Java 2 - 2024
Week 3
- Sorting and Filtering Lists
- Functional Interfaces
- Lambda Expressions, Method References
- Collaborative GitHub
President Class
-
Update the President class to implement the Comparable interface to create a natural sort order.
-
Create Comparator objects to compare by other data.
import java.time.LocalDate;
import java.util.Comparator;
public class President implements Comparable<President> {
// Attributes, constructors, getters, setters, and toString omitted
@Override
public int compareTo(President o) {
// Compares objects by their id (natural sort order)
return this.id - o.id;
// return Integer.valueOf(this.id).compareTo(Integer.valueOf(o.id));
}
// Compares objects by their height (low to high)
public static Comparator<President> compareHeight = Comparator.comparing(President::getHeightInInches).thenComparing(President::getId);
// Compares objects by their weight (low to high)
public static Comparator<President> compareWeight = Comparator.comparing(President::getWeightInPounds).thenComparing(President::getId);
// Compares objects by their dateOfBirth (oldest to youngest)
public static Comparator<President> compareAge = Comparator.comparing(President::getDateOfBirth).thenComparing(President::getId);
}
PresidentDAO Class
-
Write code to get the list of President objects, then sort and display the data.
import java.time.LocalDate;
import java.time.format.DateTimeParseException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Collections;
public class PresidentDAO {
private static List<President> presidents = new ArrayList<>();
public static void main(String[] args) {
Collections.sort(list);
printList("Alphabetical A-Z", list);
Collections.reverse(list);
printList("Alphabetical Z-A", list);
// Collections.sort(list, President.compareHeight);
// printList("Shortest 5", list, 5);
// Collections.sort(list, President.compareHeight.reversed());
// printList("Tallest 5", list, 5);
// printOneWithLabel("Shortest", list.stream().min(President.compareHeight).get());
// printOneWithLabel("Tallest", list.stream().max(President.compareHeight).get());
// Collections.sort(list, President.compareWeight);
// printList("Lightest 5", list, 5);
// Collections.sort(list, President.compareWeight.reversed());
// printList("Heaviest 5", list, 5);
// printOneWithLabel("Lightest", list.stream().min(President.compareWeight).get());
// printOneWithLabel("Heaviest", list.stream().max(President.compareWeight).get());
// Collections.sort(list, President.compareAge);
// printList("Oldest 5", list, 5);
// Collections.sort(list, President.compareAge.reversed());
// printList("Youngest 5", list, 5);
// printOneWithLabel("Youngest", list.stream().min(President.compareAge).get());
// printOneWithLabel("Oldest", list.stream().max(President.compareAge).get());
}
public static void printList(String title, List<President> presidents) {
printList(title, presidents, presidents.size());
}
public static void printList(String title, List<President> presidents, int count) {
// The list is printed, formatted as a numbered list, with a title above it.
System.out.println("---------" + title + "---------");
for(int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
System.out.printf("%s) %s, %s\n", (i + 1), presidents.get(i).getLastName(), presidents.get(i).getFirstName());
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void printOneWithLabel(String label, President president) {
// Prints a record with a label in front
System.out.printf("%s: %s, %s\n\n", label, president.getLastName(), president.getFirstName());
}
public static List<President> getPresidents() {
if(presidents.size() == 0) {
getFromCSV();
}
return presidents;
}
private static void getFromCSV() {
List<String> lines = FileInput.readAllLines("presidents.csv");
for(String line: lines) {
String[] president = line.split(",");
try {
int id = Integer.parseInt(president[0].trim());
String firstName = president[1].trim();
String lastName = president[2].trim();
int height = Integer.parseInt(president[3].trim());
double weight = Double.parseDouble(president[4].trim());
LocalDate dateOfBirth = LocalDate.parse(president[5].trim());
presidents.add(new President(id, firstName, lastName, height, weight, dateOfBirth));
} catch(IndexOutOfBoundsException | NumberFormatException | DateTimeParseException e) {
// Skip the line if it is missing a field, or if the String cannot be converted into an int, double, or LocalDate.
continue;
}
}
}
}
Sort a List of Objects
- Create a Main class and add the following code to sort the list of books by their title.
public class Main {
public static void notUsingLambdas() {
List<Book> books = Books.all();
Collections.sort(books);
for(Book book: books) {
System.out.println(book);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
notUsingLambdas();
}
}Lambdas in Long Form
- Remove the Comparable implementation in the Book class.
- To create a lambda, after the list name add a comma followed by a pair of parenthesis.
-
Inside the parenthesis is where we define our parameters.
- To sort things, we need to compare two objects. Those will be our parameters.
- Then, after the parenthesis type an arrow/lambda operator -> (a dash and greater than sign), followed by a set of curly brackets.
- Press enter between the curly brackets. The last line will be });
- Type code in between the curly brackets.
public class Main {
public static void usingLambdasLong() {
List<Book> books = Books.all();
Collections.sort(books, (Book b1, Book b2) -> {
return b1.getTitle().compareTo(b2.getTitle());
});
for(Book book: books) {
System.out.println(book);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
usingLambdasLong();
}
}The Declarative Way
- Let's modify the method into a short declarative form.
- The compiler can figure stuff out well enough that you don't need to declare types. Remove references to Book.
-
The single line shown below is called an expression type body.
- It creates a function that takes two book objects, and returns the value from the compareTo statement.
public class Main {
public static void usingLambdasShort() {
List<Book> books = Books.all();
Collections.sort(books, (b1, b2) -> b1.getTitle().compareTo(b2.getTitle()));
for(Book book: books) {
System.out.println(book);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
usingLambdasShort();
}
}Functional Programming
- The Collections framework benefits from functional programming with the use of the .forEach() method.
- The .forEach() method is called using a Collection object (in this case, the books List).
- It takes a single Consumer. This is a lambda that takes one parameter (in this case, book) and returns void.
public class Main {
public static void usingLambdasShort() {
List<Book> books = Books.all();
Collections.sort(books, (b1, b2) -> b1.getTitle().compareTo(b2.getTitle()));
books.forEach(book -> System.out.println(book));
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
usingLambdasShort();
}
}Method References
- We use the getTitle method on each instance of Book to get the value that will be used for the comparing command.
-
The lambda in the .forEach() method can use the static method System.out and then the method we want to do, which is println.
- This returns a reference to the println method and for each applies the entry as the parameter to the function.
- Another sort example is shown using a List of Strings.
public class Main {
public static void usingMethodReferences() {
List<Book> books = Books.all();
// Collections.sort(books, Comparator.comparing(b -> b.getTitle()));
Collections.sort(books, Comparator.comparing(Book::getTitle));
books.forEach(System.out::println);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
usingMethodReferences();
List<String> names = new ArrayList<>();
names.add("Marc");
names.add("amy");
Collections.sort(names, String::compareToIgnoreCase);
names.forEach(name -> {
name = name.toUpperCase();
System.out.printf("Hello %s\n", name);
});
}
}import java.util.*;
class SortVehiclesByNumWheels implements Comparator<Vehicle> {
public int compare(Vehicle a, Vehicle b) {
int result = a.getNumWheels() - b.getNumWheels();
if(result == 0) {
SortVehiclesByName sortBy = new SortVehiclesByName();
result = sortBy.compare(a, b);
}
return result;
}
}
class SortVehiclesByMpg implements Comparator<Vehicle> {
public int compare(Vehicle a, Vehicle b) {
int result = 0;
if (a.getMpg() < b.getMpg()) result = -1;
if (a.getMpg() > b.getMpg()) result = 1;
if(result == 0) {
SortVehiclesByName sortBy = new SortVehiclesByName();
result = sortBy.compare(a, b);
}
return result;
}
}
class SortVehiclesByName implements Comparator<Vehicle> {
public int compare(Vehicle a, Vehicle b) {
int result = a.getMake().compareToIgnoreCase(b.getMake());
if(result == 0) {
result = a.getModel().compareToIgnoreCase(b.getModel());
}
return result;
}
}
class Vehicle implements Comparable<Vehicle> {
private String make;
private String model;
private double mpg;
private int numWheels;
public Vehicle(String make, String model, double mpg, int numWheels) {
this.make = make;
this.model = model;
this.mpg = mpg;
this.numWheels = numWheels;
}
public String getMake() {
return make;
}
public String getModel() {
return model;
}
public double getMpg() {
return mpg;
}
public int getNumWheels() {
return numWheels;
}
public String toString() {
return "Make: " + make + ", Model: " + model + ", MPG: " + mpg + ", Num Wheels: " + numWheels;
}
public int compareTo(Vehicle other) {
SortVehiclesByName sortBy = new SortVehiclesByName();
int result = sortBy.compare(this, other);
return result;
}
}
public class MyClass {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Vehicle v1 = new Vehicle("Ford", "F-150", 12.8, 4);
Vehicle v2 = new Vehicle("Chevrolet", "Corvette", 12.8, 4);
Vehicle v3 = new Vehicle("Ford", "Mustang", 20.2, 4);
Vehicle v4 = new Vehicle("Chevrolet", "Camaro", 19.5, 4);
Vehicle v5 = new Vehicle("Harley Davidson", "Iron 883", 51, 2);
List<Vehicle> vehicles = new ArrayList<>();
vehicles.add(v1);
vehicles.add(v2);
vehicles.add(v3);
vehicles.add(v4);
vehicles.add(v5);
System.out.println("Show vehicles left to right");
printCars(vehicles);
System.out.println("Show vehicles alphabetically");
Collections.sort(vehicles);
printCars(vehicles);
System.out.println("Show vehicles by MPG");
Collections.sort(vehicles, new SortVehiclesByMpg());
printCars(vehicles);
System.out.println("Show vehicles by number of wheels");
Collections.sort(vehicles, new SortVehiclesByNumWheels());
printCars(vehicles);
}
public static void printCars(List<Vehicle> vehicles) {
for(int i = 0; i < vehicles.size(); i++) {
System.out.println((i+1) + ") " + vehicles.get(i));
}
System.out.println();
}
}import java.util.*;
class CompareClass implements Comparator<Vehicle> {
public int compare(Vehicle a, Vehicle b) {
int result = a.getClass().getName().compareTo(b.getClass().getName());
return result;
}
}
class SortVehiclesByNumWheels implements Comparator<Vehicle> {
public int compare(Vehicle a, Vehicle b) {
int result = a.getNumWheels() - b.getNumWheels();
if(result == 0) {
SortVehiclesByName sortBy = new SortVehiclesByName();
result = sortBy.compare(a, b);
}
return result;
}
}
class SortVehiclesByMpg implements Comparator<Vehicle> {
public int compare(Vehicle a, Vehicle b) {
int result = 0;
if (a.getMpg() < b.getMpg()) result = -1;
if (a.getMpg() > b.getMpg()) result = 1;
if(result == 0) {
SortVehiclesByName sortBy = new SortVehiclesByName();
result = sortBy.compare(a, b);
}
return result;
}
}
class SortVehiclesByName implements Comparator<Vehicle> {
public int compare(Vehicle a, Vehicle b) {
int result = a.getMake().compareToIgnoreCase(b.getMake());
if(result == 0) {
result = a.getModel().compareToIgnoreCase(b.getModel());
}
return result;
}
}
class Car extends Vehicle {
public Car(String make, String model, double mpg, int numWheels) {
super(make, model, mpg, numWheels);
}
}
class Truck extends Vehicle {
public Truck(String make, String model, double mpg, int numWheels) {
super(make, model, mpg, numWheels);
}
}
class Motorcycle extends Vehicle {
public Motorcycle(String make, String model, double mpg, int numWheels) {
super(make, model, mpg, numWheels);
}
}
class Vehicle implements Comparable<Vehicle> {
private String make;
private String model;
private double mpg;
private int numWheels;
public Vehicle(String make, String model, double mpg, int numWheels) {
this.make = make;
this.model = model;
this.mpg = mpg;
this.numWheels = numWheels;
}
public String getMake() {
return make;
}
public String getModel() {
return model;
}
public double getMpg() {
return mpg;
}
public int getNumWheels() {
return numWheels;
}
public String toString() {
return "Make: " + make + ", Model: " + model + ", MPG: " + mpg + ", Num Wheels: " + numWheels;
}
public int compareTo(Vehicle other) {
SortVehiclesByName sortBy = new SortVehiclesByName();
int result = sortBy.compare(this, other);
return result;
}
}
public class MyClass {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Vehicle v1 = new Truck("Ford", "F-150", 12.8, 4);
Vehicle v2 = new Car("Chevrolet", "Corvette", 12.8, 4);
Vehicle v3 = new Car("Ford", "Mustang", 20.2, 4);
Vehicle v4 = new Car("Chevrolet", "Camaro", 19.5, 4);
Vehicle v5 = new Motorcycle("Harley Davidson", "Iron 883", 51, 2);
List<Vehicle> vehicles = new ArrayList<>();
vehicles.add(v1);
vehicles.add(v2);
vehicles.add(v3);
vehicles.add(v4);
vehicles.add(v5);
System.out.println("Show vehicles left to right");
printCars(vehicles);
System.out.println("Show vehicles alphabetically");
Collections.sort(vehicles);
printCars(vehicles);
System.out.println("Show vehicles by MPG");
Collections.sort(vehicles, new SortVehiclesByMpg());
printCars(vehicles);
System.out.println("Show vehicles by number of wheels");
Collections.sort(vehicles, new SortVehiclesByNumWheels());
printCars(vehicles);
System.out.println("Show cars, then motorcycles, then trucks");
Collections.sort(vehicles, new CompareClass());
printCars(vehicles);
}
public static void printCars(List<Vehicle> vehicles) {
for(int i = 0; i < vehicles.size(); i++) {
System.out.println((i+1) + ") " + vehicles.get(i));
}
System.out.println();
}
}import java.time.LocalDate;
import java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter;
import java.util.SortedSet;
import java.util.TreeSet;
import java.util.SortedMap;
import java.util.TreeMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Comparator;
class Book implements Comparable<Book>{
private String title;
private LocalDate dateAdded;
public Book (String title, LocalDate dateAdded) {
this.title = title;
this.dateAdded = dateAdded;
}
public String getTitle() {
return title;
}
public LocalDate getDateAdded() {
return dateAdded;
}
public String toString() {
return title + " was added on " + dateAdded;
}
public int compareTo (Book other) {
// return this.title.compareTo(other.title);
return dateAdded.compareTo(other.dateAdded);
}
}
public class MyClass {
public static void main(String args[]) {
DateTimeFormatter formatter = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd");
Book b1 = new Book ("Book1", LocalDate.parse("2005-11-12", formatter));
Book b2 = new Book ("Book2", LocalDate.parse("2006-09-19", formatter));
Book b3 = new Book ("Book3", LocalDate.parse("2004-04-23", formatter));
SortedSet<Book> books = new TreeSet<>();
books.add(b1);
books.add(b2);
books.add(b3);
System.out.println("*** Printing books in a SortedSet ***");
for(Book b: books) {
System.out.println(b);
}
System.out.println(books);
System.out.println();
SortedMap<Integer, Book> books2 = new TreeMap<>();
books2.put(1, b1);
books2.put(2, b2);
books2.put(3, b3);
System.out.println("*** Printing books in a SortedMap ***");
for(Map.Entry<Integer, Book> entry : books2.entrySet()) {
Integer key = entry.getKey();
Book value = entry.getValue();
System.out.println(key + " - " + value);
}
System.out.println(books2);
System.out.println(entriesSortedByValues(books2));
}
// Code from https://stackoverflow.com/questions/2864840/treemap-sort-by-value
static <K,V extends Comparable<? super V>> SortedSet<Map.Entry<K,V>> entriesSortedByValues(Map<K,V> map) {
SortedSet<Map.Entry<K,V>> sortedEntries = new TreeSet<Map.Entry<K,V>>(
new Comparator<Map.Entry<K,V>>() {
@Override public int compare(Map.Entry<K,V> e1, Map.Entry<K,V> e2) {
int res = e1.getValue().compareTo(e2.getValue());
return res != 0 ? res : 1;
}
}
);
sortedEntries.addAll(map.entrySet());
return sortedEntries;
}
}Project Setup
- Download the textbook data files for the version you purchased.
- The instructor (aka the maintainer) will create a new Java project using IntelliJ, push it to a public GitHub repo, and share the URL.
- Students (aka contributors) must fork the project.
- A fork is a copy of the maintainer's repository, allowing contributors to make changes.
- In IntelliJ, contributors must click the "Get from VCS" button to clone their forked copy to their computer.
- Cloning is the process of making a local copy of a project to your local machine.
- You may get a notification saying you need to install the Java Development Kit (JDK) chosen by the maintainer.
Origin vs Upstream
- Contributors will open the Terminal in IntelliJ.
- Windows users, please set Git Bash as the default terminal.
- Enter this command to view the list of remote repositories. Your forked repository will display as "origin".
git remote -v- Origin is a reference to your project.
- Enter this command to specify the upstream repository that will be synced with the fork. Replace the x's with the repo path.
git remote add upstream https://github.com/mlhaus/xxxx.git- Upstream is a reference to the maintainer's project.
- Enter this command again to confirm that the new upstream repository you've specified.
git remote -v
Step 1: Create a GitHub Issue
- On the maintainer's repository, create a new Issue.
- Explain a feature you want to add or a bug you want to fix.
- Have a discussion with the maintainer to ensure your ideas are harmonious and don't conflict with other's work.
- The maintainer will create an issue stating they will contribute the following:
- "CompFuel" class from the Beginner's Guide, Chapter 4, Pages 119-120.
- Contributors will do this later.
Step 2: Create a New Branch
- The maintainer will start. Contributors will do this later.
- Use the Git > Branches command to create and checkout a new branch called "yourname-contribution1".
- Or they can enter this command:
git checkout -b yourname-contribution1
- Or they can enter this command:
Step 3: Add New Code
- The work done on a new branch does not affect the main branch.
- This is particularly useful when developing features or trying out new ideas.
- When working collaboratively, never work on the main branch!
- Add new packages and files on the new branch.
- The maintainer will create a package called "beginners-guide.chapter04.pages119-120", and a class called "CompFuel". Copy, paste, and edit textbook sample code.
- Contributors will do this later with a different package and class.
- Please do not edit or delete any existing files. Ensure you are not duplicating the work of another developer. These things will later cause merge conflicts, which is a topic for a different lesson.
Step 4: Commit and Push
- The maintainer will start. Contributors will do this later.
- Use the Git menu to commit and push the changes.
- For now, only add .java files, no .idea files like workspace.xml
- Make sure the commit message is meaningful and concise.
- Ensure you are pushing the "yourname-contribution1" branch, not the "main" branch.
- Or you can enter these commands:
git add .
git commit -m 'A meaningful message'
git push origin yourname-contribution1
Step 5: Make a Pull Request
- The maintainer will start. Contributors will do this later.
- Go to the "origin" GitHub repository.
- A message will appear in a yellow box saying "yourname-contribution1 had recent pushes".
- Click the green "Compare & Pull request" button.
- Scroll down the page and inspect the changes made (green means added, red means deleted).
- Click the green "Create pull request" button.
- GitHub will redirect you to the "upstream" GitHub repository.
- Wait until the maintainer approves and merges the pull request. Remote branches can be deleted after they are merged.
Step 6: Update Main Branch
- Back in IntelliJ, switch back to the main branch.
- Or you can enter this command:
git checkout main
- Or you can enter this command:
- It will appear that the new work is gone. Don't worry, it's on a different branch.
- You can safely delete the local "yourname-contribution1" branch.
- Maintainer only:
- Update the project by pulling changes from origin.
-
Or you can enter this command:
git pull origin main
-
Or you can enter this command:
- All files will be merged into the main branch.
Step 7: Fetch Changes
-
Contributors only:
-
Note: If you made any changes to the main branch (which you shouldn't have), you must remove or commit the code before continuing.
-
Use the Git > Fetch command to obtain the change history (branches and commits) from the upstream repo.
-
Or you can enter this command:
git fetch upstream
-
-
When you fetch changes from upstream, all new commits are downloaded and stored as a remote branch.
- This new data is not integrated into your local files yet.
- This allows you to check out and review the branch before merging it with your files.
Step 8: Merge Changes
-
Contributors only:
-
Use the Git > Merge command to merge changes from the upstream main branch into your local main branch.
- Or you can enter this command:
git merge upstream/main
- Or you can enter this command:
- This syncs your local main branch with the upstream repository without losing your local changes.
- Your project now contains your work along with the work of others on your team.
Step 9: Push Changes
-
Push changes to the origin repository so everything is up-to-date.
- Or you can enter this command:
git push origin main
- Or you can enter this command:
Repeat Steps 1-9
- Step 1: Create an issue
- The maintainer will say they're adding the "BoxDemo3" class from the Complete Reference, Chapter 6, Pages 119-120.
- Step 2: Create a new branch "yourname-contribution2".
- Step 3: Add new packages and files.
- The maintainer will create a package called "complete-reference.chapter06.page126", and a class called "BoxDemo3". Copy, paste, and edit textbook sample code.
- Step 4: Commit (with a meaningful message) and push the new branch.
- Step 5: Make a pull request. Wait for the maintainer to approve and merge the pull request.
- Steps 6-8: Go back to the main branch. Fetch and merge (or pull) all changes from other contributors.
- Step 9: Push the main branch to origin.
Original
Repo
Your
Copy
Local Computer
Fork it
Clone to
set Origin
Set Upstream
Fetch
Changes
Push Changes
Summary
- Git is a distributed version control system that allows developers to save and retrieve different versions of their work.
- A maintainer is a person that maintains an open source project.
- A contributor is a person that contributes to another developer's open source project.
- Forking is the process of creating a copy of a repository from one user's account to another. This allows contributors to make changes without affecting the maintainer's project.
- Cloning means making a local copy of a project to your local machine.
- Origin is the name of the remote alias from your local machine to your forked copy of the project.
- Upstream is the name of the remote alias from your local machine to the original project.
Summary
- A branch is a parallel version of a repository. It is contained within the repository, but does not affect the main branch allowing the developer to work freely without disrupting the "live" version.
- After making changes on a branch and you want those changes to be incorporated in the "live" version, you can create a pull request. The owners/maintainers will review your changes and decide whether to merge them.
- Developers can merge changes from other developers to the main branch.
- Git has built-in mechanisms to help resolve potential conflicts. A merge conflict occurs when two developers make changes to the same file.
Summary
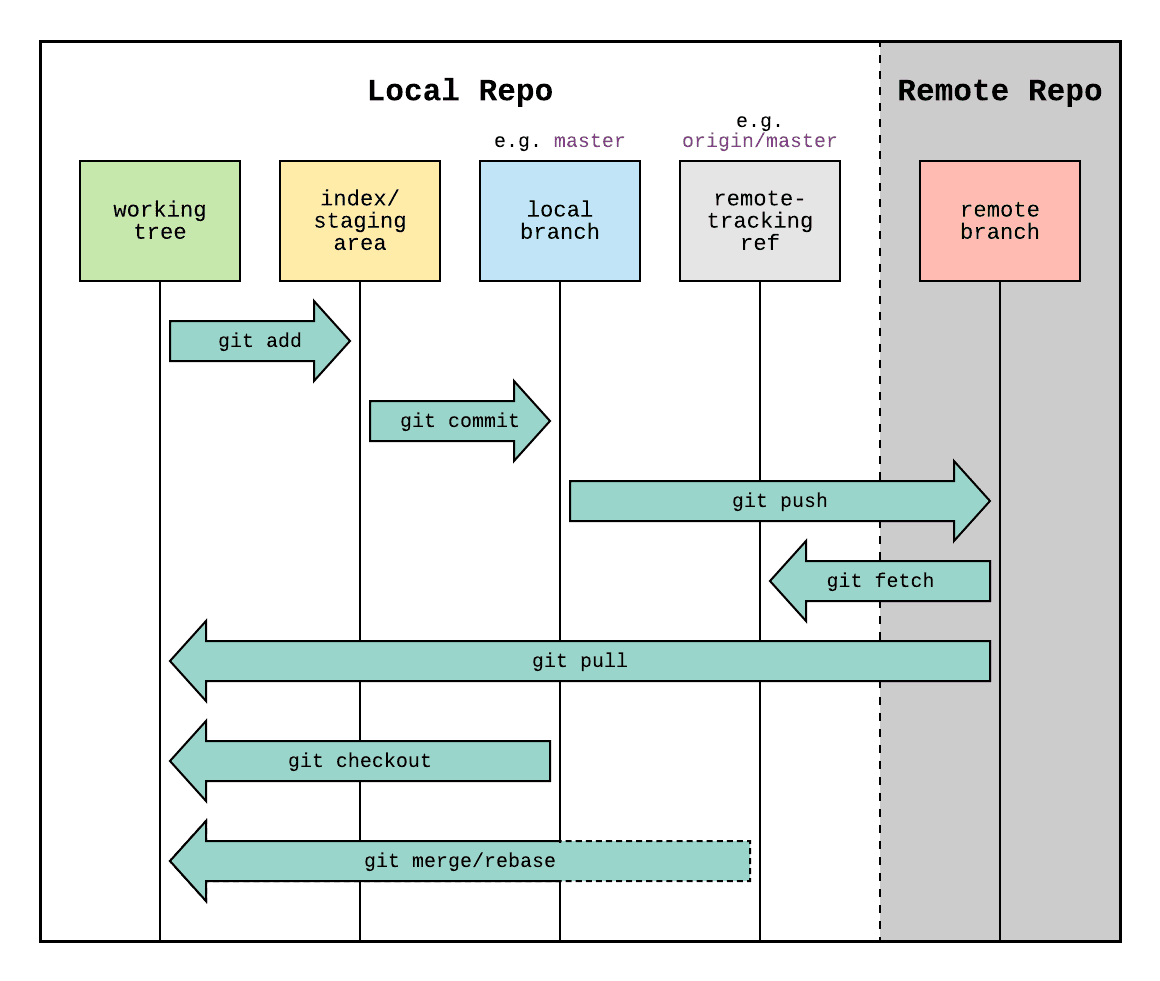
- Here’s a picture that describes how the Git workflow works.
- Note: Prior to 2020, master was the default branch name.
In-Class Activity
- Using the textbook files, pick two code samples (with a minimum of 10 lines each) from any chapter we have already covered.
- Complete steps 1-9 two times.
- Each branch must have at least one working .java file placed in a related package.
- src/main/java/edu/kirkwood/
- beginners-guide/chapterX/pageX
- complete-reference/chapterX/pageX
- src/main/java/edu/kirkwood/
- After several pull requests have been received, the instructor will demonstrate how a maintainer would review and merge pull requests.
Hacktoberfest
-
During the month of October, there is a global open source contribution initiative called Hacktoberfest.
To participate, you need to register your GitHub account on their website and make at least 4 meaningful pull requests in the month of October.
-
Here are some examples of open source projects