
Matt Hale
Director, School of Interdisciplinary Informatics
Director, NebraskaCYBER
Associate Professor of Cybersecurity
Introduction to Containers
CYBR 8470 - Secure Web Development
slides.com/matthale/cybr8470-containers
Today
- What Are Containers?
- Key Concepts
- Use Cases
- Benefits
- Containers vs Virtual Machines
- Migrating Apps to Containers
- Why migrate?
- Docker Overview
- Migration steps
- Challenges & Best Practices
- Infrastructure as Code (IaC)
- Example containerization

slides.com/matthale/cybr8470-containers
What are Containers?

slides.com/matthale/cybr8470-containers
Definition
Lightweight, standalone packages encapsulating an application and its dependencies.

slides.com/matthale/cybr8470-containers
What are Containers?

Isolation
- Provides an isolated environment for applications.
- Prevents conflicts between different software components.
Portability
- Runs uniformly across various environments.
- From developer’s laptop to production servers.
Scalability
- Easily replicated and scaled to handle varying loads.
- Ideal for modern, scalable applications.

slides.com/matthale/cybr8470-containers
What are Containers?: Key Concepts
Microservices Architecture: Breaking down applications into smaller, manageable services.
DevOps and CI/CD Pipelines: Streamlining development, testing, and deployment processes.
Hybrid and Multi-Cloud Deployments: Ensuring consistency across different cloud providers and on-premises environments.

slides.com/matthale/cybr8470-containers
What are Containers?: Use Cases
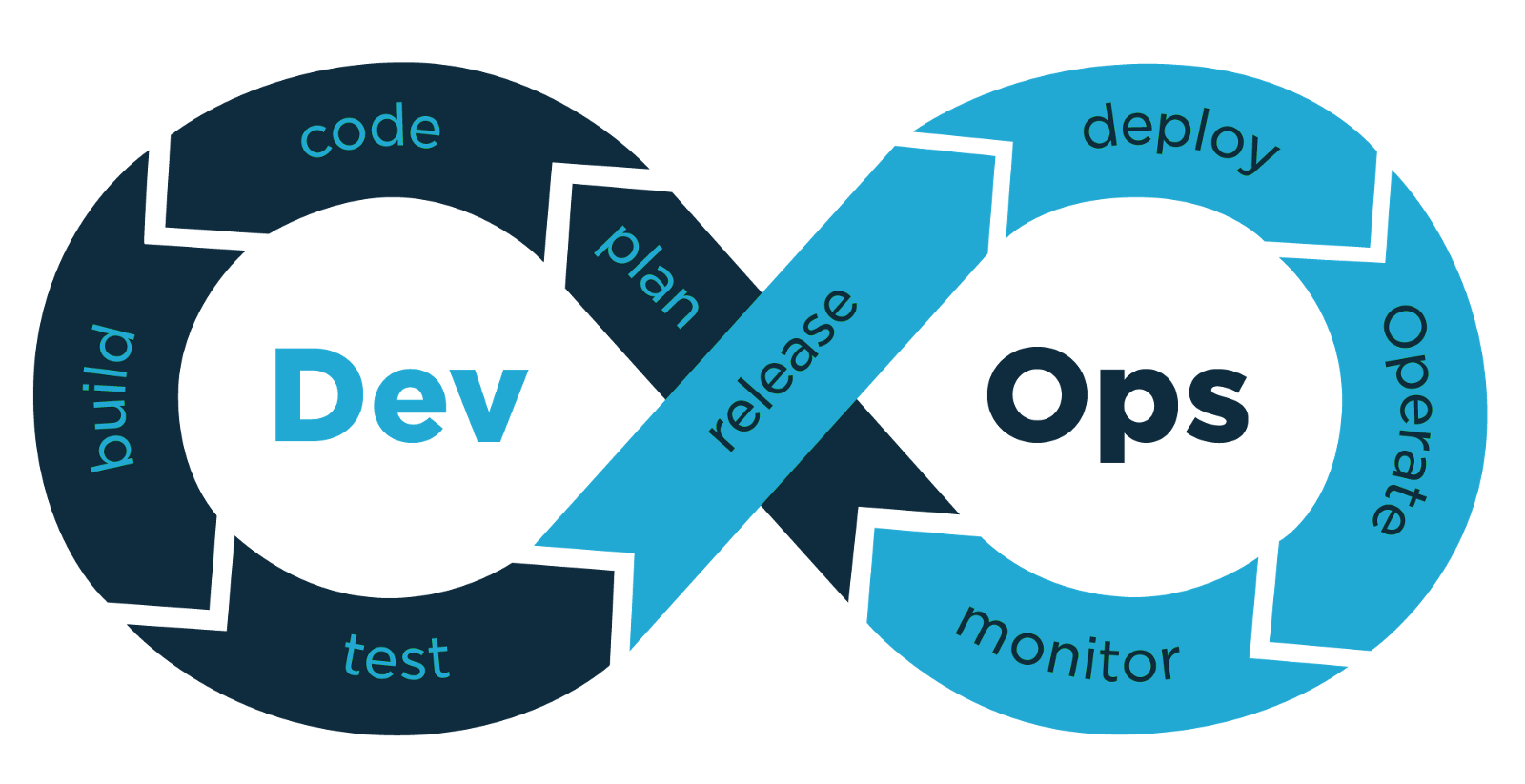
Consistency Across Environments:
Eliminates "it works on my machine" issues.
Resource Efficiency:
Consume fewer resources than VMs.
Rapid Deployment:
Facilitate continuous integration and deployment (CI/CD).
Simplified Maintenance:
Easy to update or replace containers without affecting the host.

slides.com/matthale/cybr8470-containers
What are Containers?: Benefits of containers
|
Feature |
Containers |
Virtual Machines (VMs) |
|---|---|---|
|
Isolation Level |
OS-level isolation |
Hardware-level isolation |
|
Resource Efficiency |
Lightweight, share host OS |
Heavier, each VM includes a full OS |
|
Startup Time |
Seconds |
Minutes |
|
Portability |
Highly portable across environments |
Less portable, dependent on hypervisor |

slides.com/matthale/cybr8470-containers
What are Containers?: Containers vs VMs
Migrating Apps to Containers

slides.com/matthale/cybr8470-containers
Enhanced Portability: Containers ensure applications run consistently across various environments.
- This helps with testability and repeatability.
- It makes testing 'at home' the same as testing in production.
Improved Scalability: Easily scale applications horizontally by adding more container instances.
Resource Efficiency: Optimize resource usage, reducing costs and improving performance.
Faster Deployment: Accelerate the development lifecycle with quicker deployment and rollback capabilities.
Migrating apps to Containers: Why Migrate?

slides.com/matthale/cybr8470-containers
Most widely used containerization platform.
Key Components:
- Docker Images: Read-only templates that define the application and its environment. Images can be versioned and stored in repositories like Docker Hub.
- Docker Containers: Running instances of Docker images. Containers can be started, stopped, moved, and deleted using Docker commands.
- Dockerfile: A script containing a series of instructions to build a Docker image. It specifies the base image, application code, dependencies, and configuration.
- Docker Hub: Repository for storing and sharing images.
Migrating apps to Containers: Docker Overview

slides.com/matthale/cybr8470-containers

Docker Engine
- The core component that enables containerization by building and running containers.
- Manages container lifecycle, including creation, execution, and monitoring.
Docker Compose
- A tool for defining and running multi-container Docker applications.
- Uses a YAML file to configure application services, making it easier to manage complex setups.
Docker CLI:
- Command-line interface for interacting with Docker Engine, allowing users to execute Docker commands.
Docker Desktop:
- An application providing a graphical interface for managing Docker containers and images on desktop environments.
Migrating apps to Containers: Docker Overview

slides.com/matthale/cybr8470-containers

Integrations with Orchestration Tools
- Kubernetes: Docker integrates seamlessly with Kubernetes for container orchestration, enabling automated deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications.
- Docker Swarm: Docker’s native clustering and orchestration tool for managing a cluster of Docker Engines.
Docker Ecosystem and Community
- Includes a wide range of tools and services that enhance Docker’s capabilities, such as Docker Hub, Docker Trusted Registry, and various plugins.
Migrating apps to Containers: Docker Overview

slides.com/matthale/cybr8470-containers

Portability and Platform Support
- Cross-Platform: Docker containers can run on any system that supports Docker, including various Linux distributions, Windows, and macOS.
- Cloud Integration: Easily deployable to major cloud platforms like AWS, Azure, Google Cloud, and others, ensuring consistent environments across dev, test, on-premises and cloud infrastructures.
Security Features
- Isolation: Ensures applications run in isolated environments, reducing security risks.
- Image Scanning: Tools available for scanning Docker images for vulnerabilities, can help with automating security checks in the deployment pipeline.
Migrating apps to Containers: Docker Overview

slides.com/matthale/cybr8470-containers

-
Assess Current Applications:
- Identify Dependencies: Catalog all libraries, frameworks, and services the application relies on.
- Evaluate Architecture: Determine if the application is monolithic or already uses microservices.
-
Containerize Dependencies:
- Base Image Selection: Choose an appropriate Docker base image (e.g. python, node, ubuntu)
- Separate Services: Break down the application into services if moving towards a microservices architecture.
-
Create Dockerfile:
-
Define Environment: Specify the base image, install dependencies, and set environment variables.
-
Copy Application Code: Add the application source code into the image, or use a bound volume if you need it to change without rebuilding.
-
Configure Startup Commands: Define how the application should start within the container.
-
Migrating apps to Containers: Migration steps

slides.com/matthale/cybr8470-containers


simple dockerfile example, src: https://docs.docker.com/get-started/workshop/02_our_app/
4. Build Docker Images:
- Use the
docker buildcommand to create an image from the Dockerfile. - Tag images appropriately for version control and deployment.
5. Test Containers Locally:
- Run containers locally to ensure they function as expected.
- Use
docker runwith necessary configurations for testing.
6. Deploy to Production:
- Choose a container orchestration platform (e.g., Docker Swarm, Kubernetes).
- Implement CI/CD pipelines to automate deployment processes.
Migrating apps to Containers: Migration steps

slides.com/matthale/cybr8470-containers

Migrating apps to Containers: Common Challenges and solutions

slides.com/matthale/cybr8470-containers

State Management
- Challenge: Managing persistent data.
- Solution: Use Docker volumes or external storage.
Networking
- Challenge: Configuring inter-container communication.
- Solution: Use Docker networks to manage and isolate networks.
Security Minimization
- Challenge: Reducing vulnerabilities and attack surfaces.
- Solution: Update images regularly, use minimal base images, implement security best practices.
Migrating apps to Containers: Dockerization best practices

slides.com/matthale/cybr8470-containers

Start Small: Begin with non-critical components to understand the process.
Automate Builds: Use CI/CD tools for building and testing Docker images.
Use Multi-Stage Builds: Optimize image sizes and enhance security.
Implement Monitoring and Logging: Utilize tools like Prometheus and the ELK stack for performance and logs.

slides.com/matthale/cybr8470-containers
Infrastructure as Code (IaC)
Definition: Managing and provisioning infrastructure through machine-readable configuration files.
Advantages:
-
Automated, consistent, and scalable infrastructure management.

slides.com/matthale/cybr8470-containers
Infrastructure as Code (IaC)
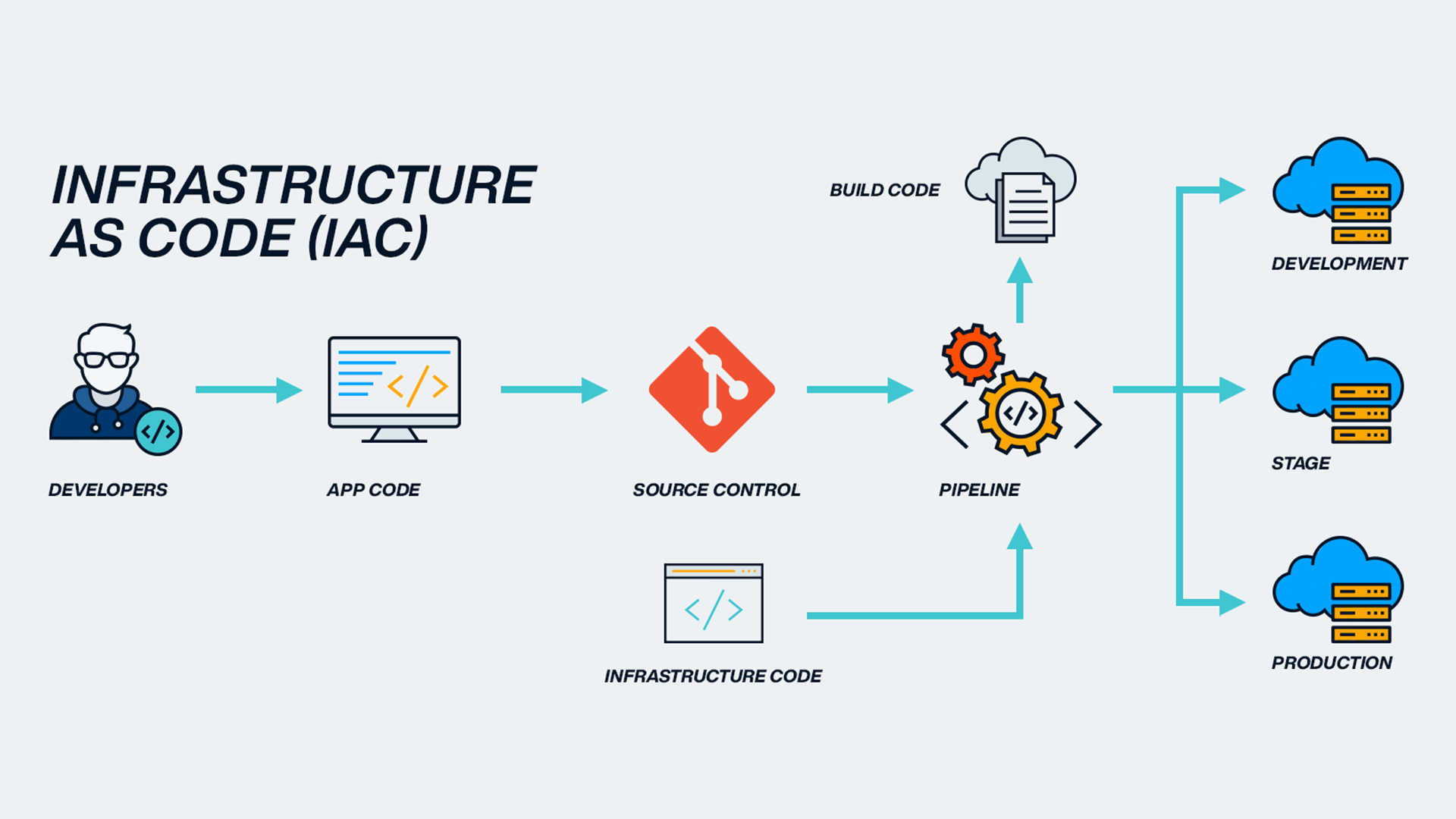
img credit: https://blog.sparkfabrik.com/en/infrastructure-as-code-what-is-it-and-its-benefits
Version Control: Track and manage changes using systems like Git.
Repeatability: Easily reproduce environments, reducing drift.
Scalability: Automate infrastructure provisioning to meet demand.
Collaboration: Shared configuration files facilitate teamwork.
Automation: Integrate with CI/CD pipelines for deployment and updates.

slides.com/matthale/cybr8470-containers
Infrastructure as Code (IaC): Benefits
Role of Docker in IaC: Define and manage application environments programmatically.
Key Tools:
- Docker Compose: Defines multi-container applications with YAML.
- Dockerfile: Blueprint for building Docker images.

slides.com/matthale/cybr8470-containers
Infrastructure as Code (IaC): w/ Docker
Define Multi-Container Applications:
All dependencies specified in a single docker-compose.yml file.
Components:
- Services: Individual containers with configurations.
- Networks: Communication setup between containers and external systems.
- Volumes: Persistent data storage outside containers.

slides.com/matthale/cybr8470-containers
Infrastructure as Code (IaC): w/ Docker compose
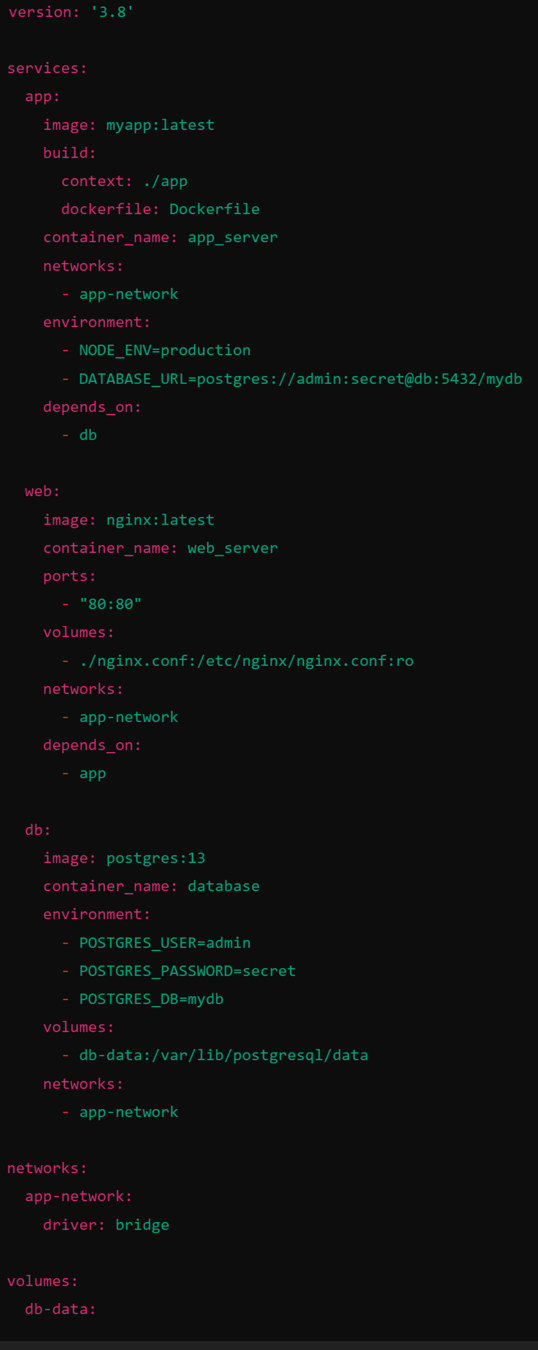
Define Services:
Specify Docker image/build context, ports, environment variables, dependencies.
Configure Networks:
Create custom networks for secure communication.
Manage Volumes:
Persist data across container restarts.
Deploy with a Single Command:
docker-compose up -d

slides.com/matthale/cybr8470-containers
Infrastructure as Code (IaC): w/ Docker compose
View Logs:
docker-compose logs -f
Stop Containers:
docker-compose down
Remove Containers, Networks, and Volumes:
docker-compose down -v

slides.com/matthale/cybr8470-containers
Docker management commands
Store Configuration Files:
Keep Dockerfile and docker-compose.yml in version control (e.g., Git).
Advantages:
- Track Changes: Review and revert infrastructure changes.
- Team Collaboration: Multiple members can work on infrastructure definitions.

slides.com/matthale/cybr8470-containers
Infrastructure as Code (IaC): Version control and collaboration
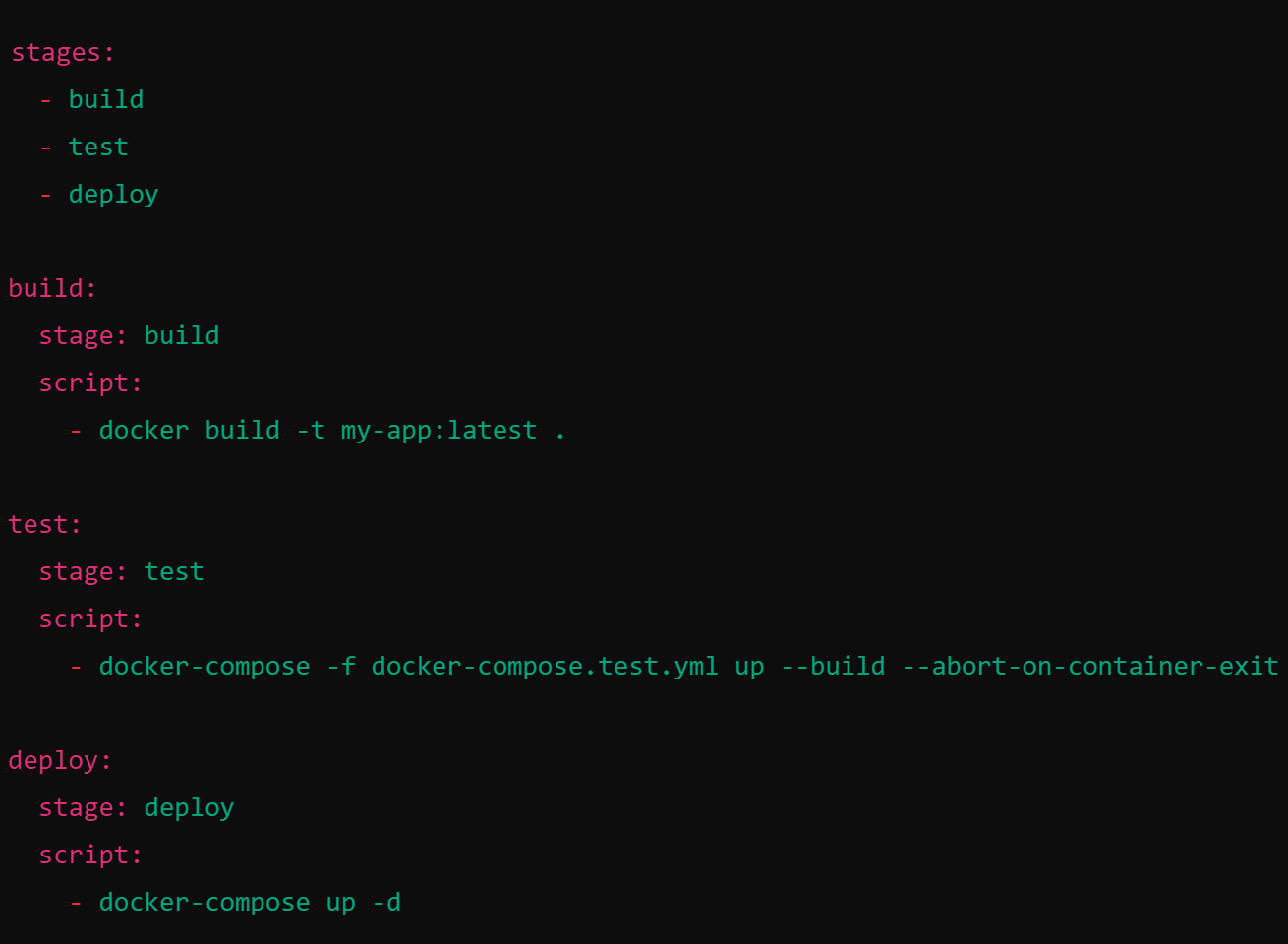
IaC allows for seamless deployment using CI/CD (continuous integration / continuous deployment) pipelines
Pipeline Phases:
- Build Phase: Automatically build Docker images.
- Test Phase: Deploy containers in a test environment for integration and security tests.
- Deploy Phase: Push images to a registry and deploy to production using IaC scripts.

slides.com/matthale/cybr8470-containers
Infrastructure as Code (IaC): Integrating IaC with CI/CD Pipelines
Least Privilege: Define minimal permissions for services and components.
Secrets Management: Use environment variables or secret management tools for sensitive data.
Image Scanning: Regularly scan Docker images for vulnerabilities.
Immutable Infrastructure: Avoid manual changes to deployed infrastructure to maintain consistency.

slides.com/matthale/cybr8470-containers
Infrastructure as Code (IaC): Security

slides.com/matthale/cybr8470-containers
Example Containerization
Example 1: Native Install
Example 2: Docker Install
-
Update System Packages:
sudo apt update sudo apt upgrade -y -
Install Node.js and npm:
curl -fsSL https://deb.nodesource.com/setup_14.x | sudo -E bash - sudo apt-get install -y nodejs -
Verify Installation:
node -v npm -v

slides.com/matthale/cybr8470-containers
Example1: Native install step-by-step
-
Install PostgreSQL:
sudo apt-get install -y postgresql postgresql-contrib -
Start and Enable PostgreSQL:
sudo systemctl start postgresql sudo systemctl enable postgresql -
Configure PostgreSQL:
sudo -i -u postgres createdb app_db createuser admin -P psql GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON DATABASE app_db TO admin; \q exit

slides.com/matthale/cybr8470-containers
Example1: Native install step-by-step
-
Clone the Application Repository:
git clone https://github.com/username/my-node-app.git cd my-node-app -
Install Dependencies:
npm install -
Configure Environment Variables:
touch .envAdd to
.env:NODE_ENV=production PORT=8080 DATABASE_URL=postgres://admin:secret@localhost:5432/app_db

slides.com/matthale/cybr8470-containers
Example1: Native install step-by-step
-
Start the Application:
npm start -
Access the Application:
Navigate to http://localhost:8080

slides.com/matthale/cybr8470-containers
Example1: Native install step-by-step
Pros and Cons
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Direct access to host resources | Potential for dependency conflicts |
| Simpler for small, single applications | Harder to replicate environments |
| Easier debugging on the host | Scaling requires manual intervention |

slides.com/matthale/cybr8470-containers
Example1: Native install step-by-step
-
Clone the Application Repository:
git clone https://github.com/username/my-node-app.git cd my-node-app -
Create a Dockerfile:
FROM node:14-alpine WORKDIR /usr/src/app COPY package*.json ./ RUN npm install --production COPY . . EXPOSE 8080 CMD ["node", "app.js"]

slides.com/matthale/cybr8470-containers
Example2: Docker install step-by-step
-
Create
docker-compose.yml:version: '3' services: web: build: . ports: - "8080:8080" environment: - NODE_ENV=production - DATABASE_URL=postgres://admin:secret@db:5432/app_db depends_on: - db db: image: postgres:13 environment: - POSTGRES_USER=admin - POSTGRES_PASSWORD=secret - POSTGRES_DB=app_db volumes: - db-data:/var/lib/postgresql/data volumes: db-data:

slides.com/matthale/cybr8470-containers
Example2: Docker install step-by-step
-
Build and Run Containers:
docker-compose up -d --build -
Verify Containers Are Running:
docker-compose ps -
Access the Application:
Navigate to http://localhost:8080

slides.com/matthale/cybr8470-containers
Example2: Docker install step-by-step
Pros and Cons
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Consistent environments across all stages | Initial learning curve with Docker tools |
| Easy to scale horizontally | Additional layer may obscure debugging |
| Isolation of dependencies | Potential overhead in resource-constrained environments |
| Simplified deployment and rollback | Requires Docker and Docker Compose on all environments |

slides.com/matthale/cybr8470-containers
Example2: Docker install container management
| Aspect | Native Installation | Dockerized Installation |
|---|---|---|
| Setup Complexity | Manual installation of dependencies | Automated through Dockerfiles and Compose |
| Environment Consistency | Prone to differences across environments | Ensures identical environments across stages |
| Scalability | Manual scaling; complex for multiple instances | Easy horizontal scaling with orchestration |
| Isolation | Limited; potential dependency conflicts | High; containers encapsulate all dependencies |
| Deployment Speed | Slower; individual environment configuration | Rapid deployment using pre-built images |
| Resource Utilization | Significant overhead from OS if using VMs | Efficient with shared kernel and isolated containers |
| Maintenance | Manual updates and dependency management | Automated builds and updates via Docker pipelines |
| Portability | Less portable; environment-specific configurations | Highly portable; runs anywhere Docker is supported |

slides.com/matthale/cybr8470-containers
Comparison: Native vs Dockerized install
Questions?
©2024 Matthew L. Hale


Matt Hale, PHD
University of Nebraska at Omaha
Associate Professor, Cybersecurity
Director, School of Interdisciplinary Informatics
Director, NebraskaCYBER
mlhale@unomaha.edu
twitter: X: @mlhale
slides.com/matthale/cybr8470-containers