Michael Küffmeier






Synthetic polarization maps around embedded protostars
Advisors: Zhi-Yun Li & Paola Caselli
Stars are born in large assemblies of gas
Star-disk systems form in different environments provided by Giant Molecular Clouds (Size: 10 - 100 pc)
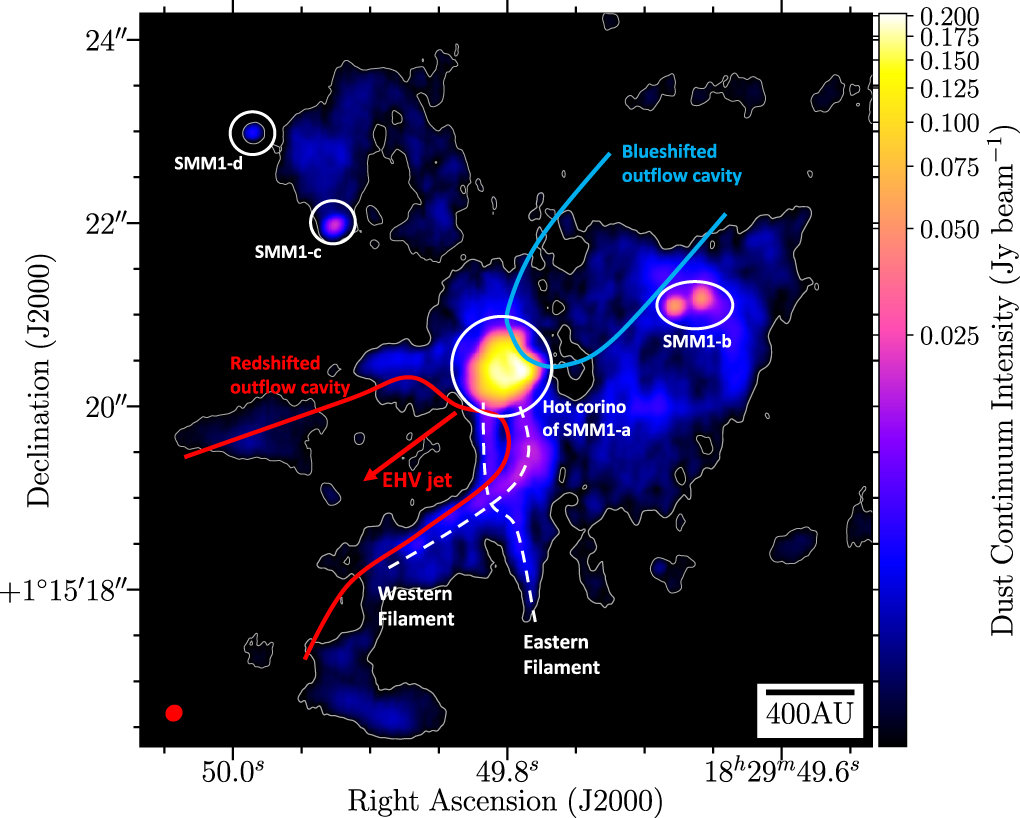
Serpens SMM1 (Le Gouellec et al. 2019)
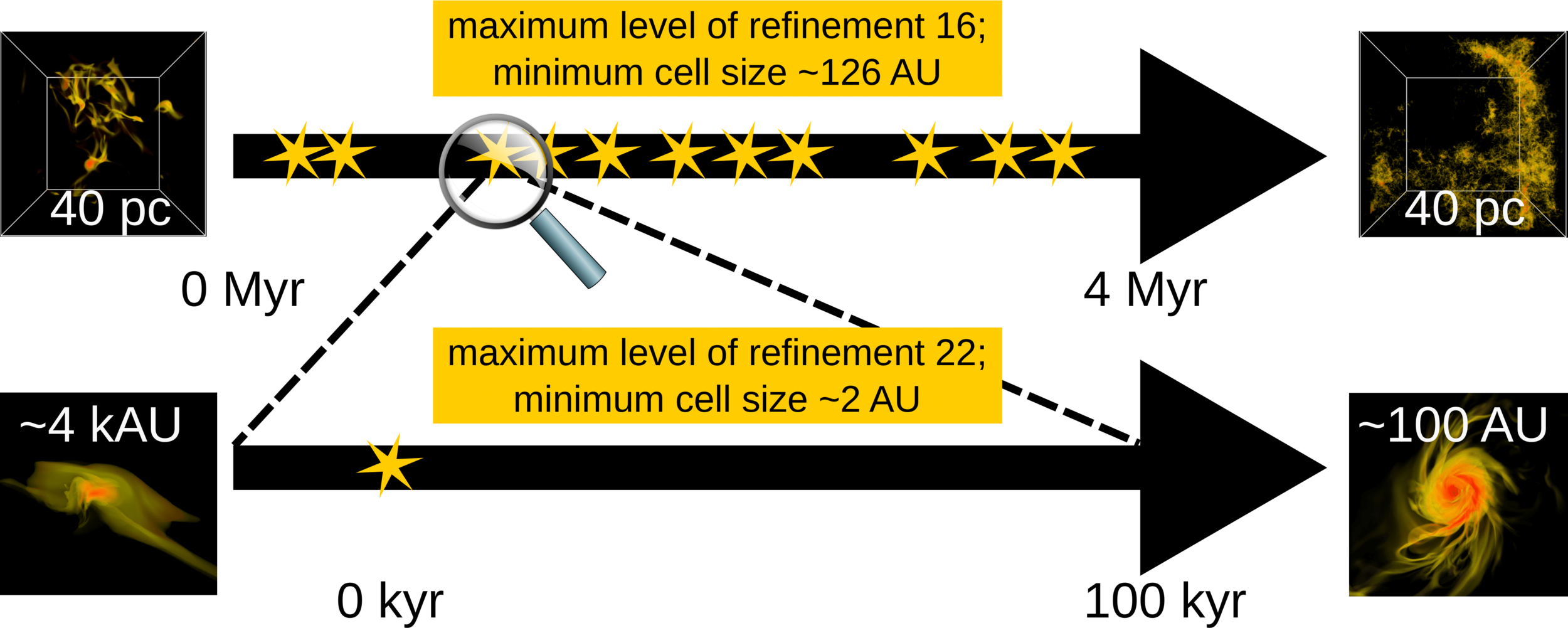
Zoom-in method
Küffmeier et al. 2017
- adaptive mesh refinement
- ideal magnetohydrodynamics
- turbulence driven by supernovae
- stars modelled as sink particles

Magnetic fields in simulation
Küffmeier, Reißl et al. 2020
...in bridge
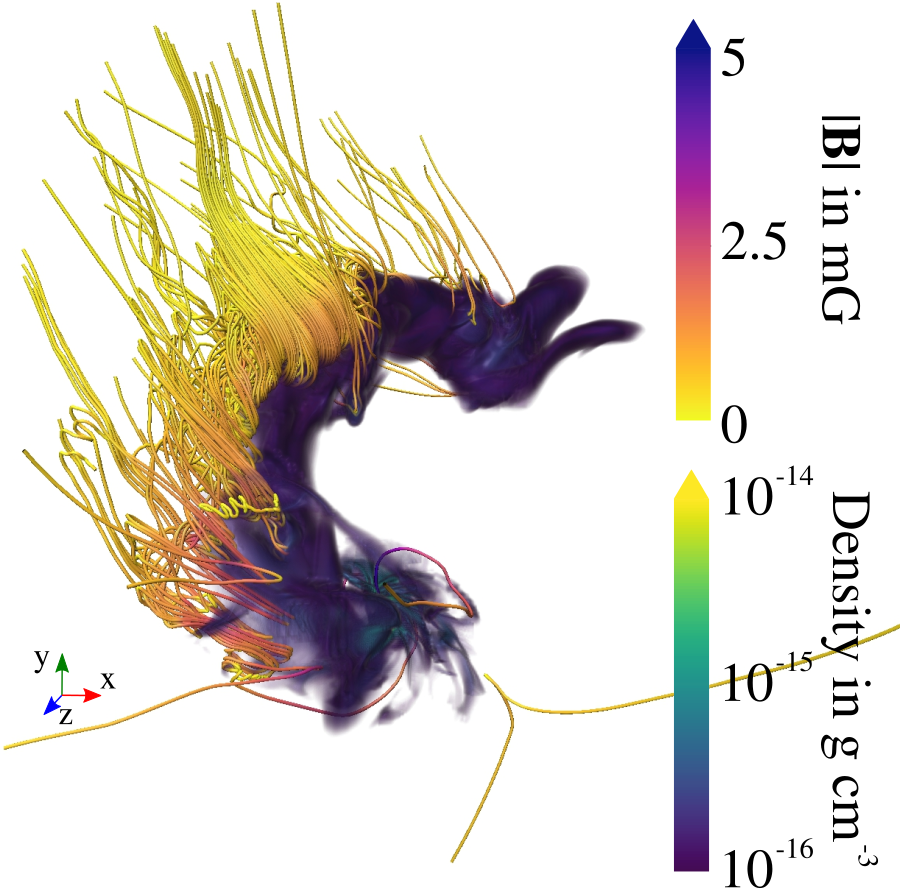
Field strength in bridge:
about 1 to 2 mG
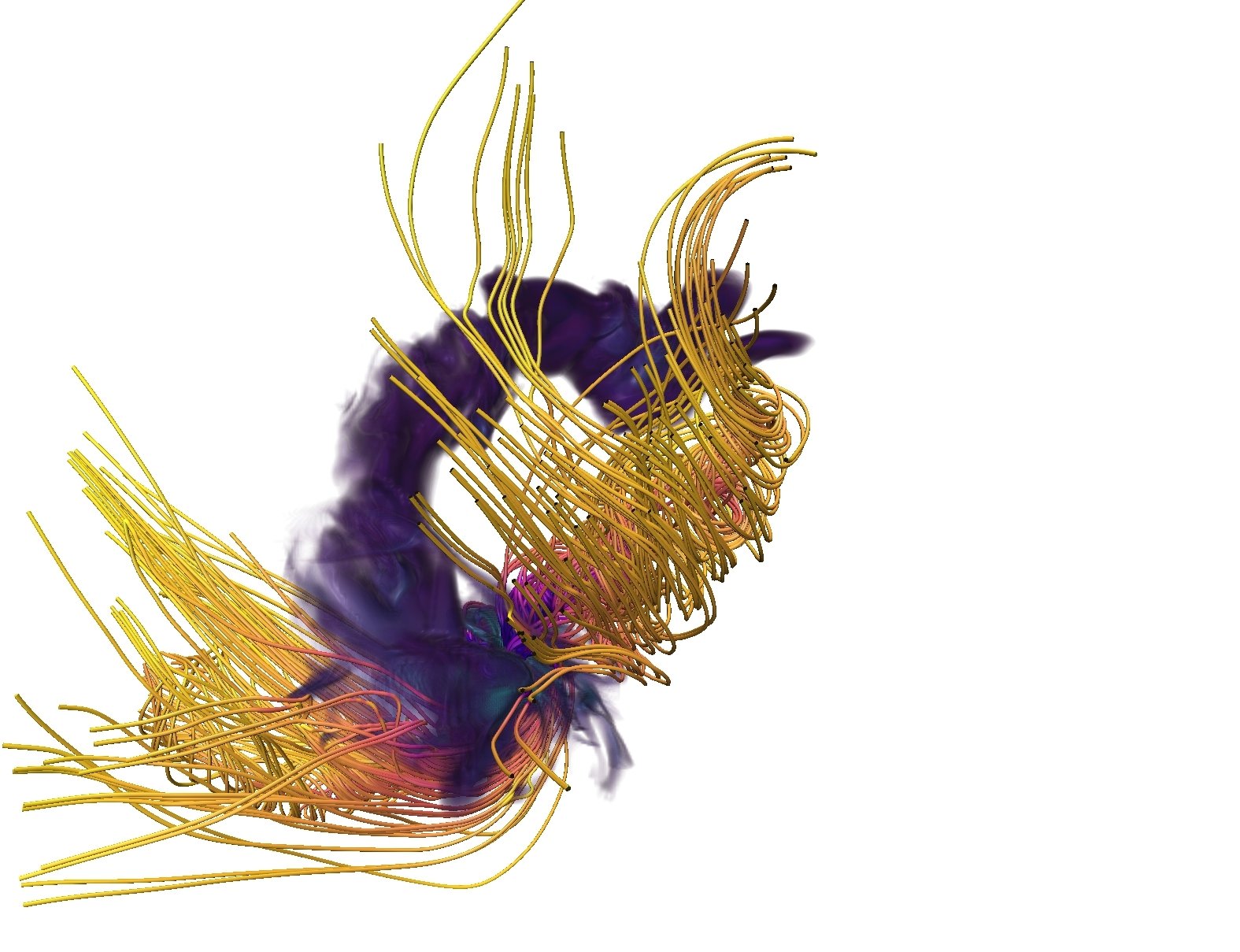
...around primary protostar
Field strength close to foot point:
>100 mG
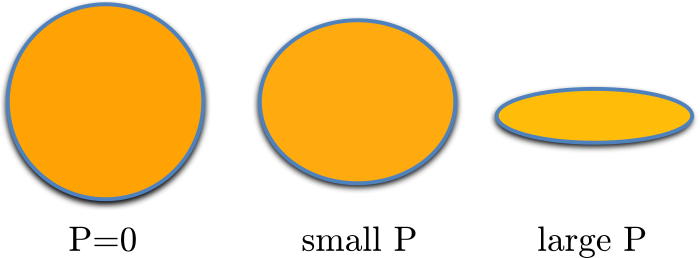
Dust polarization to measure magnetic fields
Polarization depends on degree of grain alignment and elongation
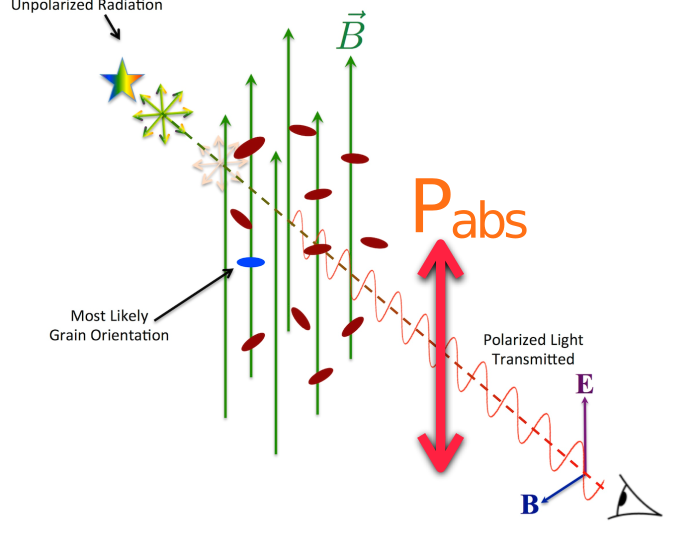
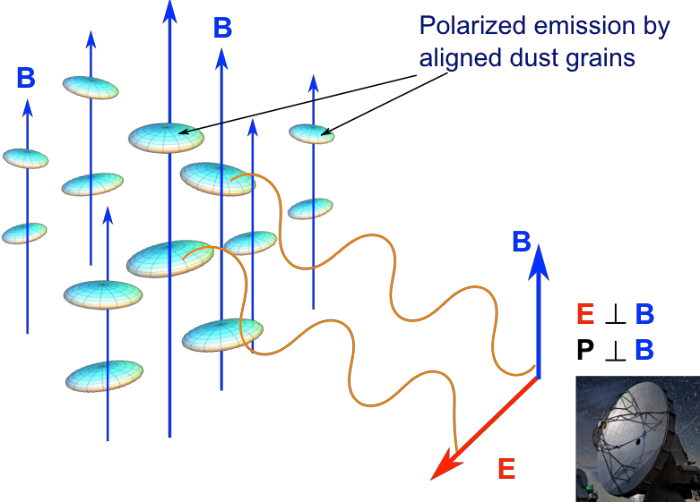
Credit: B. G. Anderson
Measuring linear polarization of dust grains allows to determine magnetic field orientation ...
... if alignment mechanism is known!
Stokes vector: description of polarized light
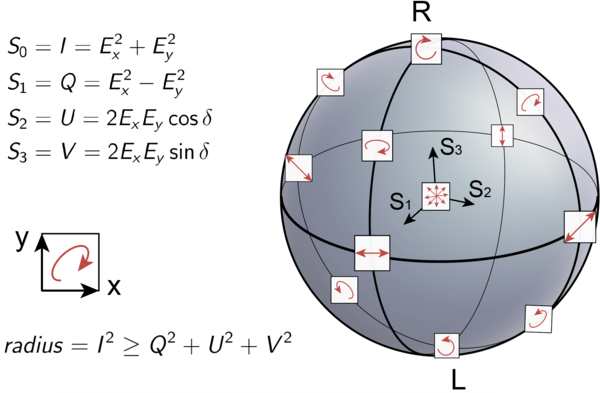
Poincaré sphere; credit: wikipedia
Synthetic observation with POLARIS
Küffmeier, Reißl et al. 2020
Perfect alignment
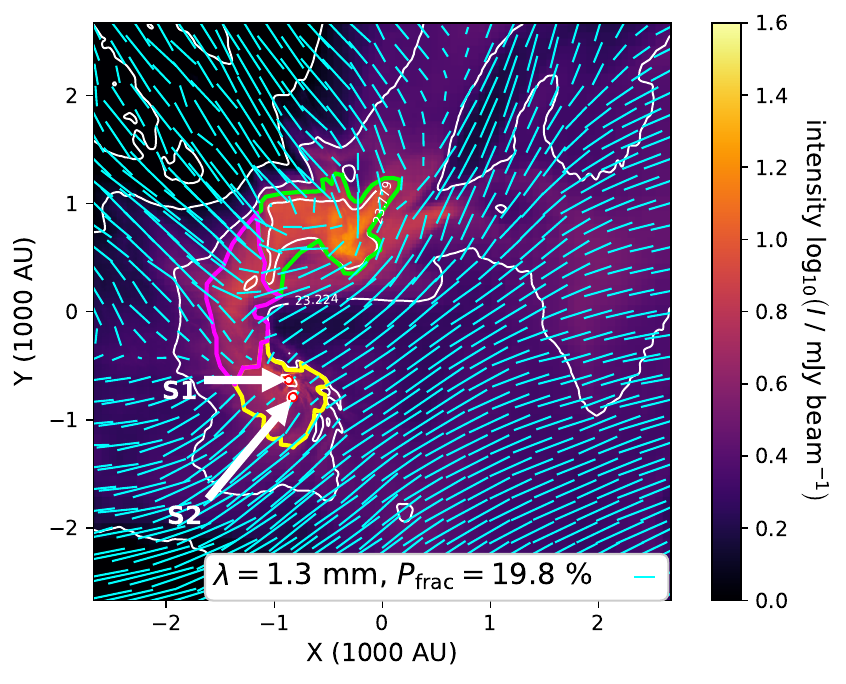

assuming perfect alignment at 1.3 mm: polarization traces magnetic field structure
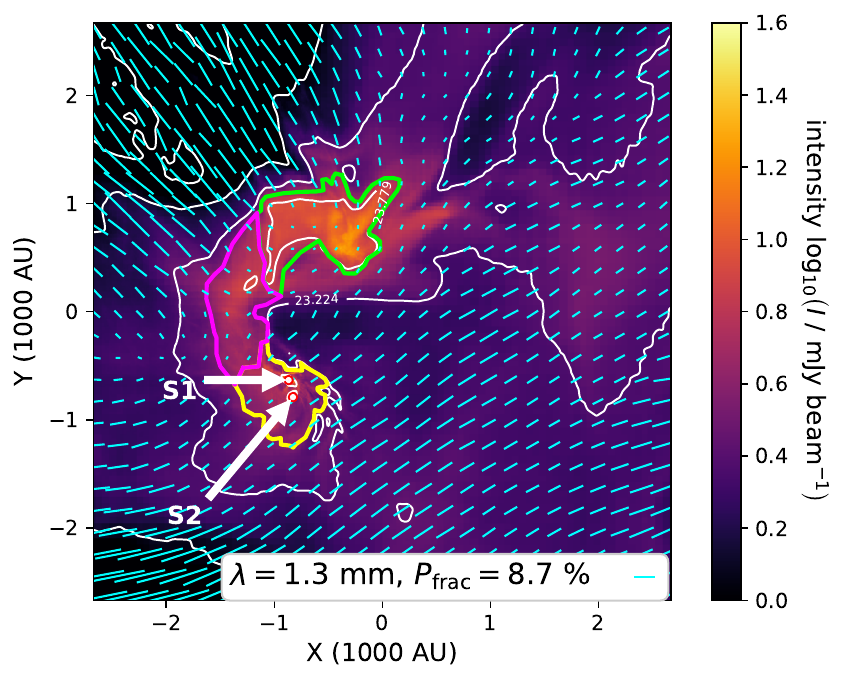
Synthetic dust polarization maps at 1.3 mm
Küffmeier, Reißl et al. 2020
Perfect alignment only

Emitted radiation
Polarization fraction in bridge:
> 20 %
Polarization fraction in bridge:
a few %

assuming perfect alignment at 1.3 mm: polarization strength is overestimated
Synthetic dust polarization maps at 1.3 mm
Küffmeier, Reißl et al. 2020

Emitted radiation
Polarization fraction in bridge:
a few %
Polarization fraction in bridge:
up to 20 %
IRAS 16293--2422
Sadavoy et al. 2018
alignment efficiency higher than efficiency produced by standard RAT alignment
(also Le Goeullec+20)
Wavelength dependence: 1.3 mm vs 53 micron

Emitted radiation
1.3 mm: good tracer of magnetic field
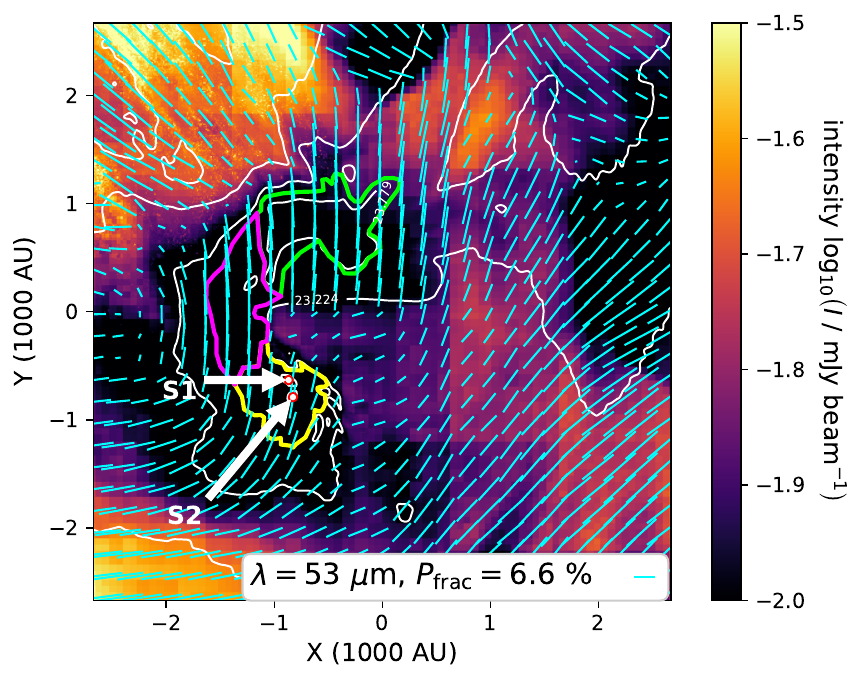
53 micron: poor tracer of magnetic field
Küffmeier, Reißl et al. 2020
Two reasons for wavelength dependence
Küffmeier, Reißl et al. 2020
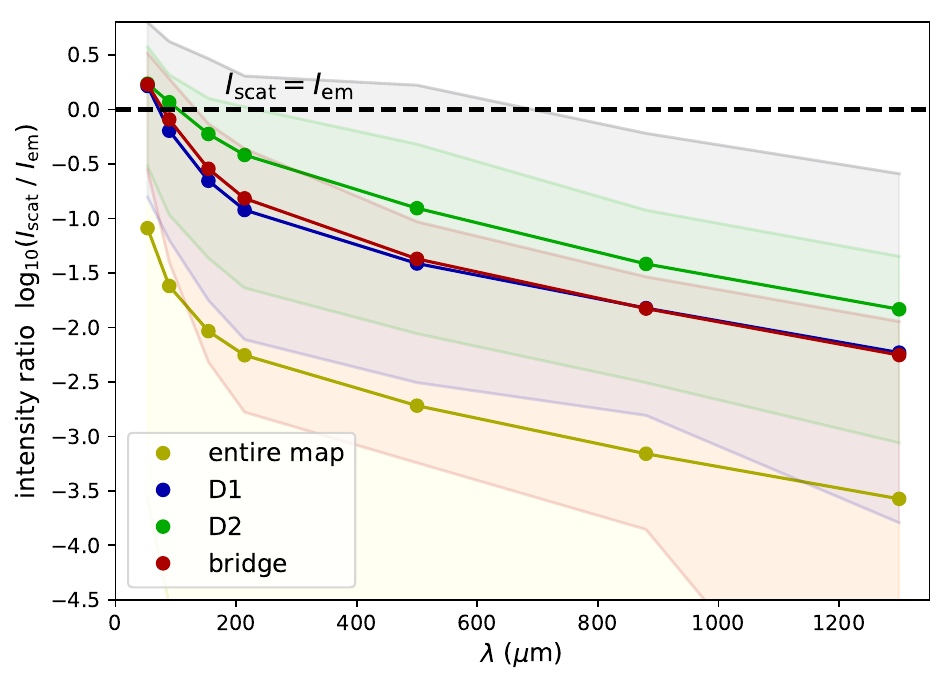
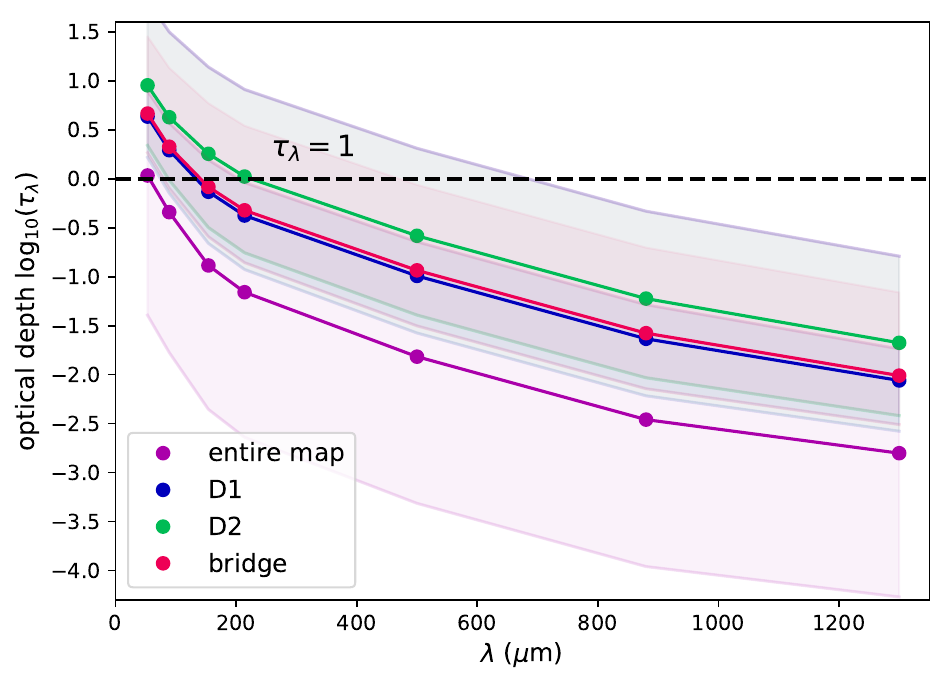
Self-scattering
Dichroic extinction
Take-away for scales beyond >100 au
< 200 micron: dichroic extinction and self-scattering; no trace of B
> 200 micron: thermal emission; linear polarization traces B
Results and outlook
Linear polarization of dust reemission at wavelength >200 micron is good tracer of magnetic field structure on scales >100 au

Goal: more synthetic polarization maps of protostellar sites
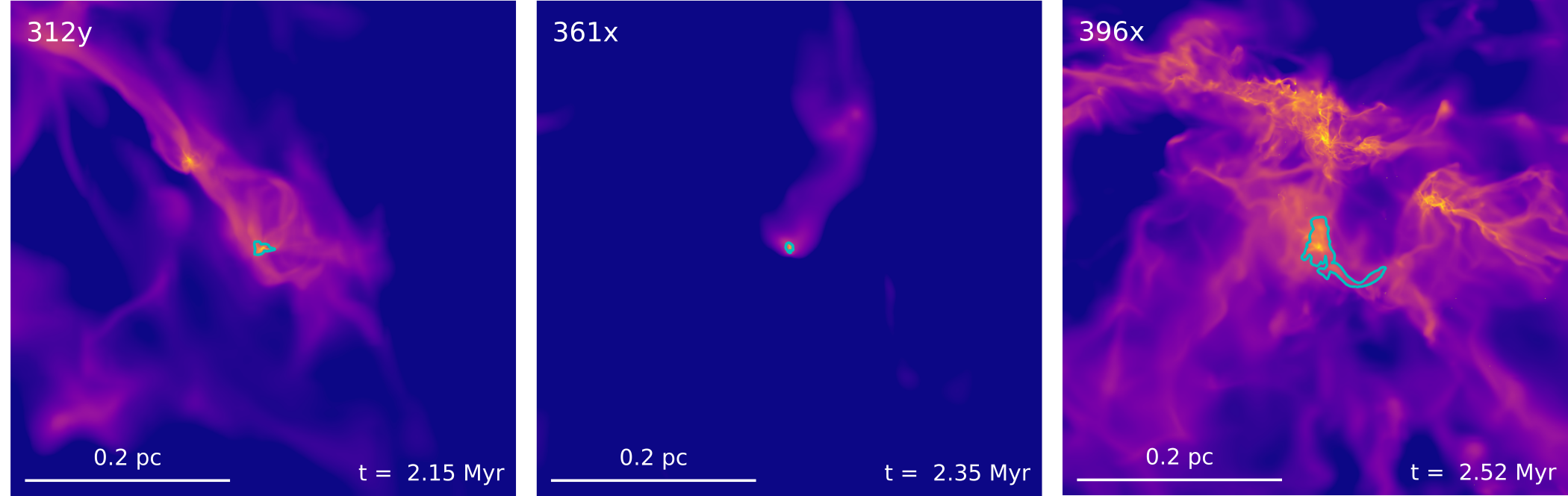
Credit: Pelkonen et al. 2021