IEEE Genomic Survey Paper
Datatypes and Methods
Sachin Kumar
Project BL2403, SCoS & SBS, NISER


Outline
-
Data types covered in the paper
-
Methods based on the datatypes
-
Applications
-
Comparison of Models
Not covered: Detailed discussion of models' architecture
Datatypes at different molecular level
-
Genomics Data
-
Transcriptomics Data
-
Epigenomics Data
-
Pharmacogenomics Data
-
Proteomics Data
Tasks
Prognostic Predictions
-
Detect various expressions in omics data.
-
Deeply mine complex genomics data Classify critical regulators.
-
Detect representations in every omics data.
-
Identify cancer cells with related Epigenomics.
Cancer Applications
-
Patient Survival Rate
-
Early Prognosis
-
Cancer Classification
Tasks
Therapeutics Predictions
-
Identify drugs giving a desired gene expression.
-
Drug response prediction based on mutation.
-
Sensitivity classification of each anticancer drug.
-
Detect therapeutic biomarkers for drug response prediction.
Cancer Applications
-
Drug Response
-
Drug Target Discovery
-
Biomarker Discovery
Base Deep Learning models covered
Auto Encoder, Vision Transformers, GNN, CNN, GCN, bi-LSTM, Denoising AE, SGCN, Kernel DNN, NN Triplet Loss, Multi-Task NN, CNN-LSTM, VNN
Specific Deep Learning models covered
CITRUS, RDAClone, dpAE, DeepDEP, MOMA, GTN, MOGONET, MultiCoFusion, SWnet, GTN, GCN-CRISPR, MultiCoFusion, CDNN, DeepCellEss, DeepSynergy, DeepDRK, Super.FELT, CSynergy, CCSynergy, DeepSynergy, Apindel, DeepDep, BioVNN
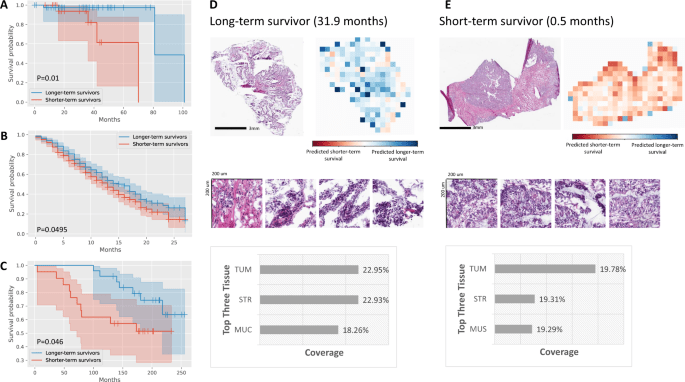
MOMA 13 April 2023
Multi-Omics Multi-cohort Assessment
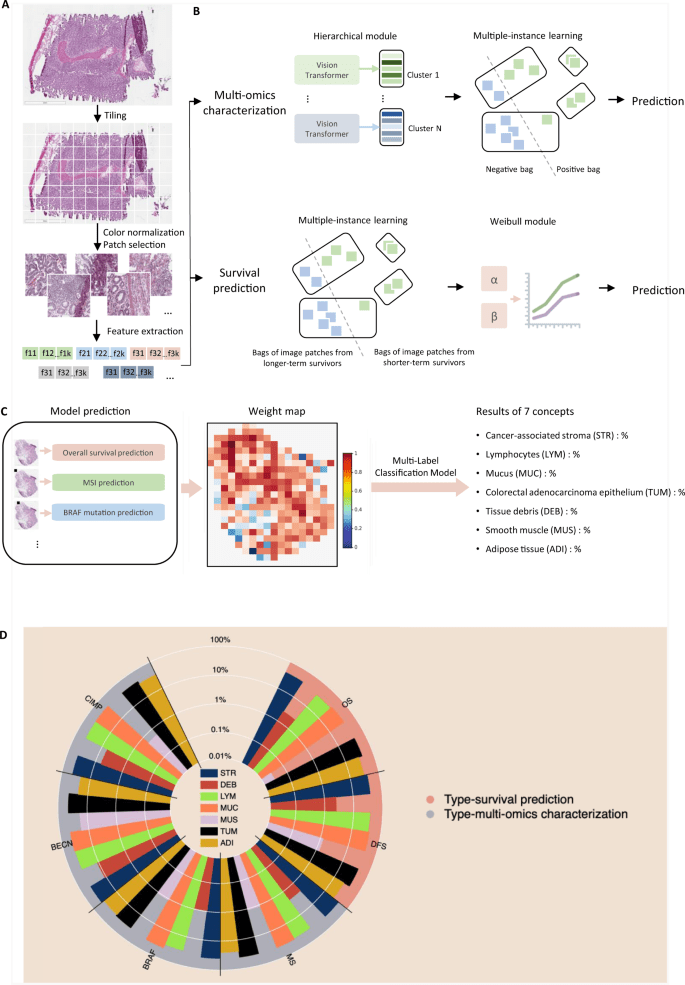
MOMA 13 April 2023
Multi-Omics Multi-cohort Assessment
CITRUS 28 Oct 2022
Chromatin-informed Inference of Transcriptional Regulators Using Self-attention
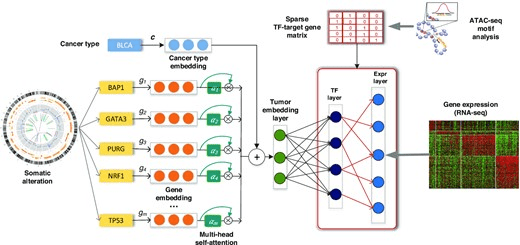
CITRUS 28 Oct 2022
Chromatin-informed Inference of Transcriptional Regulators Using Self-attention
Overview of CITRUS: An attention-based model with TF-target gene priors. The input to our framework includes somatic alteration and copy number variation, assay for transposase-accessible chromatin with high-throughput sequencing (ATAC-seq), tumor expression datasets and TF recognition motifs. CITRUS takes somatic alteration and copy number variation data as input and encodes them as a tumor embedding using a self-attention mechanism. Cancer type embedding is used to stratify the confounding factor of tissue type. The middle layer further transforms the tumor embeddings into a TF layer, which represents the inferred activities of 320 TFs. Finally, gene expression levels are predicted from the TF activities through a TF-target gene priors constrained sparse layer based on ATAC-seq.
MultiCoFusion April 2022
multi-modal fusion framework based on multi-task correlation
code
site
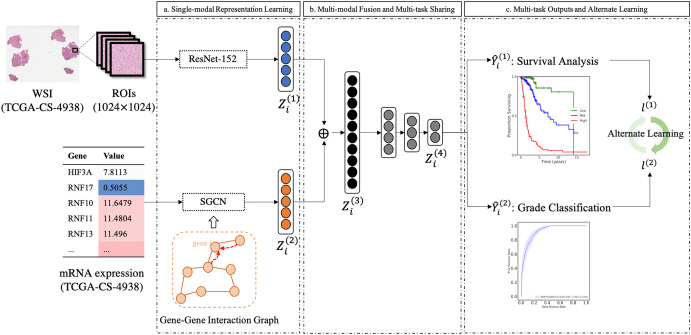
MultiCoFusion April 2022
multi-modal fusion framework based on multi-task correlation
code
site
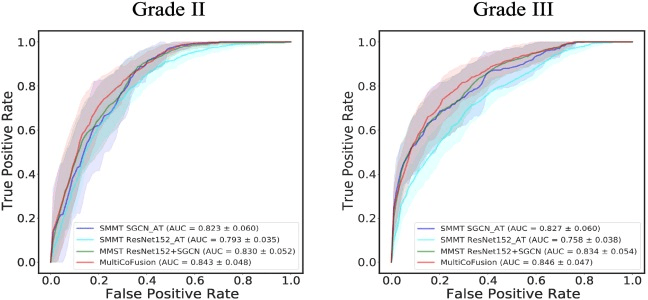
MOGONET 08 June 2021
Multi-Omics Graph cOnvolutional NETworks: patient classification and biomarker identification
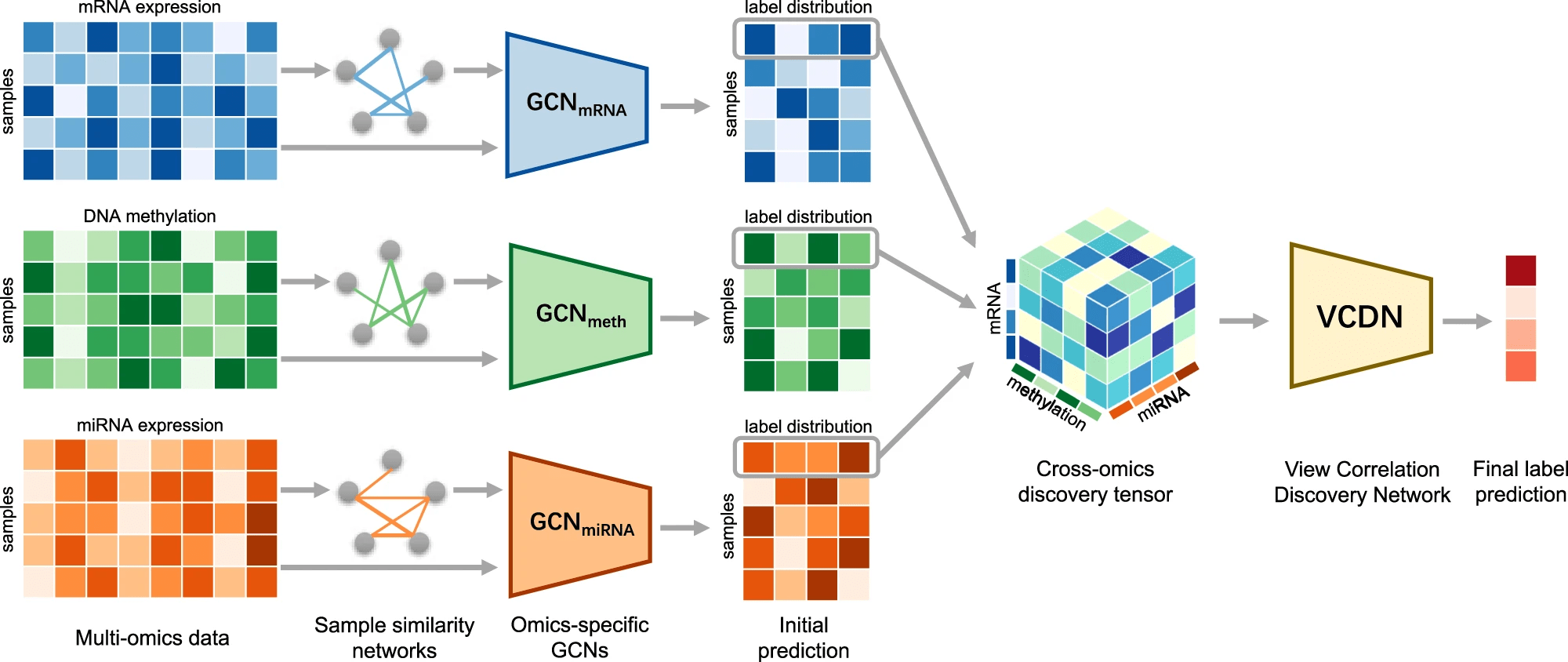
MOGONET 08 June 2021
Multi-Omics Graph cOnvolutional NETworks: patient classification and biomarker identification
MOGONET combines GCN for multi-omics-specific learning and VCDN for multi-omics integration. For clear and concise illustration, an example of one sample is chosen to demonstrate the VCDN component for multi-omics integration. Preprocessing is first performed on each omics data type to remove noise and redundant features. Each omics-specific GCN is trained to perform class prediction using omics features and the corresponding sample similarity network generated from the omics data. The cross-omics discovery tensor is calculated from the initial predictions of omics-specific GCNs and forwarded to VCDN for final prediction. MOGONET is an end-to-end model and all networks are trained jointly.
MultiCoFusion April 2022
Chromatin-informed Inference of Transcriptional Regulators Using Self-attention
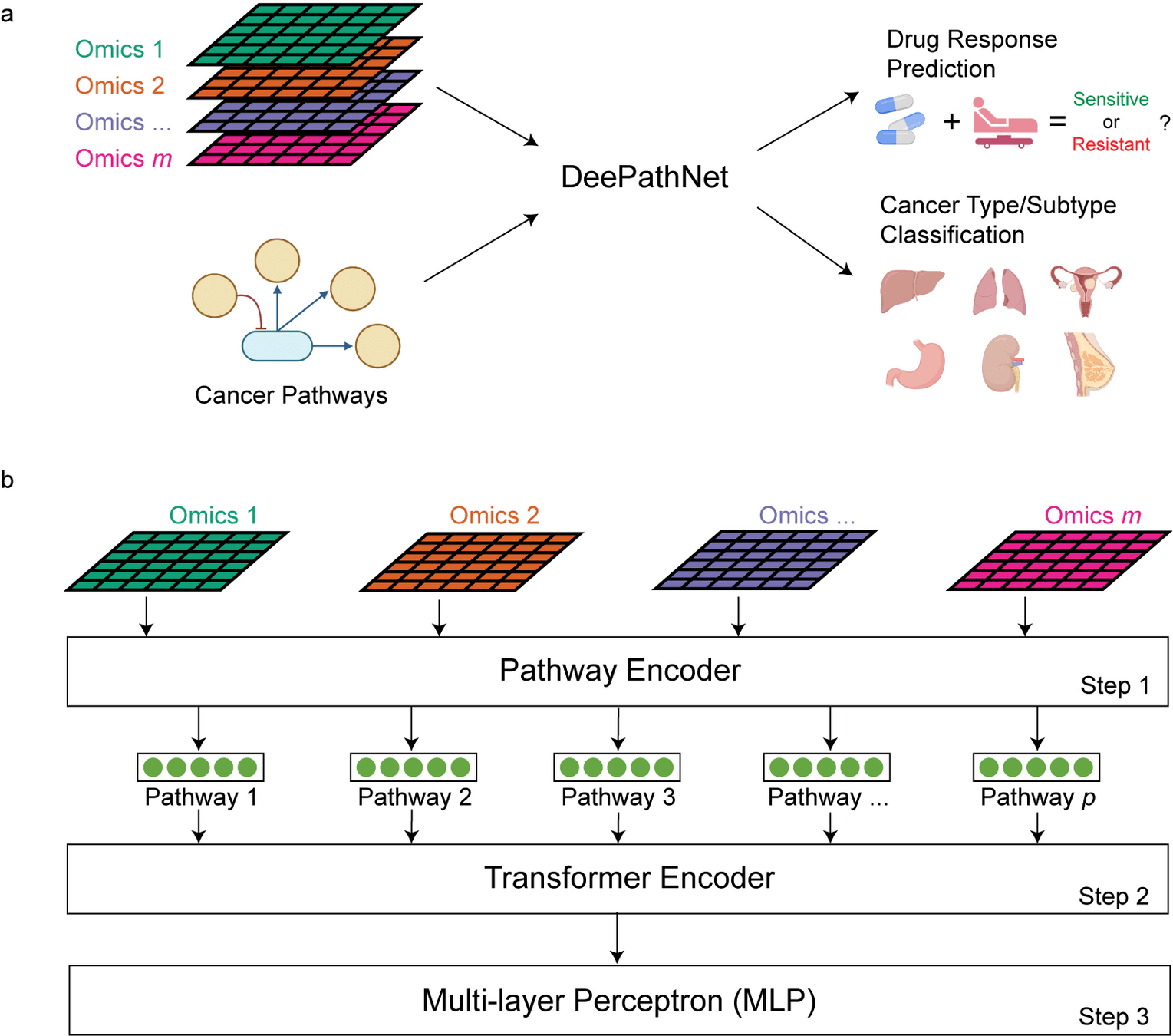
DeepPathNet 22 April 2024