Microsoft Fabric
SQL Database
(preview)
Jeff Taylor


jssug.org
Every 3rd Wednesday 6-8pm
Except for May, November and December


Annual Free Data Conference
May 2nd & 3rd, 2025

JSSUG
January Sponsor
Jeff Taylor
Principal Data Consultant
Database Consulting, LLC






Jeff Taylor
Microsoft Fabric
SQL Database
(preview)

Introduction to Microsoft Fabric SQL Database
-
Overview: Developer-friendly transactional database based on Azure SQL Database.
-
Integration: Integrated with development frameworks and analytics.
-
Replication: Automatic data replication into OneLake for analytics.
- Performance: Intelligent performance features like automatic index creation.
Key Features of Microsoft Fabric SQL Database
-
OLTP Workloads: Home for OLTP workloads, easy to configure and manage.
-
Analytics Setup: Automatically replicates data into OneLake in near real-time.
-
Development Tools: Supports SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS), Azure Data Studio, and web-based editor in the Fabric portal.
- Intelligent Performance: Features like automatic tuning and index creation.
Analytical Endpoint
-
Paired Endpoint: Each Fabric SQL database has a paired SQL analytics endpoint.
-
Reporting Queries: Run reporting queries against the OneLake copy of the data.
- Access Methods: Accessible via the Fabric portal, SSMS, and Visual Studio Code.
Connecting to the Database
-
Web-Based Editor: Use the web-based editor in the Fabric portal.
-
SSMS and Azure Data Studio: Connect using SQL Server Management Studio and Azure Data Studio.
- Connection Strings: Provided for various tools including ADO.NET, JDBC, ODBC, PHP, and Go.
Semantic Model
-
Default Model: Automatically created for each SQL database.
-
Custom Models: Ability to create multiple models from one database.
-
Business-Friendly: Enables deeper analysis with metrics and business-friendly terminology.
- Integration: Integrated with Power BI for visualizations and analysis.
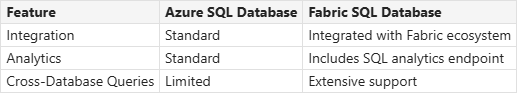
Cross-Database Queries
- Querying Across Databases: Write cross-database queries joining data from other SQL databases, mirrored databases, warehouses, and the SQL analytics endpoint.
Azure SQL vs. Fabric SQL Database
- Common Code Base: Both share a common code base with the latest stable version of the Microsoft SQL Database Engine.
Differences
- Always Encrypted: Supported in Azure SQL but not in Fabric SQL.
- Change Data Capture (CDC): Supported in Azure SQL but not in Fabric SQL.
- Elastic Pools: Available in Azure SQL but not in Fabric SQL.
- Provisioning Control: Detailed control in Azure SQL, autonomous management in Fabric SQL.
- Integration: Fabric SQL is fully integrated with other workloads in the Microsoft Fabric platform by default
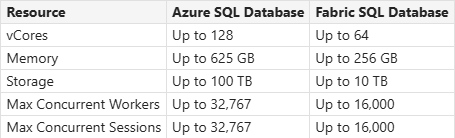
Azure SQL vs. Fabric SQL Database
Azure SQL Database
Fabric SQL Database
- Compute Tiers: Provisioned or serverless.
- Hardware Configurations: Gen5, Fsv2, DC.
- Elastic Pools: Yes.
- Maximum Resource Limits: Higher limits for vCores, DTUs, and storage.
- Compute Tiers: Serverless.
- Hardware Configurations: Latest configurations.
- Elastic Pools: No.
- Maximum Resource Limits: Lower limits compared to Azure SQL Database, subject to change before general availability.
Azure SQL vs. Fabric SQL Database
Demo
Create a SQL database in the Fabric portal
Demo
Use SQL Analytics Endpoint
Demo
Connect to the Database - SSMS, Azure Data Studio
Demo
Semantic Model
Resources
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/fabric/database/sql/overview
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/shows/data-exposed/sql-integration-with-microsoft-fabric-data-exposed
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/fabric/data-warehouse/tutorial-sql-cross-warehouse-query-editor
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/fabric/database/sql/mirroring-limitations
Questions?
Thank you
Jeff Taylor
Thank you for attending my session today. If you have any additional questions please don't hesitate to reach out. My contact information is below.

