Research About Photography
'Photography' is an important element in media studies to help achieve our preliminary task - designing a school magazine and main task - designing a magazine according to the genre. For this reason we were having our photography classes from a couple of weeks. Before I discuss about my magazine portrait, I would like to discuss about the basics of photography on which my portrait will be based - following rules of photography.
Text
Importance of Light in Photography
It is the most important part of of every photo we take. It creates everything we see and affects how it appears. In many cases, good and bad photos are differentiated on the availability of light in the scene. It created shadows, highlights, textures, accents color, creates moods and emotions and a vast array of other enhancing effects. By the same token it can also create harsh contrasts, bright spots, dark spots, glare and other issues that are sometimes associated with poor photographs. I have taken a lot of photographs and yes I believe finding the good light is a skill that comes with experience. While taking a pic of a portrait for my magazine this will help me in detecting the right light an help improve quality of my image.
Fundamentals of Light:
- Exposure - How bright a scene is and the way it affects our image.
- Quality - how focused or diffused the light is. Different types of light - dark, light, soft and hard.
- Color - the color of the light in an image
- Direction - where is the light coming from?
- Highlights - the brightest part of an image
- Shadow - the darkest part of an image
- Contrast - The difference between the dark and light par of an image. High range between two - little contrast. Little range between two - high contrast.
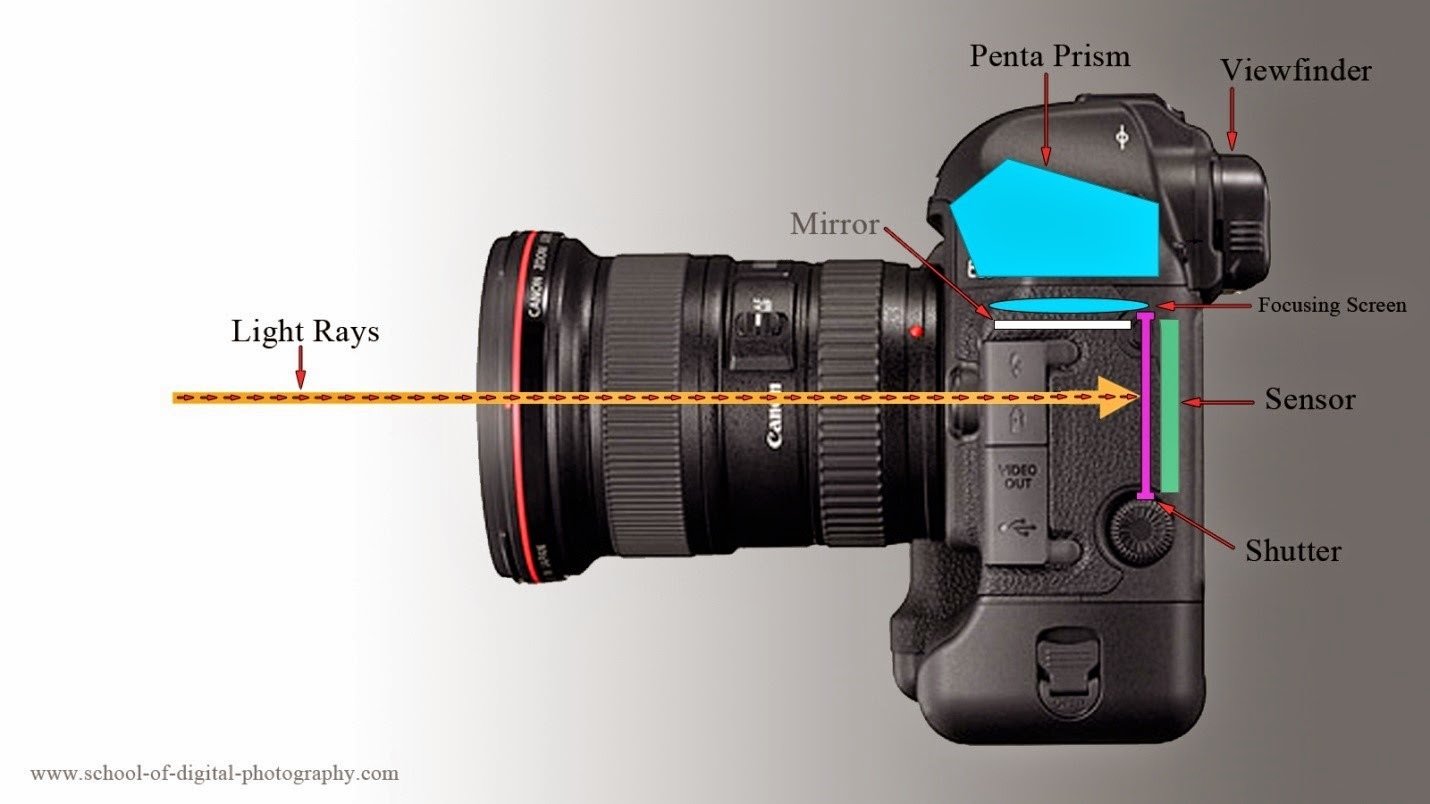
HOW THE CAMERA WORKS?
Key Terms of Photography:
- Aperture: It controls the amount of light that is allowed into the lens. It is an adjustable hole inside the lens that may be made larger or smaller to control the intensity of light. It is also used to control the 'depth of field.' It is measured in F-Stops - a change in the area of the aperture opening that either doubles or halves, thus doubling or halving the amount of light allowed into lens.
- Shutter Speed: The cameras shutter is a device that opens or closes for a specified amount of time to allow entering the light into the lens to expose the film. The duration of the opening is determined by the amount of light entering the lens. The aperture and the shutter works together to produce correct exposures. It is controlled through shutter stops - a change in shutter speed that either doubles or halves the duration of shutter opening time.
- ISO: This is a rating that describes a the sensors sensitivity to light in numbers such as 100, 200, 300 and 800. ISO 200 is twice as sensitive to light as ISO 100.
- Depth of field: It refers to the amount of photographic image that is in focus. Wide depth of field - when all the image, foreground, middle ground and distant ground is in focus. Narrow depth of field - when some parts of an image are out of focus such as background and foreground, leaving only middle ground in focus.
Focal Length: It measures the distance between the lens and the image sensor, measured in millimeters. Lenses can be classified into subgroups like prime, macro, wide angle, normal, telephoto and zoom lenses.
- Rule of Thirds: In the rule of thirds, photos are divided into thirds with two imaginary lines vertically and two lines horizontally making three columns, three rows, and nine sections in the images. Important com-positional elements and leading lines are placed on or near the imaginary lines and where the lines intersect. It stems from the theory that the human eye naturally gravitates to intersection points that occur when an image is split into thirds.
Key Terms of Photography:
Aperture: It controls the amount of light that is allowed into the lens. It is an adjustable hole inside the lens that may be made larger or smaller to control the intensity of light. It is also used to control the 'depth of field.' It is measured in F-Stops - a change in the area of the aperture opening that either doubles or halves, thus doubling or halving the amount of light allowed into lens.
Shutter Speed: The cameras shutter is a device that opens or closes for a specified amount of time to allow entering the light into the lens to expose the film. The duration of the opening is determined by the amount of light entering the lens. The aperture and the shutter works together to produce correct exposures. It is controlled through shutter stops - a change in shutter speed that either doubles or halves the duration of shutter opening time.
ISO: This is a rating that describes a the sensors sensitivity to light in numbers such as 100, 200, 300 and 800. ISO 200 is twice as sensitive to light as ISO 100.
Depth of field: It refers to the amount of photographic image that is in focus. Wide depth of field - when all the image, foreground, middle ground and distant ground is in focus. Narrow depth of field - when some parts of an image are out of focus such as background and foreground, leaving only middle ground in focus.
Key Terms of Photography:
Focal Length: It measures the distance between the lens and the image sensor, measured in millimeters. Lenses can be classified into subgroups like prime, macro, wide angle, normal, telephoto and zoom lenses.
Rule of Thirds: In the rule of thirds, photos are divided into thirds with two imaginary lines vertically and two lines horizontally making three columns, three rows, and nine sections in the images. Important com-positional elements and leading lines are placed on or near the imaginary lines and where the lines intersect. It stems from the theory that the human eye naturally gravitates to intersection points that occur when an image is split into thirds.
Low Key and High Key Photography: Low key refers to shadows in the images or the darker tones in an image where by the content in the image is not visible. On the other hand High key refers to highlights or brighter parts in an image and hence making content in the image invisible.

Rule of Thirds


Camera Shots
Camera Angles

