PhD Project Proposal:
Oscillations matter: identifying networks of dynamically expressed genes
Supervisors:
Luisa Cutillo, School of Mathematics, UoL
David Westhead, School of Molecular and Cellular Biology, UoL
Potential External Collaborators:
- Elli Marinopoulou and Nancy Papalopulu, University of Manchester (Papalopulu's Lab)
- MathWorks

- Measures the distribution of expression levels for each gene across a population of cells
- Allows to study new biological questions in which cell-specific changes in transcriptome are important, e.g. cell type identification, heterogeneity of cell responses, stochasticity of gene expression, inference of gene regulatory networks across the cells.
Focus on a single kind of omics:
Single Cell RNA sequencing
Focus on a specific kind of Networks:
genes co-oscillation networks
Why are oscillations important?
Oscillations in gene expression play a critical role in many biological developmental processes (eg. the circadian clock, cell cycle, neural development etc)
technologies for monitoring expression oscillations are limited also for well known processed like cell-cycle
Why the need for a model development?
Oscillators:
an alternative view on gene expression

Example
two co-oscillating genes and the corresponding cell state
mRNA is collected at time T from (unsynchronised) cells in varying states
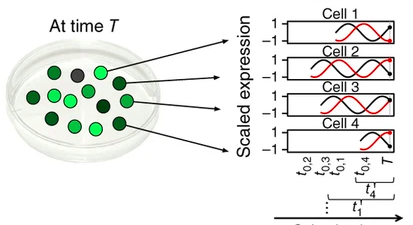
Calendar Time


Background
- Build on the approach by Leng et all. 2015 (oscope)
- Compute pairwise similarity between gene expressions
- Cluster genes in the resulting network
- Satistically validate the communities for further investigation


OscoNet: inferring oscillatory gene networks
Luisa Cutillo, Alexis Boukouvalas, Elli Marinopoulou, Nancy Papalopulu & Magnus Rattray
BMC Bioinformatics volume 21, Article number: 351 (2020)
Identification of genes with oscillatory expression in glioblastoma: the paradigm of SOX2
Richard Zhiming Fu, Oliver Cottrell, Luisa Cutillo, Andrew Rowntree,Zsolt Zador,Heiko Wurdak, Nancy Papalopulu, and Elli Marinopoulou, Sci Rep. 2024; 14: 2123. Published online 2024 Jan 24.
-
quiescent glioblastoma (GBM) stem cells (GSCs) play an important role in re-establishing the tumour
-
protein oscillations can control the exit from quiescence of neural stem cells
-
We identified a list of potential oscillators, including SOX2
-
We verified to oscillate in quiescent GSCs.

single cell RNA-seq analysis of adult and paediatric IDH-wildtype Glioblastomas (Neftel C, et al. Cell. 2019)
Starting dataset
Open problems
- Relax the assumption of homogenous cells population: assess the effect of population heterogeneity on the OscoNet performances
- Handle Data Sparsity within the model: assess how the inclusion of lowly-expressed genes affects the outcomes
- Integrate metadata (eg genes BP attributes) in the Network estimation and subsequent clustering
- Infer the period of oscillators using as prior the period of known oscillators (very few if not cell cycle!)
- Use the identified network of oscillatory genes to predict patients survival or tumour subtypes?
Questions?