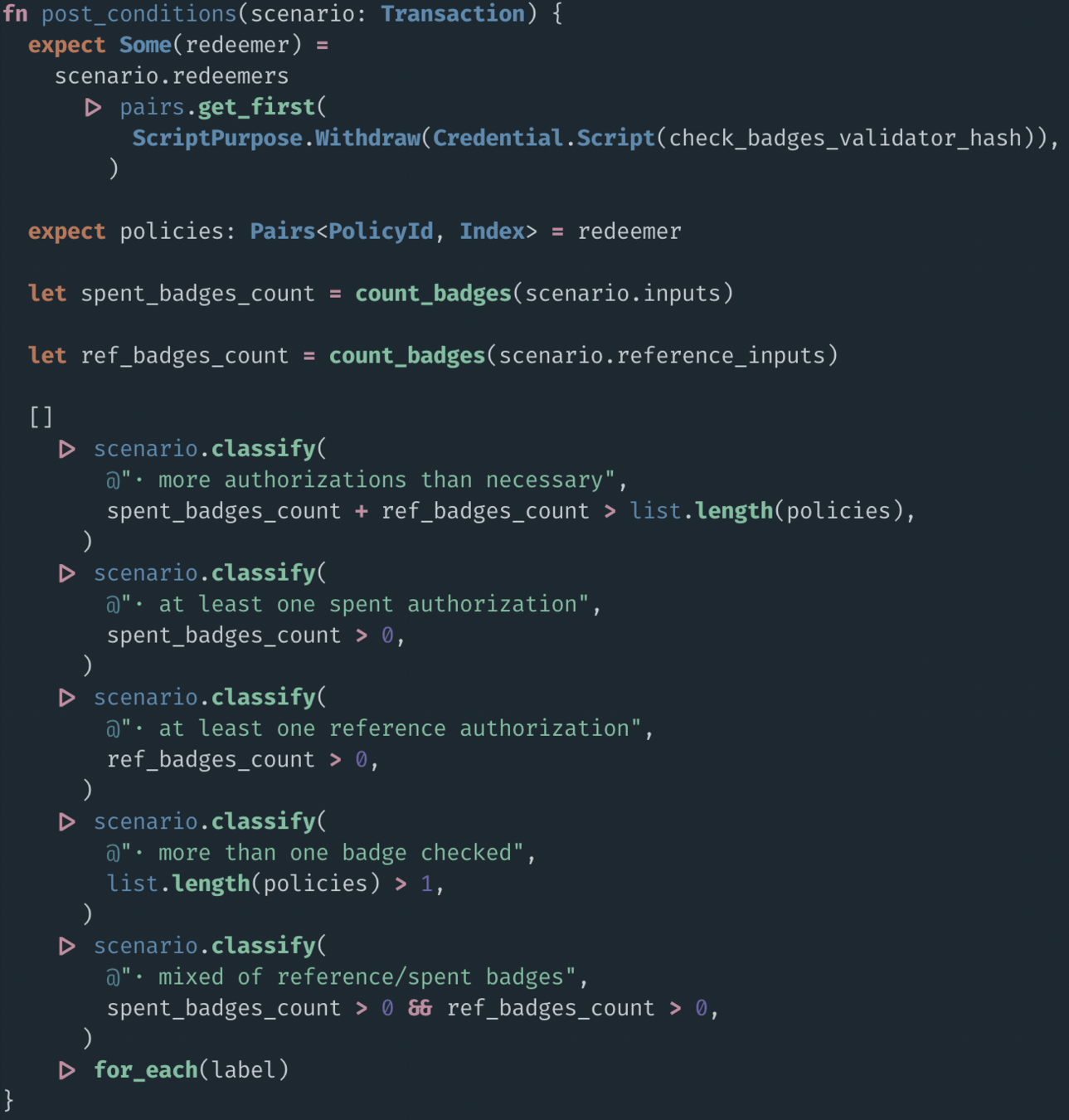
LIMITS
AND UGLY STUFF


It can be slow...
but!
- It's only when simplifying counterexamples
- New VM coming with 10x perf
- It frees up time for coffee!
finding bugs
Transactions carry noise...
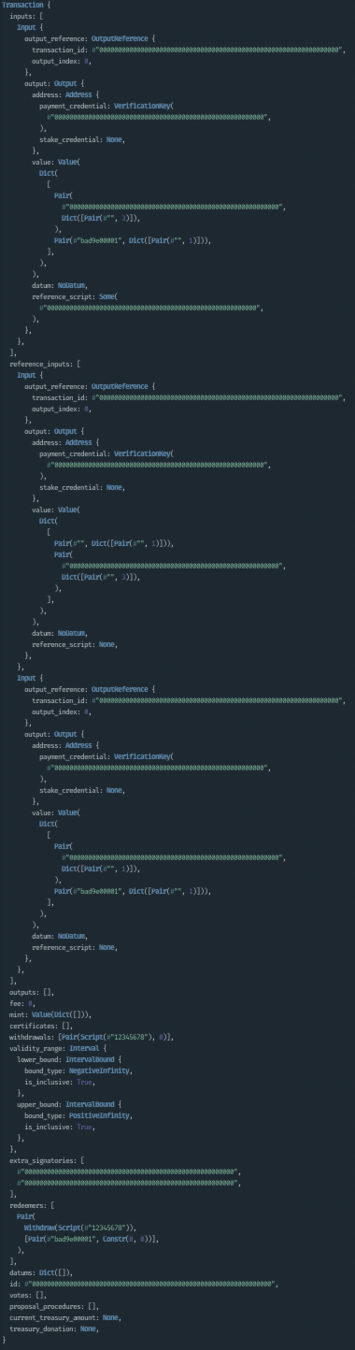
inputs
reference inputs
validity range
outputs, fees, mint, certificates, withdrawals
redeemers, datums, signatories, id, votes, gov actions, ...
but!
It's still better than raw CBOR...
Failing scenarii must be thought of...
but!
-
You'll get generators wrong... creating interesting scenarii.
-
It's re-usable and uses 'transaction' as an interface.
-
You get a free specification for auditors as an outcome!
-
It's actually fun*.
* for some definition of fun
I lied to you (a little)
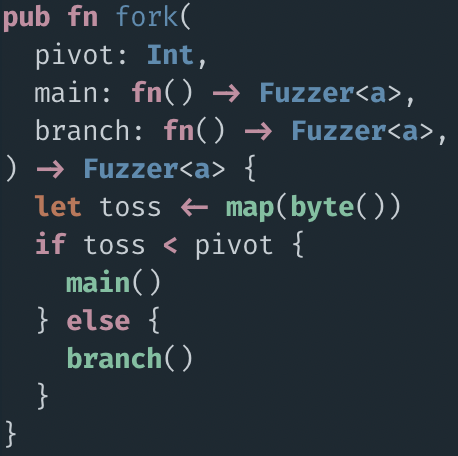
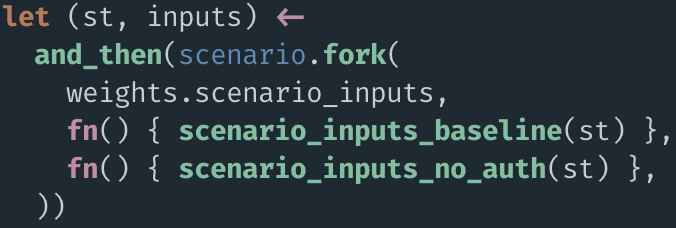

but!
- No but, it's just ugly.
WHAT NOW
?

It's Open Source!
https://github.com/aiken-lang/fuzz.git