Programmation fonctionnelle en Javascript
Un premier mot ...
Monade
Monade ???
Monade !!!

Sébastien Quenet
sebastien.quenet@abbeal.com
@Durnan
github.com/SebQuenet
Face nord, la version maths

Face sud, la version dev

Un premier pas...

Des fonctions ?
J'ai regardé mais je suis pas matheux, j'ai rien compris, et puis je sais très bien faire sans
Je fais du fonctionnel, j'ai utilisé lodash dans un projet de fin d'année
function Min (a,b:real) : real;
begin
if a < b then Min := a else Min := b;
end;
int max(int num1, int num2) {
/* local variable declaration */
int result;
if (num1 > num2)
result = num1;
else
result = num2;
return result;
}

J'ai fait Haskell 1ère langue, Ok ?
Pourquoi la programmation fonctionnelle ?
- (Vraiment) réutilisable
- (Ultra) testable
- Compréhensible (mais si !)
- Scalable
- A la mode !
Une fonction :
- Une valeur d'entrée
- Associée à une valeur de sortie
- Une valeur d'entrée n'a qu'une valeur de sortie
- Une valeur de sortie peut avoir plusieurs valeurs d'entrée
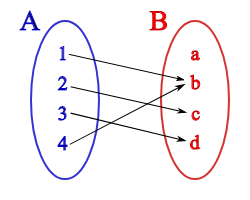
En JS ?
// readFile :: Filename -> Either String (Task Error String)
// httpPost :: String -> String -> Task Error JSON
// upload :: String -> Either String (Task Error JSON)
const upload = pipe(
readFile,
map(chain(httpPost('/uploads'))
), );
upload('myFile.txt');
const studentList = [{
ssn: '14217579245397',
forename: 'Haskell',
lastName: 'Curry',
girlfriendsList: ['Anna Miller', 'Joan Bowman', 'Emilia Clarke'],
}, /*...*/];
const findBySsnAndDisplayStudent = ssn => cssSelector => pipe(
lift(cleanInput),
join(checkLengthSsn),
tap(logIfDebug('Input was valid')),
join(findStudentBySsn(ssn)),
tap(logIfDebug('Record fetched successfully!')),
map(props(['ssn', 'firstname', 'lastname'])),
map(toCsv),
tap(logIfDebug('Student info converted to CSV')),
map(convertToHtmlTableAndAppendTo(cssSelector)),
tap(log('Student added to HTML page'))
);
const injectStudentInto = findBySsnAndDisplayStudent('14217579245397');
const displayStudentInfo = injectStudentInto('#student-info');
displayStudentInfo(studentList);
// Or findBySSnAndDisplayStudent('14217579245397')('#studentInfo')(studentList)Concepts

Objet
- Héritage
- Polymorphisme
- Encapsulation
Fonctionnel
- Pureté
- Immutabilité
- Citoyennes de 1ère classe
Pureté
- Transparence référentielle
- Pas d'effet de bord
var x = 5;
function getY() {
var y = x + 5;
return y;
}console.log('Hello world');const timeStamp = +new Date();const myDiv = document.querySelector('#myDiv');const prom = fetch('flowers.jpg');class Duck {
constructor() {
this.color = 'yellow';
}
blueify() {
this.color = 'blue';
}
getColor() {
return this.color;
}
}
const myDuck = new Duck();
console.log(myDuck.getColor());
myDuck.blueify();
console.log(myDuck.getColor());

Immutabilité
- Les données ne changent pas
- Toute fonction émet un nouvel objet
let i = 17;
i++;const incByOne = i => i+1;
const j = incByOne(17);Citoyennes de 1ère classe
- Un objet comme un autre
- Fonctions d'ordre supérieur
const add = (a, b) => a+b;
const mul = (a, b) => a*b;
const calcul = (fn, a, b) => fn(a,b);
calcul(add, 3,4);
calcul(mul, 5,6);
const getAdd = () => (a,b) => a+b;
getAdd()(3,4)const incByOne = (i) => i+1;
const ajouteUn = incByOne;
ajouteUn(4);Composition
- La composition de fonctions permet d'appliquer le résultat d'une fonction à une autre fonction
- Une composition de fonctions retourne une fonction.
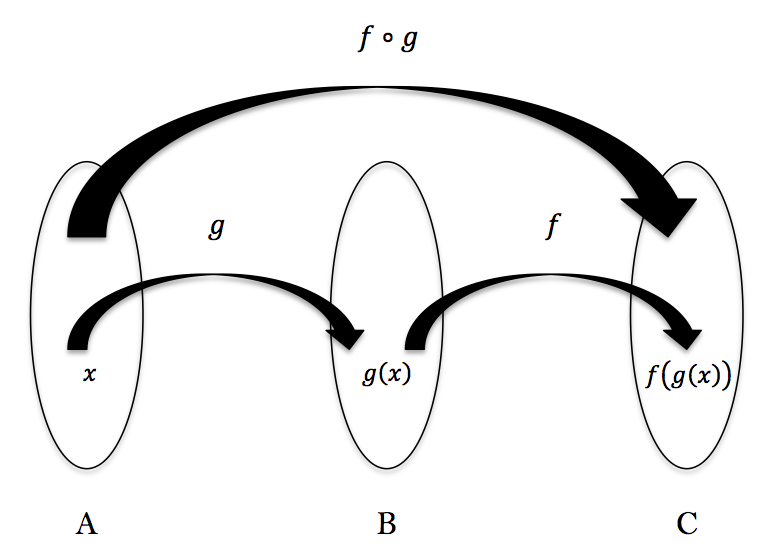
Composition
- Le paramètre passé à la composition est exécuté à partir de la dernière fonction.
- Le résultat de la dernière fonction est passé en entrée du résultat de l'avant dernière fonction ...
// Approche simplifiée de compose avec 2 paramètres
const compose = (f,g) => x => f(g(x));
const lowerCase = s => s.toLowerCase();
const addQuestionMark = s => s + ' ?';
const questionFactory = compose(
lowerCase,
addQuestionMark,
);
const str = questionFactory('DES QUESTIONS')
console.log(str);
// Cas général, implémenté par Ramda, Lodash/fp,...
// Compose prend n fonctions, pas seulement deux.
compose(
console.log,
lowerCase,
addQuestionMark,
)('DES QUESTIONS');Compose vs flow / pipe
const sortedWithSquares = compose(
sortByValue,
flatten,
valueWithSquare
);
const sortedWithSquares = pipe(
valueWithSquare,
flatten,
sortByValue
);
Limites de la composition
- Une fonction renvoie un truc unique
- Une fonction dans la chaine ne peut prendre qu'un argument
- Plein de fonctions prennent plusieurs paramètres
Applications partielles
const additionFactory = x => y => x + y;
const add3To = additionFactory(3);
// => fn
const result = add3To(4);
// => 7
const middleware = store => nextDispatch => action => {
nextDispatch(action);
}
Curryfication
const addition = (x,y) => x+y;
addition(3,4);
// => 7
// Notre JS à nous
addition(3);
// => NaN
// Dans la quatrième dimension
const add3To = addition(3);
// => function
add3To(4)
// => 7
const add5To = addition(5);
add5To(7);
// => 12Notation Hindley-Milner
Signatures par types
toLowerCase :: String -> String
curriedAdd :: Integer -> Integer -> Integer
reverse :: [a] -> [a]
head :: [a] -> a
map :: (a -> b) -> [a] -> [b]
reduce :: (b -> a -> b) -> b -> [a] -> bStyles d'écriture

Fluent
- jQuery
- Lodash
- Rx
- Async
- Promesses
Point free
- Lodash FP
- Ramda
Fluent
On utilise des méthodes qui retournent une nouvelle instance de l'objet passé en entrée auquel a été appliqué une fonction
import _ from lodash;
const myList =
_.map()
.reduce()
.filter()import _ from lodash;
const myList =
_.map()
.reduce()
.filter()Point free
import map from 'lodash/fp/map';
import flatten from 'lodash/fp/flatten';
import sortBy from 'lodash/fp/sortBy';
import compose from 'lodash/fp/compose';
const sortByValue = sortBy(x => x);
const valueWithSquare = map(x => [x, x*x]);
const sortedWithSquares = compose(
sortByValue,
flatten,
valueWithSquare
);
sortedWithSquares([1, 2, 3]);
// 1, 1, 2, 3, 4, 9Quelques mots de sagesse ...
There are only two hard things in computer science: cache invalidation
and naming things
-- Phil Karlton

Contrôle de flux

Identité
Retourner une copie de notre structure de départ
// identity :: (a) -> a
const identity = x => x;Tap
Faire quelque chose sans conséquence directe sur un flux de compositions
- Execute la fonction passée en argument
- Retourne le paramètre de la chaine de composition
import R from 'ramda';
// tap :: (a -> *) -> a -> a
const genericLogger = (
outputFn,
processName,
level,
message) =>
outputFn(`${processName} [${level}] ${message}`);
const debugConsoleLogger = R.curry(
genericLogger(console.log, 'MyProg', 'DEBUG')
);
const tLog = R.tap(debugConsoleLogger);
R.compose(
executeLastFn,
tLog,
executeFirstFn,
);Alternative
Exécuter une seconde fonction si une première retourne false
const alt = curry(
(func1, func2, val) => func1(val) || func2(val)
);
// Cherche une personne ou
// La crée si pas trouvée,
// Et affiche
const findOrCreate = compose(
console.log,
alt(findInDb, createNew)
);
findOrCreate('Jean de la Fontaine');Séquence
Itère sur un ensemble de fonctions
Passe le même argument
à chaque
const seq = function( /* arguments :
list of n functions */) {
const funcs = Array.prototype.slice.call(arguments);
return function(val) {
funcs.forEach( fn => fn(val));
}
}
const findAndShow = compose(
seq(
append('#result-field'),
console.log,
),
findOrCreate
);
findAndShow('Jean de la Fontaine')Fork / Join
Passer la sortie d'une fonction A à deux fonctions B et C, qui a leur tour passeront leurs sorties réspectives en paramètre d'entrée d'une fonction D.
const fork =
(join, func1, func2) =>
(val) =>
join(func1(val), func2(val));
const computeAverageGrade = compose(
getLetterGrade,
fork(
divide,
sum,
length
)
);
computeAverageGrade([99, 80, 89]); //-> 'B'
Des dizaines d'autres ...
https://www.ramdajs.com/docs/
Structures fonctionnelles

Sortir protégé
Création d'un container autour des objets impurs avec lesquels on traite pour protéger notre monde fonctionnel.

.of
Interface "pointed"
Consacre une valeur comme restant elle même, protégée par un container, encapsulée.
class Container {
constructor(value) {
this._value = value;
}
// Container.of :: A -> Container(A)
static of(v){
return new Container(v);
};
toString() {
return 'Container (' + this._value + ')';
}
}
const myObj = new Date();
const protectedObject = Container.of(myObj);
const wrappedInt = Container.of(42);
const wrappedWrappedInt = Container.of(wrappedInt);
const square = x => x*x;
const wrappedSquare = Container.of(square);Agir sur notre container
Récupérer notre objet protégé, le manipuler, ...

.map

La gardienne entre l'objet et le monde du dehors
.map
class Container {
constructor(value) {
this._value = value;
}
// Container.of :: A -> Container(A)
static of(v){
return new Container(v);
};
// Container.map :: (A -> B) -> A -> B
map(f) {
return f(this._value);
};
toString() {
return 'Container (' + this._value + ')';
}
}
const add = R.curry( (x,y) => x + y );
const add4 = add(4);
const myValue = Container.of(42).map(add4)
// myValue = 46
const identity = x => x;
const spawnInitialValue = Container.of(42).map(identity);
// spawnInitialValue = 42Personne n'accède directement à notre valeur privée depuis l'extérieur
Nous y accédons en demandant (poliment) via map.
.map
class Container {
constructor(value) {
this._value = value;
}
// Container.of :: A -> Container(A)
static of(v){
return new Container(v);
};
// Container.map :: (A -> B) -> [A] -> [B]
map(f) {
return Container.of(f(this._value));
};
toString() {
return 'Container (' + this._value + ')';
}
}
const add = curry( (x,y) => x + y );
const add4 = add(4);
const myValue = Container
.of(42)
.map(add4)
.map(add4)
// myValue = Container(50);Et en allant un peu plus loin.
.map nous retourne une valeur elle-même containerisée
Welcome
Functor
- Un functor est un container qui implémente map.
- Le map de notre functor nous retourne un objet de même nature.
- Il laisse intact le functor de départ
- Array est un cas particulier de functor
- Il permet de gérer correctement l'immutabilité et la pureté de nos structures
Maybe
- Retourne quelque chose
- Ou rien
- Permet d'encapsuler null comme valeur sur laquelle faire des opérations
class Maybe {
constructor(value) { this._value = value }
static of(v) { return Maybe.just(v) }
map(f) { return Maybe.of(f(this._value)) }
static just(v) { return new Just(v) }
static nothing() { return new Nothing() }
static fromNullable(v) {
return v !== null ? Maybe.just(v) : Maybe.nothing();
}
isJust() { return false }
isNothing() { return false }
}
class Just extends Maybe {
isJust() { return true }
map(f) { return Maybe.fromNullable(f(this._value)) }
}
class Nothing extends Maybe {
isNothing() { return true }
map(f) { return this }
}
const v = Maybe.of(2).map(i=>i*2).map(i=>i*3);
const n = Maybe.of(null).map(i=>i*2).map(i=>i*3);Either
- Left et Right sont des enfants de la classe Either
- Retourne un résultat
- Ou une erreur
- Permet un try/catch fonctionnel
const Left = function(x) { this.__value = x }
Left.of = function(x) { return new Left(x) }
Left.prototype.map = function(f) { return this }
const Right = function(x) { this.__value = x };
Right.of = function(x) { return new Right(x) };
Right.prototype.map = function(f) {
return Right.of(f(this.__value))
}
const moment = require('moment');
const getAge = curry(function(now, user) {
const birthdate = moment(
user.birthdate,
'YYYY-MM-DD'
);
if (!birthdate.isValid())
return Left.of('Birth date could not be parsed');
return Right.of(now.diff(birthdate, 'years'));
});
getAge((moment(), { birthdate: '2005-12-12' }))
// Right(12)
getAge(moment(), { birthdate: 'July 4, 2001'});
// Left('Birth could not be parsed')
IO
- .from injecte une fonction
- Cette fonction représente une entrée ou une sortie
class IO {
constructor(effect) { this.effect = effect }
static of(a) { return new IO( () => a ) }
static from(fn) { return new IO(fn) }
map(fn) {
return new IO(() => fn(this.effect()));
}
run() { return this.effect() }
}
const read = (document, selector) => () =>
document.querySelector(selector).innerHTML;
const write = (document, selector) => (val) => {
document.querySelector(selector).innerHTML = val;
return val;
};
const readDom = R.curry(read, document);
const writeDom = R.curry(write, document);
// <div id="student-name">Haskell Curry</div>
const changeToStartCase = IO.from(
readDom('#student-name')
)
.map(toUpperCase)
.map(writeDom('#student-name'));Composition de functors
- Plusieurs éléments d'une composition peuvent vouloir gérer des effets de bords

Jusqu'ici ...
Tout va bien...
IO.of('Bonnie').map(concat(' and Clyde'));
//////////////////////
Maybe.of(1336).map(add(1));
//////////////////////
Either.of("C'est un rabbin un prêtre
et un imam qui rentrent dans un bar...")
.map(
concat(" Et le barman leur demande :
c'est une blague ?")
);
Ca se corse avec la composition...
const R = require('ramda');
const fs = require('fs');
const IO = function(f) { this.__effect = f; };
IO.of = function(x) { return new IO(function() { return x; }); };
IO.prototype.map = function(f) { return new IO(R.compose(f, this.__effect)); };
// readFile :: String -> IO String
const readFile = (filename) => new IO(() => fs.readFileSync(filename, 'utf-8'));
// print :: String -> IO String
const print = (x) => new IO(() => {
console.log(x);
return x;
});
// cat :: String -> IO (IO String)
const cat = R.compose(R.map(print), readFile);
cat('./package.json').__effect().__effect(); // Obligatoire pour faire notre cat !
Aplatir nos couches successives ...
IO.prototype.join = function() {
var thiz = this;
return new IO(function() {
return thiz.__effect().__effect();
});
};
Maybe.prototype.join = function() {
return this.isNothing() ?
Maybe.of(null) :
this.__value;
}.join
- Chaque type aura sa propre implémentation de .join()
- On croise aussi "flatmap" ou "chain" comme équivalents à join
class Container() {
// [...]
join() {
if(!(this._value instanceof Container)) {
return this;
}
return this._value.join();
}
// [...]
}.join
Implémentation
Welcome Monade !
- Une monade est un functor qui implémente la fonction join
- Une monade permet de gérer la composition de parties de code impures, tout en conservant l'ensemble pur.

Et après ?
- La balade n'est pas terminée : Applicative functors, Free monads, F-algebra...
- Explorer Ramda et Lodash/fp
- Jeter un oeil à Fantasyland et Folktale

Bibliographie
- Functional Programming in Javascript (Luis Atenacio, Manning)
- Conceptual Mathematics : A First introduction to categories (Lawvere & Schanuel, Cambridge Press)
- Professor Frisby's Mostly adequate guide to Functional Programming

Références
- http://ramdajs.com/
- https://github.com/lodash/lodash/wiki/FP-Guide
- http://folktale.origamitower.com/
- https://github.com/fantasyland
- http://elm-lang.org/

Merci, des questions ?


http://slides.com/sebquenet/deck#/