Book 5. Risk and Investment Management
FRM Part 2
IM 2. Factors

Presented by: Sudhanshu
Module 1. Value Investing and Macroeconomic Factors
Module 2. Managing Volatility and Dynamic Risk Factors
Module 3. Value and Momentum Investment Strategies
Module 1. Value Investing and Macroeconomic Factors

Topic 1.Value Investing
Topic 2. Macroeconomic Factors
Topic 3. Economic Growth
Topic 4. Inflation
Topic 5. Volatility
Topic 6. Other Macroeconomic Factors





Topic 1. Value Investing
- Risk premiums are driven by economy-wide fundamental factors (inflation, volatility, productivity, economic growth, demographics) and tradeable investment style factors (momentum, value, firm size).
- A company's book value per share equals (total assets minus total liabilities) divided by shares outstanding, representing liquidation value per share.
- Value stocks have high book-to-market ratios while growth stocks have low book-to-market ratios, where "market" refers to the stock price.
- A value-growth strategy involves going long value stocks and short growth stocks.
-
Historical performance of value stocks:
- Value stocks have historically significantly outperformed growth stocks; $1 invested in a value-growth strategy in 1965 would be worth over $6 by 2012, peaking near $8 in 2006-2007.
- Value stock returns experienced sharp downturns during the tech boom (late 1990s), the 2007-2009 financial crisis, and in 2011, but overall value investing has been successful.
- The question remains whether value stocks' higher returns reflect a systematic risk factor or a value risk premium compensating investors for bearing losses during bad times like the late 1990s and 2007-2009.
Practice Questions: Q1
Q1. A low book-to-market value ratio is indicative of a:
A. value stock.
B. growth stock.
C. small-cap stock.
D. large-cap stock.
Practice Questions: Q1 Answer
Explanation: B is correct.
A company’s book value per share is equal to total assets minus total liabilities all divided by shares outstanding. It indicates, on a per-share basis, what a company would be worth if it liquidated its assets and paid off its liabilities. Value stocks have high book-to-market ratios while growth stocks have low book-to-market ratios.
Topic 2. Macroeconomic Factors
- Macroeconomic factors (increasing inflation, slowing economic growth) affect all investors to varying degrees, with most investors hurt by rising inflation or slowing growth.
- Shocks (unanticipated changes) to factors matter more than factor levels; for example, asset prices generally fall when inflation unexpectedly increases.
- Economic growth, inflation, and volatility are the three most important macro factors affecting asset prices.
Topic 3. Economic Growth
- Risky assets like equities perform poorly during low economic growth, while less-risky assets like bonds (especially government bonds) perform well during slow growth periods.
- Investors who can weather downturns should invest in equities for greater long-run returns, while those unable to bear large losses should invest in bonds for better downturn performance but worse long-run returns.
- During recessions (1952-2011 NBER data), government and investment-grade bonds outperformed equities with 12.3% and 12.6% returns respectively, while during expansions, large stocks yielded 12.4% and small stocks 16.8%.
- High-yield bonds showed indifference to economic growth changes, yielding 7.4% in recessions and 7.7% in expansions.
- Quarter-on-quarter real GDP and consumption growth data show similar patterns: equities outperform in high-growth periods while bonds outperform in low-growth periods, with high-yield bonds performing slightly better during high growth.
- Both stocks and bonds exhibit higher volatility during downturns and low-growth periods; large stock volatility was 23.7% during recessions versus 14.0% during expansions, while government bonds showed 15.5% recession volatility versus 9.3% expansion volatility.
Practice Questions: Q2
Q2. Which of the following asset classes has approximately the same returns in high economic growth periods and low economic growth periods?
A. Small-cap stocks.
B. Large-cap stocks.
C. Government bonds.
D. High-yield bonds.
Practice Questions: Q2 Answer
Explanation: D is correct.
During periods of recession, government and investment-grade bonds outperform equities and high-yield bonds. During expansion periods, equities outperform bonds. High-yield bond returns appear indifferent to changes in economic growth, yielding 7.4% in recessions and 7.7% in expansions.
Topic 4. Inflation
- High inflation is generally detrimental to both stock and bond prices and returns, with all asset categories performing better in low inflation periods and exhibiting higher volatilities during high inflation.
- Large and small stocks returned 14.7% and 17.6% respectively during low inflation versus 8.0% and 13.0% during high inflation periods.
- Bond yields during low inflation (8.6% government, 8.8% investment grade, 9.2% high-yield) exceeded high inflation returns by approximately 3.0%.
- Bonds, as fixed payment securities, clearly perform poorly during high inflation as inflation lowers real bond returns.
- It is less intuitive that stocks perform poorly in high inflation since they represent ownership of real, productive companies rather than claims to fixed cash flows.
Topic 5. Volatility
- The CBOE Volatility Index (VIX) represents equity market volatility and has historically shown a negative correlation with stock returns (−0.39 between 1986-2011), meaning stock returns tend to fall when VIX increases.
- Company financial leverage increases during high volatility periods as debt remains constant while equity market value falls, creating the leverage effect where increased leverage makes equities riskier and increases volatility.
-
Higher volatility increases required rates of return on equities, pushing stock prices down through two paths:
- The leverage effect creates a negative relationship between stock returns and volatility, and
- Higher volatility increases discount rates, lowering current stock prices to allow higher future returns as compensation, supported by CAPM.
Topic 6. Other Macroeconomic Factors
- Macroeconomic factors including productivity, demographic, and political risk affect asset returns, with productivity shocks showing approximately 50% correlation with stock returns (falling prices in 1960s-70s, rising prices during 1980s-90s computer revolution).
- Dynamic stochastic general equilibrium (DSGE) macro models identify seven business cycle shocks: productivity, investment, preferences, inflation, monetary policy, government spending, and labor supply, driven by actions of consumers, firms, governments, and central banks.
- Demographic risk, interpreted as a labor output shock, affects firm production through overlapping generation (OLG) models where young and middle-age workers save while retirees disinvest across overlapping cohorts.
- Demographic shocks from events like World Wars I and II, pandemics (COVID-19), and the baby boom impact returns; models predict stock price declines when baby boomers retire and liquidate assets unless offset by sufficient young and middle-age investors.
- Risk aversion increases with age, suggesting that as average population age rises, the equity risk premium should also increase, with cross-country data being essential for demographic studies.
- Political (sovereign) risk, previously considered only relevant for emerging markets, increases risk premiums in both developed and developing countries, as evidenced by the 2007-2009 financial crisis.
Module 2. Managing Volatility and Dynamic Risk Factors
Topic 1. Managing Volatility Risk
Topic 2. Volatility Premiums
Topic 3. Dynamic Risk Factors
Topic 4. Fama-French Model




Topic 1. Managing Volatility Risk
- Volatility can be mitigated by investing in less volatile assets like bonds, which are less impacted by equity market volatility than stocks but are not necessarily a safe haven.
- Bond returns showed 0.12 correlation with VIX changes (1986-2011) versus stocks' −0.39 correlation, meaning bonds outperform stocks during rising VIX but not with high positive correlation.
- During the 2007-2009 financial crisis, volatility caused both bonds and stocks to fall simultaneously, demonstrating bonds' limitations as safe havens in extreme circumstances.
- The VIX captures both volatility and uncertainty risk, which research shows are distinct but highly correlated concepts.
- Strategies like currency trading have large volatility risk exposure and perform poorly during high volatility periods.
-
Two basic approaches to mitigating volatility risk are:
- Invest in less volatile assets like bonds, recognizing their poor performance potential during extreme events, and
- Buy volatility protection through derivatives like out-of-the-money put options that pay off during high volatility.
Practice Questions: Q1
Q1. Which of the following investment options provides a means of mitigating volatility risk?
A. Buying put options.
B. Selling put options.
C. Buying equities.
D. Buying call options.
Practice Questions: Q1 Answer
Explanation: A is correct.
There are two basic approaches to mitigating volatility risk. They are investing in less volatile assets like bonds (instead of stocks) or buying volatility protection in the derivatives market, such as buying out-of-the-money put options.
Topic 2. Volatility Premiums
- Volatility has a negative premium, requiring investors to sell volatility protection (e.g., sell out-of-the-money put options) to collect the premium, as realized volatilities average 2%–3% lower than VIX implied volatilities, making options expensive on average.
- Selling volatility provides high, stable payoffs during normal periods but results in large negative returns during crashes; a Merrill Lynch volatility swap index showed steady gains from January 1989 to December 2007, then suffered nearly 70% losses between September-November 2008.
- Data through December 2007 showed minimal negative skewness (−0.37), making selling volatility appear profitable, but including the crisis period revealed extreme negative skewness of −8.26 for the full sample.
-
The theoretical relationship between expected market risk premium and volatility is:
- where γ represents average investor risk aversion, though empirical studies have estimated the coefficient as positive, negative, or zero.
- Only investors capable of withstanding massive losses during high volatility periods should consider selling volatility strategies.
Topic 3. Dynamic Risk Factors
- The CAPM is a single-factor model where market risk is the sole risk factor; high-beta stocks with high market factor exposure should earn higher long-run returns to compensate investors for losses during bad periods.
- The market portfolio can be readily traded through low-cost index funds, stock futures, and exchange-traded funds (ETFs).
- Macro factors like political, inflation, and growth risks are generally not directly traded (with volatility risk being the exception), allowing dynamic factors to be easily employed in portfolios.
- The Fama-French model, introduced in 1993, is the best-known example of a tradeable multifactor model.
Topic 4. Fama-French Model
-
The Fama-French model (called the Fama-French three-factor model) explains asset returns based on three dynamic factors. The model includes:
-
The traditional CAPM market risk factor (MKT).
-
A factor that captures the size effect (SMB).
-
A factor that captures the value/growth effect (HML).
-
-
The Fama-French three-factor model is expressed as follows:
-
- The SMB (Small Minus Big) factor represents the return difference between small-cap and large-cap stocks, capturing the historical outperformance of small companies relative to large companies, though the average stock only has market exposure.
- The HML (High Minus Low) factor captures the return differential between high book-to-market (value) stocks and low book-to-market (growth) stocks, with value stocks historically outperforming growth stocks.
- Fama-French factors are constructed as factor-mimicking portfolios to capture size (SMB) and value (HML) premiums through tradeable strategies.
- A value investor with positive HML beta experiences upward-adjusted returns by × E(HML) relative to CAPM, while growth stocks with negative HML betas have downward-adjusted expected returns.
Topic 4. Fama-French Model
-
In the Fama-French model, HML and SMB betas center on zero (versus CAPM's market beta of one), meaning the average investor earns market return without value or size tilt unless specifically choosing value or size plays.
- Both CAPM and Fama-French models assume constant betas, though empirical research shows betas vary and increase during bad times.
Practice Questions: Q2
Q2. Which of the following is not a factor in the Fama-French three-factor model?
A. The capital asset pricing model market risk factor.
B. The small capitalization minus big capitalization risk factor.
C. The winners minus losers risk factor.
D. The high book-to-market value minus low book-to-market value risk factor.
Practice Questions: Q2 Answer
Explanation: C is correct.
The Fama-French model includes the following three risk factors:
The traditional capital asset pricingmodel market risk factor.
- A factor that captures the size effect (SMB).
- A factor that captures the value/growth effect (HML).
The winners minus losers (WML) momentum factor was discovered by Jegadeesh and Titman.
Module 3. Value and Momentum Investment Strategies
Topic 1. Value Vs Momentum Strategies
Topic 2. Value Investing
Topic 3. Rational Theories of the Value Premium
Topic 4. Behavioral Theories of the Value Premium
Topic 3. Momentum Investing






Topic 1. Value Vs Momentum Strategies
-
The small stock outperformance effect (after adjusting for beta) was discovered by Banz (1981) and Reinganum (1981), but disappeared after publication, with SMB strategy returns peaking in the early 1980s and no subsequent evidence of a small stock premium from 1965-2011. The two possible explanations for the disappearing size effect are as follows:
- Data mining, suggested by Fischer Black (1993), provides one explanation: the finding appeared in in-sample data but was not substantiated in out-of-sample studies.
- Investor actions provide another explanation consistent with the efficient market hypothesis (EMH): investors rationally bid up small-cap stock prices after publication until the SMB effect was eliminated, suggesting size should be removed as a Fama-French risk factor.
- Small stocks still tend to have higher returns (weak size effect) partially due to lower liquidity than large-caps, and value and momentum effects are stronger for small stocks, though risk-adjusted excess returns over the market are no longer capturable.
Practice Questions: Q1
Q1. Which of the following investment strategies stabilizes asset prices?
A. A value investment strategy.
B. A momentum investment strategy.
C. A size investment strategy.
D. Value, momentum, and size strategies all stabilize asset prices.
Practice Questions: Q1 Answer
Explanation: A is correct.
Value and momentum are opposite to each other in that value investing is inherently stabilizing. It is a negative feedback strategy where stocks that have fallen in value eventually are priced low enough to become value investments, pushing prices back up. Momentum is inherently destabilizing. It is a positive feedback strategy where stocks that have been increasing in value are attractive to investors, so investors buy them, and prices increase evenmore.
Topic 2. Value Investing
- Unlike the disappearing size premium, the value risk premium has provided investors with higher risk-adjusted returns for over 50 years, despite suffering losses during the 1990s recession, the late 1990s dot-com bull market, and the 2007-2009 financial crisis.
- Value investing dates back to Graham and Dodd's 1934 publication "Security Analysis," which focused on finding stocks priced below their fundamental values.
-
Two general explanations exist for the value premium:
- Rational and
- Behavioral.
Topic 3. Rational Theories of the Value Premium
- In the rational explanation, value stocks co-vary with each other and growth stocks, performing well or poorly together, with the value premium compensating investors for periods of poor performance during "bad times," though not all value risk can be diversified away.
- Labor income risk, investment growth, luxury consumption, long-run consumption risk, and housing risk explain the value premium, with value stock betas increasing during bad times defined by these risks, making them particularly risky through the same macro-based and CAPM factors affecting value firms.
- Growth firms are more adaptable with human capital that can adjust to changing times, while value firms have fixed assets with high asymmetric adjustment costs that cannot be redeployed, making value stocks fundamentally riskier than growth stocks.
- The average investor holds the market portfolio, with some choosing value or growth tilts based on their ability to withstand bad times; investors must assess whether factor-defined bad times (labor income risk, low investment growth, etc.) are personally bad relative to the average investor.
- Investors with comparative advantages in bearing value risk during times that are not personally adverse can earn the value premium by holding value stocks.
Topic 4. Behavioral Theories of the Value Premium
- Behavioral theories explain the value premium through: (1) over-extrapolation and over-reaction, and (2) loss aversion and mental accounting.
- Overextrapolation occurs when investors assume past growth rates will continue, bidding up growth stock prices beyond intrinsic values due to unwarranted optimism, leading to lower returns when expected growth doesn't materialize compared to value stocks.
- Loss aversion and mental accounting suggest that investors dislike losses more than gains and view investments case-by-case rather than portfolio-wide; value stocks with high book-to-market ratios are perceived as riskier after poor performance, requiring higher expected returns.
- The value premium persists because investors may find value investing difficult despite easy internet screening tools, or because required investment horizons (three to six months minimum) may be too long for many institutions to adopt value strategies.
- Value investing exists across all asset classes through strategies including riding the yield curve in fixed income, roll return in commodities, and carry in foreign exchange (long high-interest-rate currencies, short low-interest-rate currencies, where high yields parallel low equity prices).
- Both retail investors (via low-cost index products) and large institutional investors can implement value strategies cheaply across markets.
Topic 5. Momentum Investing
- Jegadeesh and Titman (1993) identified the momentum effect, where strategies involve buying past "winners" (stocks rising over 6 months) and shorting past "losers" (falling stocks), denoted as WML (Winners Minus Losers) or UMD (Up Minus Down).
- Momentum premiums exist across fixed income (government and corporate bonds), international equities, commodities, real estate, and specific industries and sectors.
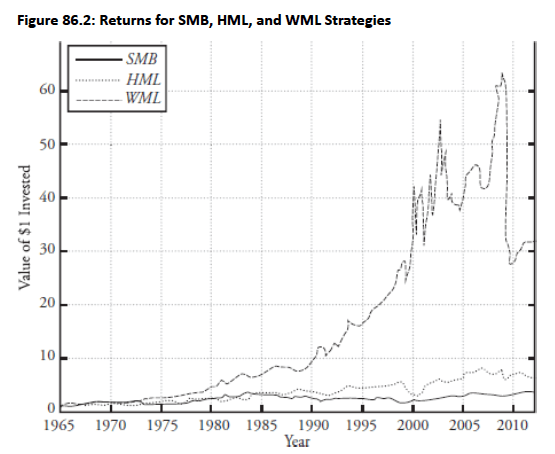
- Momentum returns significantly exceed size and value premiums; $1 invested in WML in January 1965 reached over $60 before dropping below $30 during the 2007-2009 crisis, with only −0.16 correlation to value premium.
- Value investing is a stabilizing negative feedback strategy where falling stocks become value investments, pushing prices back up, while momentum is a destabilizing positive feedback strategy where rising stocks attract more buyers, increasing prices further.
- Momentum investing can lead to crashes (50%+ drop in 2007-2009), more dramatic than value/growth returns, though portfolio rebalancing remains essential.
-
Momentum is often added to the Fama-French model as a fourth factor:
-
Topic 5. Momentum Investing
- Momentum is riskier than value or size investing with 11 recorded crashes: seven during the 1930s Great Depression, three during 2007-2009 financial crisis, and one in 2001.
- During the 2007-2009 crisis, government bailouts of financial firms created floors on stock prices, causing large losses for momentum investors who were short these stocks as markets rebounded unexpectedly.
- Momentum risk includes tendency toward crashes, monetary policy and government intervention risk (disrupting natural asset price progression), and macro factors like business cycles, stock market state, and liquidity risk.
Topic 5. Momentum Investing
-
Behavioral theories suggest investor biases explain momentum through two camps:
- Overreaction to good news where overconfident investors attribute performance to skill, pushing prices above fundamental values, and
- Underreaction to good news where investors partially incorporate information, causing price drift.
- In both overreaction and underreaction scenarios, prices eventually revert to fundamental values over the long run.
- Investors considering momentum must assess whether they lean toward overreaction or underreaction biases and determine their tolerance for large losses during crash periods.
- Historical crashes concentrate around periods when policymakers (e.g., central banks) interrupt momentum by changing the natural course of asset prices.
- Assets are exposed to factor risks like value and momentum, with factor premiums compensating investors for losses during bad times.