Building Secure Cloud Solutions in Microsoft Azure
Rainer Stropek | @rstropek@fosstodon.org | @rstropek
Agenda
Security is of paramount importance when building web APIs or Apps running in the cloud. In this session, long-time Microsoft MVP Rainer Stropek introduces you to the top five technologies in Microsoft Azure that will make your PaaS-based solutions in this cloud environment significantly more secure. You will hear about Managed Identities, Private Endpoints, Key Vaults, logging/monitoring/telemetry, and Azure Policies. The knowledge gathered in this session can help you to create cloud architectures that have a high level of security built-in.
Introduction
Rainer Stropek
- Passionate software developers for 25+ years
- Microsoft MVP, Regional Director
- Trainer, Teacher, Mentor
- 💕 community





What Are You
Going to See?
PaaS
PaaS
- Always prefer PaaS over IaaS if technically possible
- Cloud is expensive when using IaaS
- Not using PaaS is wasting productivity
- Apply Lean principles
- "...a way to do more and more with less and less [...] while coming closer and closer to providing customers exactly what they want" 🔗
- Azure PaaS offerings have a lot of security measures built-in
- Authentication, encryption, key/certificate management, etc.
IaC
Infrastructure-as-Code
- Always prefer IaC over manual maintenance of cloud artifacts
- Native in Azure: Bicep, PowerShell, Azure CLI
- Lots of OSS and 3rd party options (e.g. Terraform, Pulumi, etc.)
- IaC is a security measure
- Enables code reviews
- Repeatable (e.g. for staging)
- IaC combined with source control ➡️ auditability
- Good practices written in code can be shared
- IaC only leads to enhanced security if access to Azure control plane is properly secured!
- Investment in AAD and RBAC is required for that
- MFA, PIM, Conditional Access, secured deployment processes, etc.
Sample:
IaC
Managed Identity
Managed Identity
- Problem: Where to store secrets for M2M communication?
- How to create those secrets?
- How to regularly update those secrets?
- Secrets in the hand of admins circumvent MFA
- Assumption: Deployment process is secure
- We have to make sure of that (more about that later)
-
The fact that code is running in a specific Azure service is proof of identity
- Uses developer identity (MFA) for local debugging
- Managed Identity can get rid of most secrets for apps inside Azure

Areas of Application
- Access PaaS/Serverless services provided by Azure
- E.g. Storage, Key Vault, Container Registry, etc.
- Access databases provided by Azure
- E.g. Azure SQL DB, Cosmos DB, etc.
- Access backend services
- Can be custom-built
- Don't even need to run in Azure
Sample:
Azure MI
Key Vault
Managed Identity is nice, but...
- ...what about services that don't support MI?
- New Azure services
- External services not related to Azure
- Solution: Azure Key Vault
- Secure place to store secrets, encryption keys, and certs
- Authenticate to Key Vault with Managed Identity
- As always: Follow the principle of least privilege
- Use Azure RBAC for access management
- Managed Identities are service principles
Sample:
Key Vault
Private Endpoints
Private Endpoints
- Azure supports virtual networks (VNets)
- Lots of security components available for VNets
- E.g. NSGs, Azure Firewall, App Gateway, Frontdoor, etc.
- Problem: Most PaaS offerings cannot be moved into VNets
- They are run by Microsoft
- Solution: Private Endpoints
- Enables accessing PaaS services over PE in your own VNet
- PaaS services does not need to be available on public Internet
- Available for many Azure PaaS offerings 🔗
Azure AD
Storage
Databases
Key Vault
VNet
Jumphost
(Bastion)
Corp
Net
Sample:
Private
Endpoints
Policies
Policies
- Problem: How to ensure that teams follow security practices?
- Manual checking is error-prone and doesn't scale
- Solution: Azure Security Policies
- Coded rule about specific security conditions that must be controlled
- Audit: Check condition, for compliance reports
- Enforce: Actively change/deny certain settings
- Built-in vs. custom
- Azure has lots of policies built in 🔗
- You can define custom policies
Sample:
Key Vault
Policy
Logging, Monitoring,
Telemetry
Azure Logs
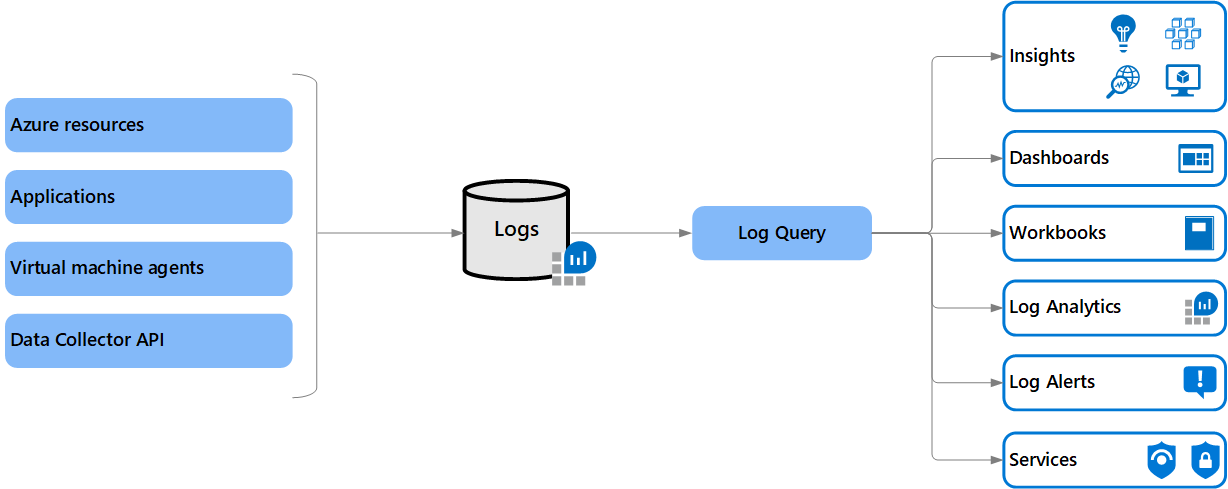
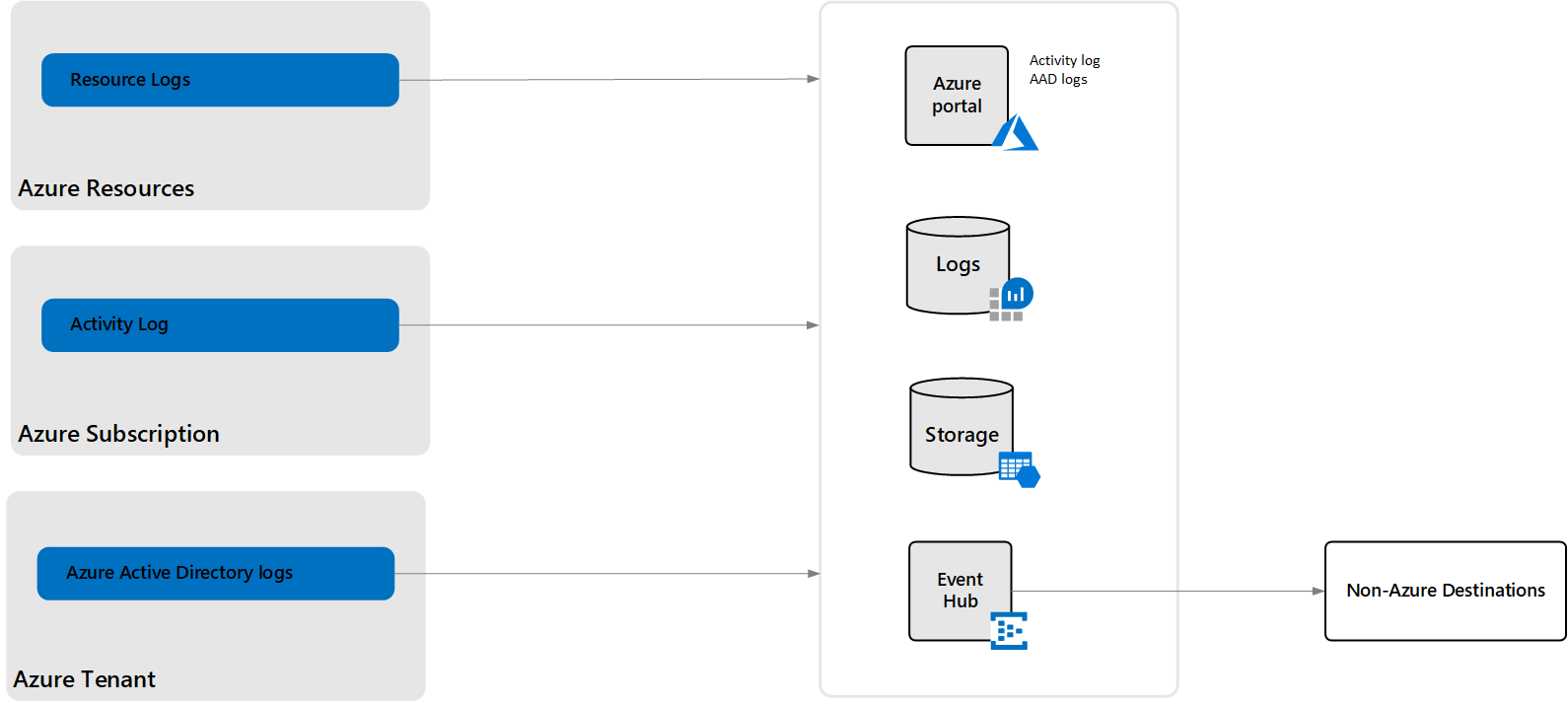
Azure Platform Logs
Q&A
Rainer Stropek | @rstropek@fosstodon.org | @rstropek