How the coagulation system works
Oct 22: Warfarin, heparins, LMWH, heparinoids, direct thrombin inhibitors
Oct 29: How the coagulation system works
Nov 5: Anti-platelet agents
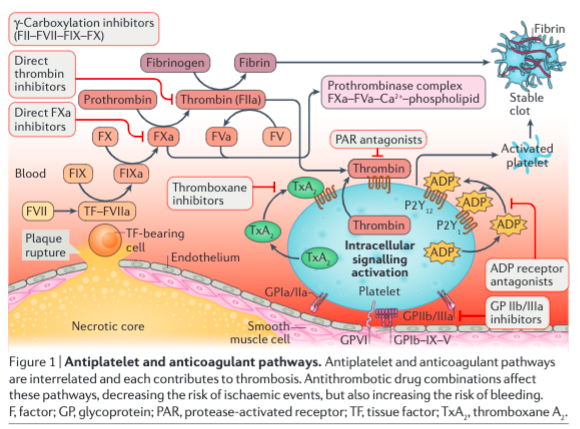
Bhatt, D.(2018). Advances in atherosclerosis, atrial fibrillation, and valvular disease. Nature Reviews Cardiology 15(2), 71-72. https://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nrcardio.2017.212
Platelets
Hemostasis
Objectives
- The mechanism of platelet aggregation and propagation
- Understanding the intrinsic pathway
- Understanding the extrinsic pathway
- Understanding the common pathway
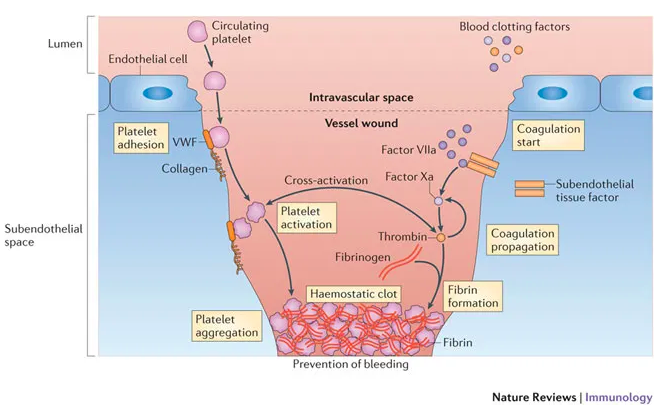
Engelmann, B., Massberg, S.(2013). Thrombosis as an intravascular effector of innate immunityNature Reviews Immunology 13(1), 34-45. https://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nri3345
The Platelet Plug
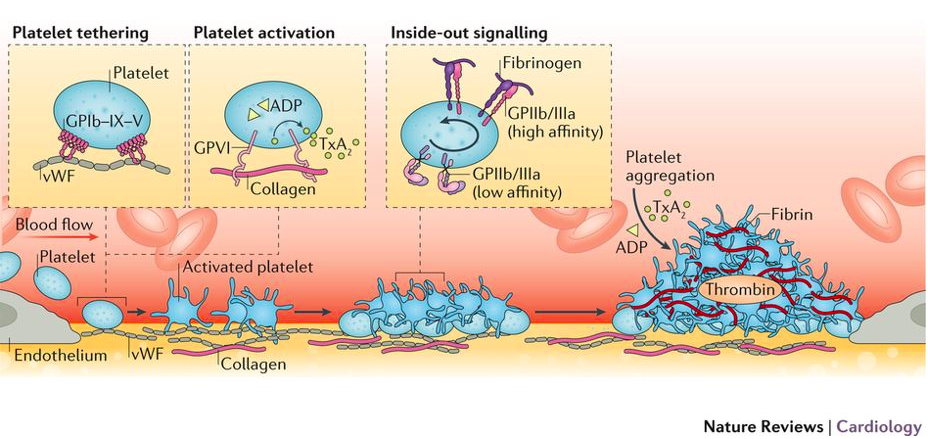
McFadyen, J., Schaff, M., Peter, K.(2018). Current and future antiplatelet therapies: emphasis on preserving haemostasisNature Reviews Cardiology 15(3), 181-191. https://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nrcardio.2017.206
Platelet Adhesion
- Pseudopod formation
- Binding to surface receptors:
- GPIb/IX/V complex --> VWF
- GPIa/IIa and VIa complex --> collagen
Platelet aggregation
Mediated by Receptor GPIIb/IIIa
- In active platelets --> binds fibrinogen
- Interacts with VWF --> platelet "spread" and retraction
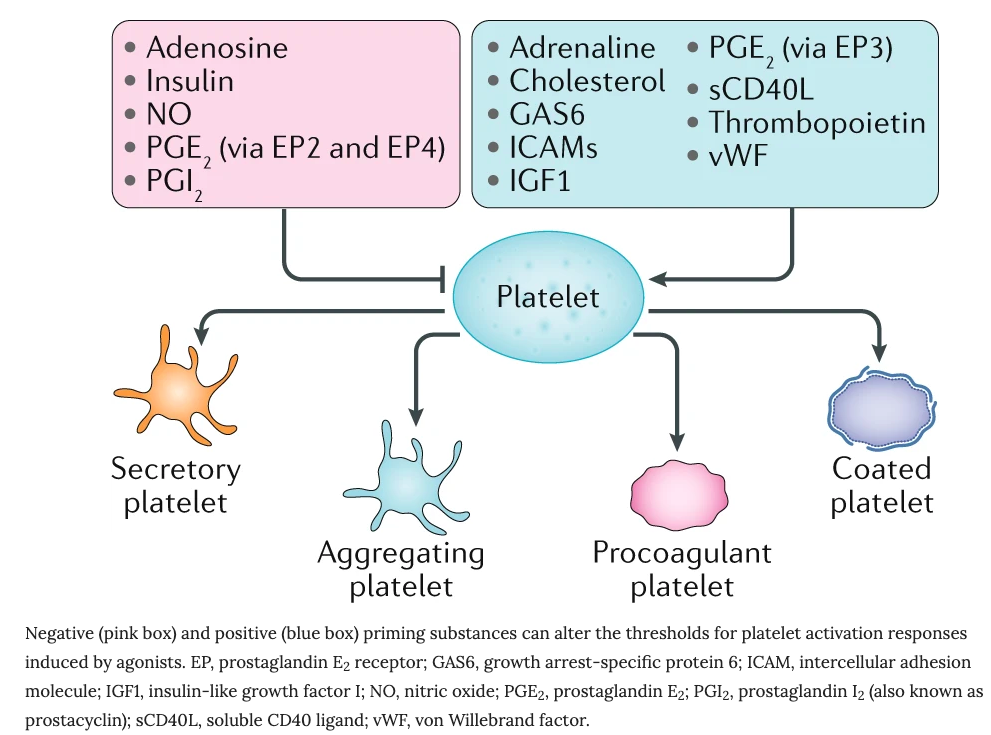
Meijden, P., Heemskerk, J.(2018). Platelet biology and functions: new concepts and clinical perspectivesNature Reviews Cardiology 16(3), 1. https://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41569-018-0110-0
Platelet activation
-
Strong activators
-
Thrombin *activates the core of the platelets*
-
Activated by:
-
PAR-1(Receptor) [Vorapaxar (antagonist)]
-
PAR-4 (Receptor)
-
-
-
Collagen *bear integrins e.g. GPIa/IIa and GPVIa that interact with platelets*
-
-
Weak activators:
-
ADP *acts on loosely packed platelets*
-
Binds GPcR:
-
P2Y1: Ca mobilization, platelet shape change, reversible aggregation
-
P2Y12: Platelet secretion and stable aggregation e.g. [Thienopyridine (antagonist)]
-
-
Platelet aggregation --> more ADP release --> more aggregation
-
-
Epinephrine
-
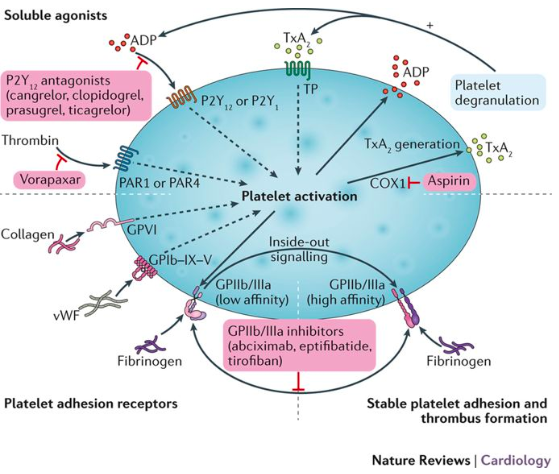
McFadyen, J., Schaff, M., Peter, K.(2018). Current and future antiplatelet therapies: emphasis on preserving haemostasisNature Reviews Cardiology 15(3), 181-191. https://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nrcardio.2017.206
Platelet secretion
-
Alpha Granules: VWF, P-selectin, platelet factor 4
- Repair of smooth muscle cells (/mediate atherosclerosis): PDGF
- Fibrinogen
- Re-inforce + stabilize clot: Fibronectin, thrombospondin
-
Dense Granules:
- Recruit more platelets: ADP, serotonin
- ATP, Ca++, histamine
- Vasoconstriction and platelet aggregation: Thromboxane A2: prostaglandin
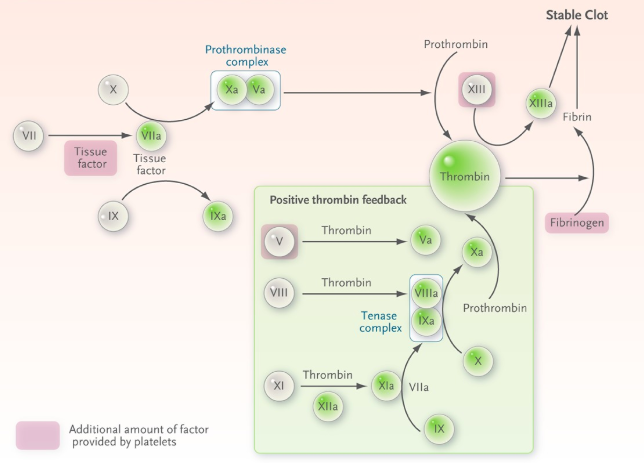
Borissoff, J.I., Spronk, H.M. and ten Cate, H., 2011. The hemostatic system as a modulator of atherosclerosis. New England Journal of Medicine, 364(18), pp.1746-1760.
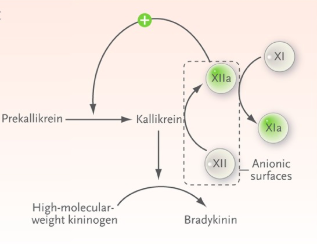
Clot propagation
CLOTTING CASCADE
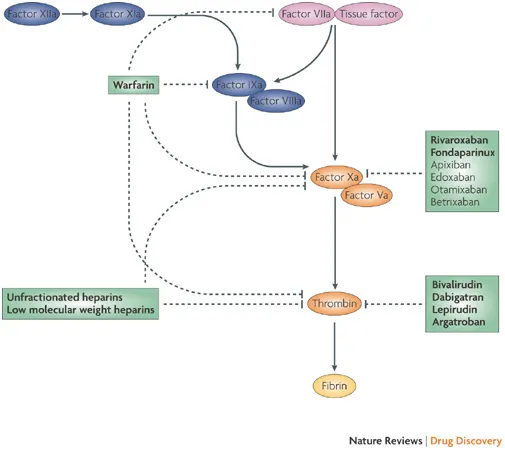
Melnikova, I.(2009). The anticoagulants marketNature Reviews Drug Discovery 8(5), 353-353. https://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nrd2851
Multicomponent complexes
- Extrinsic X-ase (VIIa + TF + X): X-->Xa + IX-->IXa
- Intrinsic X-ase (IXa + VIIIa + X): X--> Xa
- Prothombinase (Xa+Va+ prothrombin)
- Protein C anticoagulant complex: IIa+ thrombomodulin + protein C
Common Pathway
FACTOR X
PROTHROMBIN --> THROMBIN
FIBRINOGEN --> FIBRIN
- Thrombin begets more thrombin:
- VIIa --> thrombin formation --> activates XI
- Final plug:
- Activated platelets: initial plug + more multicompent complexes
- Endothelial cells: binding site for coagulation factors