Integrating
Human and Machine Intelligence
for Enhanced Curriculum Design
Shayan Doroudi
Thesis Defense
April 11, 2019



UN Millennium Development Goals (2000-2015)
UN Sustainable Development Goals (2016-2030)
Personalized adaptive curriculum for all learners
Bloom, 1984: Students with individualized tutoring perform 2 standard deviations better.
1940
1920

1960
1980
2000
2020
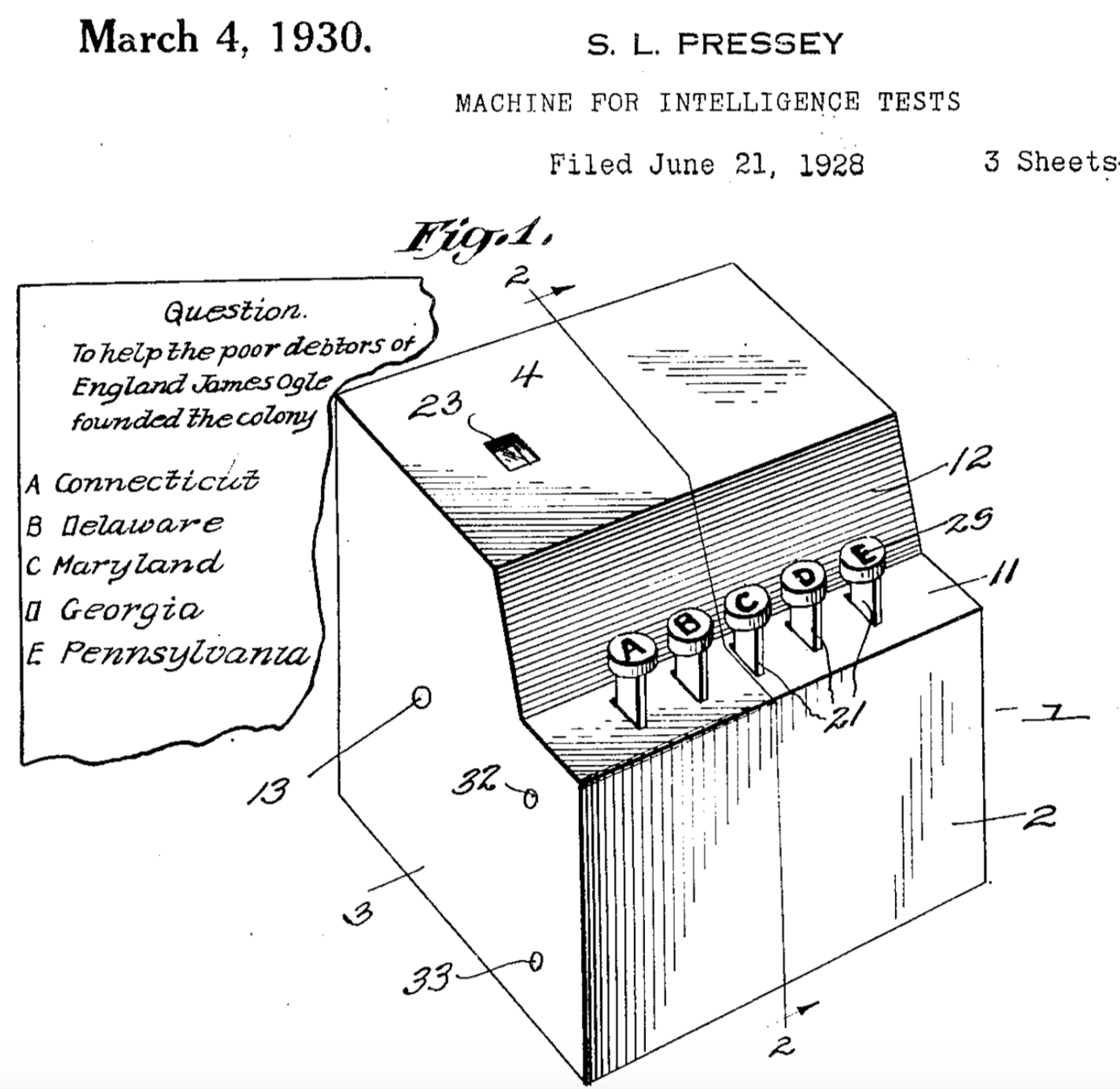
Teaching Machines
1940
1960
1980
2000
2020
1920



Computer-Assisted
Instruction
Photos from suppes-corpus.stanford.edu
1940
1960
1980
2000
2020
1920

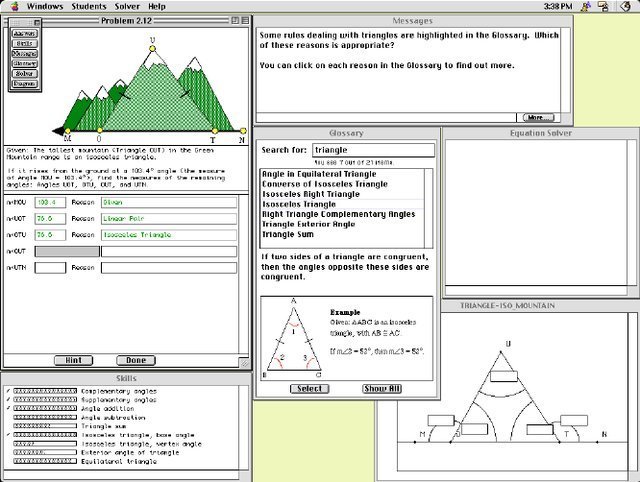

Intelligent Tutoring Systems

1940
1960
1980
2000
2020
1920



Machine
Learning

1940
1960
1980
2000
2020




1920
Two Approaches
1940
1960
1980
2000
2020




Theory-Driven
Can be used to develop successful ITSs with high quality content.
1920
Content development is costly (25+ hours for each instructional hour)
Limited form of adaptive instructional sequencing.
Two Approaches
1940
1960
1980
2000
2020
1920




Data-Driven
Two Approaches
Underconstrained
Cannot be used to create high quality content.
Can be used to automatically infer how to sequence instruction.
Combine human intelligence and machine intelligence for more impactful curriculum design
Thesis Statement
I demonstrate several techniques for impactful, cost-effective semi-automated curriculum design that combine machine learning, human computation, and principles from the learning sciences
- Using learner-generated work for content creation combined with machine learning for content curation.
- Finding ways to mitigate the bias-variance tradeoff in instructional sequencing.
Instructional Sequencing
Content Creation and Curation
Two Parts
Research Landscape
Properties of Student Models
Sequencing Instruction
Learner-Generated Content
Doroudi, Aleven, & Brunskill - L@S '17
Doroudi & Brunskill - LAK '19
Doroudi, Aleven, & Brunskill - Under Review
Doroudi et al. - EDM '15
Doroudi et al. - EDM '16
Doroudi, Thomas, and Brunskill - UAI '17
*Best Paper*
Doroudi & Brunskill - EDM '17
*Best Paper Nominee*
Doroudi et al. - CHI '16
Doroudi et al. - ICLS '18
Doroudi et al. - Under Preparation
Research Landscape
Properties of Student Models
Sequencing Instruction
Learner-Generated Content
Doroudi, Aleven, & Brunskill - L@S '17
Doroudi & Brunskill - LAK '19
Doroudi, Aleven, & Brunskill - Under Review
Doroudi et al. - EDM '15
Doroudi et al. - EDM '16
Doroudi, Thomas, and Brunskill - UAI '17
*Best Paper*
Doroudi & Brunskill - EDM '17
*Best Paper Nominee*
Doroudi et al. - CHI '16
Doroudi et al. - ICLS '18
Doroudi et al. - Under Preparation
My Thesis
Content Creation and Curation
Learnersourced Content Creation
- Learnersourcing: Using work done by crowds of learners to help improve the educational experience of future learners [Kim et al., 2015].
- Prior work has shown crowdsourced content can be used to create effective content---in some cases on par with expert content [Aleahmad et al. 2009; Williams et al., 2016; Whitehill & Seltzer, 2017].
- However, we are interested in passive learnersourcing:
using artifacts that learners naturally generate.


Can we use these to help other learners learn?
Learners Naturally Generate Artifacts
Learners Naturally Generate Artifacts
Can we use these to help other learners learn?

Want workers to become more skilled
No existing curriculum
Tasks changing over time
Content Creation and Curation
Validating Peer Solutions
Web Search Task
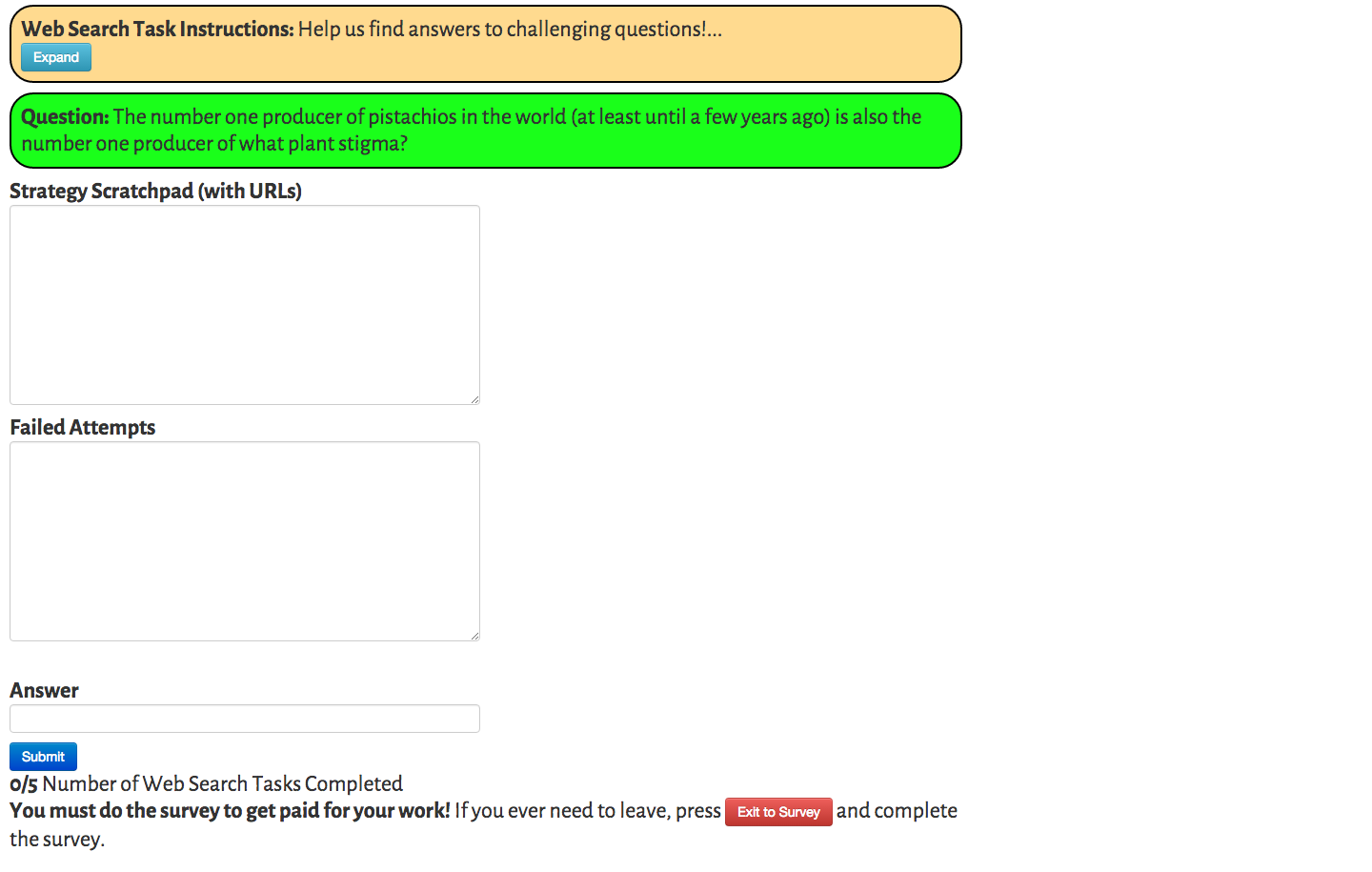
Doroudi, Kamar, Brunskill, and Horvitz, CHI 2016
Peer-Generated Content

Doroudi, Kamar, Brunskill, and Horvitz, CHI 2016
Expert Solutions ≠ Peer Solutions


Doroudi, Kamar, Brunskill, and Horvitz, CHI 2016

Validating Peer Solutions
Doroudi, Kamar, Brunskill, and Horvitz, CHI 2016
Web Search: Experiment I
Doroudi, Kamar, Brunskill, and Horvitz, CHI 2016
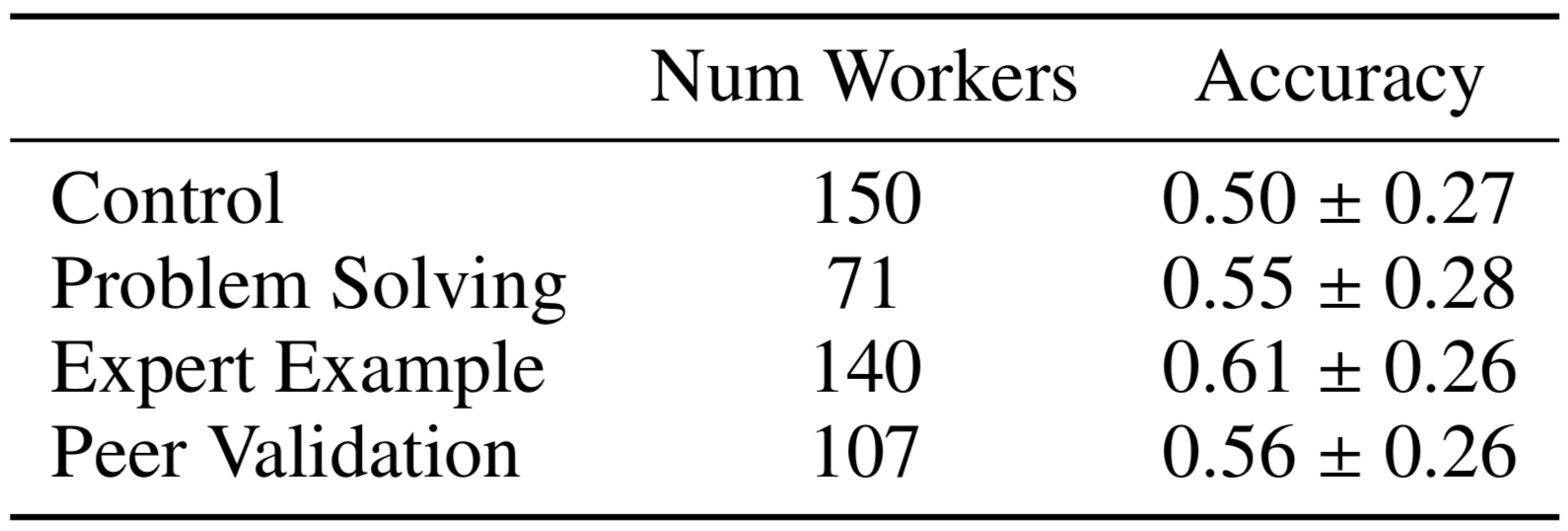
Web Search: Experiment I
Doroudi, Kamar, Brunskill, and Horvitz, CHI 2016
Sig. difference between example and control
(Mann-Whitney U test, \(p < 0.05\))

Filtering Peer Solutions
Doroudi, Kamar, Brunskill, and Horvitz, CHI 2016
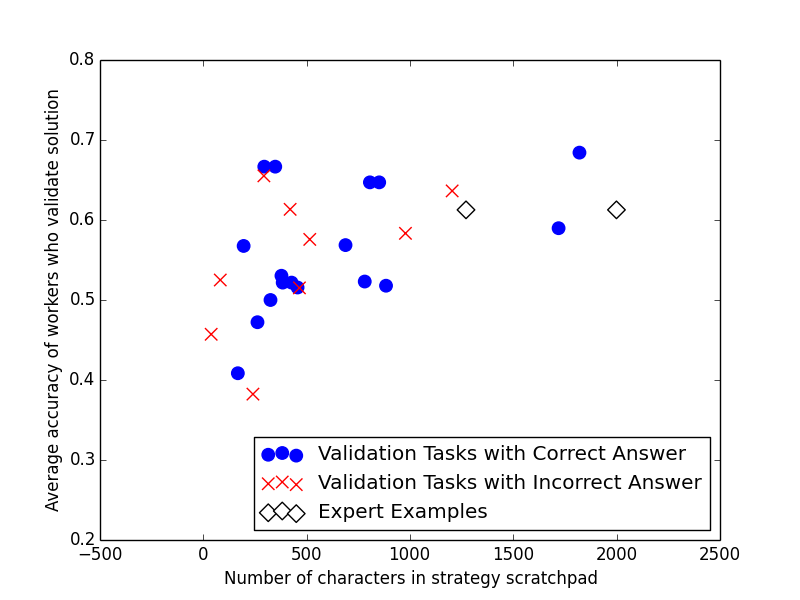
Predict which solutions lead to highest future performance when validated
Number of characters in solution only feature with non-zero coefficient
LASSO regression
Web Search: Experiment II
Doroudi, Kamar, Brunskill, and Horvitz, CHI 2016
* Workers see one short (<800 char) and one long (>800 char) solution
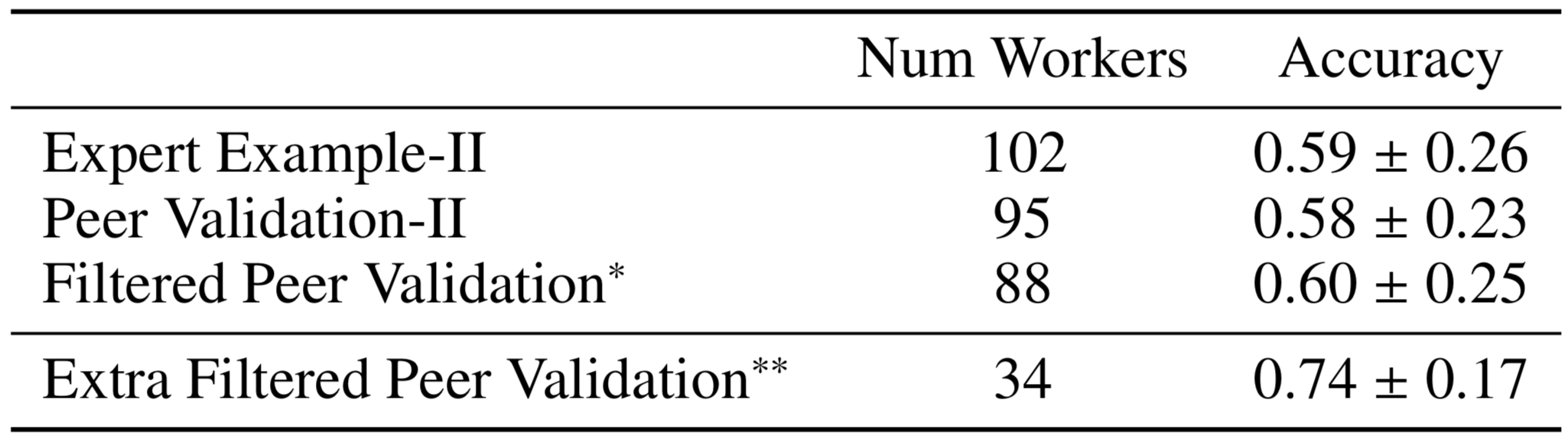
Web Search: Experiment II
* Workers see one short (<800 char) and one long (>800 char) solution
** Post Hoc analysis of workers who saw one medium (500-800 char)
and one extra long (>1000 char) solution
Doroudi, Kamar, Brunskill, and Horvitz, CHI 2016

Content Creation and Curation
Reading Peer Examples
Product Comparison Task
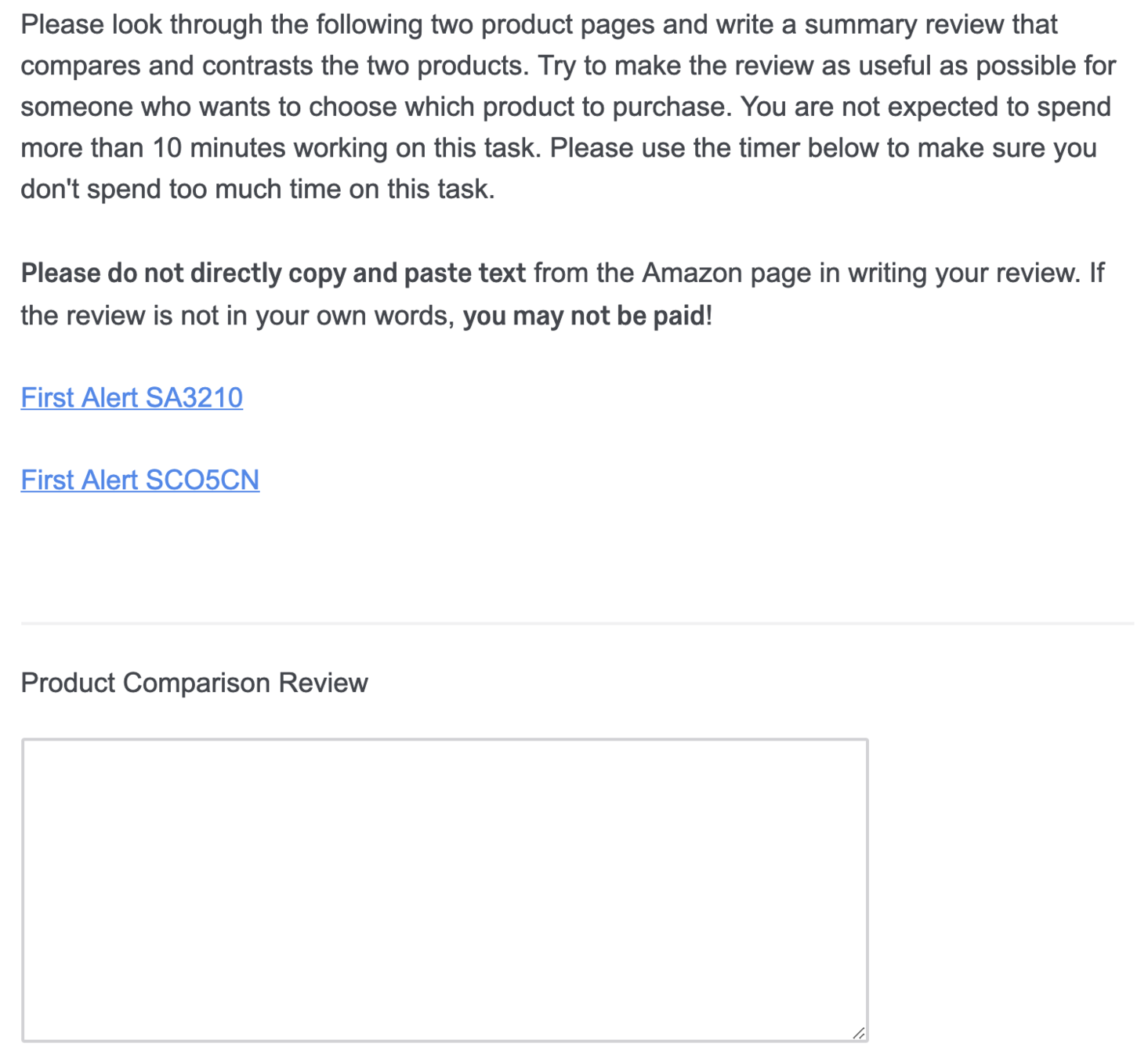

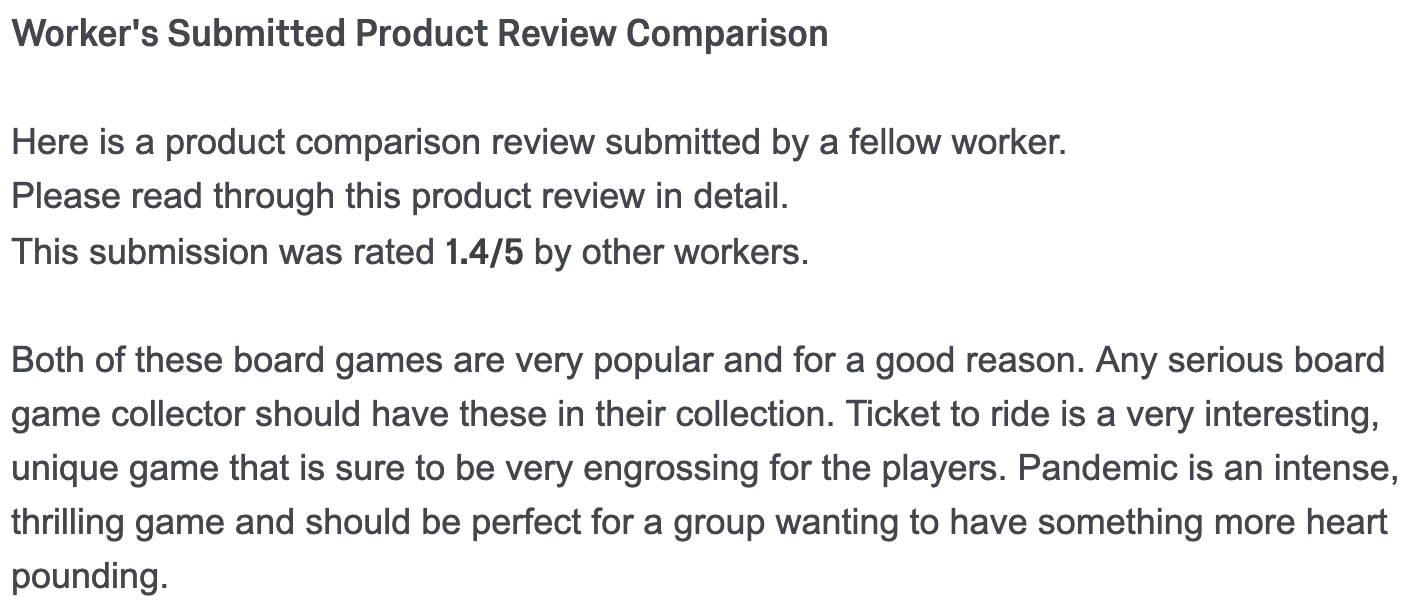
Peer-Generated Examples
Experimental Design
Experiment 1 Results


No sig. differences between conditions
Experiment 1 Results


No sig. differences between conditions
Experiment 1 Results


No sig. differences between conditions
Experiment 2

3 Highest Quality Examples

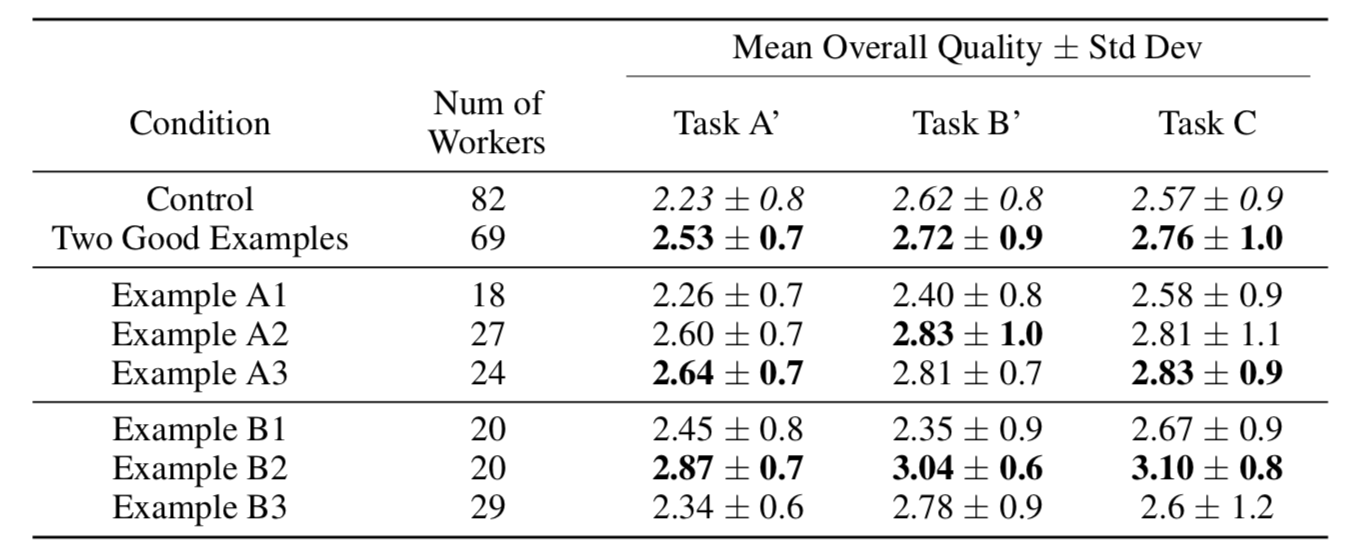

Experiment 2 Results
Sig. difference between two good examples and control on Task A'
(Mann-Whitney U test, \(p < 0.01\))


Experiment 2 Results
Sig. difference between two good examples and control on Task A'
(Mann-Whitney U test, \(p < 0.01\))


Experiment 2 Results
Sig. difference between two good examples and control on Task A'
(Mann-Whitney U test, \(p < 0.01\))

Top Three Examples A
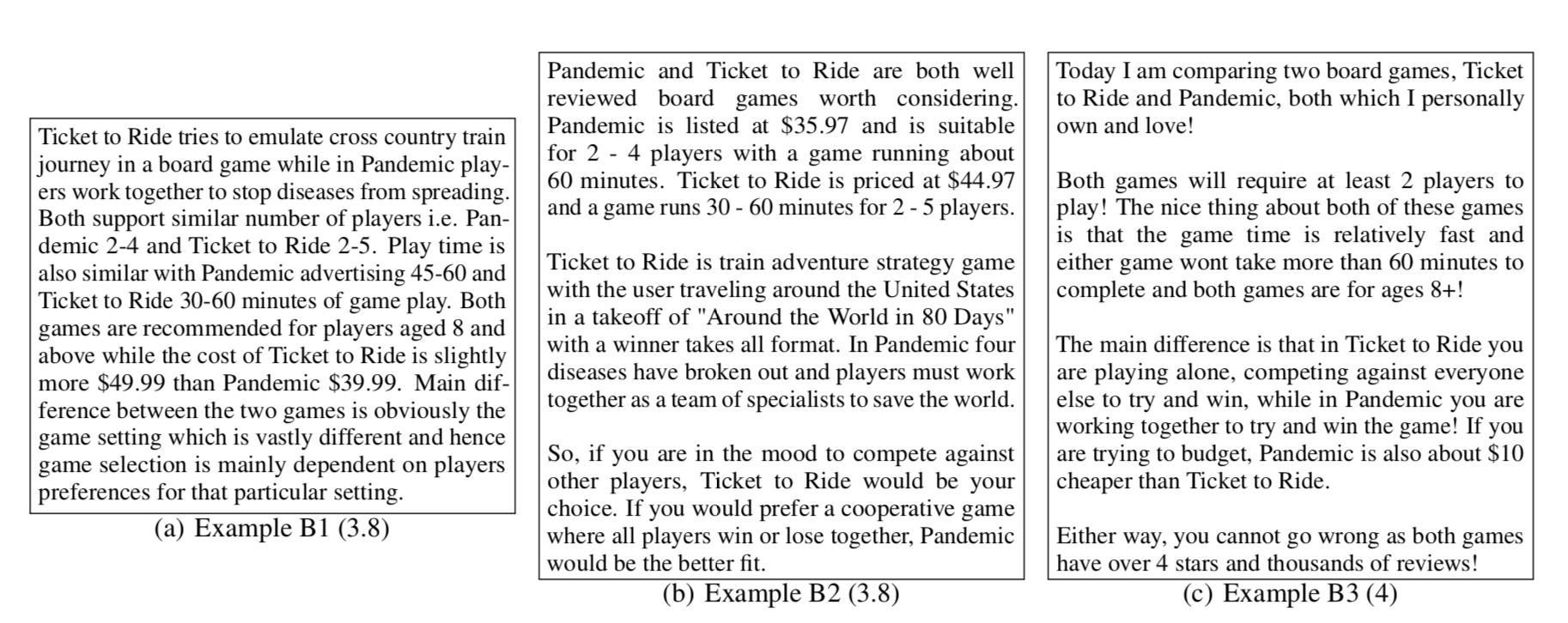
Top Three Examples B
Is Quality all that Matters?
Learnersourced Content as a Tool for Scientific Discovery

Peer Work
ML
Model
Can lead to new insights about how people learn.
Length
Spacing
Word choice
What makes a pedagogically effective example?
Quality
for each student


Takeaway Message
Seeing peer work that is curated with simple rules can be an effective form of training.
Future direction: use more sophisticated machine learning models to curate better solutions
However, our results suggest we can do better!
and to learn more about how peer work leads to learning.
Peer-generated work can be used for cost-effective content generation
Instructional Sequencing
Limitations of Status Quo
Model-Based RL
Overconstrained
Biased
Underconstrained
High Variance
Bias-Variance Tradeoff
Cognitive
Mastery Learning
Deep RL
Importance Sampling
Model/Theory-Driven
Data-Driven
Model-Based RL
Overconstrained
Biased
Underconstrained
High Variance
Bias-Variance Tradeoff
Cognitive
Mastery Learning
Deep RL
Importance Sampling
Model/Theory-Driven
Data-Driven
Bayesian Knowledge Tracing (BKT)

Corbett and Anderson, 1995
Cognitive Mastery Learning
Keep giving practice opportunities on a skill/concept until student reaches mastery:
Then move onto the next skill/concept
Corbett and Anderson, 1995
The Promise of Mastery Learning
One Size Fits All
Mastery Learning
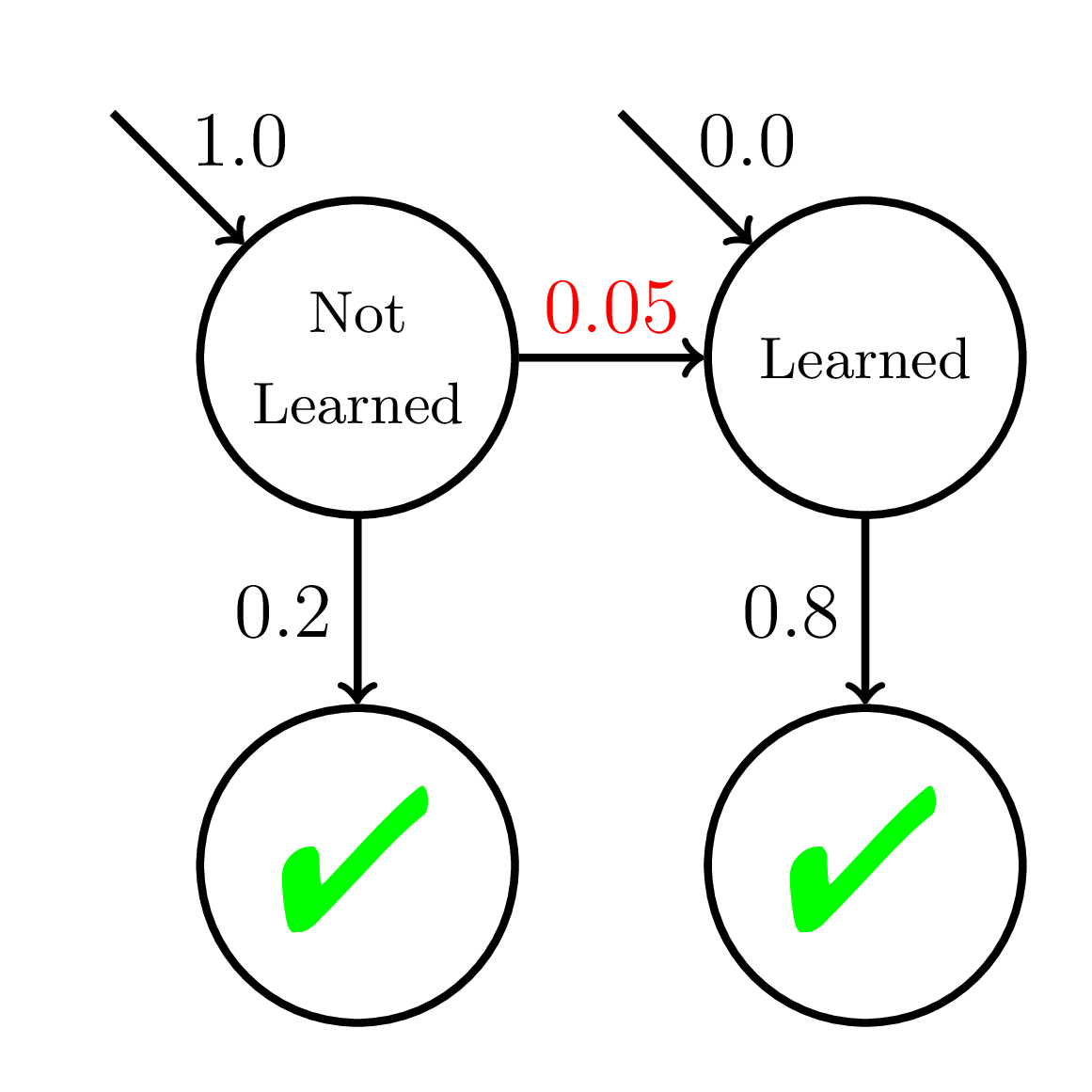
“The [BKT] model overestimates the true learning and performance parameters for below-average students who make many errors. While these students receive more remedial exercises than the above average students, they nevertheless receive less remedial practice than they need and perform worse on the test than expected.”
Corbett and Anderson, 1995
The Reality of Mastery Learning
Even though mastery learning is better than one-size fits all, it may not always be give enough practice.
Model Misspecification
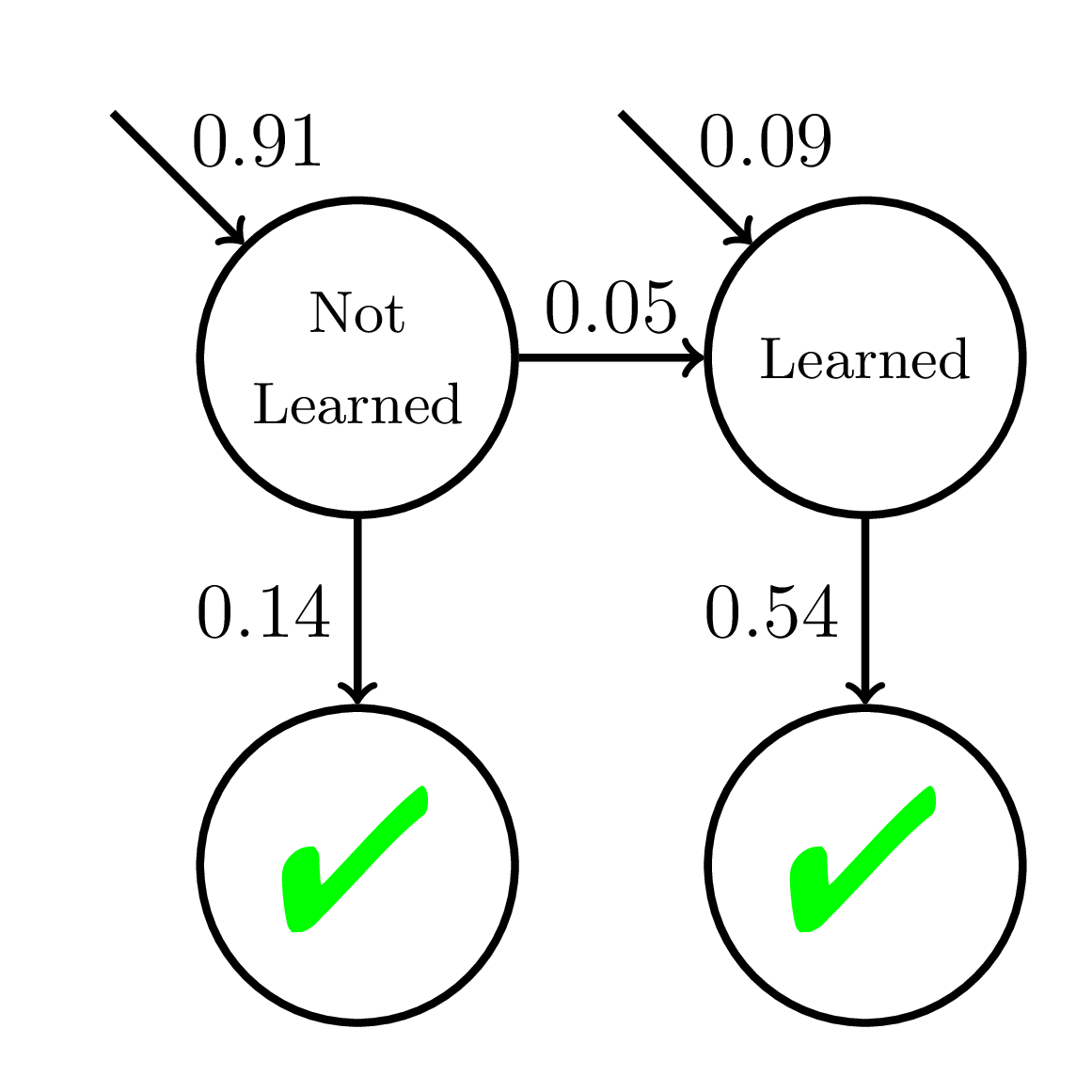

500 students
20 practice opportunities
High P(slip)!
P(Correct)
Doroudi and Brunskill, Educational Data Mining 2017, Best Paper Nominee
Model Misspecification
Average P(Correct)
at Mastery:
0.54


P(Correct)

Mastery
Learning
Declare
Mastery
Equity of Mastery Learning
200 students
20 practice opportunities
200 students
20 practice opportunities
Fast Learners
Slow Learners
Doroudi and Brunskill, Learning Analytics & Knowledge 2019
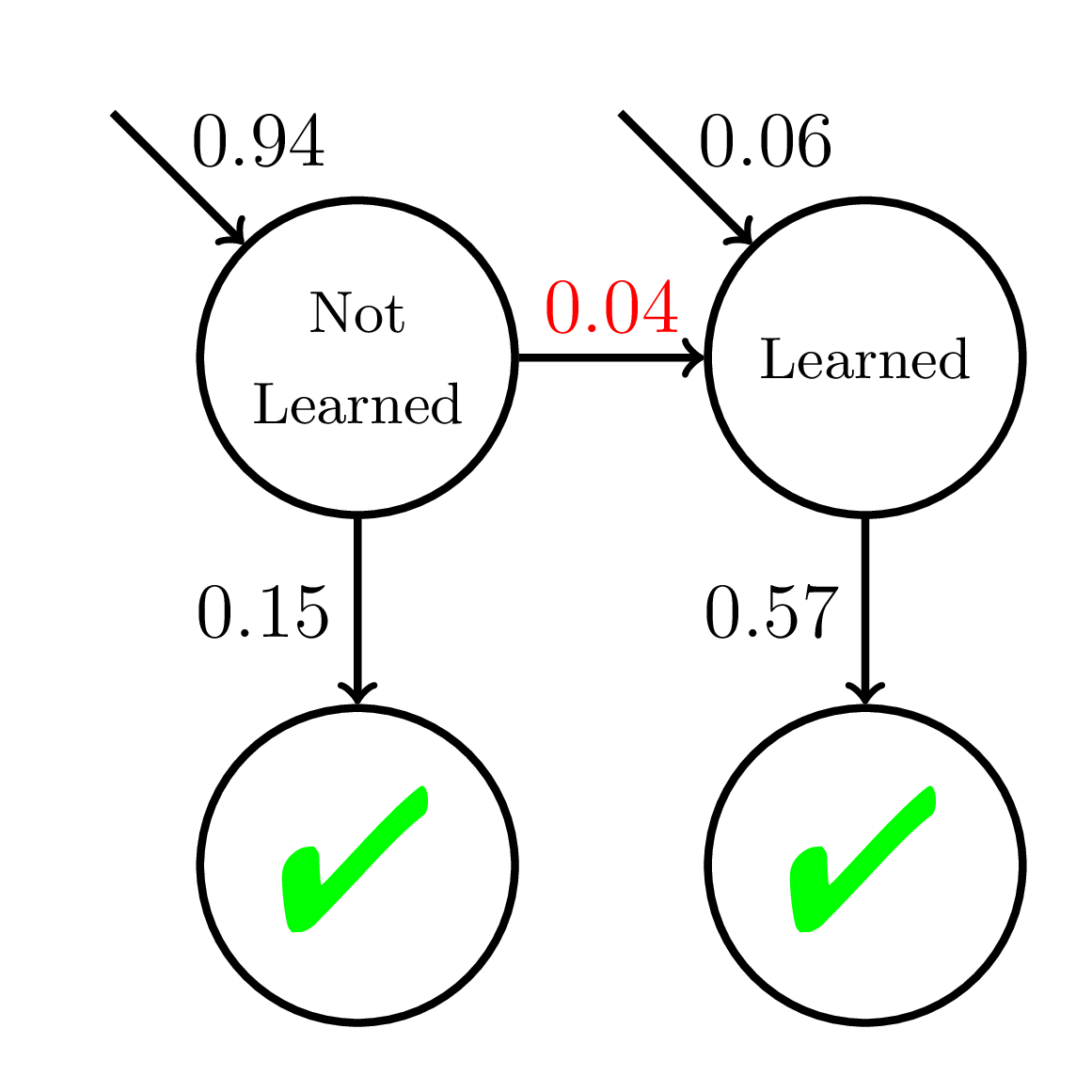
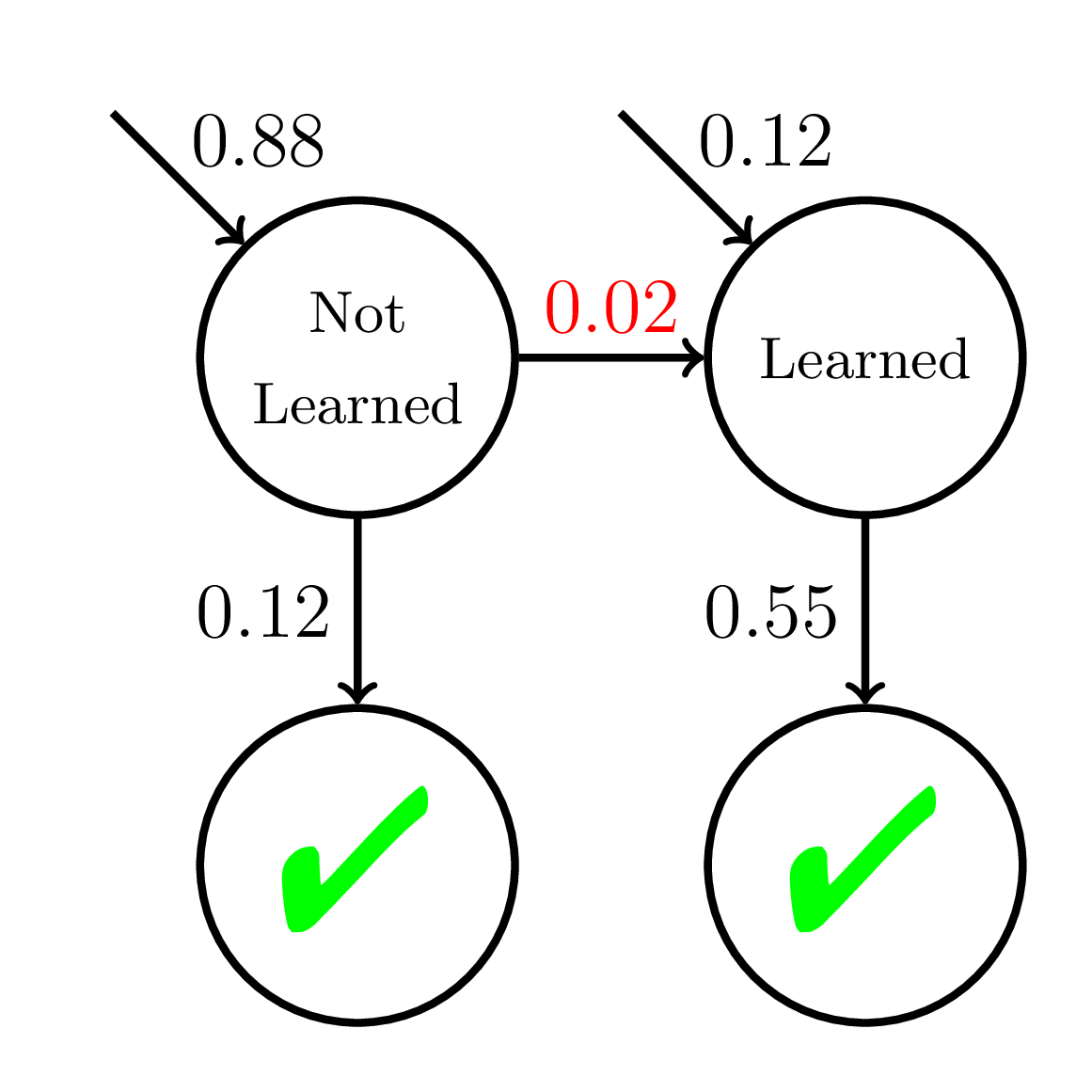
Equity of Mastery Learning
Average P(Correct)
at Mastery:
0.56
Average P(Correct) at Mastery:
0.45


Mastery
Learning


Mastery
Learning
Fast Learners
Slow Learners


Doroudi and Brunskill, Learning Analytics & Knowledge 2019
Instructional Sequencing
Towards Navigating the Tradeoff
Model-Based RL
Overconstrained
Biased
Underconstrained
High Variance
Bias-Variance Tradeoff
Cognitive
Mastery Learning
Deep Learning
Importance Sampling
Model/Theory-Driven
Data-Driven
Theoretically Plausible Models
Productively
Constrained
Doroudi, Aleven, and Brunskill, Under Review
Model-Based RL
Overconstrained
Biased
Underconstrained
High Variance
Bias-Variance Tradeoff
Cognitive
Mastery Learning
Deep Learning
Importance Sampling
Model/Theory-Driven
Data-Driven
Robustness to Many Models
Not Constrained by a Single Model
Doroudi, Aleven, and Brunskill, L@S 2017
Takeaway
Existing approaches typically either rely on a single biased model or are very high variance
Can try to mitigate this by:
-
Using models that are more in line with psychological theory.
-
Being robust to multiple models rather than assuming a single model is correct.
Can combine both approaches!
Conclusion
Integrating Human and Machine
Intelligence
Using theories of learning to inform automated instructional sequencing
Using learner contributions to generate new content
+
machine learning to curate new content
Using learner input to inform instructional sequencing
Using teacher input to inform instructional sequencing
Integrating Human and Machine
Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence
Rule-Based + Logical AI
Statistical AI
Rule-Based
Theory-Driven
Machine Learning
Data-Driven
Automated Instruction





Integrating Human and Machine
Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence
Rule-Based + Logical AI
Statistical AI
Rule-Based
Theory-Driven
Machine Learning
Data-Driven





Semi-Automated Instruction
Integrating human and machine
intelligence to improve education and build better machines
Acknowledgements
The research reported here was supported in part by the Institute of Education Sciences, U.S. Department of Education, through Grants R305A130215 and R305B150008 to Carnegie Mellon University. The opinions expressed are those of the authors and do not represent views of the Institute or the U.S. Dept. of Education. Some of the research was also funded with the generous support of Microsoft Research and Google.
I am fortunate to have worked on the research presented here with a number of collaborators including Emma Brunskill, Vincent Aleven,
Ece Kamar, Eric Horvitz, and Phil Thomas.
I also acknowledge the support of my thesis committee,
Emma Brunskill, Vincent Aleven, Ken Koedinger, Chinmay Kulkarni, and Eric Horvitz,
as well as Sharon Carver and David Klahr.
Backup Slides
Model-Based RL
Overconstrained
Biased
Underconstrained
High Variance
Bias-Variance Tradeoff
Cognitive
Mastery Learning
Deep RL
Model/Theory-Driven
Data-Driven
Importance Sampling
Data
Instructional Policy




Reinforcement Learning (RL)
Model
(MDP)
Data
Instructional Policy





Single Model Simulation
Model
(MDP)
Model
(MDP)
Chi et al., 2011
Rowe et al., 2014
Doroudi, Aleven, and Brunskill, Learning @ Scale 2017
Single Model Simulation
-
We predicted a new instructional policy would outperform several baseline policies
- But in an experiment, no significant difference was found.
- Rowe, Mott, and Lester (2014): New content selection policy estimated to be much better than random policy.
- But in experiment, no significant difference found (Rowe and Lester, 2015).
Doroudi, Aleven, and Brunskill, Learning @ Scale 2017
Overconstrained
Biased
Underconstrained
High Variance
Bias-Variance Tradeoff
Cognitive
Mastery Learning
Deep RL
Importance Sampling
Model/Theory-Driven
Data-Driven
Model-Based RL
Importance Sampling
Estimator that gives unbiased and consistent estimates for a policy!
Can have very high variance when policy is different from prior data.
-
Example: Worked example or problem-solving?
20 sequential decisions ⇒ need over 2^{20}$20\(2^{20}\) students!
Importance sampling can prefer the worse of two policies more often than not (Doroudi, Thomas, and Brunskill, 2017).
Doroudi, Thomas, and Brunskill, Uncertainty in Artificial Intelligence 2017, Best Paper
Model-Based RL
Overconstrained
Biased
Underconstrained
High Variance
Bias-Variance Tradeoff
Cognitive
Mastery Learning
Deep Learning
Importance Sampling
Model/Theory-Driven
Data-Driven
Deep Learning?
Significant advances in computer vision, natural language processing, and game playing
Recent work on instructional sequencing, but only simulations
Limitations
Not enough data
Learning is fundamentally different from images, language, and games
Baselines are much stronger for instructional sequencing
Data
New Instructional Policy





Going Beyond Mastery Learning
New
Model
Fractions
Tutor
Fractions
Tutor
Around 1000 students
Data
New Instructional Policy





Experiment
New
Model
Fractions
Tutor
Fractions
Tutor


Fractions
Tutor
vs.
Baseline Policy
Doroudi, Aleven, and Brunskill, Learning @ Scale 2017
Simulated Experiment
New
Model
New
Model
Doroudi, Aleven, and Brunskill, Learning @ Scale 2017
Data
New Instructional Policy





New
Model
Fractions
Tutor


vs.
Baseline Policy
Robust Evaluation Matrix
| Student Models | Policy 1 |
Policy 2 |
Policy 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Student Model 1 | |||
| Student Model 2 | |||
| Student Model 3 |
\(V_{SM_1,P_1}\) \(V_{SM_1,P_2}\) \(V_{SM_1,P_3}\)
\(V_{SM_2,P_1}\) \(V_{SM_2,P_2}\) \(V_{SM_2,P_3}\)
\(V_{SM_3,P_1}\) \(V_{SM_3,P_2}\) \(V_{SM_3,P_3}\)
Doroudi, Aleven, and Brunskill, Learning @ Scale 2017
Robust Evaluation Matrix
| Student Models |
Baseline Policy |
Adaptive Policy |
|---|---|---|
| New Model | 5.9 ± 0.9 | 9.1 ± 0.8 |
Doroudi, Aleven, and Brunskill, Learning @ Scale 2017
Posttest Scores (out of 16 points)
Robust Evaluation Matrix
| Student Models |
Baseline Policy |
Adaptive Policy |
|---|---|---|
| New Model | 5.9 ± 0.9 | 9.1 ± 0.8 |
| Bayesian Knowledge Tracing | 6.5 ± 0.8 | 7.0 ± 1.0 |
Doroudi, Aleven, and Brunskill, Learning @ Scale 2017
Posttest Scores (out of 16 points)
Robust Evaluation Matrix
| Student Models |
Baseline Policy |
Adaptive Policy |
|---|---|---|
| New Model | 5.9 ± 0.9 | 9.1 ± 0.8 |
| Bayesian Knowledge Tracing | 6.5 ± 0.8 | 7.0 ± 1.0 |
| Deep Knowledge Tracing | 9.9 ± 1.5 | 8.6 ± 2.1 |
Doroudi, Aleven, and Brunskill, Learning @ Scale 2017
Posttest Scores (out of 16 points)
Robust Evaluation Matrix
| Student Models |
Baseline Policy |
Adaptive Policy | Awesome Policy |
|---|---|---|---|
| New Model | 5.9 ± 0.9 | 9.1 ± 0.8 | 16 |
| Bayesian Knowledge Tracing | 6.5 ± 0.8 | 7.0 ± 1.0 | 16 |
| Deep Knowledge Tracing | 9.9 ± 1.5 | 8.6 ± 2.1 | 16 |
Posttest Scores (out of 16 points)
Doroudi, Aleven, and Brunskill, Learning @ Scale 2017
Data
Instructional Policy





Review of RL-Based Sequencing
Student
Model


vs.
Baseline Policy
Doroudi, Aleven, and Brunskill, In Submission
Doroudi, Aleven, and Brunskill, In Submission
leer

to read
Paired-Association Tasks
Concept Learning Tasks
Sequencing Activity Types
Sequencing Interdependent Content
Four Clusters of Studies
Doroudi, Aleven, and Brunskill, In Submission


reading
Paired-Association Tasks
Concept Learning Tasks
Sequencing Activity Types
Sequencing Interdependent Content
Four Clusters of Studies
Doroudi, Aleven, and Brunskill, In Submission
Worked Example
Problem
Solving
\(x^2 - 4 = 12\)
Solve for \(x\):
\(x^2 - 4 = 12\)
\(x^2 = 4 + 12\)
\(x^2 = 16\)
\(x = \sqrt{16} = \pm4\)
\(x^2 - 4 = 12\)
Solve for \(x\):
Paired-Association Tasks
Concept Learning Tasks
Sequencing Activity Types
Sequencing Interdependent Content
Four Clusters of Studies
Doroudi, Aleven, and Brunskill, In Submission

Paired-Association Tasks
Concept Learning Tasks
Sequencing Activity Types
Sequencing Interdependent Content
Four Clusters of Studies
Four Clusters of Studies
Doroudi, Aleven, and Brunskill, In Submission
| RL Policy Outperformed Baseline |
Mixed Results |
RL Policy Did Not Outperform Baseline |
|
|---|---|---|---|
| Paired-Association Tasks | 10 | 0 | 3 |
| Concept Learning Tasks | 2 | 3 | 0 |
| Sequencing Activity Types | 4 | 4 | 0 |
| Sequencing Interdependent Content | 0 | 0 | 6 |
Four Clusters of Studies
Doroudi, Aleven, and Brunskill, In Submission
Paired-Association Tasks
Concept Learning Tasks
Sequencing Activity Types
Sequencing Interdependent Content
Use Psychologically-Inspired Models
Spacing Effect
Expertise Reversal Effect
Use Data-Driven
Models
Theoretical Basis
More
Less
We attempt to treat the same problem with several alternative models each with different simplifications but with a common...assumption. Then, if these models, despite their different assumptions, lead to similar results, we have what we can call a robust theorem that is relatively free of the details of the model.
Hence, our truth is the intersection of independent lies.
- Richard Levins, 1966
200 students
20 practice opportunities
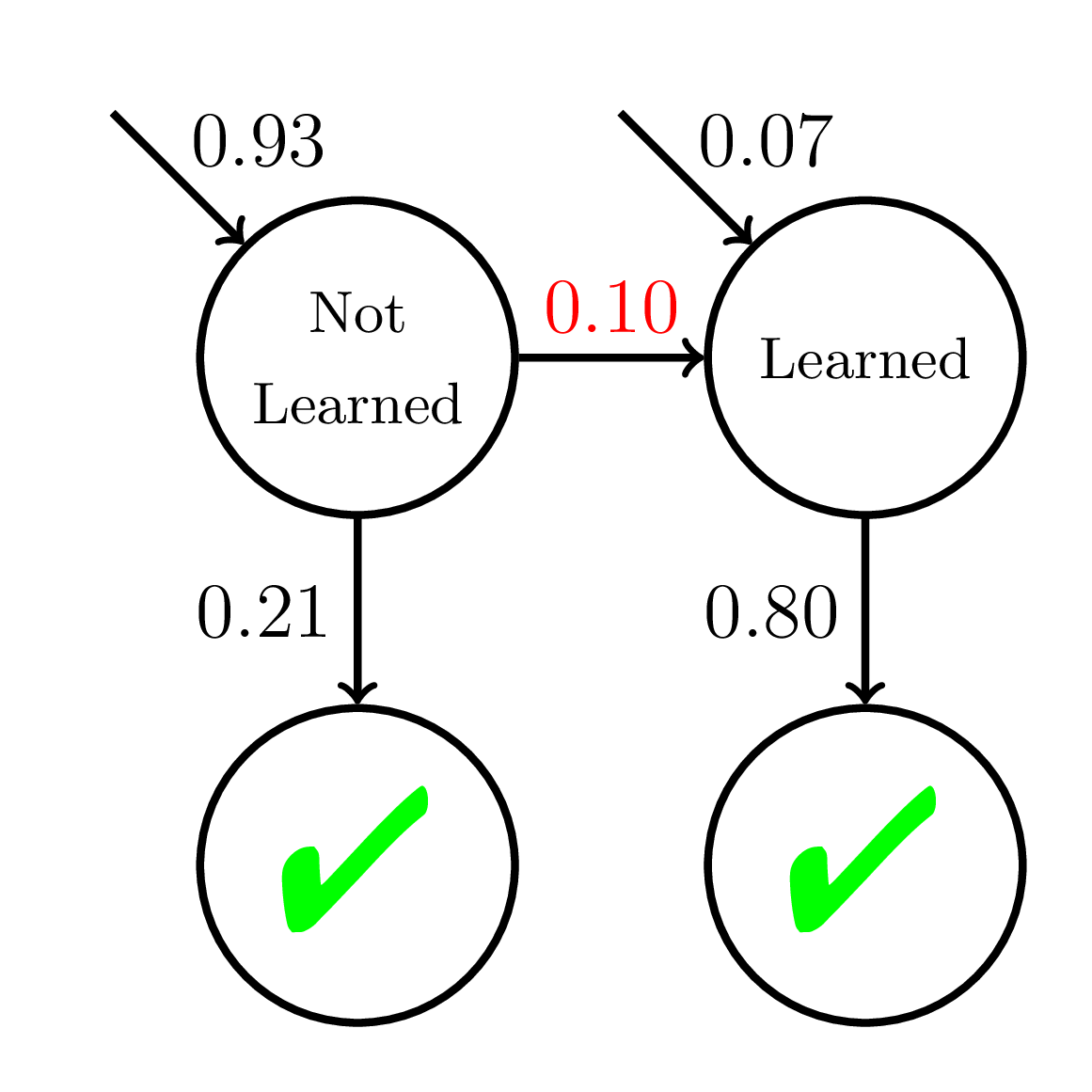
Fast Learners
Slow Learners
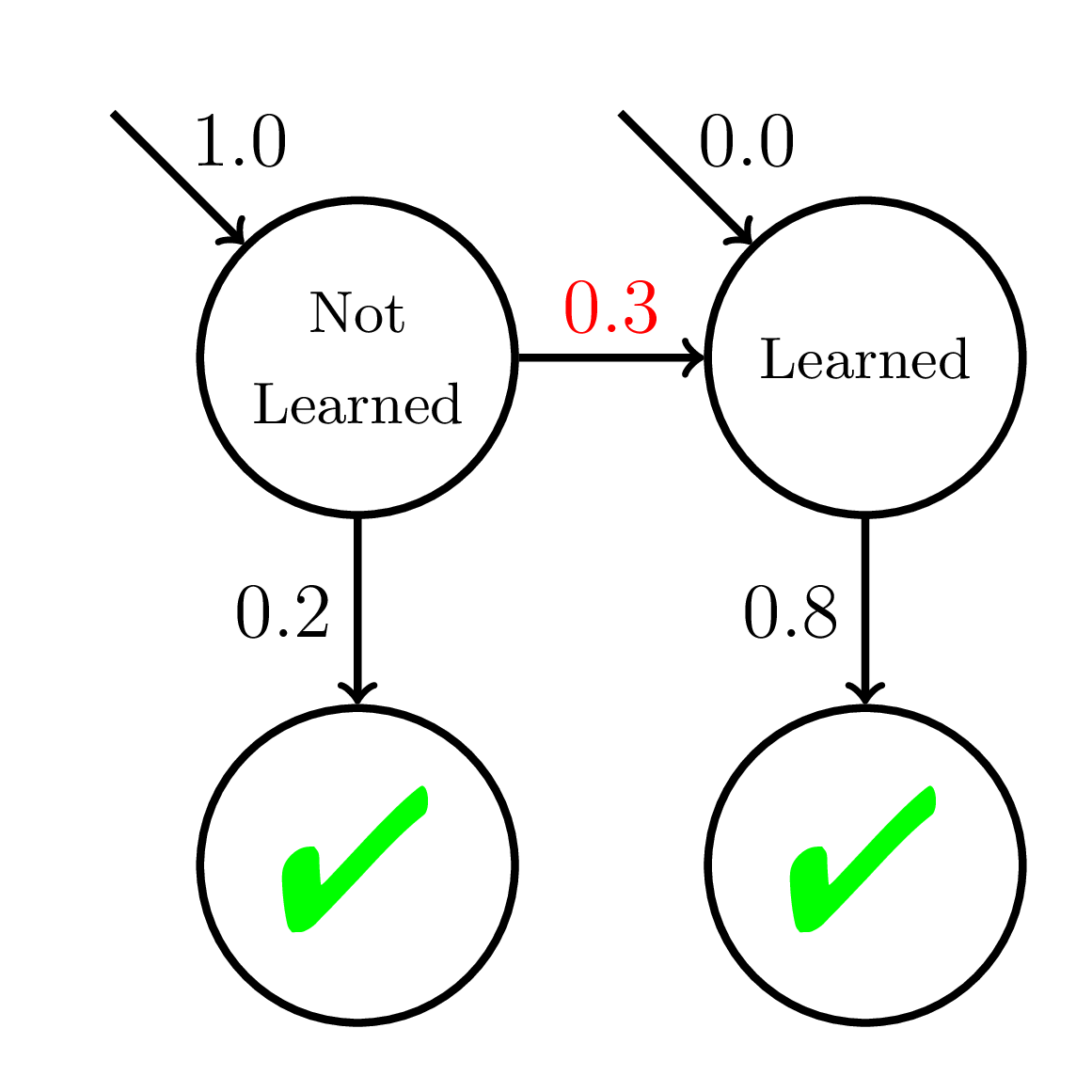
Doroudi and Brunskill, Learning Analytics & Knowledge 2019