FLARE
Flipped learning & AI for reflective education
M.Sc. Lauri Hellsten
math and physics teacher in Espoon yhteislyseo
Physics teacher of the year 2025 (Finnish society of sciences and letters)
STEAM teacher of the year 2023 (MAOL ry)
ASEFClassNet EmpowerEd Project 2025
-
Keep Your Microphone Muted 🎤 – Mute yourself when not speaking to avoid background noise.
-
Turn On Your Camera 📷 – Helps create a more engaging and connected atmosphere.
-
Use the Chat & Raise Hand ✋💬 – Share quick thoughts in chat or use “raise hand” before speaking to ensure smooth discussion.
Guidelines for online sessions
-
Guidelines on AI use in classroom
-
Examples on use of AI in creating Flipped learning material for self-assessment
Today
AI in schools
AI is a new tool in education – it brings opportunities (e.g. speed, creativity, personalization)...
...but also responsibilities (data protection, copyright, fair assessment, ethics).
Remeber that everything given to the AI can be used in training of the AI!
AI in finnish schools
In the summer of 2025 Finnish National Agency for Education released guidelines to provide the framework for using AI in the classrooms
AI applications can serve as support, but conclusions related to assessment and the design of teaching are always the teacher’s responsibility.”
The teacher/school should establish clear local guidelines for AI use, for example, how students’ use of AI in assignments should be documented.
Inclusion and equality must be ensured. The use of AI must not discriminate against learners.
Example uses of AI for teacher
- Drafting and editing learning materials
- Differentiation!
-
Designing tests and assignments
-
Summarizing & analyzing student responses
-
Proofreading and translation support
-
Creating images for lessons and materials
-
Brainstorming & developing pedagogical solutions
Discussion
What kind of quidelines for the use of AI are in place at your school?
The teacher guides the student to recognize what the studied topic is about and to compare their own conceptions and views with the overall context of the topic
Guides for self-assessment
-
Make the criteria clear and understandable tools
-
Design tools (e.g. skill level tables, lists of criteria, guiding question lists). Provide instructions and support for their use.
-
Give students practice and routines for self-assessment, and provide them with feedback on the quality of their self-assessment.
-
Teach self-assessment as a central goal that supports their self-regulation and the development of their own learning (Brown & Harris, 2014).
-
In your feedback, use language that supports students’ self-assessment.
-
Use self-assessment more for supporting learning than for determining grades.
Using Feedback to Improve Learning (2018), Maria Araceli Ruiz-Primo and Susan M Bookhart
AI agent
-
AI model (e.g GPT-5) → General knowledge, "core brain" but it doesn’t remember what you uploaded to it.
-
AI agent → Built on top of the "core brain" with extra abilities (memory, goals, tools, etc.).


Finnish national curriculum
Old exam problems
ChatGPT / Copilot
Own material
📓


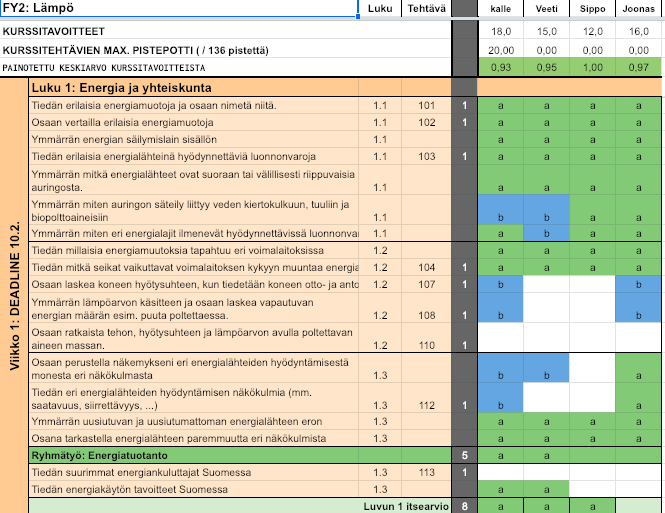
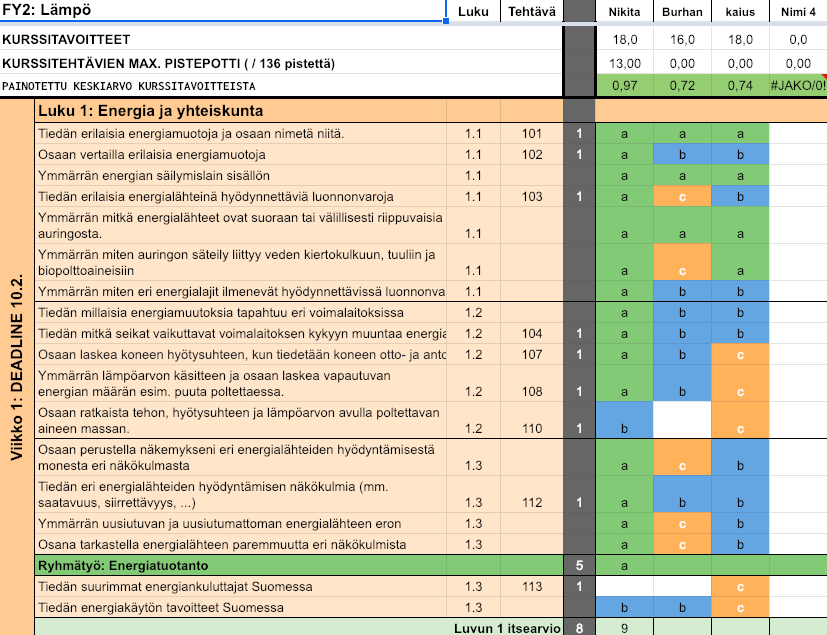

Developing self-assessment
I understand this so well I could
teach it to a friend.
I feel I have understood this.
I feel I somehow understand this, but there still is something unclear to me.
I need more practice and time to understand this.
This is not included in my studies.
Self-assessment throughout the course
Developing self-assessment
Example prompt for guided self-assessment
You are a secondary teacher and assessment expert. Create a guided self-assessment checklist for students in a flipped learning setting (used after pre-class study, before in-class practice).
Produce 12–15 student-friendly statements that help learners reflect on what they understand (concepts) and what they can do (skills).
Use both stems: “I understand …” (concepts) and “I can …” (skills).
Keep language clear, positive, and supportive; avoid grading/judgmental wording.
Make items concrete and observable so students know what evidence they could show....
role & context
precise task
specification
Example prompt for guided self-assessment
Structure (progression)
-
Foundational understanding – core ideas, terms, relationships (recognize what the topic is about).
-
Application & practice – problem solving/methods/interpretation or creation.
-
Reflection & transfer – connect new knowledge to prior conceptions, broader contexts, or ethics.
Self-regulation features
-
Add a one-line student instruction at the top.
-
For each statement, include a 3-point self-rating: ▢ Not yet ▢ Getting there ▢ Got it.
Structured
progression
(scaffolding)
Self-regulation
Example prompt for guided self-assessment
Output format (strict)
Return Markdown exactly like this:
-
H2 title: “Self-Assessment – {Subject}: {Topic}”
-
Short student instruction (1 sentence).
-
Three H3 sections with the exact headings: “Foundational understanding”, “Application & practice”, “Reflection & transfer”.
-
Under each section, 3–5 checkbox items using “- [ ] …”.
Parameters
- Subject: {insert}
- Topic: {insert}
- Language: {English / Finnish}
- Level: {upper secondary / specify grade if needed}
Output format constraints
Clear input parameters
“Self-Assessment – Physics: Newton’s laws”
After your pre-class study, use this to check what you know and what you can do; be honest and pick one or two items to improve next.
Foundational understanding
-
I understand what a force is (vector with magnitude and direction) and what “net force” means for an object’s motion. — ▢ Not yet ▢ Getting there ▢ Got it
-
I understand Newton’s First Law (inertia) and can recognize when velocity stays constant because the net force is zero. — ▢ Not yet ▢ Getting there ▢ Got it
-
...
Application & practice
-
I can draw a clear free-body diagram (FBD) for a situation, labeling weight, normal, tension, friction/drag, and choosing sensible axes. — ▢ Not yet ▢ Getting there ▢ Got it
-
I can resolve forces into components (e.g., on an incline) and compute the net force along chosen axes.
— ▢ Not yet ▢ Getting there ▢ Got it -
...
Reflection & transfer
-
I can explain and correct common misconceptions (e.g., “motion needs a force,” “action and reaction cancel motion”). — ▢ Not yet ▢ Getting there ▢ Got it
-
I understand how modeling choices (neglecting friction/air resistance, massless rope) affect predictions, and I can state my assumptions. — ▢ Not yet ▢ Getting there ▢ Got it
-
...
Discussion
- How useful do you find self-assessment for student learning?
- What would help make self-assessment easier and more realistic in your classroom?
- What concerns or challenges do you see with using AI in the classroom?
Task for next session (15.9.)
Task
Use AI tools to create a student self-assessment form (e.g., in Google Sheets, Microsoft Forms). Use AI to draft questions, criteria, and instructions, but rememebr to review the content before use.
Questions:
-
Is the assessment diagnostic, formative, or summative?
-
What aspects are emphasized?
-
What information does the student receive from the form?
-
How does the student use this information in learning?
-
Does the form support understanding of the course grade?
-
How does the form align with curriculum goals (general, subject-specific, course-specific)?
Post your work in Padlet!