Optics Applications
M. Rocha
Physics 4C
Geometric Optics, The Eye, Microscopes and Telescopes
Lenses (Refraction)
Direction of Refraction
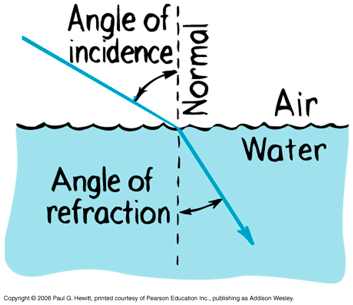
Waves bend towards the normal when going from fast to slow
and
away from the normal when going from slow to fast
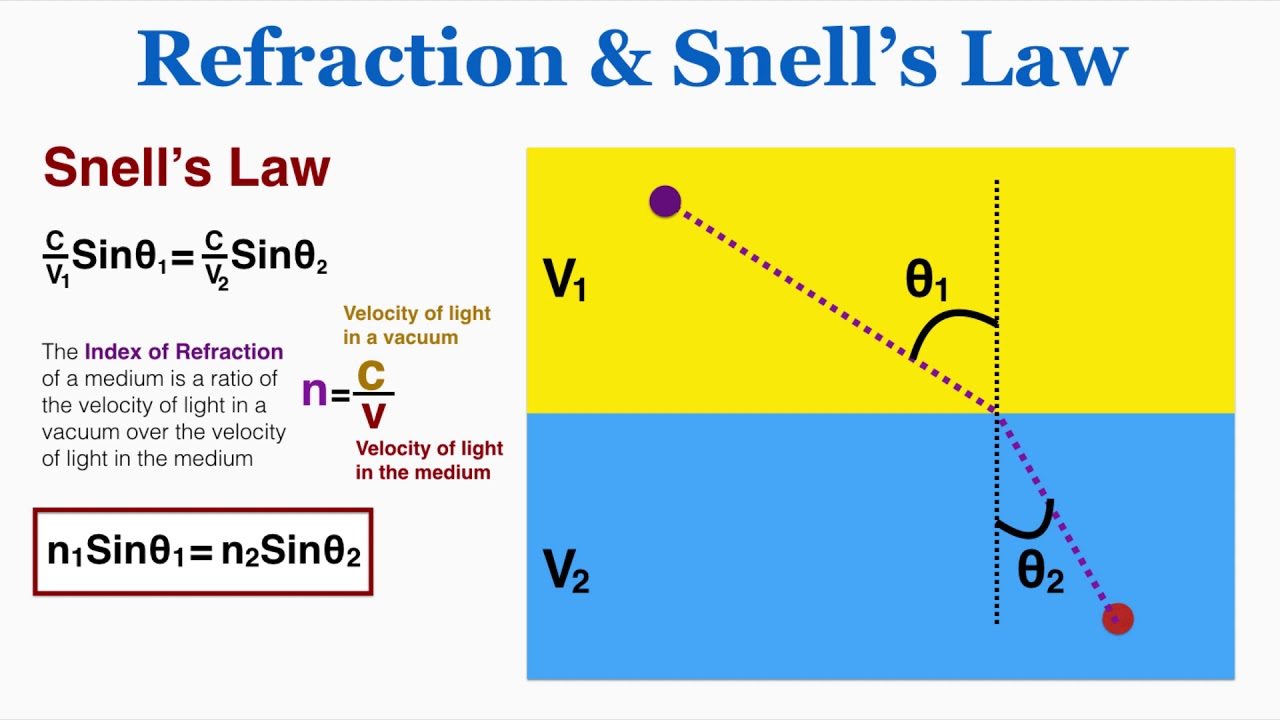

Small angle approximation
Arc Length = Angle in radians x Radius
r = Hypotenuse
Adjacent
Arc Length and The Small Angle Approximation
r
Oposite =
Oposite
L

Lenses
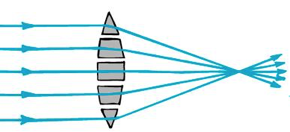
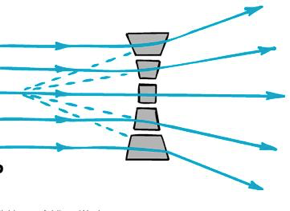
Curved surface of a convex lens causes light rays to converge, magnifying images
Convex Lenses

Curved surface of a concave lens causes light rays to diverge, shrinking images

Concave Lenses

Lenses
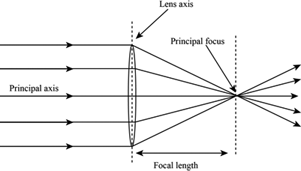
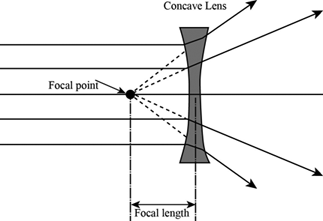
Focal Length

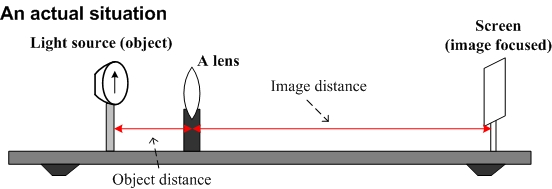
Thin Lens Equation

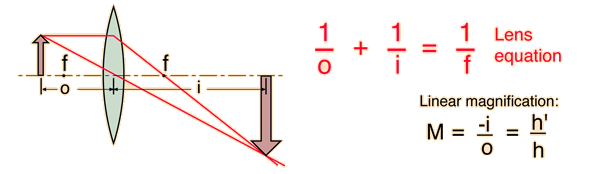
Virtual vs. Real Images in Convex Lenses
Real Image
Virtual Image
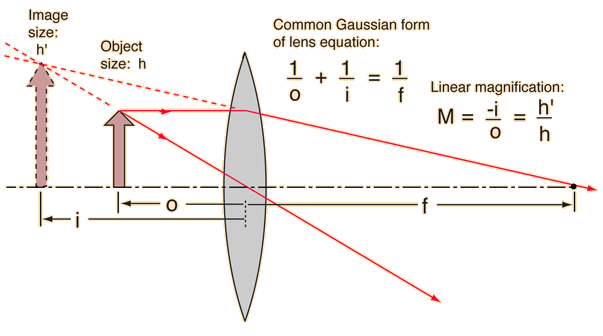

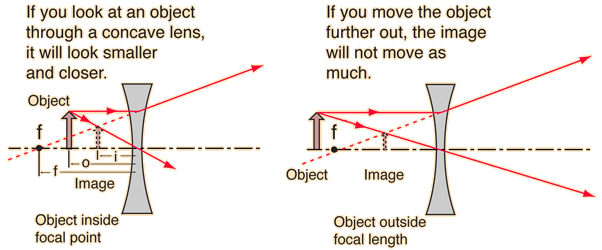
Virtual Images in Concave Lenses
Virtual Images
Checkpoint
o = 10cm
i = 30cm
What is the focal length of the lens in the system below?
f = 7.5 cm
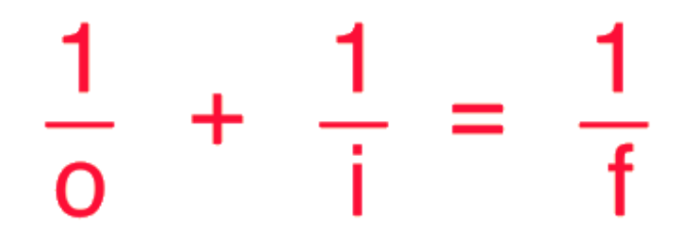
Checkpoint
If we move the light source (object) to a position 2.5 cm from the lens, in the same setup of the previous checkpoint, what would be the magnification?
f = 7.5 cm
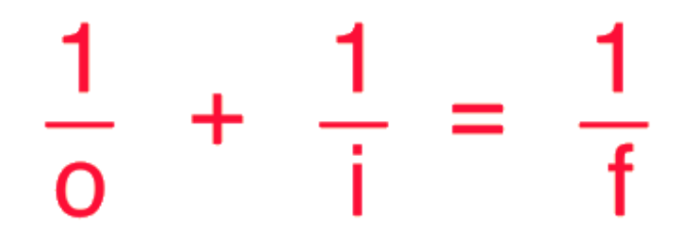
Checkpoint
Repeat the previous checkpoint now for a Convex lens?
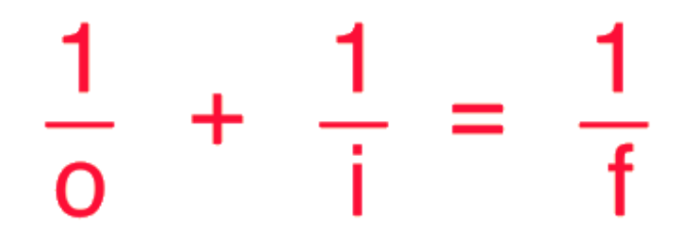
f = -7.5 cm, O = 2.5, i = ?, M = ?
Mirrors (Reflection)
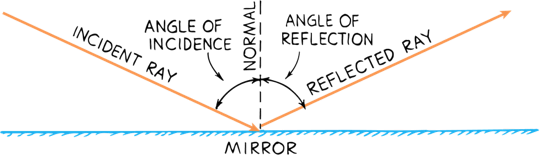
Law of Reflection
The angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection
Mirrors
Mirrors are the result of specular reflection
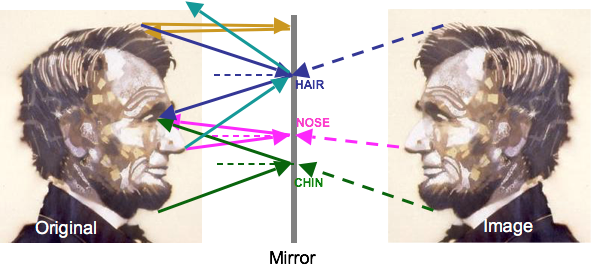
Tracing light rays from original, to mirror, to eye allows us to construct the image
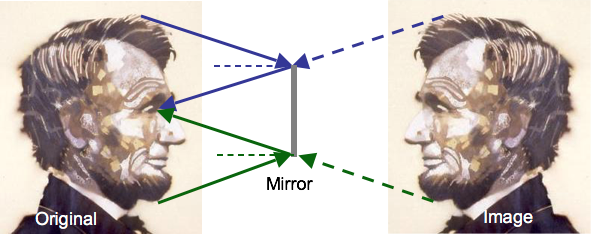
Convex Mirrors
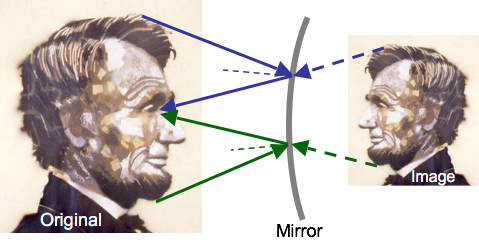
Image from convex mirror is smaller and closer than original
Concave Mirrors
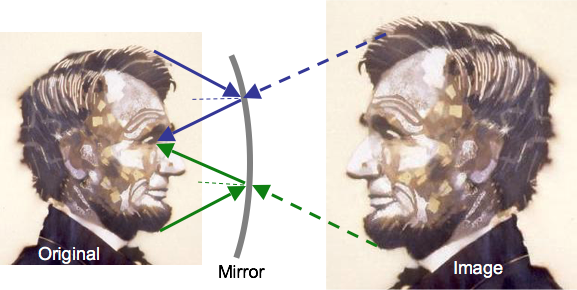
Image from concave mirror is larger and farther than original if object close to mirror
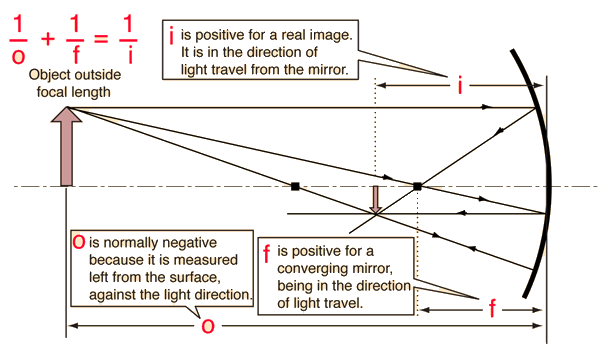
Concave Mirror Image
O > f (object outside focal length)
Concave Mirror Image
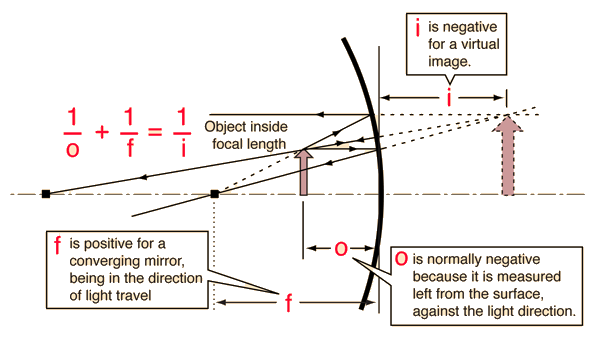
O < f (object inside focal length)
Covex Mirror Image
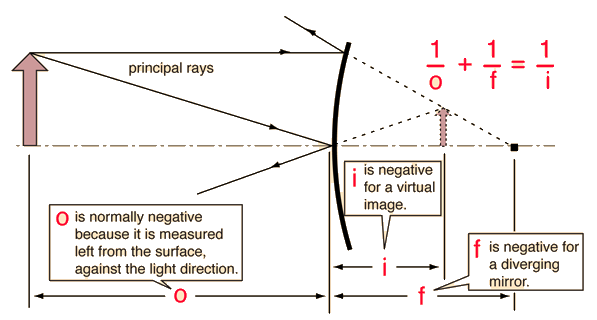
f < 0 (always virtual image)
Virtual vs. Real Images in Mirrors
Real Image
Virtual Image
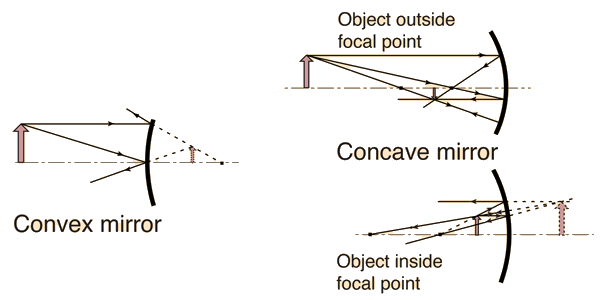
The Eye
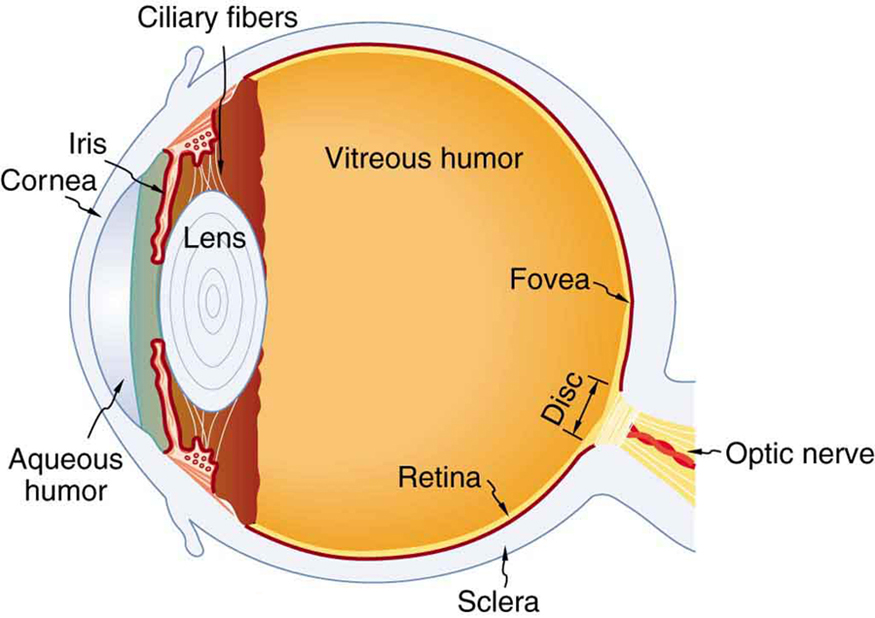
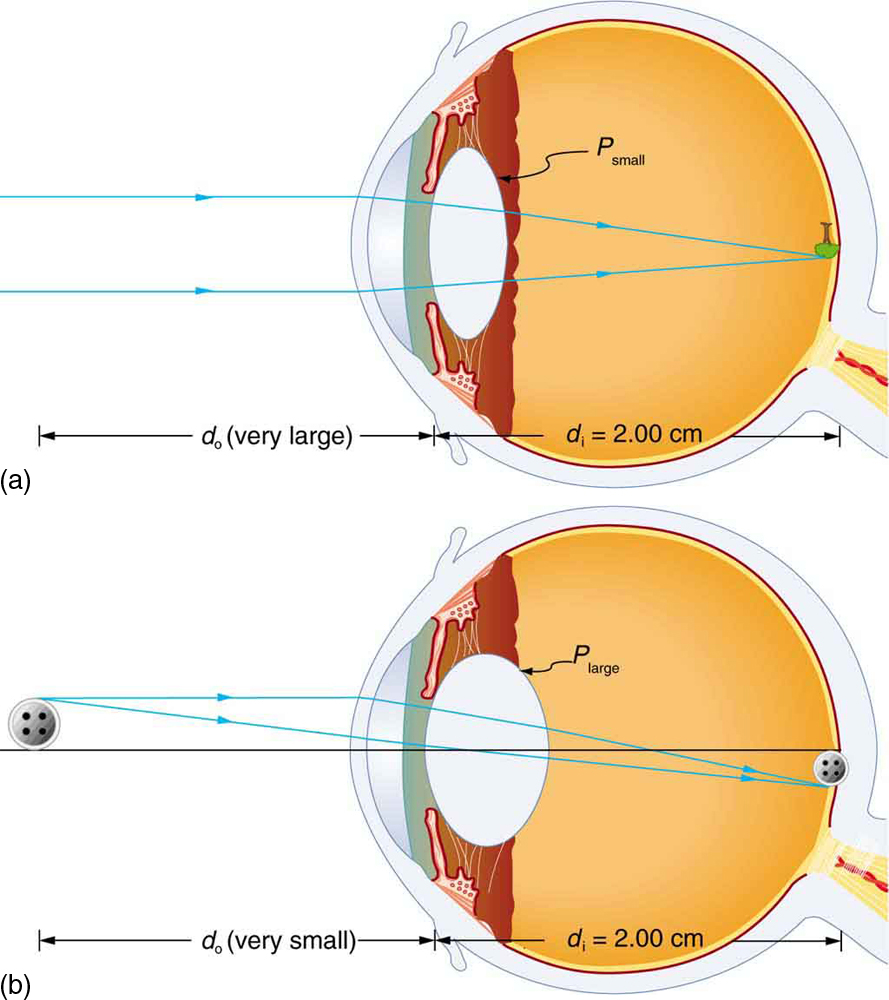
Physics of the Eye
Vision Correction
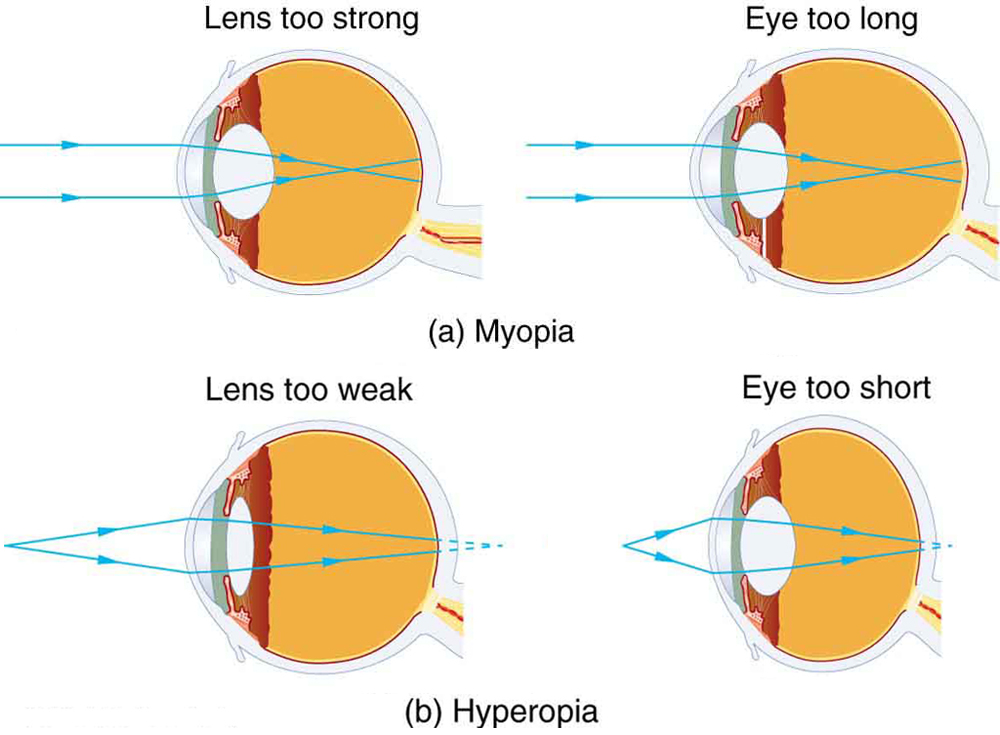
(nearsighted)
(farsighted)
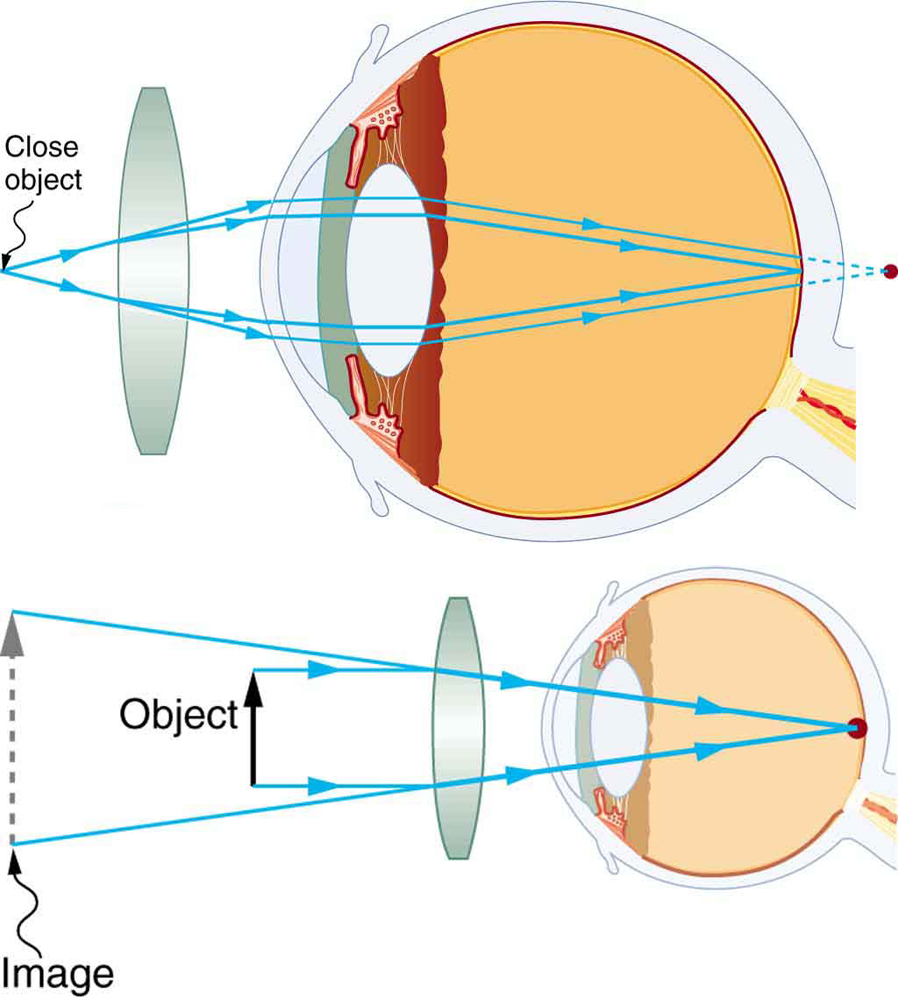
Vision Correction
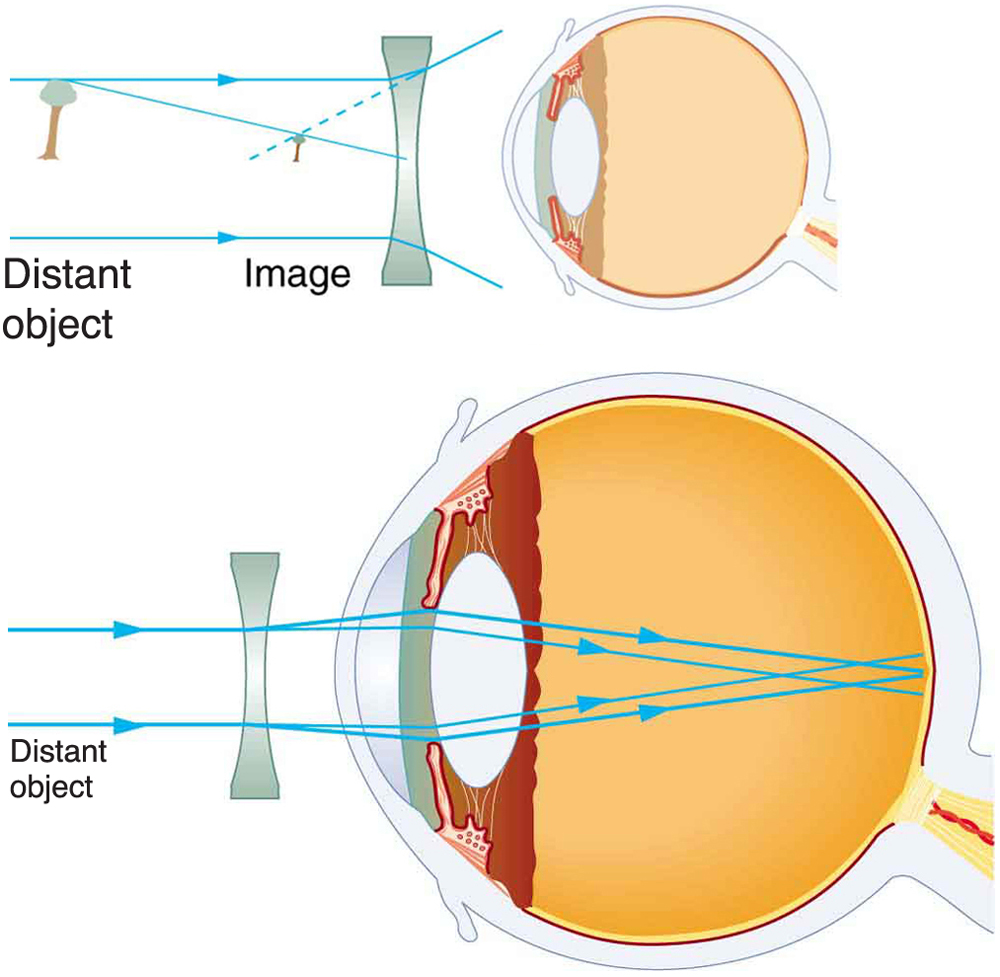
Myopia Correction
Hyperopia Correction
Microscopes
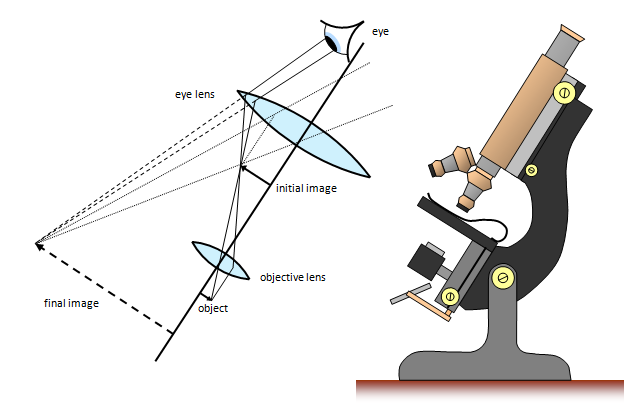
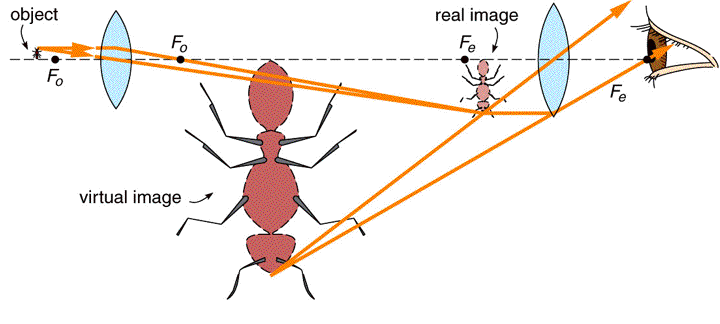
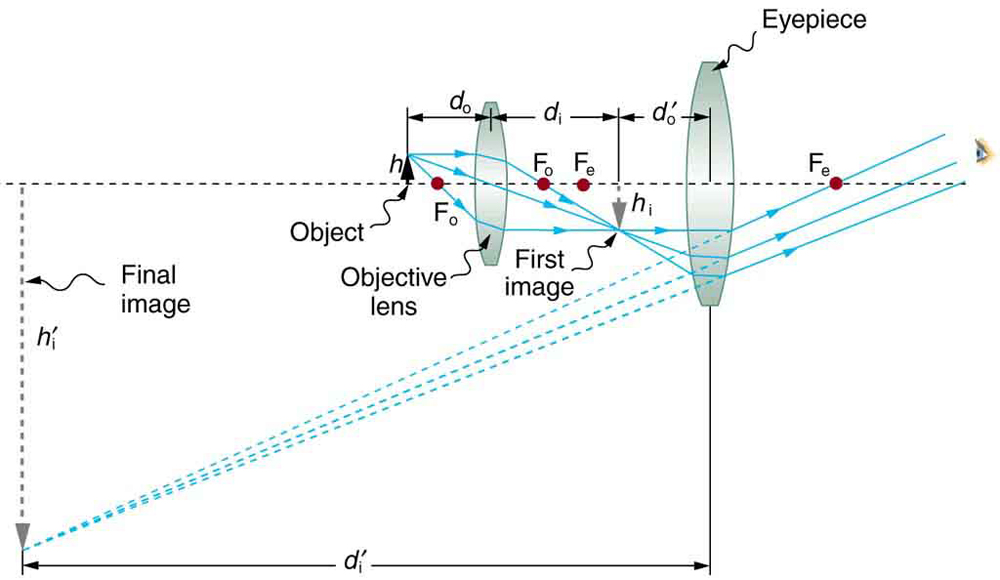
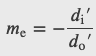
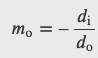
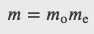
Total Magnification:
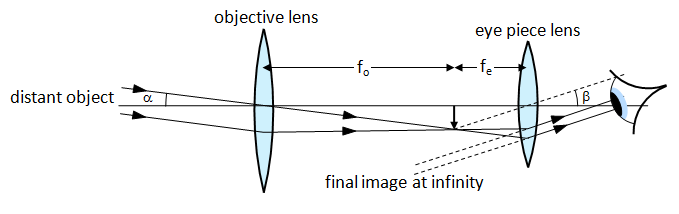
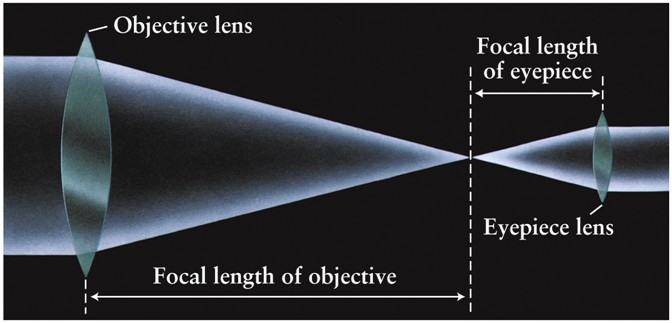
Telescopes
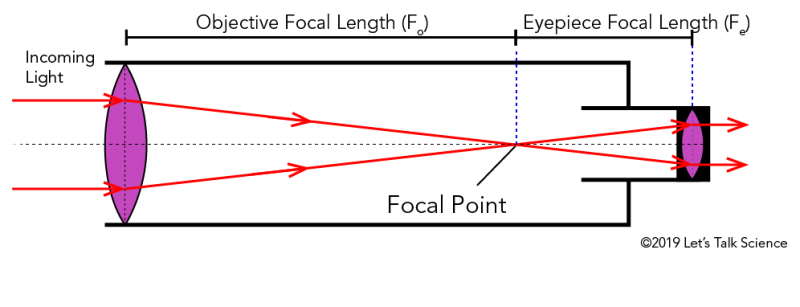
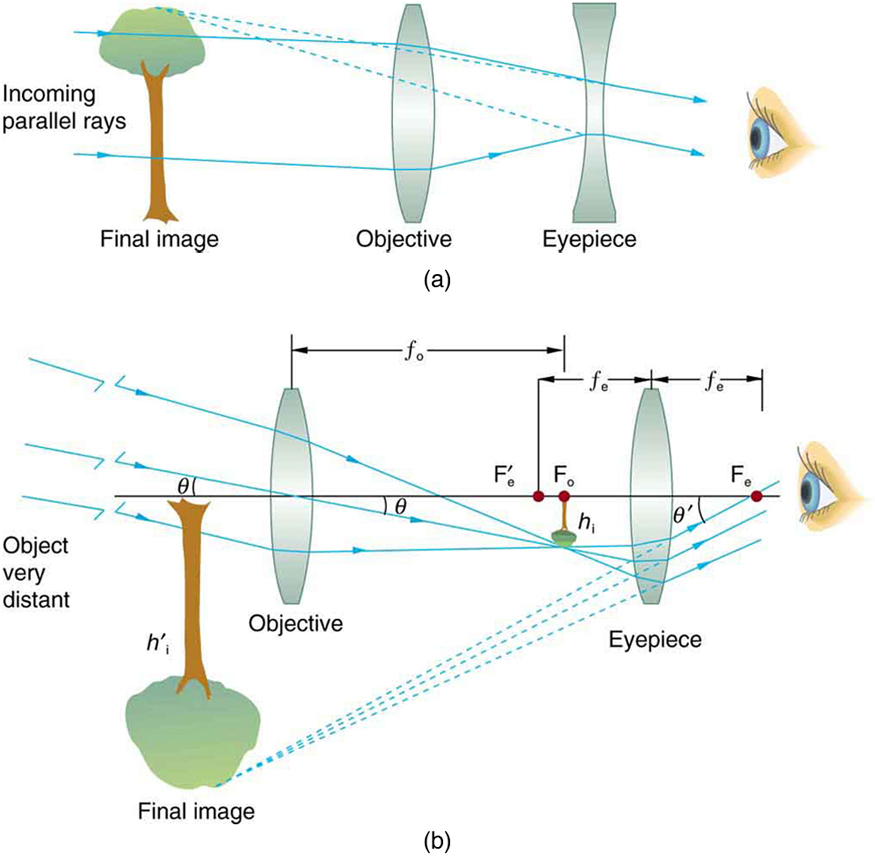
Telescope Magnification
h
Telescope Magnification
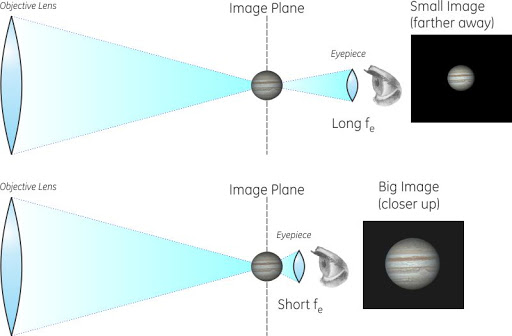
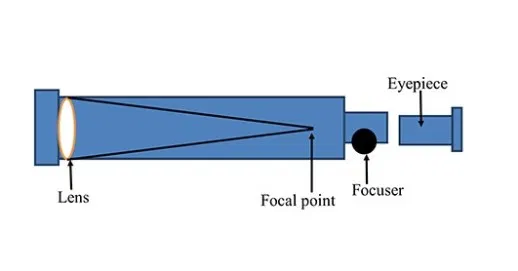
Text
Checkpoint
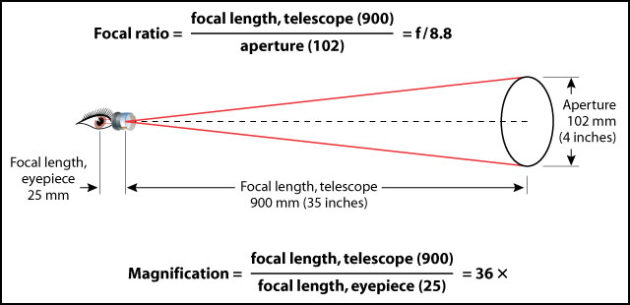
If a telescope has a focal length of 1200 mm. What is the magnification when using a 25 mm eyepiece?
M = 1200 mm/ 25 mm = 48
Telescopes are Light Buckets
The main purpose of telescopes is to collect as much light as possible while maintaining as much detail as possible
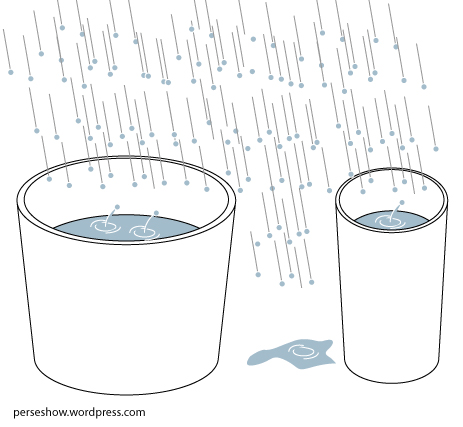
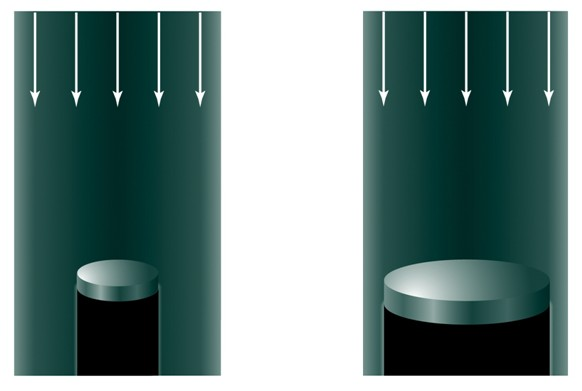
Both the light gathering power and resolution of a telescope increases with the diameter/area of the telescope
Refractors vs. Reflectors
There are two ways to collect light in a telescope. By refraction or by reflection
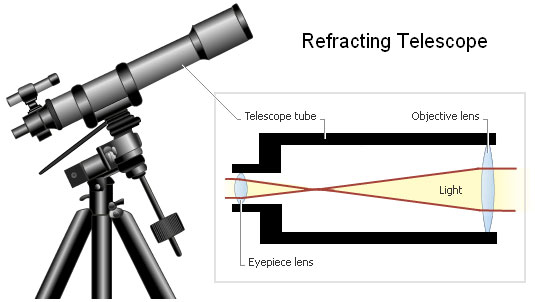
Refracting telescopes use a primary/objective lens to collect light by refraction
Reflecting telescopes use a primary/objective mirror to collect light by reflection
Refracting Telescopes

Refracting telescopes have many disadvantages:
- The become too long for not that much light collecting area
- Large lenses are extremely expensive to fabricate
- A large lens will sag in the center since it can only be supported on the edges
- Dispersion causes images to have colored fringes

Refraction of light is frequency dependent
This is because higher frequencies travel slower inside the prism
Slowest
Fastest
Refracting Telescopes Suffer from Chromatic Aberration
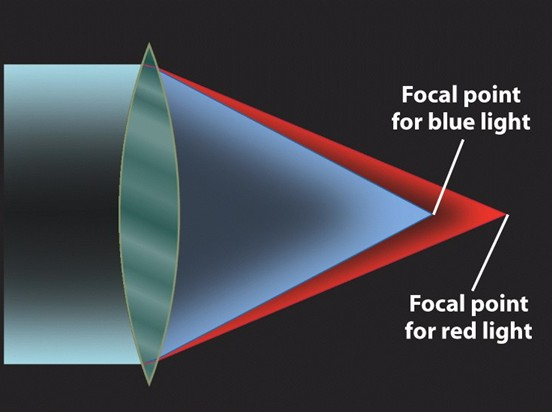

Slowest
Fastest
Refracting Telescopes Suffer from Chromatic Aberration
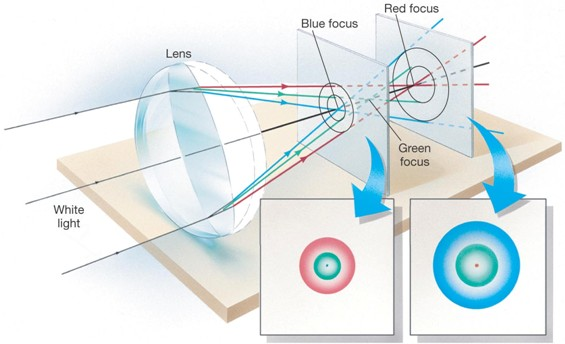

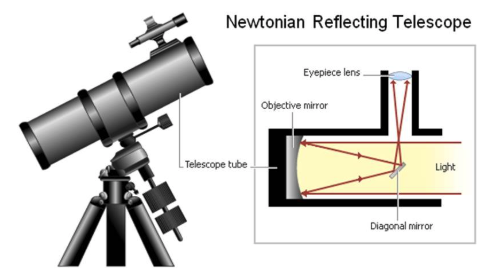
Reflecting Telescopes
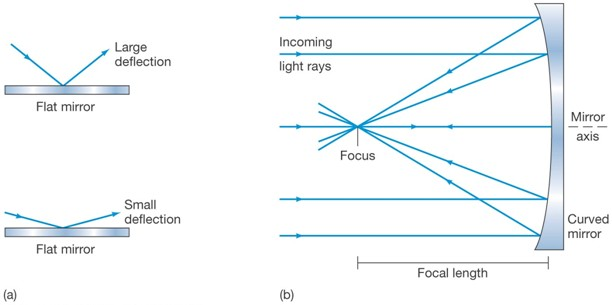
Reflecting telescopes use a parabolic primary mirror to collect light. Light is focused in front of the mirror, how you observed it without blocking the incoming light?
Reflecting Telescopes
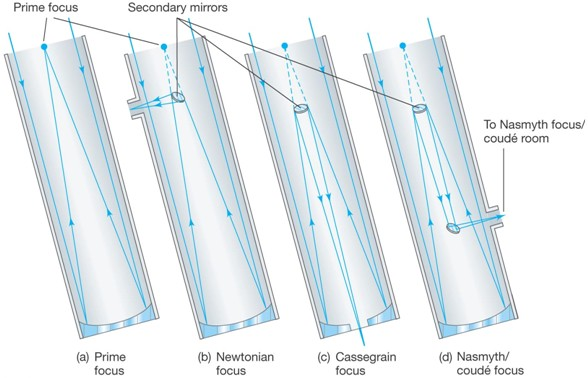
Reflecting telescopes use either detectors or secondary mirrors to gather or re-direct the focused light from the primary mirror
Concave Mirrors
We use concave mirrors to build telescopes in order to focus the light to the detector
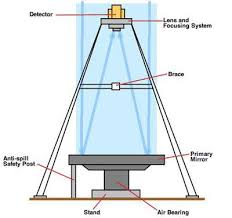
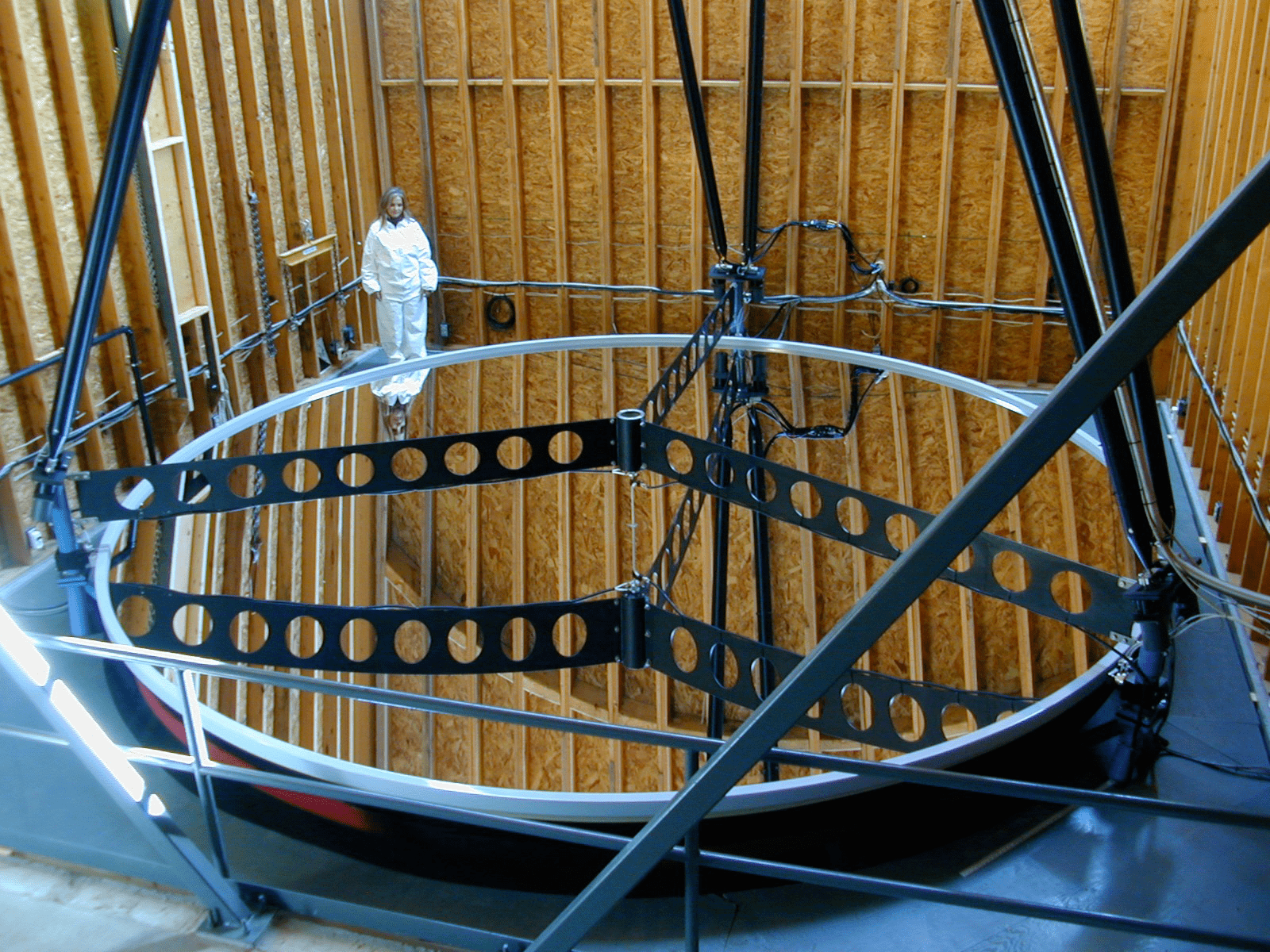
Telescope Instruments
Cameras and Charged Coupled Devices (CCDs)
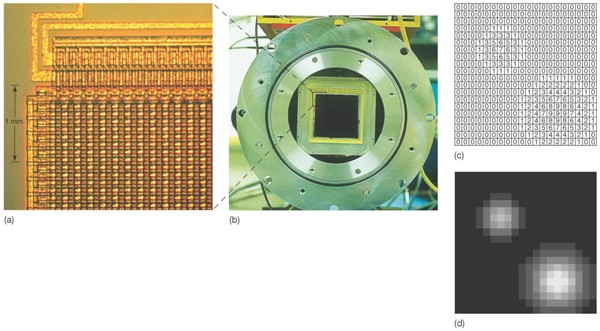

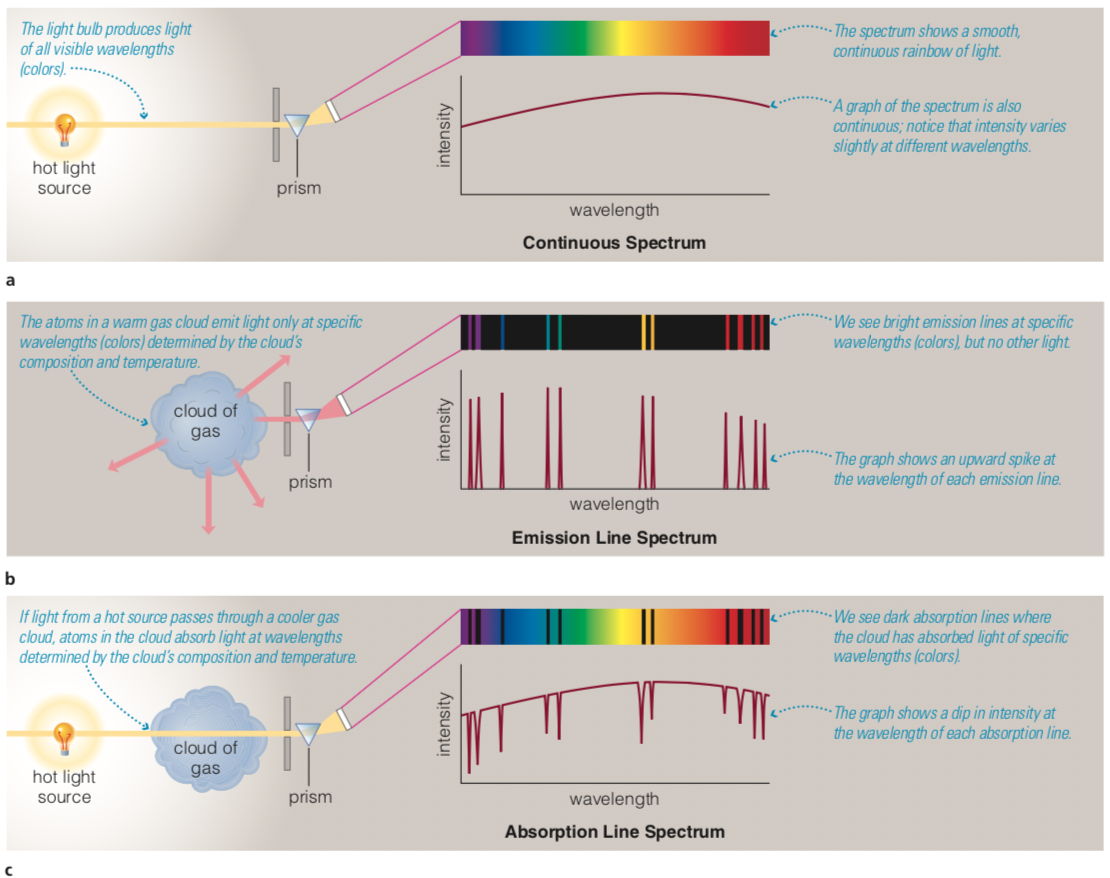
Spectrographs