Mateo Sanabria ArdilaConflict-Free Replicated Data Type (CRDT)
Les't remember some CS foundation
The CAP THEOREM
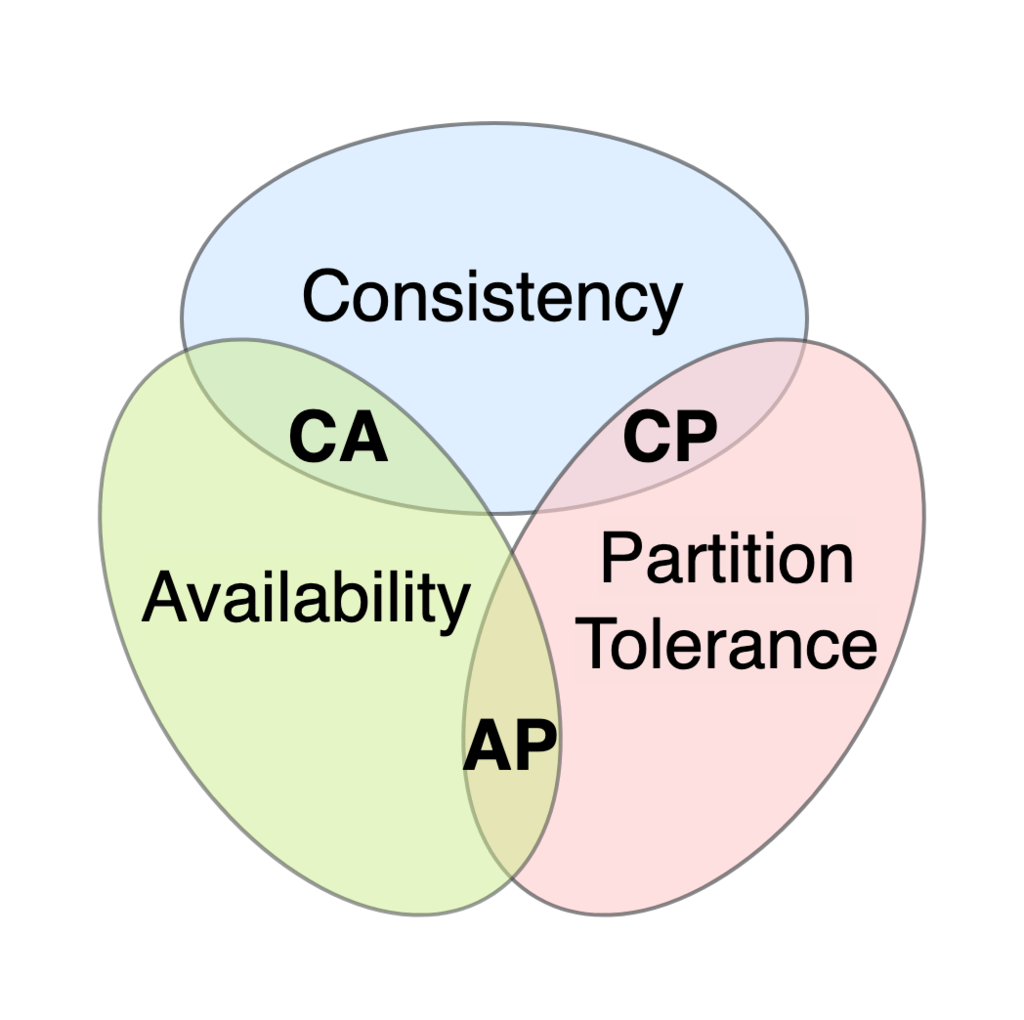
(CAP) a distributed data store can provide only two of the following three guarantees:
- Consistency: Every read receives the most recent write or an error
-
Availability: Every request receives a (non-error) response, without the guarantee that it contains the most recent write
-
Partition Tolerance: The system continues to operate despite an arbitrary number of messages being dropped (or delayed) by the network between nodes
Consistency
Availability
Partition Tolerance
Achieving internet-scale distribution with low latency and high availability
Strong Consistency
-
Requires coordination for executing operations.
-
Challenges arise during network partitions or failures.
Weak Consistency
-
Allows temporary divergence among replicas. -
Requires merging concurrent updates into a common state.
Weak Consistency WC
Strong Consistency SC
Eventual Consistency EC
Eventual Consistency
Replicas will eventually converge to the same final value if no further updates are submitted:
Eventual Delivery An update sent to any correct replica is guaranteed to be eventually received by all correct replicas. Convergence Correct replicas, having received the same updates, will eventually reach an equivalent state.
Weak Consistency WC
Strong Consistency SC
Eventual Consistency EC




Weak Consistency WC
Strong Consistency SC
Eventual Consistency EC

?
-
Some EC systems execute updates, identify conflicts later, and roll back, leading to wastage.
-
Resolving conflicts often requires consensus among replicas.
-
A stronger condition is needed to improve efficiency and minimize wastage in EC systems.
Eventual Consistency
strong Eventual Consistency (SEC)
Strong Convergence Correct replicas that have delivered the same updates have equivalent stateEventualConsitency \wedge StrongConvergence \equiv SEC

Conflict-free Replicated Data Types (CRDT)
Is an abstract data type designed for replication at multiple nodes with the following properties:
-
Any replica can be modified without coordination with others. -
Once any two replicas have received the same updates they must share the same state.
CRDTs use commutative operations to ensure strong eventual consistency, eliminating the need for synchronization and achieving high availability and low latency.
Availability + Partition Tolerance + SEC
Operation-based CRDTs

State-based CRDTs
defmodule GSet do
defstruct elements: MapSet.new()
def new(), do: %GSet{}
def add(set, element) do
%GSet{set | elements: MapSet.put(set.elements, element)}
end
def lookup(set, element) do
MapSet.member?(set.elements, element)
end
def compare(set1, set2) do
MapSet.subset?(set1.elements, set2.elements)
end
def merge(set1, set2) do
%GSet{elements: MapSet.union(set1.elements, set2.elements)}
end
endstate
based
CRDT
defmodule CounterCRDT do
defstruct value: 0
def new(), do: %CounterCRDT{}
def increment(counter, amount \\ 1) do
%CounterCRDT{counter | value: counter.value + amount}
end
def decrement(counter, amount \\ 1) when counter.value
>= amount do
%CounterCRDT{counter | value: counter.value - amount}
end
endOperation
based
CRDT
Complex Crdts
Crdts challenges
-
Interleavings
-
Byzantine Faults
-
...
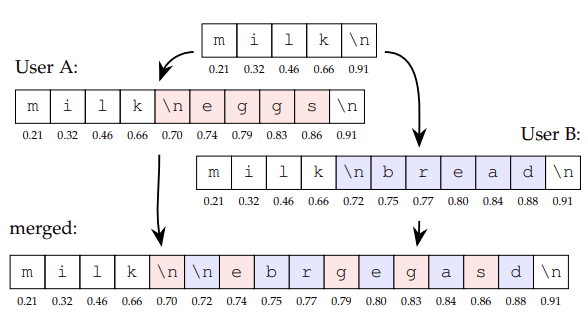
INTERLEAVING ANOMALIES