Galaxies, Cosmology and Galaxy Evolution
Galaxies

Stars form in groups, within regions where gravity is strong (high density) and gas is cold

Galaxies host many of this star formation regions. With a higher density in the spiral arms
A healthy spiral galaxy the size of the Milky Way hosts about 100 billion (10^11) stars
Galaxies host many of this star formation regions. With a higher density in the spiral arms
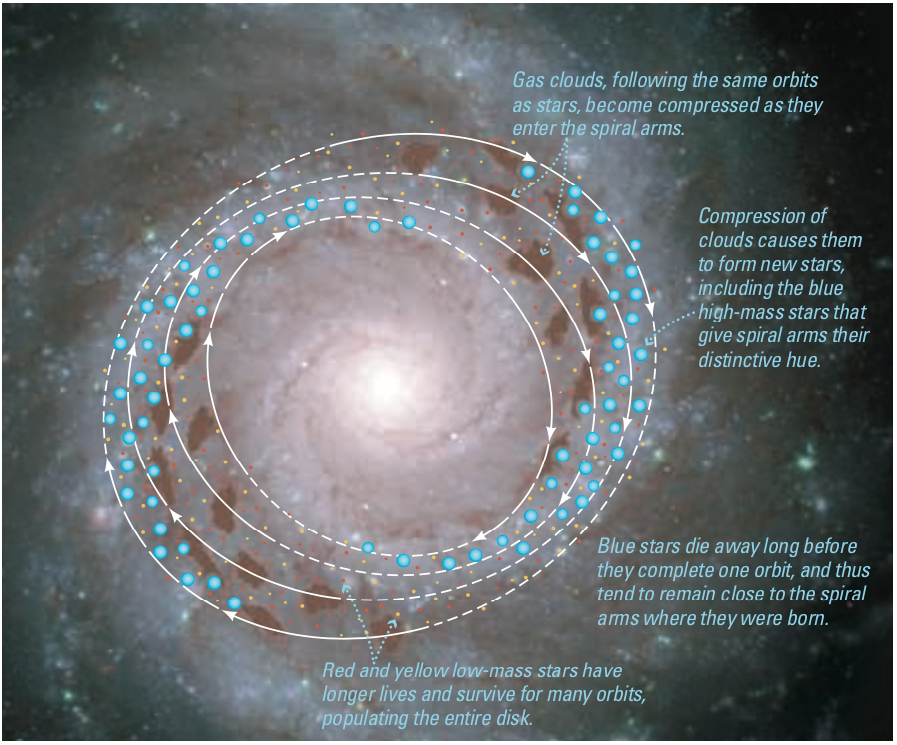
A healthy spiral galaxy the size of the Milky Way hosts about 100 billion (10^11) stars
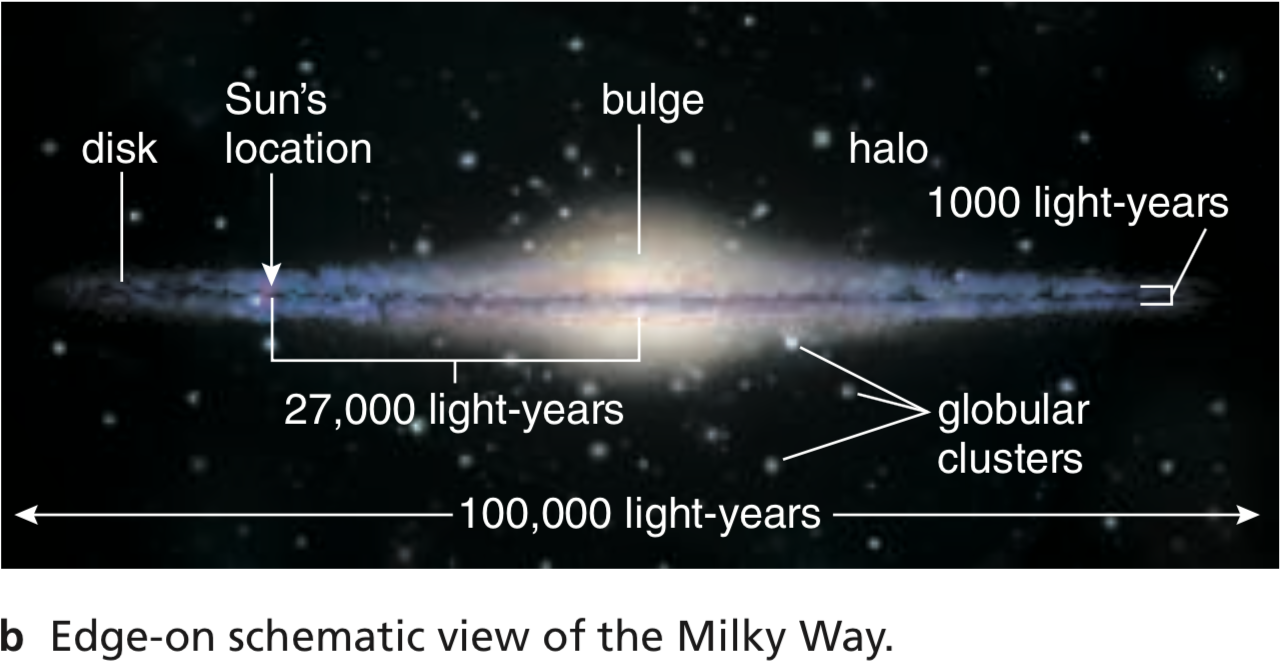
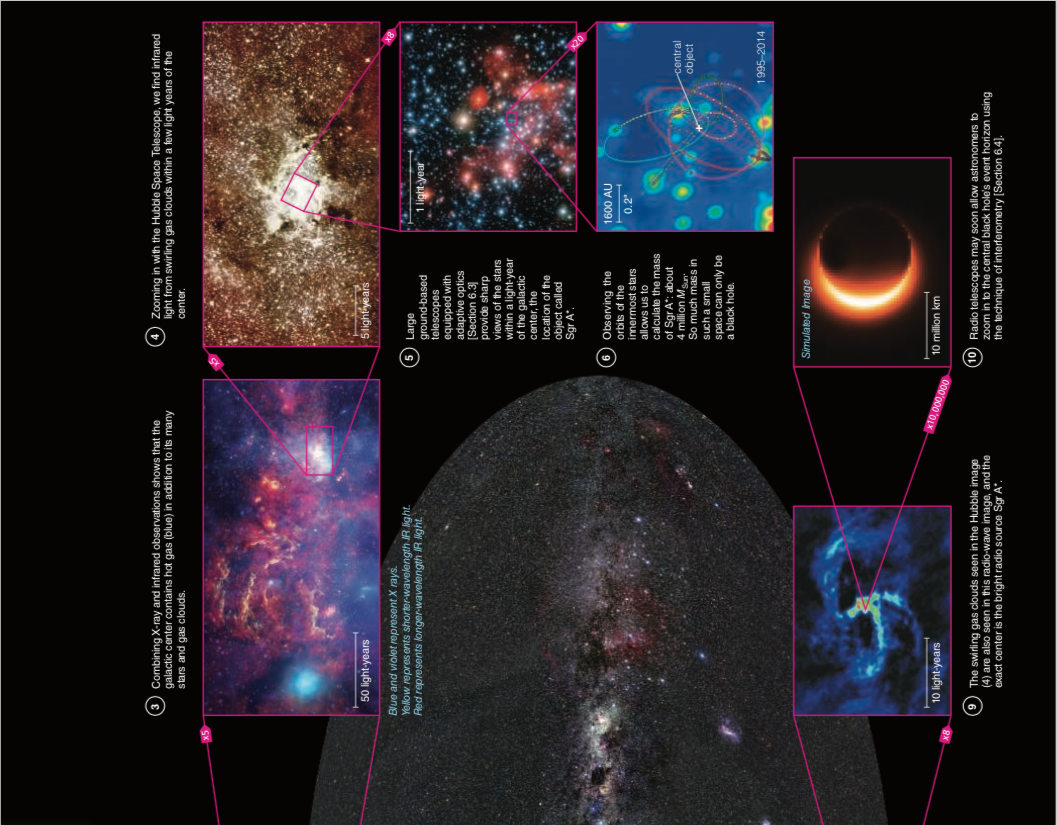
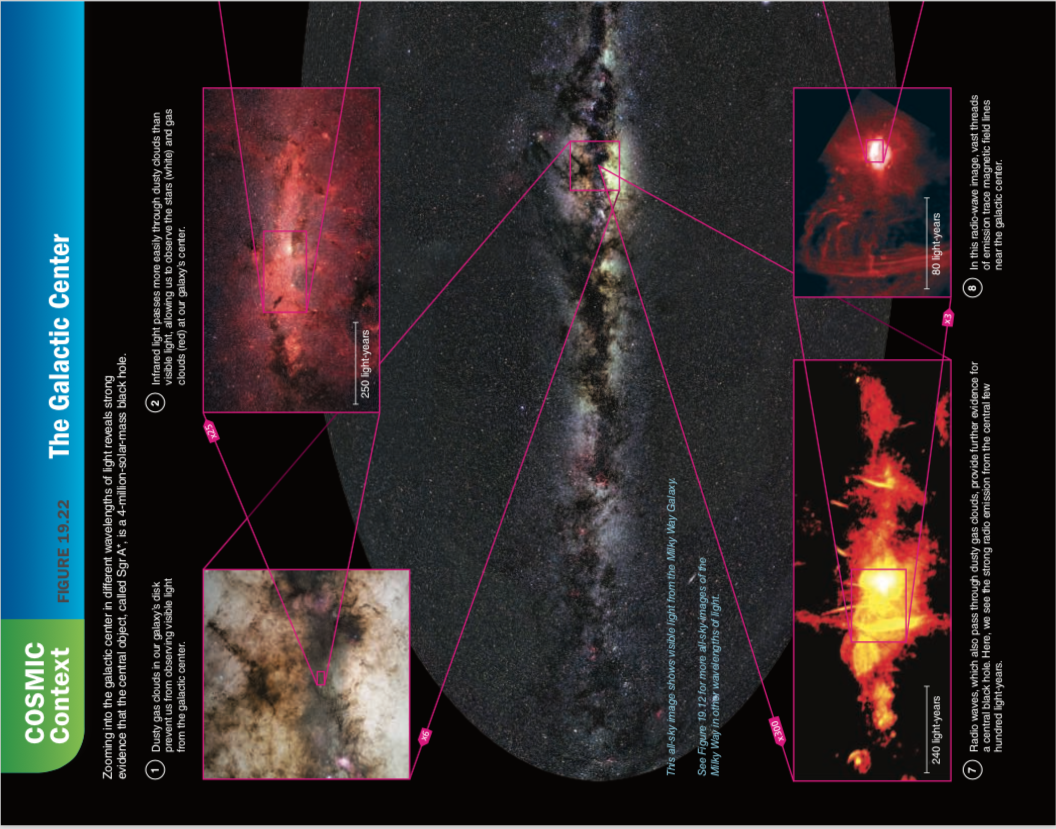
The Milky Way


The Hubble eXtreme Deep Field (XDF) showing thousands of galaxies. There are about 100-200 billion galaxies in the visible Universe
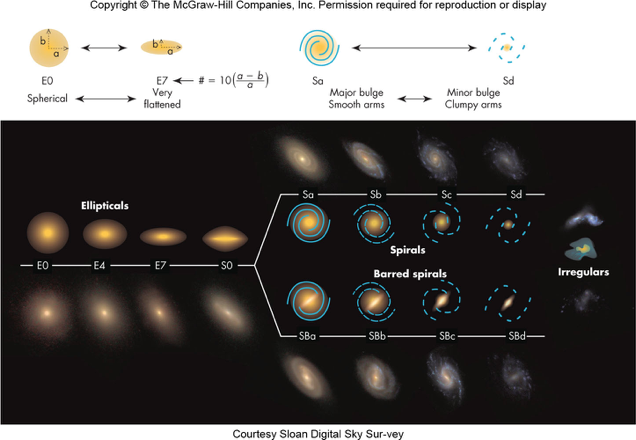
Not all galaxies look the same!







Hubble Classification of Galaxies
The Expanding Universe


Edwin Hubble at Mount Wilson
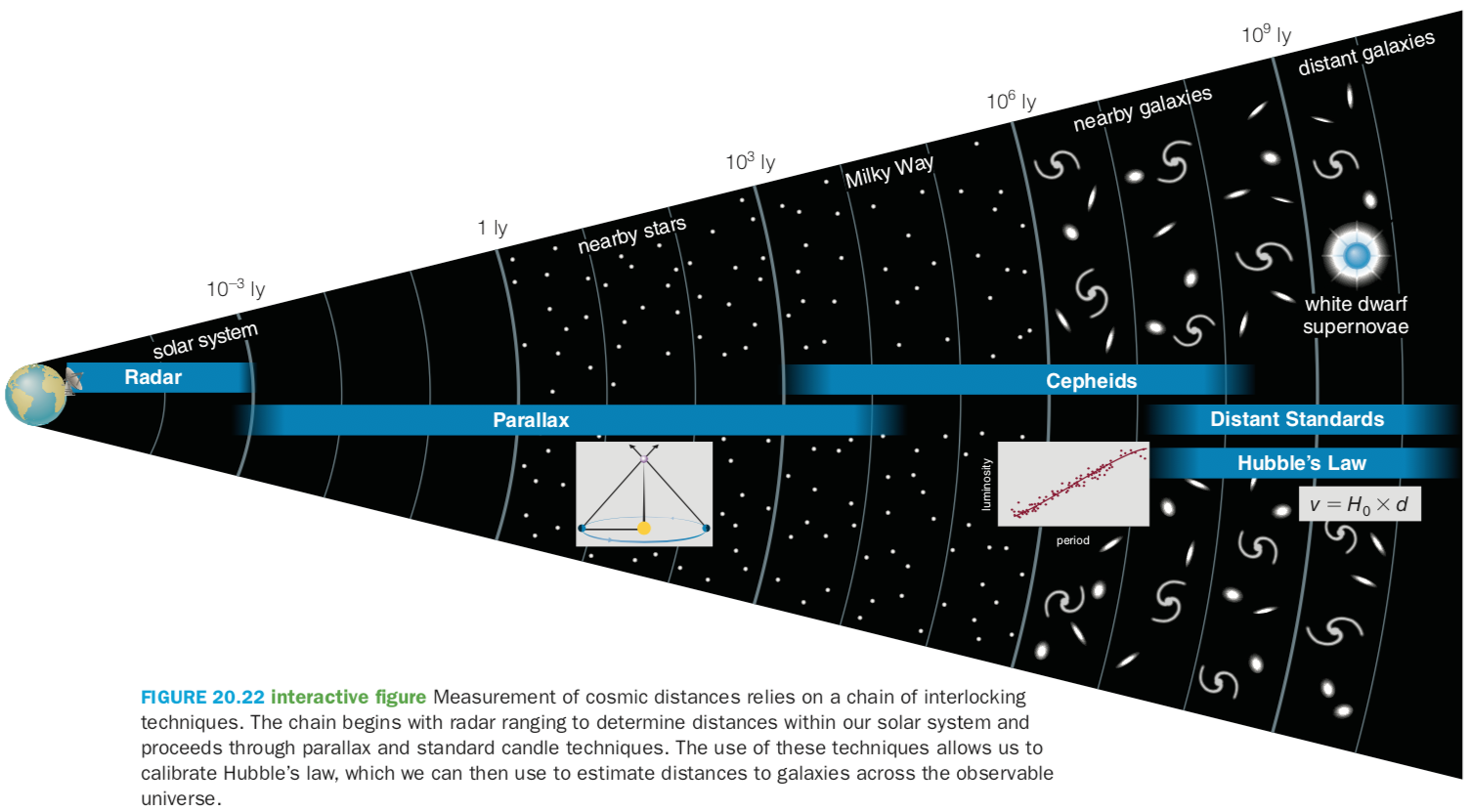
Measuring Distances
Measuring Velocity
We can measure the velocity of stars along the line of sight by using the doppler effect
When the source of waves moves the frequency increases in front of the source and decreases behind the source
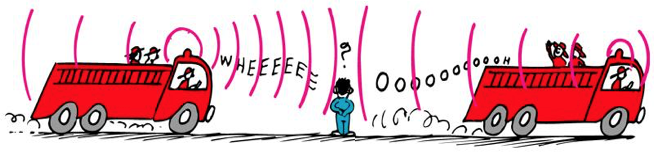
If moving towards you, wavelength shorter and frequency higher.
If moving away, wavelength longer and frequency lower.
Doppler Effect
When the source of waves moves the frequency increases in front of the source and decreases behind the source
Police use the Doppler effect of radar waves to measure the speeds of cars on the highway.
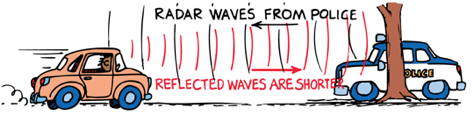
Doppler Effect
When the source of waves moves the frequency increases in front of the source and decreases behind the source
Astronomers use the Doppler effect to measure the rotation speed of galaxies.

Hubble Law
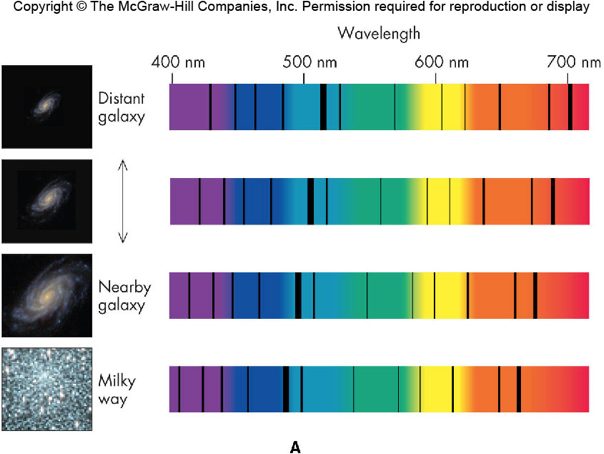
Galaxies are moving away from us (red-shifted), and the farther they are the the greater their recession speed (more red-shifted)
Hubble Law
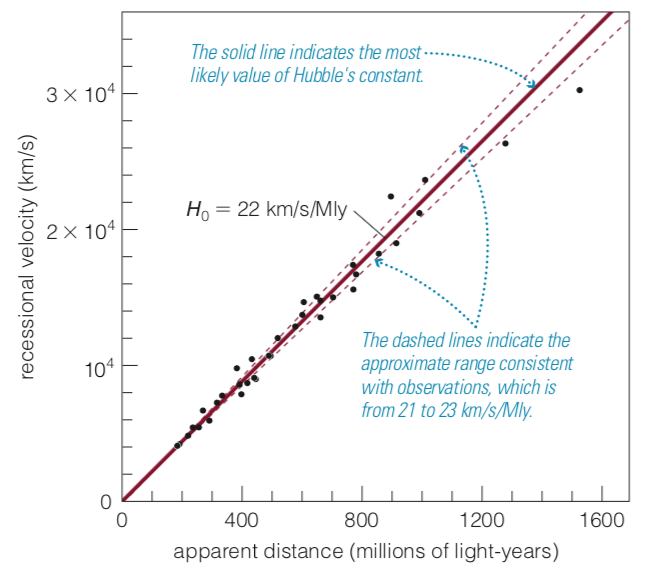
Galaxies are moving away from us, and the farther they are the greater their recession speed
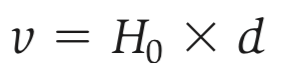
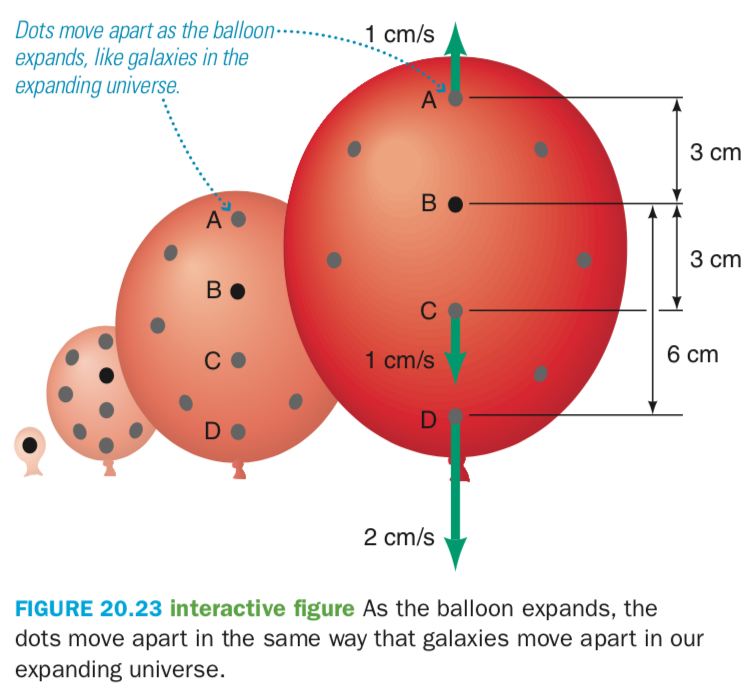
The fact that galaxies move away from us at the same rate regardless of which direction we are looking at suggest that space itself is expanding
Relativity
Classical Relativity
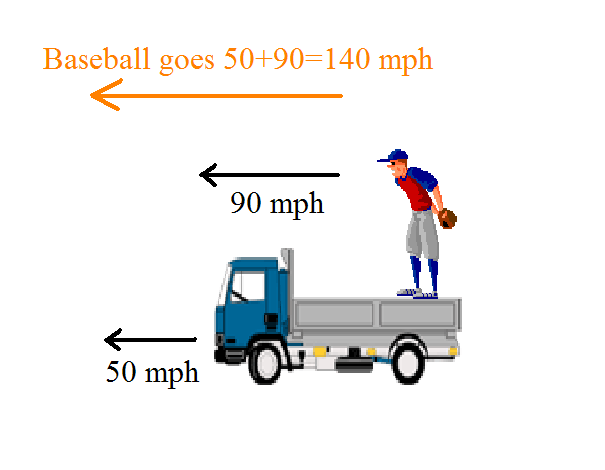
Relativity in physics is just a way for two observers moving relative to each other to agree on what they are observing
In classical relativity you just add the velocities of the moving frame (truck) and the ball
Einstein's Special Relativity
In 1905 Einstein postulated that:
- The laws of physics must be the same for all observers independent on their relative motions
- Thus the speed of light (a fundamental physics constant) must be the same for all observers independent on their relative motions
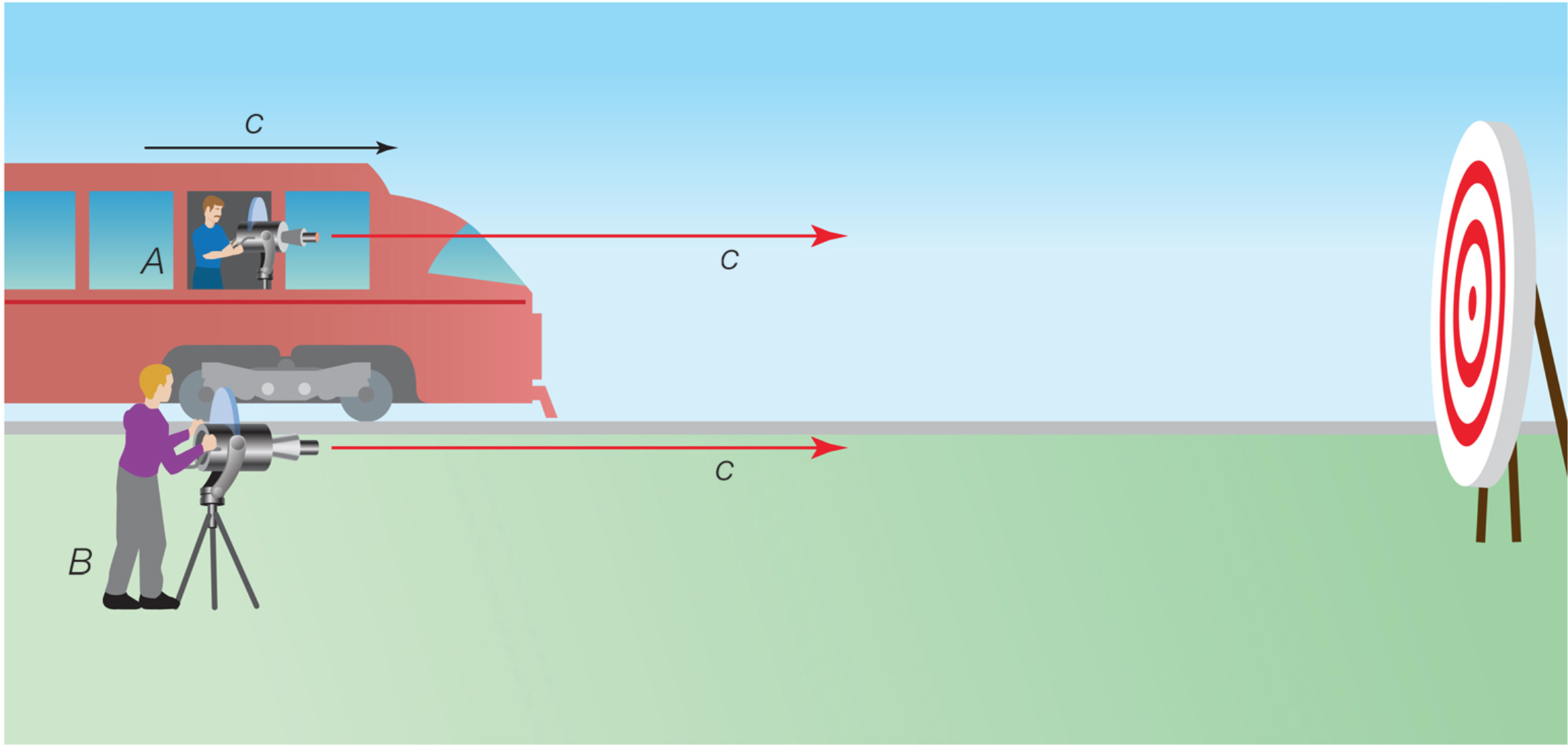
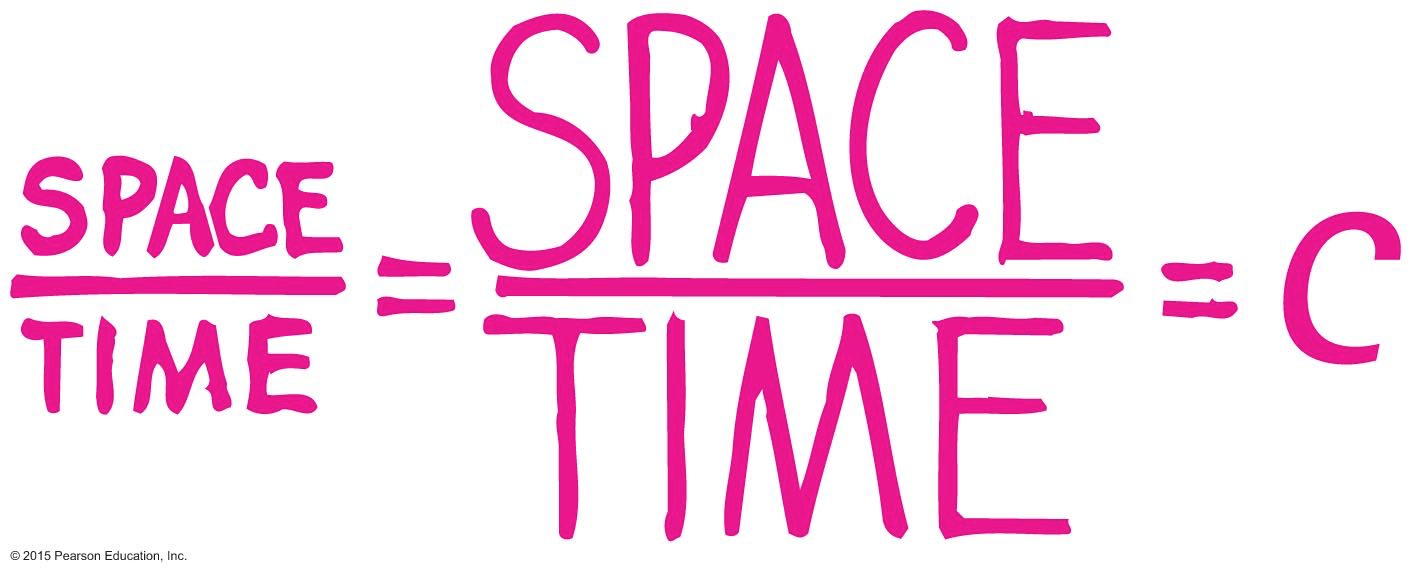
Space-Time in Relativity
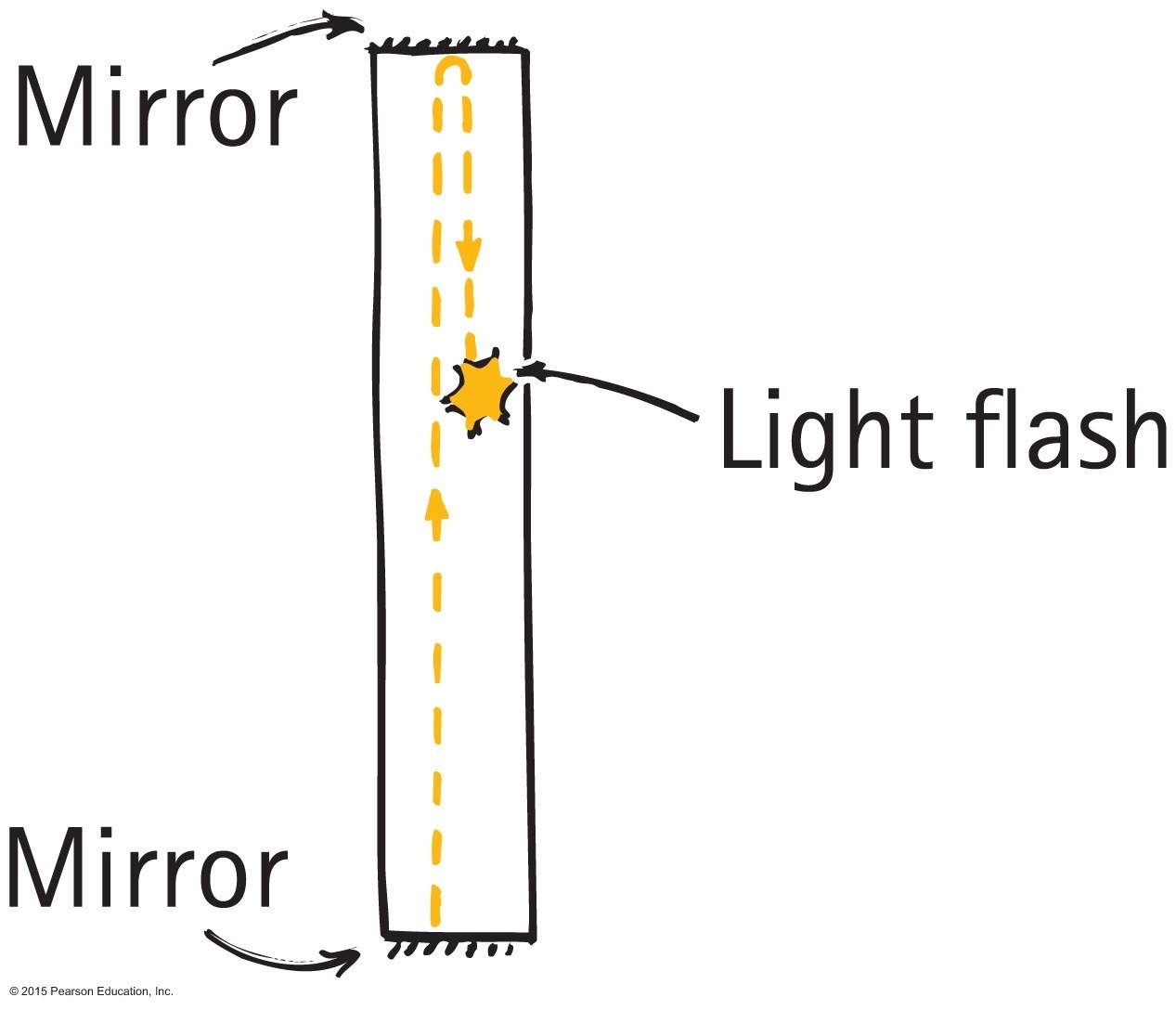
If the speed of light is constant for all observers regardless of their velocity, the distance and time must be different
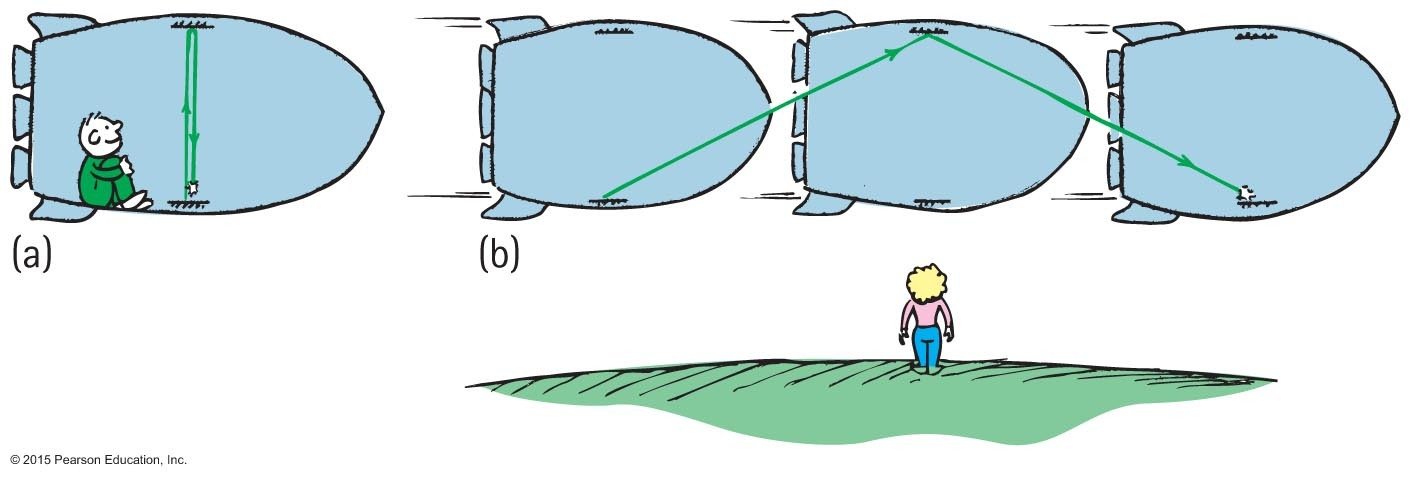
(a)
(b)
Space-Time in Relativity
General Relativity
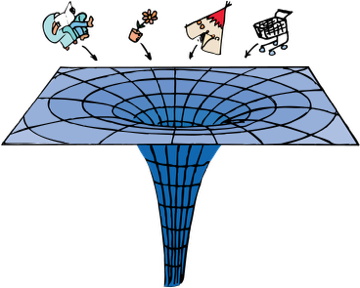
Einstein's
Gravity is the curvature of space and time due to massive objects
V.S.
Newton's
Gravity is a force field surrounding massive objects. Other masses interact with this force field
Einstein extended his theory of relativity to accelerating frames. This lead to the postulate that gravity is the curvature of space-time
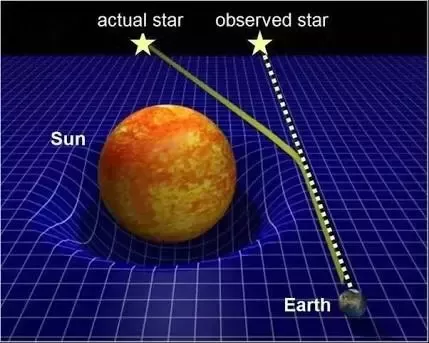
Gravitational Lensing
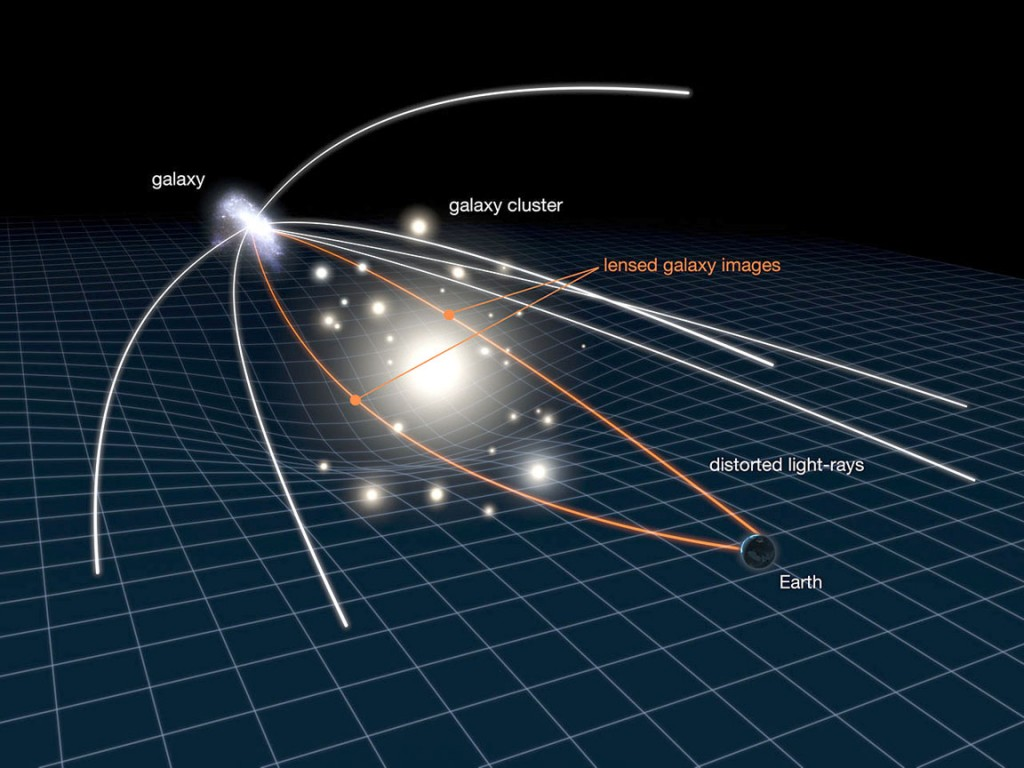
Gravitational lensing is evidence of the curvature of space-time. Light has no mass, in order to experience gravity massive objects must curve space and time

Gravitational Waves
First observed in 2015
Modern Cosmology
The study of the Universe as a whole
With General Relativity and Hubble's observations of the expanding universe modern Cosmology was born
What happens if you apply General Relativity to the whole Universe?

Accelerated Expansion
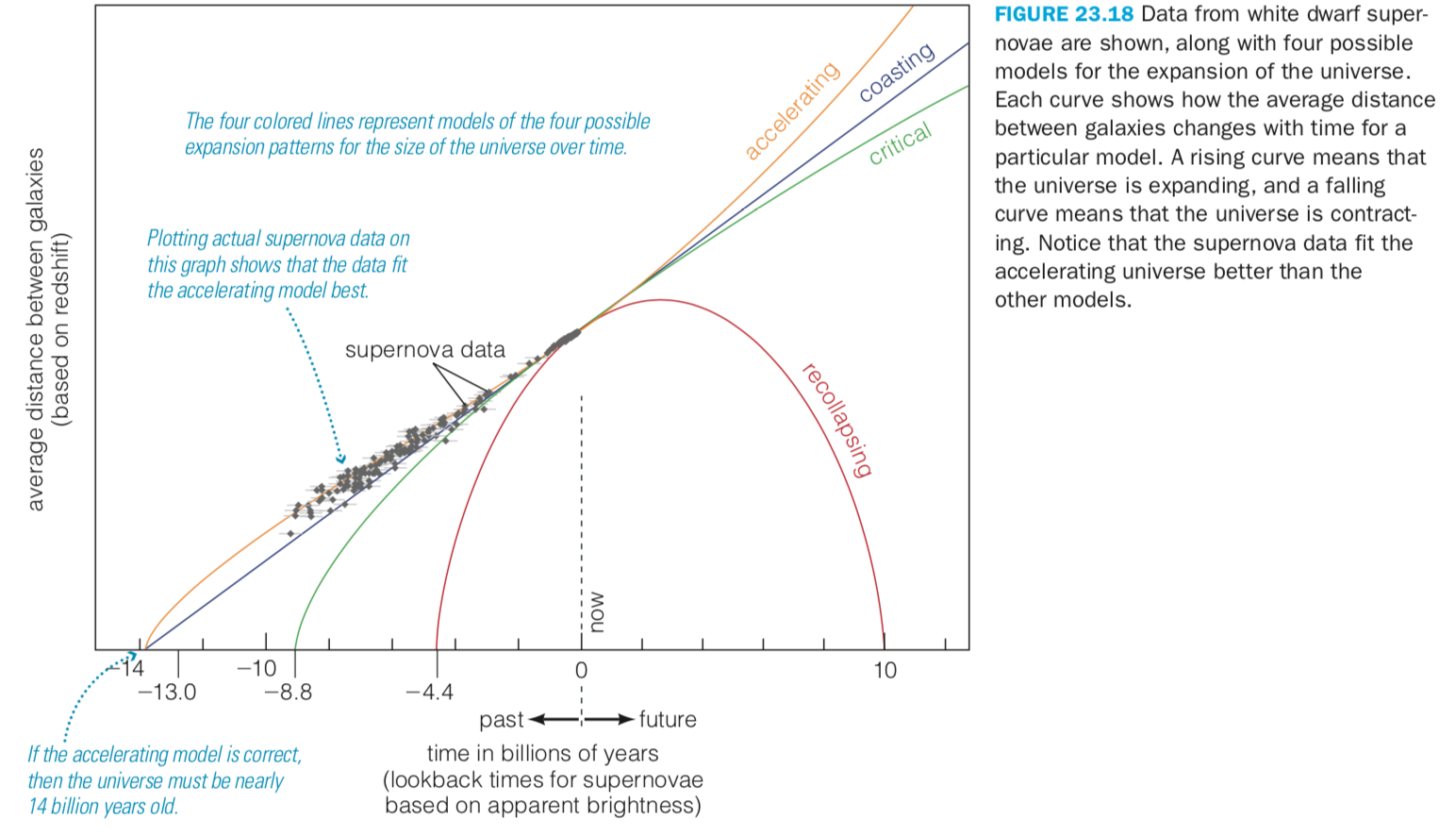
Modern observations suggest the expansion of the Universe is accelerating!
Big Bang Cosmology

If the Universe is expanding, at some time in the past must have been infinitely hot and infinitely dense
This doesn't mean that the Universe was infinitely small though.
Big Bang Cosmology doesn't state anything about the size of the Universe when was "born"!
Cosmic Inventory
From General Relativity, the expansion rate of the Universe tells us the curvature of the Universe and thus the amount of mass/energy in it
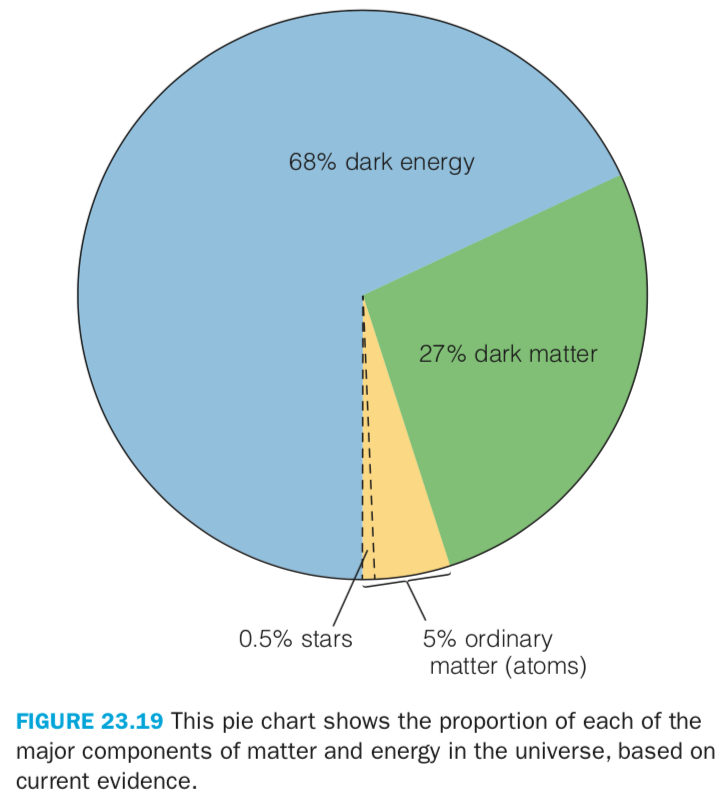
Matter provides positive gravity (attraction): we can infer the amount of mass in the universe from its gravitational effects, even though we can only directly see ordinary matter
Dark energy provides negative gravity (repulsion): We know how much dark energy there is from the expansion rate and the amount of matter we infer
Dark Matter
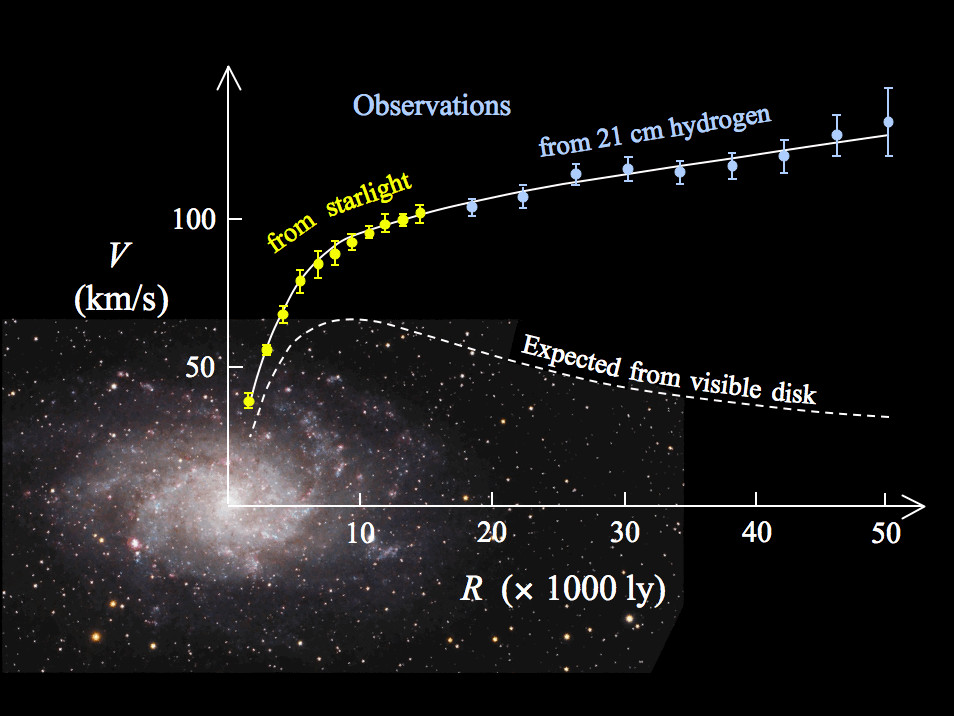
~85% of matter in the universe is made of something that does not interact with light, thus we can not see. We call this dark matter
We know dark matter is there and how much is there purely by its gravitational effects. Dark matter holds the universe together.
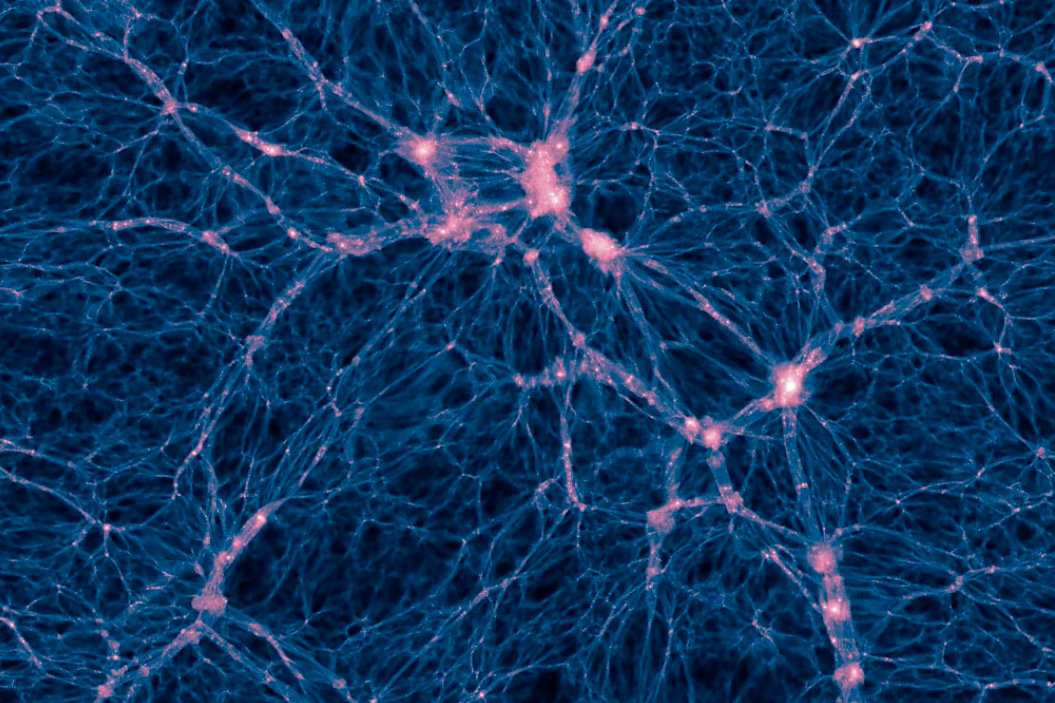
Dark Matter
Large Scale Structure and Galaxy Formation
Large Scale Structure
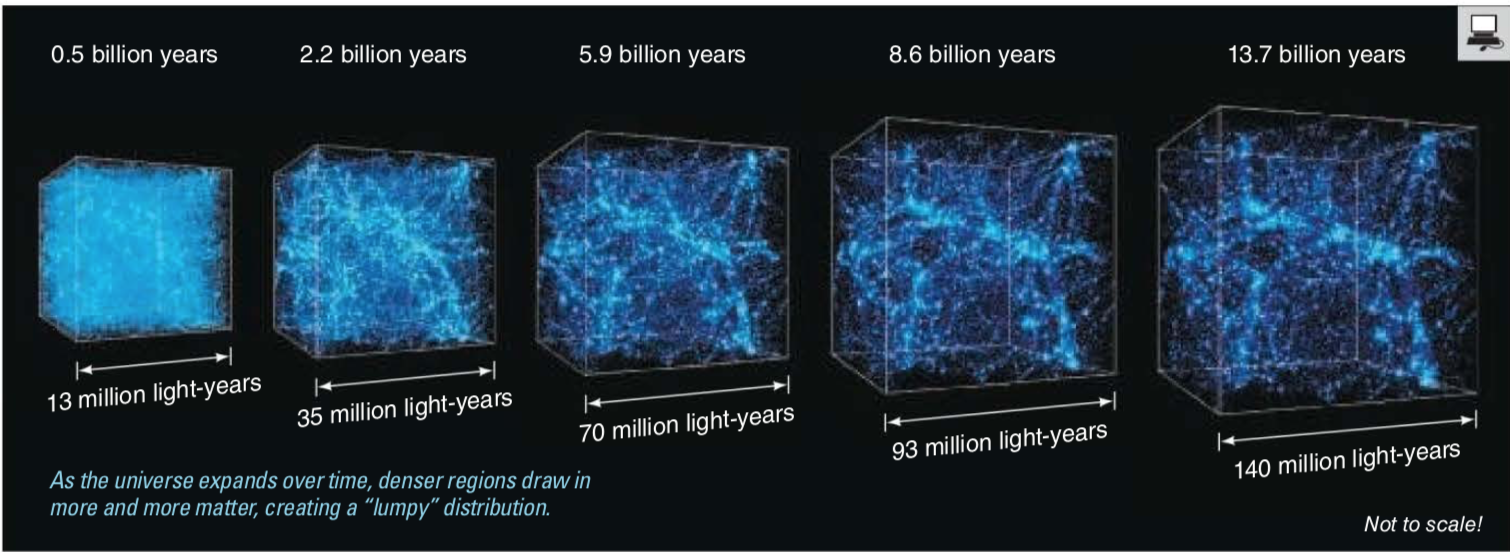
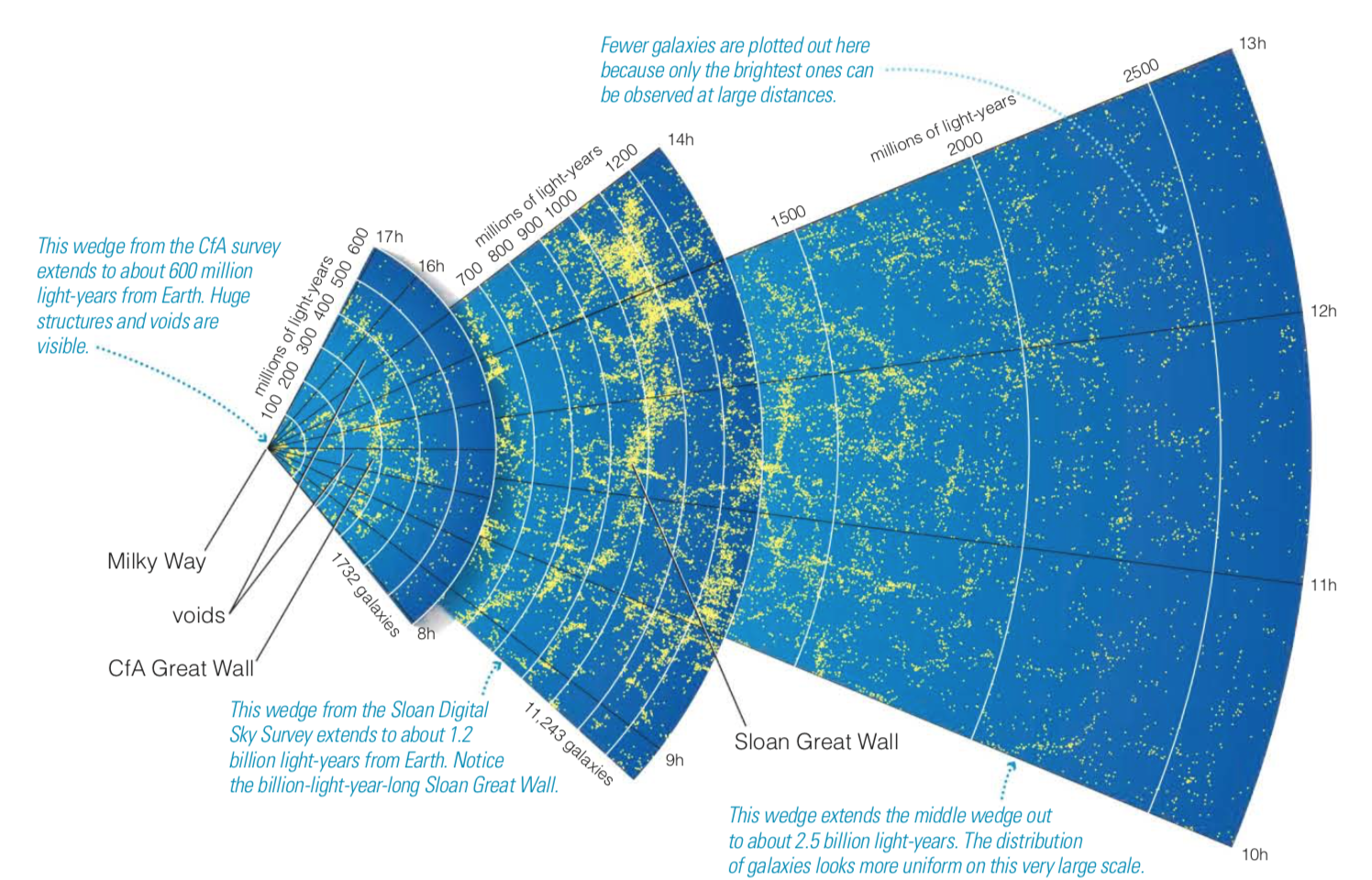
The Big Bang cosmological model reproduces the observed large scale structure of the Universe
The Cosmic Web
Galaxy Formation


Galaxy Formation
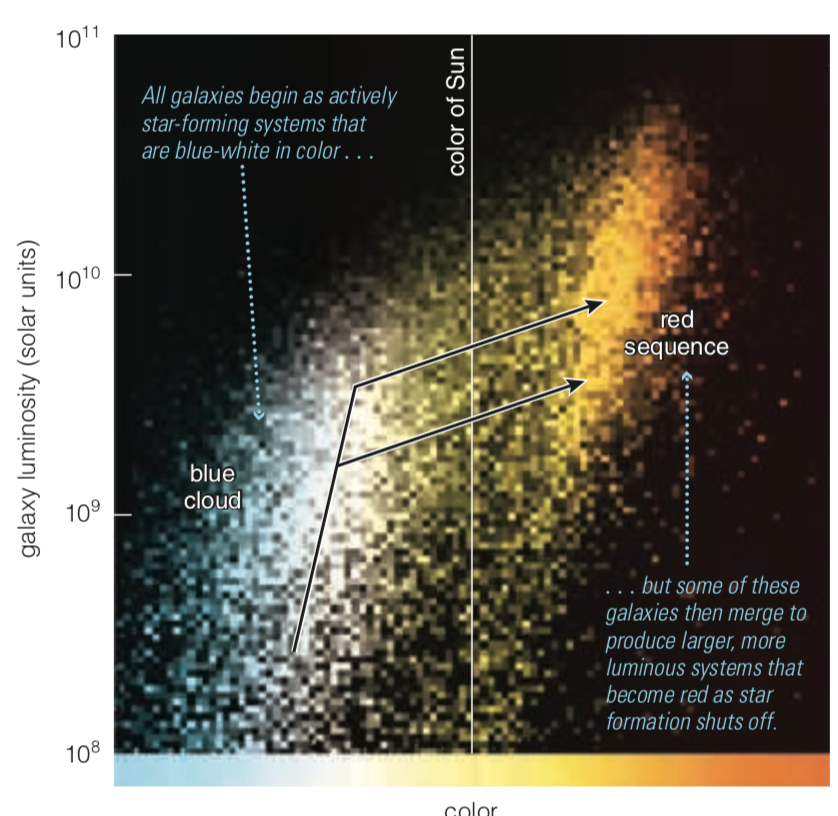
Galaxy Evolution
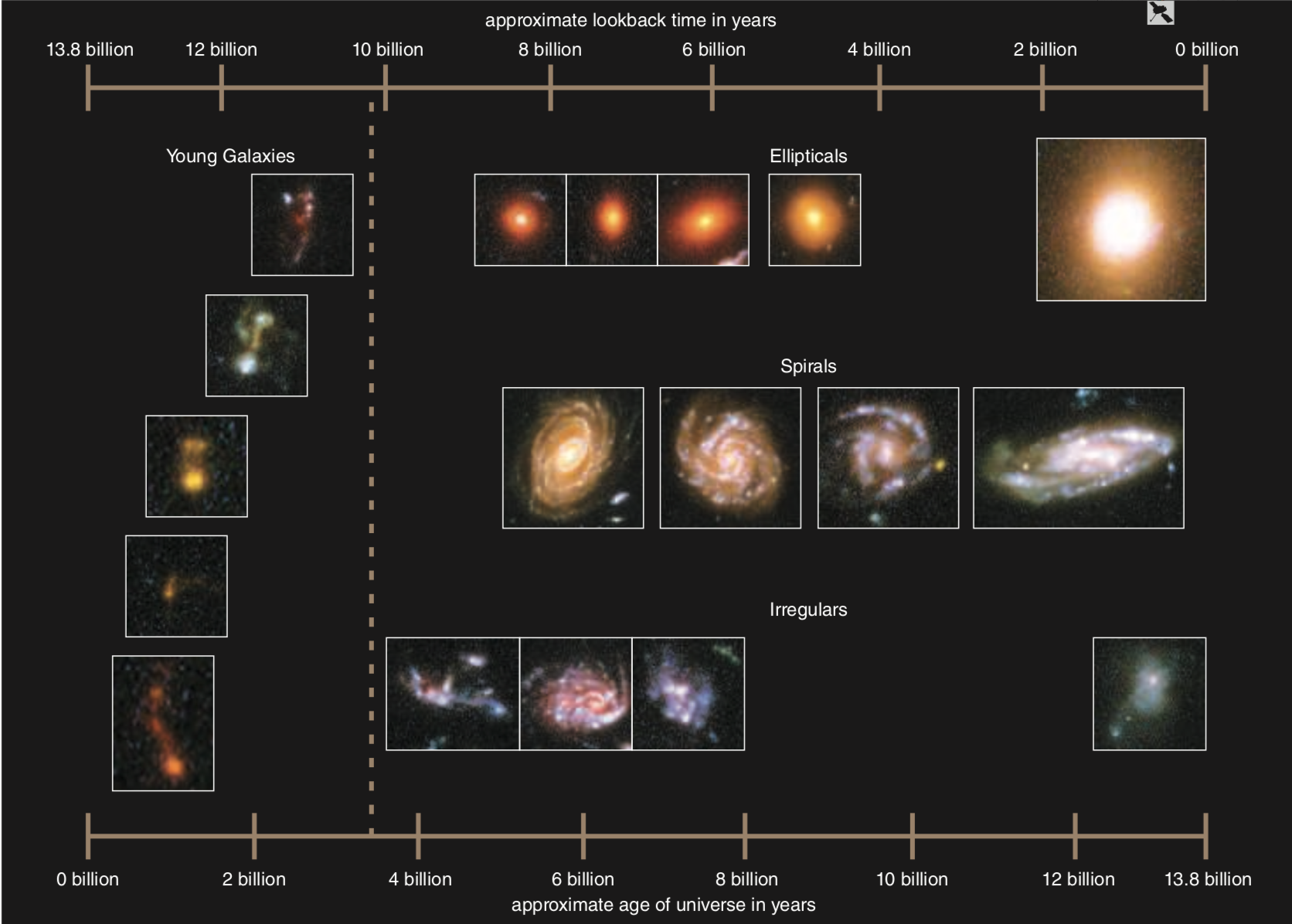

Galaxy Evolution

The End
The Standard Model

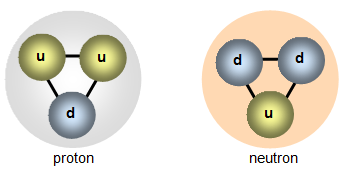
Protons and Neutrons are made of Quarks
Fundamental Forces:
Strong, Electromagnetic + Weak
Gravity?
All of the matter that we know is made of this fundamental particles
Antimatter

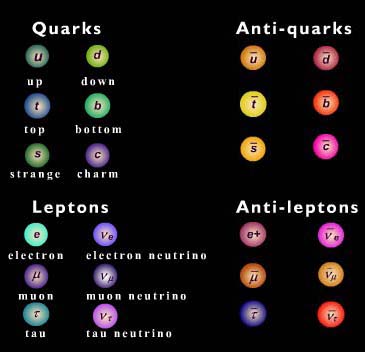
All particles have an anti-particle with the same properties but opposite charge. When matter and anti-matter combine they annihilate to produce pure energy