Functional Programming in Javascript
Özgün Bal
Contents
- Programming Paradigms
- Functional concepts
- Pros & Cons of FP
- Functional JS
- Functional DOM manipulation
- Functional libraries
- References
Programming Paradigms
- Imperative
- Functional
- Object Oriented
Imperative
- Reads like a recipe
- Easy to read and write
- Does not scale well
- Updates global state
- Easily can turn into spaghetti code
Object Oriented
- Most common paradigm
- Holds application state and functionality into objects
- Intuitive to reason about
- Scale well
Functional
- Logic inside of pure functions
- Chain functions
- Avoids global state mutation
- Easy and safe to scale

Functional concepts
- Pure functions
- Side effects
- AJAX
- DOM manipulations
- I/O operations
- any changes except function return
- Immutability

Functional concepts (cont.)
compose(Math.abs, add(1), multiply(2))(-4) // 7pipe(multiply(2), add(1), Math.abs)(-4) // 7const sum = (a,b,c,d) = a + b + c + d;
const curriedSum = curry(sum);
curriedSum(1)(2)(3)(4) // 10;Pros
- easier to test
- more predictable
- less bugs due to pure functions
Cons
- higher learning curve
- limited with programming language's capabilities
- less resources and libraries in the ecosystem
Functional Programming
Functional Javascript
- Array/List methods
- Variables
- Immutable objects
- Higher Order Functions
Array methods
- Array.prototype.map
- same length as the original
- Array.prototype.filter
- subset of the original
- Array.prototype.reduce
- one accumulated value

Variables
- var
- pre ES2015, function scope
- let
- reassignable, block scope
- const
- cannot reassign, block scope
Immutable Object
- For one level Object.freeze()
- For nested objects you need to use helper function/library
- Copy operations with Object.assign()

Higher Order Functions
- Either
- takes functions as a parameter
- returns a function
- Array/List methods are all higher order functions
- In JS functions are first-class citizen
- passed as argument
- can be return from a function
- can assign a variable
- can be stored in data structures
Functional DOM Manipulations
- Limit DOM rendering , only specific function(s) can touch
- Limit manipulation of global state and make it immutable



Functional libraries
- Immutable.js
- Ramda.js
- RxJS (Observable)
- Redux (Flux Pattern)




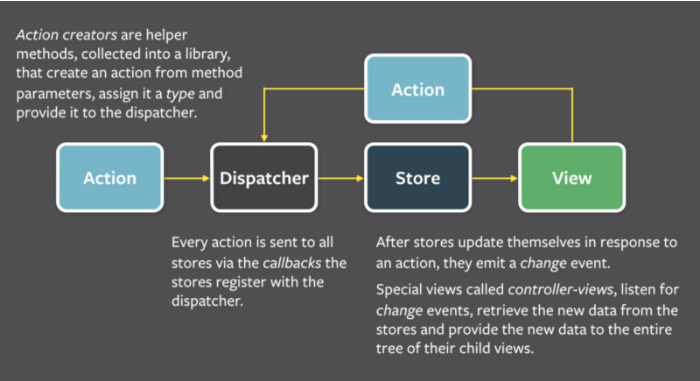
Flux Pattern
References
- Udacity - Intermediate Javascript Nanodegree
- Kyle Simpson - Functional-Light JS
- Marijn Haverbeke - Eloquent Javascript
Thank you for listening

Any questions?