Hacktrophy - the rise of crowdsourced security

Traditional & crowdsourced approach
Bug bounty programs in details
Objections
Commercial bug bounty programs




Traditional & crowdsourced approach
Bug bounty programs in details
Objections
Commercial bug bounty programs
Victims of Hackers' attacks

Victims of hacker's attacks
(Czech Republic & Slovakia)
| Customer | Vulnerability | Damage | Fix time |
|---|---|---|---|
| Czech Construction Company | Vulnerable contact form allowing to send malware including ransomware | Direct 4000 EUR + indirect costs (loss of reputation) | 5 days |
| Czech e-shop | Dump of the whole database using SQL injection | Direct 10000 EUR + indirect costs (loss of reputation) | 14 days |
| Slovak IT company | Weak password to the admin interface leading to compromise VPN & access to the internal network | Direct 250000 EUR | 6 months |
| Slovak e-shop | The application vulnerability allowing to send spams to their customers | Indirect costs (loss of reputation) | 3 days |
Threats vs typical attacks
| Threats | Typical attacks |
|---|---|
| Insiders (disgruntled employee) | Leakage, Backdooring, Espionage |
| Ransomware (Malware) | Forced disk encryption with unknown passphrase |
| Automated botnets | Simple infrastructure scans, simple WebAppSec attacks, DDoS attacks |
| Cyber Crime Syndicates, Rented blackhat hackers | Complex & Sophisticated WebAppsec attacks + infrastructure attacks, installing malware |
| Social Engineers | Pretexting, Phishing, Vishing, Baiting, Piggybacking, Typosquatting... |
| Hacktivists, political hackers | Web defacing, DDoS attacks |
Traditional approach
-
customer chooses one specific company for penetration testing that means:
-
a limited number of ethical hackers is used for the given testing
-
a limited amount of time is used for the given testing
-
a limited competition of the given company in the given region leading to high prices
-
- on the other hand, the traditional penetration testing company guarantees the given testing is always performed, but with no guarantee of real results (revealed vulnerabilities)
Crowdsourced approach
-
customer sets an economic incentive (bounty) for a big group of ethical hackers around the globe to test his application/service that means:
-
a big crowd of ethical hackers is used for the given testing
-
almost unlimited amount of time is used for the given testing
-
because of global competition of ethical hackers, prices could be relatively low or reasonable
-
- in case of insufficient incentive (bounty), there is no guarantee of being tested by the ethical hackers, but there is a guarantee of revealing real vulnerabilities when the customer is obligated to pay
Hackers vs. companies
-
their relationship is usually strongly asymmetrical:
-
army of skilled blackhat hackers need to reveal at least one vulnerability
-
usually defender (company) have to patch all vulnerabilities
-
-
bug bounty programs change this paradigm:
- they allow to use the crowd of ethical whitehat hackers, use their knowledge and experience to protect customers and their systems
Bug bounty programs
-
benefits from the global market
-
more eyes (of the crowd) usually mean better security
-
allow people with hacker skills to gain their money in a completely legal way without a risk of prosecution
-
end-to-end connection between the customer and the ethical hackers may lead to a reduction of transaction costs (the same for Uber, Airbnb, ...)
-
because of the relatively anonymous crowd, the reputation becomes much more important
Bug bounty program flow
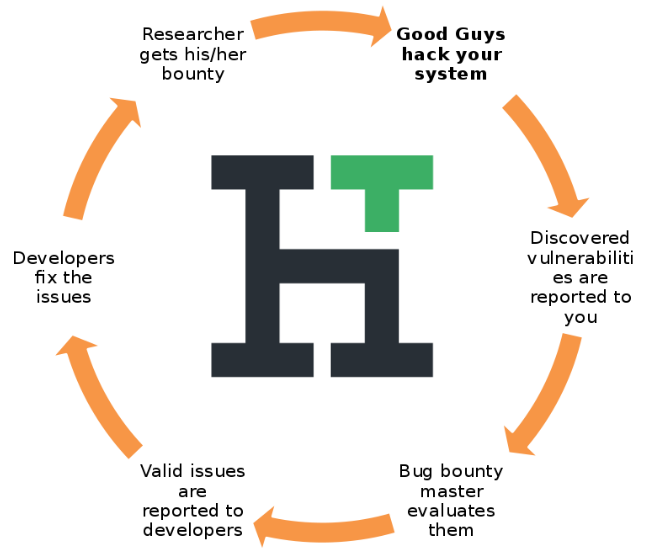
Bug bounty program as "Uber for hackers"
-
Bug bounty programs represent a sharing economy model ("Uber for hackers") with all related advantages:
-
strong reputation of the ethical hackers
-
lower transaction costs in case of end-to-end connection between the customer and the hacker
-
strong economic incentive to do the job properly (and firstly try to find the most "valuable" critical vulnerabilities)
-
Bounty pricing
Example price template
| Priority | Vulnerability Types | Pricing in EUR |
|---|---|---|
| Critical | RCE, SQLi, XXE, Vertical Authentication Bypass | 700 / 2200 / 6000 |
| High | Stored XSS, CSRF, Lateral Authentical Bypass | 400 / 750 / 1200 |
| Medium | Reflective XSS, URL redirect | 125 / 250 / 425 |
| Low | SSL misconfigurations, XSS/CSRF with limited impact | 45 / 60 / 135 |
Bug bounty pricing rules
- customers can choose a bug bounty pricing template according to their needs to create a sufficient incentive for the ethical hackers, e.g. according to the answers of the following questions:
- What is your company´s annual turnover?
- Do you process your client´s personal data through your application/web?
-
Do you process your client´s economic data (such as accountancy) OR financial transactions (such as credit card payment) through your application/web?
-
How extensive are potential consequences of your application/web when being hacked?
Bug bounty price template
- security should always make an economic sense - you should not invest more money to your IT security than you can potentially loose (but consider also non-financial losses that cannot be quantified)
- bug bounty price template should be chosen carefully:
- if bug bounties are too low, the hackers are simply not motivated to hack your website/application
- probably a good strategy:
- if you are not sure about the real security of your application, start with low bug bounties and increase them over time if no vulnerabilities are reported
- if you have a secure application, start with higher bug bounties
Commercial bug bounty programs



Thanks for your audience!

Objection #1
- Question: "How can I be sure hackers from my subscribed bug-bounty program do not misuse the revealed vulnerabilities for their personal profit and keep informing me about them?"
- Answer: "Firstly, the hackers don't need to be registered in any bug-bounty program to hack your website or application to reveal the given vulnerabilities and exploit them for their personal profit. That's exactly why you need to be a part of bug bounty programs where you can rely on the hackers' background checking and strict "firing" policy if they fail to follow the defined ethical rules. Secondly, the hacker in the bug bounty programs compete with others. If he does not submit the revealed vulnerability, it is quite likely it'll be revealed by the other hacker who receives "his" bounty.
Objection #2
- Question: "I am already paying for regular penetration tests. Does it still make sense for me to use bug bounty programs?"
- Answer: "Yes, especially during the periods when your application is not in the process of testing to achieve a continuous security. And thanks to bug bounty programs, you have a guarantee of "many eyes" that might be a problem for the most traditional penetration tests."
Objection #3
- Question: "Our web application is PCI-DSS certified with highly trusted EV-SSL certificate. Does it still make sense for me to use bug bounty programs?"
- Answer: "Of course. PCI-DSS or EV-SSL certification are for sure fine, but they are just a small part of the complex security process and do not reflect an overall real security of your web application".
Objection #4
- Question: "I have never heard about bug bounty programs. Why do you think it is a good idea to prefer them instead of a regular penetration test?"
- Answer: "The penetration test is definitely a good choice if you require a systematic security approach during the specific period. Unfortunately it can be quite expensive (usually starts at 1000 EUR and more for one test). In case of bug bounty programs you pay for real vulnerabilities and you pay as much as you wish. This may be a viable solution even for small e-shops and companies with a limited budget which cannot afford relatively expensive penetration tests."