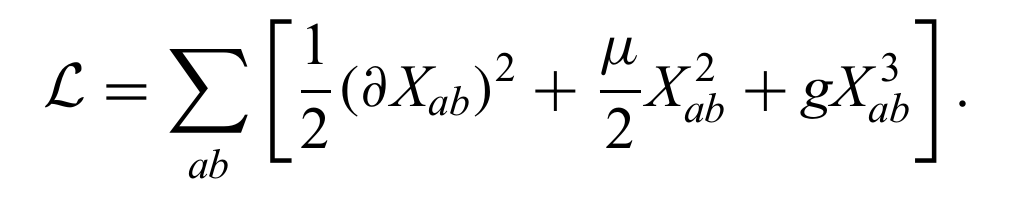Replica Trick, Symmetry and Breaking in context of Measurement Induced Phase Transitions:
A very brief intro
Sagnik Ghosh •Uni Bonn •JC • Nov 06, 2024
What is Replica Trick?
Consider a system with Quench disorder, i.e, for a thermodynamic quantity f, over a disorder parameter J obeys,
and we are interested in computing the disorder averaged free energy.
Analytically speaking taking disorder average over log is complicated.
Replica trick lets you rewrite the disorder averaged log in terms of the disorder average over multiple copies.
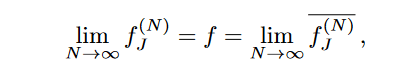
Formulation:
The definition of replica trick essentially relies on the following (and some other similar) formulae.
For example your Z can be partition function and you can get free energy (like in SK model; tbd)
Or it can be a reduced density matrix (time dependent) and one can compute half-chain entanglement entropy.
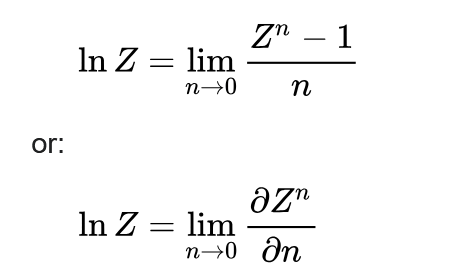
Formulation:
One can urgue that the formulae makes sense,by looking at the following Taylor Series Expansions. For the first one,
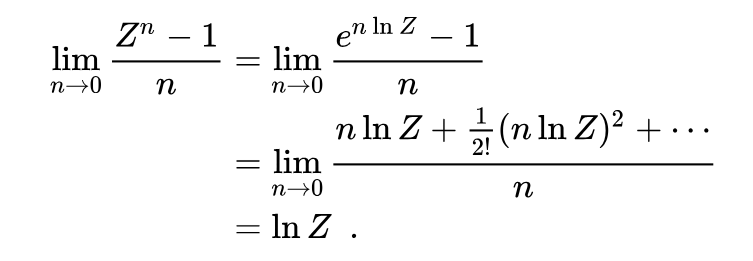
And for the second one:
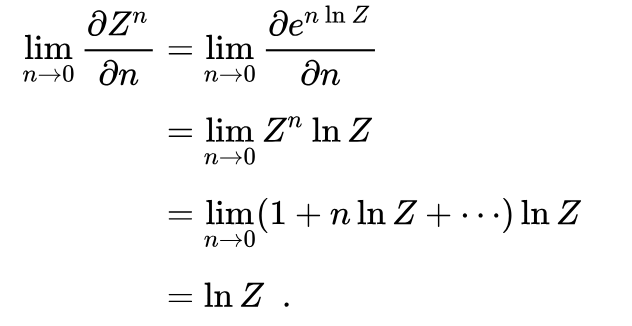
Formulation:
The key point here is that (in most physically relevant settings) one can actually compute the averages for integer n, and the by sending n continuously to zero, using extrapolation.
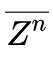
Strictly speaking, its not extremely rigorous to take the continuous limit to zero from only extrapolating over integer values of n, but there exist a sufficient condition, that if,
holds, then by Carlson's theorem, extrapolation becomes exact.
Sherrington-Kirkpatrick model
The Hamiltonian is given by,
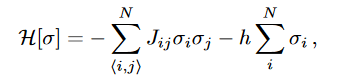
with spin being either -1 or 1, h is uniform and J is sampled from
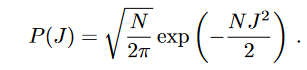
The partition function reads,
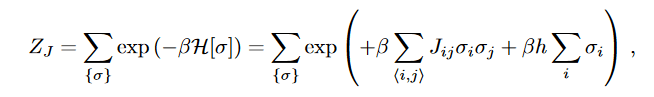
Replicas:
Lets say we wish to compute the Free energy. We can employ the replica trick
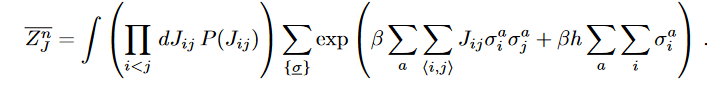
where a denotes the replica index. Note we have interacting spins but replicas still dont talk to each other
Some prerequisites:
In the following the following Identity is heavily used!
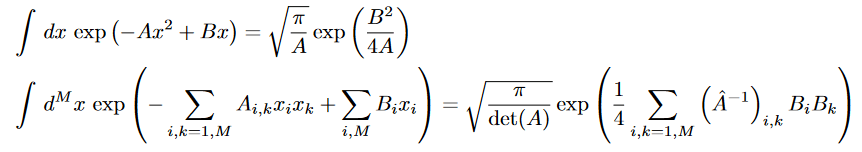
Which if read from left to right is definition of Gaussian integral and if read from right to left is the Hubbard Stratanovich transformation
Replicas:
Using that on the replicated partition function one can get rid of the disorder and obtain,
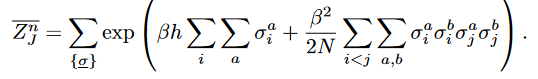
Note that the spins within a replica are now free but replicas are now interacting, this interaction term can be rewritten as,
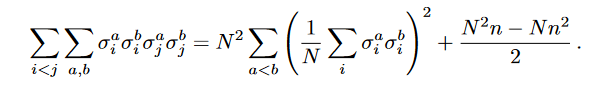
And the partition function reads,
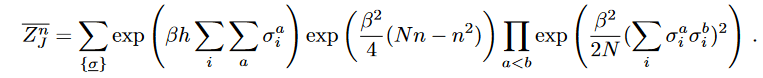
Replicas:
We can again do a Hubbard Stratanovich here, with
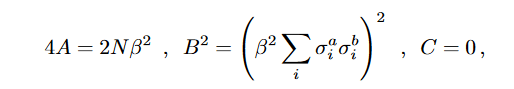
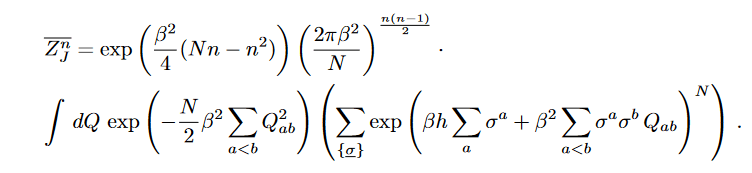
To obtain,
Where Q is a symmetric matrix at the price of introducing which spins within replicas has been decoupled
Large Integrals, Steepest Descent, Saddles:
Now, in the above integral we have a leading N dependent term of the form,
The key observation is, if f(z) has a saddle point then most of the contribution for the integration comes from here for a finite N and at N tends to ininity limit the approximation becomes exact.
The key game here is to find a saddle of the "action" w.r.t Q which then allows us to drop all the subleading terms with N.
In addition we only keep terms exponential in n, as for free energy computation, n2 terms will vanish as n goes to 0
With the approximation the action becomes,
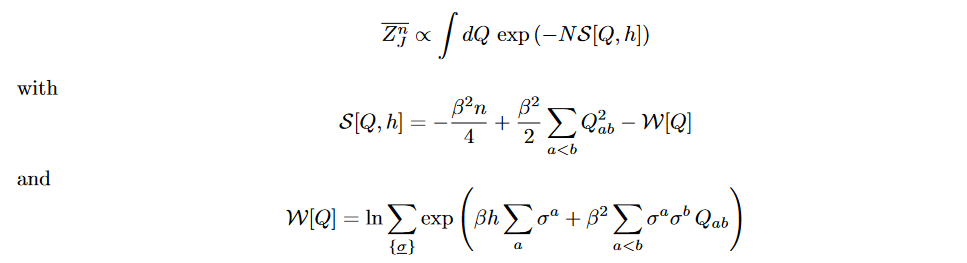
and the free energy then is,
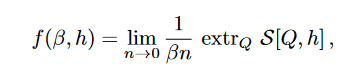
Free Energy
Which is damn hard problem!
Replica Symmetry
Q is a symmetric matrix coming from Hubbard-Stratanovich, we can parametrized it however we want.
Replica Symmetry: Permutation of the layers does not change the partition function.
Replica Symmetry breaking: We are after finding a saddle of the partition function. Let's say we have such a saddle.
Question is does the permutation of the layers leaves it unchanged or does it map it to another saddle.
(In principle the choice of Q fixes a "realisation", the minimas obtained from it might or might not be global.
Toy Example
Consider a symmetric function of two variables, g(x,y). Let (x',y') be a local saddle of this function
Case I: Symmetry leaves it unchanged. so x'=y' and we can restrict our search to the x-y line. If it is global minima we are done.
Case II: Symmetry changes it. so (x',y') and (y',x') are distinct minimas. This is the case that goes as replica symmetry breaking.
Replica Syemmtric solution:
We assume the group action,
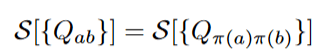
Leaves the extremum unchanged
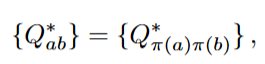
One possible choice of this is,
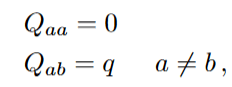
A few Algebra Later...
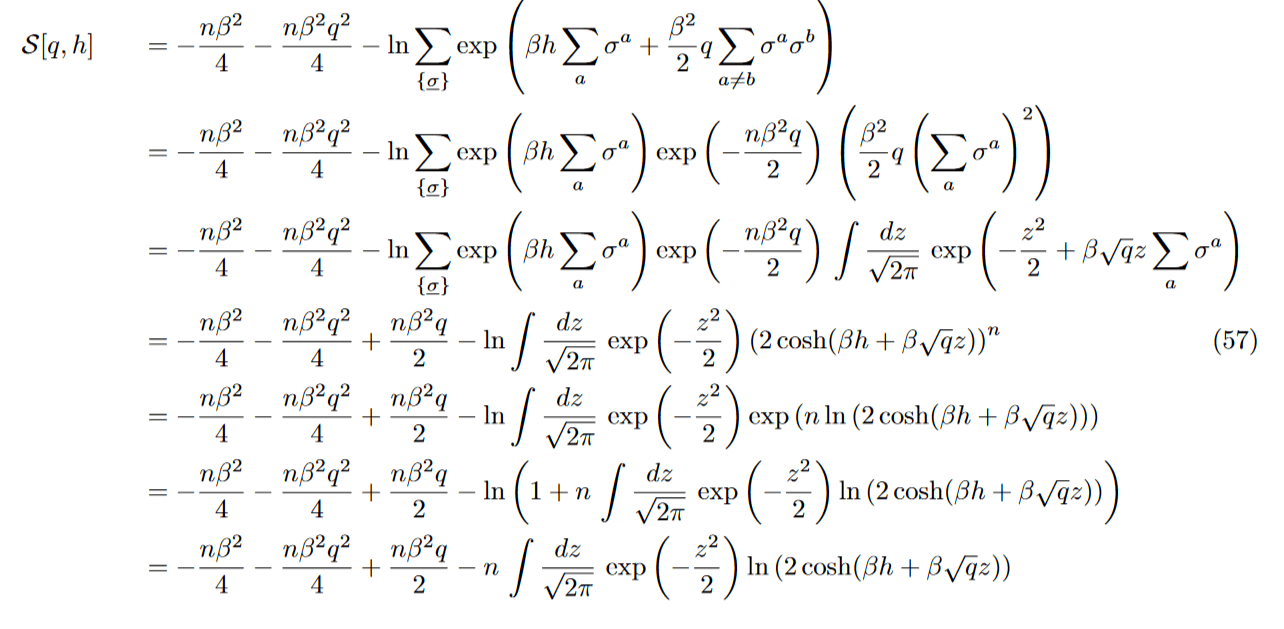
Free Energy
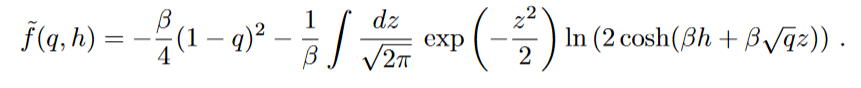
The Gibbs free energy reads,
Statics steady states are the one where free energy is stationary.
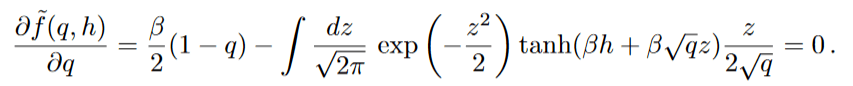
Phenomenology
I. for finite h the only solution is trivial, so no phase transitions.
II. for h=0, there are two solutions.
for β<1 the only solution is q=0 for β>1 there is another physical solution so there is a phase transition.
But, also predicts negeative entropy at low temperature, in particular
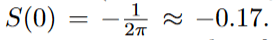
So the replica symmetry is brocken in low temperatures.
de Almeida-Thouless Line
One way to check where the symmetry is brocken is to see where the saddle becomes unstable.
And this is done by looking at the eigenvalues of Hessian Matrix corresponding to the saddle. The onset of instability happens when one of them becomes zero. This with the self-consistency condition for minimal q, gives,
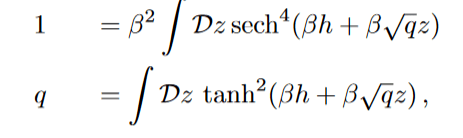
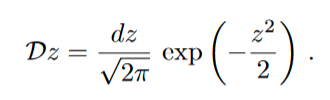
On the left of this line replica symmetry is brocken.
RSB Ansatz (Parisi scheme)
We can try to improve the scheme by first assuming there are instead n/m groups of m replicas and if two replicas belong to the same group the have weight q1 and if two replicas are in different groups then they have weight q0
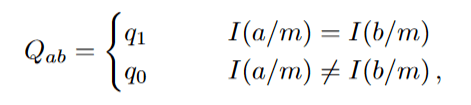
Then free energy becomes
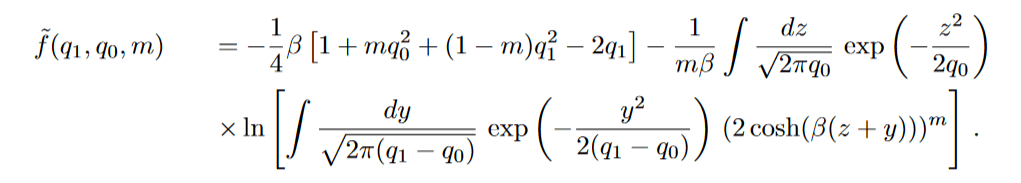
One can show with this choice S(0)=-0.01
RSB-1, RSB-2...
This is called RSB-1, but we dont need to stop there, we can further break the quotients into smaller groups.
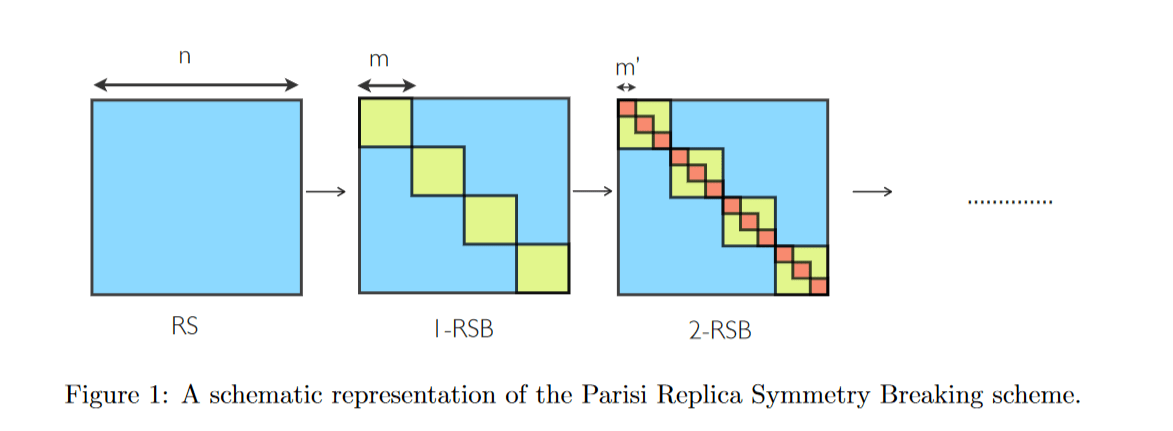
Doing this progressively gets us to the correct criticality

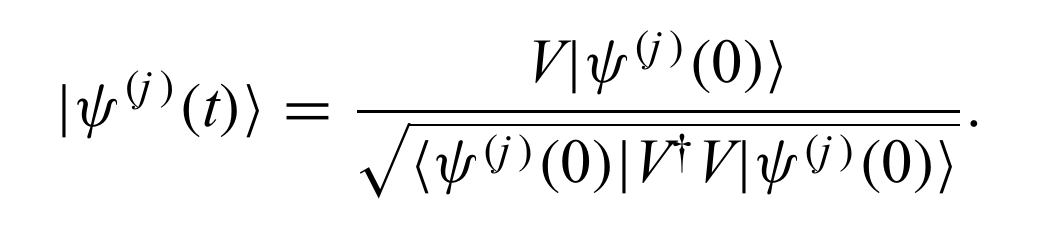
Replicas in Measurement Induced Phase Transition
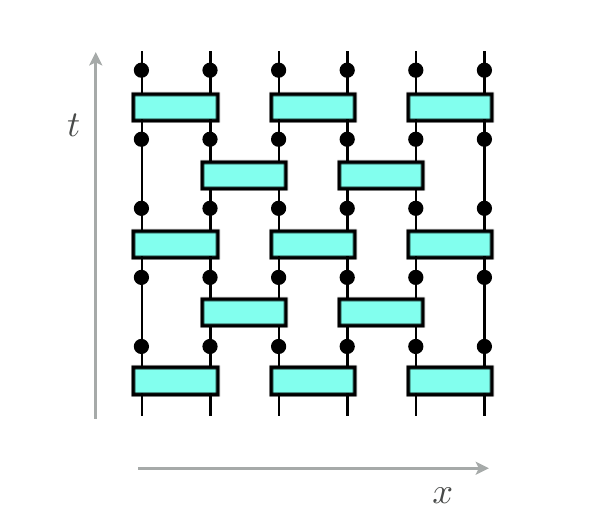
Circuit:
Tev:
Replicas in Measurement Induced Phase Transition:
To compute lets say entropy one can use replicas:
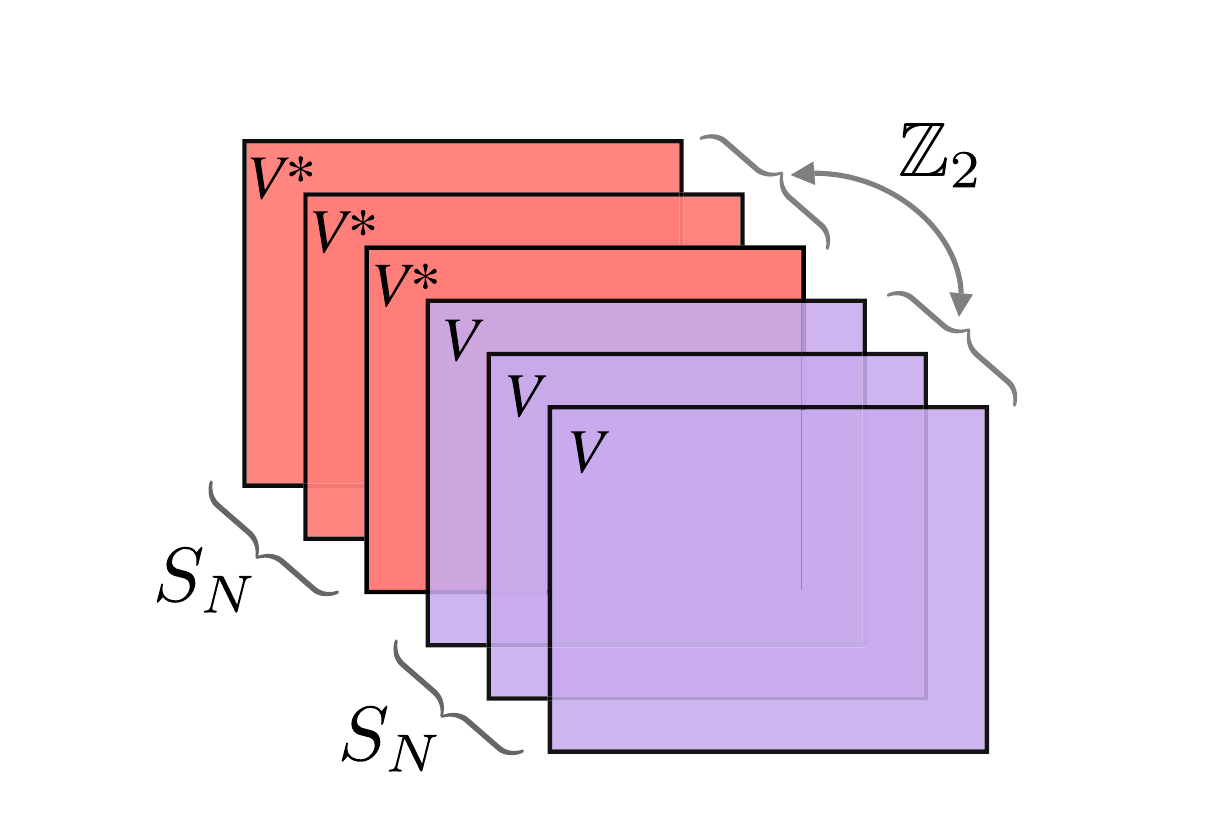
The Symmetry group:
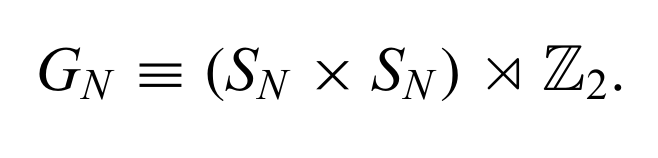
Boundary condition breaks the symmetry
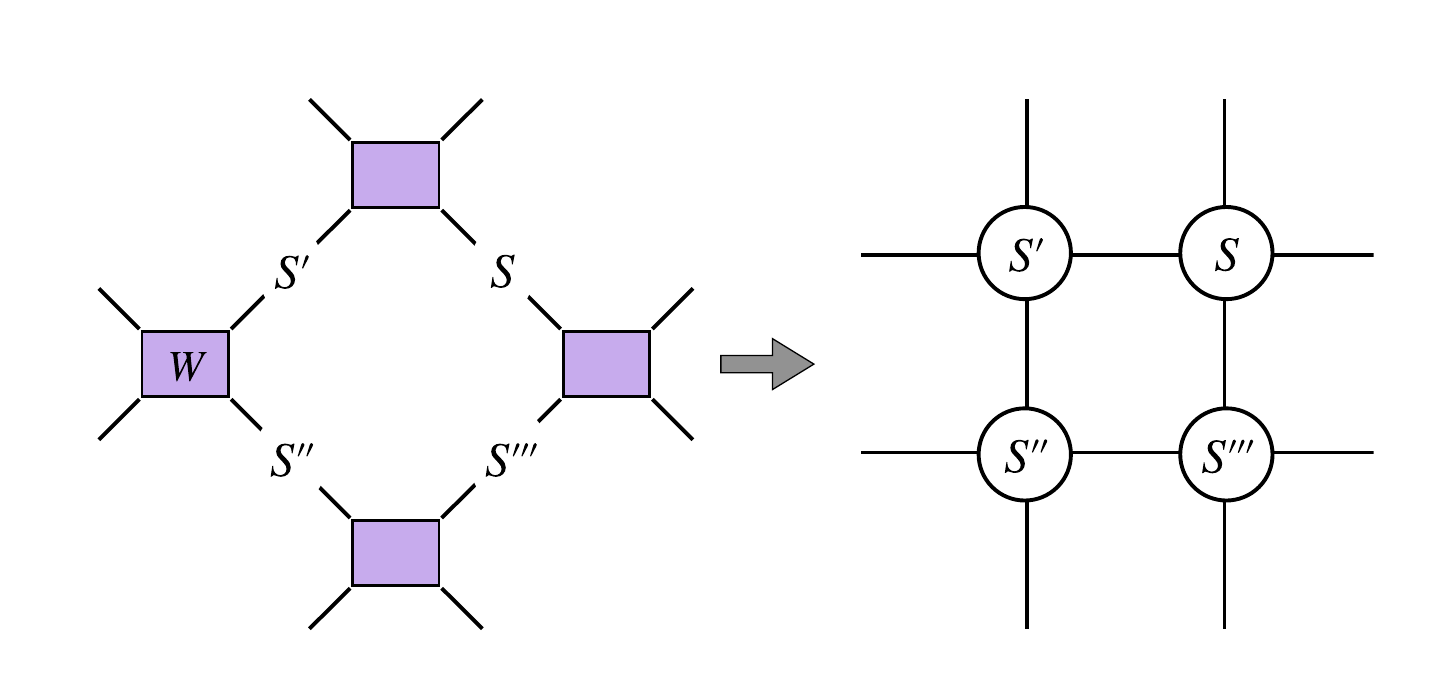
Mapping to a spin model:
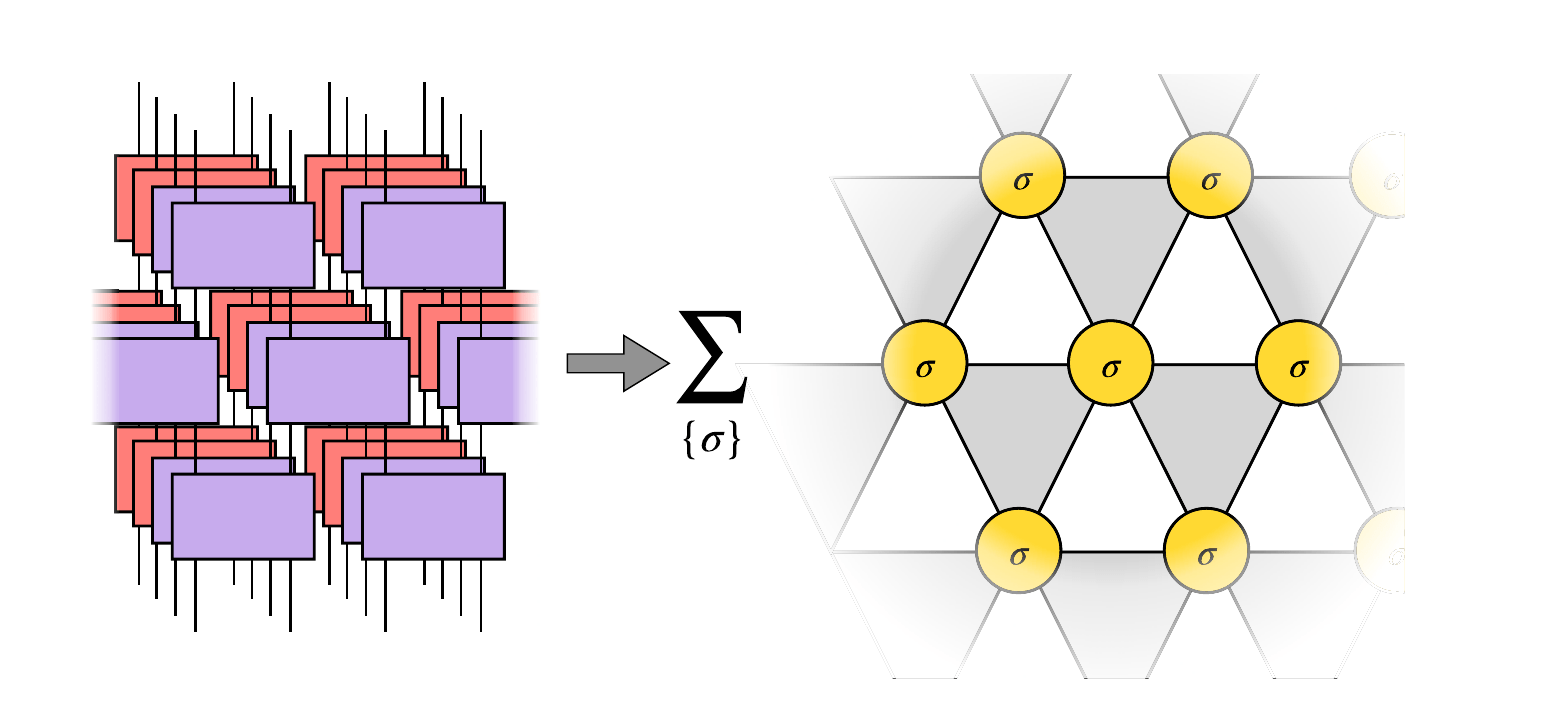
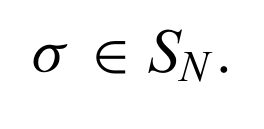
Can Write a replicated partition function here,
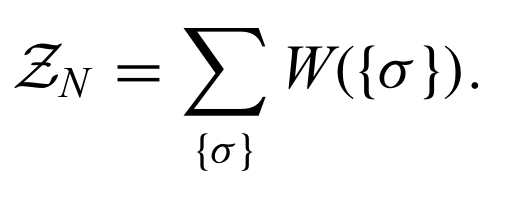
The spins here are permutation of layers. For eg with three layers,
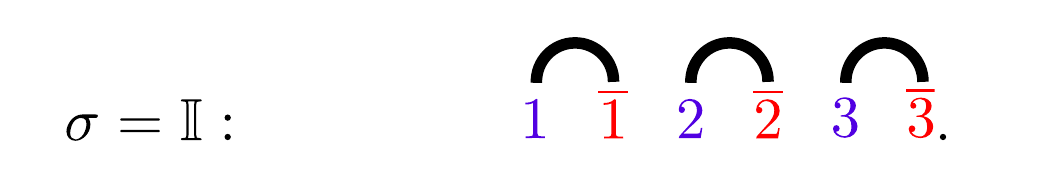
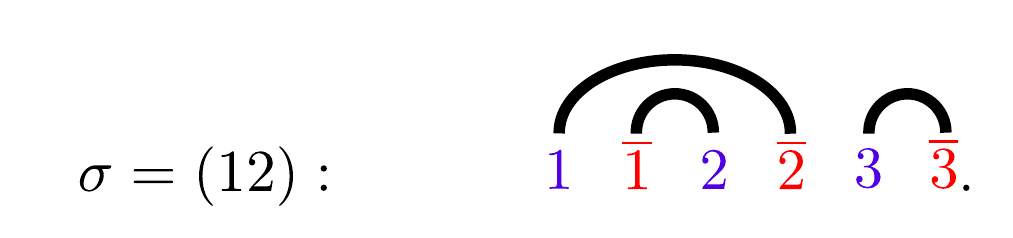
With this transformation it becomes an "ising" model assuming the contributions from contractions of far layers are ignorable.
Replica Limit:
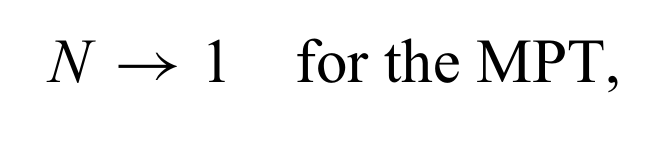
because of the Born Rule. Note post selection problem comes from the fact that the disorder is not quench anymore.
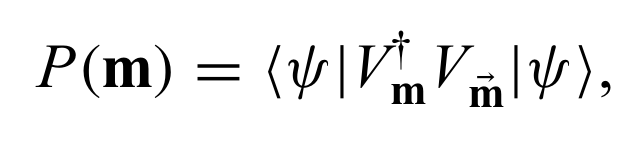
Boundary conditions:
Cones from contraction of layers or with a initial state. With that, with two copy of layers we have normally,
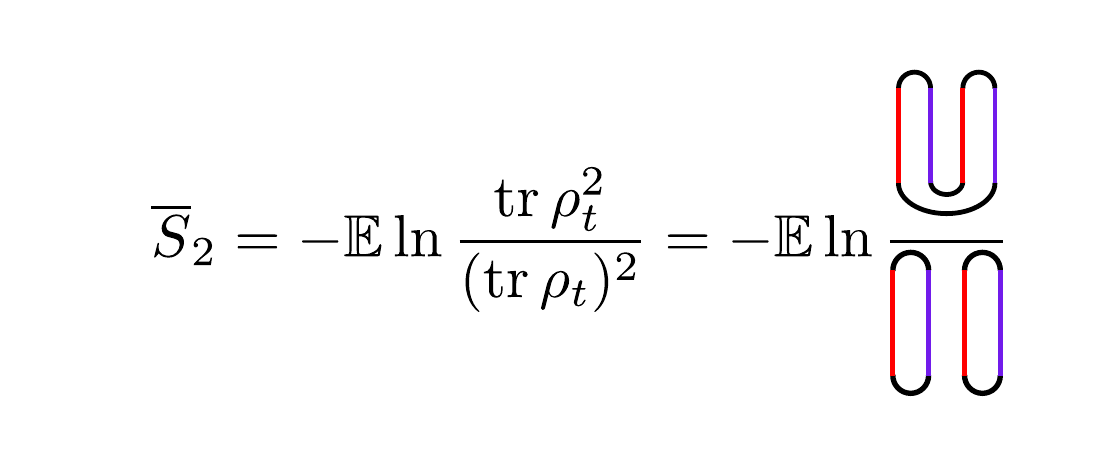
where,
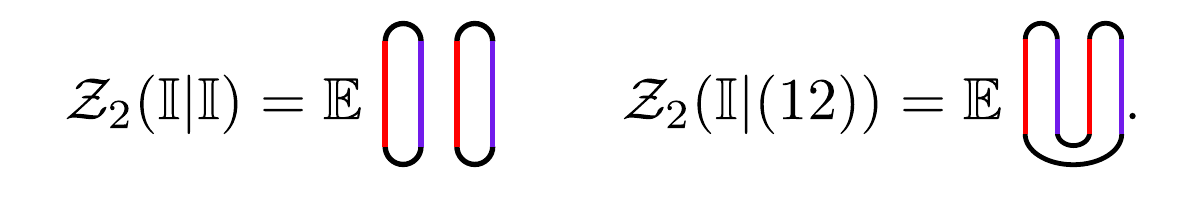
Boundary conditions:
For many layers for the free problem,
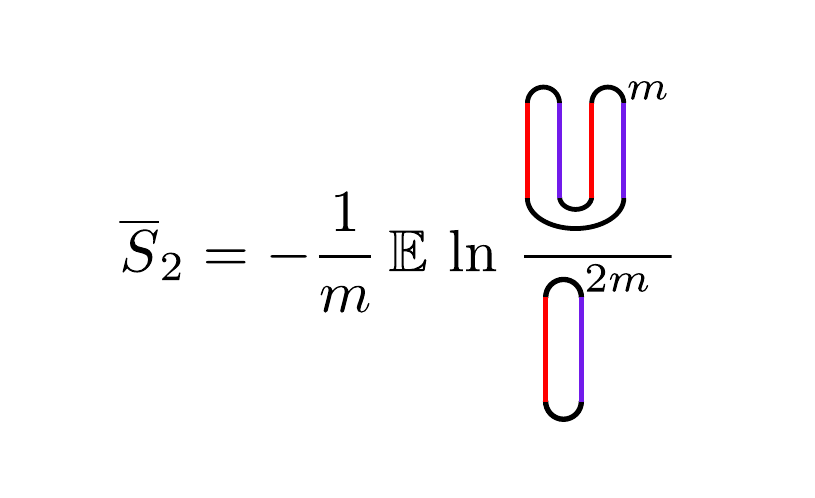
For MPT we have
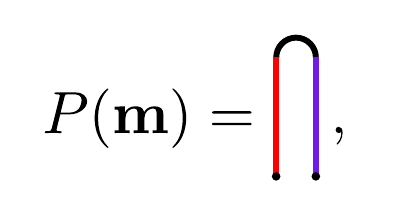
So,
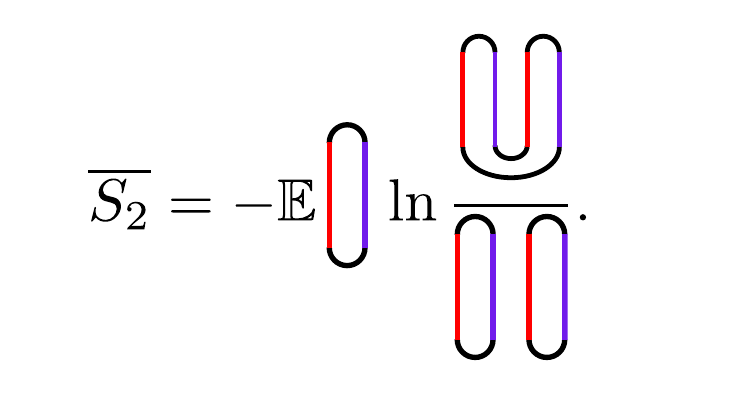
Motivating a Landau Field Theory:
Remember the Q? Similar to that question is whats the simplest action one can write that has the correct replica symmetry?
We can represent permutations as,
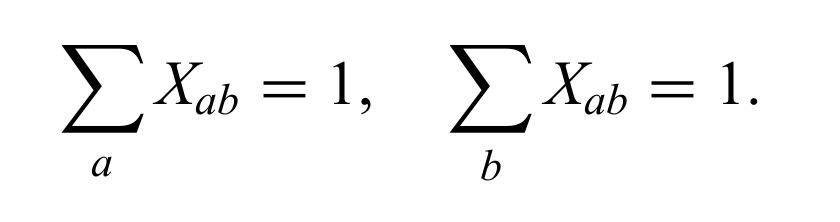
With such a constraint, one can write a simple Ising model, on that square lattice,
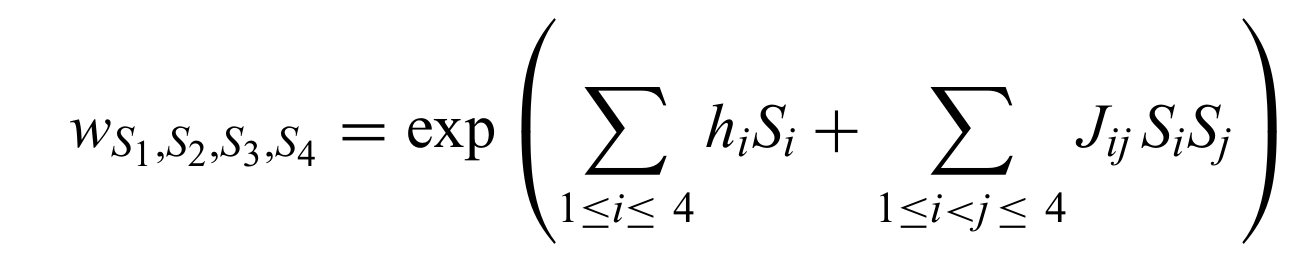
And write the partition function.
Motivating a Landau Field Theory:
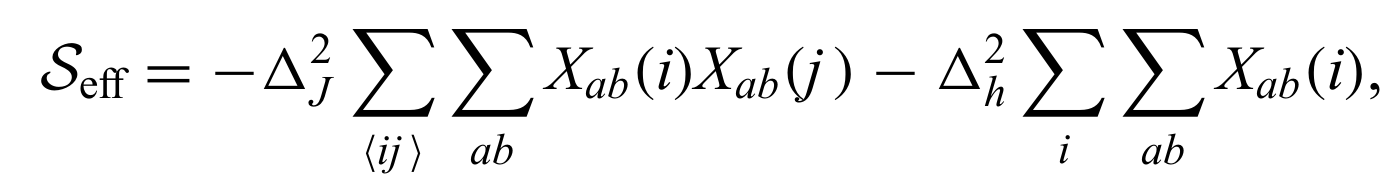
where
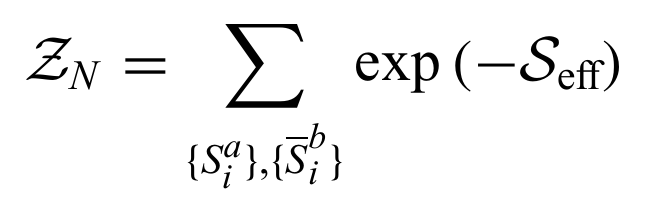
This with coarse graining and imposing some symmetry constraints gives, which is the simplest Lagrangian to survive the replica limit non-trivially,