Intro to SQL


https://slides.com/lizh/gdi-intro-to-sql
I'm LizTheDeveloper
17+ years in tech
I've taught over 3500 people to code in person
& nearly a million online
I've been a CTO for hot, VC-funded silicon valley startups twice,
I helped found Hackbright Academy and wrote the curriculum for Galvanize's Web Development Immersive
I wrote the fraud prevention system for 8 of the top 10 banks in the country
and yeah, people still ask me if I'm technical.
No one is perfect
Even though I'm awesome I have definitely:
Taken down production at least once at every job
Crashed a payments server during peak purchase hours
Dropped the
Not had a backup
Faiza Khan
Professor and Data Scientist
Taught Statistics and Probability for nearly 3 years, to over 700 data scientists
Transitioned from Academia to Tech through Data Science
Welcome!
Girl Develop It is here to provide affordable and accessible programs to learn software through mentorship and hands-on instruction.
We have a Code of Conduct here
In Summary:
- You're important and valued
- Be excellent to each other
- Help everyone out, it helps you learn!

Objectives
- Describe what a Relational Database is and what SQL is used for
- Create, Read, Update and Delete with SQL
- Aggregations with SQL
- Select related data in multiple tables
- Create and Read a SQL Schema
You'll revisit these!

Relational Databases
What are they?
What makes them "relational"?

Relational Databases
Tables
| ID | Name | Phone | Zip | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Liz | liz@liz.com | 555-2323 | 94110 |
| 2 | Tyler | tyler@teb.com | 555-3232 | 94110 |
| 3 | Matt | matt@williams.com | 555-4455 | 94110 |
Relational Databases
Relationships
| ID | Name | Phone | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Liz | liz@liz.com | 555-2323 |
| 2 | Tyler | tyler@teb.com | 555-3232 |
| 3 | Matt | matt@williams.com | 555-4455 |
| ID | User_ID | Zip |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 94110 |
| 2 | 1 | 94102 |
| 3 | 2 | 94110 |
| 4 | 2 | 94114 |
Schemas
CREATE TABLE users (
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
name TEXT,
email VARCHAR(256),
phone VARCHAR(12)
);
CREATE TABLE zip_codes (
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
user_id INT FOREIGN KEY,
zip VARCHAR(10)
);Defining A Table

Objectives
- Describe what a Relational Database is and what SQL is used for
- Create, Read, Update and Delete with SQL
- Aggregations with SQL
- Select related data in multiple tables
- Create and Read a SQL Schema
You'll revisit these!

Structured Query Language
| Create | INSERT |
|---|---|
| Read | SELECT |
| Update | UPDATE |
| Delete | DELETE |

Structured Query Language


Structured Query Language
SELECT id, name, email, phone FROM users;SELECT [ a list of column names] FROM [a table name]
| ID | Name | Phone | Zip | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Liz | liz@liz.com | 555-2323 | 94110 |
| 2 | Faiza | faiza@khan.com | 555-3232 | 94110 |
| 3 | Kelly | kelly@tran.com | 555-4455 | 94110 |
Getting Data Out
Structured Query Language
SELECT id, name, email, phone FROM users
WHERE id = 1;SELECT [ a list of column names] FROM [a table name]
WHERE [some condition is true]
| ID | Name | Phone | Zip | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Liz | liz@liz.com | 555-2323 | 94110 |
Specific Data Out
Structured Query Language
INSERT INTO users (id, name, email, phone)
VALUES (5, 'Aaron', 'aa@ron.com', '555-2156');INSERT INTO [ a table name ] ([a list of column names])
VALUES ([comma-separated expressions in the same order as the column names])
Putting Data In
Demo time
http://sqlfiddle.com/#!9/974537
CRUD Queries
5-8 min
play along!
Practice Time
Let's Query Real Data
https://data.stackexchange.com/stackoverflow/query/new
The Stack Overflow Dataset
5 min
Find Out:
1. Find the post with id 2162271
2. Find posts that have a score higher than 25
3. Find posts created 3 years ago today
To limit queries:
SELECT TOP 10 * FROM posts;Objectives
- Describe what a Relational Database is and what SQL is used for
- Create, Read, Update and Delete with SQL
- Aggregations with SQL
- Select related data in multiple tables
- Create and Read a SQL Schema
You'll revisit these!

Aggregations
Count the number of rows
SELECT COUNT(*), zip_code FROM users
GROUP BY zip_code; Aggregations
Many Functions
VAR(*) / OVERnumber of rows that match a grouping
AVG(*)average of values in a grouping
SUM(*)sum of values
MAX(*) / MIN(*)COUNT(*)maximum / minimum value in values
STDEVP(*)standard deviation of populations
statistical variance (OVER range)
Ordering
ORDER BY
Which column to order the query by
ASCLowest value first
DESCHighest value first
ORDER BYSELECT count(zip_code), zip_code from users
GROUP BY zip_code
ORDER BY count(zip_code) DESC;What zip code has the most users?
Aggregations
WHERE is to rows returned without a group by statement
as HAVING is to rows returned with a GROUP BY statement
HAVING
SELECT DeptID, SUM(SaleAmount)
FROM Sales
WHERE SaleDate = '01-Jan-2000'
GROUP BY DeptID
HAVING SUM(SaleAmount) > 1000Demo
http://sqlfiddle.com/#!9/974537/9
Group By
5-8 min
play along!
Practice Time
Let's Query Real Data
https://data.stackexchange.com/stackoverflow/query/new
The Stack Overflow Dataset
5 min
Practice Time
5 min + 10 min stretch break!
Find Out:
1. 10 oldest posts / 10 newest posts
2. count of posts on this day 3 years ago
3. count of posts every day for the last 10 days
4. the count of all answers for posts in the last 10 days
When you're done, stand up and stretch up as high as you can!
🙆♀️
Objectives
- Describe what a Relational Database is and what SQL is used for
- Create, Read, Update and Delete with SQL
- Aggregations with SQL
- Select related data in multiple tables
- Create and Read a SQL Schema
You'll revisit these!

JOINs
| id | username |
|---|---|
| 1 | coolguy86 |
| 2 | vampgurl |
| id | user_id | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | coolguy86@aol.com |
| 2 | 2 | vampgurl@aol.com |
| 3 | 2 | karen.smith@gmail.com |
SELECT users.username, emails.email FROM users
INNER JOIN emails ON users.id = emails.user_id;JOINs
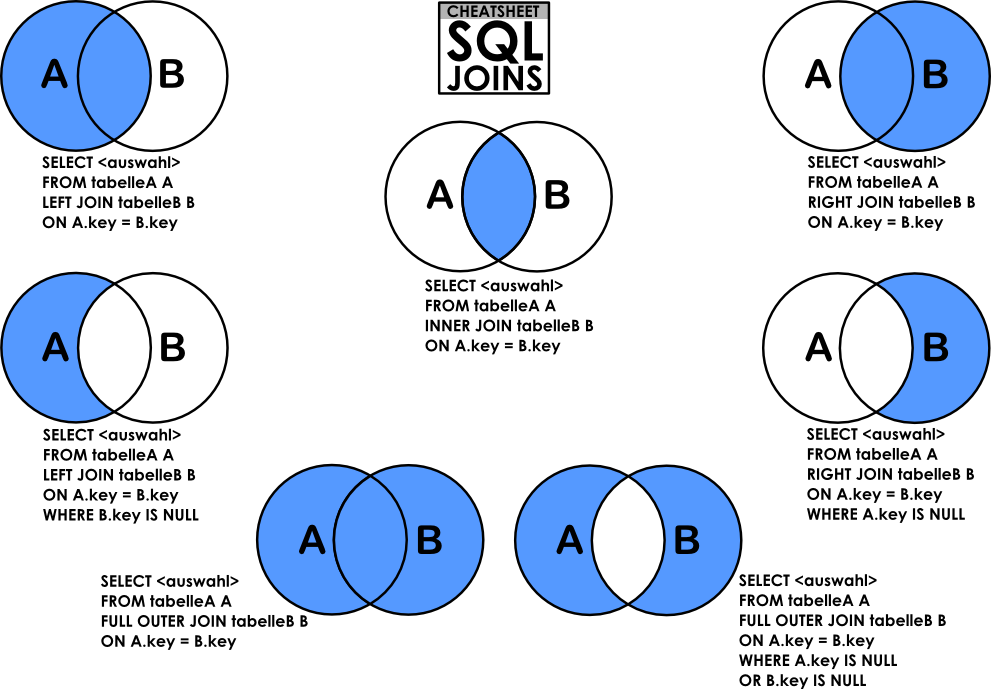
INNER vs OUTER JOINs
Inner = a record is present in both tables
Outer = a record is present in either table
SELECT users.name, zip_codes.zip_code FROM users
INNER JOIN zip_codes ON users.id = zip_codes.user_idSELECT users.name, zip_codes.zip_code FROM users
OUTER JOIN zip_codes ON users.id = zip_codes.user_idAll users that have a zip code
All users, and if they have a zip code, their zip code
Left vs Right JOINs
SELECT users.name, zip_codes.zip_code FROM users
LEFT JOIN zip_codes ON users.id = zip_codes.user_idSELECT users.name, zip_codes.zip_code FROM users
RIGHT JOIN zip_codes ON users.id = zip_codes.user_idAll users and their zip codes
All zip codes and their users
FULL JOINs
Get rows that have no corresponding row in the other table
SELECT users.name, users.id, zip_codes.id, zip_codes.zip_code FROM users
FULL OUTER JOIN zip_codes ON users.id = zip_codes.user_id
WHERE zip_codes.user_id IS NULL;Find users with no zip code and zip codes with no user
Demo
http://sqlfiddle.com/#!9/974537/10
JOINs
5-8 min
play along!
| 1 SELECT | selects variables |
| 2 FROM | opens datasets |
| 3 WHERE | restricts observations |
| 4 GROUP BY | groups observations |
| 5 HAVING | restricts groups |
| 6 ORDER BY | sorts results |
SQL clauses
required order
Practice / Homework
- Practice:
- https://sqlzoo.net/
- https://pgexercises.com/
- https://sqlbolt.com/lesson/select_queries_introduction
- https://www.datacamp.com/courses/intro-to-sql-for-data-science
- Create your own examples: https://sqlfiddle.com/
- Connect to a real database: https://franchise.cloud
- https://enki.com/ - an app I made with practice questions :D
Homework 2
-
Practice Datasets:
- Stack Overflow Dataset (and challenges)
- Sales Data Example
- https://www.hackerrank.com/domains/sql
- Create your own examples: https://sqlfiddle.com/
Pros:
Ask for access to any SQL database you know about at work and try to answer questions using it
(social engineering tip: say it's for a class you're taking! 😉)
Thanks!
Thanks To:
Faiza Khan
Kelly Tran
Sarah Kwak
Carly Fujiyoshi
Everyone who came to class on time
Everyone who was late also I guess