From cells to maps: studying arrhythmia mechanisms using network theory


Nele Vandersickel
Core Team

Nele Vandersickel
Nele Vandersickel




Sander Hendrickx
Robin Van den Abeele
Arthur Bezerra
Bjorn Verstraeten
Arstanbek Okenov
Timur Nezlobinskii
Eike Wülfers




Sebastiaan Lootens






Mattias Duytschaever
Sebastiaan Knecht
Armin Luik
Annika Haas



Main Clinical collaborations
Nele Vandersickel
From the cell to the arrhythmia
Nele Vandersickel
Anatomical reentry
Functional reentry = rotors
Focal sources
Many different cell models: atrial
Nele Vandersickel
Simulations done by OpenCARP
Notice the big differences!
Many different cell models: ventricle models
Nele Vandersickel
Simulations done by OpenCARP
Notice the big differences!
Tracking rotational activity
Nele Vandersickel
Most used method: phase mapping
Shors et al, IEEE, 1996,
Gray et al, Nature, 1998,
Bray et al, IEEE, 2002,
Umapathy et al, Circ A&E, 2010
Kuklik et al, TBME, 2014


-Pi
Pi
Problems with phase mapping (Kuklik et al, 2017, IEEE Trans Biomed Eng.)
- Frequent false positive PS detection due to chance
- Phase mapping ignores fractionation and double potentials
- Ignores conduction block
- Presents waves coming from opposite directions are seen as transient rotation.
Tracking rotational activity
Most used method: phase mapping
Most used method: phase mapping
Most used method: phase mapping
Nele Vandersickel
Phase mapping is a very local method!

Tracking rotational activity

New alternative method: directed graph mapping
Network theory is very popular in science and technology...
Search algorithm

Brain


Nele Vandersickel
Rotating electrical waves are just the cycles in our network!

Tracking rotational activity
Alternative method: directed graph mapping
Nele Vandersickel
Is a global method!
Tracking focal activity
Alternative method: directed graph mapping

Can also track focal sources!
Nele Vandersickel
New version almost ready open source/source available with some restrictions for commercial use

You can create your own pipeline!
www.dgmapping.com
Directed graph mapping: mature software package
Nele Vandersickel
We also added different implementations of phase mapping
Spatial organization of datapoints is not required!
Computational data
- any subset
Input
- Coordinates of the measuring electrodes
- Local Activation Times or full signal



Experimental data
- needle data
- socket data
- grid data
- ...
Clinical data
- CARTO
- RHTYHMIA
- Basket Catheter
- ECGI data

DGM: a software package to analyze reentry automatically
Nele Vandersickel

DGM: a software package to analyze reentry automatically



Nele Vandersickel
DGM: a software package to analyze reentry automatically


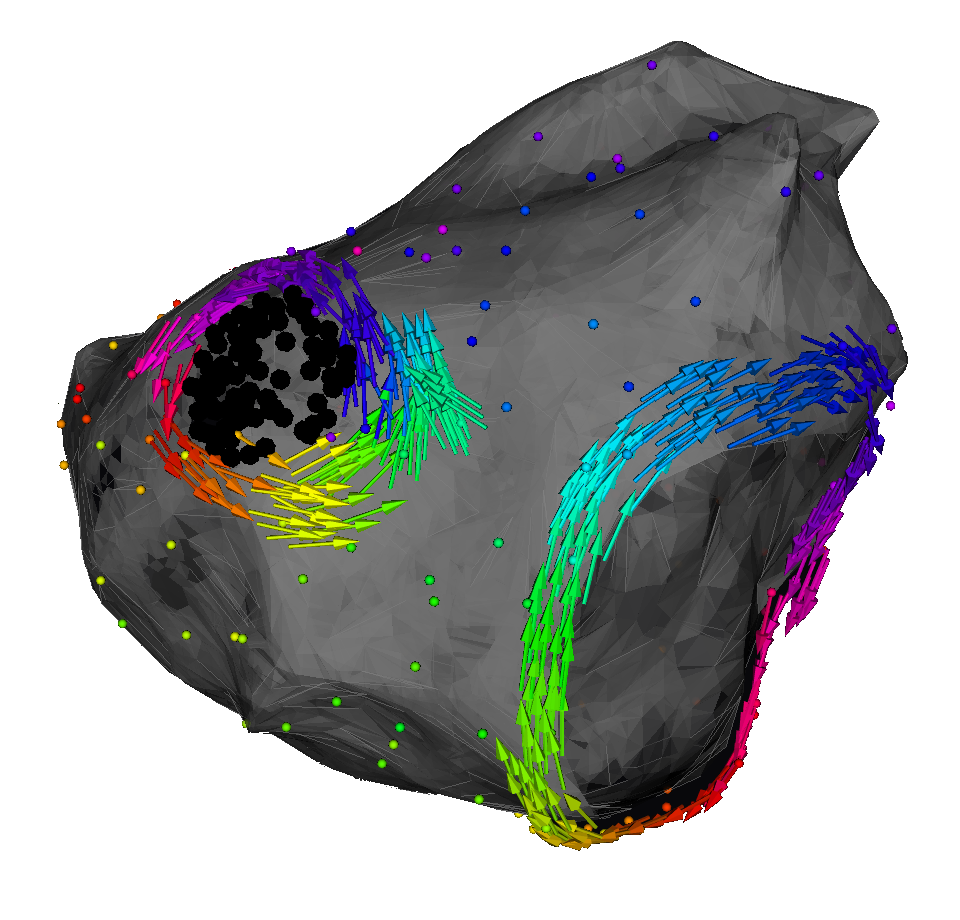
Nele Vandersickel
Extended toolkit for visualization
DGM: a software package to analyze reentry automatically


Nele Vandersickel
Study 1: tracking core of rotors in simulations of different models
Nele Vandersickel

Study 1: tracking core of rotors in simulations of different models
Nele Vandersickel

Ongoing study
Study 2: analysis of Torsade de Pointes in the experimental CAVB dog model

Episodes are focal or reentry?

Nele Vandersickel
Chronic CAVB block
Dofetilide challenge
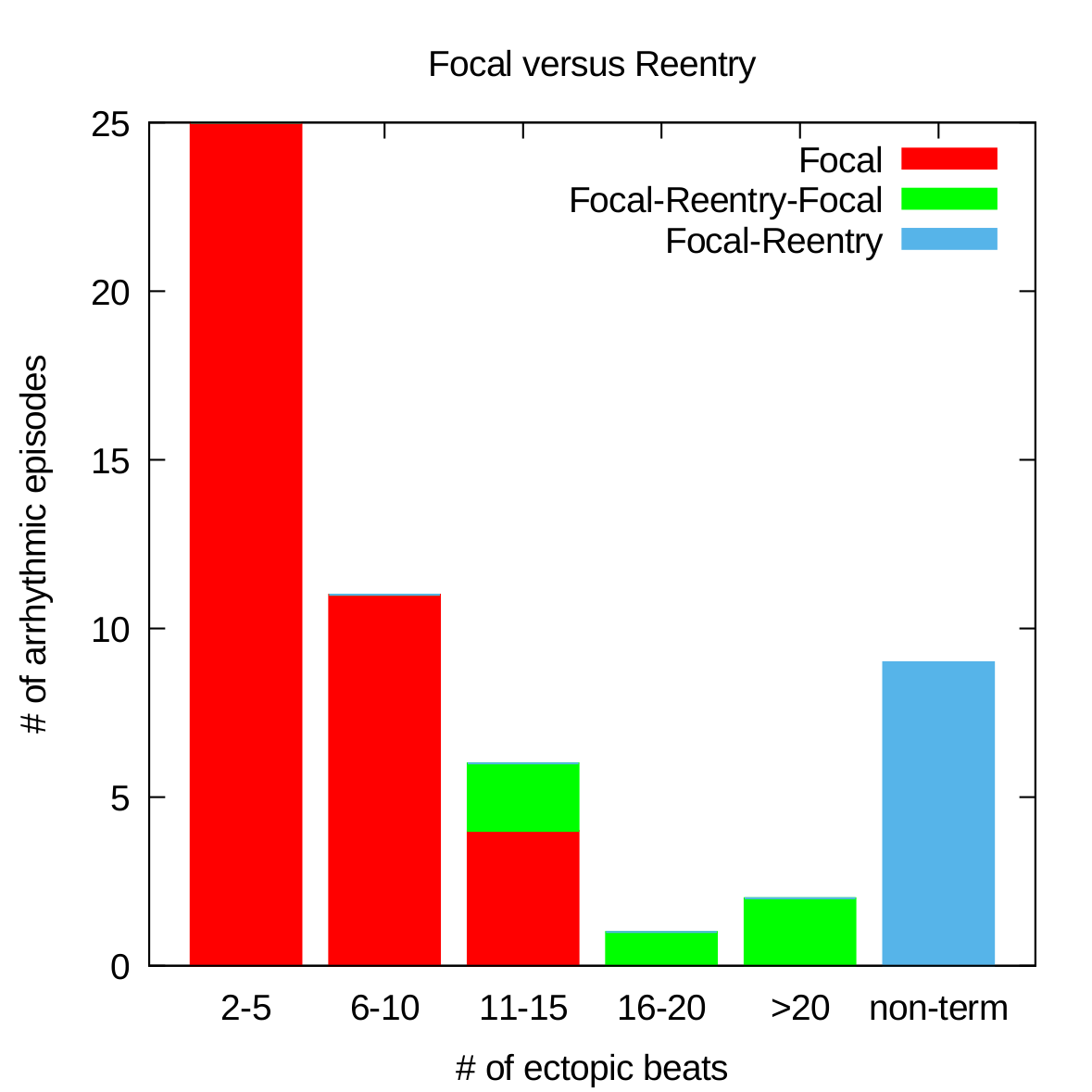
Study 2: analysis of Torsade de Pointes in the experimental CAVB dog model
DGM lab
Vandersickel et al, JACC: EP 2017
- Non-terminating episodes have many more reentries than terminating episode
- Focal sources have preferred locations
Nele Vandersickel
Van den Abeele et al, Frontier in Physiology 2023
Study 3: analysis of VF in optical mapping data in rats

We found a new network method in addition to cycle search, which can find rotational activity:
Helmholtz decomposition of graphs
Nele Vandersickel
Experiment performed by lab of Fu Siong, Imperial College Londen
Ongoing study
Study 4: analysis of VT in clinical data

DGM can analyze mapping data in VT
Hawson et al., JACC EP, 2023
Nele Vandersickel
Why do often slower ATs arise after ablation of the reentry? (can be up to 1/3 cases...)


Anterior
Posterior
Reentry at the roof
Slower AT at the MV


Anterior
Posterior
Roof ablation
Study 5: solving AT
Nele Vandersickel

MV
LPV
RPV

Text
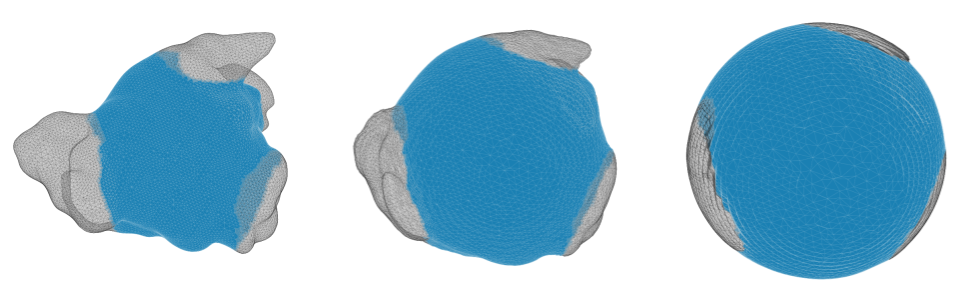
Study 5: solving AT- Anatomy of the left atrium: 3 natural boundaries: topology!
Nele Vandersickel
600 different simulations: 2 holes, 3 holes and 4 holes
All possible virtual ablation lines
Study 5: solving AT- Simulation on spheres with 3 natural boundaries: topology
Nele Vandersickel
3 Patterns
Complete rotation
Incomplete rotation
Parallel activation
Good entrainment
Bad entrainment
Bad entrainment
Study 5: solving AT- Simulation on spheres with 3 natural boundaries
Nele Vandersickel

Incomplete rotation becomes complete rotation, resulting in a slower AT
100% of simulations!
Study 5: solving AT- Simple ablation strategy
Nele Vandersickel


Study 5: solving AT- Index theorem > 20 years old
Nele Vandersickel
Reentries come in pairs of 2: clockwise and counterclockwise


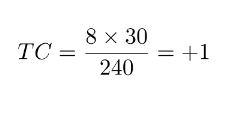
Complete rotation

Parallel activation



Incomplete rotation
Critical Boundary
Critical Boundary
Non-Critical Boundary
CB: Santucci et al. JACC EP 2023
Study 5: solving AT- Index theorem > 20 years old
Nele Vandersickel

CB:
CB:
NCB: 0
Incomplete rotation becomes complete rotation, resulting in a slower AT
Loops come in pairs of 2: currently second loop is always missed
Study 5: solving AT- Index theorem > 20 years old
Nele Vandersickel
Study 5: solving AT- Scar creates additional holes

MV
LPV
RPV

131 MRAT cases



Study 5: solving AT- Clinical cases
Nele Vandersickel
20 detailed cases with slowing after ablation



Study 5: solving AT- We explain why ablation gives slower ATs!
Nele Vandersickel
Study 5: solving AT- Current classification can be replaced
Macro reentry
Localized reentry
Micro reentry
Focal
Rotor
Around anatomic obstacle, like valve or vessels.
Around non conducting area > 2-1.5cm, e.g. scar or functional block
-
Atypical Flutter (LA involving valves or vessels)
-
Atypical Flutter (RA involving valves or vessels)
-
Typical Flutter (clockwise and counter clockwise)
-
WPW
-
Atypical Flutter (LA with scar or previous ablation lines with gaps)
-
AVNRT (considering slow and fast pathway)
Around non conducting area < 1cm, e.g. scar or functional block
-
Atypical Flutter (LA with scar)
-
Atypical Flutter (RA crista terminalis region)
-
Ectopic AT
Spiral activation pattern with no scar in the core.
Focal activation from one single spot with centrifugal activation pattern
CL tends to be longer >350ms due to larger path
CL range varies and CL can shift around 20-40 ms during arrhythmia due to slight path variations
CL tends to be shorter due to short path, whole CL is covered by signals found in a small area like e.g. 4cm2 often a combination of double potentials in the „middle“ and very long fractionated signals surrounding
CL often not presented completely in one chamber
Focal activation patterns could also hint to epicardial entries – look for potential conducting structure like vein of Marshall, Bachmann´s etc. and exits that would fit a macro reentry with epicardial parts
We think non-existent in AT, especially as a stable configuration leading to a stable AT.
Maybe something close to a spiral pattern can exist in AF
-
AF
All of this is replaced by our simple classification!
Study 5: solving AT- Current classification can be replaced
Macro reentry
Localized reentry
Micro reentry
Focal
Rotor
Around anatomic obstacle, like valve or vessels.
Around non conducting area > 2-1.5cm, e.g. scar or functional block
-
Atypical Flutter (LA involving valves or vessels)
-
Atypical Flutter (RA involving valves or vessels)
-
Typical Flutter (clockwise and counter clockwise)
-
WPW
-
Atypical Flutter (LA with scar or previous ablation lines with gaps)
-
AVNRT (considering slow and fast pathway)
Around non conducting area < 1cm, e.g. scar or functional block
-
Atypical Flutter (LA with scar)
-
Atypical Flutter (RA crista terminalis region)
-
Ectopic AT
Spiral activation pattern with no scar in the core.
Focal activation from one single spot with centrifugal activation pattern
CL tends to be longer >350ms due to larger path
CL range varies and CL can shift around 20-40 ms during arrhythmia due to slight path variations
CL tends to be shorter due to short path, whole CL is covered by signals found in a small area like e.g. 4cm2 often a combination of double potentials in the „middle“ and very long fractionated signals surrounding
CL often not presented completely in one chamber
Focal activation patterns could also hint to epicardial entries – look for potential conducting structure like vein of Marshall, Bachmann´s etc. and exits that would fit a macro reentry with epicardial parts
We think non-existent in AT, especially as a stable configuration leading to a stable AT.
Maybe something close to a spiral pattern can exist in AF
-
AF

2nd Submitted paper
Atrial topology for a unified understanding of typical and atypical flutter
Mattias Duytschaever, Robin Van Den Abeele ... Annika Haas, Armin Luik, ... Sander Hendrickx, Nele Vandersickel
Study 5: solving AT- European Heart Journal
Nele Vandersickel

Study 5: solving AT- Live case!

Study 5: solving AT- Live case!
www.dgmapping.com
Study 5: DGM can compute the critical boundaries automatically!
Nele Vandersickel
www.dgmapping.com
Study 5: DGM can compute the critical boundaries automatically!
Nele Vandersickel

Working on the final step: automatization scar detection
Take home message

DGM: diagnostic tool based on network theory

www.dgmapping.com

CB:
CB:
NCB: 0
Incomplete rotation becomes complete rotation, resulting in a slower AT
Able to change ablation therapy in AT!
Can be applied to many different datasets!
- Needle data of Torsade de Pointes in dogs
- Optical mapping
- Simulated datasets
- Clinical datasets
Nele Vandersickel