Probing the link between planet-forming disks and their environments
Michael Küffmeier



Temidayo Akinbi and Louis Seyfritz
Students:
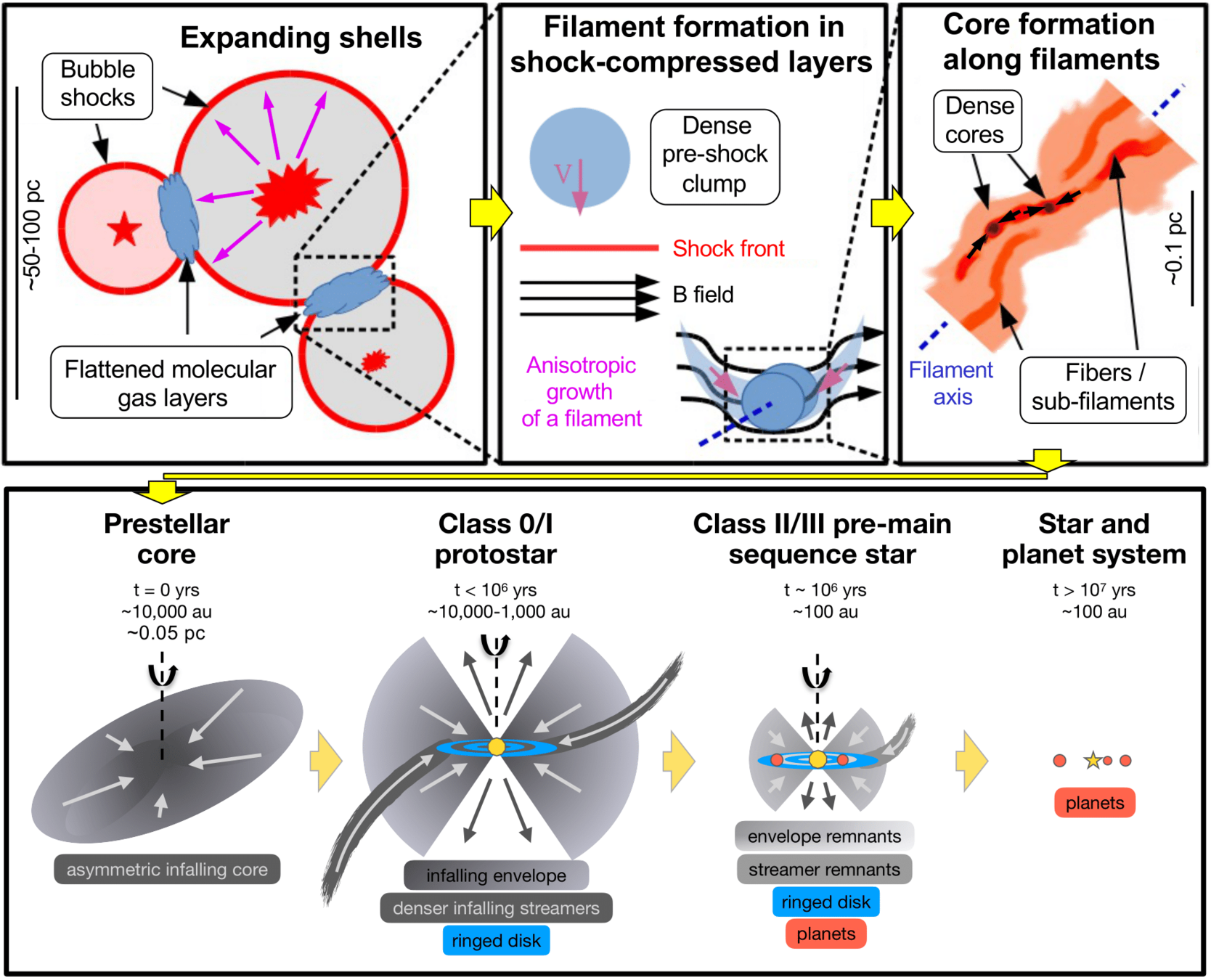
Star (and planet) formation
Pineda et al. 2022 'Protostars and Planets VII' review
.
.
Star and planet formation are two sides of the same medal
The disk is not a static entity, but rather a buffer zone

Why care about magnetic fields?
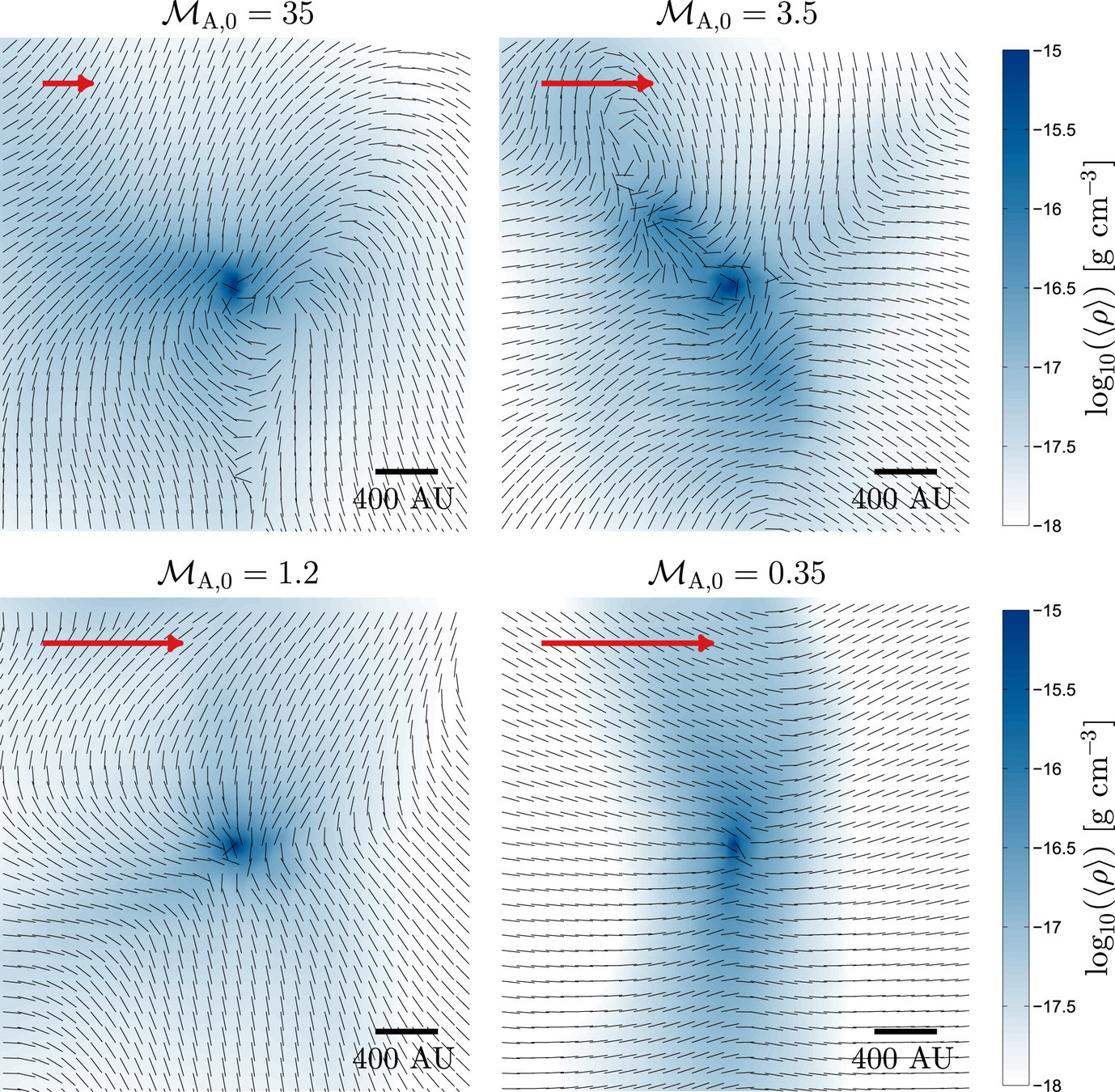
Mocz, Burkhart et al. 2017
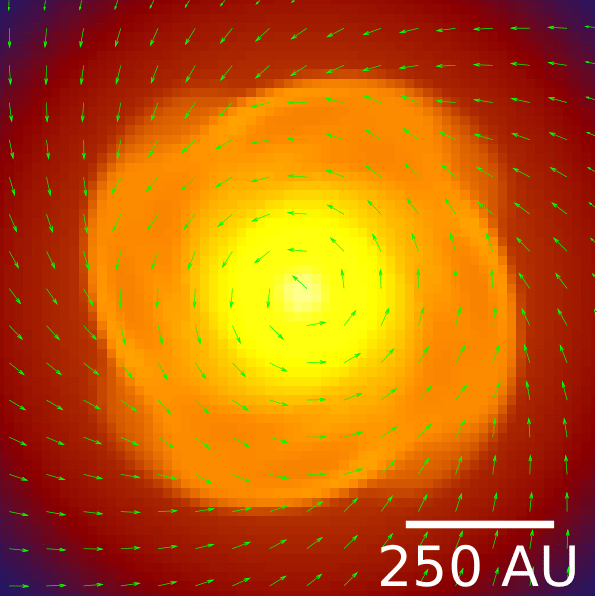
hydro
MHD
Santos-Lima et al. 2012
Magnetic fields in simulation
Küffmeier, Reißl et al. 2020
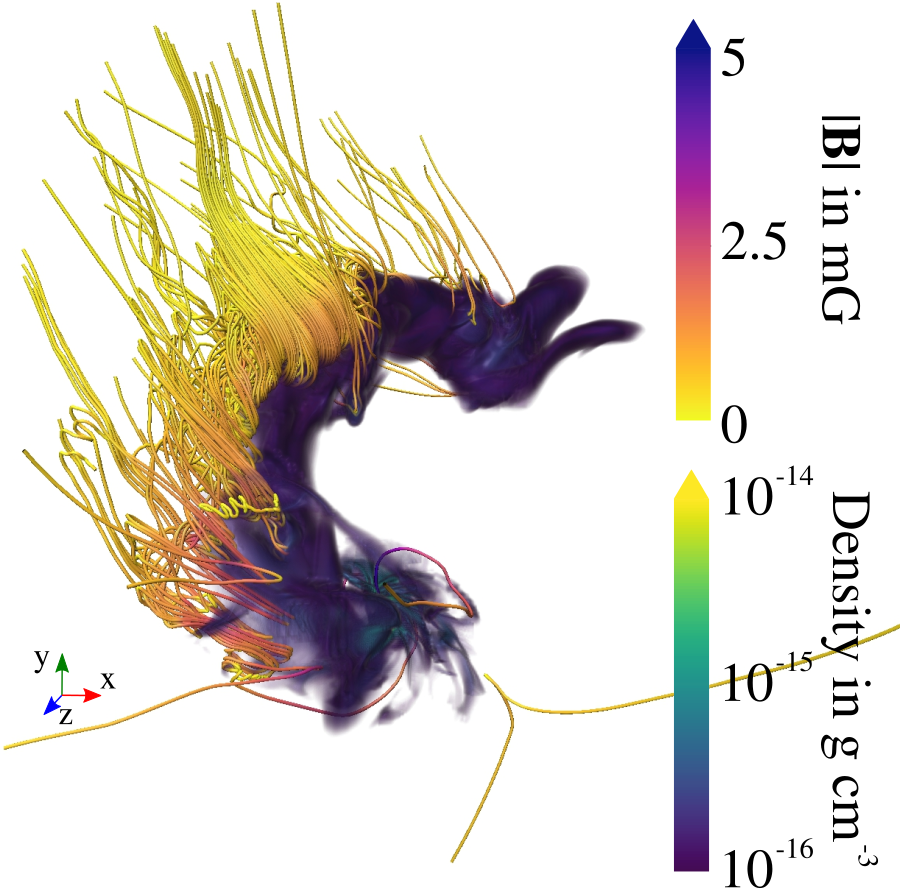
Field strength in bridge:
about 1 to 2 mG
~1500 AU
bridge structure similar to IRAS 16293--2422 (e.g. Sadavoy+ 2018, van der Wiel+ 2019, Maureira+ 2020)
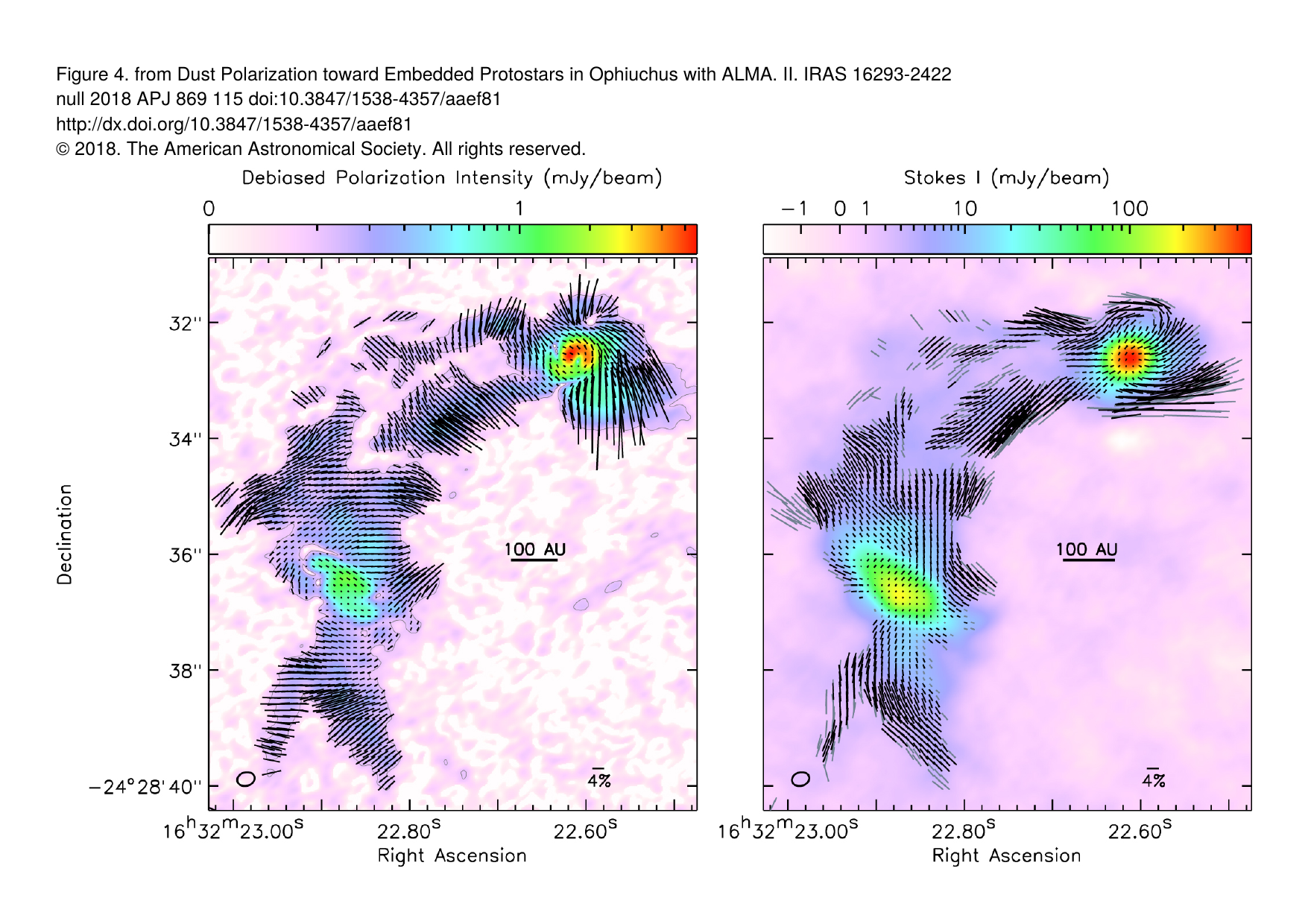
Dust polarization to measure magnetic fields
Polarization depends on degree of grain alignment and elongation
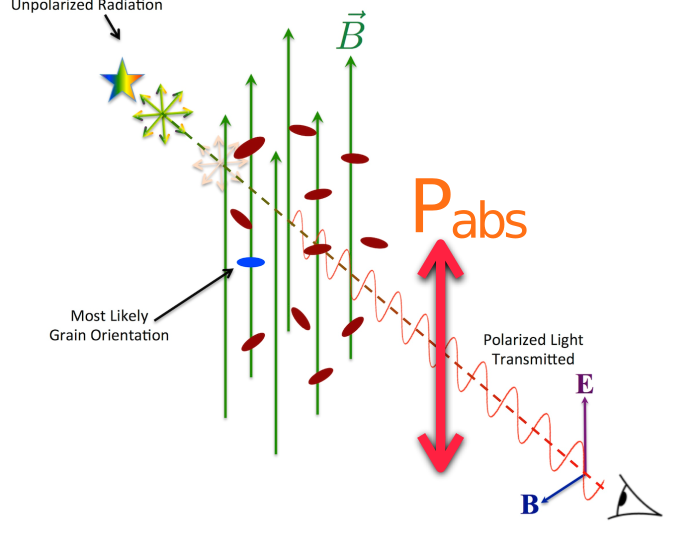
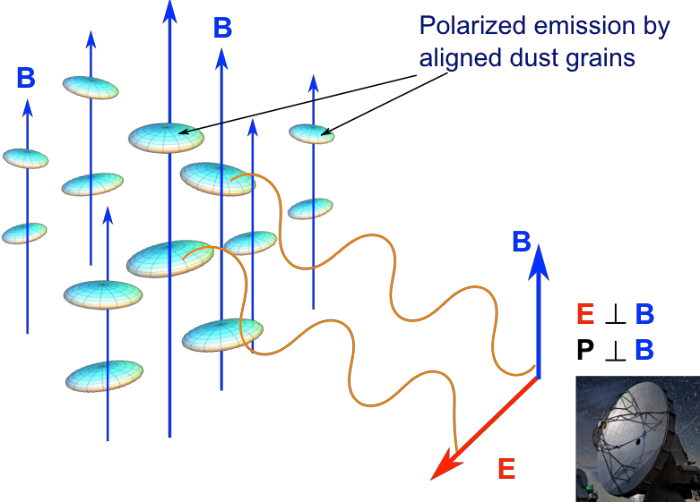
Credit: B. G. Anderson
Measuring linear polarization of dust grains allows to determine magnetic field orientation ...
... if you know the origin of polarization.
Synthetic observation with POLARIS
Küffmeier, Reißl et al. 2020
Emitted radiation

at 1.3 mm: polarization traces magnetic field structure
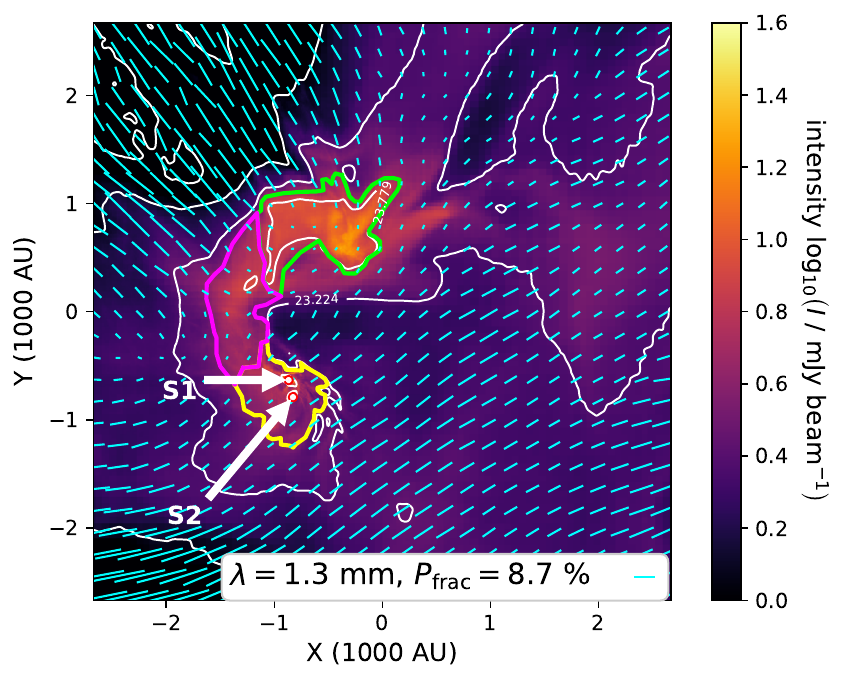
(we display e-vectors rotated by 90°)
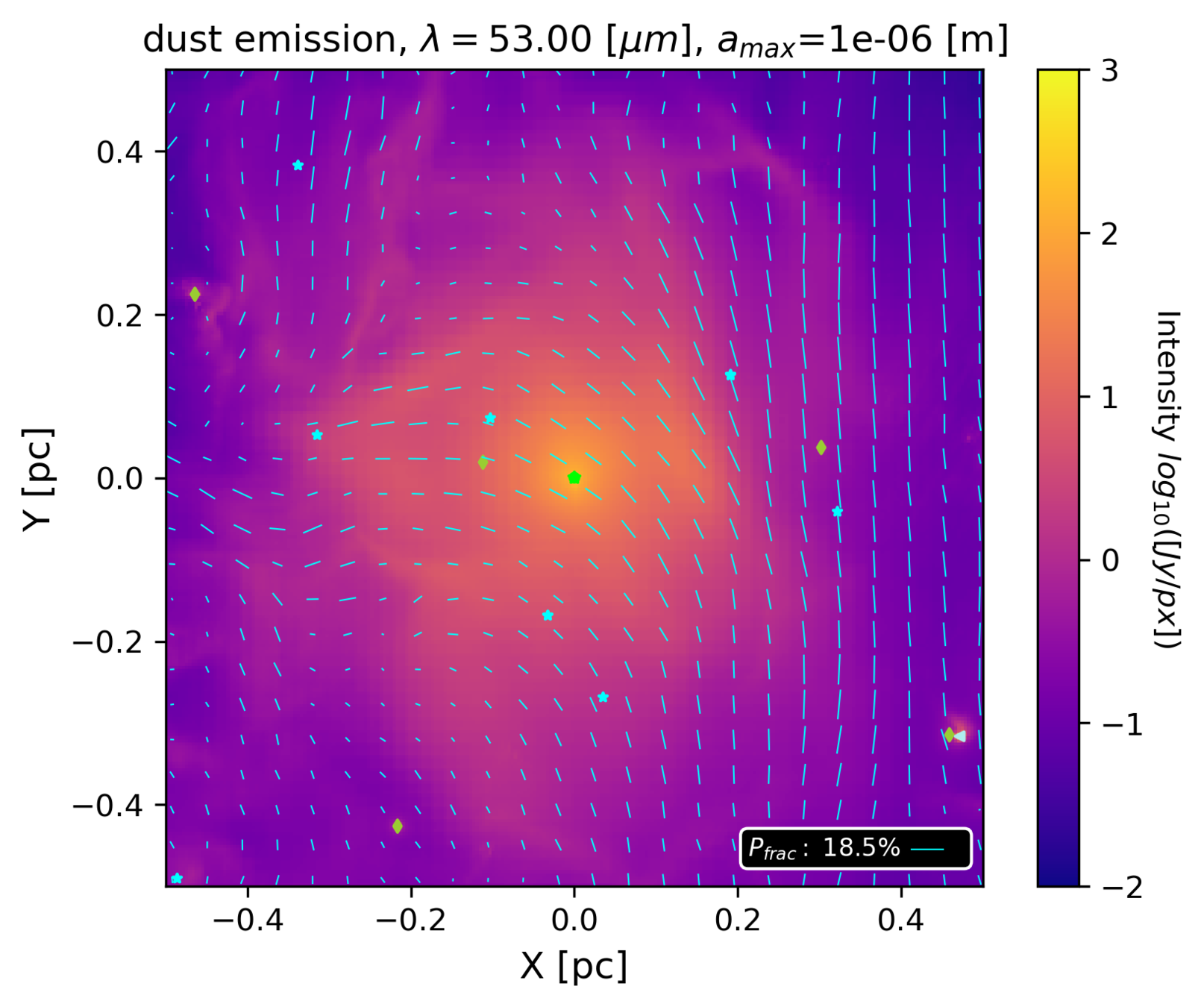
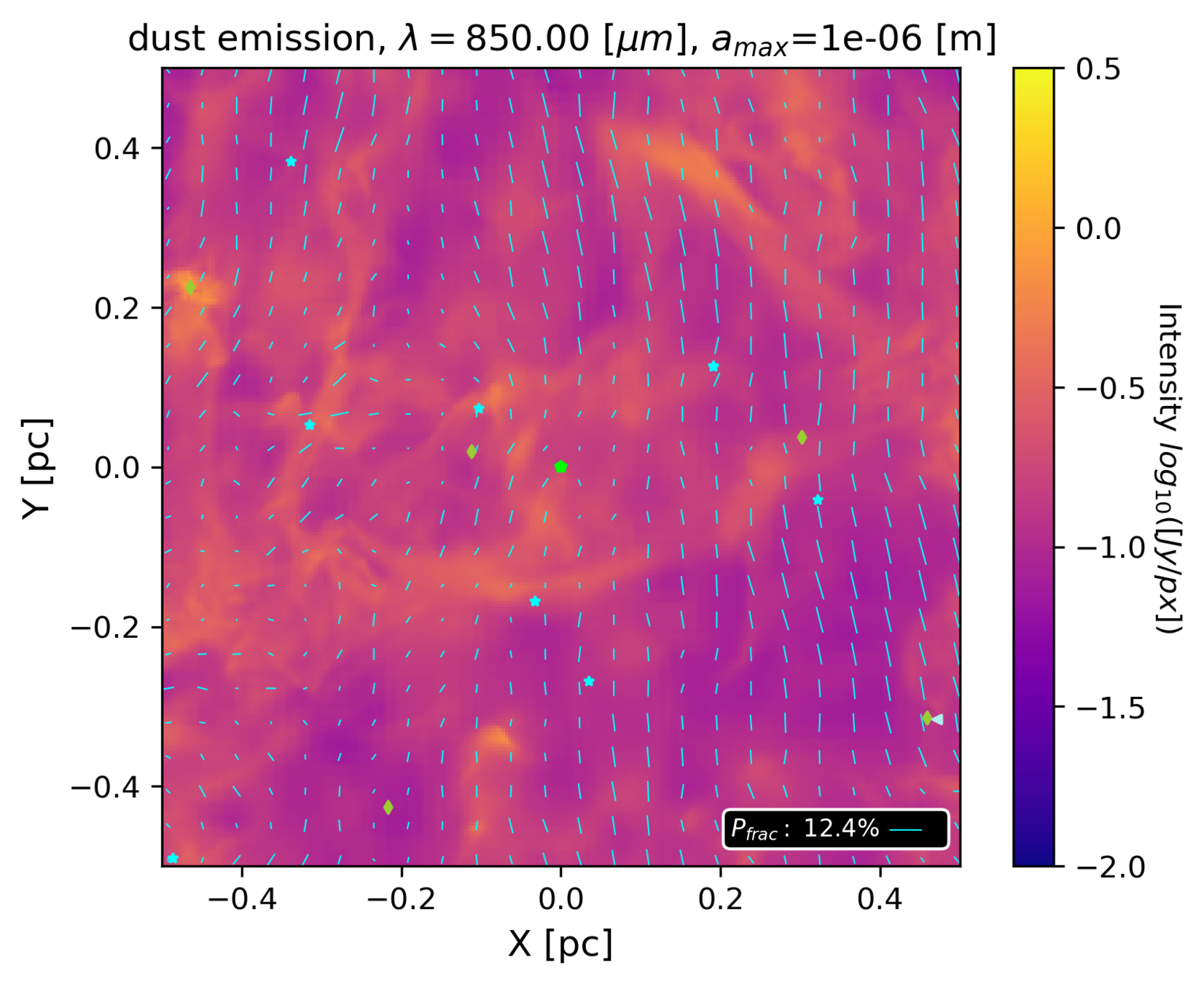
Wavelength dependence: 1.3 mm vs 53 micron

Emitted radiation
1.3 mm: good tracer of magnetic field
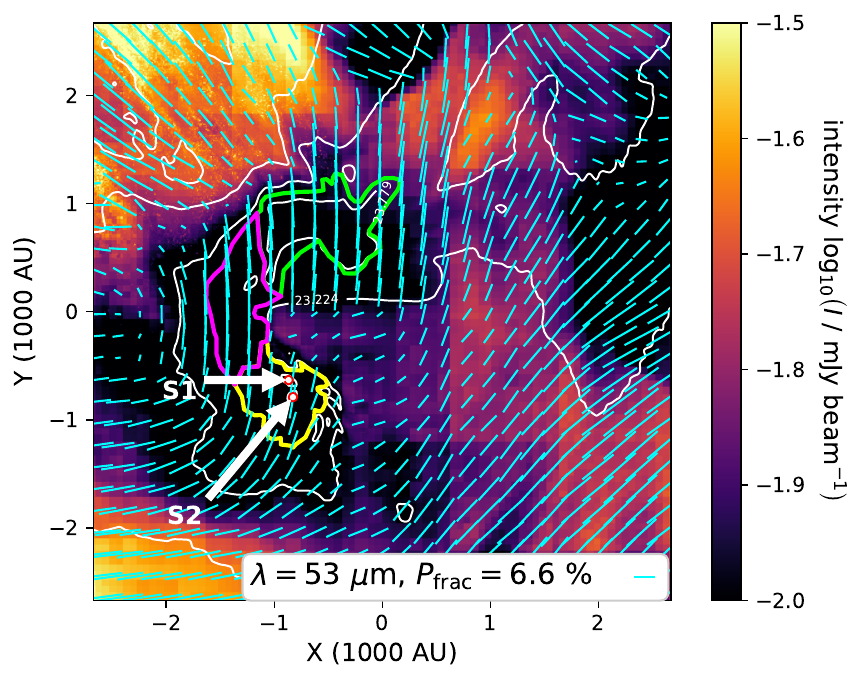
53 micron: poor tracer of magnetic field
Küffmeier, Reißl et al. 2020
Reason for wavelength dependence
Küffmeier, Reißl et al. 2020
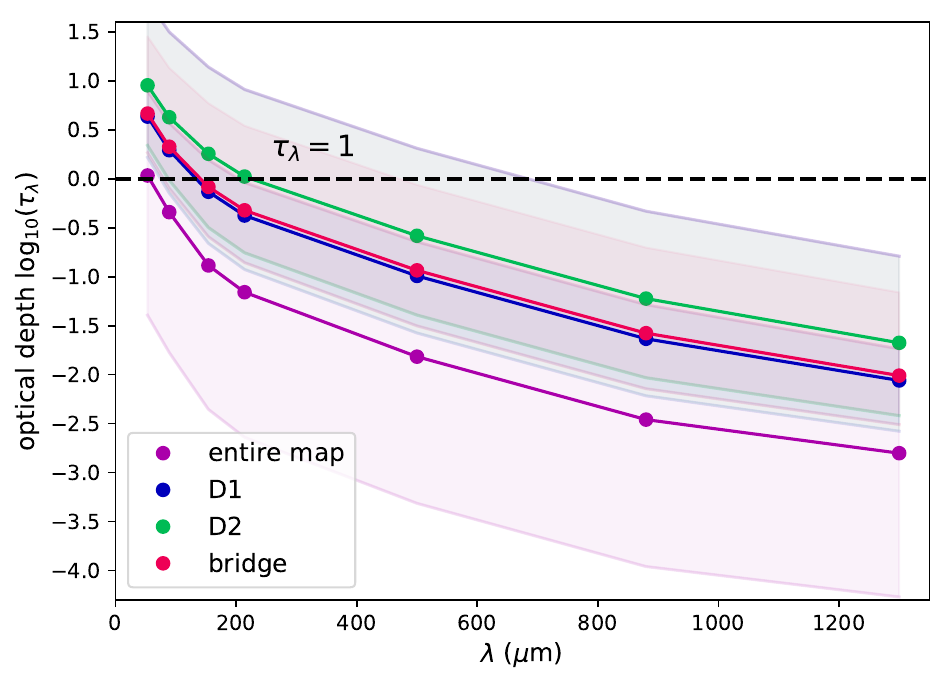
Dichroic extinction
Take-away for scales beyond the disk
< 200 micron: dichroic extinction; challenging to trace B reliably
> 200 micron: thermal emission; linear polarization traces B


(see also H. Woodward's 2021 project and Chi Yan "Paul" Law's talk on G28.20-0.05 tomorrow. Stay tuned for Louis Seyfritz's results.)
see also Reissl et al. 2014, 2016 for more discussion of the flip
Star (and planet) formation
Pineda et al. 2022 'Protostars and Planets VII' review
.
.

Possibility of late infall
Late infall

AB Aurigae

HD 100546
Credit: Grady+ 1999, Fukagawa+ 2004
Can (late) infall cause misalignment of inner and outer disk?
Credit: Ardila+ 2007
SU Aur
Credit: Ginski+ 2021
Extended arc-like structures can be induced by late infall
(Dullemond, Küffmeier, Goicovic+ 2019, Küffmeier, Goicovic & Dullemond 2020)
Possibility of "second-generation" disk
Shadows due to misaligned inner and outer disk
Credit: Marino+ 2015

Simulate cloudlet infall onto disk
AREPO, pure hydrodynamical
isothermal gas
vary infalling angle
vary rotation (prograde, retrograde)
Küffmeier, Dullemond, Reißl, Goicovic 2021
Effect of infall angle on disk
Open questions: What about...
- ... long-term evolution?
- ... infall in binary systems?
- ... the effect on dust dynamics in the disk?
(The topic of Temidayo Akinbi's summer project.)
Formation of misaligned disks
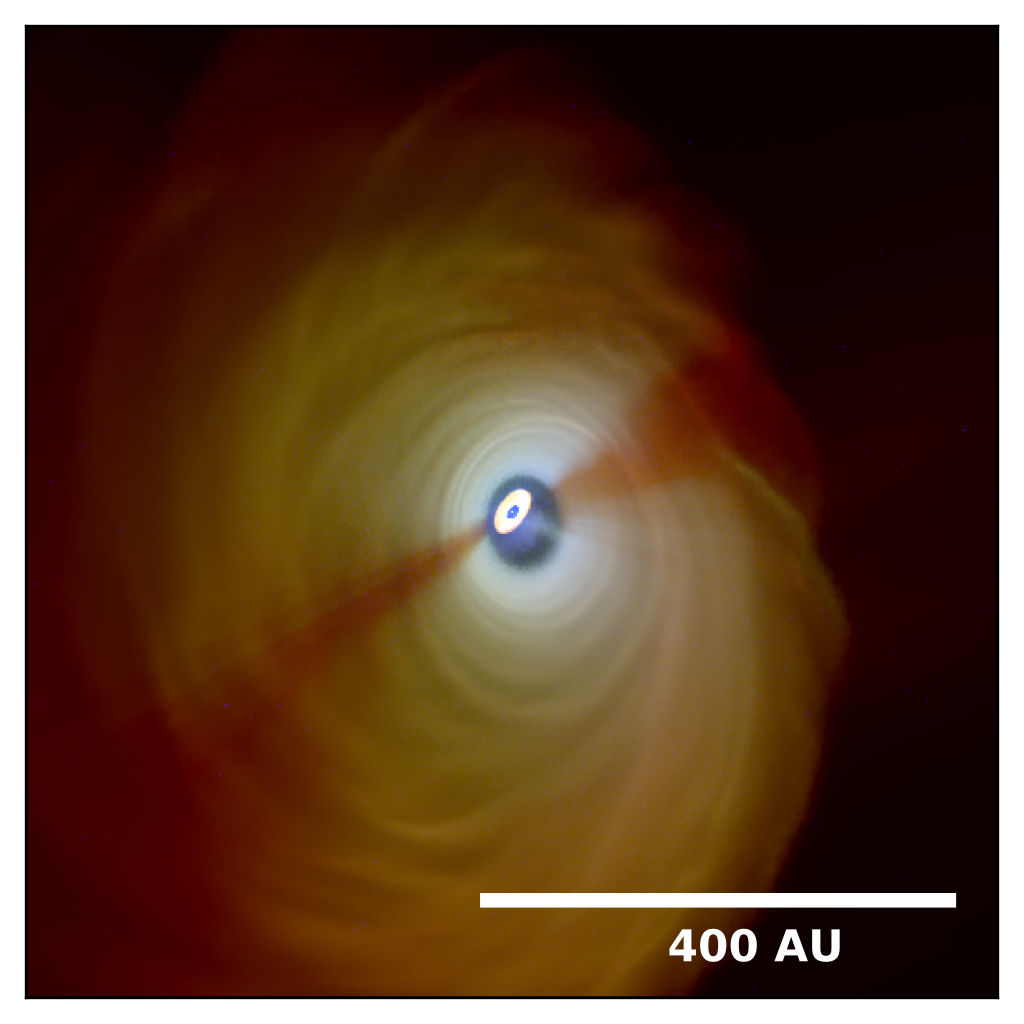
Observable as shadows in outer disk
Take-away points
Infall is one explanation for misalignment between inner and outer disk.

Linear polarization of dust reemission at wavelength >200 micron is a good tracer of magnetic field structure on scales beyond the disk.

At smaller wavelengths the signal tends to be dominated by absorption causing a "flip".

WIP: study synthetic observations of infall-induced shadows

RGB image of misaligned system forming from infall with 60°
blue (1.66 micron), green (53 micron), red (870 micron); Credit: S. Reißl
Synthetic dust polarization maps at 1.3 mm
Küffmeier, Reißl et al. 2020

Emitted radiation
Polarization fraction in bridge:
a few %
Polarization fraction in bridge:
up to 20 %
IRAS 16293--2422
Sadavoy et al. 2018
alignment efficiency higher than efficiency produced by standard RAT alignment
(also Le Goeullec+20)
IRAS 16293-2422 highly magnetized?
Synthetic maps from ~pc to ~10 000 au scales

Hannah Woodward
UVA undergraduate; graduate at University Wisconsin-Madison from September 2022
Woodward, Küffmeier & Li in prep
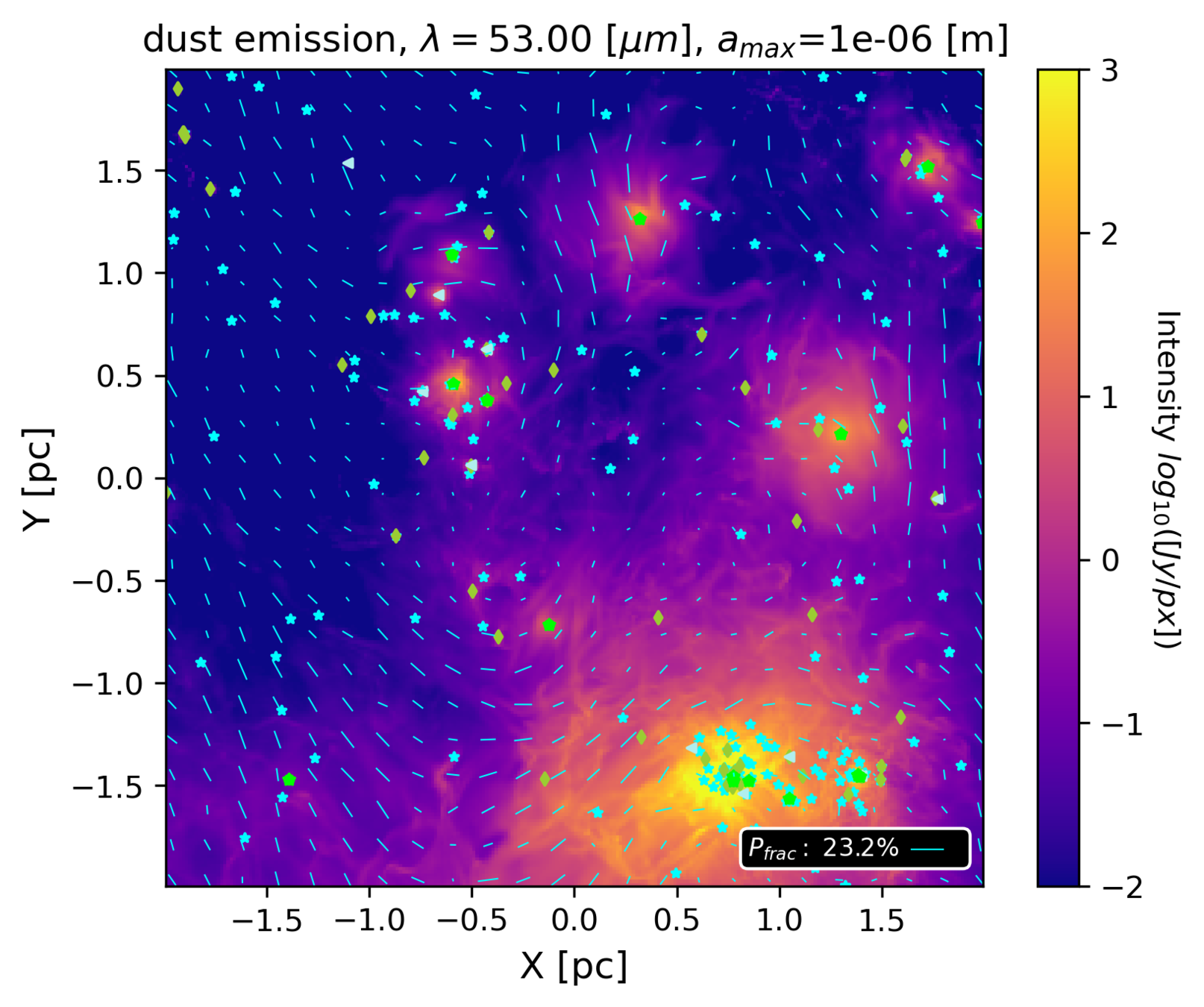
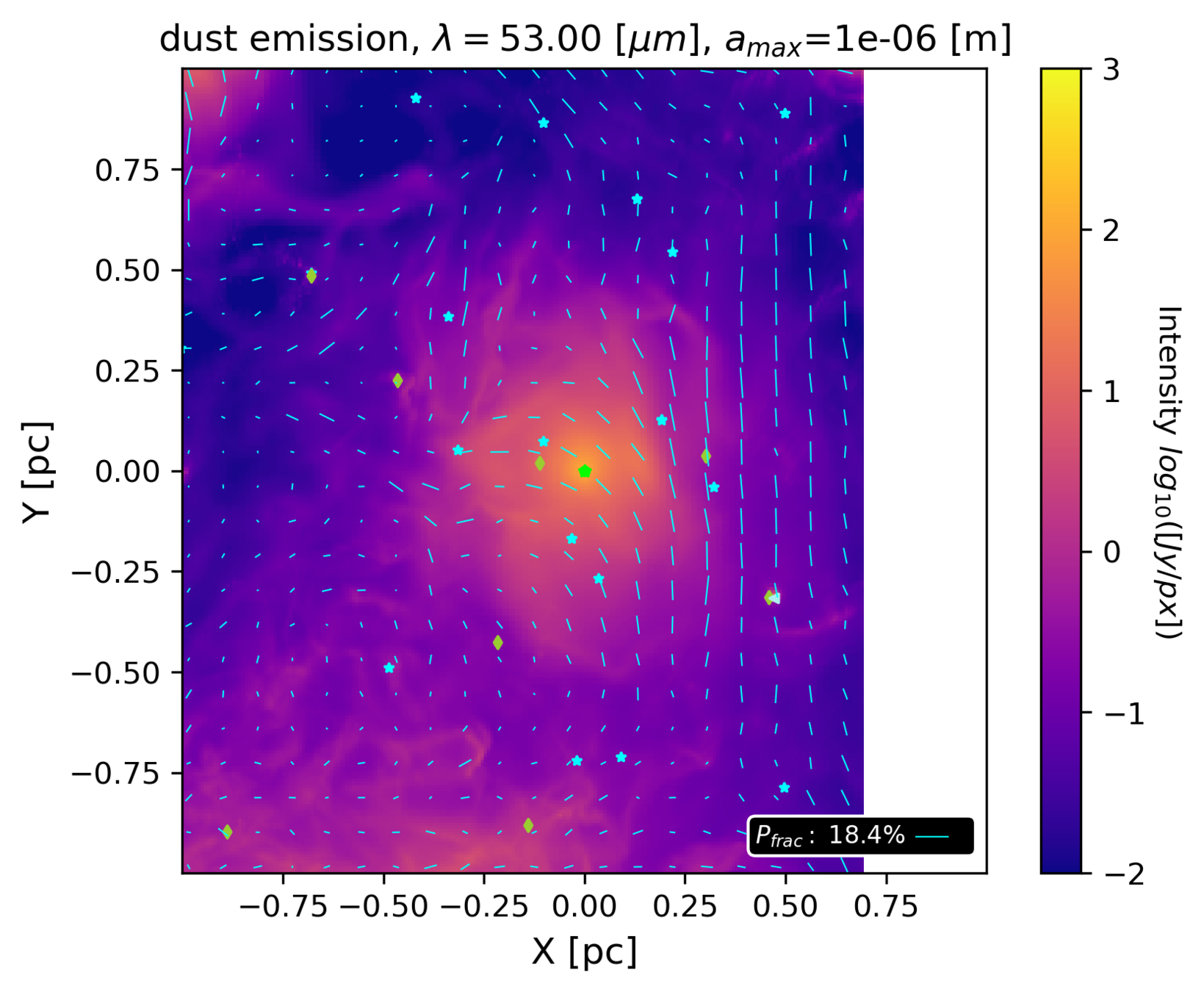
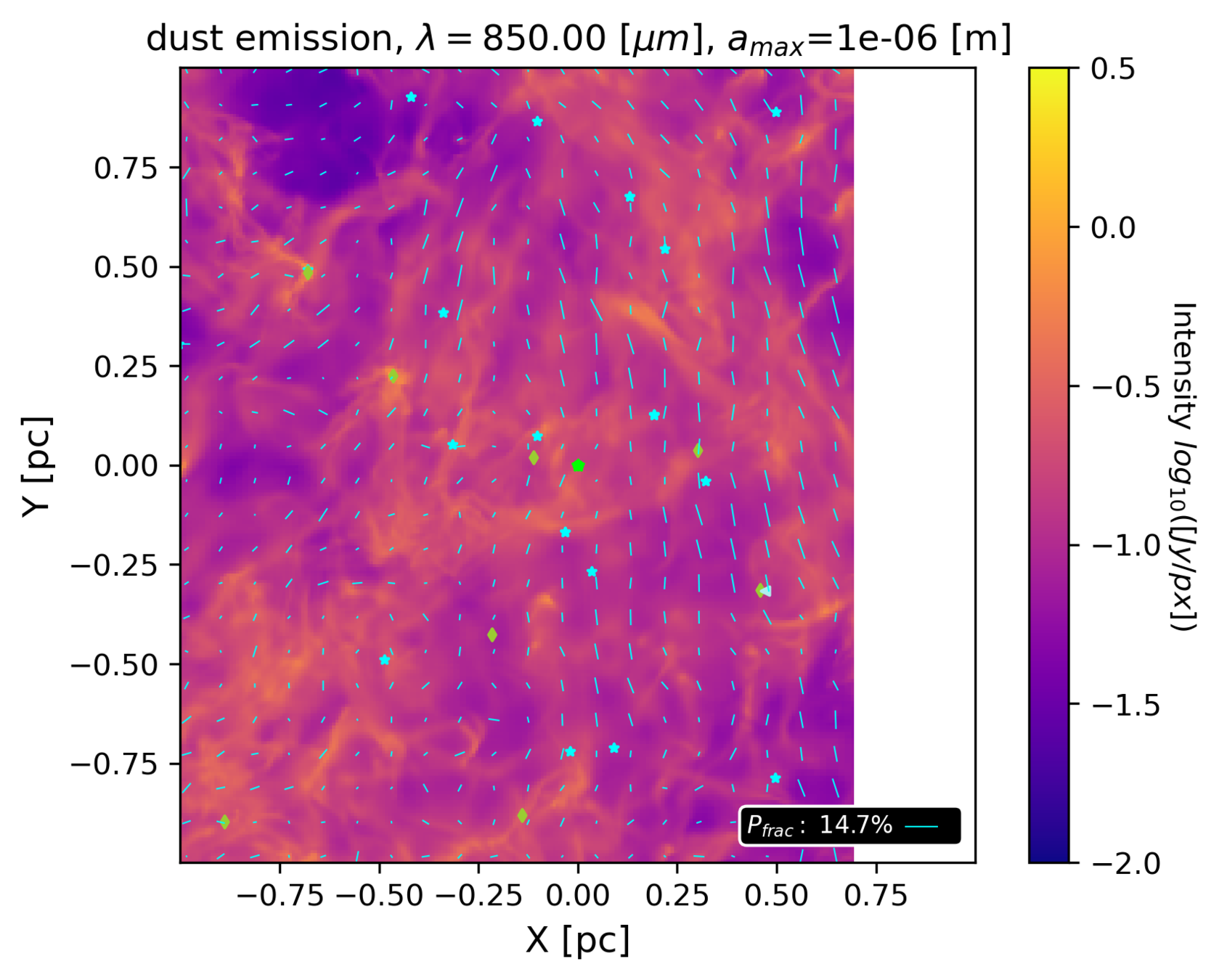
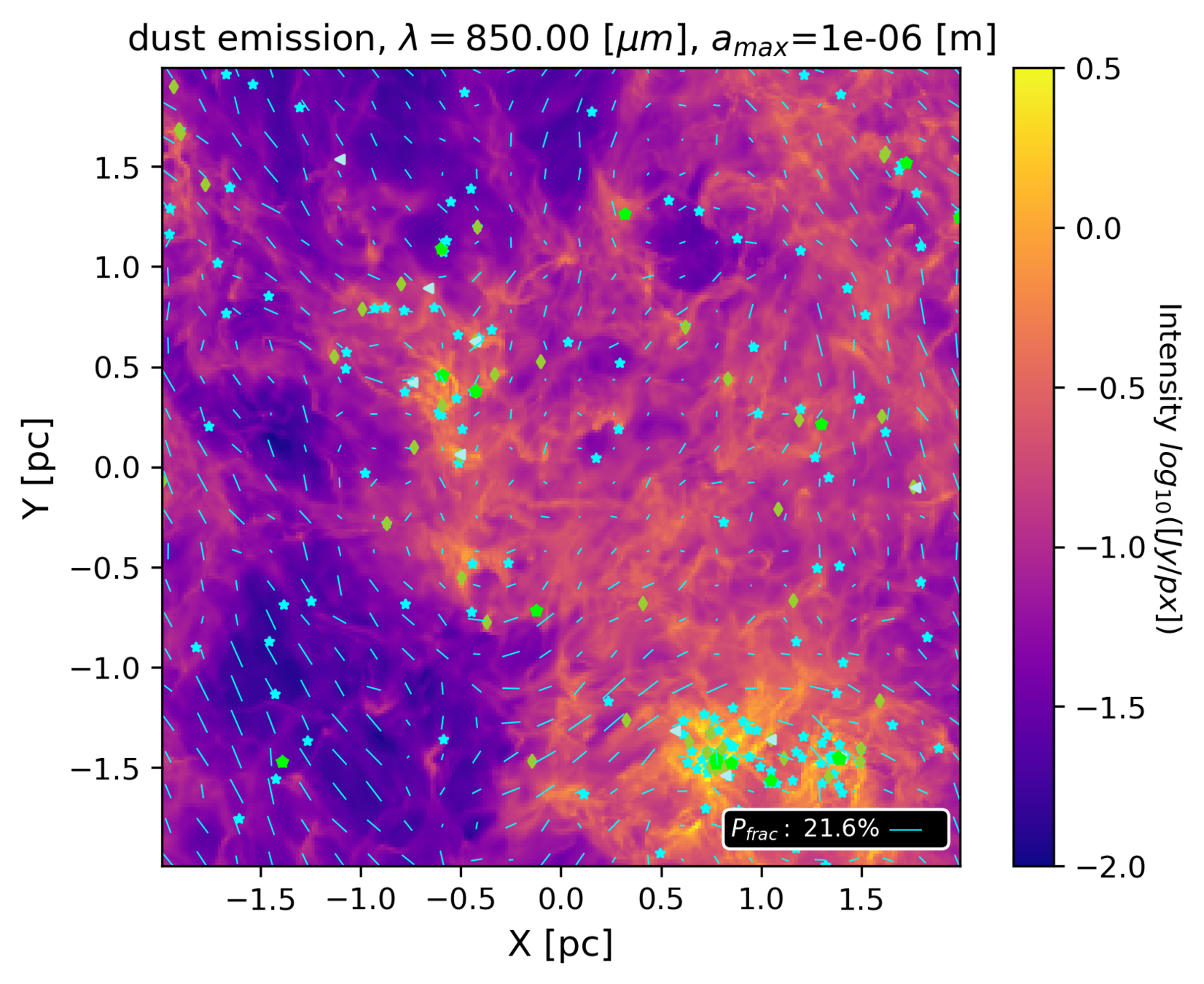
based on MHD simulations of Haugbølle et al. 2018 (see R. Kuruwita's poster)
Simulate cloudlet infall onto disk
AREPO, pure hydrodynamical
isothermal gas
vary infalling angle
vary rotation (prograde, retrograde)
Küffmeier, Dullemond, Reißl, Goicovic 2021
Outer disk forms around inner disk
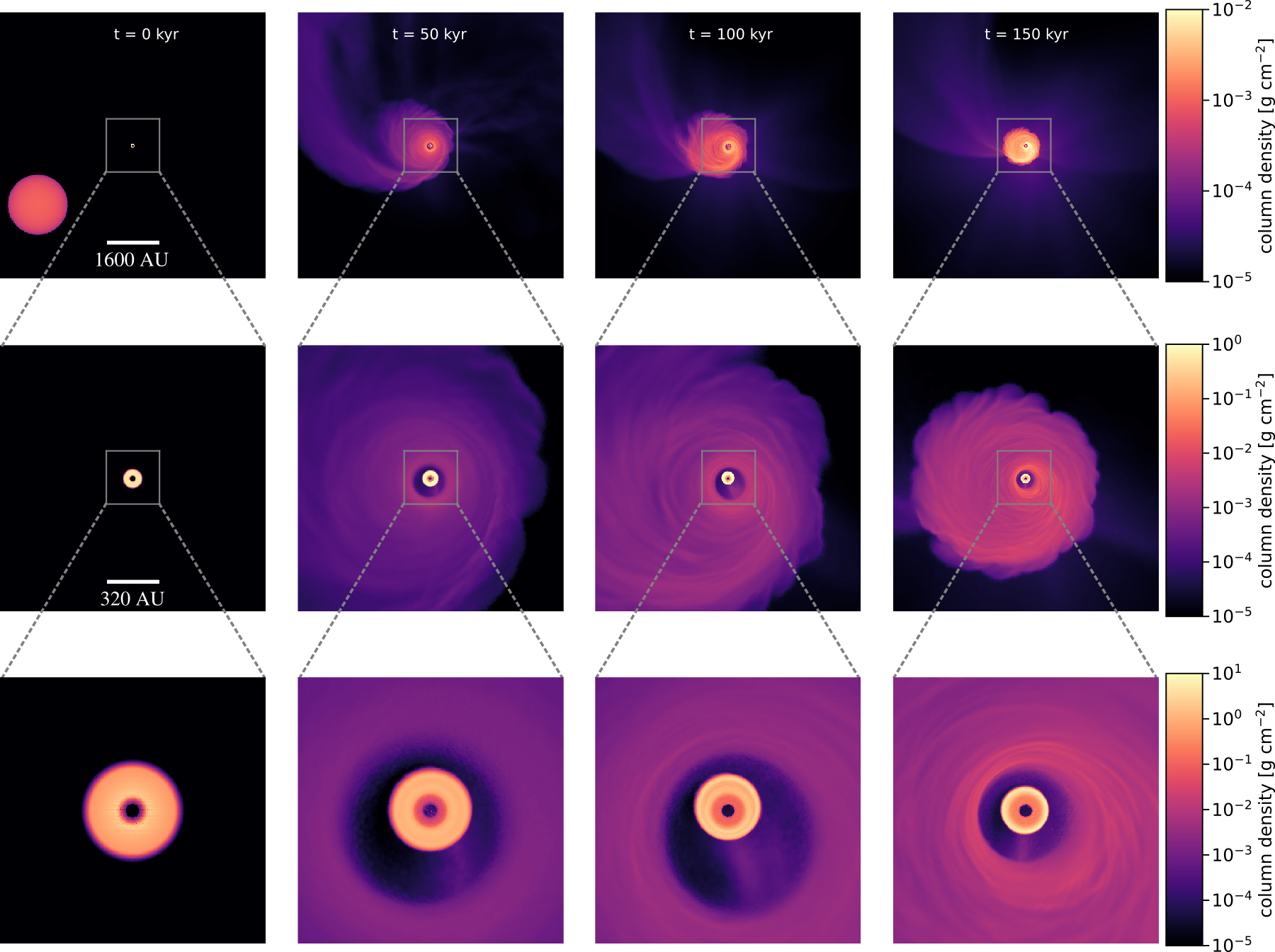
Küffmeier+ subm
consistent with star formation simulations by Bate '18

Prograde vs. retrograde infall
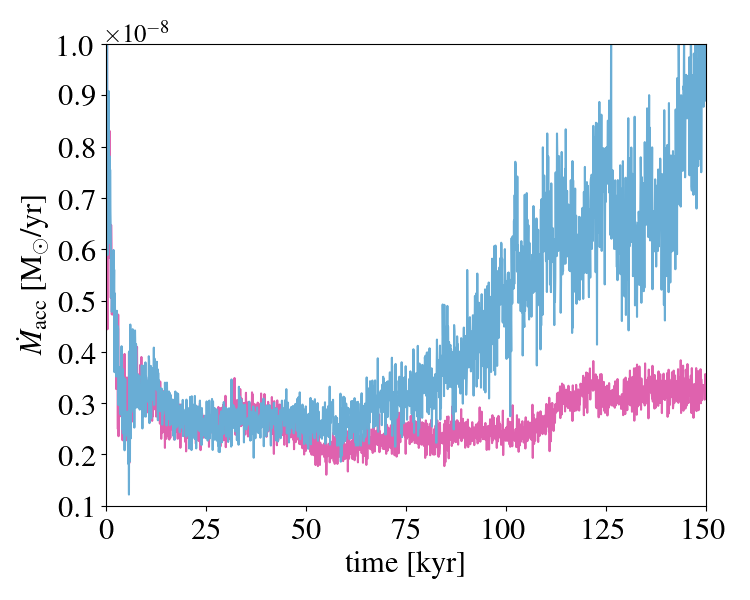
Retrograde infall causes:
- counter-rotating inner and outer disk
- shrinking of inner disk
- enhanced accretion
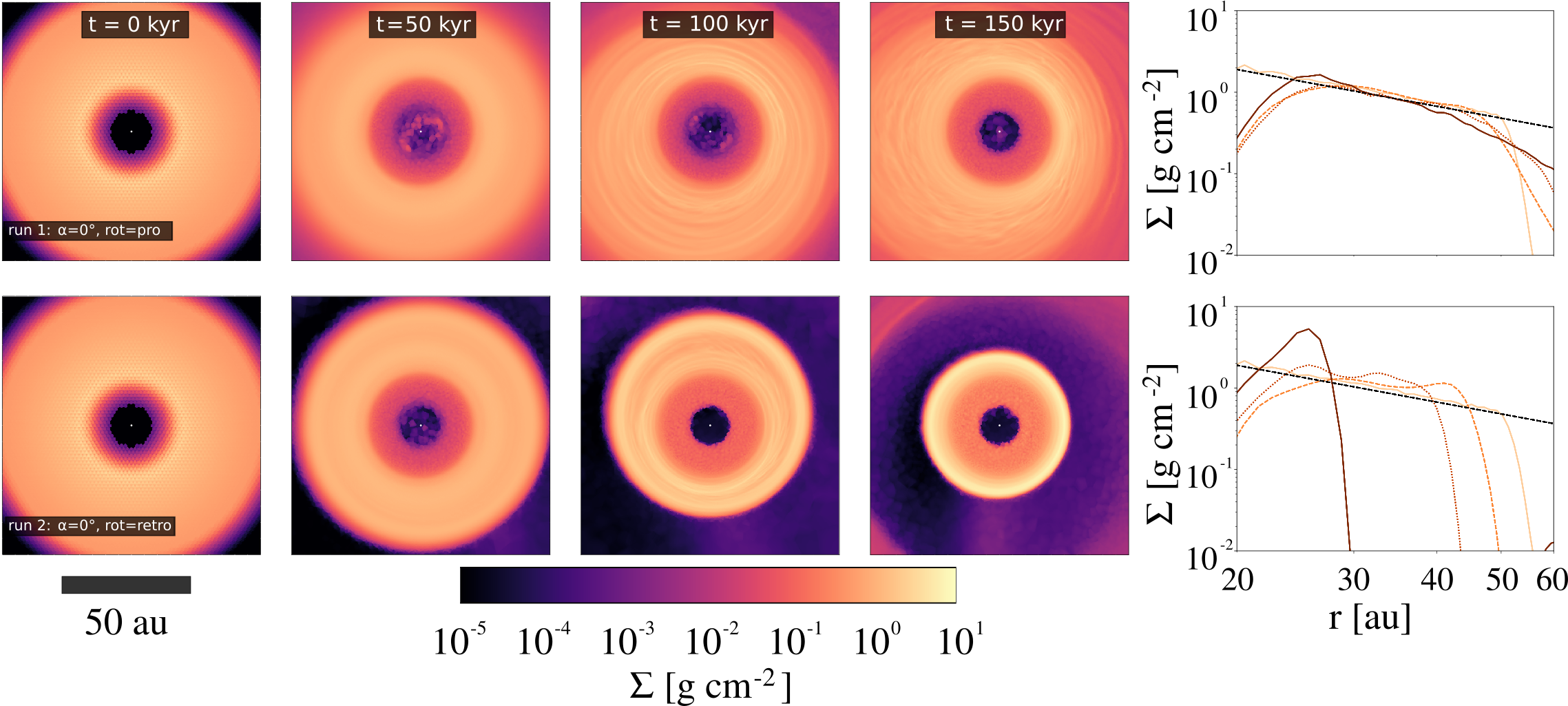
- larger and deeper gap between disks
see also Vorobyov+ 2016

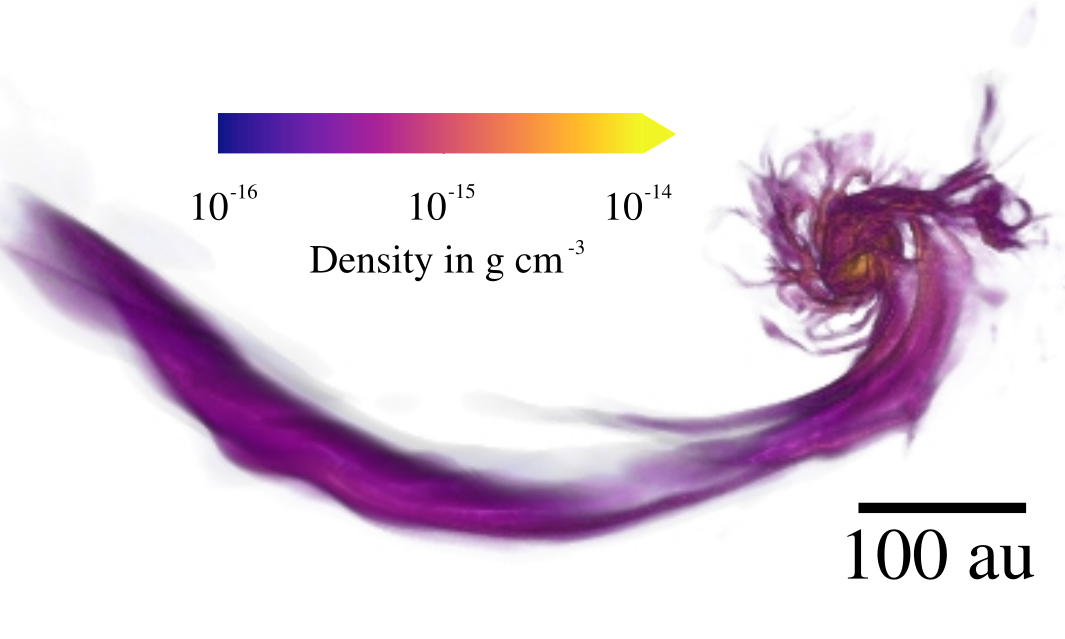
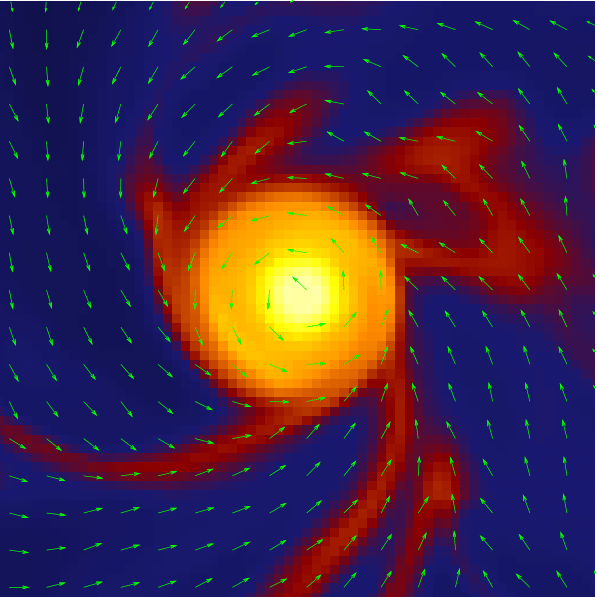
Zoom-in on embedded protostellar multiple
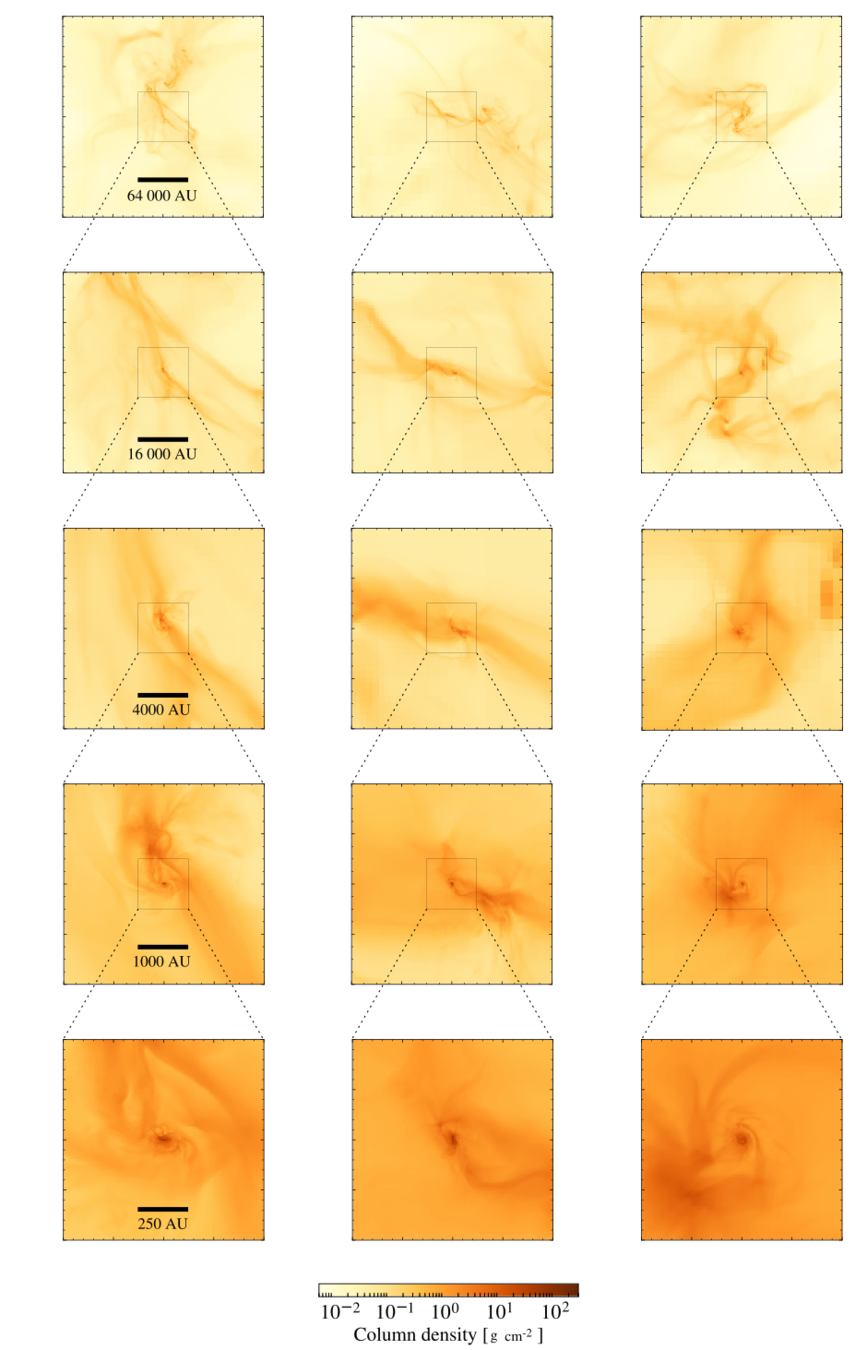
Küffmeier et al.
2019

Küffmeier, Reißl et al. 2020
~1500 AU
bridge structure similar to IRAS 16293--2422 (e.g. Sadavoy+ 2018, van der Wiel+ 2019, Maureira+ 2020)