An Invitation to Reinforcement Learning
To fix ideas: Formulation of a DTMC-SIS model




























































Nonlinear control: HJB and DP
Given
Goal:
Desing
to follow
s. t. optimize cost
Agent
Nonlinear control: HJB and DP
Bellman Optimality
Optimal Control Problem
s.t.
Data
- Modelling
Control
Spread Dynamics
Controller
- Bayesian Methods MCMC
- Expectation Maximization
- Maximum likelihood
- Deterministic: ODE, FD, FDD, PDE
- Stochastic: SDEs
- Pontryagin
- Dynamic Programming

Data
- Modelling
Control
Nonlinear control: Example
To fix ideas:
- TYLCV Disease
- is spread by the insect whitefly (Bemisia tabaci)
-
How to Manage TYLCV?



-
Replanting infected plants suffers random fluctuations due to is leading identification because a yellow plant is not necessarily infected.
- The protocol to manage infected plants suggests replanting neighbors. Then naturally, a farmer could randomly replant a healthy plant instead of a latent one.
- Thus strategies like fumigation with insecticide suffer random fluctuationsin their efficiency.
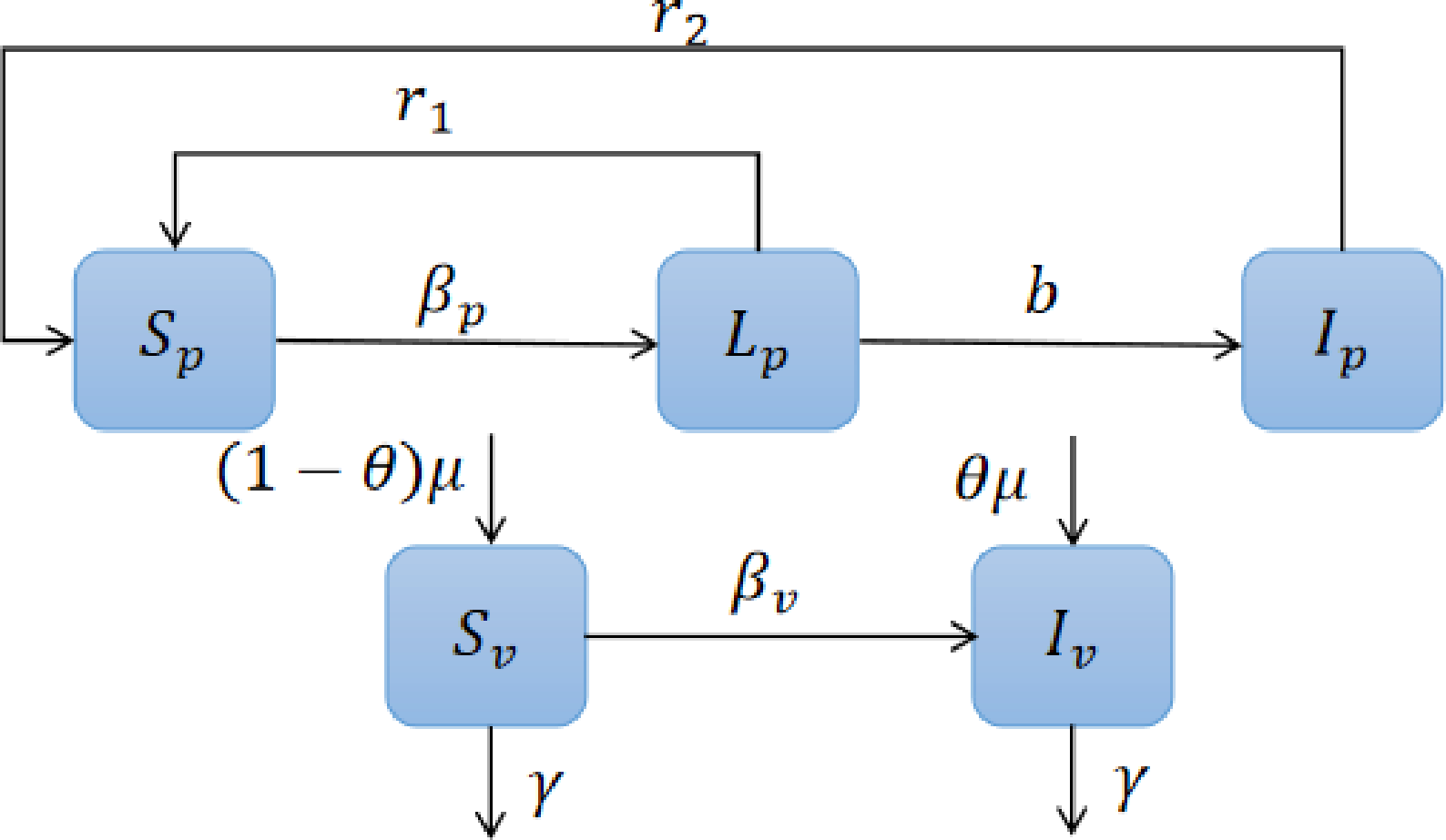
Controls
- Replanting
- Fumigation
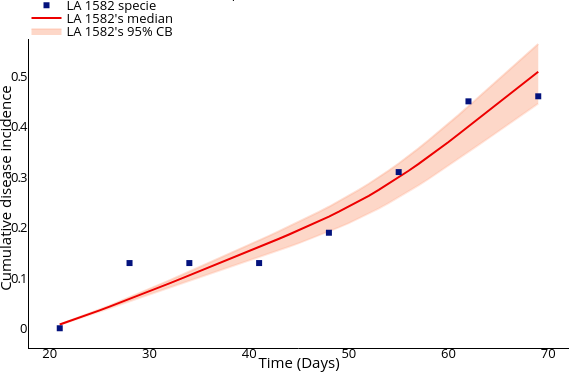
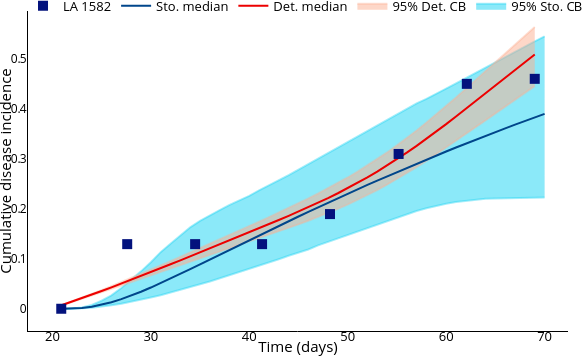
Performing parameter calibration using MCMC (Markov Chain Monte Carlo).
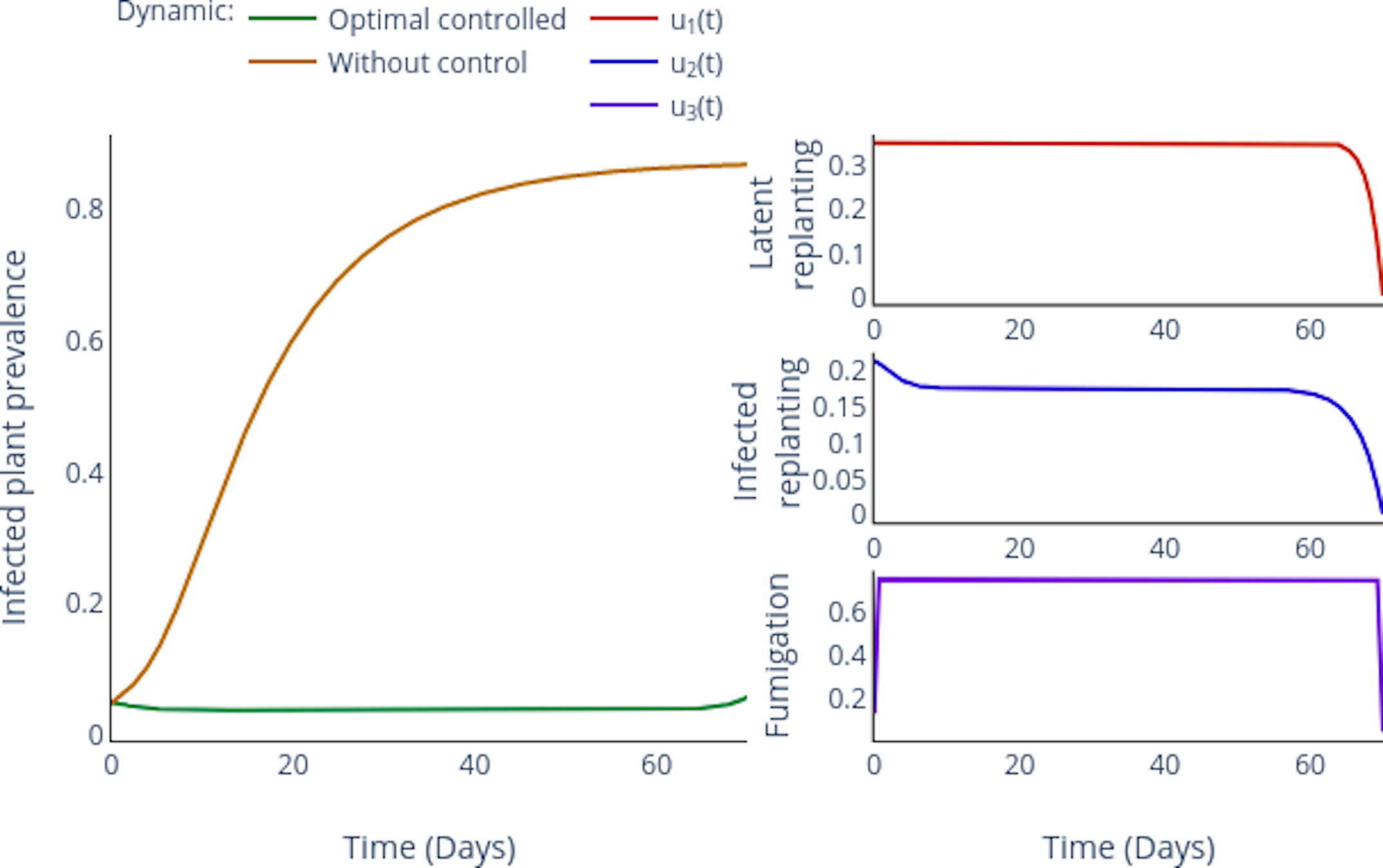
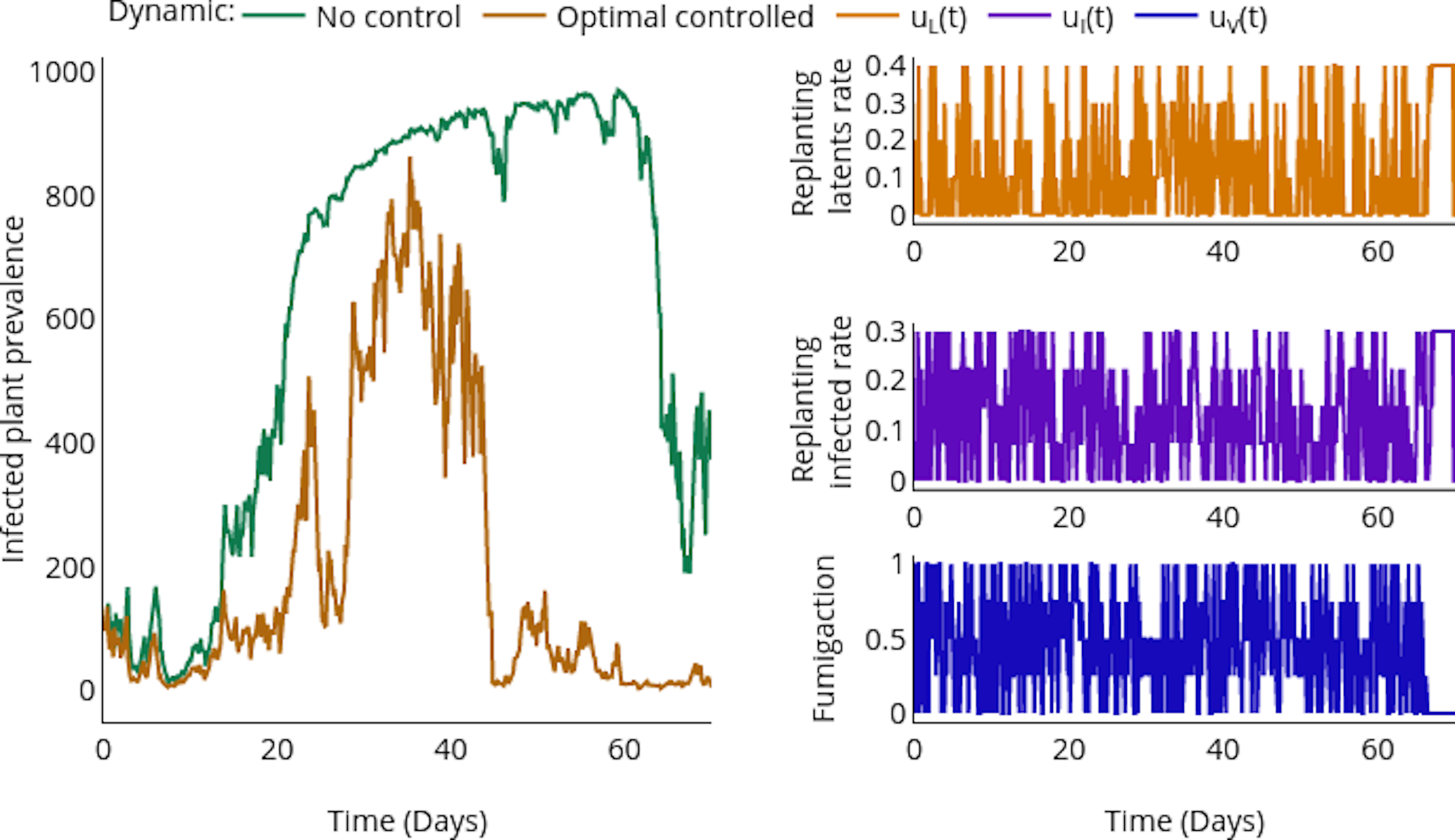
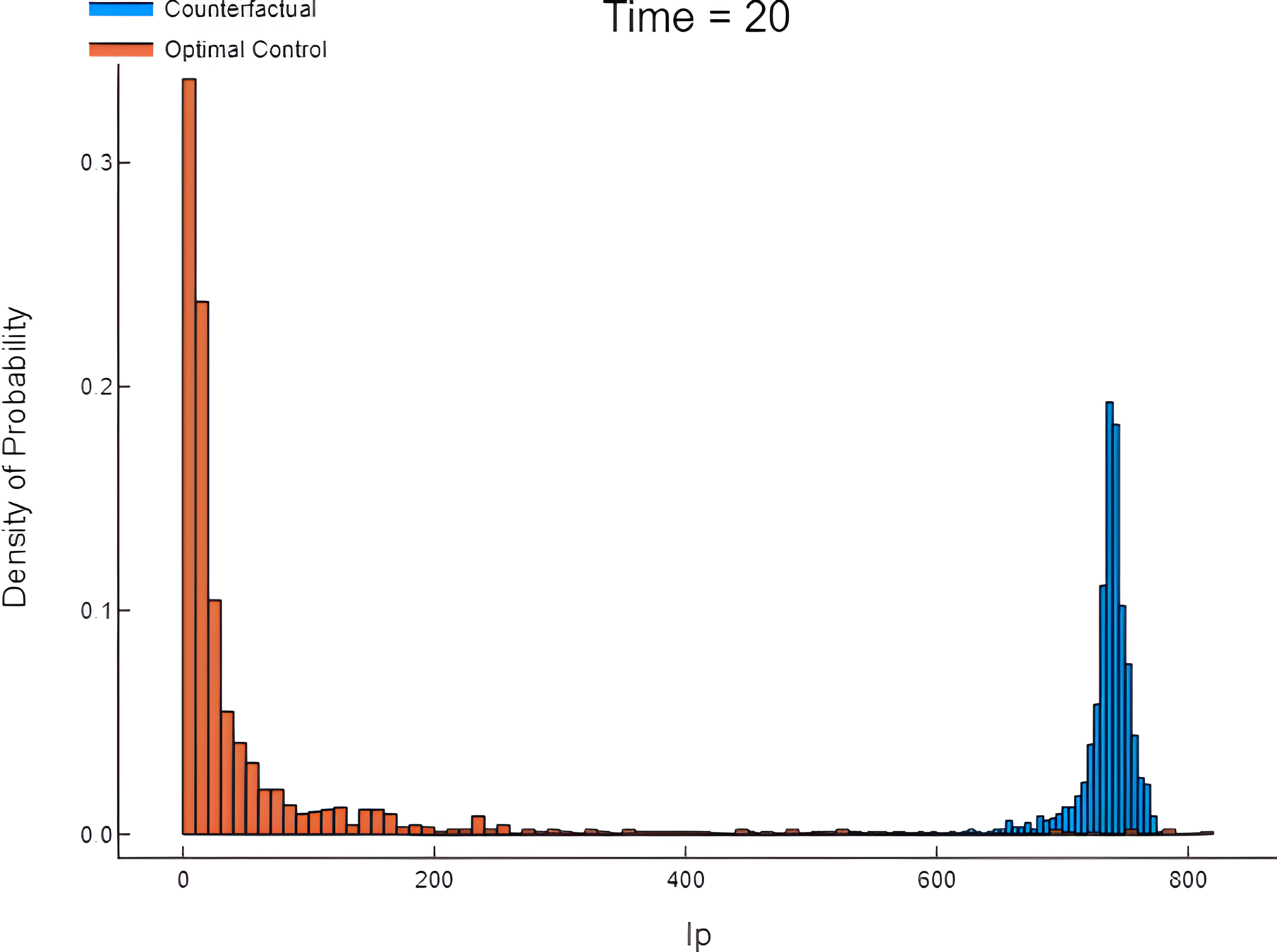
Simulation: Counterfactual vs Controlled.
Spread Dynamics
Controller
SDEs, CTMC, Sto-Per
Data
Sto-Modelling
Control

Stochastic extension
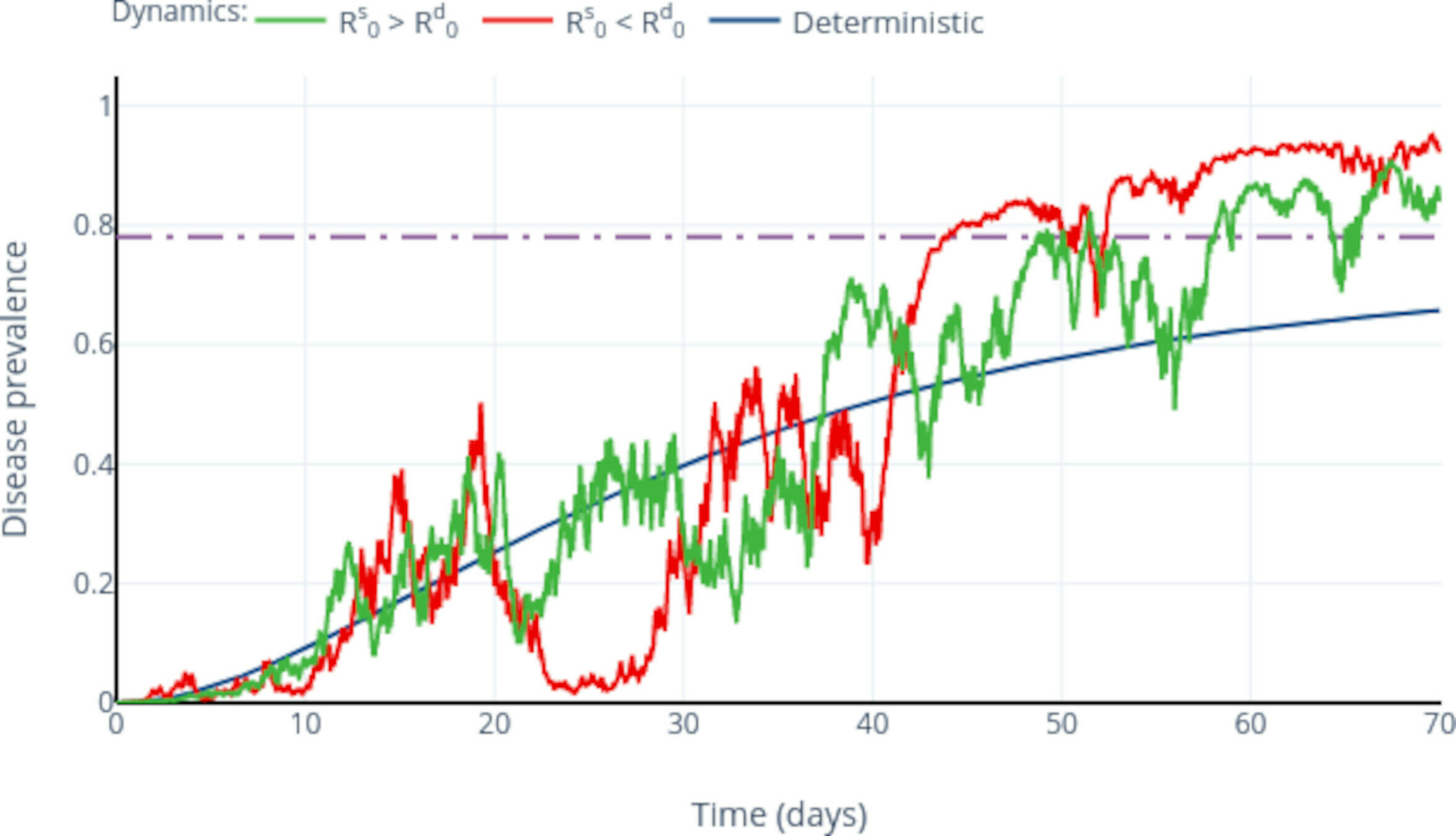
Enhancing parameter calibration through noise
OPC:
Value Function
HJB
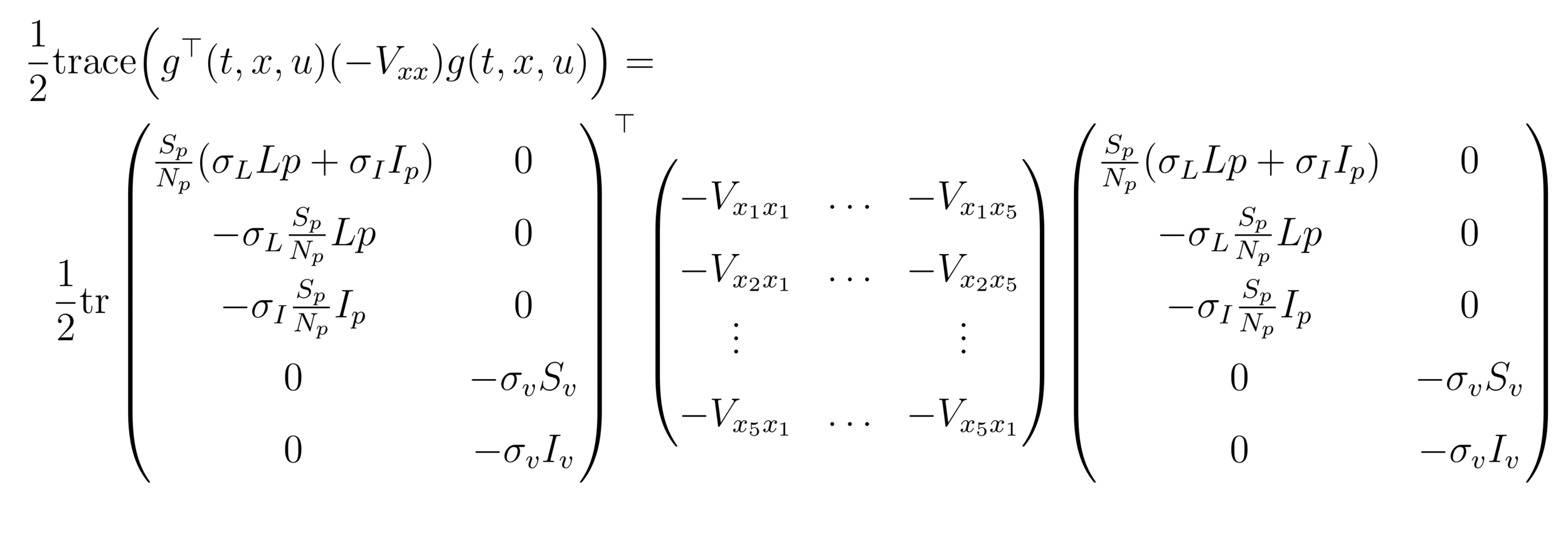
HJB (Dynamic Programming)- Course of dimensionality
HJB(Neuro-Dynamic Programming)

Abstract dynamic programming.
Athena Scientific, Belmont, MA, 2013. viii+248 pp.
ISBN:978-1-886529-42-7
ISBN:1-886529-42-6

Rollout, policy iteration, and distributed reinforcement learning.
Revised and updated second printing
Athena Sci. Optim. Comput. Ser.
Athena Scientific, Belmont, MA, [2020], ©2020. xiii+483 pp.
ISBN:978-1-886529-07-6
Reinforcement learning and optimal control
Athena Sci. Optim. Comput. Ser.
Athena Scientific, Belmont, MA, 2019, xiv+373 pp.
ISBN: 978-1-886529-39-7




Agent
Agent
action
state
reward
Discounted return
Total return

Modeling a traffic light warning system for acute respiratory infections as an optimal control problem
Saul Diaz Infante Velasco
Adrian Acuña Zegarra
Jorge Velasco Hernandez
sauldiazinfante@gmail.com
Introduction
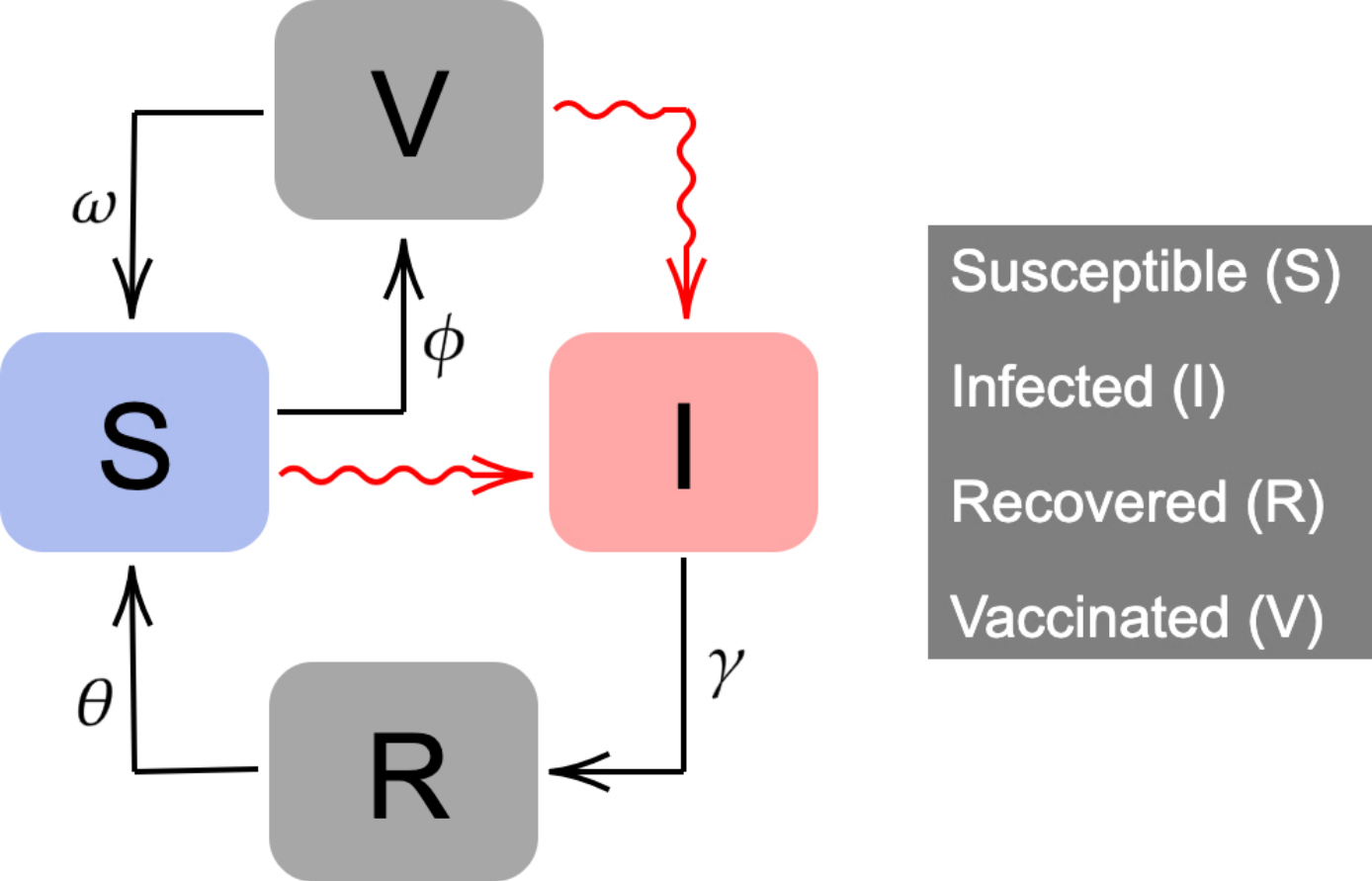
We propose an extension of the classic Kermack-McKendrick mathematical model. 𝑁(𝑡) is constant and is split into four compartments:
- susceptible (𝑆(𝑡)),
- infected (𝐼(𝑡)),
- recovered (𝑅(𝑡)),
- and vaccinated (𝑉 (𝑡)).
Susceptible individuals can become infected when interacting with an infectious individual. After a period of time (1∕𝛾), infected people recover. Recovered people lose their natural immunity after a period of time 1∕𝜃.
Risk index
Another closely related index that has been used to monitor and evaluate the development of ARI is the event gathering risk, developed by Chande (2020).
Chande, A., Lee, S., Harris, M. et al. Real-time, interactive website for US-county-level COVID-19 event risk assessment. at Hum Behav, 1313–1319 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41562-020-01000-9

# MODEL FORMULATION
Risk index
gives the probability of finding at time t an infected person in a group of k individuals.
# REPRODUCTIVE NUMBER
Normalization
Invariance
Basic Reproductive number
FDE
Effective reproduction number
# Light Traffic Policies and Optimal Control
- A decision-maker can apply a strategy from a finite set of actions.
- The set of actions implies a particular effect accordingly to the light semaphore.
- We describe this effect by modulating the transmission rate and size of gathering :
- A decision-maker can apply a strategy from a finite set of actions.
- The set of actions implies a particular effect accordingly to the light semaphore.
- We describe this effect by modulating the transmission rate and size of gathering.
- The decision maker only chooses the strategy from a finite set of actions--as mentioned above-- and according to the light traffic protocol. Thus, the controller decides which color from the plausible light-traffic actions for the next period.
- The corresponding authorities periodically meet every few weeks and make a decision.
- The decision taken minimizes the functional J subject to the mentioned dynamics.
Hypothesis
(OCP) Decide in each stage (a week), the light color that minimize functional cost J
subject to:
Counterfactual vs controlled dynamics
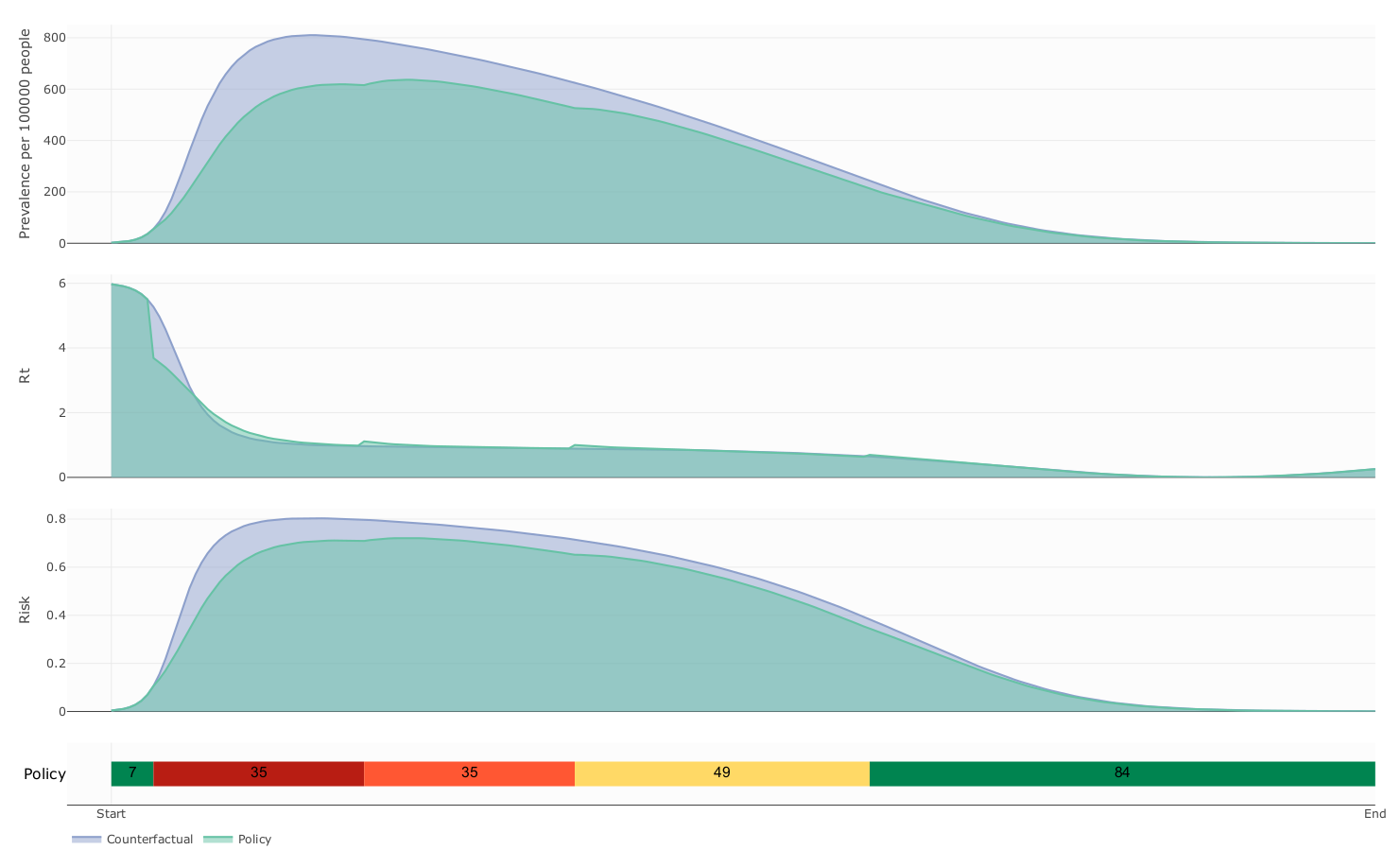
Counterfactual vs controlled dynamics
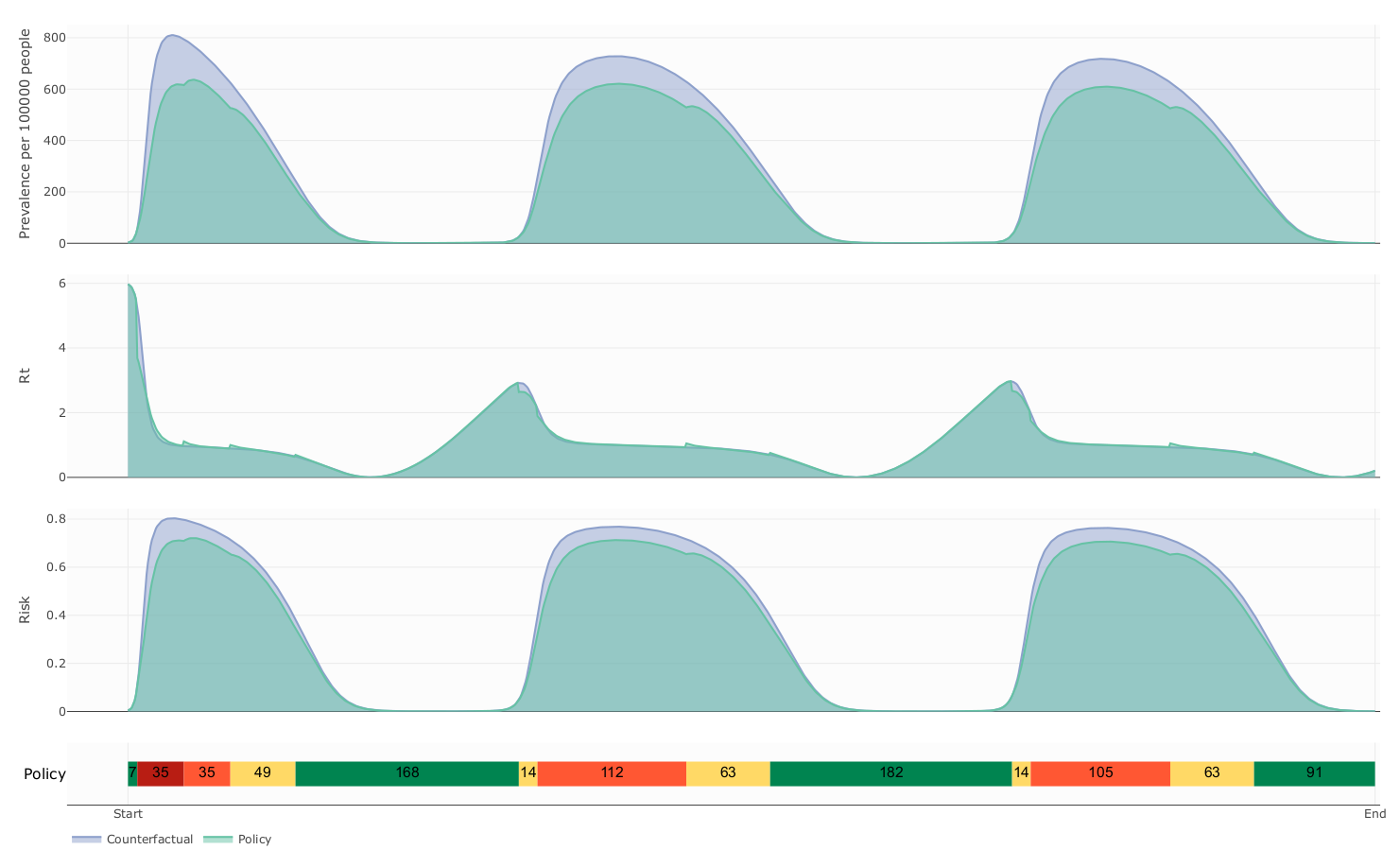
Counterfactual vs controlled dynamics
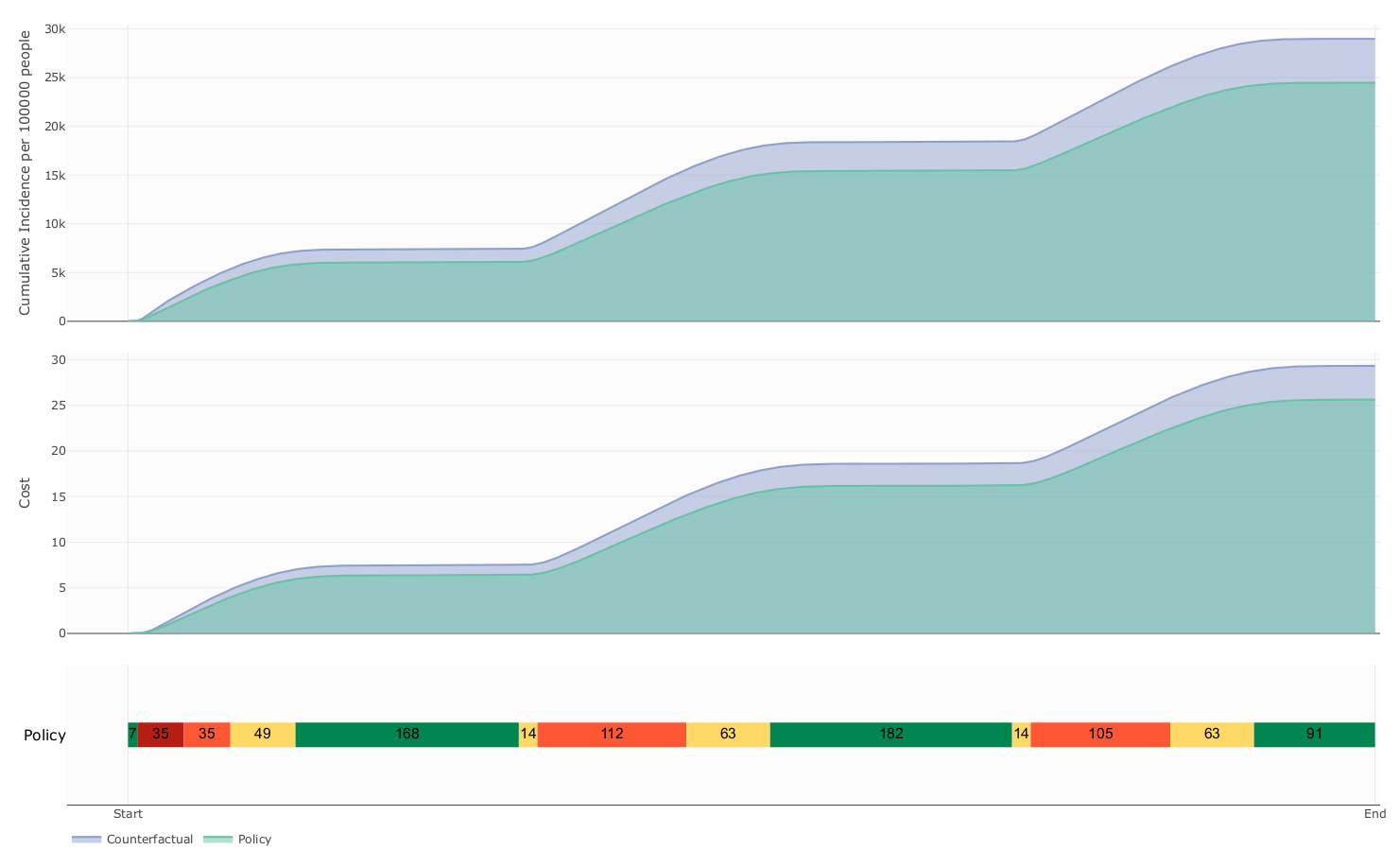
The influence of mobility restriction expenses over prevalence and cost
Expenses
due to mobility restrictions
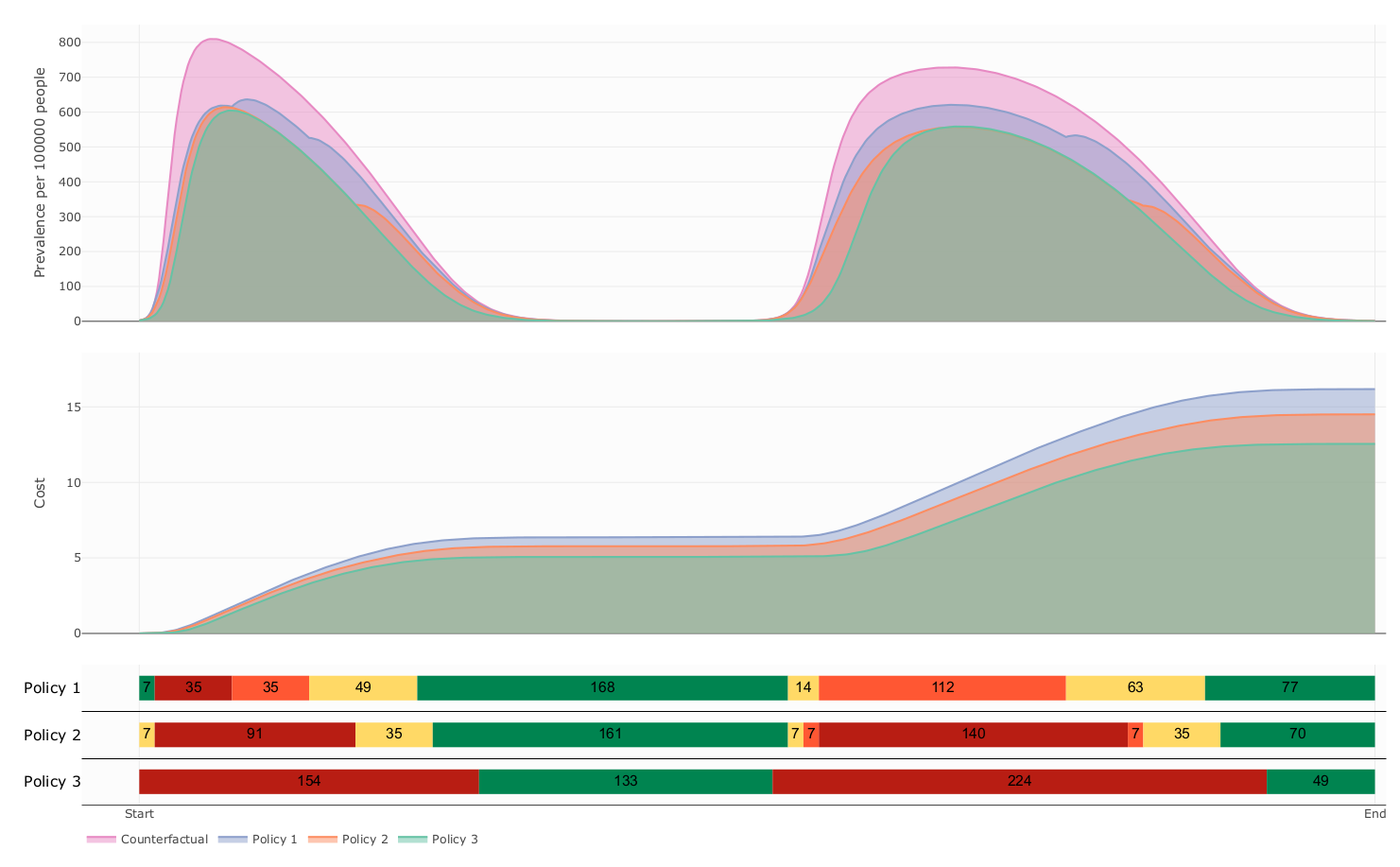
The influence of decision period span over prevalence and cost
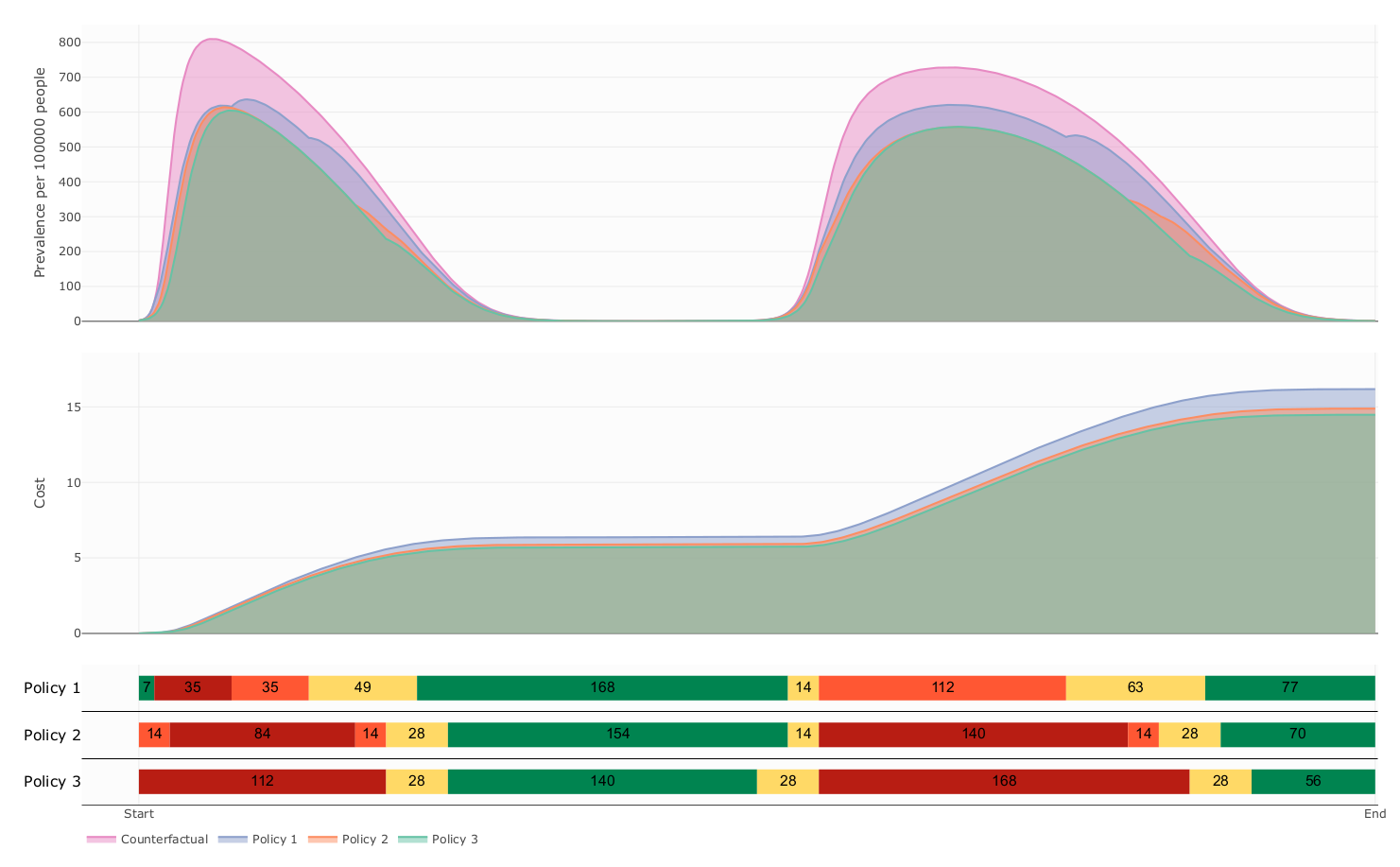
- Our model suggest that this kind of Policies follows a delicate balanced between health benefit and economic cost
Perspectives
- Uncertainty quantification
- Partial information
- Games
References
- Chande, A., Lee, S., Harris, M. et al. Real-time, interactive website for US-county-level COVID-19 event risk assessment. Nat Hum Behav 4, 1313–1319 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41562-020-01000-9
- Chan, H.F., Skali, A., Savage, D.A. et al. Risk attitudes and human mobility during the COVID-19 pandemic. Sci Rep 10, 19931 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-76763-2
- P. van den Driessche, James Watmough, Reproduction numbers and sub-threshold endemic equilibria for compartmental models of disease transmission, Mathematical Biosciences, Volume 180, Issues 1–2, 2002,Pages 29-48,ISSN 0025-5564, https://doi.org/10.1016/S0025-5564(02)00108-6
- Allen, L.J.S. (2008). An Introduction to Stochastic Epidemic Models. In: Brauer, F., van den Driessche, P., Wu, J. (eds) Mathematical Epidemiology. Lecture Notes in Mathematics, vol 1945. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-78911-6_3
Gracias
- Salcedo-Varela, G. & Diaz-Infante, S. Threshold behaviour of a stochastic vector plant model for Tomato Yellow Curl Leaves disease: a study based on mathematical analysis and simulation. Int J Comput Math 1–0 (2022) doi:10.1080/00207160.2022.2152680.
- Salcedo‐Varela, G. A., Peñuñuri, F., González‐Sánchez, D. & Díaz‐Infante, S. Synchronizing lockdown and vaccination policies for COVID‐19: An optimal control approach based on piecewise constant strategies. Optim. Control Appl. Methods (2023) doi:10.1002/oca.3032.
- Diaz-Infante, S., Gonzalez-Sanchez, D. & Salcedo-Varela, G. Handbook of Visual, Experimental and Computational Mathematics, Bridges through Data. 1–19 (2023) doi:10.1007/978-3-030-93954-0_37-1.
https://slides.com/sauldiazinfantevelasco/code-33ee77/fullscreen

