Gauss's Law
Physics 4B - Week 3
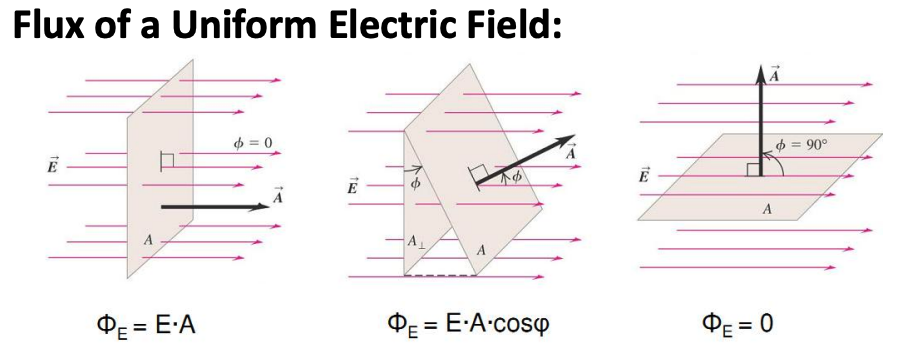

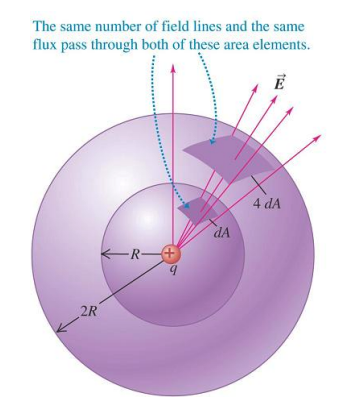

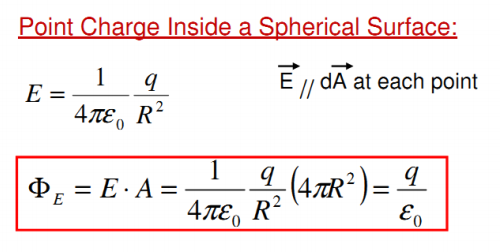
Gauss's Law for a point charge
E \propto 1/R^2 \\
A \propto R^2
Flux is independent of R
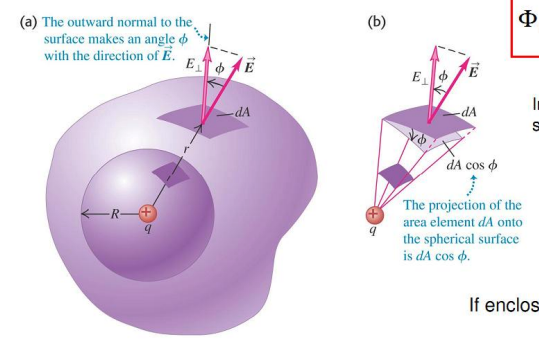
E_\perp \propto \cos{\phi} \\
A \propto 1/\cos{\phi}
Gauss's Law for a point charge
Flux is independent of the surface shape!
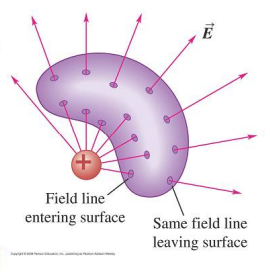
For charges outside of the enclosing surface flux cancels out
\Phi = 0
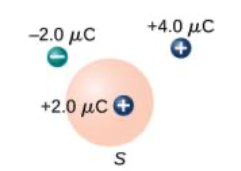
For charges not at the center of the enclosing surface, the flux is the same as if they were in the center
Gauss's Law
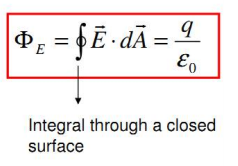
\Phi \ =\ \oint \vec{E} \cdot \overrightarrow{dA} \ =\ \frac{Q_{enc}}{\epsilon _{o}}
According to Gauss’s law, the flux of the electric field through any closed surface, also called a Gaussian surface, is equal to the net charge enclosed divided by the permittivity of free space
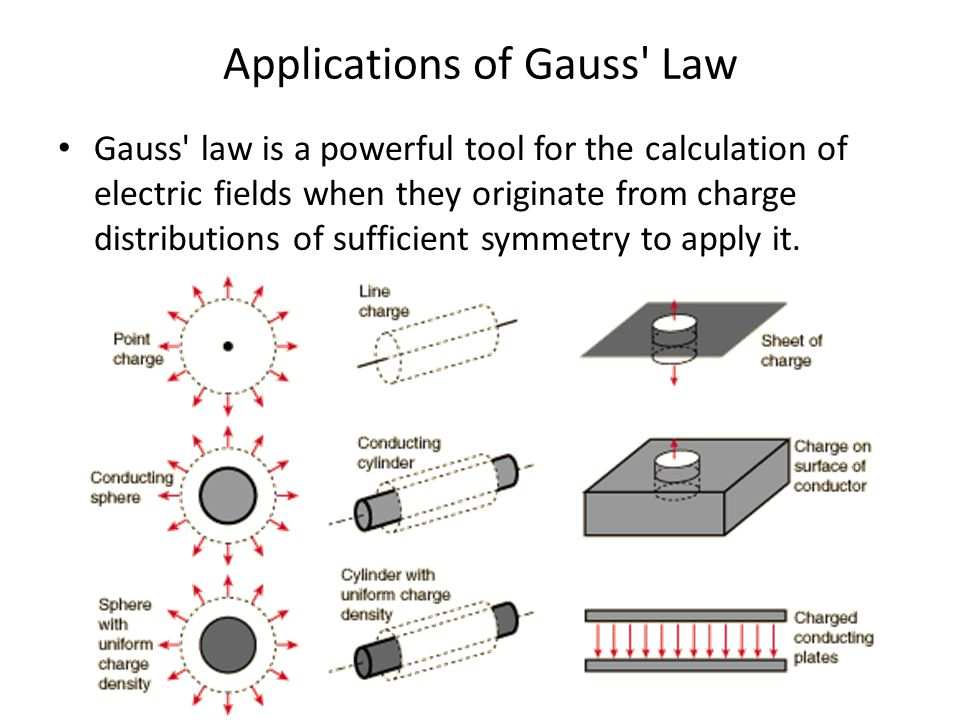
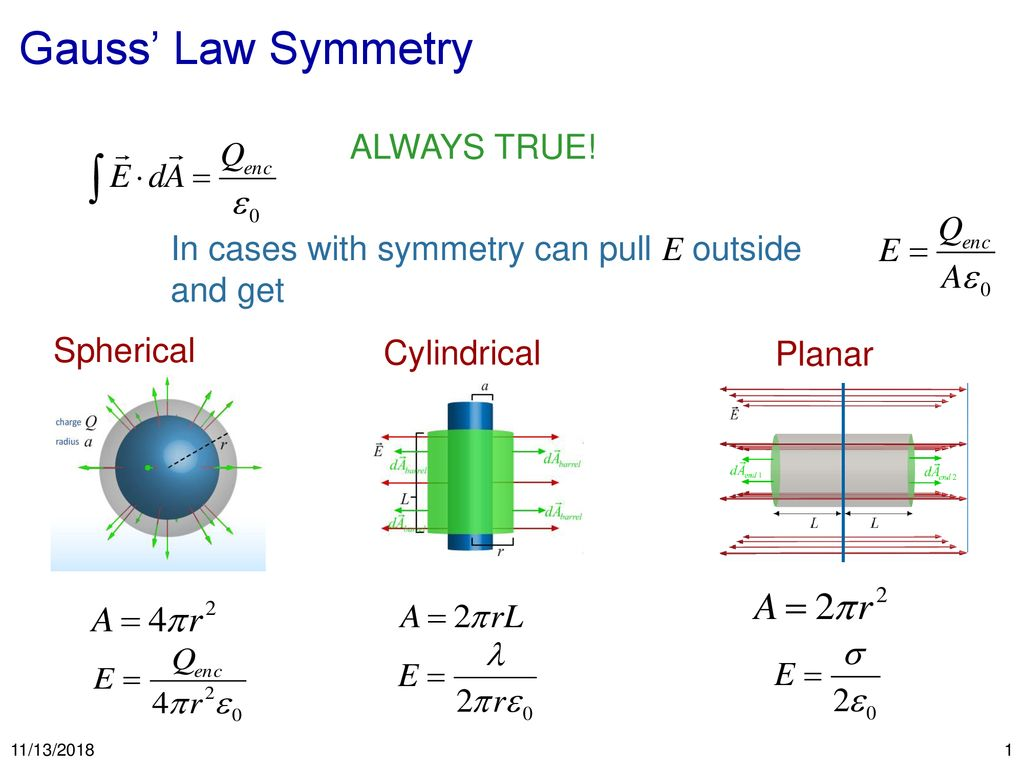
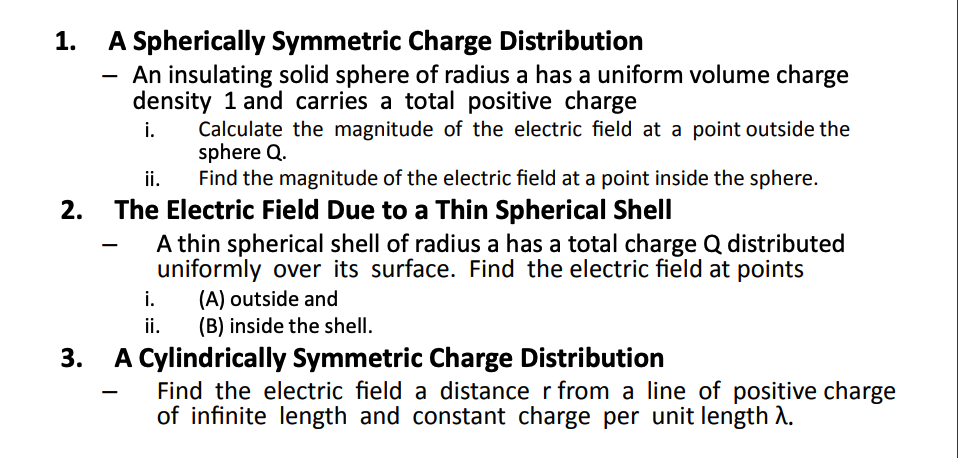
Exercises
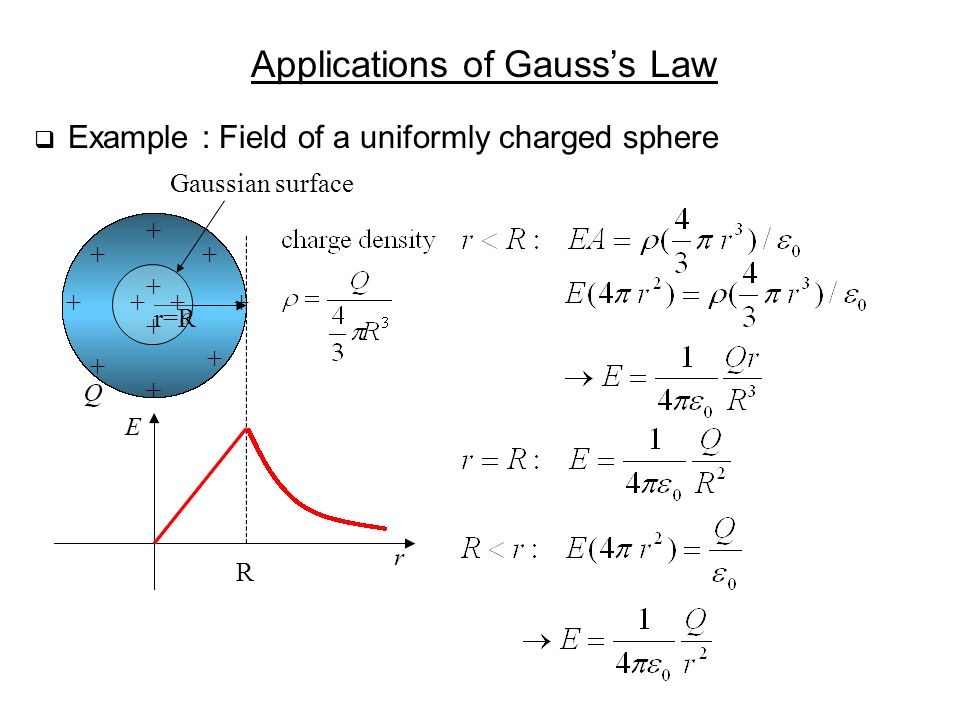

Exercises
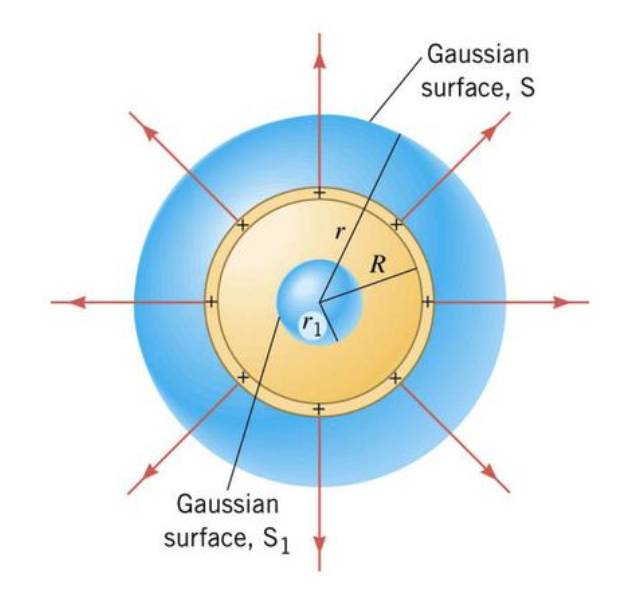

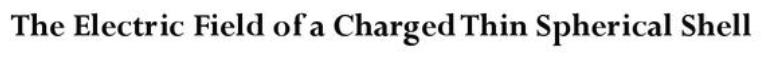
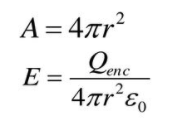
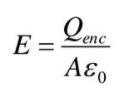
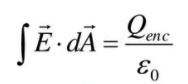



Exercises