Toledo: an automated translation solution

Powered by
Python, OmegaT, Okapi, OpenXLIFF & Github
(instant) translation
These are the main needs Toledo aims to fulfil.
A couple of keywords
(platform) integration
Other needs
Other needs that we've (or our partners) had in the past but could not always be fulfilled (or not optimally):
- create OmegaT projects (setup in PISA25)
- create correct XLIFF files
- generate target files off OmegaT projects (ETS/ACER)
- etc.
Some of those things ETS or ACER could not do because they didn't have the infrastructure or the expertise.
What Toledo allows users to do
- Create a localization kit and translate it
-
Create a localization kit (translation project)
- for human translation
- for other tasks (create a project template)
- for machine translation later
- Translate an existing translation project
- Fetch the target files from a translation project
- Create an XLIFF file from the source document
- Create the target document from a translated XLIFF file
- Other tasks to come...
In a nutshell
Basically, the main services provided (at the moment) are the following:
- localization kit creation (omegat/xliff)
- machine translation (with quality estimation)
But what is the point?
Toledo provides a service that the user can use autonomously to get the job done in real time.
Caveat
- supported file formats must be negotiated in advance, especially if XLIFF is used
- currently, only QTI
Integration
In the context of RESTful APIs, integration refers to the process of connecting and enabling communication between different software systems or components through the use of web services.
Integration typically involves two systems: the client, which makes HTTP requests to the server, which exposes a REST API, in order to perform CRUD operations:
-
Send data (to create a resource)
-
Retrieve (or read) data
-
update existing data
-
delete data
Technically, what is Toledo?
Any of the following would be fine names to refer to it:
- a server application
- a (translation or language) solution
- a web service
- a backend service
- a RESTful API
- an API-driven web app
What is an API?
Application Programming Interface
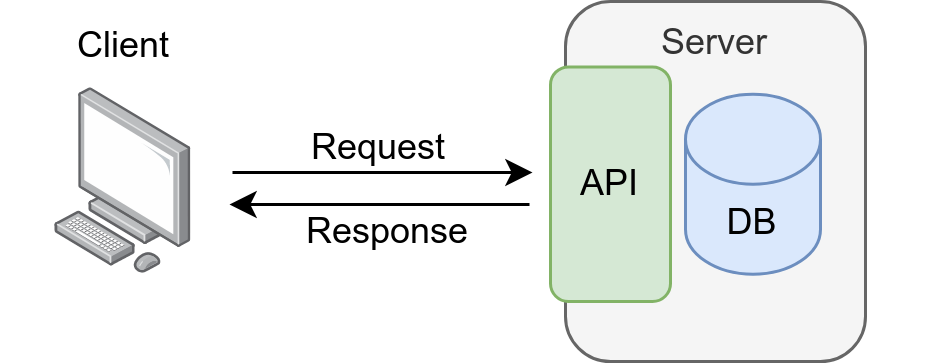
The client application
The API can be consumed by different client applications, which will send the request to Toledo and receive a response from it. Clients may be:
- IIL platform developed by Theodo (FLIP+)
- PISA platform developed by ACER
- any other platform
- a web app (for our PMs) ~ coming soon
- OmegaT ~ coming soon
- etc.
The workflow





IIL
API
request


source text
translation + score




confidence label





International Item Library
- Member countries want to share their materials with the other members.
- For that, materials must be translated into a common language (English) before they can be used by other members.
- A user would upload a QTI package to the IIL platform.
- The package is translated on the fly and the instrument will appear in English.
- A confidence label will indicate how good the translation is.
The workflow


IIL
API
request



source text
MT




confidence label

QE



e.g.
0,098
platform
confidence label

The language profile
- Each user is assigned a language profile
- The language profile determines:
- the language pairs the user is entitled to consume
- the translation providers that will be used
- how quality estimation scores are to be interpreted
The translation providers
- We have set up connections to several MT providers.
- Which provider(s) may be used can be defined in the language profile, by means of a list sorted by preference. For example:
- DeepL: first option
- Google: first fall-back plan
- Widn: second fall-back plan
- etc.
- Another option is used only if the one being tried fails.
* deepl
* google
* modernMT
* widn
* lara



QE and confidence labels
If the language profile assigned to the user has defined quality ranges, confidence labels will be used.
e.g. for IIL, we have determined three labels
- Good quality: between 1 and 𝑥
- Good enough quality: between 𝑥 and 𝑦
- Lower quality: between 𝑦 and 0
The client receives an average, but each segment has its own QE score and confidence label.
The quality estimation (QE) score is a number between 0 and 1, e.g. 0.8567. It might be difficult to interpret.
{
"_id": {
"$oid": "67d025106f45d6580aa4ada5"
},
"name": "IIL",
"language_pairs": [
{
"source_lang": "pt-BR",
"target_lang": "en-GB",
"engines": [
"deepl",
"google",
"widn"
],
"quality_ranges": [
{
"label": "Good quality",
"max": 1,
"min": 0.8566
},
{
"label": "Good enough quality",
"max": 0.8565,
"min": 0.8076
},
{
"label": "Lower quality",
"max": 0.8075,
"min": 0
}
]
},
(...){
"...": [
{
"source_lang": "nb-NO",
"target_lang": "en-GB",
"engines": [
"widn",
"deepl",
"google"
],
"quality_ranges": [
{
"label": "Good quality",
"max": 1,
"min": 0.8
},
{
"label": "Good enough quality",
"max": 0.7999,
"min": 0.71
},
{
"label": "Lower quality",
"max": 0.7099,
"min": 0
}
]
},The workflow


API
target?

response


The workflow




PE?

post-editor
文

or
The workflow


API
target?

response


Keeping track of expense
- Every MT and QE request induces an expense
- typically 20 euros / 1M words
-
Toledo-track is a separate component/app that is used to keep track of MT and QE expense:
- Toledo logs the number of characters of each translation or QE request and some other details
- It can be called from outside Toledo, e.g. from the FLASH app that runs in UR
- In the backlog: add token-based expenses
demo
Next steps
- Create new endpoints for new tasks:
- Translate ✅
- Add quality estimation scores
- Repair matches
- Insert tags
- Perform automatic adaptations:
- Alphabets / spelling
- Formality
- etc.
Documentation
OmegaT
OmegaT is a CAT tool (or translation editor). It is:
- Free software (free as in freedom and free of cost)
- Multiplatform (it works on Windows, macOS, Linux)
- Filters for more than 30 file formats (XLIFF, DOCX, etc.)
- Follows translation industry's open standards closely
- Open source: one may modify the code (or hire a developer to do it for you) to suit your own requirements
- Customisable and expandable by means of scripts/macros and plugins
Some key takeaways
Some key takeaways:
- we provide translation for content that users upload without any human looking at it first
- a translation project is created as a by-product which allows human intervention if required later (e.g. PE, localization engineering, etc.)
- the translation is consumed by our customer's user almost instantly with a hint about quality
A team effort
Different TTT members have contributed to this work:
- Gergoe: code reviews, refactoring, coding advice
- Kos: testing, feedback, omegat scripts
- Laura: selection of MT providers, definition of quality ranges and confidence labels, AI advice
- Manuel: design and planning, coding, code reviews





* omegat + okapi
* openxliff
* github
* python 3.12
* mongodb

What's in a name
Other APIs coming soon
- VeryFire 2.0
- Langtags
- xDiff
The workflow


client
Toledo
translation request



source text
MT


confidence label
QE


e.g.
0,098
customer's platform

post-editor
文
( )