A Tour of the Milky Way

Manuel Pichardo Marcano
he/him/his
Department of Physics and Astronomy


One-Third of Humanity Can't See the Milky Way


The legend

Acáyouman:
Celestial Caiman

"Discovery" of the Milky Way
-
Galileo Galilei (1610):
- “The Milky Way is nothing else but a mass of innumerable stars planted together in clusters.”
- William Herschel (1784):

Center of the Galaxy
“It is believed that the great mass of the stars ... are arranged in the form of a lens-or bun-shaped system ... considerably flattened towards one plane ... the Sun occupies a fairly central position.”
—Arthur Eddington, 1914
"It is worthy of notice...that the brighter variables have longer periods.
—Henrietta Swan Leavitt (1908)
A tool to measure distances

"It is worthy of notice...that the brighter variables have longer periods.
—Henrietta Swan Leavitt (1908)
A tool to measure distances
Star Clusters

Globular Clusters
Variables in GCs
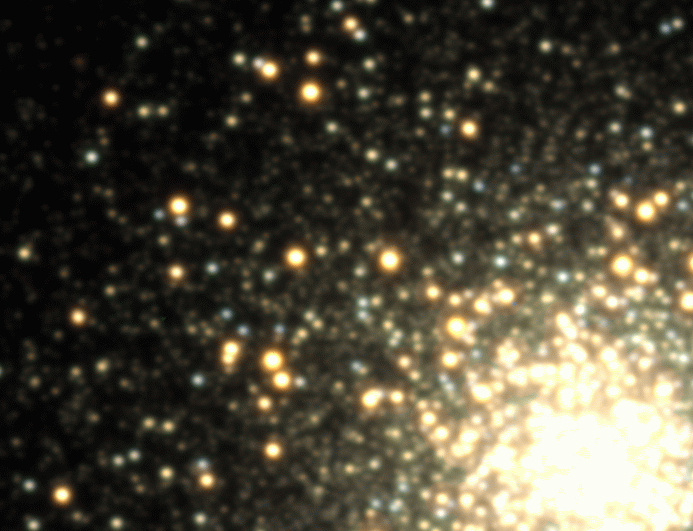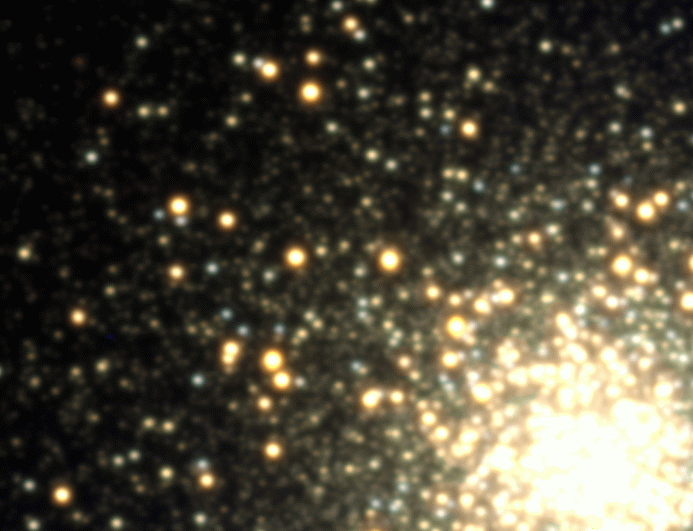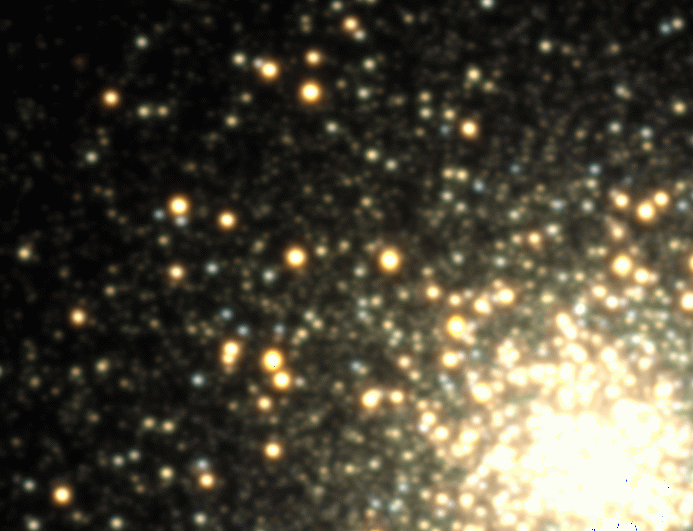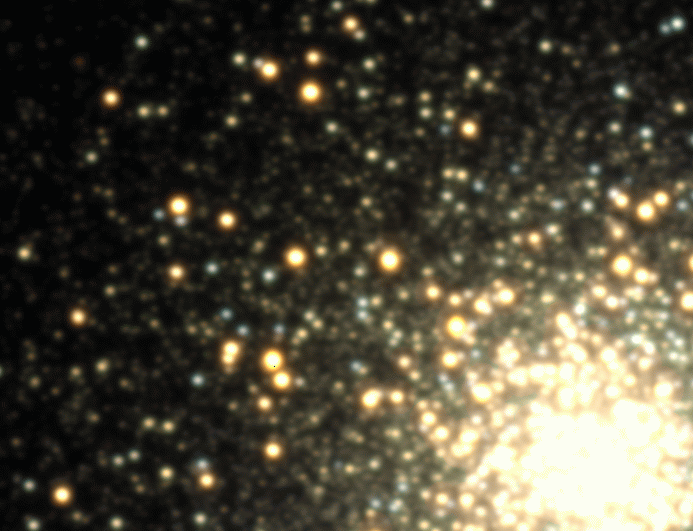
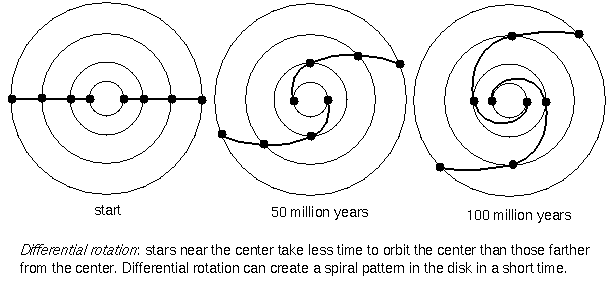
The Galactocentric Revolution

The center of the sidereal system is distant from the Earth.
— Harlow Shapley (1918)
Do the same with other regions


Current Model

How big is the Milky Way Galaxy?

The Milky Way (to scale)
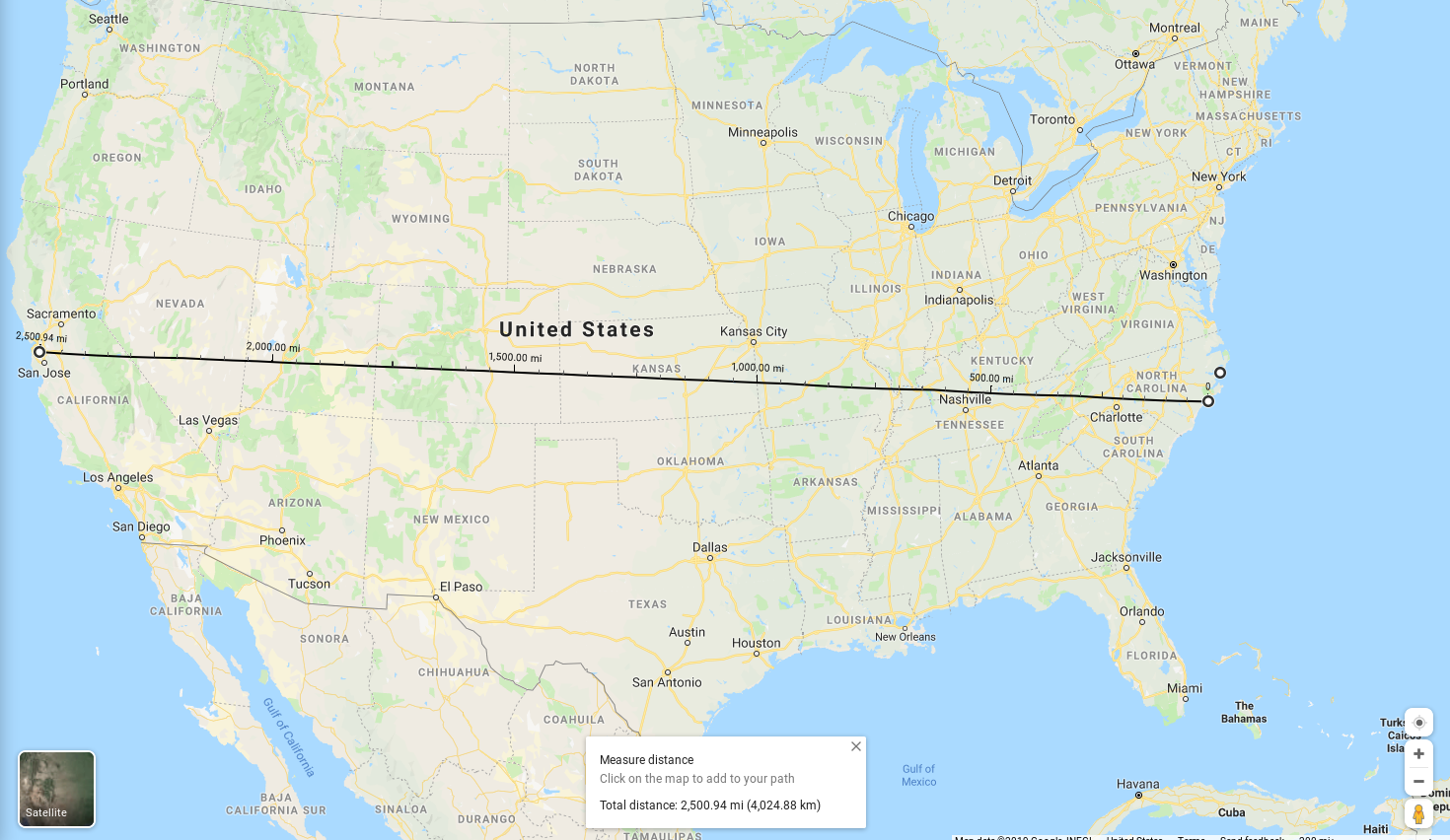
How far is 100,000 light years?
- 1 inch represents 5.5 light hours (Sun to Pluto)
- 1 mile represents 40 light years

2,500 miles
represents
100,000 light years
North America
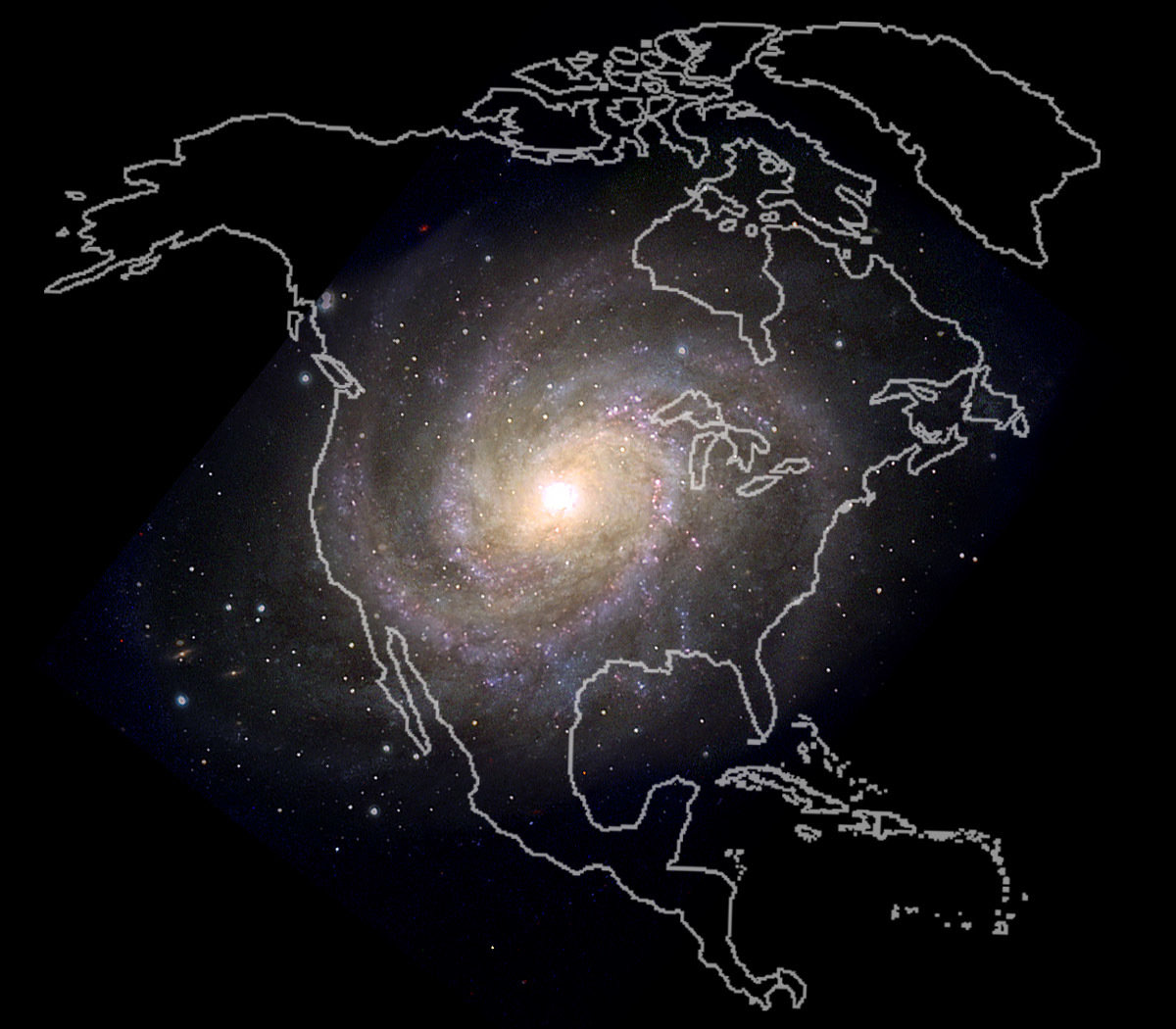
And how thick is our Galaxy?

How thick is 1,000 light years?
If 2,500 miles represents 100,000 light years
25 miles represents 1,000 light years
200 Billion Stars

Bird seeds 4 feet deep

The Tour
Dark Matter Halo
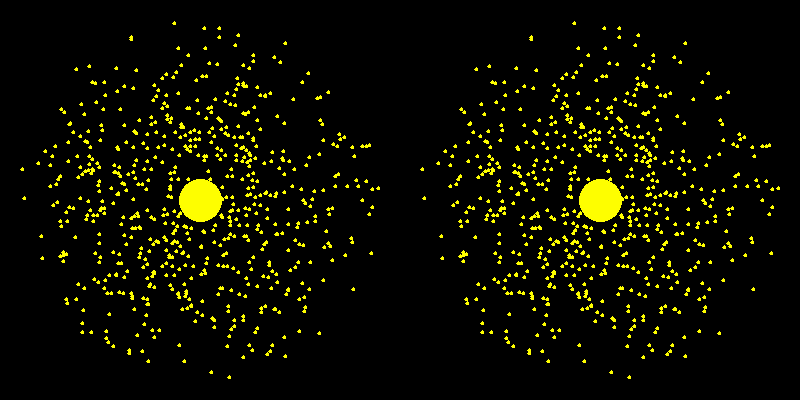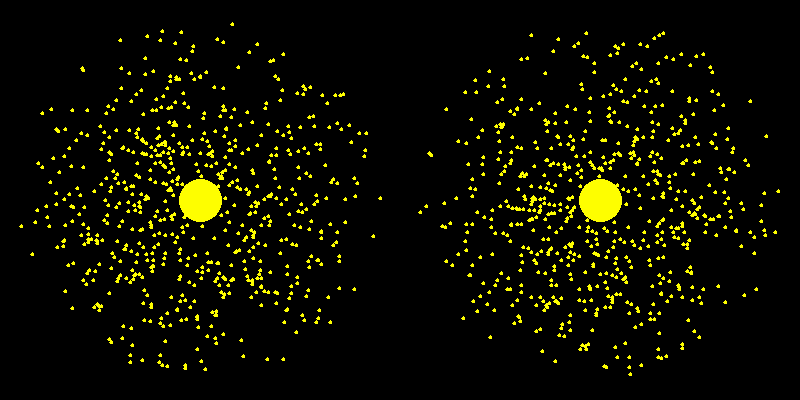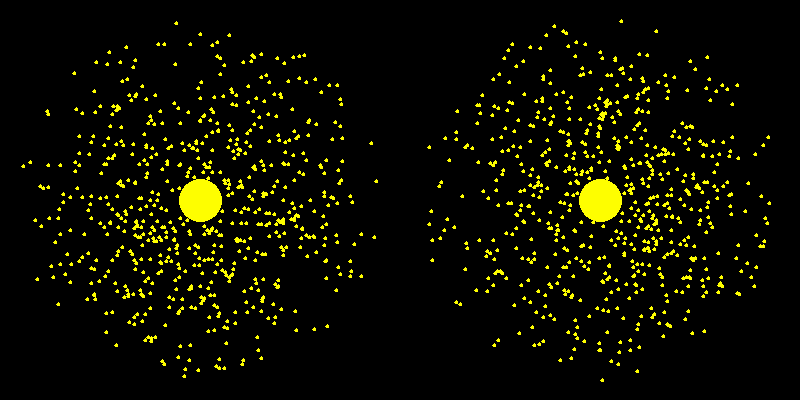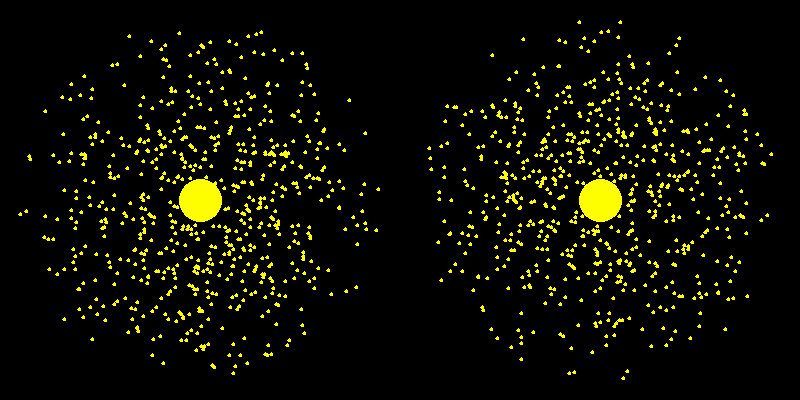
No dark matter Dark matter


Globular Clusters
~150 known in the Milky Way

A Zoo of Exotic Objects
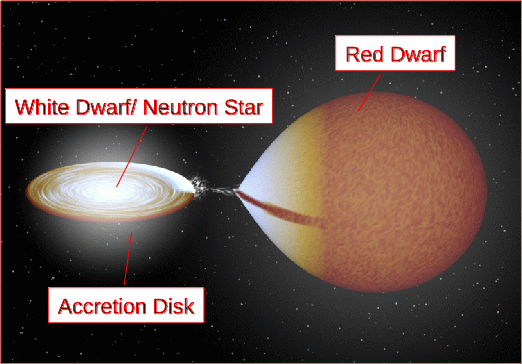





Gas around BH


Thank you
Extra slides
Subtitle