SENG2021
Team Dynamics &
Team Theory
(2024)
In this lecture
- Theory of Team Needs - Task, Team Maintenance and Individual
- Team Roles
- Culture
- Stages of group development
Theory of Team Needs
- Three components
- Interconnected + tightly coupled
- Managing a team - a balancing act
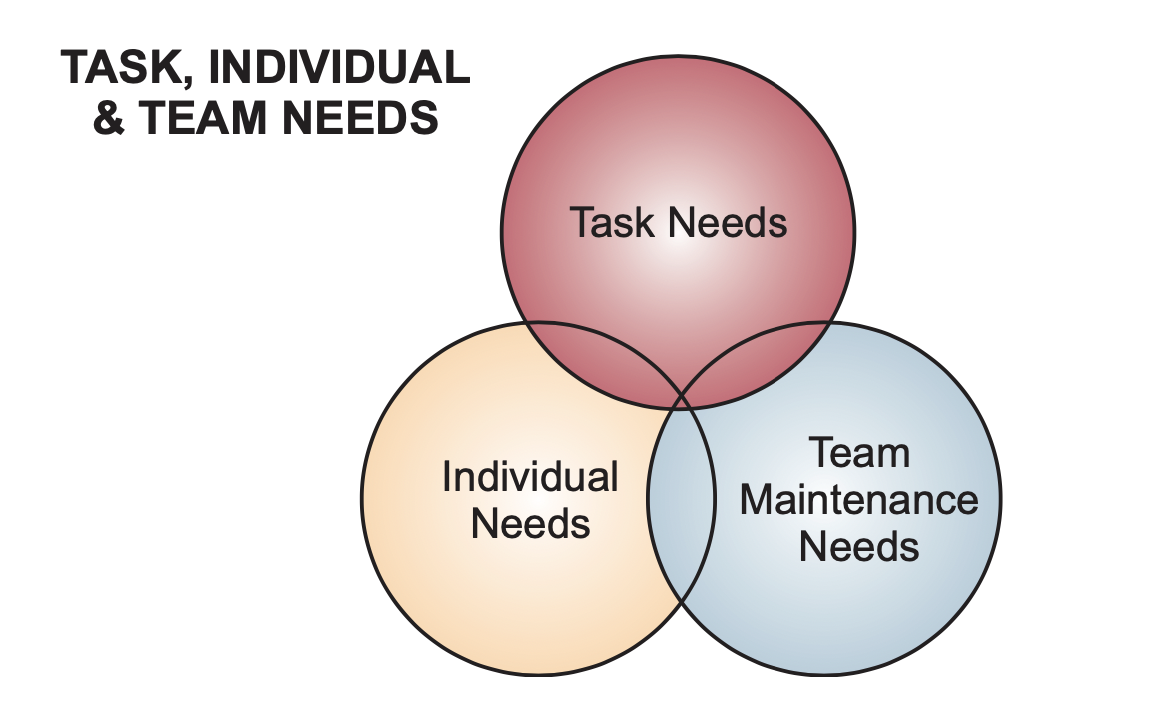
Task Needs
- Team works towards a vision
- Vision is achieved through strategy
- Strategy is achieved through tactics
- How does a team manage task needs?
- Planning
- Organising
- Directing
- Reviewing
- Revising
Team Maintenance Needs
- Communicate and build trust
- Keeping the team informed and involved in decision making
- Collaboration and saturation
- Make people aware and feeling involved
- Organising the team
- Training the team
- Establishing and maintaining team standards
- Foster morale and esprit de corps
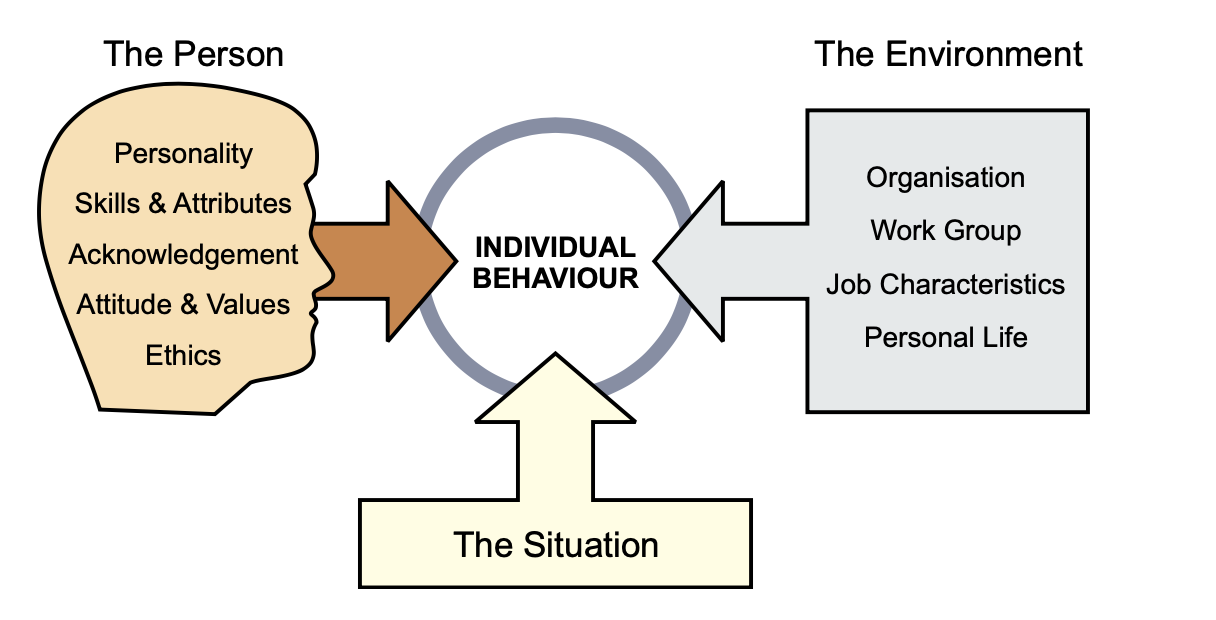
Individual Needs
- People are unique ❤️
- Values
- Attitudes
- Personality
- Capability - strengths and weaknesses
- Important to recognise and accomodate for this
- Motivation of an individual
- People are a product of their environment + situation
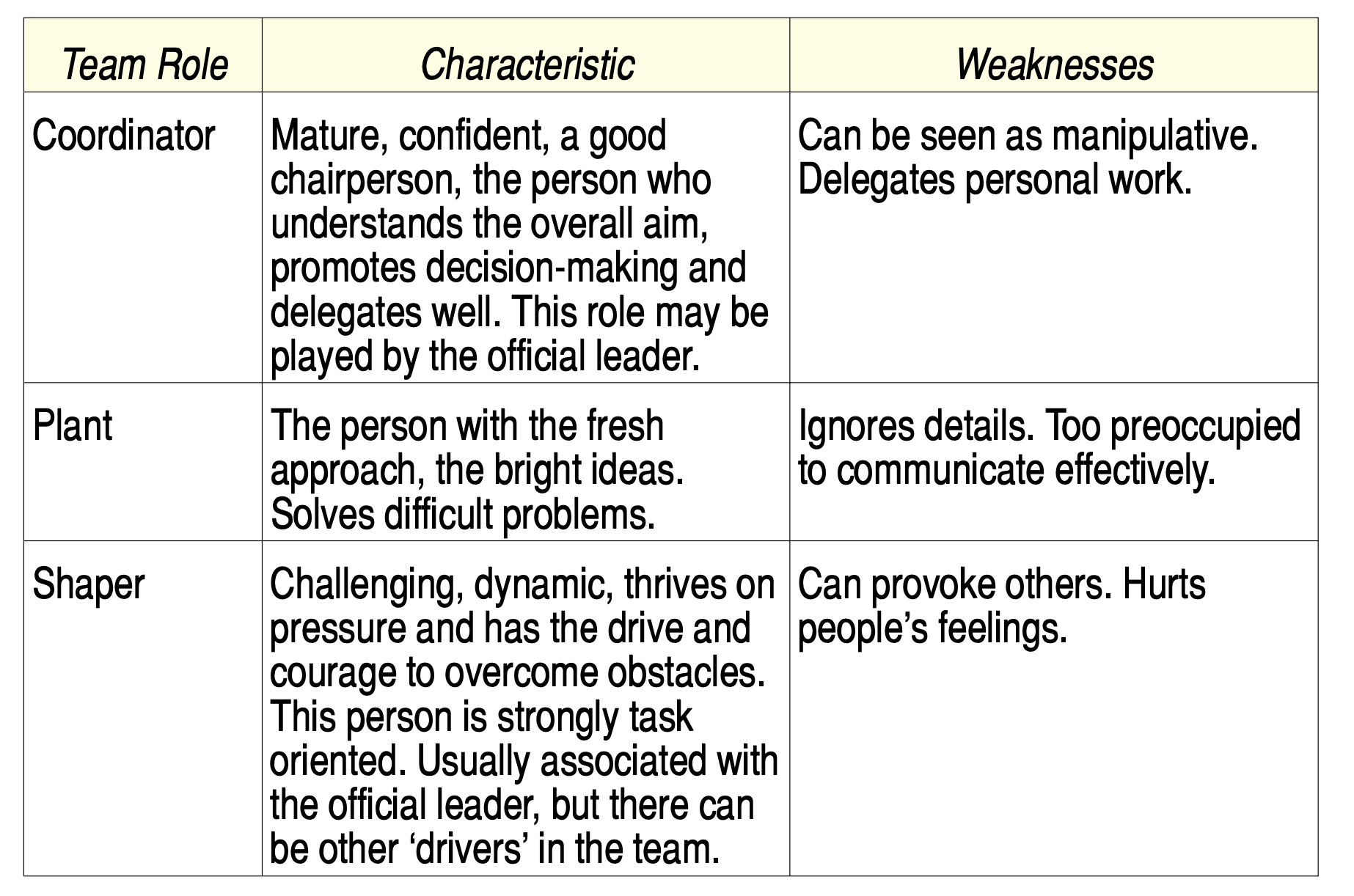
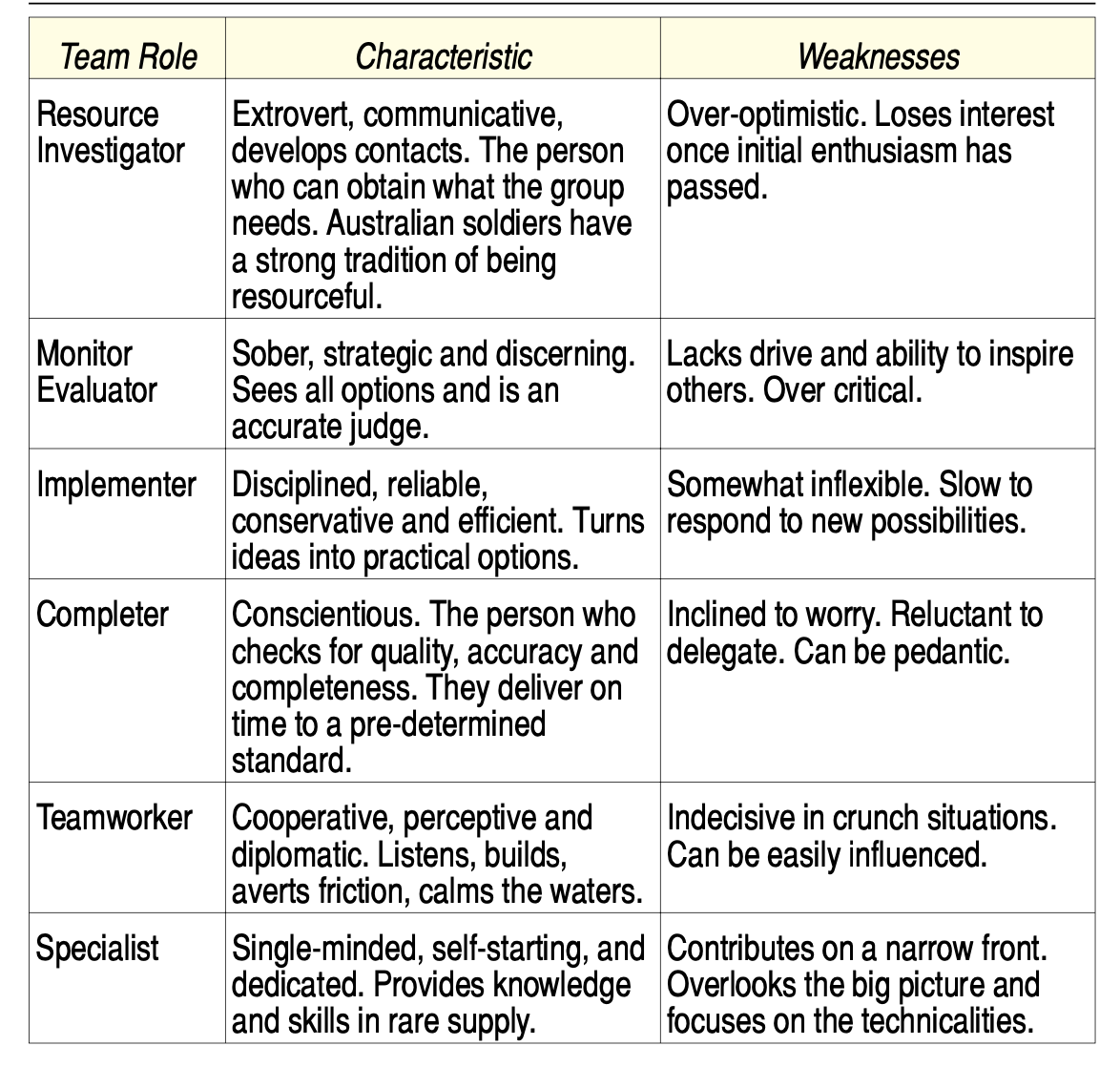
Team Roles
- Personality and capability influence the roles people play in a team - unofficially as well as officially
Types of Groups
-
Formal - created by an organisation for a specific purpose
- Organisation of talent
- Means to achieving a vision/strategy
-
Informal - result from areas of shared interest
- Informal groups can form a 'shadow' organisation
- Can exert a powerful force on the formal organisation
- Can influence culture
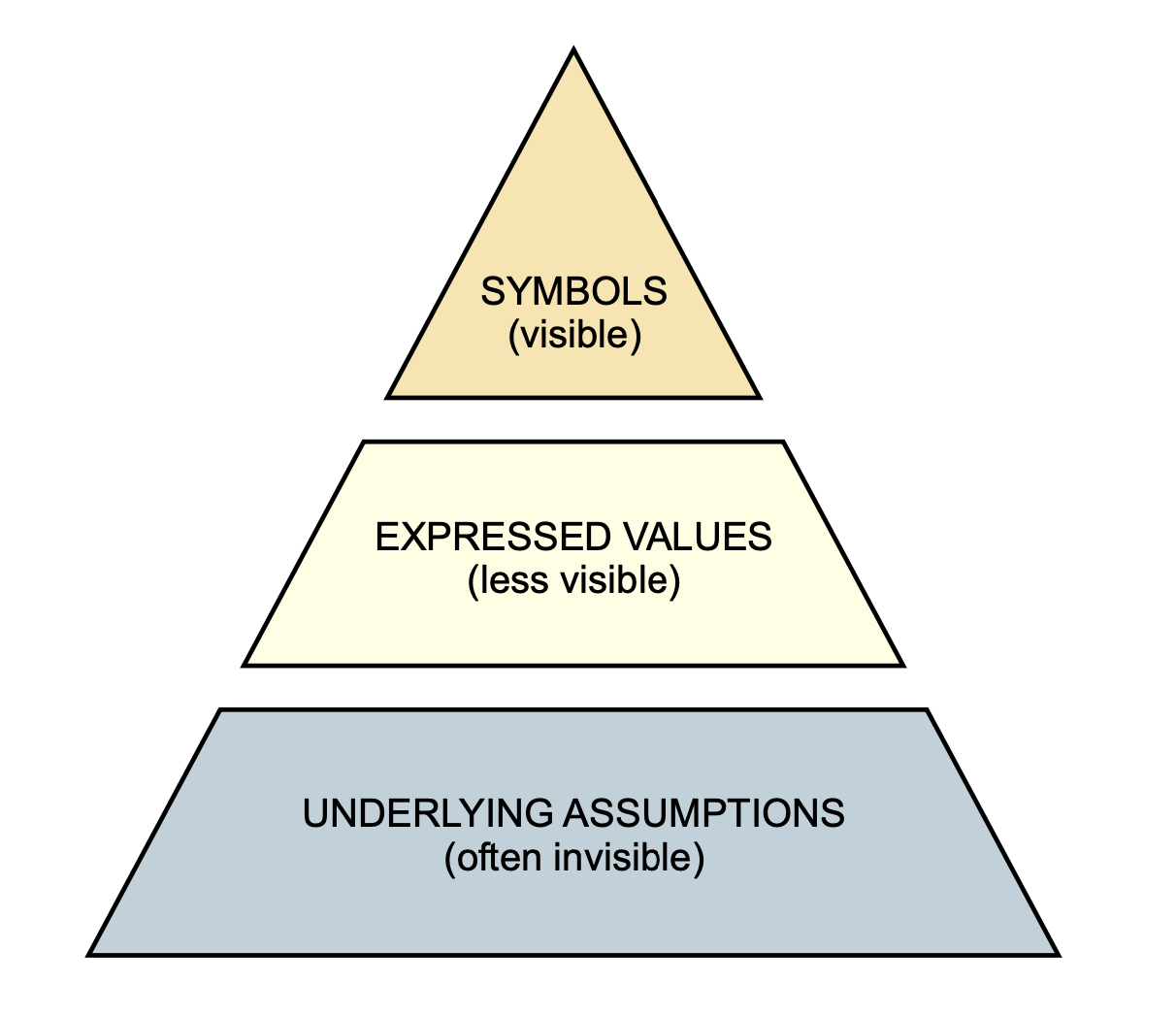
Culture
- Personality at the scale of a group
- Traditions + norms
- Codes of behaviour and moral frameworks (unwritten)
- Socialisation + enculturation of new members of the team
- Strongly cohesive groups will inherently pressure new members to conform to their culture
Culture
- Toxic culture
- In a business, culture is by design to suit the needs of the business
- This often happens organically and unconsciously
- Examples
- Law firm - billable hours
- Big tech
- Oil rigs
- Culture is set by the people in charge
Group Development
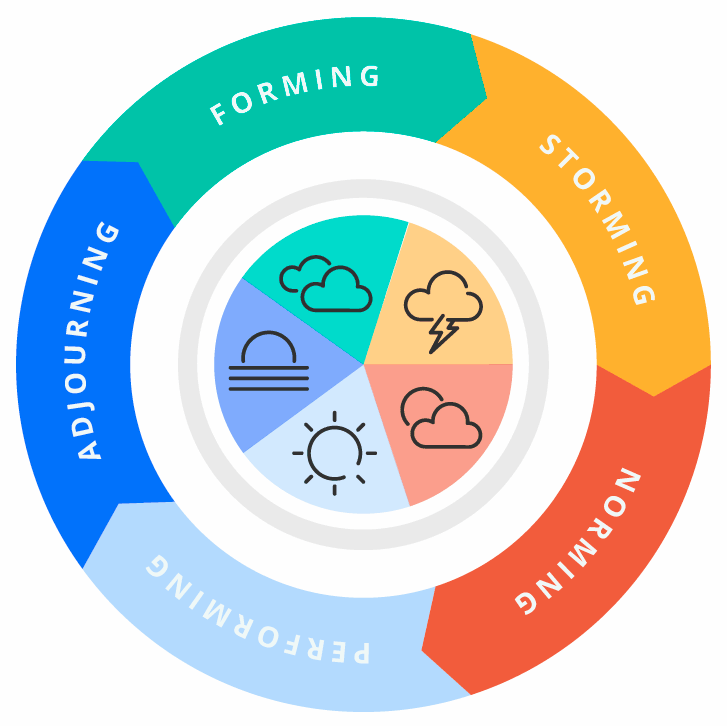
Tuckman's model of team dynamics:
- Forming
- Storming
- Norming
- Performing
- Adjourning
Forming Stage
- Team members meet each other
- Learn about the task/tasks at hand
- Agile - the type of work that gets done
- Group establishes boundaries socially and professionally
- People begin to understand each other as individuals
Storming Stage
- People become more comfortable and have settled in to the environment + culture
- Members have had the chance to get to know one another
- Sub-groups and hierarchies can emerge
- Internal power struggles
- Things go wrong and conflict ensues
- Teams may fail to get past this stage and collapse
Norming Stage
- Team goes through process of overcoming differences and conflict
- Team becomes cohesive and adapts to the strengths & weaknesses of individuals
- Roles and relationships are clearly defined
- Group culture starts to emerge
- Codes of behaviour and group norms
- Team develops its individual identity
Performing Stage
- Team is working well
- Members of the group are comfortable with one another
- Work is smooth and productive
- Balancing team, task and individual needs ensures harmony and order
Adjourning Stage
- All good things come to an end - people leave, task is completed
- Recognising efforts and value
- Helping successful transition to new teams
What influences group behaviour?
- Team composition
- Organisational Strategy
- Organisational Culture
- Resources + technology
- Authority Structures
- Regulations
- Selection processes
- Performance appraisal & reward systems
- Physical work setting
References
- Australian Army Land Warfare Doctrine - LWD-02 - Leadership (2002)