Working with Legacy Apps: Patterns to Get Things Done

Let ME INTRODUCE MYSELF


I traveled here from Poland, specifically from Gdańsk—a city on the Baltic Sea.

I’ve been programming in PHP since 2007.

From time to time, I contribute to open-source projects;
throughout my career, I’ve made few contributions to Symfony, Doctrine, Gaufrette, and SymfonyDocs and Composer.

I am organizing polish PHP community "PHPers" meetups in Gdańsk


I work at as a tech lead, where I often help our clients work with existing (legacy) code, SOFTWARE DESIGN, SELECT ARCHITECTURES and support teamS developing their technical skillS


How do I define the legacy system?


Lack of Upgradeability: Legacy systems are typically older and may no longer be supported by the vendor. They are not regularly updated, which can lead to security and compatibility issues.

Business Critical: They are often critical to the operation of the business, as they have been developed over the years and integrate many business processes. Replacing them suddenly would be expensive and risky.

Difficult to Maintain: Legacy systems can be difficult and expensive to maintain. Often, their writing style is outdated and unreadable. Changes require a lot of debugging time.

Lack of Flexibility: These systems are typically inflexible and difficult to modify or integrate with modern technology solutions.

Security Issues: Legacy systems may have security holes that are no longer patched, exposing the company to the risk of attacks.

Dependence on Outdated Technologies: They may be dependent on technologies that are no longer used or difficult to acquire, making them difficult to maintain and develop
My Legacy STORIES

Story 1: Lease Offer Calculator

Story 1: Lease Offer Calculator

- The project was over 15 years old (migrated from svn in 2017)
- A part of the monolithic system based on PHP which was responsible for the appropriate calculation of leasing costs for given offers and contracts
- Maintenance problems, the structure changed over the years, old unused code was not removed for many years. Version control through inheritance + if - ology, many not used classes in inheritance tree
Story 1: Lease Offer Calculator

- Attempts to restructure and transfer part of the code to Laravel, unfortunately unfinished which only made the project even less understandable
- No separation of views from business logic
- Lack of sensible routing and framework (it was web app)
- High interconnection (coupling) of everything - changes in the form could change something in the calculation
- Persistence in an archaic database (FireBird)
Story 1: Lease Offer Calculator

- A system critical to the operation of the business - changes in the system or rates must be confirmed by a resolution of the management board
- 1 person who is able to maintain the system and with know how
- We decided that we rewrite only part related with calculation engine without frontend, but we have high coupling to frontend with logic as well
Story 1: Lease Offer Calculator

- Code Audit
- Event Storming
- More detailed analysis of code, with debugging of current code
- Preparation of migration plan, document solution architecture (including graphs from C4 model)
- We decide to use Parallel Model pattern - https://martinfowler.com/eaaDev/ParallelModel.html
how we worked on the project
Story 1: Lease Offer Calculator
Story 1: Lease Offer Calculator

Parallel model
Story 1: Lease Offer Calculator
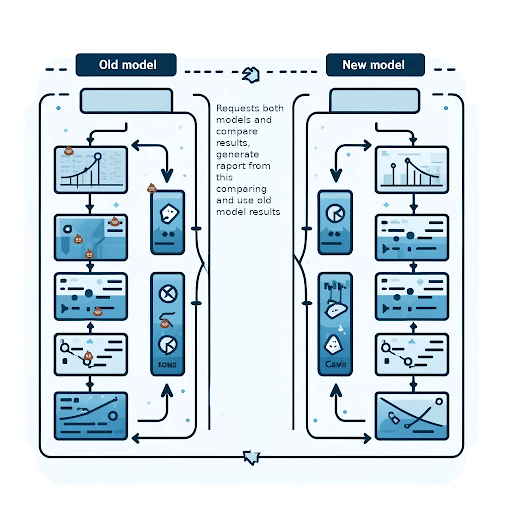
Pattern description: Embedded Parallel Models involves creating multiple models in one application at the same time. These models results can be compared, for example, taking into account different architectural drivers, choose the right one for your needs. Models can be temporary. In my case, this pattern was to enable gradual migration of data and functionality without interrupting the system, and comparing the results returned by the new model to what is returned by the old model.
https://martinfowler.com/eaaDev/ParallelModel.html
Story 1: Lease Offer Calculator

WHY did we use this pattern in this story?
Story 1: Lease Offer Calculator
- The ability to test on production data by comparing old and new results - parameters mapped to the input of the old and new models, and comparing the results
- after obtaining 100% compliance, the ability to switch the model to the new one
- The ability to separate the calculator to a new context (application), without rewrite old code and model logic
Story 1: Lease Offer Calculator

Story 1: Lease Offer Calculator
https://tinyurl.com/iteo-legacy-calculator

Story 1: Lease Offer Calculator

How did this story end?
Story 1: Lease Offer Calculator
- New calculator engine model added to production after 6 months of work, then started to compare results. First months focused on debugging, and be able to separate logic from forms and learn legacy system in the team (3 ppl), then we implemented mechanism to compare results between old and new model
- Legacy model was constantly being updated so we had to port those updates as well
- After like 9 months we connected fully working new model to production, and after months we switch to new model
- Client decided that he want to rewrite frontend for that solution (using react, laravel and inertiajs)
Story 2: ATS (APPLICANT TRACKING SYSTEM) with integration to the Electronic Customer Service Office

Story 2: ATS with ECSO integration

- The project was over 15 years old
- A monolithic system that served HR agencies
- Proof of concept created quickly by people without much experience
- Very difficult to maintain; adding new features took a long time
- A business development system—many ideas to implement, some funded by EU grants
Story 2: ATS with ECSO integration

- No proper routing or framework, no composer (index.php and include_once mabo jumbo)
- Only one person is capable of maintaining the system (but not efficiently)
- Our task: introduce the ECSO module without extensive integration into the existing solution (maintained by another person)
- We decided to use ACL (Anti-corruption layer)
Story 2: ATS with ECSO integration

- Code Audit
-
Detailed debugging of existing code
-
BDD approach to describing ECSO features
-
Identification of places where we can hook in to integrate with the old system via the so-called ACL (Anti-corruption Layer)
-
Debugging and understanding the old model
-
Extensive layer of functional tests using characterization testing approach
how we worked on the project
Story 2: ATS with ECSO integration

The goal of characterization tests is to help developers verify that the modifications made to a reference version of a software system did not modify its behavior in unwanted or undesirable ways.
We test all behaviors we want to rewrite in existing/legacy system even if behaviors seems to not working as we would expect from them
characterization testing Approach
Story 2: ATS with ECSO integration

The Anti-corruption Layer (ACL) creates a layer isolating the old system from the new one, protecting it from potential “corruption” by unwanted dependencies and differences in data models. (Check also Bubble Context)
ACL - Anti-corruption Layer
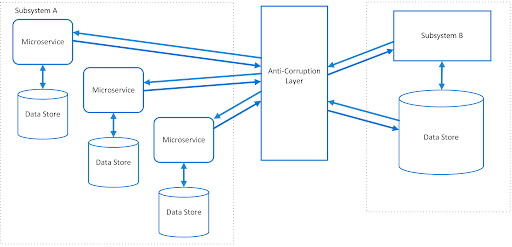
Story 2: ATS with ECSO integration

WHY did we use this pattern in this story?
- The ability to write new code and synchronize with the old system via API, direct database access, or message queues (in our case database)
- No need to worry excessively about changes in the legacy portion outside of our context (with was done by freelancer developer in our case)
Story 2: ATS with ECSO integration

https://tinyurl.com/iteo-legacy-acl

Story 2: ATS with ECSO integration

How did this story end?
- We able to provide ECSO module after few months
- Older parts was causing more issues so later we rewrite those as well
- We finish with few smaller context but we use modular instead of microservices cause we have small teams and want to maintains all bubble context in one repository and via one team
- Right now system is still maintained and working quite fine
Story 3: BfF (Backend for frontend) API Modernization

Story 3: BFF API MODERNIZATION

- The project is over 7 years old
- BFF (Backend For Frontend) written in Symfony 3.x
- Access available via both REST and GraphQL
- Uses API Platform
- The project is primarily CRUD-based
- Significant performance issues—had to introduce Varnish as an HTTP proxy cache
- Numerous annotations/attributes to control serialization
Story 3: BFF API MODERNIZATION

- The system could be maintained by several people
- Lots of integrations
- Our task: Add new entrypoints and handle the most not performant ones
- We decided to use Stranger Fig Pattern

- Code Audit
-
Profiling with blackfire
-
Create new entrypoint in new Symfony application and move it on infrastructure layer (nginx proxy) - Stranger Fig Pattern
-
Rewrite old not performant entrypoints to new application, use event driven architecture with async messanger
-
Provide CQRS in some model parts, to be able to write performant indexes read model without changing write model
how we worked on the project
Story 3: BFF API MODERNIZATION

Method of gradually replacing the old system with a new one by slicing off and replacing specific functionalities. It ensures continuous operation and minimizes risk
In our case using infrastructure, we could redirect particular REST entrypoints to the new application.
Strangler Fig Application
Story 3: BFF API MODERNIZATION
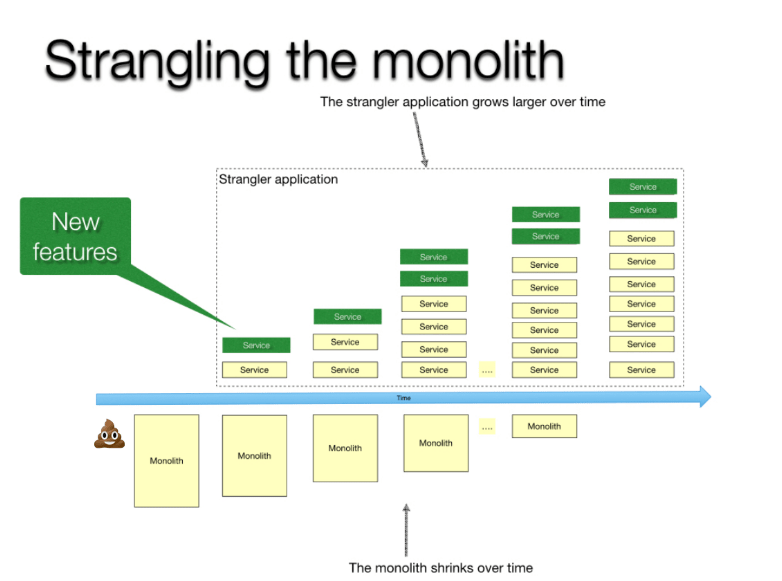

Method of gradually replacing the old system with a new one by slicing off and replacing specific functionalities. It ensures continuous operation and minimizes risk
In our case using infrastructure, we could redirect particular REST entrypoints to the new application.
Strangler Fig Application
Story 3: BFF API MODERNIZATION


WHY did we use this pattern in this story?
- The ability to rewrite parts of the web application without integrating into the current system while addressing business needs (lower cost)
- We could preserve the contract of the old application but replace entrypoint responsible for generate that contract, so we can for example rewrite non performant entrypoints in new application
Story 3: BFF API MODERNIZATION

Story 3: BFF API MODERNIZATION
https://tinyurl.com/iteo-legacy-strangler


How did this story end?
- We create new functionality
- Provide newer version of Symfony and PHP our new application
- Install all statistic checkers like PHPStan, PHPCSFixer to maintainer higher quality of code
- Handle for good performances using materialized views in postgresql, async messanger and CQRS
- Fixed performance issues for rewritten entrypoints
- Have some issues with integration with old db layer but be able to move some part to our side
- Sadly not be able to rewrite all entrypoints from old/legacy app, some of them was good enough and it wasn't worth to rewrite
Story 3: BFF API MODERNIZATION
THAT aLL MY STORIES FOR TODAY

THANK YOU / DZIĘKUJE!

https://www.linkedin.com/in/leszek-prabucki/


https://phpc.social/@l3l0