Introducing
The stylish Node.js middleware engine
for AWS Lambda

Luciano Mammino (@loige)

Munich, 9 Dec 2017

Luciano... who?
... just a Fullstack developer

The problem with Lambdas
exports.myLambda = function (
event,
context,
callback
) {
// get input from event and context
// use callback to return output or errors
}Anatomy of a Node.js lambda on AWS
(event, context, callback) => {
// decrypt environment variables with KMS
// deserialize the content of the event
// validate input, authentication, authorization
// REAL BUSINESS LOGIC
// (process input, generate output)
// validate output
// serialize response
// handle errors
}
A typical "REAL" Lambda function
LOTS of BOILERPLATE 😓
The solution
npm install middy
Usage
const middy = require('middy')
const { middleware1, middleware2, middleware3 } = require('middy/middlewares')
const originalHandler = (event, context, callback) => {
/* your business logic */
}
const handler = middy(originalHandler)
handler
.use(middleware1())
.use(middleware2())
.use(middleware3())
module.exports = { handler }1. define handler
2. "middify" handler
3. attach middlewares
4. export "middyfied" handler
const middy = require('middy')
const { urlEncodedBodyParser, validator, httpErrorHandler } = require('middy/middlewares')
const processPaymentHandler = (event, context, callback) => {
const {
creditCardNumber,
expiryMonth,
expiryYear,
cvc,
nameOnCard,
amount
} = event.body
// do stuff with this data ...
return callback(null,
{ result: 'success', message: 'payment processed correctly'}
)
}
const inputSchema = {
// define validation schema here ...
}
const handler = middy(processPaymentHandler)
.use(urlEncodedBodyParser())
.use(validator(inputSchema))
.use(httpErrorHandler())
module.exports = { handler }Handler
Attach middlewares
Export enhanced handler
Why?
- Simplify code
-
Reusability
- input parsing
- input & output validation
- output serialization
- error handling
- ...
- Focus MORE on business logic
How it works
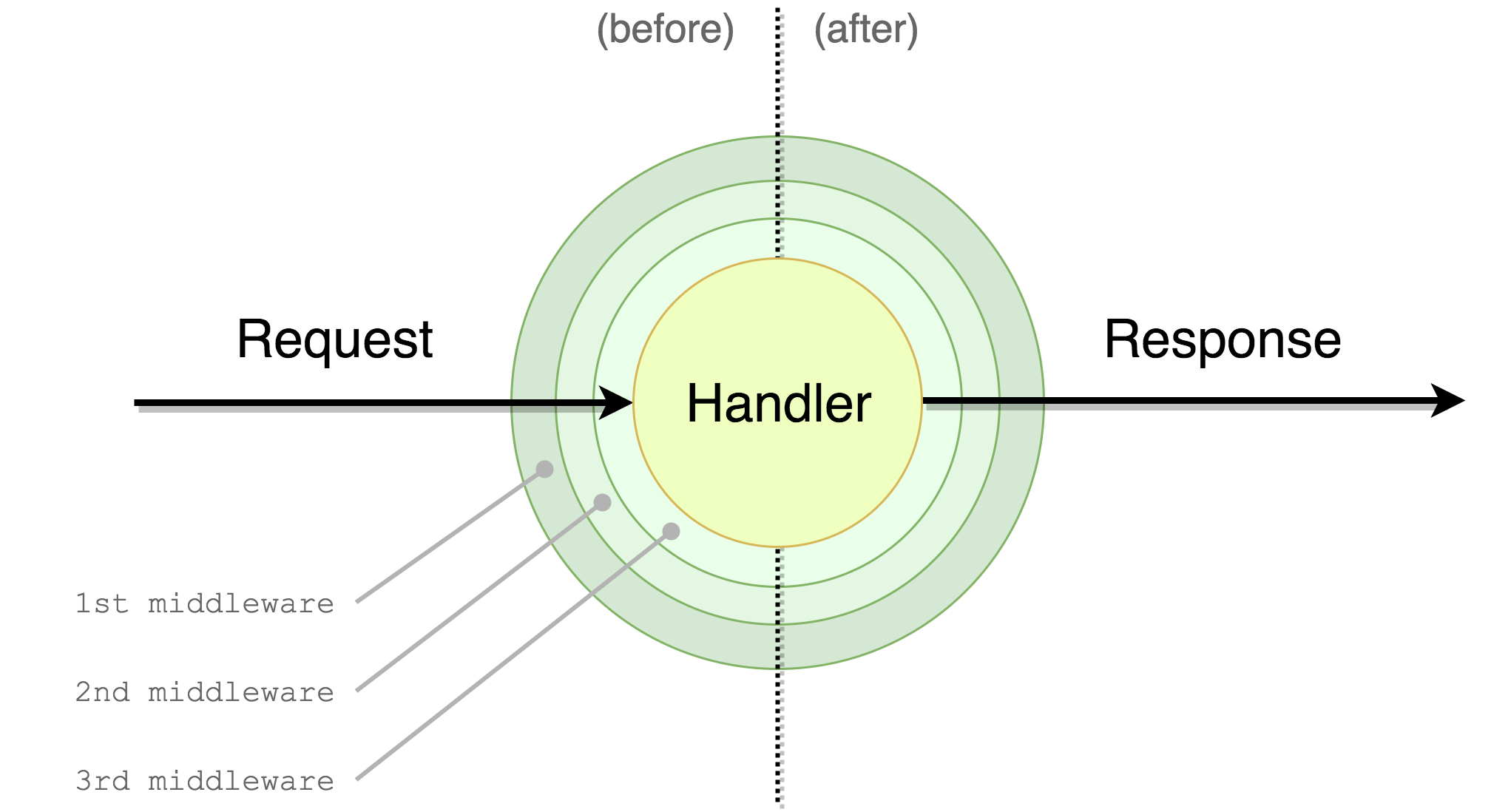
Execution order

- middleware1 (before)
- middleware2 (before)
- middleware3 (before)
- handler
- middleware3 (after)
- middleware2 (after)
- middleware1 (after)









When an error happens...
- Flow is stopped
- First middleware implementing `onError` gets control
- It can choose to handle the error, or delegate it to the next handler
- If the error is handler a response is returned
- If the error is not handled the execution fails reporting the unhandled error
Writing a middleware
const myMiddleware = (config) => {
// might set default options in config
return ({
before: (handler, next) => {
// might read options from `config`
},
after: (handler, next) => {
// might read options from `config`
},
onError: (handler, next) => {
// might read options from `config`
}
})
}
module.exports = myMiddlewareInline middlewares
const middy = require('middy')
const handler = middy((event, context, callback) => {
// do stuff
})
handler.before((handler, next) => {
// do something in the before phase
next()
})
handler.after((handler, next) => {
// do something in the after phase
next()
})
handler.onError((handler, next) => {
// do something in the on error phase
next()
})
module.exports = { handler }Currently availble middlewares
JSON Body Parser
Url Encoded Body Parser
Validator
HTTP Error Handler
CORS
S3 Key Normalizer
Do Not Wait for event loop
Support for async/await handlers (just return, don't need to use callback)
XML Body parser
API Gateway Event normalizer
In development
That's all folks
(for now!)