COMP3900
DevOps
Presented by Atlassian

In this lecture
- DevOps
- Continuous Integration
- Continuous Delivery & Continuous Deployment
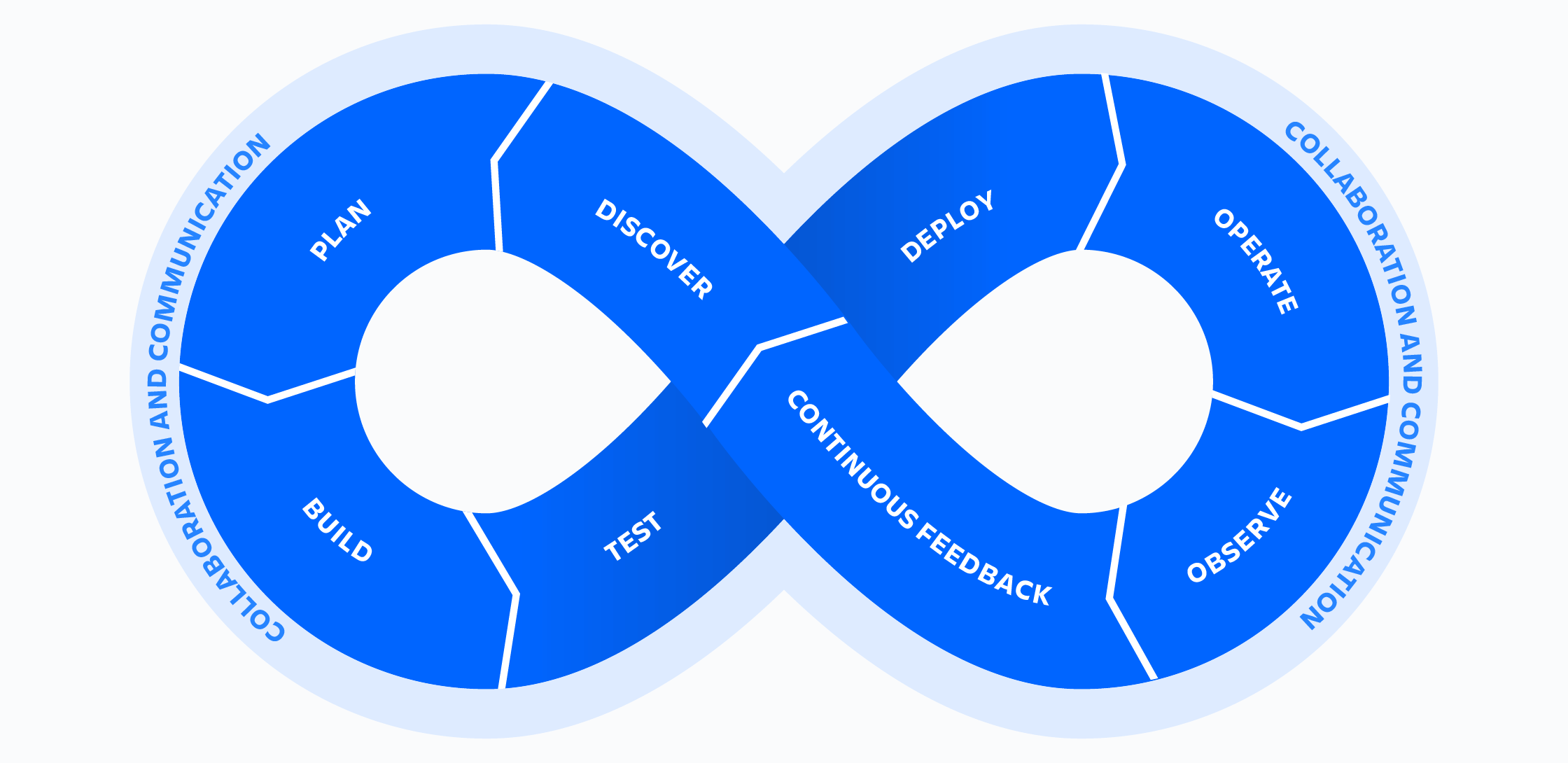
DevOps
"Traditional" Software Development
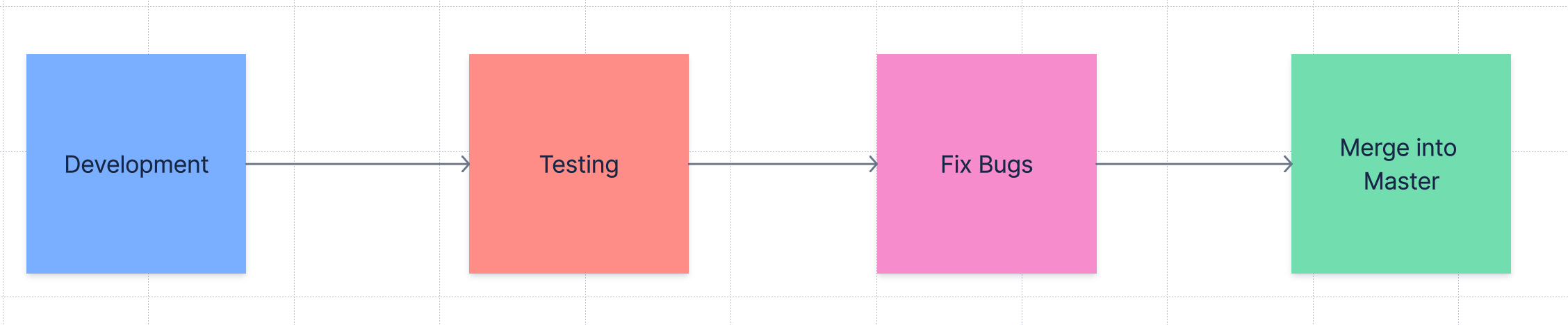
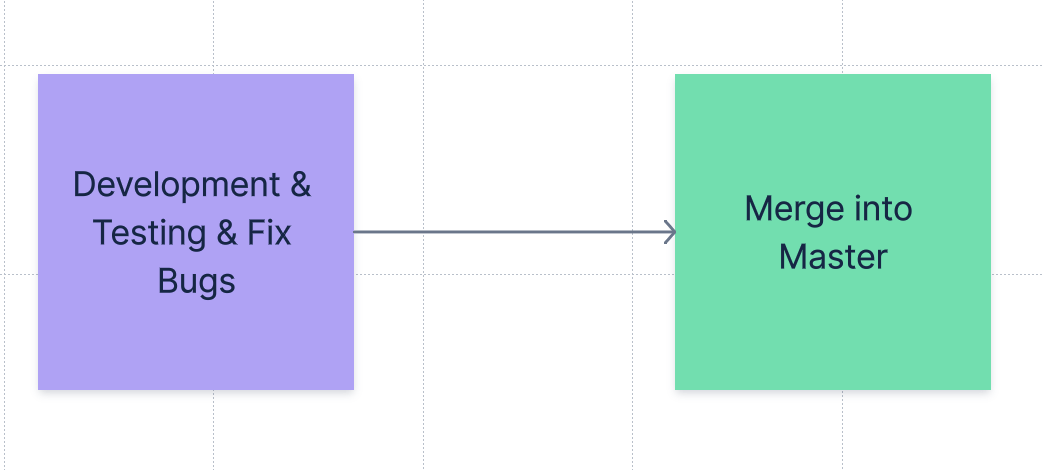
DevOps & Continuous Integration
DevOps
DevOps: The consolidation of "development" and "operations"
DevOps is a set of practices, tools, and a cultural philosophy that automate and integrate the processes between software development and IT teams. It emphasizes team empowerment, cross-team communication and collaboration, and technology automation.
What's included in DevOps?
-
Continuous Integration
-
Strong automated testing
-
Continuous Delivery and/or Deployment
-
Platform Engineering
-
Agile practices
DevOps Process
1. Platform Engineering
- Software in the modern era is built on platforms
- Improves cost and resource efficiency (don't need to maintain your own hardware/OS)
- Allows extensibility to build what you need and focus on the business logic
- Provides us with pre-packaged tools to build, test and deploy software
- We're going to use a platform built by Atlassian called Forge
- Forge documentation: https://developer.atlassian.com/platform/forge/
Let's create a simple forge app.
2. Continuous Integration
Continuous integration (CI) is the practice of automating the integration of code changes from multiple contributors into a single software project. It’s a primary DevOps best practice, allowing developers to frequently merge code changes into a central repository where builds and tests then run. Automated tools are used to assert the new code’s correctness before integration.
A software development practice where members of a team integrate their work frequently, usually each person integrates at least daily - leading to multiple integrations per day. Each integration is verified by an automated build (including tests) to detect integration errors as quickly as possible.
Martin Fowler, 2006
Why CI?
- Quality assurance:
- Automates layers of quality checks (testing, type checking, linting) on code
-
Ensures that master/main remains a "safe source of truth"
- Your code on master should be suitable for release at any momen
- "But miss, it works on my computer!" - CI is run in a standardised environment
- Minimises risk by continuously integrating small changes, rather than making lots of changes at once
-
CI procedures should be
- Reproducible
- Largely (if not entirely) automated
CI is more than just pipelines
- Version control management (Git)
- Automated build processes (Maven/Gradle, Cmake, Cargo, Yarn)
- Automated testing (frontend and backend) (JUnit, Pytest, Jest, Selenium)
- Team processes (PR cycles, code reviews)
-
CI server to automate processes (CI runners, GitHub Actions)
Let's build a CI pipeline for our app using GitHub actions.
3. Continuous Delivery
Continuous delivery is an approach where teams release quality products frequently and predictably from source code repository to production in an automated fashion.
A software development discipline where you build software in such a way that the software can be released to production at any time.
Martin Fowler, 2013
3. Continuous Deployment
Continuous deployment (CD) is a software release process that uses automated testing to validate if changes to a codebase are correct and stable for immediate autonomous deployment to a production environment.
A continuation of the Continuous Delivery process, where the software application is automatically deployed to the customer.
Aims to automate the release of every working version of software to production environment.