Collections,generics, streams
COMP16412 landing lecture, week 7/8
What you should have done so far
| Video lectures | Book | Workshops | Labs | Quiz | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Week 7 | Arrays[] and ArrayList Stack Queue and Set Revisiting Loops |
Sec 15.1--15.5 Sec 15.7 |
Stacks Queues Sets |
Palindromes in ArrayList Stack & List impl. Loops Workshop exercises |
4 questions |
| Week 8 |
Generic types Optional type and null handling Streams and demo |
Generics: Section 13.7 Wrapper classes: Section 9.11 Enhanced loop: Section 6.7. Lambda expressions: Section 13.6 Polymorphism: Section 13.9 Null-Pointer Exceptions: Section 14.6 Stream API: Chapter 22 |
Records Optional Using sets Generics |
Workshop revisit Using generics Defining generics Streaming |
6 Questions |

Q&A at menti.com code 2335 3741
int a = 1;
int b = 2;
int c = a;
HashSet<Integer> mySet = new HashSet<Integer>();
System.out.println(mySet.add(a));
System.out.println(mySet.add(b));
System.out.println(mySet.add(c));
System.out.println(mySet.add(c));
System.out.println(mySet.toString());HashSet: What will be the printed output?
Q&A at menti.com code 2335 3741
int a = 1;
int b = 2;
int c = a;
HashSet<Integer> mySet = new HashSet<Integer>();
System.out.println(mySet.add(a));
System.out.println(mySet.add(b));
System.out.println(mySet.add(b));
System.out.println(mySet.add(c));
System.out.println(mySet.toString());HashSet: What will be the printed output?
true
true
false
false
[1, 2]
Q&A at menti.com code 2335 3741
Stack<Integer> myStack = new Stack<Integer>();
myStack.push(1);
myStack.add(2);
Integer a = myStack.peek();
Integer b = myStack.pop();
myStack.push(3);
System.out.println(a);
System.out.println(b);
System.out.println(myStack.toString());Stack: What will be the printed output?
Q&A at menti.com code 2335 3741
Stack<Integer> myStack = new Stack<Integer>();
myStack.push(1);
myStack.add(2);
Integer a = myStack.peek();
Integer b = myStack.pop();
myStack.push(3);
System.out.println(a);
System.out.println(b);
System.out.println(myStack.toString());Stack: What will be the printed output?
2
2
[1, 3]
Q&A at menti.com code 2335 3741
Questions and answers
Q&A at menti.com code 2335 3741
Which Set implementations?
// Set is an interface, must choose implementation
🛑 private Set<String> = new Set<>();
// Use .hashCode() for efficiency
private Set<String> = new HashSet<>();
// .. and also preserve order
private Set<String> = new LinkedHashSet<>();
// Preserve order using comparator (e.g. alphabetical)
private SortedSet<String> = new TreeSet<>();
# Set
menti.com
2335 3741
Why do Stacks have add and push?
Stack<String> stack = new Stack<String>();
stack.push("Take train");
stack.push("Buy ticket");
stack.push("Find time");
System.out.println(stack.pop());
System.out.println(stack.pop());
stack.push("Wait");
System.out.println(stack.pop());
System.out.println(stack.pop());# Stack
menti.com
2335 3741
Why do Stacks have add and push?
Stack<String> stack = new Stack<String>();
stack.push("Take train");
stack.push("Buy ticket");
stack.push("Find time");
System.out.println(stack.pop());
System.out.println(stack.pop());
stack.push("Wait");
System.out.println(stack.pop());
System.out.println(stack.pop());# Stack
Find time
Buy ticket
Wait
Take train
menti.com
2335 3741
Why do Stacks have add and push?
Stack<String> stack = new Stack<String>();
stack.add("Take train");
stack.addElement("Buy ticket");
stack.push("Find time");
System.out.println(stack.pop());
System.out.println(stack.pop());
stack.push("Wait");
System.out.println(stack.pop());
System.out.println(stack.pop());# Stack
Find time
Buy ticket
Wait
Take train
menti.com
2335 3741
Why do Stacks have add and push?
/*
* Copyright (c) 1994, 2022, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
* DO NOT ALTER OR REMOVE COPYRIGHT NOTICES OR THIS FILE HEADER.
*
* This code is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify it
* under the terms of the GNU General Public License version 2 only, as
* published by the Free Software Foundation. Oracle designates this
* particular file as subject to the "Classpath" exception as provided
* by Oracle in the LICENSE file that accompanied this code.
*
* This code is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT
* ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or
* FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU General Public License
* version 2 for more details (a copy is included in the LICENSE file that
* accompanied this code).
*
* You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License version
* 2 along with this work; if not, write to the Free Software Foundation,
* Inc., 51 Franklin St, Fifth Floor, Boston, MA 02110-1301 USA.
*
* Please contact Oracle, 500 Oracle Parkway, Redwood Shores, CA 94065 USA
* or visit www.oracle.com if you need additional information or have any
* questions.
*/
package java.util;
/**
* The {@code Stack} class represents a last-in-first-out
* (LIFO) stack of objects. It extends class {@code Vector} with five
* operations that allow a vector to be treated as a stack. The usual
* {@code push} and {@code pop} operations are provided, as well as a
* method to {@code peek} at the top item on the stack, a method to test
* for whether the stack is {@code empty}, and a method to {@code search}
* the stack for an item and discover how far it is from the top.
* <p>
* When a stack is first created, it contains no items.
*
* <p>A more complete and consistent set of LIFO stack operations is
* provided by the {@link Deque} interface and its implementations, which
* should be used in preference to this class. For example:
* <pre> {@code
* Deque<Integer> stack = new ArrayDeque<Integer>();}</pre>
*
* @param <E> Type of component elements
*
* @author Jonathan Payne
* @since 1.0
*/
public class Stack<E> extends Vector<E> {
/**
* Creates an empty Stack.
*/
public Stack() {
}
/**
* Pushes an item onto the top of this stack. This has exactly
* the same effect as:
* <blockquote><pre>
* addElement(item)</pre></blockquote>
*
* @param item the item to be pushed onto this stack.
* @return the {@code item} argument.
* @see java.util.Vector#addElement
*/
public E push(E item) {
addElement(item);
return item;
}
/**
* Removes the object at the top of this stack and returns that
* object as the value of this function.
*
* @return The object at the top of this stack (the last item
* of the {@code Vector} object).
* @throws EmptyStackException if this stack is empty.
*/
public synchronized E pop() {
E obj;
int len = size();
obj = peek();
removeElementAt(len - 1);
return obj;
}
/**
* Looks at the object at the top of this stack without removing it
* from the stack.
*
* @return the object at the top of this stack (the last item
* of the {@code Vector} object).
* @throws EmptyStackException if this stack is empty.
*/
public synchronized E peek() {
int len = size();
if (len == 0)
throw new EmptyStackException();
return elementAt(len - 1);
}
/**
* Tests if this stack is empty.
*
* @return {@code true} if and only if this stack contains
* no items; {@code false} otherwise.
*/
public boolean empty() {
return size() == 0;
}
/**
* Returns the 1-based position where an object is on this stack.
* If the object {@code o} occurs as an item in this stack, this
* method returns the distance from the top of the stack of the
* occurrence nearest the top of the stack; the topmost item on the
* stack is considered to be at distance {@code 1}. The {@code equals}
* method is used to compare {@code o} to the
* items in this stack.
*
* @param o the desired object.
* @return the 1-based position from the top of the stack where
* the object is located; the return value {@code -1}
* indicates that the object is not on the stack.
*/
public synchronized int search(Object o) {
int i = lastIndexOf(o);
if (i >= 0) {
return size() - i;
}
return -1;
}
/** use serialVersionUID from JDK 1.0.2 for interoperability */
@java.io.Serial
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1224463164541339165L;
}
# Stack
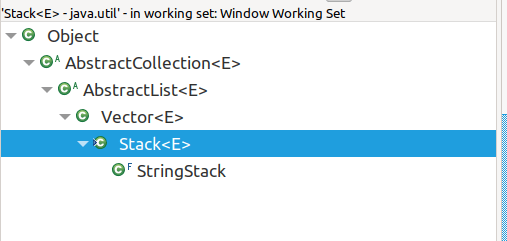
menti.com
2335 3741
Why do Stacks have add and push?
/*
* Copyright (c) 1994, 2019, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
* DO NOT ALTER OR REMOVE COPYRIGHT NOTICES OR THIS FILE HEADER.
*
* This code is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify it
* under the terms of the GNU General Public License version 2 only, as
* published by the Free Software Foundation. Oracle designates this
* particular file as subject to the "Classpath" exception as provided
* by Oracle in the LICENSE file that accompanied this code.
*
* This code is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT
* ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or
* FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU General Public License
* version 2 for more details (a copy is included in the LICENSE file that
* accompanied this code).
*
* You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License version
* 2 along with this work; if not, write to the Free Software Foundation,
* Inc., 51 Franklin St, Fifth Floor, Boston, MA 02110-1301 USA.
*
* Please contact Oracle, 500 Oracle Parkway, Redwood Shores, CA 94065 USA
* or visit www.oracle.com if you need additional information or have any
* questions.
*/
package java.util;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
import java.io.StreamCorruptedException;
import java.util.function.Consumer;
import java.util.function.Predicate;
import java.util.function.UnaryOperator;
import jdk.internal.util.ArraysSupport;
/**
* The {@code Vector} class implements a growable array of
* objects. Like an array, it contains components that can be
* accessed using an integer index. However, the size of a
* {@code Vector} can grow or shrink as needed to accommodate
* adding and removing items after the {@code Vector} has been created.
*
* <p>Each vector tries to optimize storage management by maintaining a
* {@code capacity} and a {@code capacityIncrement}. The
* {@code capacity} is always at least as large as the vector
* size; it is usually larger because as components are added to the
* vector, the vector's storage increases in chunks the size of
* {@code capacityIncrement}. An application can increase the
* capacity of a vector before inserting a large number of
* components; this reduces the amount of incremental reallocation.
*
* <p id="fail-fast">
* The iterators returned by this class's {@link #iterator() iterator} and
* {@link #listIterator(int) listIterator} methods are <em>fail-fast</em>:
* if the vector is structurally modified at any time after the iterator is
* created, in any way except through the iterator's own
* {@link ListIterator#remove() remove} or
* {@link ListIterator#add(Object) add} methods, the iterator will throw a
* {@link ConcurrentModificationException}. Thus, in the face of
* concurrent modification, the iterator fails quickly and cleanly, rather
* than risking arbitrary, non-deterministic behavior at an undetermined
* time in the future. The {@link Enumeration Enumerations} returned by
* the {@link #elements() elements} method are <em>not</em> fail-fast; if the
* Vector is structurally modified at any time after the enumeration is
* created then the results of enumerating are undefined.
*
* <p>Note that the fail-fast behavior of an iterator cannot be guaranteed
* as it is, generally speaking, impossible to make any hard guarantees in the
* presence of unsynchronized concurrent modification. Fail-fast iterators
* throw {@code ConcurrentModificationException} on a best-effort basis.
* Therefore, it would be wrong to write a program that depended on this
* exception for its correctness: <i>the fail-fast behavior of iterators
* should be used only to detect bugs.</i>
*
* <p>As of the Java 2 platform v1.2, this class was retrofitted to
* implement the {@link List} interface, making it a member of the
* <a href="{@docRoot}/java.base/java/util/package-summary.html#CollectionsFramework">
* Java Collections Framework</a>. Unlike the new collection
* implementations, {@code Vector} is synchronized. If a thread-safe
* implementation is not needed, it is recommended to use {@link
* ArrayList} in place of {@code Vector}.
*
* @param <E> Type of component elements
*
* @author Lee Boynton
* @author Jonathan Payne
* @see Collection
* @see LinkedList
* @since 1.0
*/
public class Vector<E>
extends AbstractList<E>
implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
{
/**
* The array buffer into which the components of the vector are
* stored. The capacity of the vector is the length of this array buffer,
* and is at least large enough to contain all the vector's elements.
*
* <p>Any array elements following the last element in the Vector are null.
*
* @serial
*/
@SuppressWarnings("serial") // Conditionally serializable
protected Object[] elementData;
/**
* The number of valid components in this {@code Vector} object.
* Components {@code elementData[0]} through
* {@code elementData[elementCount-1]} are the actual items.
*
* @serial
*/
protected int elementCount;
/**
* The amount by which the capacity of the vector is automatically
* incremented when its size becomes greater than its capacity. If
* the capacity increment is less than or equal to zero, the capacity
* of the vector is doubled each time it needs to grow.
*
* @serial
*/
protected int capacityIncrement;
/** use serialVersionUID from JDK 1.0.2 for interoperability */
@java.io.Serial
private static final long serialVersionUID = -2767605614048989439L;
/**
* Constructs an empty vector with the specified initial capacity and
* capacity increment.
*
* @param initialCapacity the initial capacity of the vector
* @param capacityIncrement the amount by which the capacity is
* increased when the vector overflows
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the specified initial capacity
* is negative
*/
public Vector(int initialCapacity, int capacityIncrement) {
super();
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+
initialCapacity);
this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];
this.capacityIncrement = capacityIncrement;
}
/**
* Constructs an empty vector with the specified initial capacity and
* with its capacity increment equal to zero.
*
* @param initialCapacity the initial capacity of the vector
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the specified initial capacity
* is negative
*/
public Vector(int initialCapacity) {
this(initialCapacity, 0);
}
/**
* Constructs an empty vector so that its internal data array
* has size {@code 10} and its standard capacity increment is
* zero.
*/
public Vector() {
this(10);
}
/**
* Constructs a vector containing the elements of the specified
* collection, in the order they are returned by the collection's
* iterator.
*
* @param c the collection whose elements are to be placed into this
* vector
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null
* @since 1.2
*/
public Vector(Collection<? extends E> c) {
Object[] a = c.toArray();
elementCount = a.length;
if (c.getClass() == ArrayList.class) {
elementData = a;
} else {
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(a, elementCount, Object[].class);
}
}
/**
* Copies the components of this vector into the specified array.
* The item at index {@code k} in this vector is copied into
* component {@code k} of {@code anArray}.
*
* @param anArray the array into which the components get copied
* @throws NullPointerException if the given array is null
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException if the specified array is not
* large enough to hold all the components of this vector
* @throws ArrayStoreException if a component of this vector is not of
* a runtime type that can be stored in the specified array
* @see #toArray(Object[])
*/
public synchronized void copyInto(Object[] anArray) {
System.arraycopy(elementData, 0, anArray, 0, elementCount);
}
/**
* Trims the capacity of this vector to be the vector's current
* size. If the capacity of this vector is larger than its current
* size, then the capacity is changed to equal the size by replacing
* its internal data array, kept in the field {@code elementData},
* with a smaller one. An application can use this operation to
* minimize the storage of a vector.
*/
public synchronized void trimToSize() {
modCount++;
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
if (elementCount < oldCapacity) {
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, elementCount);
}
}
/**
* Increases the capacity of this vector, if necessary, to ensure
* that it can hold at least the number of components specified by
* the minimum capacity argument.
*
* <p>If the current capacity of this vector is less than
* {@code minCapacity}, then its capacity is increased by replacing its
* internal data array, kept in the field {@code elementData}, with a
* larger one. The size of the new data array will be the old size plus
* {@code capacityIncrement}, unless the value of
* {@code capacityIncrement} is less than or equal to zero, in which case
* the new capacity will be twice the old capacity; but if this new size
* is still smaller than {@code minCapacity}, then the new capacity will
* be {@code minCapacity}.
*
* @param minCapacity the desired minimum capacity
*/
public synchronized void ensureCapacity(int minCapacity) {
if (minCapacity > 0) {
modCount++;
if (minCapacity > elementData.length)
grow(minCapacity);
}
}
/**
* Increases the capacity to ensure that it can hold at least the
* number of elements specified by the minimum capacity argument.
*
* @param minCapacity the desired minimum capacity
* @throws OutOfMemoryError if minCapacity is less than zero
*/
private Object[] grow(int minCapacity) {
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
int newCapacity = ArraysSupport.newLength(oldCapacity,
minCapacity - oldCapacity, /* minimum growth */
capacityIncrement > 0 ? capacityIncrement : oldCapacity
/* preferred growth */);
return elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
private Object[] grow() {
return grow(elementCount + 1);
}
/**
* Sets the size of this vector. If the new size is greater than the
* current size, new {@code null} items are added to the end of
* the vector. If the new size is less than the current size, all
* components at index {@code newSize} and greater are discarded.
*
* @param newSize the new size of this vector
* @throws ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException if the new size is negative
*/
public synchronized void setSize(int newSize) {
modCount++;
if (newSize > elementData.length)
grow(newSize);
final Object[] es = elementData;
for (int to = elementCount, i = newSize; i < to; i++)
es[i] = null;
elementCount = newSize;
}
/**
* Returns the current capacity of this vector.
*
* @return the current capacity (the length of its internal
* data array, kept in the field {@code elementData}
* of this vector)
*/
public synchronized int capacity() {
return elementData.length;
}
/**
* Returns the number of components in this vector.
*
* @return the number of components in this vector
*/
public synchronized int size() {
return elementCount;
}
/**
* Tests if this vector has no components.
*
* @return {@code true} if and only if this vector has
* no components, that is, its size is zero;
* {@code false} otherwise.
*/
public synchronized boolean isEmpty() {
return elementCount == 0;
}
/**
* Returns an enumeration of the components of this vector. The
* returned {@code Enumeration} object will generate all items in
* this vector. The first item generated is the item at index {@code 0},
* then the item at index {@code 1}, and so on. If the vector is
* structurally modified while enumerating over the elements then the
* results of enumerating are undefined.
*
* @return an enumeration of the components of this vector
* @see Iterator
*/
public Enumeration<E> elements() {
return new Enumeration<E>() {
int count = 0;
public boolean hasMoreElements() {
return count < elementCount;
}
public E nextElement() {
synchronized (Vector.this) {
if (count < elementCount) {
return elementData(count++);
}
}
throw new NoSuchElementException("Vector Enumeration");
}
};
}
/**
* Returns {@code true} if this vector contains the specified element.
* More formally, returns {@code true} if and only if this vector
* contains at least one element {@code e} such that
* {@code Objects.equals(o, e)}.
*
* @param o element whose presence in this vector is to be tested
* @return {@code true} if this vector contains the specified element
*/
public boolean contains(Object o) {
return indexOf(o, 0) >= 0;
}
/**
* Returns the index of the first occurrence of the specified element
* in this vector, or -1 if this vector does not contain the element.
* More formally, returns the lowest index {@code i} such that
* {@code Objects.equals(o, get(i))},
* or -1 if there is no such index.
*
* @param o element to search for
* @return the index of the first occurrence of the specified element in
* this vector, or -1 if this vector does not contain the element
*/
public int indexOf(Object o) {
return indexOf(o, 0);
}
/**
* Returns the index of the first occurrence of the specified element in
* this vector, searching forwards from {@code index}, or returns -1 if
* the element is not found.
* More formally, returns the lowest index {@code i} such that
* {@code (i >= index && Objects.equals(o, get(i)))},
* or -1 if there is no such index.
*
* @param o element to search for
* @param index index to start searching from
* @return the index of the first occurrence of the element in
* this vector at position {@code index} or later in the vector;
* {@code -1} if the element is not found.
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException if the specified index is negative
* @see Object#equals(Object)
*/
public synchronized int indexOf(Object o, int index) {
if (o == null) {
for (int i = index ; i < elementCount ; i++)
if (elementData[i]==null)
return i;
} else {
for (int i = index ; i < elementCount ; i++)
if (o.equals(elementData[i]))
return i;
}
return -1;
}
/**
* Returns the index of the last occurrence of the specified element
* in this vector, or -1 if this vector does not contain the element.
* More formally, returns the highest index {@code i} such that
* {@code Objects.equals(o, get(i))},
* or -1 if there is no such index.
*
* @param o element to search for
* @return the index of the last occurrence of the specified element in
* this vector, or -1 if this vector does not contain the element
*/
public synchronized int lastIndexOf(Object o) {
return lastIndexOf(o, elementCount-1);
}
/**
* Returns the index of the last occurrence of the specified element in
* this vector, searching backwards from {@code index}, or returns -1 if
* the element is not found.
* More formally, returns the highest index {@code i} such that
* {@code (i <= index && Objects.equals(o, get(i)))},
* or -1 if there is no such index.
*
* @param o element to search for
* @param index index to start searching backwards from
* @return the index of the last occurrence of the element at position
* less than or equal to {@code index} in this vector;
* -1 if the element is not found.
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException if the specified index is greater
* than or equal to the current size of this vector
*/
public synchronized int lastIndexOf(Object o, int index) {
if (index >= elementCount)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(index + " >= "+ elementCount);
if (o == null) {
for (int i = index; i >= 0; i--)
if (elementData[i]==null)
return i;
} else {
for (int i = index; i >= 0; i--)
if (o.equals(elementData[i]))
return i;
}
return -1;
}
/**
* Returns the component at the specified index.
*
* <p>This method is identical in functionality to the {@link #get(int)}
* method (which is part of the {@link List} interface).
*
* @param index an index into this vector
* @return the component at the specified index
* @throws ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException if the index is out of range
* ({@code index < 0 || index >= size()})
*/
public synchronized E elementAt(int index) {
if (index >= elementCount) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index + " >= " + elementCount);
}
return elementData(index);
}
/**
* Returns the first component (the item at index {@code 0}) of
* this vector.
*
* @return the first component of this vector
* @throws NoSuchElementException if this vector has no components
*/
public synchronized E firstElement() {
if (elementCount == 0) {
throw new NoSuchElementException();
}
return elementData(0);
}
/**
* Returns the last component of the vector.
*
* @return the last component of the vector, i.e., the component at index
* {@code size() - 1}
* @throws NoSuchElementException if this vector is empty
*/
public synchronized E lastElement() {
if (elementCount == 0) {
throw new NoSuchElementException();
}
return elementData(elementCount - 1);
}
/**
* Sets the component at the specified {@code index} of this
* vector to be the specified object. The previous component at that
* position is discarded.
*
* <p>The index must be a value greater than or equal to {@code 0}
* and less than the current size of the vector.
*
* <p>This method is identical in functionality to the
* {@link #set(int, Object) set(int, E)}
* method (which is part of the {@link List} interface). Note that the
* {@code set} method reverses the order of the parameters, to more closely
* match array usage. Note also that the {@code set} method returns the
* old value that was stored at the specified position.
*
* @param obj what the component is to be set to
* @param index the specified index
* @throws ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException if the index is out of range
* ({@code index < 0 || index >= size()})
*/
public synchronized void setElementAt(E obj, int index) {
if (index >= elementCount) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index + " >= " +
elementCount);
}
elementData[index] = obj;
}
/**
* Deletes the component at the specified index. Each component in
* this vector with an index greater or equal to the specified
* {@code index} is shifted downward to have an index one
* smaller than the value it had previously. The size of this vector
* is decreased by {@code 1}.
*
* <p>The index must be a value greater than or equal to {@code 0}
* and less than the current size of the vector.
*
* <p>This method is identical in functionality to the {@link #remove(int)}
* method (which is part of the {@link List} interface). Note that the
* {@code remove} method returns the old value that was stored at the
* specified position.
*
* @param index the index of the object to remove
* @throws ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException if the index is out of range
* ({@code index < 0 || index >= size()})
*/
public synchronized void removeElementAt(int index) {
if (index >= elementCount) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index + " >= " +
elementCount);
}
else if (index < 0) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index);
}
int j = elementCount - index - 1;
if (j > 0) {
System.arraycopy(elementData, index + 1, elementData, index, j);
}
modCount++;
elementCount--;
elementData[elementCount] = null; /* to let gc do its work */
}
/**
* Inserts the specified object as a component in this vector at the
* specified {@code index}. Each component in this vector with
* an index greater or equal to the specified {@code index} is
* shifted upward to have an index one greater than the value it had
* previously.
*
* <p>The index must be a value greater than or equal to {@code 0}
* and less than or equal to the current size of the vector. (If the
* index is equal to the current size of the vector, the new element
* is appended to the Vector.)
*
* <p>This method is identical in functionality to the
* {@link #add(int, Object) add(int, E)}
* method (which is part of the {@link List} interface). Note that the
* {@code add} method reverses the order of the parameters, to more closely
* match array usage.
*
* @param obj the component to insert
* @param index where to insert the new component
* @throws ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException if the index is out of range
* ({@code index < 0 || index > size()})
*/
public synchronized void insertElementAt(E obj, int index) {
if (index > elementCount) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index
+ " > " + elementCount);
}
modCount++;
final int s = elementCount;
Object[] elementData = this.elementData;
if (s == elementData.length)
elementData = grow();
System.arraycopy(elementData, index,
elementData, index + 1,
s - index);
elementData[index] = obj;
elementCount = s + 1;
}
/**
* Adds the specified component to the end of this vector,
* increasing its size by one. The capacity of this vector is
* increased if its size becomes greater than its capacity.
*
* <p>This method is identical in functionality to the
* {@link #add(Object) add(E)}
* method (which is part of the {@link List} interface).
*
* @param obj the component to be added
*/
public synchronized void addElement(E obj) {
modCount++;
add(obj, elementData, elementCount);
}
/**
* Removes the first (lowest-indexed) occurrence of the argument
* from this vector. If the object is found in this vector, each
* component in the vector with an index greater or equal to the
* object's index is shifted downward to have an index one smaller
* than the value it had previously.
*
* <p>This method is identical in functionality to the
* {@link #remove(Object)} method (which is part of the
* {@link List} interface).
*
* @param obj the component to be removed
* @return {@code true} if the argument was a component of this
* vector; {@code false} otherwise.
*/
public synchronized boolean removeElement(Object obj) {
modCount++;
int i = indexOf(obj);
if (i >= 0) {
removeElementAt(i);
return true;
}
return false;
}
/**
* Removes all components from this vector and sets its size to zero.
*
* <p>This method is identical in functionality to the {@link #clear}
* method (which is part of the {@link List} interface).
*/
public synchronized void removeAllElements() {
final Object[] es = elementData;
for (int to = elementCount, i = elementCount = 0; i < to; i++)
es[i] = null;
modCount++;
}
/**
* Returns a clone of this vector. The copy will contain a
* reference to a clone of the internal data array, not a reference
* to the original internal data array of this {@code Vector} object.
*
* @return a clone of this vector
*/
public synchronized Object clone() {
try {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Vector<E> v = (Vector<E>) super.clone();
v.elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, elementCount);
v.modCount = 0;
return v;
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
// this shouldn't happen, since we are Cloneable
throw new InternalError(e);
}
}
/**
* Returns an array containing all of the elements in this Vector
* in the correct order.
*
* @since 1.2
*/
public synchronized Object[] toArray() {
return Arrays.copyOf(elementData, elementCount);
}
/**
* Returns an array containing all of the elements in this Vector in the
* correct order; the runtime type of the returned array is that of the
* specified array. If the Vector fits in the specified array, it is
* returned therein. Otherwise, a new array is allocated with the runtime
* type of the specified array and the size of this Vector.
*
* <p>If the Vector fits in the specified array with room to spare
* (i.e., the array has more elements than the Vector),
* the element in the array immediately following the end of the
* Vector is set to null. (This is useful in determining the length
* of the Vector <em>only</em> if the caller knows that the Vector
* does not contain any null elements.)
*
* @param <T> type of array elements. The same type as {@code <E>} or a
* supertype of {@code <E>}.
* @param a the array into which the elements of the Vector are to
* be stored, if it is big enough; otherwise, a new array of the
* same runtime type is allocated for this purpose.
* @return an array containing the elements of the Vector
* @throws ArrayStoreException if the runtime type of a, {@code <T>}, is not
* a supertype of the runtime type, {@code <E>}, of every element in this
* Vector
* @throws NullPointerException if the given array is null
* @since 1.2
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public synchronized <T> T[] toArray(T[] a) {
if (a.length < elementCount)
return (T[]) Arrays.copyOf(elementData, elementCount, a.getClass());
System.arraycopy(elementData, 0, a, 0, elementCount);
if (a.length > elementCount)
a[elementCount] = null;
return a;
}
// Positional Access Operations
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
E elementData(int index) {
return (E) elementData[index];
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
static <E> E elementAt(Object[] es, int index) {
return (E) es[index];
}
/**
* Returns the element at the specified position in this Vector.
*
* @param index index of the element to return
* @return object at the specified index
* @throws ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException if the index is out of range
* ({@code index < 0 || index >= size()})
* @since 1.2
*/
public synchronized E get(int index) {
if (index >= elementCount)
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index);
return elementData(index);
}
/**
* Replaces the element at the specified position in this Vector with the
* specified element.
*
* @param index index of the element to replace
* @param element element to be stored at the specified position
* @return the element previously at the specified position
* @throws ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException if the index is out of range
* ({@code index < 0 || index >= size()})
* @since 1.2
*/
public synchronized E set(int index, E element) {
if (index >= elementCount)
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index);
E oldValue = elementData(index);
elementData[index] = element;
return oldValue;
}
/**
* This helper method split out from add(E) to keep method
* bytecode size under 35 (the -XX:MaxInlineSize default value),
* which helps when add(E) is called in a C1-compiled loop.
*/
private void add(E e, Object[] elementData, int s) {
if (s == elementData.length)
elementData = grow();
elementData[s] = e;
elementCount = s + 1;
}
/**
* Appends the specified element to the end of this Vector.
*
* @param e element to be appended to this Vector
* @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Collection#add})
* @since 1.2
*/
public synchronized boolean add(E e) {
modCount++;
add(e, elementData, elementCount);
return true;
}
/**
* Removes the first occurrence of the specified element in this Vector
* If the Vector does not contain the element, it is unchanged. More
* formally, removes the element with the lowest index i such that
* {@code Objects.equals(o, get(i))} (if such
* an element exists).
*
* @param o element to be removed from this Vector, if present
* @return true if the Vector contained the specified element
* @since 1.2
*/
public boolean remove(Object o) {
return removeElement(o);
}
/**
* Inserts the specified element at the specified position in this Vector.
* Shifts the element currently at that position (if any) and any
* subsequent elements to the right (adds one to their indices).
*
* @param index index at which the specified element is to be inserted
* @param element element to be inserted
* @throws ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException if the index is out of range
* ({@code index < 0 || index > size()})
* @since 1.2
*/
public void add(int index, E element) {
insertElementAt(element, index);
}
/**
* Removes the element at the specified position in this Vector.
* Shifts any subsequent elements to the left (subtracts one from their
* indices). Returns the element that was removed from the Vector.
*
* @param index the index of the element to be removed
* @return element that was removed
* @throws ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException if the index is out of range
* ({@code index < 0 || index >= size()})
* @since 1.2
*/
public synchronized E remove(int index) {
modCount++;
if (index >= elementCount)
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index);
E oldValue = elementData(index);
int numMoved = elementCount - index - 1;
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index,
numMoved);
elementData[--elementCount] = null; // Let gc do its work
return oldValue;
}
/**
* Removes all of the elements from this Vector. The Vector will
* be empty after this call returns (unless it throws an exception).
*
* @since 1.2
*/
public void clear() {
removeAllElements();
}
// Bulk Operations
/**
* Returns true if this Vector contains all of the elements in the
* specified Collection.
*
* @param c a collection whose elements will be tested for containment
* in this Vector
* @return true if this Vector contains all of the elements in the
* specified collection
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null
*/
public synchronized boolean containsAll(Collection<?> c) {
return super.containsAll(c);
}
/**
* Appends all of the elements in the specified Collection to the end of
* this Vector, in the order that they are returned by the specified
* Collection's Iterator. The behavior of this operation is undefined if
* the specified Collection is modified while the operation is in progress.
* (This implies that the behavior of this call is undefined if the
* specified Collection is this Vector, and this Vector is nonempty.)
*
* @param c elements to be inserted into this Vector
* @return {@code true} if this Vector changed as a result of the call
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null
* @since 1.2
*/
public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) {
Object[] a = c.toArray();
modCount++;
int numNew = a.length;
if (numNew == 0)
return false;
synchronized (this) {
Object[] elementData = this.elementData;
final int s = elementCount;
if (numNew > elementData.length - s)
elementData = grow(s + numNew);
System.arraycopy(a, 0, elementData, s, numNew);
elementCount = s + numNew;
return true;
}
}
/**
* Removes from this Vector all of its elements that are contained in the
* specified Collection.
*
* @param c a collection of elements to be removed from the Vector
* @return true if this Vector changed as a result of the call
* @throws ClassCastException if the types of one or more elements
* in this vector are incompatible with the specified
* collection
* (<a href="Collection.html#optional-restrictions">optional</a>)
* @throws NullPointerException if this vector contains one or more null
* elements and the specified collection does not support null
* elements
* (<a href="Collection.html#optional-restrictions">optional</a>),
* or if the specified collection is null
* @since 1.2
*/
public boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c) {
Objects.requireNonNull(c);
return bulkRemove(e -> c.contains(e));
}
/**
* Retains only the elements in this Vector that are contained in the
* specified Collection. In other words, removes from this Vector all
* of its elements that are not contained in the specified Collection.
*
* @param c a collection of elements to be retained in this Vector
* (all other elements are removed)
* @return true if this Vector changed as a result of the call
* @throws ClassCastException if the types of one or more elements
* in this vector are incompatible with the specified
* collection
* (<a href="Collection.html#optional-restrictions">optional</a>)
* @throws NullPointerException if this vector contains one or more null
* elements and the specified collection does not support null
* elements
* (<a href="Collection.html#optional-restrictions">optional</a>),
* or if the specified collection is null
* @since 1.2
*/
public boolean retainAll(Collection<?> c) {
Objects.requireNonNull(c);
return bulkRemove(e -> !c.contains(e));
}
/**
* @throws NullPointerException {@inheritDoc}
*/
@Override
public boolean removeIf(Predicate<? super E> filter) {
Objects.requireNonNull(filter);
return bulkRemove(filter);
}
// A tiny bit set implementation
private static long[] nBits(int n) {
return new long[((n - 1) >> 6) + 1];
}
private static void setBit(long[] bits, int i) {
bits[i >> 6] |= 1L << i;
}
private static boolean isClear(long[] bits, int i) {
return (bits[i >> 6] & (1L << i)) == 0;
}
private synchronized boolean bulkRemove(Predicate<? super E> filter) {
int expectedModCount = modCount;
final Object[] es = elementData;
final int end = elementCount;
int i;
// Optimize for initial run of survivors
for (i = 0; i < end && !filter.test(elementAt(es, i)); i++)
;
// Tolerate predicates that reentrantly access the collection for
// read (but writers still get CME), so traverse once to find
// elements to delete, a second pass to physically expunge.
if (i < end) {
final int beg = i;
final long[] deathRow = nBits(end - beg);
deathRow[0] = 1L; // set bit 0
for (i = beg + 1; i < end; i++)
if (filter.test(elementAt(es, i)))
setBit(deathRow, i - beg);
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
modCount++;
int w = beg;
for (i = beg; i < end; i++)
if (isClear(deathRow, i - beg))
es[w++] = es[i];
for (i = elementCount = w; i < end; i++)
es[i] = null;
return true;
} else {
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
return false;
}
}
/**
* Inserts all of the elements in the specified Collection into this
* Vector at the specified position. Shifts the element currently at
* that position (if any) and any subsequent elements to the right
* (increases their indices). The new elements will appear in the Vector
* in the order that they are returned by the specified Collection's
* iterator.
*
* @param index index at which to insert the first element from the
* specified collection
* @param c elements to be inserted into this Vector
* @return {@code true} if this Vector changed as a result of the call
* @throws ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException if the index is out of range
* ({@code index < 0 || index > size()})
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null
* @since 1.2
*/
public synchronized boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) {
if (index < 0 || index > elementCount)
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index);
Object[] a = c.toArray();
modCount++;
int numNew = a.length;
if (numNew == 0)
return false;
Object[] elementData = this.elementData;
final int s = elementCount;
if (numNew > elementData.length - s)
elementData = grow(s + numNew);
int numMoved = s - index;
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index,
elementData, index + numNew,
numMoved);
System.arraycopy(a, 0, elementData, index, numNew);
elementCount = s + numNew;
return true;
}
/**
* Compares the specified Object with this Vector for equality. Returns
* true if and only if the specified Object is also a List, both Lists
* have the same size, and all corresponding pairs of elements in the two
* Lists are <em>equal</em>. (Two elements {@code e1} and
* {@code e2} are <em>equal</em> if {@code Objects.equals(e1, e2)}.)
* In other words, two Lists are defined to be
* equal if they contain the same elements in the same order.
*
* @param o the Object to be compared for equality with this Vector
* @return true if the specified Object is equal to this Vector
*/
public synchronized boolean equals(Object o) {
return super.equals(o);
}
/**
* Returns the hash code value for this Vector.
*/
public synchronized int hashCode() {
return super.hashCode();
}
/**
* Returns a string representation of this Vector, containing
* the String representation of each element.
*/
public synchronized String toString() {
return super.toString();
}
/**
* Returns a view of the portion of this List between fromIndex,
* inclusive, and toIndex, exclusive. (If fromIndex and toIndex are
* equal, the returned List is empty.) The returned List is backed by this
* List, so changes in the returned List are reflected in this List, and
* vice-versa. The returned List supports all of the optional List
* operations supported by this List.
*
* <p>This method eliminates the need for explicit range operations (of
* the sort that commonly exist for arrays). Any operation that expects
* a List can be used as a range operation by operating on a subList view
* instead of a whole List. For example, the following idiom
* removes a range of elements from a List:
* <pre>
* list.subList(from, to).clear();
* </pre>
* Similar idioms may be constructed for indexOf and lastIndexOf,
* and all of the algorithms in the Collections class can be applied to
* a subList.
*
* <p>The semantics of the List returned by this method become undefined if
* the backing list (i.e., this List) is <i>structurally modified</i> in
* any way other than via the returned List. (Structural modifications are
* those that change the size of the List, or otherwise perturb it in such
* a fashion that iterations in progress may yield incorrect results.)
*
* @param fromIndex low endpoint (inclusive) of the subList
* @param toIndex high endpoint (exclusive) of the subList
* @return a view of the specified range within this List
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException if an endpoint index value is out of range
* {@code (fromIndex < 0 || toIndex > size)}
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the endpoint indices are out of order
* {@code (fromIndex > toIndex)}
*/
public synchronized List<E> subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
return Collections.synchronizedList(super.subList(fromIndex, toIndex),
this);
}
/**
* Removes from this list all of the elements whose index is between
* {@code fromIndex}, inclusive, and {@code toIndex}, exclusive.
* Shifts any succeeding elements to the left (reduces their index).
* This call shortens the list by {@code (toIndex - fromIndex)} elements.
* (If {@code toIndex==fromIndex}, this operation has no effect.)
*/
protected synchronized void removeRange(int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
modCount++;
shiftTailOverGap(elementData, fromIndex, toIndex);
}
/** Erases the gap from lo to hi, by sliding down following elements. */
private void shiftTailOverGap(Object[] es, int lo, int hi) {
System.arraycopy(es, hi, es, lo, elementCount - hi);
for (int to = elementCount, i = (elementCount -= hi - lo); i < to; i++)
es[i] = null;
}
/**
* Loads a {@code Vector} instance from a stream
* (that is, deserializes it).
* This method performs checks to ensure the consistency
* of the fields.
*
* @param in the stream
* @throws java.io.IOException if an I/O error occurs
* @throws ClassNotFoundException if the stream contains data
* of a non-existing class
*/
@java.io.Serial
private void readObject(ObjectInputStream in)
throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
ObjectInputStream.GetField gfields = in.readFields();
int count = gfields.get("elementCount", 0);
Object[] data = (Object[])gfields.get("elementData", null);
if (count < 0 || data == null || count > data.length) {
throw new StreamCorruptedException("Inconsistent vector internals");
}
elementCount = count;
elementData = data.clone();
}
/**
* Saves the state of the {@code Vector} instance to a stream
* (that is, serializes it).
* This method performs synchronization to ensure the consistency
* of the serialized data.
*
* @param s the stream
* @throws java.io.IOException if an I/O error occurs
*/
@java.io.Serial
private void writeObject(java.io.ObjectOutputStream s)
throws java.io.IOException {
final java.io.ObjectOutputStream.PutField fields = s.putFields();
final Object[] data;
synchronized (this) {
fields.put("capacityIncrement", capacityIncrement);
fields.put("elementCount", elementCount);
data = elementData.clone();
}
fields.put("elementData", data);
s.writeFields();
}
/**
* Returns a list iterator over the elements in this list (in proper
* sequence), starting at the specified position in the list.
* The specified index indicates the first element that would be
* returned by an initial call to {@link ListIterator#next next}.
* An initial call to {@link ListIterator#previous previous} would
* return the element with the specified index minus one.
*
* <p>The returned list iterator is <a href="#fail-fast"><i>fail-fast</i></a>.
*
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public synchronized ListIterator<E> listIterator(int index) {
if (index < 0 || index > elementCount)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Index: "+index);
return new ListItr(index);
}
/**
* Returns a list iterator over the elements in this list (in proper
* sequence).
*
* <p>The returned list iterator is <a href="#fail-fast"><i>fail-fast</i></a>.
*
* @see #listIterator(int)
*/
public synchronized ListIterator<E> listIterator() {
return new ListItr(0);
}
/**
* Returns an iterator over the elements in this list in proper sequence.
*
* <p>The returned iterator is <a href="#fail-fast"><i>fail-fast</i></a>.
*
* @return an iterator over the elements in this list in proper sequence
*/
public synchronized Iterator<E> iterator() {
return new Itr();
}
/**
* An optimized version of AbstractList.Itr
*/
private class Itr implements Iterator<E> {
int cursor; // index of next element to return
int lastRet = -1; // index of last element returned; -1 if no such
int expectedModCount = modCount;
public boolean hasNext() {
// Racy but within spec, since modifications are checked
// within or after synchronization in next/previous
return cursor != elementCount;
}
public E next() {
synchronized (Vector.this) {
checkForComodification();
int i = cursor;
if (i >= elementCount)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
cursor = i + 1;
return elementData(lastRet = i);
}
}
public void remove() {
if (lastRet == -1)
throw new IllegalStateException();
synchronized (Vector.this) {
checkForComodification();
Vector.this.remove(lastRet);
expectedModCount = modCount;
}
cursor = lastRet;
lastRet = -1;
}
@Override
public void forEachRemaining(Consumer<? super E> action) {
Objects.requireNonNull(action);
synchronized (Vector.this) {
final int size = elementCount;
int i = cursor;
if (i >= size) {
return;
}
final Object[] es = elementData;
if (i >= es.length)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
while (i < size && modCount == expectedModCount)
action.accept(elementAt(es, i++));
// update once at end of iteration to reduce heap write traffic
cursor = i;
lastRet = i - 1;
checkForComodification();
}
}
final void checkForComodification() {
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
/**
* An optimized version of AbstractList.ListItr
*/
final class ListItr extends Itr implements ListIterator<E> {
ListItr(int index) {
super();
cursor = index;
}
public boolean hasPrevious() {
return cursor != 0;
}
public int nextIndex() {
return cursor;
}
public int previousIndex() {
return cursor - 1;
}
public E previous() {
synchronized (Vector.this) {
checkForComodification();
int i = cursor - 1;
if (i < 0)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
cursor = i;
return elementData(lastRet = i);
}
}
public void set(E e) {
if (lastRet == -1)
throw new IllegalStateException();
synchronized (Vector.this) {
checkForComodification();
Vector.this.set(lastRet, e);
}
}
public void add(E e) {
int i = cursor;
synchronized (Vector.this) {
checkForComodification();
Vector.this.add(i, e);
expectedModCount = modCount;
}
cursor = i + 1;
lastRet = -1;
}
}
/**
* @throws NullPointerException {@inheritDoc}
*/
@Override
public synchronized void forEach(Consumer<? super E> action) {
Objects.requireNonNull(action);
final int expectedModCount = modCount;
final Object[] es = elementData;
final int size = elementCount;
for (int i = 0; modCount == expectedModCount && i < size; i++)
action.accept(elementAt(es, i));
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
/**
* @throws NullPointerException {@inheritDoc}
*/
@Override
public synchronized void replaceAll(UnaryOperator<E> operator) {
Objects.requireNonNull(operator);
final int expectedModCount = modCount;
final Object[] es = elementData;
final int size = elementCount;
for (int i = 0; modCount == expectedModCount && i < size; i++)
es[i] = operator.apply(elementAt(es, i));
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
// TODO(8203662): remove increment of modCount from ...
modCount++;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
@Override
public synchronized void sort(Comparator<? super E> c) {
final int expectedModCount = modCount;
Arrays.sort((E[]) elementData, 0, elementCount, c);
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
modCount++;
}
/**
* Creates a <em><a href="Spliterator.html#binding">late-binding</a></em>
* and <em>fail-fast</em> {@link Spliterator} over the elements in this
* list.
*
* <p>The {@code Spliterator} reports {@link Spliterator#SIZED},
* {@link Spliterator#SUBSIZED}, and {@link Spliterator#ORDERED}.
* Overriding implementations should document the reporting of additional
* characteristic values.
*
* @return a {@code Spliterator} over the elements in this list
* @since 1.8
*/
@Override
public Spliterator<E> spliterator() {
return new VectorSpliterator(null, 0, -1, 0);
}
/** Similar to ArrayList Spliterator */
final class VectorSpliterator implements Spliterator<E> {
private Object[] array;
private int index; // current index, modified on advance/split
private int fence; // -1 until used; then one past last index
private int expectedModCount; // initialized when fence set
/** Creates new spliterator covering the given range. */
VectorSpliterator(Object[] array, int origin, int fence,
int expectedModCount) {
this.array = array;
this.index = origin;
this.fence = fence;
this.expectedModCount = expectedModCount;
}
private int getFence() { // initialize on first use
int hi;
if ((hi = fence) < 0) {
synchronized (Vector.this) {
array = elementData;
expectedModCount = modCount;
hi = fence = elementCount;
}
}
return hi;
}
public Spliterator<E> trySplit() {
int hi = getFence(), lo = index, mid = (lo + hi) >>> 1;
return (lo >= mid) ? null :
new VectorSpliterator(array, lo, index = mid, expectedModCount);
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public boolean tryAdvance(Consumer<? super E> action) {
Objects.requireNonNull(action);
int i;
if (getFence() > (i = index)) {
index = i + 1;
action.accept((E)array[i]);
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
return true;
}
return false;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public void forEachRemaining(Consumer<? super E> action) {
Objects.requireNonNull(action);
final int hi = getFence();
final Object[] a = array;
int i;
for (i = index, index = hi; i < hi; i++)
action.accept((E) a[i]);
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
public long estimateSize() {
return getFence() - index;
}
public int characteristics() {
return Spliterator.ORDERED | Spliterator.SIZED | Spliterator.SUBSIZED;
}
}
void checkInvariants() {
// assert elementCount >= 0;
// assert elementCount == elementData.length || elementData[elementCount] == null;
}
}
# Stack
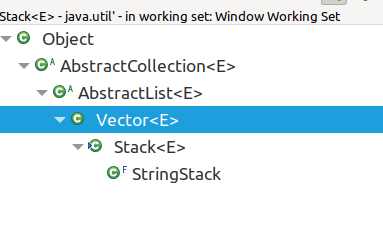
menti.com
2335 3741
Why do Stacks have add and push?
# Stack

menti.com
2335 3741
Difference between Vector and ArrayList
# ArrayList
menti.com 2335 3741
Difference between Vector and ArrayList
# ArrayList
menti.com 2335 3741
Difference between Vector and ArrayList
# ArrayList
/*
* Copyright (c) 1997, 2023, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
* DO NOT ALTER OR REMOVE COPYRIGHT NOTICES OR THIS FILE HEADER.
*
* This code is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify it
* under the terms of the GNU General Public License version 2 only, as
* published by the Free Software Foundation. Oracle designates this
* particular file as subject to the "Classpath" exception as provided
* by Oracle in the LICENSE file that accompanied this code.
*
* This code is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT
* ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or
* FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU General Public License
* version 2 for more details (a copy is included in the LICENSE file that
* accompanied this code).
*
* You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License version
* 2 along with this work; if not, write to the Free Software Foundation,
* Inc., 51 Franklin St, Fifth Floor, Boston, MA 02110-1301 USA.
*
* Please contact Oracle, 500 Oracle Parkway, Redwood Shores, CA 94065 USA
* or visit www.oracle.com if you need additional information or have any
* questions.
*/
package java.util;
import java.util.function.Consumer;
import java.util.function.Predicate;
import java.util.function.UnaryOperator;
import jdk.internal.access.SharedSecrets;
import jdk.internal.util.ArraysSupport;
/**
* Resizable-array implementation of the {@code List} interface. Implements
* all optional list operations, and permits all elements, including
* {@code null}. In addition to implementing the {@code List} interface,
* this class provides methods to manipulate the size of the array that is
* used internally to store the list. (This class is roughly equivalent to
* {@code Vector}, except that it is unsynchronized.)
*
* <p>The {@code size}, {@code isEmpty}, {@code get}, {@code set},
* {@code iterator}, and {@code listIterator} operations run in constant
* time. The {@code add} operation runs in <i>amortized constant time</i>,
* that is, adding n elements requires O(n) time. All of the other operations
* run in linear time (roughly speaking). The constant factor is low compared
* to that for the {@code LinkedList} implementation.
*
* <p>Each {@code ArrayList} instance has a <i>capacity</i>. The capacity is
* the size of the array used to store the elements in the list. It is always
* at least as large as the list size. As elements are added to an ArrayList,
* its capacity grows automatically. The details of the growth policy are not
* specified beyond the fact that adding an element has constant amortized
* time cost.
*
* <p>An application can increase the capacity of an {@code ArrayList} instance
* before adding a large number of elements using the {@code ensureCapacity}
* operation. This may reduce the amount of incremental reallocation.
*
* <p><strong>Note that this implementation is not synchronized.</strong>
* If multiple threads access an {@code ArrayList} instance concurrently,
* and at least one of the threads modifies the list structurally, it
* <i>must</i> be synchronized externally. (A structural modification is
* any operation that adds or deletes one or more elements, or explicitly
* resizes the backing array; merely setting the value of an element is not
* a structural modification.) This is typically accomplished by
* synchronizing on some object that naturally encapsulates the list.
*
* If no such object exists, the list should be "wrapped" using the
* {@link Collections#synchronizedList Collections.synchronizedList}
* method. This is best done at creation time, to prevent accidental
* unsynchronized access to the list:<pre>
* List list = Collections.synchronizedList(new ArrayList(...));</pre>
*
* <p id="fail-fast">
* The iterators returned by this class's {@link #iterator() iterator} and
* {@link #listIterator(int) listIterator} methods are <em>fail-fast</em>:
* if the list is structurally modified at any time after the iterator is
* created, in any way except through the iterator's own
* {@link ListIterator#remove() remove} or
* {@link ListIterator#add(Object) add} methods, the iterator will throw a
* {@link ConcurrentModificationException}. Thus, in the face of
* concurrent modification, the iterator fails quickly and cleanly, rather
* than risking arbitrary, non-deterministic behavior at an undetermined
* time in the future.
*
* <p>Note that the fail-fast behavior of an iterator cannot be guaranteed
* as it is, generally speaking, impossible to make any hard guarantees in the
* presence of unsynchronized concurrent modification. Fail-fast iterators
* throw {@code ConcurrentModificationException} on a best-effort basis.
* Therefore, it would be wrong to write a program that depended on this
* exception for its correctness: <i>the fail-fast behavior of iterators
* should be used only to detect bugs.</i>
*
* <p>This class is a member of the
* <a href="{@docRoot}/java.base/java/util/package-summary.html#CollectionsFramework">
* Java Collections Framework</a>.
*
* @param <E> the type of elements in this list
*
* @author Josh Bloch
* @author Neal Gafter
* @see Collection
* @see List
* @see LinkedList
* @see Vector
* @since 1.2
*/
public class ArrayList<E> extends AbstractList<E>
implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
{
@java.io.Serial
private static final long serialVersionUID = 8683452581122892189L;
/**
* Default initial capacity.
*/
private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10;
/**
* Shared empty array instance used for empty instances.
*/
private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};
/**
* Shared empty array instance used for default sized empty instances. We
* distinguish this from EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA to know how much to inflate when
* first element is added.
*/
private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};
/**
* The array buffer into which the elements of the ArrayList are stored.
* The capacity of the ArrayList is the length of this array buffer. Any
* empty ArrayList with elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA
* will be expanded to DEFAULT_CAPACITY when the first element is added.
*/
transient Object[] elementData; // non-private to simplify nested class access
/**
* The size of the ArrayList (the number of elements it contains).
*
* @serial
*/
private int size;
/**
* Constructs an empty list with the specified initial capacity.
*
* @param initialCapacity the initial capacity of the list
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the specified initial capacity
* is negative
*/
public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) {
if (initialCapacity > 0) {
this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];
} else if (initialCapacity == 0) {
this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
} else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+
initialCapacity);
}
}
/**
* Constructs an empty list with an initial capacity of ten.
*/
public ArrayList() {
this.elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
}
/**
* Constructs a list containing the elements of the specified
* collection, in the order they are returned by the collection's
* iterator.
*
* @param c the collection whose elements are to be placed into this list
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null
*/
public ArrayList(Collection<? extends E> c) {
Object[] a = c.toArray();
if ((size = a.length) != 0) {
if (c.getClass() == ArrayList.class) {
elementData = a;
} else {
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(a, size, Object[].class);
}
} else {
// replace with empty array.
elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
}
}
/**
* Trims the capacity of this {@code ArrayList} instance to be the
* list's current size. An application can use this operation to minimize
* the storage of an {@code ArrayList} instance.
*/
public void trimToSize() {
modCount++;
if (size < elementData.length) {
elementData = (size == 0)
? EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA
: Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size);
}
}
/**
* Increases the capacity of this {@code ArrayList} instance, if
* necessary, to ensure that it can hold at least the number of elements
* specified by the minimum capacity argument.
*
* @param minCapacity the desired minimum capacity
*/
public void ensureCapacity(int minCapacity) {
if (minCapacity > elementData.length
&& !(elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA
&& minCapacity <= DEFAULT_CAPACITY)) {
modCount++;
grow(minCapacity);
}
}
/**
* Increases the capacity to ensure that it can hold at least the
* number of elements specified by the minimum capacity argument.
*
* @param minCapacity the desired minimum capacity
* @throws OutOfMemoryError if minCapacity is less than zero
*/
private Object[] grow(int minCapacity) {
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
if (oldCapacity > 0 || elementData != DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) {
int newCapacity = ArraysSupport.newLength(oldCapacity,
minCapacity - oldCapacity, /* minimum growth */
oldCapacity >> 1 /* preferred growth */);
return elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
} else {
return elementData = new Object[Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity)];
}
}
private Object[] grow() {
return grow(size + 1);
}
/**
* Returns the number of elements in this list.
*
* @return the number of elements in this list
*/
public int size() {
return size;
}
/**
* Returns {@code true} if this list contains no elements.
*
* @return {@code true} if this list contains no elements
*/
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size == 0;
}
/**
* Returns {@code true} if this list contains the specified element.
* More formally, returns {@code true} if and only if this list contains
* at least one element {@code e} such that
* {@code Objects.equals(o, e)}.
*
* @param o element whose presence in this list is to be tested
* @return {@code true} if this list contains the specified element
*/
public boolean contains(Object o) {
return indexOf(o) >= 0;
}
/**
* Returns the index of the first occurrence of the specified element
* in this list, or -1 if this list does not contain the element.
* More formally, returns the lowest index {@code i} such that
* {@code Objects.equals(o, get(i))},
* or -1 if there is no such index.
*/
public int indexOf(Object o) {
return indexOfRange(o, 0, size);
}
int indexOfRange(Object o, int start, int end) {
Object[] es = elementData;
if (o == null) {
for (int i = start; i < end; i++) {
if (es[i] == null) {
return i;
}
}
} else {
for (int i = start; i < end; i++) {
if (o.equals(es[i])) {
return i;
}
}
}
return -1;
}
/**
* Returns the index of the last occurrence of the specified element
* in this list, or -1 if this list does not contain the element.
* More formally, returns the highest index {@code i} such that
* {@code Objects.equals(o, get(i))},
* or -1 if there is no such index.
*/
public int lastIndexOf(Object o) {
return lastIndexOfRange(o, 0, size);
}
int lastIndexOfRange(Object o, int start, int end) {
Object[] es = elementData;
if (o == null) {
for (int i = end - 1; i >= start; i--) {
if (es[i] == null) {
return i;
}
}
} else {
for (int i = end - 1; i >= start; i--) {
if (o.equals(es[i])) {
return i;
}
}
}
return -1;
}
/**
* Returns a shallow copy of this {@code ArrayList} instance. (The
* elements themselves are not copied.)
*
* @return a clone of this {@code ArrayList} instance
*/
public Object clone() {
try {
ArrayList<?> v = (ArrayList<?>) super.clone();
v.elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size);
v.modCount = 0;
return v;
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
// this shouldn't happen, since we are Cloneable
throw new InternalError(e);
}
}
/**
* Returns an array containing all of the elements in this list
* in proper sequence (from first to last element).
*
* <p>The returned array will be "safe" in that no references to it are
* maintained by this list. (In other words, this method must allocate
* a new array). The caller is thus free to modify the returned array.
*
* <p>This method acts as bridge between array-based and collection-based
* APIs.
*
* @return an array containing all of the elements in this list in
* proper sequence
*/
public Object[] toArray() {
return Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size);
}
/**
* Returns an array containing all of the elements in this list in proper
* sequence (from first to last element); the runtime type of the returned
* array is that of the specified array. If the list fits in the
* specified array, it is returned therein. Otherwise, a new array is
* allocated with the runtime type of the specified array and the size of
* this list.
*
* <p>If the list fits in the specified array with room to spare
* (i.e., the array has more elements than the list), the element in
* the array immediately following the end of the collection is set to
* {@code null}. (This is useful in determining the length of the
* list <i>only</i> if the caller knows that the list does not contain
* any null elements.)
*
* @param a the array into which the elements of the list are to
* be stored, if it is big enough; otherwise, a new array of the
* same runtime type is allocated for this purpose.
* @return an array containing the elements of the list
* @throws ArrayStoreException if the runtime type of the specified array
* is not a supertype of the runtime type of every element in
* this list
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified array is null
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public <T> T[] toArray(T[] a) {
if (a.length < size)
// Make a new array of a's runtime type, but my contents:
return (T[]) Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size, a.getClass());
System.arraycopy(elementData, 0, a, 0, size);
if (a.length > size)
a[size] = null;
return a;
}
// Positional Access Operations
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
E elementData(int index) {
return (E) elementData[index];
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
static <E> E elementAt(Object[] es, int index) {
return (E) es[index];
}
/**
* Returns the element at the specified position in this list.
*
* @param index index of the element to return
* @return the element at the specified position in this list
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public E get(int index) {
Objects.checkIndex(index, size);
return elementData(index);
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*
* @throws NoSuchElementException {@inheritDoc}
* @since 21
*/
public E getFirst() {
if (size == 0) {
throw new NoSuchElementException();
} else {
return elementData(0);
}
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*
* @throws NoSuchElementException {@inheritDoc}
* @since 21
*/
public E getLast() {
int last = size - 1;
if (last < 0) {
throw new NoSuchElementException();
} else {
return elementData(last);
}
}
/**
* Replaces the element at the specified position in this list with
* the specified element.
*
* @param index index of the element to replace
* @param element element to be stored at the specified position
* @return the element previously at the specified position
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public E set(int index, E element) {
Objects.checkIndex(index, size);
E oldValue = elementData(index);
elementData[index] = element;
return oldValue;
}
/**
* This helper method split out from add(E) to keep method
* bytecode size under 35 (the -XX:MaxInlineSize default value),
* which helps when add(E) is called in a C1-compiled loop.
*/
private void add(E e, Object[] elementData, int s) {
if (s == elementData.length)
elementData = grow();
elementData[s] = e;
size = s + 1;
}
/**
* Appends the specified element to the end of this list.
*
* @param e element to be appended to this list
* @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Collection#add})
*/
public boolean add(E e) {
modCount++;
add(e, elementData, size);
return true;
}
/**
* Inserts the specified element at the specified position in this
* list. Shifts the element currently at that position (if any) and
* any subsequent elements to the right (adds one to their indices).
*
* @param index index at which the specified element is to be inserted
* @param element element to be inserted
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public void add(int index, E element) {
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
modCount++;
final int s;
Object[] elementData;
if ((s = size) == (elementData = this.elementData).length)
elementData = grow();
System.arraycopy(elementData, index,
elementData, index + 1,
s - index);
elementData[index] = element;
size = s + 1;
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*
* @since 21
*/
public void addFirst(E element) {
add(0, element);
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*
* @since 21
*/
public void addLast(E element) {
add(element);
}
/**
* Removes the element at the specified position in this list.
* Shifts any subsequent elements to the left (subtracts one from their
* indices).
*
* @param index the index of the element to be removed
* @return the element that was removed from the list
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public E remove(int index) {
Objects.checkIndex(index, size);
final Object[] es = elementData;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") E oldValue = (E) es[index];
fastRemove(es, index);
return oldValue;
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*
* @throws NoSuchElementException {@inheritDoc}
* @since 21
*/
public E removeFirst() {
if (size == 0) {
throw new NoSuchElementException();
} else {
Object[] es = elementData;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") E oldValue = (E) es[0];
fastRemove(es, 0);
return oldValue;
}
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*
* @throws NoSuchElementException {@inheritDoc}
* @since 21
*/
public E removeLast() {
int last = size - 1;
if (last < 0) {
throw new NoSuchElementException();
} else {
Object[] es = elementData;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") E oldValue = (E) es[last];
fastRemove(es, last);
return oldValue;
}
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*/
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (o == this) {
return true;
}
if (!(o instanceof List)) {
return false;
}
final int expectedModCount = modCount;
// ArrayList can be subclassed and given arbitrary behavior, but we can
// still deal with the common case where o is ArrayList precisely
boolean equal = (o.getClass() == ArrayList.class)
? equalsArrayList((ArrayList<?>) o)
: equalsRange((List<?>) o, 0, size);
checkForComodification(expectedModCount);
return equal;
}
boolean equalsRange(List<?> other, int from, int to) {
final Object[] es = elementData;
if (to > es.length) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
var oit = other.iterator();
for (; from < to; from++) {
if (!oit.hasNext() || !Objects.equals(es[from], oit.next())) {
return false;
}
}
return !oit.hasNext();
}
private boolean equalsArrayList(ArrayList<?> other) {
final int otherModCount = other.modCount;
final int s = size;
boolean equal;
if (equal = (s == other.size)) {
final Object[] otherEs = other.elementData;
final Object[] es = elementData;
if (s > es.length || s > otherEs.length) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
for (int i = 0; i < s; i++) {
if (!Objects.equals(es[i], otherEs[i])) {
equal = false;
break;
}
}
}
other.checkForComodification(otherModCount);
return equal;
}
private void checkForComodification(final int expectedModCount) {
if (modCount != expectedModCount) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*/
public int hashCode() {
int expectedModCount = modCount;
int hash = hashCodeRange(0, size);
checkForComodification(expectedModCount);
return hash;
}
int hashCodeRange(int from, int to) {
final Object[] es = elementData;
if (to > es.length) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
int hashCode = 1;
for (int i = from; i < to; i++) {
Object e = es[i];
hashCode = 31 * hashCode + (e == null ? 0 : e.hashCode());
}
return hashCode;
}
/**
* Removes the first occurrence of the specified element from this list,
* if it is present. If the list does not contain the element, it is
* unchanged. More formally, removes the element with the lowest index
* {@code i} such that
* {@code Objects.equals(o, get(i))}
* (if such an element exists). Returns {@code true} if this list
* contained the specified element (or equivalently, if this list
* changed as a result of the call).
*
* @param o element to be removed from this list, if present
* @return {@code true} if this list contained the specified element
*/
public boolean remove(Object o) {
final Object[] es = elementData;
final int size = this.size;
int i = 0;
found: {
if (o == null) {
for (; i < size; i++)
if (es[i] == null)
break found;
} else {
for (; i < size; i++)
if (o.equals(es[i]))
break found;
}
return false;
}
fastRemove(es, i);
return true;
}
/**
* Private remove method that skips bounds checking and does not
* return the value removed.
*/
private void fastRemove(Object[] es, int i) {
modCount++;
final int newSize;
if ((newSize = size - 1) > i)
System.arraycopy(es, i + 1, es, i, newSize - i);
es[size = newSize] = null;
}
/**
* Removes all of the elements from this list. The list will
* be empty after this call returns.
*/
public void clear() {
modCount++;
final Object[] es = elementData;
for (int to = size, i = size = 0; i < to; i++)
es[i] = null;
}
/**
* Appends all of the elements in the specified collection to the end of
* this list, in the order that they are returned by the
* specified collection's Iterator. The behavior of this operation is
* undefined if the specified collection is modified while the operation
* is in progress. (This implies that the behavior of this call is
* undefined if the specified collection is this list, and this
* list is nonempty.)
*
* @param c collection containing elements to be added to this list
* @return {@code true} if this list changed as a result of the call
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null
*/
public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) {
Object[] a = c.toArray();
modCount++;
int numNew = a.length;
if (numNew == 0)
return false;
Object[] elementData;
final int s;
if (numNew > (elementData = this.elementData).length - (s = size))
elementData = grow(s + numNew);
System.arraycopy(a, 0, elementData, s, numNew);
size = s + numNew;
return true;
}
/**
* Inserts all of the elements in the specified collection into this
* list, starting at the specified position. Shifts the element
* currently at that position (if any) and any subsequent elements to
* the right (increases their indices). The new elements will appear
* in the list in the order that they are returned by the
* specified collection's iterator.
*
* @param index index at which to insert the first element from the
* specified collection
* @param c collection containing elements to be added to this list
* @return {@code true} if this list changed as a result of the call
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null
*/
public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) {
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
Object[] a = c.toArray();
modCount++;
int numNew = a.length;
if (numNew == 0)
return false;
Object[] elementData;
final int s;
if (numNew > (elementData = this.elementData).length - (s = size))
elementData = grow(s + numNew);
int numMoved = s - index;
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index,
elementData, index + numNew,
numMoved);
System.arraycopy(a, 0, elementData, index, numNew);
size = s + numNew;
return true;
}
/**
* Removes from this list all of the elements whose index is between
* {@code fromIndex}, inclusive, and {@code toIndex}, exclusive.
* Shifts any succeeding elements to the left (reduces their index).
* This call shortens the list by {@code (toIndex - fromIndex)} elements.
* (If {@code toIndex==fromIndex}, this operation has no effect.)
*
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException if {@code fromIndex} or
* {@code toIndex} is out of range
* ({@code fromIndex < 0 ||
* toIndex > size() ||
* toIndex < fromIndex})
*/
protected void removeRange(int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
if (fromIndex > toIndex) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(
outOfBoundsMsg(fromIndex, toIndex));
}
modCount++;
shiftTailOverGap(elementData, fromIndex, toIndex);
}
/** Erases the gap from lo to hi, by sliding down following elements. */
private void shiftTailOverGap(Object[] es, int lo, int hi) {
System.arraycopy(es, hi, es, lo, size - hi);
for (int to = size, i = (size -= hi - lo); i < to; i++)
es[i] = null;
}
/**
* A version of rangeCheck used by add and addAll.
*/
private void rangeCheckForAdd(int index) {
if (index > size || index < 0)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
}
/**
* Constructs an IndexOutOfBoundsException detail message.
* Of the many possible refactorings of the error handling code,
* this "outlining" performs best with both server and client VMs.
*/
private String outOfBoundsMsg(int index) {
return "Index: "+index+", Size: "+size;
}
/**
* A version used in checking (fromIndex > toIndex) condition
*/
private static String outOfBoundsMsg(int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
return "From Index: " + fromIndex + " > To Index: " + toIndex;
}
/**
* Removes from this list all of its elements that are contained in the
* specified collection.
*
* @param c collection containing elements to be removed from this list
* @return {@code true} if this list changed as a result of the call
* @throws ClassCastException if the class of an element of this list
* is incompatible with the specified collection
* (<a href="Collection.html#optional-restrictions">optional</a>)
* @throws NullPointerException if this list contains a null element and the
* specified collection does not permit null elements
* (<a href="Collection.html#optional-restrictions">optional</a>),
* or if the specified collection is null
* @see Collection#contains(Object)
*/
public boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c) {
return batchRemove(c, false, 0, size);
}
/**
* Retains only the elements in this list that are contained in the
* specified collection. In other words, removes from this list all
* of its elements that are not contained in the specified collection.
*
* @param c collection containing elements to be retained in this list
* @return {@code true} if this list changed as a result of the call
* @throws ClassCastException if the class of an element of this list
* is incompatible with the specified collection
* (<a href="Collection.html#optional-restrictions">optional</a>)
* @throws NullPointerException if this list contains a null element and the
* specified collection does not permit null elements
* (<a href="Collection.html#optional-restrictions">optional</a>),
* or if the specified collection is null
* @see Collection#contains(Object)
*/
public boolean retainAll(Collection<?> c) {
return batchRemove(c, true, 0, size);
}
boolean batchRemove(Collection<?> c, boolean complement,
final int from, final int end) {
Objects.requireNonNull(c);
final Object[] es = elementData;
int r;
// Optimize for initial run of survivors
for (r = from;; r++) {
if (r == end)
return false;
if (c.contains(es[r]) != complement)
break;
}
int w = r++;
try {
for (Object e; r < end; r++)
if (c.contains(e = es[r]) == complement)
es[w++] = e;
} catch (Throwable ex) {
// Preserve behavioral compatibility with AbstractCollection,
// even if c.contains() throws.
System.arraycopy(es, r, es, w, end - r);
w += end - r;
throw ex;
} finally {
modCount += end - w;
shiftTailOverGap(es, w, end);
}
return true;
}
/**
* Saves the state of the {@code ArrayList} instance to a stream
* (that is, serializes it).
*
* @param s the stream
* @throws java.io.IOException if an I/O error occurs
* @serialData The length of the array backing the {@code ArrayList}
* instance is emitted (int), followed by all of its elements
* (each an {@code Object}) in the proper order.
*/
@java.io.Serial
private void writeObject(java.io.ObjectOutputStream s)
throws java.io.IOException {
// Write out element count, and any hidden stuff
int expectedModCount = modCount;
s.defaultWriteObject();
// Write out size as capacity for behavioral compatibility with clone()
s.writeInt(size);
// Write out all elements in the proper order.
for (int i=0; i<size; i++) {
s.writeObject(elementData[i]);
}
if (modCount != expectedModCount) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
/**
* Reconstitutes the {@code ArrayList} instance from a stream (that is,
* deserializes it).
* @param s the stream
* @throws ClassNotFoundException if the class of a serialized object
* could not be found
* @throws java.io.IOException if an I/O error occurs
*/
@java.io.Serial
private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s)
throws java.io.IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
// Read in size, and any hidden stuff
s.defaultReadObject();
// Read in capacity
s.readInt(); // ignored
if (size > 0) {
// like clone(), allocate array based upon size not capacity
SharedSecrets.getJavaObjectInputStreamAccess().checkArray(s, Object[].class, size);
Object[] elements = new Object[size];
// Read in all elements in the proper order.
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
elements[i] = s.readObject();
}
elementData = elements;
} else if (size == 0) {
elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
} else {
throw new java.io.InvalidObjectException("Invalid size: " + size);
}
}
/**
* Returns a list iterator over the elements in this list (in proper
* sequence), starting at the specified position in the list.
* The specified index indicates the first element that would be
* returned by an initial call to {@link ListIterator#next next}.
* An initial call to {@link ListIterator#previous previous} would
* return the element with the specified index minus one.
*
* <p>The returned list iterator is <a href="#fail-fast"><i>fail-fast</i></a>.
*
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public ListIterator<E> listIterator(int index) {
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
return new ListItr(index);
}
/**
* Returns a list iterator over the elements in this list (in proper
* sequence).
*
* <p>The returned list iterator is <a href="#fail-fast"><i>fail-fast</i></a>.
*
* @see #listIterator(int)
*/
public ListIterator<E> listIterator() {
return new ListItr(0);
}
/**
* Returns an iterator over the elements in this list in proper sequence.
*
* <p>The returned iterator is <a href="#fail-fast"><i>fail-fast</i></a>.
*
* @return an iterator over the elements in this list in proper sequence
*/
public Iterator<E> iterator() {
return new Itr();
}
/**
* An optimized version of AbstractList.Itr
*/
private class Itr implements Iterator<E> {
int cursor; // index of next element to return
int lastRet = -1; // index of last element returned; -1 if no such
int expectedModCount = modCount;
// prevent creating a synthetic constructor
Itr() {}
public boolean hasNext() {
return cursor != size;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public E next() {
checkForComodification();
int i = cursor;
if (i >= size)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData;
if (i >= elementData.length)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
cursor = i + 1;
return (E) elementData[lastRet = i];
}
public void remove() {
if (lastRet < 0)
throw new IllegalStateException();
checkForComodification();
try {
ArrayList.this.remove(lastRet);
cursor = lastRet;
lastRet = -1;
expectedModCount = modCount;
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
@Override
public void forEachRemaining(Consumer<? super E> action) {
Objects.requireNonNull(action);
final int size = ArrayList.this.size;
int i = cursor;
if (i < size) {
final Object[] es = elementData;
if (i >= es.length)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
for (; i < size && modCount == expectedModCount; i++)
action.accept(elementAt(es, i));
// update once at end to reduce heap write traffic
cursor = i;
lastRet = i - 1;
checkForComodification();
}
}
final void checkForComodification() {
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
/**
* An optimized version of AbstractList.ListItr
*/
private class ListItr extends Itr implements ListIterator<E> {
ListItr(int index) {
super();
cursor = index;
}
public boolean hasPrevious() {
return cursor != 0;
}
public int nextIndex() {
return cursor;
}
public int previousIndex() {
return cursor - 1;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public E previous() {
checkForComodification();
int i = cursor - 1;
if (i < 0)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData;
if (i >= elementData.length)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
cursor = i;
return (E) elementData[lastRet = i];
}
public void set(E e) {
if (lastRet < 0)
throw new IllegalStateException();
checkForComodification();
try {
ArrayList.this.set(lastRet, e);
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
public void add(E e) {
checkForComodification();
try {
int i = cursor;
ArrayList.this.add(i, e);
cursor = i + 1;
lastRet = -1;
expectedModCount = modCount;
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
}
/**
* Returns a view of the portion of this list between the specified
* {@code fromIndex}, inclusive, and {@code toIndex}, exclusive. (If
* {@code fromIndex} and {@code toIndex} are equal, the returned list is
* empty.) The returned list is backed by this list, so non-structural
* changes in the returned list are reflected in this list, and vice-versa.
* The returned list supports all of the optional list operations.
*
* <p>This method eliminates the need for explicit range operations (of
* the sort that commonly exist for arrays). Any operation that expects
* a list can be used as a range operation by passing a subList view
* instead of a whole list. For example, the following idiom
* removes a range of elements from a list:
* <pre>
* list.subList(from, to).clear();
* </pre>
* Similar idioms may be constructed for {@link #indexOf(Object)} and
* {@link #lastIndexOf(Object)}, and all of the algorithms in the
* {@link Collections} class can be applied to a subList.
*
* <p>The semantics of the list returned by this method become undefined if
* the backing list (i.e., this list) is <i>structurally modified</i> in
* any way other than via the returned list. (Structural modifications are
* those that change the size of this list, or otherwise perturb it in such
* a fashion that iterations in progress may yield incorrect results.)
*
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
* @throws IllegalArgumentException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public List<E> subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
subListRangeCheck(fromIndex, toIndex, size);
return new SubList<>(this, fromIndex, toIndex);
}
private static class SubList<E> extends AbstractList<E> implements RandomAccess {
private final ArrayList<E> root;
private final SubList<E> parent;
private final int offset;
private int size;
/**
* Constructs a sublist of an arbitrary ArrayList.
*/
public SubList(ArrayList<E> root, int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
this.root = root;
this.parent = null;
this.offset = fromIndex;
this.size = toIndex - fromIndex;
this.modCount = root.modCount;
}
/**
* Constructs a sublist of another SubList.
*/
private SubList(SubList<E> parent, int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
this.root = parent.root;
this.parent = parent;
this.offset = parent.offset + fromIndex;
this.size = toIndex - fromIndex;
this.modCount = parent.modCount;
}
public E set(int index, E element) {
Objects.checkIndex(index, size);
checkForComodification();
E oldValue = root.elementData(offset + index);
root.elementData[offset + index] = element;
return oldValue;
}
public E get(int index) {
Objects.checkIndex(index, size);
checkForComodification();
return root.elementData(offset + index);
}
public int size() {
checkForComodification();
return size;
}
public void add(int index, E element) {
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
checkForComodification();
root.add(offset + index, element);
updateSizeAndModCount(1);
}
public E remove(int index) {
Objects.checkIndex(index, size);
checkForComodification();
E result = root.remove(offset + index);
updateSizeAndModCount(-1);
return result;
}
protected void removeRange(int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
checkForComodification();
root.removeRange(offset + fromIndex, offset + toIndex);
updateSizeAndModCount(fromIndex - toIndex);
}
public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) {
return addAll(this.size, c);
}
public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) {
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
int cSize = c.size();
if (cSize==0)
return false;
checkForComodification();
root.addAll(offset + index, c);
updateSizeAndModCount(cSize);
return true;
}
public void replaceAll(UnaryOperator<E> operator) {
root.replaceAllRange(operator, offset, offset + size);
}
public boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c) {
return batchRemove(c, false);
}
public boolean retainAll(Collection<?> c) {
return batchRemove(c, true);
}
private boolean batchRemove(Collection<?> c, boolean complement) {
checkForComodification();
int oldSize = root.size;
boolean modified =
root.batchRemove(c, complement, offset, offset + size);
if (modified)
updateSizeAndModCount(root.size - oldSize);
return modified;
}
public boolean removeIf(Predicate<? super E> filter) {
checkForComodification();
int oldSize = root.size;
boolean modified = root.removeIf(filter, offset, offset + size);
if (modified)
updateSizeAndModCount(root.size - oldSize);
return modified;
}
public Object[] toArray() {
checkForComodification();
return Arrays.copyOfRange(root.elementData, offset, offset + size);
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public <T> T[] toArray(T[] a) {
checkForComodification();
if (a.length < size)
return (T[]) Arrays.copyOfRange(
root.elementData, offset, offset + size, a.getClass());
System.arraycopy(root.elementData, offset, a, 0, size);
if (a.length > size)
a[size] = null;
return a;
}
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (o == this) {
return true;
}
if (!(o instanceof List)) {
return false;
}
boolean equal = root.equalsRange((List<?>)o, offset, offset + size);
checkForComodification();
return equal;
}
public int hashCode() {
int hash = root.hashCodeRange(offset, offset + size);
checkForComodification();
return hash;
}
public int indexOf(Object o) {
int index = root.indexOfRange(o, offset, offset + size);
checkForComodification();
return index >= 0 ? index - offset : -1;
}
public int lastIndexOf(Object o) {
int index = root.lastIndexOfRange(o, offset, offset + size);
checkForComodification();
return index >= 0 ? index - offset : -1;
}
public boolean contains(Object o) {
return indexOf(o) >= 0;
}
public Iterator<E> iterator() {
return listIterator();
}
public ListIterator<E> listIterator(int index) {
checkForComodification();
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
return new ListIterator<E>() {
int cursor = index;
int lastRet = -1;
int expectedModCount = SubList.this.modCount;
public boolean hasNext() {
return cursor != SubList.this.size;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public E next() {
checkForComodification();
int i = cursor;
if (i >= SubList.this.size)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
Object[] elementData = root.elementData;
if (offset + i >= elementData.length)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
cursor = i + 1;
return (E) elementData[offset + (lastRet = i)];
}
public boolean hasPrevious() {
return cursor != 0;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public E previous() {
checkForComodification();
int i = cursor - 1;
if (i < 0)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
Object[] elementData = root.elementData;
if (offset + i >= elementData.length)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
cursor = i;
return (E) elementData[offset + (lastRet = i)];
}
public void forEachRemaining(Consumer<? super E> action) {
Objects.requireNonNull(action);
final int size = SubList.this.size;
int i = cursor;
if (i < size) {
final Object[] es = root.elementData;
if (offset + i >= es.length)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
for (; i < size && root.modCount == expectedModCount; i++)
action.accept(elementAt(es, offset + i));
// update once at end to reduce heap write traffic
cursor = i;
lastRet = i - 1;
checkForComodification();
}
}
public int nextIndex() {
return cursor;
}
public int previousIndex() {
return cursor - 1;
}
public void remove() {
if (lastRet < 0)
throw new IllegalStateException();
checkForComodification();
try {
SubList.this.remove(lastRet);
cursor = lastRet;
lastRet = -1;
expectedModCount = SubList.this.modCount;
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
public void set(E e) {
if (lastRet < 0)
throw new IllegalStateException();
checkForComodification();
try {
root.set(offset + lastRet, e);
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
public void add(E e) {
checkForComodification();
try {
int i = cursor;
SubList.this.add(i, e);
cursor = i + 1;
lastRet = -1;
expectedModCount = SubList.this.modCount;
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
final void checkForComodification() {
if (root.modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
};
}
public List<E> subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
subListRangeCheck(fromIndex, toIndex, size);
return new SubList<>(this, fromIndex, toIndex);
}
private void rangeCheckForAdd(int index) {
if (index < 0 || index > this.size)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
}
private String outOfBoundsMsg(int index) {
return "Index: "+index+", Size: "+this.size;
}
private void checkForComodification() {
if (root.modCount != modCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
private void updateSizeAndModCount(int sizeChange) {
SubList<E> slist = this;
do {
slist.size += sizeChange;
slist.modCount = root.modCount;
slist = slist.parent;
} while (slist != null);
}
public Spliterator<E> spliterator() {
checkForComodification();
// This Spliterator needs to late-bind to the subList, not the outer
// ArrayList. Note that it is legal for structural changes to be made
// to a subList after spliterator() is called but before any spliterator
// operations that would causing binding are performed.
return new Spliterator<E>() {
private int index = offset; // current index, modified on advance/split
private int fence = -1; // -1 until used; then one past last index
private int expectedModCount; // initialized when fence set
private int getFence() { // initialize fence to size on first use
int hi; // (a specialized variant appears in method forEach)
if ((hi = fence) < 0) {
expectedModCount = modCount;
hi = fence = offset + size;
}
return hi;
}
public ArrayList<E>.ArrayListSpliterator trySplit() {
int hi = getFence(), lo = index, mid = (lo + hi) >>> 1;
// ArrayListSpliterator can be used here as the source is already bound
return (lo >= mid) ? null : // divide range in half unless too small
root.new ArrayListSpliterator(lo, index = mid, expectedModCount);
}
public boolean tryAdvance(Consumer<? super E> action) {
Objects.requireNonNull(action);
int hi = getFence(), i = index;
if (i < hi) {
index = i + 1;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") E e = (E)root.elementData[i];
action.accept(e);
if (root.modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
return true;
}
return false;
}
public void forEachRemaining(Consumer<? super E> action) {
Objects.requireNonNull(action);
int i, hi, mc; // hoist accesses and checks from loop
ArrayList<E> lst = root;
Object[] a;
if ((a = lst.elementData) != null) {
if ((hi = fence) < 0) {
mc = modCount;
hi = offset + size;
}
else
mc = expectedModCount;
if ((i = index) >= 0 && (index = hi) <= a.length) {
for (; i < hi; ++i) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") E e = (E) a[i];
action.accept(e);
}
if (lst.modCount == mc)
return;
}
}
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
public long estimateSize() {
return getFence() - index;
}
public int characteristics() {
return Spliterator.ORDERED | Spliterator.SIZED | Spliterator.SUBSIZED;
}
};
}
}
/**
* @throws NullPointerException {@inheritDoc}
*/
@Override
public void forEach(Consumer<? super E> action) {
Objects.requireNonNull(action);
final int expectedModCount = modCount;
final Object[] es = elementData;
final int size = this.size;
for (int i = 0; modCount == expectedModCount && i < size; i++)
action.accept(elementAt(es, i));
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
/**
* Creates a <em><a href="Spliterator.html#binding">late-binding</a></em>
* and <em>fail-fast</em> {@link Spliterator} over the elements in this
* list.
*
* <p>The {@code Spliterator} reports {@link Spliterator#SIZED},
* {@link Spliterator#SUBSIZED}, and {@link Spliterator#ORDERED}.
* Overriding implementations should document the reporting of additional
* characteristic values.
*
* @return a {@code Spliterator} over the elements in this list
* @since 1.8
*/
@Override
public Spliterator<E> spliterator() {
return new ArrayListSpliterator(0, -1, 0);
}
/** Index-based split-by-two, lazily initialized Spliterator */
final class ArrayListSpliterator implements Spliterator<E> {
/*
* If ArrayLists were immutable, or structurally immutable (no
* adds, removes, etc), we could implement their spliterators
* with Arrays.spliterator. Instead we detect as much
* interference during traversal as practical without
* sacrificing much performance. We rely primarily on
* modCounts. These are not guaranteed to detect concurrency
* violations, and are sometimes overly conservative about
* within-thread interference, but detect enough problems to
* be worthwhile in practice. To carry this out, we (1) lazily
* initialize fence and expectedModCount until the latest
* point that we need to commit to the state we are checking
* against; thus improving precision. (2) We perform only a single
* ConcurrentModificationException check at the end of forEach
* (the most performance-sensitive method). When using forEach
* (as opposed to iterators), we can normally only detect
* interference after actions, not before. Further
* CME-triggering checks apply to all other possible
* violations of assumptions for example null or too-small
* elementData array given its size(), that could only have
* occurred due to interference. This allows the inner loop
* of forEach to run without any further checks, and
* simplifies lambda-resolution. While this does entail a
* number of checks, note that in the common case of
* list.stream().forEach(a), no checks or other computation
* occur anywhere other than inside forEach itself. The other
* less-often-used methods cannot take advantage of most of
* these streamlinings.
*/
private int index; // current index, modified on advance/split
private int fence; // -1 until used; then one past last index
private int expectedModCount; // initialized when fence set
/** Creates new spliterator covering the given range. */
ArrayListSpliterator(int origin, int fence, int expectedModCount) {
this.index = origin;
this.fence = fence;
this.expectedModCount = expectedModCount;
}
private int getFence() { // initialize fence to size on first use
int hi; // (a specialized variant appears in method forEach)
if ((hi = fence) < 0) {
expectedModCount = modCount;
hi = fence = size;
}
return hi;
}
public ArrayListSpliterator trySplit() {
int hi = getFence(), lo = index, mid = (lo + hi) >>> 1;
return (lo >= mid) ? null : // divide range in half unless too small
new ArrayListSpliterator(lo, index = mid, expectedModCount);
}
public boolean tryAdvance(Consumer<? super E> action) {
if (action == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
int hi = getFence(), i = index;
if (i < hi) {
index = i + 1;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") E e = (E)elementData[i];
action.accept(e);
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
return true;
}
return false;
}
public void forEachRemaining(Consumer<? super E> action) {
int i, hi, mc; // hoist accesses and checks from loop
Object[] a;
if (action == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
if ((a = elementData) != null) {
if ((hi = fence) < 0) {
mc = modCount;
hi = size;
}
else
mc = expectedModCount;
if ((i = index) >= 0 && (index = hi) <= a.length) {
for (; i < hi; ++i) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") E e = (E) a[i];
action.accept(e);
}
if (modCount == mc)
return;
}
}
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
public long estimateSize() {
return getFence() - index;
}
public int characteristics() {
return Spliterator.ORDERED | Spliterator.SIZED | Spliterator.SUBSIZED;
}
}
// A tiny bit set implementation
private static long[] nBits(int n) {
return new long[((n - 1) >> 6) + 1];
}
private static void setBit(long[] bits, int i) {
bits[i >> 6] |= 1L << i;
}
private static boolean isClear(long[] bits, int i) {
return (bits[i >> 6] & (1L << i)) == 0;
}
/**
* @throws NullPointerException {@inheritDoc}
*/
@Override
public boolean removeIf(Predicate<? super E> filter) {
return removeIf(filter, 0, size);
}
/**
* Removes all elements satisfying the given predicate, from index
* i (inclusive) to index end (exclusive).
*/
boolean removeIf(Predicate<? super E> filter, int i, final int end) {
Objects.requireNonNull(filter);
int expectedModCount = modCount;
final Object[] es = elementData;
// Optimize for initial run of survivors
for (; i < end && !filter.test(elementAt(es, i)); i++)
;
// Tolerate predicates that reentrantly access the collection for
// read (but writers still get CME), so traverse once to find
// elements to delete, a second pass to physically expunge.
if (i < end) {
final int beg = i;
final long[] deathRow = nBits(end - beg);
deathRow[0] = 1L; // set bit 0
for (i = beg + 1; i < end; i++)
if (filter.test(elementAt(es, i)))
setBit(deathRow, i - beg);
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
modCount++;
int w = beg;
for (i = beg; i < end; i++)
if (isClear(deathRow, i - beg))
es[w++] = es[i];
shiftTailOverGap(es, w, end);
return true;
} else {
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
return false;
}
}
@Override
public void replaceAll(UnaryOperator<E> operator) {
replaceAllRange(operator, 0, size);
// TODO(8203662): remove increment of modCount from ...
modCount++;
}
private void replaceAllRange(UnaryOperator<E> operator, int i, int end) {
Objects.requireNonNull(operator);
final int expectedModCount = modCount;
final Object[] es = elementData;
for (; modCount == expectedModCount && i < end; i++)
es[i] = operator.apply(elementAt(es, i));
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
@Override
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public void sort(Comparator<? super E> c) {
final int expectedModCount = modCount;
Arrays.sort((E[]) elementData, 0, size, c);
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
modCount++;
}
void checkInvariants() {
// assert size >= 0;
// assert size == elementData.length || elementData[size] == null;
}
}
menti.com 2335 3741
Why is Queue an interface and Stack isn't?
# Stack
import java.util.Optional;
public interface MyStack<T> {
T push(T obj);
Optional<T> peek();
T pop();
boolean empty();
}
/*
* Copyright (c) 1994, 2022, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
* DO NOT ALTER OR REMOVE COPYRIGHT NOTICES OR THIS FILE HEADER.
*
* This code is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify it
* under the terms of the GNU General Public License version 2 only, as
* published by the Free Software Foundation. Oracle designates this
* particular file as subject to the "Classpath" exception as provided
* by Oracle in the LICENSE file that accompanied this code.
*
* This code is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT
* ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or
* FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU General Public License
* version 2 for more details (a copy is included in the LICENSE file that
* accompanied this code).
*
* You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License version
* 2 along with this work; if not, write to the Free Software Foundation,
* Inc., 51 Franklin St, Fifth Floor, Boston, MA 02110-1301 USA.
*
* Please contact Oracle, 500 Oracle Parkway, Redwood Shores, CA 94065 USA
* or visit www.oracle.com if you need additional information or have any
* questions.
*/
package java.util;
/**
* The {@code Stack} class represents a last-in-first-out
* (LIFO) stack of objects. It extends class {@code Vector} with five
* operations that allow a vector to be treated as a stack. The usual
* {@code push} and {@code pop} operations are provided, as well as a
* method to {@code peek} at the top item on the stack, a method to test
* for whether the stack is {@code empty}, and a method to {@code search}
* the stack for an item and discover how far it is from the top.
* <p>
* When a stack is first created, it contains no items.
*
* <p>A more complete and consistent set of LIFO stack operations is
* provided by the {@link Deque} interface and its implementations, which
* should be used in preference to this class. For example:
* <pre> {@code
* Deque<Integer> stack = new ArrayDeque<Integer>();}</pre>
*
* @param <E> Type of component elements
*
* @author Jonathan Payne
* @since 1.0
*/
public class Stack<E> extends Vector<E> {
/**
* Creates an empty Stack.
*/
public Stack() {
}
/**
* Pushes an item onto the top of this stack. This has exactly
* the same effect as:
* <blockquote><pre>
* addElement(item)</pre></blockquote>
*
* @param item the item to be pushed onto this stack.
* @return the {@code item} argument.
* @see java.util.Vector#addElement
*/
public E push(E item) {
addElement(item);
return item;
}
/**
* Removes the object at the top of this stack and returns that
* object as the value of this function.
*
* @return The object at the top of this stack (the last item
* of the {@code Vector} object).
* @throws EmptyStackException if this stack is empty.
*/
public synchronized E pop() {
E obj;
int len = size();
obj = peek();
removeElementAt(len - 1);
return obj;
}
/**
* Looks at the object at the top of this stack without removing it
* from the stack.
*
* @return the object at the top of this stack (the last item
* of the {@code Vector} object).
* @throws EmptyStackException if this stack is empty.
*/
public synchronized E peek() {
int len = size();
if (len == 0)
throw new EmptyStackException();
return elementAt(len - 1);
}
/**
* Tests if this stack is empty.
*
* @return {@code true} if and only if this stack contains
* no items; {@code false} otherwise.
*/
public boolean empty() {
return size() == 0;
}
/**
* Returns the 1-based position where an object is on this stack.
* If the object {@code o} occurs as an item in this stack, this
* method returns the distance from the top of the stack of the
* occurrence nearest the top of the stack; the topmost item on the
* stack is considered to be at distance {@code 1}. The {@code equals}
* method is used to compare {@code o} to the
* items in this stack.
*
* @param o the desired object.
* @return the 1-based position from the top of the stack where
* the object is located; the return value {@code -1}
* indicates that the object is not on the stack.
*/
public synchronized int search(Object o) {
int i = lastIndexOf(o);
if (i >= 0) {
return size() - i;
}
return -1;
}
/** use serialVersionUID from JDK 1.0.2 for interoperability */
@java.io.Serial
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1224463164541339165L;
}
menti.com 2335 3741
Why is Queue an interface and Stack isn't?
# Stack
import java.util.Optional;
public interface MyStack<T> {
T push(T obj);
Optional<T> peek();
T pop();
boolean empty();
}
public class StackImpl<T> implements MyStack<T> {
private List<T> stack = new ArrayList<>();
@Override
public T push(T obj) {
stack.add(Objects.requireNonNull(obj));
return obj;
}
@Override
public Optional<T> peek() {
if (stack.isEmpty()) {
return Optional.empty();
} else {
return Optional.of(stack.getLast());
}
}
@Override
public T pop() {
Optional<T> obj = peek();
if (obj.isPresent()) {
stack.removeLast();
return obj.get();
} else {
throw new IllegalStateException("Stack is empty");
}
}
@Override
public boolean empty() {
return stack.isEmpty();
}
}
menti.com 2335 3741
Why is Queue an interface and Stack isn't?
# Stack
import java.util.Optional;
public interface MyStack<T> {
T push(T obj);
Optional<T> peek();
T pop();
boolean empty();
}
Stack<String> s = new StackImpl<String>();
s.push("Train");
s.push("Cancelled");
System.out.println(s.pop());
System.out.println(s.peek());
s.pop();
System.out.println(s.peek());
System.out.println(s.empty());menti.com 2335 3741
Why is Queue an interface and Stack isn't?
# Stack
import java.util.Optional;
public interface MyStack<T> {
T push(T obj);
Optional<T> peek();
T pop();
boolean empty();
}
Stack<String> s = new StackImpl<String>();
s.push("Train");
s.push("Cancelled");
System.out.println(s.pop());
System.out.println(s.peek());
s.pop();
System.out.println(s.peek());
System.out.println(s.empty());Cancelled
Optional[Train]
Optional.empty
truementi.com 2335 3741
Why is Queue an interface and Stack isn't?
# Queue
menti.com 2335 3741
What's the difference between ArrayList and LinkedList
# Queue
menti.com 2335 3741
What's the difference between ArrayList and LinkedList
# Queue
/*
* Copyright (c) 1997, 2023, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
* DO NOT ALTER OR REMOVE COPYRIGHT NOTICES OR THIS FILE HEADER.
*
* This code is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify it
* under the terms of the GNU General Public License version 2 only, as
* published by the Free Software Foundation. Oracle designates this
* particular file as subject to the "Classpath" exception as provided
* by Oracle in the LICENSE file that accompanied this code.
*
* This code is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT
* ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or
* FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU General Public License
* version 2 for more details (a copy is included in the LICENSE file that
* accompanied this code).
*
* You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License version
* 2 along with this work; if not, write to the Free Software Foundation,
* Inc., 51 Franklin St, Fifth Floor, Boston, MA 02110-1301 USA.
*
* Please contact Oracle, 500 Oracle Parkway, Redwood Shores, CA 94065 USA
* or visit www.oracle.com if you need additional information or have any
* questions.
*/
package java.util;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.ObjectInput;
import java.io.ObjectOutput;
import java.util.function.Consumer;
import java.util.function.IntFunction;
import java.util.function.Predicate;
import java.util.function.UnaryOperator;
import java.util.stream.Stream;
/**
* Doubly-linked list implementation of the {@code List} and {@code Deque}
* interfaces. Implements all optional list operations, and permits all
* elements (including {@code null}).
*
* <p>All of the operations perform as could be expected for a doubly-linked
* list. Operations that index into the list will traverse the list from
* the beginning or the end, whichever is closer to the specified index.
*
* <p><strong>Note that this implementation is not synchronized.</strong>
* If multiple threads access a linked list concurrently, and at least
* one of the threads modifies the list structurally, it <i>must</i> be
* synchronized externally. (A structural modification is any operation
* that adds or deletes one or more elements; merely setting the value of
* an element is not a structural modification.) This is typically
* accomplished by synchronizing on some object that naturally
* encapsulates the list.
*
* If no such object exists, the list should be "wrapped" using the
* {@link Collections#synchronizedList Collections.synchronizedList}
* method. This is best done at creation time, to prevent accidental
* unsynchronized access to the list:<pre>
* List list = Collections.synchronizedList(new LinkedList(...));</pre>
*
* <p>The iterators returned by this class's {@code iterator} and
* {@code listIterator} methods are <i>fail-fast</i>: if the list is
* structurally modified at any time after the iterator is created, in
* any way except through the Iterator's own {@code remove} or
* {@code add} methods, the iterator will throw a {@link
* ConcurrentModificationException}. Thus, in the face of concurrent
* modification, the iterator fails quickly and cleanly, rather than
* risking arbitrary, non-deterministic behavior at an undetermined
* time in the future.
*
* <p>Note that the fail-fast behavior of an iterator cannot be guaranteed
* as it is, generally speaking, impossible to make any hard guarantees in the
* presence of unsynchronized concurrent modification. Fail-fast iterators
* throw {@code ConcurrentModificationException} on a best-effort basis.
* Therefore, it would be wrong to write a program that depended on this
* exception for its correctness: <i>the fail-fast behavior of iterators
* should be used only to detect bugs.</i>
*
* <p>This class is a member of the
* <a href="{@docRoot}/java.base/java/util/package-summary.html#CollectionsFramework">
* Java Collections Framework</a>.
*
* @author Josh Bloch
* @see List
* @see ArrayList
* @since 1.2
* @param <E> the type of elements held in this collection
*/
public class LinkedList<E>
extends AbstractSequentialList<E>
implements List<E>, Deque<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
{
transient int size = 0;
/**
* Pointer to first node.
*/
transient Node<E> first;
/**
* Pointer to last node.
*/
transient Node<E> last;
/*
void dataStructureInvariants() {
assert (size == 0)
? (first == null && last == null)
: (first.prev == null && last.next == null);
}
*/
/**
* Constructs an empty list.
*/
public LinkedList() {
}
/**
* Constructs a list containing the elements of the specified
* collection, in the order they are returned by the collection's
* iterator.
*
* @param c the collection whose elements are to be placed into this list
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null
*/
public LinkedList(Collection<? extends E> c) {
this();
addAll(c);
}
/**
* Links e as first element.
*/
private void linkFirst(E e) {
final Node<E> f = first;
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(null, e, f);
first = newNode;
if (f == null)
last = newNode;
else
f.prev = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
/**
* Links e as last element.
*/
void linkLast(E e) {
final Node<E> l = last;
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null);
last = newNode;
if (l == null)
first = newNode;
else
l.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
/**
* Inserts element e before non-null Node succ.
*/
void linkBefore(E e, Node<E> succ) {
// assert succ != null;
final Node<E> pred = succ.prev;
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, succ);
succ.prev = newNode;
if (pred == null)
first = newNode;
else
pred.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
/**
* Unlinks non-null first node f.
*/
private E unlinkFirst(Node<E> f) {
// assert f == first && f != null;
final E element = f.item;
final Node<E> next = f.next;
f.item = null;
f.next = null; // help GC
first = next;
if (next == null)
last = null;
else
next.prev = null;
size--;
modCount++;
return element;
}
/**
* Unlinks non-null last node l.
*/
private E unlinkLast(Node<E> l) {
// assert l == last && l != null;
final E element = l.item;
final Node<E> prev = l.prev;
l.item = null;
l.prev = null; // help GC
last = prev;
if (prev == null)
first = null;
else
prev.next = null;
size--;
modCount++;
return element;
}
/**
* Unlinks non-null node x.
*/
E unlink(Node<E> x) {
// assert x != null;
final E element = x.item;
final Node<E> next = x.next;
final Node<E> prev = x.prev;
if (prev == null) {
first = next;
} else {
prev.next = next;
x.prev = null;
}
if (next == null) {
last = prev;
} else {
next.prev = prev;
x.next = null;
}
x.item = null;
size--;
modCount++;
return element;
}
/**
* Returns the first element in this list.
*
* @return the first element in this list
* @throws NoSuchElementException if this list is empty
*/
public E getFirst() {
final Node<E> f = first;
if (f == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return f.item;
}
/**
* Returns the last element in this list.
*
* @return the last element in this list
* @throws NoSuchElementException if this list is empty
*/
public E getLast() {
final Node<E> l = last;
if (l == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return l.item;
}
/**
* Removes and returns the first element from this list.
*
* @return the first element from this list
* @throws NoSuchElementException if this list is empty
*/
public E removeFirst() {
final Node<E> f = first;
if (f == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return unlinkFirst(f);
}
/**
* Removes and returns the last element from this list.
*
* @return the last element from this list
* @throws NoSuchElementException if this list is empty
*/
public E removeLast() {
final Node<E> l = last;
if (l == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return unlinkLast(l);
}
/**
* Inserts the specified element at the beginning of this list.
*
* @param e the element to add
*/
public void addFirst(E e) {
linkFirst(e);
}
/**
* Appends the specified element to the end of this list.
*
* <p>This method is equivalent to {@link #add}.
*
* @param e the element to add
*/
public void addLast(E e) {
linkLast(e);
}
/**
* Returns {@code true} if this list contains the specified element.
* More formally, returns {@code true} if and only if this list contains
* at least one element {@code e} such that
* {@code Objects.equals(o, e)}.
*
* @param o element whose presence in this list is to be tested
* @return {@code true} if this list contains the specified element
*/
public boolean contains(Object o) {
return indexOf(o) >= 0;
}
/**
* Returns the number of elements in this list.
*
* @return the number of elements in this list
*/
public int size() {
return size;
}
/**
* Appends the specified element to the end of this list.
*
* <p>This method is equivalent to {@link #addLast}.
*
* @param e element to be appended to this list
* @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Collection#add})
*/
public boolean add(E e) {
linkLast(e);
return true;
}
/**
* Removes the first occurrence of the specified element from this list,
* if it is present. If this list does not contain the element, it is
* unchanged. More formally, removes the element with the lowest index
* {@code i} such that
* {@code Objects.equals(o, get(i))}
* (if such an element exists). Returns {@code true} if this list
* contained the specified element (or equivalently, if this list
* changed as a result of the call).
*
* @param o element to be removed from this list, if present
* @return {@code true} if this list contained the specified element
*/
public boolean remove(Object o) {
if (o == null) {
for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
if (x.item == null) {
unlink(x);
return true;
}
}
} else {
for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
if (o.equals(x.item)) {
unlink(x);
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
/**
* Appends all of the elements in the specified collection to the end of
* this list, in the order that they are returned by the specified
* collection's iterator. The behavior of this operation is undefined if
* the specified collection is modified while the operation is in
* progress. (Note that this will occur if the specified collection is
* this list, and it's nonempty.)
*
* @param c collection containing elements to be added to this list
* @return {@code true} if this list changed as a result of the call
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null
*/
public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) {
return addAll(size, c);
}
/**
* Inserts all of the elements in the specified collection into this
* list, starting at the specified position. Shifts the element
* currently at that position (if any) and any subsequent elements to
* the right (increases their indices). The new elements will appear
* in the list in the order that they are returned by the
* specified collection's iterator.
*
* @param index index at which to insert the first element
* from the specified collection
* @param c collection containing elements to be added to this list
* @return {@code true} if this list changed as a result of the call
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null
*/
public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) {
checkPositionIndex(index);
Object[] a = c.toArray();
int numNew = a.length;
if (numNew == 0)
return false;
Node<E> pred, succ;
if (index == size) {
succ = null;
pred = last;
} else {
succ = node(index);
pred = succ.prev;
}
for (Object o : a) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") E e = (E) o;
Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, null);
if (pred == null)
first = newNode;
else
pred.next = newNode;
pred = newNode;
}
if (succ == null) {
last = pred;
} else {
pred.next = succ;
succ.prev = pred;
}
size += numNew;
modCount++;
return true;
}
/**
* Removes all of the elements from this list.
* The list will be empty after this call returns.
*/
public void clear() {
// Clearing all of the links between nodes is "unnecessary", but:
// - helps a generational GC if the discarded nodes inhabit
// more than one generation
// - is sure to free memory even if there is a reachable Iterator
for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; ) {
Node<E> next = x.next;
x.item = null;
x.next = null;
x.prev = null;
x = next;
}
first = last = null;
size = 0;
modCount++;
}
// Positional Access Operations
/**
* Returns the element at the specified position in this list.
*
* @param index index of the element to return
* @return the element at the specified position in this list
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public E get(int index) {
checkElementIndex(index);
return node(index).item;
}
/**
* Replaces the element at the specified position in this list with the
* specified element.
*
* @param index index of the element to replace
* @param element element to be stored at the specified position
* @return the element previously at the specified position
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public E set(int index, E element) {
checkElementIndex(index);
Node<E> x = node(index);
E oldVal = x.item;
x.item = element;
return oldVal;
}
/**
* Inserts the specified element at the specified position in this list.
* Shifts the element currently at that position (if any) and any
* subsequent elements to the right (adds one to their indices).
*
* @param index index at which the specified element is to be inserted
* @param element element to be inserted
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public void add(int index, E element) {
checkPositionIndex(index);
if (index == size)
linkLast(element);
else
linkBefore(element, node(index));
}
/**
* Removes the element at the specified position in this list. Shifts any
* subsequent elements to the left (subtracts one from their indices).
* Returns the element that was removed from the list.
*
* @param index the index of the element to be removed
* @return the element previously at the specified position
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public E remove(int index) {
checkElementIndex(index);
return unlink(node(index));
}
/**
* Tells if the argument is the index of an existing element.
*/
private boolean isElementIndex(int index) {
return index >= 0 && index < size;
}
/**
* Tells if the argument is the index of a valid position for an
* iterator or an add operation.
*/
private boolean isPositionIndex(int index) {
return index >= 0 && index <= size;
}
/**
* Constructs an IndexOutOfBoundsException detail message.
* Of the many possible refactorings of the error handling code,
* this "outlining" performs best with both server and client VMs.
*/
private String outOfBoundsMsg(int index) {
return "Index: "+index+", Size: "+size;
}
private void checkElementIndex(int index) {
if (!isElementIndex(index))
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
}
private void checkPositionIndex(int index) {
if (!isPositionIndex(index))
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
}
/**
* Returns the (non-null) Node at the specified element index.
*/
Node<E> node(int index) {
// assert isElementIndex(index);
if (index < (size >> 1)) {
Node<E> x = first;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++)
x = x.next;
return x;
} else {
Node<E> x = last;
for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--)
x = x.prev;
return x;
}
}
// Search Operations
/**
* Returns the index of the first occurrence of the specified element
* in this list, or -1 if this list does not contain the element.
* More formally, returns the lowest index {@code i} such that
* {@code Objects.equals(o, get(i))},
* or -1 if there is no such index.
*
* @param o element to search for
* @return the index of the first occurrence of the specified element in
* this list, or -1 if this list does not contain the element
*/
public int indexOf(Object o) {
int index = 0;
if (o == null) {
for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
if (x.item == null)
return index;
index++;
}
} else {
for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
if (o.equals(x.item))
return index;
index++;
}
}
return -1;
}
/**
* Returns the index of the last occurrence of the specified element
* in this list, or -1 if this list does not contain the element.
* More formally, returns the highest index {@code i} such that
* {@code Objects.equals(o, get(i))},
* or -1 if there is no such index.
*
* @param o element to search for
* @return the index of the last occurrence of the specified element in
* this list, or -1 if this list does not contain the element
*/
public int lastIndexOf(Object o) {
int index = size;
if (o == null) {
for (Node<E> x = last; x != null; x = x.prev) {
index--;
if (x.item == null)
return index;
}
} else {
for (Node<E> x = last; x != null; x = x.prev) {
index--;
if (o.equals(x.item))
return index;
}
}
return -1;
}
// Queue operations.
/**
* Retrieves, but does not remove, the head (first element) of this list.
*
* @return the head of this list, or {@code null} if this list is empty
* @since 1.5
*/
public E peek() {
final Node<E> f = first;
return (f == null) ? null : f.item;
}
/**
* Retrieves, but does not remove, the head (first element) of this list.
*
* @return the head of this list
* @throws NoSuchElementException if this list is empty
* @since 1.5
*/
public E element() {
return getFirst();
}
/**
* Retrieves and removes the head (first element) of this list.
*
* @return the head of this list, or {@code null} if this list is empty
* @since 1.5
*/
public E poll() {
final Node<E> f = first;
return (f == null) ? null : unlinkFirst(f);
}
/**
* Retrieves and removes the head (first element) of this list.
*
* @return the head of this list
* @throws NoSuchElementException if this list is empty
* @since 1.5
*/
public E remove() {
return removeFirst();
}
/**
* Adds the specified element as the tail (last element) of this list.
*
* @param e the element to add
* @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Queue#offer})
* @since 1.5
*/
public boolean offer(E e) {
return add(e);
}
// Deque operations
/**
* Inserts the specified element at the front of this list.
*
* @param e the element to insert
* @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Deque#offerFirst})
* @since 1.6
*/
public boolean offerFirst(E e) {
addFirst(e);
return true;
}
/**
* Inserts the specified element at the end of this list.
*
* @param e the element to insert
* @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Deque#offerLast})
* @since 1.6
*/
public boolean offerLast(E e) {
addLast(e);
return true;
}
/**
* Retrieves, but does not remove, the first element of this list,
* or returns {@code null} if this list is empty.
*
* @return the first element of this list, or {@code null}
* if this list is empty
* @since 1.6
*/
public E peekFirst() {
final Node<E> f = first;
return (f == null) ? null : f.item;
}
/**
* Retrieves, but does not remove, the last element of this list,
* or returns {@code null} if this list is empty.
*
* @return the last element of this list, or {@code null}
* if this list is empty
* @since 1.6
*/
public E peekLast() {
final Node<E> l = last;
return (l == null) ? null : l.item;
}
/**
* Retrieves and removes the first element of this list,
* or returns {@code null} if this list is empty.
*
* @return the first element of this list, or {@code null} if
* this list is empty
* @since 1.6
*/
public E pollFirst() {
final Node<E> f = first;
return (f == null) ? null : unlinkFirst(f);
}
/**
* Retrieves and removes the last element of this list,
* or returns {@code null} if this list is empty.
*
* @return the last element of this list, or {@code null} if
* this list is empty
* @since 1.6
*/
public E pollLast() {
final Node<E> l = last;
return (l == null) ? null : unlinkLast(l);
}
/**
* Pushes an element onto the stack represented by this list. In other
* words, inserts the element at the front of this list.
*
* <p>This method is equivalent to {@link #addFirst}.
*
* @param e the element to push
* @since 1.6
*/
public void push(E e) {
addFirst(e);
}
/**
* Pops an element from the stack represented by this list. In other
* words, removes and returns the first element of this list.
*
* <p>This method is equivalent to {@link #removeFirst()}.
*
* @return the element at the front of this list (which is the top
* of the stack represented by this list)
* @throws NoSuchElementException if this list is empty
* @since 1.6
*/
public E pop() {
return removeFirst();
}
/**
* Removes the first occurrence of the specified element in this
* list (when traversing the list from head to tail). If the list
* does not contain the element, it is unchanged.
*
* @param o element to be removed from this list, if present
* @return {@code true} if the list contained the specified element
* @since 1.6
*/
public boolean removeFirstOccurrence(Object o) {
return remove(o);
}
/**
* Removes the last occurrence of the specified element in this
* list (when traversing the list from head to tail). If the list
* does not contain the element, it is unchanged.
*
* @param o element to be removed from this list, if present
* @return {@code true} if the list contained the specified element
* @since 1.6
*/
public boolean removeLastOccurrence(Object o) {
if (o == null) {
for (Node<E> x = last; x != null; x = x.prev) {
if (x.item == null) {
unlink(x);
return true;
}
}
} else {
for (Node<E> x = last; x != null; x = x.prev) {
if (o.equals(x.item)) {
unlink(x);
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
/**
* Returns a list-iterator of the elements in this list (in proper
* sequence), starting at the specified position in the list.
* Obeys the general contract of {@code List.listIterator(int)}.<p>
*
* The list-iterator is <i>fail-fast</i>: if the list is structurally
* modified at any time after the Iterator is created, in any way except
* through the list-iterator's own {@code remove} or {@code add}
* methods, the list-iterator will throw a
* {@code ConcurrentModificationException}. Thus, in the face of
* concurrent modification, the iterator fails quickly and cleanly, rather
* than risking arbitrary, non-deterministic behavior at an undetermined
* time in the future.
*
* @param index index of the first element to be returned from the
* list-iterator (by a call to {@code next})
* @return a ListIterator of the elements in this list (in proper
* sequence), starting at the specified position in the list
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
* @see List#listIterator(int)
*/
public ListIterator<E> listIterator(int index) {
checkPositionIndex(index);
return new ListItr(index);
}
private class ListItr implements ListIterator<E> {
private Node<E> lastReturned;
private Node<E> next;
private int nextIndex;
private int expectedModCount = modCount;
ListItr(int index) {
// assert isPositionIndex(index);
next = (index == size) ? null : node(index);
nextIndex = index;
}
public boolean hasNext() {
return nextIndex < size;
}
public E next() {
checkForComodification();
if (!hasNext())
throw new NoSuchElementException();
lastReturned = next;
next = next.next;
nextIndex++;
return lastReturned.item;
}
public boolean hasPrevious() {
return nextIndex > 0;
}
public E previous() {
checkForComodification();
if (!hasPrevious())
throw new NoSuchElementException();
lastReturned = next = (next == null) ? last : next.prev;
nextIndex--;
return lastReturned.item;
}
public int nextIndex() {
return nextIndex;
}
public int previousIndex() {
return nextIndex - 1;
}
public void remove() {
checkForComodification();
if (lastReturned == null)
throw new IllegalStateException();
Node<E> lastNext = lastReturned.next;
unlink(lastReturned);
if (next == lastReturned)
next = lastNext;
else
nextIndex--;
lastReturned = null;
expectedModCount++;
}
public void set(E e) {
if (lastReturned == null)
throw new IllegalStateException();
checkForComodification();
lastReturned.item = e;
}
public void add(E e) {
checkForComodification();
lastReturned = null;
if (next == null)
linkLast(e);
else
linkBefore(e, next);
nextIndex++;
expectedModCount++;
}
public void forEachRemaining(Consumer<? super E> action) {
Objects.requireNonNull(action);
while (modCount == expectedModCount && nextIndex < size) {
action.accept(next.item);
lastReturned = next;
next = next.next;
nextIndex++;
}
checkForComodification();
}
final void checkForComodification() {
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
private static class Node<E> {
E item;
Node<E> next;
Node<E> prev;
Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) {
this.item = element;
this.next = next;
this.prev = prev;
}
}
/**
* @since 1.6
*/
public Iterator<E> descendingIterator() {
return new DescendingIterator();
}
/**
* Adapter to provide descending iterators via ListItr.previous
*/
private class DescendingIterator implements Iterator<E> {
private final ListItr itr = new ListItr(size());
public boolean hasNext() {
return itr.hasPrevious();
}
public E next() {
return itr.previous();
}
public void remove() {
itr.remove();
}
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
private LinkedList<E> superClone() {
try {
return (LinkedList<E>) super.clone();
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
throw new InternalError(e);
}
}
/**
* Returns a shallow copy of this {@code LinkedList}. (The elements
* themselves are not cloned.)
*
* @return a shallow copy of this {@code LinkedList} instance
*/
public Object clone() {
LinkedList<E> clone = superClone();
// Put clone into "virgin" state
clone.first = clone.last = null;
clone.size = 0;
clone.modCount = 0;
// Initialize clone with our elements
for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next)
clone.add(x.item);
return clone;
}
/**
* Returns an array containing all of the elements in this list
* in proper sequence (from first to last element).
*
* <p>The returned array will be "safe" in that no references to it are
* maintained by this list. (In other words, this method must allocate
* a new array). The caller is thus free to modify the returned array.
*
* <p>This method acts as bridge between array-based and collection-based
* APIs.
*
* @return an array containing all of the elements in this list
* in proper sequence
*/
public Object[] toArray() {
Object[] result = new Object[size];
int i = 0;
for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next)
result[i++] = x.item;
return result;
}
/**
* Returns an array containing all of the elements in this list in
* proper sequence (from first to last element); the runtime type of
* the returned array is that of the specified array. If the list fits
* in the specified array, it is returned therein. Otherwise, a new
* array is allocated with the runtime type of the specified array and
* the size of this list.
*
* <p>If the list fits in the specified array with room to spare (i.e.,
* the array has more elements than the list), the element in the array
* immediately following the end of the list is set to {@code null}.
* (This is useful in determining the length of the list <i>only</i> if
* the caller knows that the list does not contain any null elements.)
*
* <p>Like the {@link #toArray()} method, this method acts as bridge between
* array-based and collection-based APIs. Further, this method allows
* precise control over the runtime type of the output array, and may,
* under certain circumstances, be used to save allocation costs.
*
* <p>Suppose {@code x} is a list known to contain only strings.
* The following code can be used to dump the list into a newly
* allocated array of {@code String}:
*
* <pre>
* String[] y = x.toArray(new String[0]);</pre>
*
* Note that {@code toArray(new Object[0])} is identical in function to
* {@code toArray()}.
*
* @param a the array into which the elements of the list are to
* be stored, if it is big enough; otherwise, a new array of the
* same runtime type is allocated for this purpose.
* @return an array containing the elements of the list
* @throws ArrayStoreException if the runtime type of the specified array
* is not a supertype of the runtime type of every element in
* this list
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified array is null
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public <T> T[] toArray(T[] a) {
if (a.length < size)
a = (T[])java.lang.reflect.Array.newInstance(
a.getClass().getComponentType(), size);
int i = 0;
Object[] result = a;
for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next)
result[i++] = x.item;
if (a.length > size)
a[size] = null;
return a;
}
@java.io.Serial
private static final long serialVersionUID = 876323262645176354L;
/**
* Saves the state of this {@code LinkedList} instance to a stream
* (that is, serializes it).
*
* @serialData The size of the list (the number of elements it
* contains) is emitted (int), followed by all of its
* elements (each an Object) in the proper order.
*/
@java.io.Serial
private void writeObject(java.io.ObjectOutputStream s)
throws java.io.IOException {
// Write out any hidden serialization magic
s.defaultWriteObject();
// Write out size
s.writeInt(size);
// Write out all elements in the proper order.
for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next)
s.writeObject(x.item);
}
/**
* Reconstitutes this {@code LinkedList} instance from a stream
* (that is, deserializes it).
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
@java.io.Serial
private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s)
throws java.io.IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
// Read in any hidden serialization magic
s.defaultReadObject();
// Read in size
int size = s.readInt();
// Read in all elements in the proper order.
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
linkLast((E)s.readObject());
}
/**
* Creates a <em><a href="Spliterator.html#binding">late-binding</a></em>
* and <em>fail-fast</em> {@link Spliterator} over the elements in this
* list.
*
* <p>The {@code Spliterator} reports {@link Spliterator#SIZED} and
* {@link Spliterator#ORDERED}. Overriding implementations should document
* the reporting of additional characteristic values.
*
* @implNote
* The {@code Spliterator} additionally reports {@link Spliterator#SUBSIZED}
* and implements {@code trySplit} to permit limited parallelism..
*
* @return a {@code Spliterator} over the elements in this list
* @since 1.8
*/
@Override
public Spliterator<E> spliterator() {
return new LLSpliterator<>(this, -1, 0);
}
/** A customized variant of Spliterators.IteratorSpliterator */
static final class LLSpliterator<E> implements Spliterator<E> {
static final int BATCH_UNIT = 1 << 10; // batch array size increment
static final int MAX_BATCH = 1 << 25; // max batch array size;
final LinkedList<E> list; // null OK unless traversed
Node<E> current; // current node; null until initialized
int est; // size estimate; -1 until first needed
int expectedModCount; // initialized when est set
int batch; // batch size for splits
LLSpliterator(LinkedList<E> list, int est, int expectedModCount) {
this.list = list;
this.est = est;
this.expectedModCount = expectedModCount;
}
final int getEst() {
int s; // force initialization
final LinkedList<E> lst;
if ((s = est) < 0) {
if ((lst = list) == null)
s = est = 0;
else {
expectedModCount = lst.modCount;
current = lst.first;
s = est = lst.size;
}
}
return s;
}
public long estimateSize() { return (long) getEst(); }
public Spliterator<E> trySplit() {
Node<E> p;
int s = getEst();
if (s > 1 && (p = current) != null) {
int n = batch + BATCH_UNIT;
if (n > s)
n = s;
if (n > MAX_BATCH)
n = MAX_BATCH;
Object[] a = new Object[n];
int j = 0;
do { a[j++] = p.item; } while ((p = p.next) != null && j < n);
current = p;
batch = j;
est = s - j;
return Spliterators.spliterator(a, 0, j, Spliterator.ORDERED);
}
return null;
}
public void forEachRemaining(Consumer<? super E> action) {
Node<E> p; int n;
if (action == null) throw new NullPointerException();
if ((n = getEst()) > 0 && (p = current) != null) {
current = null;
est = 0;
do {
E e = p.item;
p = p.next;
action.accept(e);
} while (p != null && --n > 0);
}
if (list.modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
public boolean tryAdvance(Consumer<? super E> action) {
Node<E> p;
if (action == null) throw new NullPointerException();
if (getEst() > 0 && (p = current) != null) {
--est;
E e = p.item;
current = p.next;
action.accept(e);
if (list.modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
return true;
}
return false;
}
public int characteristics() {
return Spliterator.ORDERED | Spliterator.SIZED | Spliterator.SUBSIZED;
}
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
* <p>
* Modifications to the reversed view are permitted and will be propagated to this list.
* In addition, modifications to this list will be visible in the reversed view.
*
* @return {@inheritDoc}
* @since 21
*/
public LinkedList<E> reversed() {
return new ReverseOrderLinkedListView<>(this, super.reversed(), Deque.super.reversed());
}
// all operations are delegated to the reverse-ordered views.
// TODO audit all overridden methods
@SuppressWarnings("serial")
static class ReverseOrderLinkedListView<E> extends LinkedList<E> implements java.io.Externalizable {
final LinkedList<E> list;
final List<E> rlist;
final Deque<E> rdeque;
ReverseOrderLinkedListView(LinkedList<E> list, List<E> rlist, Deque<E> rdeque) {
this.list = list;
this.rlist = rlist;
this.rdeque = rdeque;
}
public String toString() {
return rlist.toString();
}
public boolean retainAll(Collection<?> c) {
return rlist.retainAll(c);
}
public boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c) {
return rlist.removeAll(c);
}
public boolean containsAll(Collection<?> c) {
return rlist.containsAll(c);
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return rlist.isEmpty();
}
public Stream<E> parallelStream() {
return rlist.parallelStream();
}
public Stream<E> stream() {
return rlist.stream();
}
public boolean removeIf(Predicate<? super E> filter) {
return rlist.removeIf(filter);
}
public <T> T[] toArray(IntFunction<T[]> generator) {
return rlist.toArray(generator);
}
public void forEach(Consumer<? super E> action) {
rlist.forEach(action);
}
public Iterator<E> iterator() {
return rlist.iterator();
}
public int hashCode() {
return rlist.hashCode();
}
public boolean equals(Object o) {
return rlist.equals(o);
}
public List<E> subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
return rlist.subList(fromIndex, toIndex);
}
public ListIterator<E> listIterator() {
return rlist.listIterator();
}
public void sort(Comparator<? super E> c) {
rlist.sort(c);
}
public void replaceAll(UnaryOperator<E> operator) {
rlist.replaceAll(operator);
}
public LinkedList<E> reversed() {
return list;
}
public Spliterator<E> spliterator() {
return rlist.spliterator();
}
public <T> T[] toArray(T[] a) {
return rlist.toArray(a);
}
public Object[] toArray() {
return rlist.toArray();
}
public Iterator<E> descendingIterator() {
return rdeque.descendingIterator();
}
public ListIterator<E> listIterator(int index) {
return rlist.listIterator(index);
}
public boolean removeLastOccurrence(Object o) {
return rdeque.removeLastOccurrence(o);
}
public boolean removeFirstOccurrence(Object o) {
return rdeque.removeFirstOccurrence(o);
}
public E pop() {
return rdeque.pop();
}
public void push(E e) {
rdeque.push(e);
}
public E pollLast() {
return rdeque.pollLast();
}
public E pollFirst() {
return rdeque.pollFirst();
}
public E peekLast() {
return rdeque.peekLast();
}
public E peekFirst() {
return rdeque.peekFirst();
}
public boolean offerLast(E e) {
return rdeque.offerLast(e);
}
public boolean offerFirst(E e) {
return rdeque.offerFirst(e);
}
public boolean offer(E e) {
return rdeque.offer(e);
}
public E remove() {
return rdeque.remove();
}
public E poll() {
return rdeque.poll();
}
public E element() {
return rdeque.element();
}
public E peek() {
return rdeque.peek();
}
public int lastIndexOf(Object o) {
return rlist.lastIndexOf(o);
}
public int indexOf(Object o) {
return rlist.indexOf(o);
}
public E remove(int index) {
return rlist.remove(index);
}
public void add(int index, E element) {
rlist.add(index, element);
}
public E set(int index, E element) {
return rlist.set(index, element);
}
public E get(int index) {
return rlist.get(index);
}
public void clear() {
rlist.clear();
}
public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) {
return rlist.addAll(index, c);
}
public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) {
return rlist.addAll(c);
}
public boolean remove(Object o) {
return rlist.remove(o);
}
public boolean add(E e) {
return rlist.add(e);
}
public int size() {
return rlist.size();
}
public boolean contains(Object o) {
return rlist.contains(o);
}
public void addLast(E e) {
rdeque.addLast(e);
}
public void addFirst(E e) {
rdeque.addFirst(e);
}
public E removeLast() {
return rdeque.removeLast();
}
public E removeFirst() {
return rdeque.removeFirst();
}
public E getLast() {
return rdeque.getLast();
}
public E getFirst() {
return rdeque.getFirst();
}
public void readExternal(ObjectInput in) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
throw new java.io.InvalidObjectException("not serializable");
}
public void writeExternal(ObjectOutput out) throws IOException {
throw new java.io.InvalidObjectException("not serializable");
}
}
}
menti.com 2335 3741
How big can an ArrayList get?
# Queue
/*
* Copyright (c) 1997, 2023, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
* DO NOT ALTER OR REMOVE COPYRIGHT NOTICES OR THIS FILE HEADER.
*
* This code is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify it
* under the terms of the GNU General Public License version 2 only, as
* published by the Free Software Foundation. Oracle designates this
* particular file as subject to the "Classpath" exception as provided
* by Oracle in the LICENSE file that accompanied this code.
*
* This code is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT
* ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or
* FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU General Public License
* version 2 for more details (a copy is included in the LICENSE file that
* accompanied this code).
*
* You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License version
* 2 along with this work; if not, write to the Free Software Foundation,
* Inc., 51 Franklin St, Fifth Floor, Boston, MA 02110-1301 USA.
*
* Please contact Oracle, 500 Oracle Parkway, Redwood Shores, CA 94065 USA
* or visit www.oracle.com if you need additional information or have any
* questions.
*/
package java.util;
import java.util.function.Consumer;
import java.util.function.Predicate;
import java.util.function.UnaryOperator;
import jdk.internal.access.SharedSecrets;
import jdk.internal.util.ArraysSupport;
/**
* Resizable-array implementation of the {@code List} interface. Implements
* all optional list operations, and permits all elements, including
* {@code null}. In addition to implementing the {@code List} interface,
* this class provides methods to manipulate the size of the array that is
* used internally to store the list. (This class is roughly equivalent to
* {@code Vector}, except that it is unsynchronized.)
*
* <p>The {@code size}, {@code isEmpty}, {@code get}, {@code set},
* {@code iterator}, and {@code listIterator} operations run in constant
* time. The {@code add} operation runs in <i>amortized constant time</i>,
* that is, adding n elements requires O(n) time. All of the other operations
* run in linear time (roughly speaking). The constant factor is low compared
* to that for the {@code LinkedList} implementation.
*
* <p>Each {@code ArrayList} instance has a <i>capacity</i>. The capacity is
* the size of the array used to store the elements in the list. It is always
* at least as large as the list size. As elements are added to an ArrayList,
* its capacity grows automatically. The details of the growth policy are not
* specified beyond the fact that adding an element has constant amortized
* time cost.
*
* <p>An application can increase the capacity of an {@code ArrayList} instance
* before adding a large number of elements using the {@code ensureCapacity}
* operation. This may reduce the amount of incremental reallocation.
*
* <p><strong>Note that this implementation is not synchronized.</strong>
* If multiple threads access an {@code ArrayList} instance concurrently,
* and at least one of the threads modifies the list structurally, it
* <i>must</i> be synchronized externally. (A structural modification is
* any operation that adds or deletes one or more elements, or explicitly
* resizes the backing array; merely setting the value of an element is not
* a structural modification.) This is typically accomplished by
* synchronizing on some object that naturally encapsulates the list.
*
* If no such object exists, the list should be "wrapped" using the
* {@link Collections#synchronizedList Collections.synchronizedList}
* method. This is best done at creation time, to prevent accidental
* unsynchronized access to the list:<pre>
* List list = Collections.synchronizedList(new ArrayList(...));</pre>
*
* <p id="fail-fast">
* The iterators returned by this class's {@link #iterator() iterator} and
* {@link #listIterator(int) listIterator} methods are <em>fail-fast</em>:
* if the list is structurally modified at any time after the iterator is
* created, in any way except through the iterator's own
* {@link ListIterator#remove() remove} or
* {@link ListIterator#add(Object) add} methods, the iterator will throw a
* {@link ConcurrentModificationException}. Thus, in the face of
* concurrent modification, the iterator fails quickly and cleanly, rather
* than risking arbitrary, non-deterministic behavior at an undetermined
* time in the future.
*
* <p>Note that the fail-fast behavior of an iterator cannot be guaranteed
* as it is, generally speaking, impossible to make any hard guarantees in the
* presence of unsynchronized concurrent modification. Fail-fast iterators
* throw {@code ConcurrentModificationException} on a best-effort basis.
* Therefore, it would be wrong to write a program that depended on this
* exception for its correctness: <i>the fail-fast behavior of iterators
* should be used only to detect bugs.</i>
*
* <p>This class is a member of the
* <a href="{@docRoot}/java.base/java/util/package-summary.html#CollectionsFramework">
* Java Collections Framework</a>.
*
* @param <E> the type of elements in this list
*
* @author Josh Bloch
* @author Neal Gafter
* @see Collection
* @see List
* @see LinkedList
* @see Vector
* @since 1.2
*/
public class ArrayList<E> extends AbstractList<E>
implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
{
@java.io.Serial
private static final long serialVersionUID = 8683452581122892189L;
/**
* Default initial capacity.
*/
private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10;
/**
* Shared empty array instance used for empty instances.
*/
private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};
/**
* Shared empty array instance used for default sized empty instances. We
* distinguish this from EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA to know how much to inflate when
* first element is added.
*/
private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};
/**
* The array buffer into which the elements of the ArrayList are stored.
* The capacity of the ArrayList is the length of this array buffer. Any
* empty ArrayList with elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA
* will be expanded to DEFAULT_CAPACITY when the first element is added.
*/
transient Object[] elementData; // non-private to simplify nested class access
/**
* The size of the ArrayList (the number of elements it contains).
*
* @serial
*/
private int size;
/**
* Constructs an empty list with the specified initial capacity.
*
* @param initialCapacity the initial capacity of the list
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the specified initial capacity
* is negative
*/
public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) {
if (initialCapacity > 0) {
this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];
} else if (initialCapacity == 0) {
this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
} else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+
initialCapacity);
}
}
/**
* Constructs an empty list with an initial capacity of ten.
*/
public ArrayList() {
this.elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
}
/**
* Constructs a list containing the elements of the specified
* collection, in the order they are returned by the collection's
* iterator.
*
* @param c the collection whose elements are to be placed into this list
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null
*/
public ArrayList(Collection<? extends E> c) {
Object[] a = c.toArray();
if ((size = a.length) != 0) {
if (c.getClass() == ArrayList.class) {
elementData = a;
} else {
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(a, size, Object[].class);
}
} else {
// replace with empty array.
elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
}
}
/**
* Trims the capacity of this {@code ArrayList} instance to be the
* list's current size. An application can use this operation to minimize
* the storage of an {@code ArrayList} instance.
*/
public void trimToSize() {
modCount++;
if (size < elementData.length) {
elementData = (size == 0)
? EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA
: Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size);
}
}
/**
* Increases the capacity of this {@code ArrayList} instance, if
* necessary, to ensure that it can hold at least the number of elements
* specified by the minimum capacity argument.
*
* @param minCapacity the desired minimum capacity
*/
public void ensureCapacity(int minCapacity) {
if (minCapacity > elementData.length
&& !(elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA
&& minCapacity <= DEFAULT_CAPACITY)) {
modCount++;
grow(minCapacity);
}
}
/**
* Increases the capacity to ensure that it can hold at least the
* number of elements specified by the minimum capacity argument.
*
* @param minCapacity the desired minimum capacity
* @throws OutOfMemoryError if minCapacity is less than zero
*/
private Object[] grow(int minCapacity) {
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
if (oldCapacity > 0 || elementData != DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) {
int newCapacity = ArraysSupport.newLength(oldCapacity,
minCapacity - oldCapacity, /* minimum growth */
oldCapacity >> 1 /* preferred growth */);
return elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
} else {
return elementData = new Object[Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity)];
}
}
private Object[] grow() {
return grow(size + 1);
}
/**
* Returns the number of elements in this list.
*
* @return the number of elements in this list
*/
public int size() {
return size;
}
/**
* Returns {@code true} if this list contains no elements.
*
* @return {@code true} if this list contains no elements
*/
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size == 0;
}
/**
* Returns {@code true} if this list contains the specified element.
* More formally, returns {@code true} if and only if this list contains
* at least one element {@code e} such that
* {@code Objects.equals(o, e)}.
*
* @param o element whose presence in this list is to be tested
* @return {@code true} if this list contains the specified element
*/
public boolean contains(Object o) {
return indexOf(o) >= 0;
}
/**
* Returns the index of the first occurrence of the specified element
* in this list, or -1 if this list does not contain the element.
* More formally, returns the lowest index {@code i} such that
* {@code Objects.equals(o, get(i))},
* or -1 if there is no such index.
*/
public int indexOf(Object o) {
return indexOfRange(o, 0, size);
}
int indexOfRange(Object o, int start, int end) {
Object[] es = elementData;
if (o == null) {
for (int i = start; i < end; i++) {
if (es[i] == null) {
return i;
}
}
} else {
for (int i = start; i < end; i++) {
if (o.equals(es[i])) {
return i;
}
}
}
return -1;
}
/**
* Returns the index of the last occurrence of the specified element
* in this list, or -1 if this list does not contain the element.
* More formally, returns the highest index {@code i} such that
* {@code Objects.equals(o, get(i))},
* or -1 if there is no such index.
*/
public int lastIndexOf(Object o) {
return lastIndexOfRange(o, 0, size);
}
int lastIndexOfRange(Object o, int start, int end) {
Object[] es = elementData;
if (o == null) {
for (int i = end - 1; i >= start; i--) {
if (es[i] == null) {
return i;
}
}
} else {
for (int i = end - 1; i >= start; i--) {
if (o.equals(es[i])) {
return i;
}
}
}
return -1;
}
/**
* Returns a shallow copy of this {@code ArrayList} instance. (The
* elements themselves are not copied.)
*
* @return a clone of this {@code ArrayList} instance
*/
public Object clone() {
try {
ArrayList<?> v = (ArrayList<?>) super.clone();
v.elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size);
v.modCount = 0;
return v;
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
// this shouldn't happen, since we are Cloneable
throw new InternalError(e);
}
}
/**
* Returns an array containing all of the elements in this list
* in proper sequence (from first to last element).
*
* <p>The returned array will be "safe" in that no references to it are
* maintained by this list. (In other words, this method must allocate
* a new array). The caller is thus free to modify the returned array.
*
* <p>This method acts as bridge between array-based and collection-based
* APIs.
*
* @return an array containing all of the elements in this list in
* proper sequence
*/
public Object[] toArray() {
return Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size);
}
/**
* Returns an array containing all of the elements in this list in proper
* sequence (from first to last element); the runtime type of the returned
* array is that of the specified array. If the list fits in the
* specified array, it is returned therein. Otherwise, a new array is
* allocated with the runtime type of the specified array and the size of
* this list.
*
* <p>If the list fits in the specified array with room to spare
* (i.e., the array has more elements than the list), the element in
* the array immediately following the end of the collection is set to
* {@code null}. (This is useful in determining the length of the
* list <i>only</i> if the caller knows that the list does not contain
* any null elements.)
*
* @param a the array into which the elements of the list are to
* be stored, if it is big enough; otherwise, a new array of the
* same runtime type is allocated for this purpose.
* @return an array containing the elements of the list
* @throws ArrayStoreException if the runtime type of the specified array
* is not a supertype of the runtime type of every element in
* this list
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified array is null
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public <T> T[] toArray(T[] a) {
if (a.length < size)
// Make a new array of a's runtime type, but my contents:
return (T[]) Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size, a.getClass());
System.arraycopy(elementData, 0, a, 0, size);
if (a.length > size)
a[size] = null;
return a;
}
// Positional Access Operations
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
E elementData(int index) {
return (E) elementData[index];
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
static <E> E elementAt(Object[] es, int index) {
return (E) es[index];
}
/**
* Returns the element at the specified position in this list.
*
* @param index index of the element to return
* @return the element at the specified position in this list
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public E get(int index) {
Objects.checkIndex(index, size);
return elementData(index);
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*
* @throws NoSuchElementException {@inheritDoc}
* @since 21
*/
public E getFirst() {
if (size == 0) {
throw new NoSuchElementException();
} else {
return elementData(0);
}
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*
* @throws NoSuchElementException {@inheritDoc}
* @since 21
*/
public E getLast() {
int last = size - 1;
if (last < 0) {
throw new NoSuchElementException();
} else {
return elementData(last);
}
}
/**
* Replaces the element at the specified position in this list with
* the specified element.
*
* @param index index of the element to replace
* @param element element to be stored at the specified position
* @return the element previously at the specified position
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public E set(int index, E element) {
Objects.checkIndex(index, size);
E oldValue = elementData(index);
elementData[index] = element;
return oldValue;
}
/**
* This helper method split out from add(E) to keep method
* bytecode size under 35 (the -XX:MaxInlineSize default value),
* which helps when add(E) is called in a C1-compiled loop.
*/
private void add(E e, Object[] elementData, int s) {
if (s == elementData.length)
elementData = grow();
elementData[s] = e;
size = s + 1;
}
/**
* Appends the specified element to the end of this list.
*
* @param e element to be appended to this list
* @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Collection#add})
*/
public boolean add(E e) {
modCount++;
add(e, elementData, size);
return true;
}
/**
* Inserts the specified element at the specified position in this
* list. Shifts the element currently at that position (if any) and
* any subsequent elements to the right (adds one to their indices).
*
* @param index index at which the specified element is to be inserted
* @param element element to be inserted
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public void add(int index, E element) {
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
modCount++;
final int s;
Object[] elementData;
if ((s = size) == (elementData = this.elementData).length)
elementData = grow();
System.arraycopy(elementData, index,
elementData, index + 1,
s - index);
elementData[index] = element;
size = s + 1;
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*
* @since 21
*/
public void addFirst(E element) {
add(0, element);
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*
* @since 21
*/
public void addLast(E element) {
add(element);
}
/**
* Removes the element at the specified position in this list.
* Shifts any subsequent elements to the left (subtracts one from their
* indices).
*
* @param index the index of the element to be removed
* @return the element that was removed from the list
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public E remove(int index) {
Objects.checkIndex(index, size);
final Object[] es = elementData;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") E oldValue = (E) es[index];
fastRemove(es, index);
return oldValue;
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*
* @throws NoSuchElementException {@inheritDoc}
* @since 21
*/
public E removeFirst() {
if (size == 0) {
throw new NoSuchElementException();
} else {
Object[] es = elementData;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") E oldValue = (E) es[0];
fastRemove(es, 0);
return oldValue;
}
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*
* @throws NoSuchElementException {@inheritDoc}
* @since 21
*/
public E removeLast() {
int last = size - 1;
if (last < 0) {
throw new NoSuchElementException();
} else {
Object[] es = elementData;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") E oldValue = (E) es[last];
fastRemove(es, last);
return oldValue;
}
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*/
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (o == this) {
return true;
}
if (!(o instanceof List)) {
return false;
}
final int expectedModCount = modCount;
// ArrayList can be subclassed and given arbitrary behavior, but we can
// still deal with the common case where o is ArrayList precisely
boolean equal = (o.getClass() == ArrayList.class)
? equalsArrayList((ArrayList<?>) o)
: equalsRange((List<?>) o, 0, size);
checkForComodification(expectedModCount);
return equal;
}
boolean equalsRange(List<?> other, int from, int to) {
final Object[] es = elementData;
if (to > es.length) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
var oit = other.iterator();
for (; from < to; from++) {
if (!oit.hasNext() || !Objects.equals(es[from], oit.next())) {
return false;
}
}
return !oit.hasNext();
}
private boolean equalsArrayList(ArrayList<?> other) {
final int otherModCount = other.modCount;
final int s = size;
boolean equal;
if (equal = (s == other.size)) {
final Object[] otherEs = other.elementData;
final Object[] es = elementData;
if (s > es.length || s > otherEs.length) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
for (int i = 0; i < s; i++) {
if (!Objects.equals(es[i], otherEs[i])) {
equal = false;
break;
}
}
}
other.checkForComodification(otherModCount);
return equal;
}
private void checkForComodification(final int expectedModCount) {
if (modCount != expectedModCount) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*/
public int hashCode() {
int expectedModCount = modCount;
int hash = hashCodeRange(0, size);
checkForComodification(expectedModCount);
return hash;
}
int hashCodeRange(int from, int to) {
final Object[] es = elementData;
if (to > es.length) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
int hashCode = 1;
for (int i = from; i < to; i++) {
Object e = es[i];
hashCode = 31 * hashCode + (e == null ? 0 : e.hashCode());
}
return hashCode;
}
/**
* Removes the first occurrence of the specified element from this list,
* if it is present. If the list does not contain the element, it is
* unchanged. More formally, removes the element with the lowest index
* {@code i} such that
* {@code Objects.equals(o, get(i))}
* (if such an element exists). Returns {@code true} if this list
* contained the specified element (or equivalently, if this list
* changed as a result of the call).
*
* @param o element to be removed from this list, if present
* @return {@code true} if this list contained the specified element
*/
public boolean remove(Object o) {
final Object[] es = elementData;
final int size = this.size;
int i = 0;
found: {
if (o == null) {
for (; i < size; i++)
if (es[i] == null)
break found;
} else {
for (; i < size; i++)
if (o.equals(es[i]))
break found;
}
return false;
}
fastRemove(es, i);
return true;
}
/**
* Private remove method that skips bounds checking and does not
* return the value removed.
*/
private void fastRemove(Object[] es, int i) {
modCount++;
final int newSize;
if ((newSize = size - 1) > i)
System.arraycopy(es, i + 1, es, i, newSize - i);
es[size = newSize] = null;
}
/**
* Removes all of the elements from this list. The list will
* be empty after this call returns.
*/
public void clear() {
modCount++;
final Object[] es = elementData;
for (int to = size, i = size = 0; i < to; i++)
es[i] = null;
}
/**
* Appends all of the elements in the specified collection to the end of
* this list, in the order that they are returned by the
* specified collection's Iterator. The behavior of this operation is
* undefined if the specified collection is modified while the operation
* is in progress. (This implies that the behavior of this call is
* undefined if the specified collection is this list, and this
* list is nonempty.)
*
* @param c collection containing elements to be added to this list
* @return {@code true} if this list changed as a result of the call
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null
*/
public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) {
Object[] a = c.toArray();
modCount++;
int numNew = a.length;
if (numNew == 0)
return false;
Object[] elementData;
final int s;
if (numNew > (elementData = this.elementData).length - (s = size))
elementData = grow(s + numNew);
System.arraycopy(a, 0, elementData, s, numNew);
size = s + numNew;
return true;
}
/**
* Inserts all of the elements in the specified collection into this
* list, starting at the specified position. Shifts the element
* currently at that position (if any) and any subsequent elements to
* the right (increases their indices). The new elements will appear
* in the list in the order that they are returned by the
* specified collection's iterator.
*
* @param index index at which to insert the first element from the
* specified collection
* @param c collection containing elements to be added to this list
* @return {@code true} if this list changed as a result of the call
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null
*/
public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) {
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
Object[] a = c.toArray();
modCount++;
int numNew = a.length;
if (numNew == 0)
return false;
Object[] elementData;
final int s;
if (numNew > (elementData = this.elementData).length - (s = size))
elementData = grow(s + numNew);
int numMoved = s - index;
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index,
elementData, index + numNew,
numMoved);
System.arraycopy(a, 0, elementData, index, numNew);
size = s + numNew;
return true;
}
/**
* Removes from this list all of the elements whose index is between
* {@code fromIndex}, inclusive, and {@code toIndex}, exclusive.
* Shifts any succeeding elements to the left (reduces their index).
* This call shortens the list by {@code (toIndex - fromIndex)} elements.
* (If {@code toIndex==fromIndex}, this operation has no effect.)
*
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException if {@code fromIndex} or
* {@code toIndex} is out of range
* ({@code fromIndex < 0 ||
* toIndex > size() ||
* toIndex < fromIndex})
*/
protected void removeRange(int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
if (fromIndex > toIndex) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(
outOfBoundsMsg(fromIndex, toIndex));
}
modCount++;
shiftTailOverGap(elementData, fromIndex, toIndex);
}
/** Erases the gap from lo to hi, by sliding down following elements. */
private void shiftTailOverGap(Object[] es, int lo, int hi) {
System.arraycopy(es, hi, es, lo, size - hi);
for (int to = size, i = (size -= hi - lo); i < to; i++)
es[i] = null;
}
/**
* A version of rangeCheck used by add and addAll.
*/
private void rangeCheckForAdd(int index) {
if (index > size || index < 0)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
}
/**
* Constructs an IndexOutOfBoundsException detail message.
* Of the many possible refactorings of the error handling code,
* this "outlining" performs best with both server and client VMs.
*/
private String outOfBoundsMsg(int index) {
return "Index: "+index+", Size: "+size;
}
/**
* A version used in checking (fromIndex > toIndex) condition
*/
private static String outOfBoundsMsg(int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
return "From Index: " + fromIndex + " > To Index: " + toIndex;
}
/**
* Removes from this list all of its elements that are contained in the
* specified collection.
*
* @param c collection containing elements to be removed from this list
* @return {@code true} if this list changed as a result of the call
* @throws ClassCastException if the class of an element of this list
* is incompatible with the specified collection
* (<a href="Collection.html#optional-restrictions">optional</a>)
* @throws NullPointerException if this list contains a null element and the
* specified collection does not permit null elements
* (<a href="Collection.html#optional-restrictions">optional</a>),
* or if the specified collection is null
* @see Collection#contains(Object)
*/
public boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c) {
return batchRemove(c, false, 0, size);
}
/**
* Retains only the elements in this list that are contained in the
* specified collection. In other words, removes from this list all
* of its elements that are not contained in the specified collection.
*
* @param c collection containing elements to be retained in this list
* @return {@code true} if this list changed as a result of the call
* @throws ClassCastException if the class of an element of this list
* is incompatible with the specified collection
* (<a href="Collection.html#optional-restrictions">optional</a>)
* @throws NullPointerException if this list contains a null element and the
* specified collection does not permit null elements
* (<a href="Collection.html#optional-restrictions">optional</a>),
* or if the specified collection is null
* @see Collection#contains(Object)
*/
public boolean retainAll(Collection<?> c) {
return batchRemove(c, true, 0, size);
}
boolean batchRemove(Collection<?> c, boolean complement,
final int from, final int end) {
Objects.requireNonNull(c);
final Object[] es = elementData;
int r;
// Optimize for initial run of survivors
for (r = from;; r++) {
if (r == end)
return false;
if (c.contains(es[r]) != complement)
break;
}
int w = r++;
try {
for (Object e; r < end; r++)
if (c.contains(e = es[r]) == complement)
es[w++] = e;
} catch (Throwable ex) {
// Preserve behavioral compatibility with AbstractCollection,
// even if c.contains() throws.
System.arraycopy(es, r, es, w, end - r);
w += end - r;
throw ex;
} finally {
modCount += end - w;
shiftTailOverGap(es, w, end);
}
return true;
}
/**
* Saves the state of the {@code ArrayList} instance to a stream
* (that is, serializes it).
*
* @param s the stream
* @throws java.io.IOException if an I/O error occurs
* @serialData The length of the array backing the {@code ArrayList}
* instance is emitted (int), followed by all of its elements
* (each an {@code Object}) in the proper order.
*/
@java.io.Serial
private void writeObject(java.io.ObjectOutputStream s)
throws java.io.IOException {
// Write out element count, and any hidden stuff
int expectedModCount = modCount;
s.defaultWriteObject();
// Write out size as capacity for behavioral compatibility with clone()
s.writeInt(size);
// Write out all elements in the proper order.
for (int i=0; i<size; i++) {
s.writeObject(elementData[i]);
}
if (modCount != expectedModCount) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
/**
* Reconstitutes the {@code ArrayList} instance from a stream (that is,
* deserializes it).
* @param s the stream
* @throws ClassNotFoundException if the class of a serialized object
* could not be found
* @throws java.io.IOException if an I/O error occurs
*/
@java.io.Serial
private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s)
throws java.io.IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
// Read in size, and any hidden stuff
s.defaultReadObject();
// Read in capacity
s.readInt(); // ignored
if (size > 0) {
// like clone(), allocate array based upon size not capacity
SharedSecrets.getJavaObjectInputStreamAccess().checkArray(s, Object[].class, size);
Object[] elements = new Object[size];
// Read in all elements in the proper order.
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
elements[i] = s.readObject();
}
elementData = elements;
} else if (size == 0) {
elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
} else {
throw new java.io.InvalidObjectException("Invalid size: " + size);
}
}
/**
* Returns a list iterator over the elements in this list (in proper
* sequence), starting at the specified position in the list.
* The specified index indicates the first element that would be
* returned by an initial call to {@link ListIterator#next next}.
* An initial call to {@link ListIterator#previous previous} would
* return the element with the specified index minus one.
*
* <p>The returned list iterator is <a href="#fail-fast"><i>fail-fast</i></a>.
*
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public ListIterator<E> listIterator(int index) {
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
return new ListItr(index);
}
/**
* Returns a list iterator over the elements in this list (in proper
* sequence).
*
* <p>The returned list iterator is <a href="#fail-fast"><i>fail-fast</i></a>.
*
* @see #listIterator(int)
*/
public ListIterator<E> listIterator() {
return new ListItr(0);
}
/**
* Returns an iterator over the elements in this list in proper sequence.
*
* <p>The returned iterator is <a href="#fail-fast"><i>fail-fast</i></a>.
*
* @return an iterator over the elements in this list in proper sequence
*/
public Iterator<E> iterator() {
return new Itr();
}
/**
* An optimized version of AbstractList.Itr
*/
private class Itr implements Iterator<E> {
int cursor; // index of next element to return
int lastRet = -1; // index of last element returned; -1 if no such
int expectedModCount = modCount;
// prevent creating a synthetic constructor
Itr() {}
public boolean hasNext() {
return cursor != size;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public E next() {
checkForComodification();
int i = cursor;
if (i >= size)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData;
if (i >= elementData.length)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
cursor = i + 1;
return (E) elementData[lastRet = i];
}
public void remove() {
if (lastRet < 0)
throw new IllegalStateException();
checkForComodification();
try {
ArrayList.this.remove(lastRet);
cursor = lastRet;
lastRet = -1;
expectedModCount = modCount;
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
@Override
public void forEachRemaining(Consumer<? super E> action) {
Objects.requireNonNull(action);
final int size = ArrayList.this.size;
int i = cursor;
if (i < size) {
final Object[] es = elementData;
if (i >= es.length)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
for (; i < size && modCount == expectedModCount; i++)
action.accept(elementAt(es, i));
// update once at end to reduce heap write traffic
cursor = i;
lastRet = i - 1;
checkForComodification();
}
}
final void checkForComodification() {
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
/**
* An optimized version of AbstractList.ListItr
*/
private class ListItr extends Itr implements ListIterator<E> {
ListItr(int index) {
super();
cursor = index;
}
public boolean hasPrevious() {
return cursor != 0;
}
public int nextIndex() {
return cursor;
}
public int previousIndex() {
return cursor - 1;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public E previous() {
checkForComodification();
int i = cursor - 1;
if (i < 0)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData;
if (i >= elementData.length)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
cursor = i;
return (E) elementData[lastRet = i];
}
public void set(E e) {
if (lastRet < 0)
throw new IllegalStateException();
checkForComodification();
try {
ArrayList.this.set(lastRet, e);
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
public void add(E e) {
checkForComodification();
try {
int i = cursor;
ArrayList.this.add(i, e);
cursor = i + 1;
lastRet = -1;
expectedModCount = modCount;
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
}
/**
* Returns a view of the portion of this list between the specified
* {@code fromIndex}, inclusive, and {@code toIndex}, exclusive. (If
* {@code fromIndex} and {@code toIndex} are equal, the returned list is
* empty.) The returned list is backed by this list, so non-structural
* changes in the returned list are reflected in this list, and vice-versa.
* The returned list supports all of the optional list operations.
*
* <p>This method eliminates the need for explicit range operations (of
* the sort that commonly exist for arrays). Any operation that expects
* a list can be used as a range operation by passing a subList view
* instead of a whole list. For example, the following idiom
* removes a range of elements from a list:
* <pre>
* list.subList(from, to).clear();
* </pre>
* Similar idioms may be constructed for {@link #indexOf(Object)} and
* {@link #lastIndexOf(Object)}, and all of the algorithms in the
* {@link Collections} class can be applied to a subList.
*
* <p>The semantics of the list returned by this method become undefined if
* the backing list (i.e., this list) is <i>structurally modified</i> in
* any way other than via the returned list. (Structural modifications are
* those that change the size of this list, or otherwise perturb it in such
* a fashion that iterations in progress may yield incorrect results.)
*
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
* @throws IllegalArgumentException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public List<E> subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
subListRangeCheck(fromIndex, toIndex, size);
return new SubList<>(this, fromIndex, toIndex);
}
private static class SubList<E> extends AbstractList<E> implements RandomAccess {
private final ArrayList<E> root;
private final SubList<E> parent;
private final int offset;
private int size;
/**
* Constructs a sublist of an arbitrary ArrayList.
*/
public SubList(ArrayList<E> root, int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
this.root = root;
this.parent = null;
this.offset = fromIndex;
this.size = toIndex - fromIndex;
this.modCount = root.modCount;
}
/**
* Constructs a sublist of another SubList.
*/
private SubList(SubList<E> parent, int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
this.root = parent.root;
this.parent = parent;
this.offset = parent.offset + fromIndex;
this.size = toIndex - fromIndex;
this.modCount = parent.modCount;
}
public E set(int index, E element) {
Objects.checkIndex(index, size);
checkForComodification();
E oldValue = root.elementData(offset + index);
root.elementData[offset + index] = element;
return oldValue;
}
public E get(int index) {
Objects.checkIndex(index, size);
checkForComodification();
return root.elementData(offset + index);
}
public int size() {
checkForComodification();
return size;
}
public void add(int index, E element) {
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
checkForComodification();
root.add(offset + index, element);
updateSizeAndModCount(1);
}
public E remove(int index) {
Objects.checkIndex(index, size);
checkForComodification();
E result = root.remove(offset + index);
updateSizeAndModCount(-1);
return result;
}
protected void removeRange(int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
checkForComodification();
root.removeRange(offset + fromIndex, offset + toIndex);
updateSizeAndModCount(fromIndex - toIndex);
}
public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) {
return addAll(this.size, c);
}
public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) {
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
int cSize = c.size();
if (cSize==0)
return false;
checkForComodification();
root.addAll(offset + index, c);
updateSizeAndModCount(cSize);
return true;
}
public void replaceAll(UnaryOperator<E> operator) {
root.replaceAllRange(operator, offset, offset + size);
}
public boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c) {
return batchRemove(c, false);
}
public boolean retainAll(Collection<?> c) {
return batchRemove(c, true);
}
private boolean batchRemove(Collection<?> c, boolean complement) {
checkForComodification();
int oldSize = root.size;
boolean modified =
root.batchRemove(c, complement, offset, offset + size);
if (modified)
updateSizeAndModCount(root.size - oldSize);
return modified;
}
public boolean removeIf(Predicate<? super E> filter) {
checkForComodification();
int oldSize = root.size;
boolean modified = root.removeIf(filter, offset, offset + size);
if (modified)
updateSizeAndModCount(root.size - oldSize);
return modified;
}
public Object[] toArray() {
checkForComodification();
return Arrays.copyOfRange(root.elementData, offset, offset + size);
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public <T> T[] toArray(T[] a) {
checkForComodification();
if (a.length < size)
return (T[]) Arrays.copyOfRange(
root.elementData, offset, offset + size, a.getClass());
System.arraycopy(root.elementData, offset, a, 0, size);
if (a.length > size)
a[size] = null;
return a;
}
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (o == this) {
return true;
}
if (!(o instanceof List)) {
return false;
}
boolean equal = root.equalsRange((List<?>)o, offset, offset + size);
checkForComodification();
return equal;
}
public int hashCode() {
int hash = root.hashCodeRange(offset, offset + size);
checkForComodification();
return hash;
}
public int indexOf(Object o) {
int index = root.indexOfRange(o, offset, offset + size);
checkForComodification();
return index >= 0 ? index - offset : -1;
}
public int lastIndexOf(Object o) {
int index = root.lastIndexOfRange(o, offset, offset + size);
checkForComodification();
return index >= 0 ? index - offset : -1;
}
public boolean contains(Object o) {
return indexOf(o) >= 0;
}
public Iterator<E> iterator() {
return listIterator();
}
public ListIterator<E> listIterator(int index) {
checkForComodification();
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
return new ListIterator<E>() {
int cursor = index;
int lastRet = -1;
int expectedModCount = SubList.this.modCount;
public boolean hasNext() {
return cursor != SubList.this.size;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public E next() {
checkForComodification();
int i = cursor;
if (i >= SubList.this.size)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
Object[] elementData = root.elementData;
if (offset + i >= elementData.length)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
cursor = i + 1;
return (E) elementData[offset + (lastRet = i)];
}
public boolean hasPrevious() {
return cursor != 0;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public E previous() {
checkForComodification();
int i = cursor - 1;
if (i < 0)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
Object[] elementData = root.elementData;
if (offset + i >= elementData.length)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
cursor = i;
return (E) elementData[offset + (lastRet = i)];
}
public void forEachRemaining(Consumer<? super E> action) {
Objects.requireNonNull(action);
final int size = SubList.this.size;
int i = cursor;
if (i < size) {
final Object[] es = root.elementData;
if (offset + i >= es.length)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
for (; i < size && root.modCount == expectedModCount; i++)
action.accept(elementAt(es, offset + i));
// update once at end to reduce heap write traffic
cursor = i;
lastRet = i - 1;
checkForComodification();
}
}
public int nextIndex() {
return cursor;
}
public int previousIndex() {
return cursor - 1;
}
public void remove() {
if (lastRet < 0)
throw new IllegalStateException();
checkForComodification();
try {
SubList.this.remove(lastRet);
cursor = lastRet;
lastRet = -1;
expectedModCount = SubList.this.modCount;
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
public void set(E e) {
if (lastRet < 0)
throw new IllegalStateException();
checkForComodification();
try {
root.set(offset + lastRet, e);
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
public void add(E e) {
checkForComodification();
try {
int i = cursor;
SubList.this.add(i, e);
cursor = i + 1;
lastRet = -1;
expectedModCount = SubList.this.modCount;
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
final void checkForComodification() {
if (root.modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
};
}
public List<E> subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
subListRangeCheck(fromIndex, toIndex, size);
return new SubList<>(this, fromIndex, toIndex);
}
private void rangeCheckForAdd(int index) {
if (index < 0 || index > this.size)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
}
private String outOfBoundsMsg(int index) {
return "Index: "+index+", Size: "+this.size;
}
private void checkForComodification() {
if (root.modCount != modCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
private void updateSizeAndModCount(int sizeChange) {
SubList<E> slist = this;
do {
slist.size += sizeChange;
slist.modCount = root.modCount;
slist = slist.parent;
} while (slist != null);
}
public Spliterator<E> spliterator() {
checkForComodification();
// This Spliterator needs to late-bind to the subList, not the outer
// ArrayList. Note that it is legal for structural changes to be made
// to a subList after spliterator() is called but before any spliterator
// operations that would causing binding are performed.
return new Spliterator<E>() {
private int index = offset; // current index, modified on advance/split
private int fence = -1; // -1 until used; then one past last index
private int expectedModCount; // initialized when fence set
private int getFence() { // initialize fence to size on first use
int hi; // (a specialized variant appears in method forEach)
if ((hi = fence) < 0) {
expectedModCount = modCount;
hi = fence = offset + size;
}
return hi;
}
public ArrayList<E>.ArrayListSpliterator trySplit() {
int hi = getFence(), lo = index, mid = (lo + hi) >>> 1;
// ArrayListSpliterator can be used here as the source is already bound
return (lo >= mid) ? null : // divide range in half unless too small
root.new ArrayListSpliterator(lo, index = mid, expectedModCount);
}
public boolean tryAdvance(Consumer<? super E> action) {
Objects.requireNonNull(action);
int hi = getFence(), i = index;
if (i < hi) {
index = i + 1;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") E e = (E)root.elementData[i];
action.accept(e);
if (root.modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
return true;
}
return false;
}
public void forEachRemaining(Consumer<? super E> action) {
Objects.requireNonNull(action);
int i, hi, mc; // hoist accesses and checks from loop
ArrayList<E> lst = root;
Object[] a;
if ((a = lst.elementData) != null) {
if ((hi = fence) < 0) {
mc = modCount;
hi = offset + size;
}
else
mc = expectedModCount;
if ((i = index) >= 0 && (index = hi) <= a.length) {
for (; i < hi; ++i) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") E e = (E) a[i];
action.accept(e);
}
if (lst.modCount == mc)
return;
}
}
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
public long estimateSize() {
return getFence() - index;
}
public int characteristics() {
return Spliterator.ORDERED | Spliterator.SIZED | Spliterator.SUBSIZED;
}
};
}
}
/**
* @throws NullPointerException {@inheritDoc}
*/
@Override
public void forEach(Consumer<? super E> action) {
Objects.requireNonNull(action);
final int expectedModCount = modCount;
final Object[] es = elementData;
final int size = this.size;
for (int i = 0; modCount == expectedModCount && i < size; i++)
action.accept(elementAt(es, i));
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
/**
* Creates a <em><a href="Spliterator.html#binding">late-binding</a></em>
* and <em>fail-fast</em> {@link Spliterator} over the elements in this
* list.
*
* <p>The {@code Spliterator} reports {@link Spliterator#SIZED},
* {@link Spliterator#SUBSIZED}, and {@link Spliterator#ORDERED}.
* Overriding implementations should document the reporting of additional
* characteristic values.
*
* @return a {@code Spliterator} over the elements in this list
* @since 1.8
*/
@Override
public Spliterator<E> spliterator() {
return new ArrayListSpliterator(0, -1, 0);
}
/** Index-based split-by-two, lazily initialized Spliterator */
final class ArrayListSpliterator implements Spliterator<E> {
/*
* If ArrayLists were immutable, or structurally immutable (no
* adds, removes, etc), we could implement their spliterators
* with Arrays.spliterator. Instead we detect as much
* interference during traversal as practical without
* sacrificing much performance. We rely primarily on
* modCounts. These are not guaranteed to detect concurrency
* violations, and are sometimes overly conservative about
* within-thread interference, but detect enough problems to
* be worthwhile in practice. To carry this out, we (1) lazily
* initialize fence and expectedModCount until the latest
* point that we need to commit to the state we are checking
* against; thus improving precision. (2) We perform only a single
* ConcurrentModificationException check at the end of forEach
* (the most performance-sensitive method). When using forEach
* (as opposed to iterators), we can normally only detect
* interference after actions, not before. Further
* CME-triggering checks apply to all other possible
* violations of assumptions for example null or too-small
* elementData array given its size(), that could only have
* occurred due to interference. This allows the inner loop
* of forEach to run without any further checks, and
* simplifies lambda-resolution. While this does entail a
* number of checks, note that in the common case of
* list.stream().forEach(a), no checks or other computation
* occur anywhere other than inside forEach itself. The other
* less-often-used methods cannot take advantage of most of
* these streamlinings.
*/
private int index; // current index, modified on advance/split
private int fence; // -1 until used; then one past last index
private int expectedModCount; // initialized when fence set
/** Creates new spliterator covering the given range. */
ArrayListSpliterator(int origin, int fence, int expectedModCount) {
this.index = origin;
this.fence = fence;
this.expectedModCount = expectedModCount;
}
private int getFence() { // initialize fence to size on first use
int hi; // (a specialized variant appears in method forEach)
if ((hi = fence) < 0) {
expectedModCount = modCount;
hi = fence = size;
}
return hi;
}
public ArrayListSpliterator trySplit() {
int hi = getFence(), lo = index, mid = (lo + hi) >>> 1;
return (lo >= mid) ? null : // divide range in half unless too small
new ArrayListSpliterator(lo, index = mid, expectedModCount);
}
public boolean tryAdvance(Consumer<? super E> action) {
if (action == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
int hi = getFence(), i = index;
if (i < hi) {
index = i + 1;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") E e = (E)elementData[i];
action.accept(e);
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
return true;
}
return false;
}
public void forEachRemaining(Consumer<? super E> action) {
int i, hi, mc; // hoist accesses and checks from loop
Object[] a;
if (action == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
if ((a = elementData) != null) {
if ((hi = fence) < 0) {
mc = modCount;
hi = size;
}
else
mc = expectedModCount;
if ((i = index) >= 0 && (index = hi) <= a.length) {
for (; i < hi; ++i) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") E e = (E) a[i];
action.accept(e);
}
if (modCount == mc)
return;
}
}
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
public long estimateSize() {
return getFence() - index;
}
public int characteristics() {
return Spliterator.ORDERED | Spliterator.SIZED | Spliterator.SUBSIZED;
}
}
// A tiny bit set implementation
private static long[] nBits(int n) {
return new long[((n - 1) >> 6) + 1];
}
private static void setBit(long[] bits, int i) {
bits[i >> 6] |= 1L << i;
}
private static boolean isClear(long[] bits, int i) {
return (bits[i >> 6] & (1L << i)) == 0;
}
/**
* @throws NullPointerException {@inheritDoc}
*/
@Override
public boolean removeIf(Predicate<? super E> filter) {
return removeIf(filter, 0, size);
}
/**
* Removes all elements satisfying the given predicate, from index
* i (inclusive) to index end (exclusive).
*/
boolean removeIf(Predicate<? super E> filter, int i, final int end) {
Objects.requireNonNull(filter);
int expectedModCount = modCount;
final Object[] es = elementData;
// Optimize for initial run of survivors
for (; i < end && !filter.test(elementAt(es, i)); i++)
;
// Tolerate predicates that reentrantly access the collection for
// read (but writers still get CME), so traverse once to find
// elements to delete, a second pass to physically expunge.
if (i < end) {
final int beg = i;
final long[] deathRow = nBits(end - beg);
deathRow[0] = 1L; // set bit 0
for (i = beg + 1; i < end; i++)
if (filter.test(elementAt(es, i)))
setBit(deathRow, i - beg);
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
modCount++;
int w = beg;
for (i = beg; i < end; i++)
if (isClear(deathRow, i - beg))
es[w++] = es[i];
shiftTailOverGap(es, w, end);
return true;
} else {
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
return false;
}
}
@Override
public void replaceAll(UnaryOperator<E> operator) {
replaceAllRange(operator, 0, size);
// TODO(8203662): remove increment of modCount from ...
modCount++;
}
private void replaceAllRange(UnaryOperator<E> operator, int i, int end) {
Objects.requireNonNull(operator);
final int expectedModCount = modCount;
final Object[] es = elementData;
for (; modCount == expectedModCount && i < end; i++)
es[i] = operator.apply(elementAt(es, i));
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
@Override
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public void sort(Comparator<? super E> c) {
final int expectedModCount = modCount;
Arrays.sort((E[]) elementData, 0, size, c);
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
modCount++;
}
void checkInvariants() {
// assert size >= 0;
// assert size == elementData.length || elementData[size] == null;
}
}
menti.com 2335 3741
How big can an ArrayList get?
# Queue
List<Boolean> list1k = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i=0; i<1024;i++) {
list1k.add(Boolean.TRUE);
}
System.out.println(list1k.size());
List<Boolean> list1M = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i=0; i<1024*1024;i++) {
list1M.add(Boolean.TRUE);
}
System.out.println(list1M.size());
List<Boolean> list1G = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i=0; i<1024*1024*1024;i++) {
list1G.add(Boolean.TRUE);
}
System.out.println(list1G.size());
1024
1048576
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.OutOfMemoryError: Java heap space
at java.base/java.util.Arrays.copyOf(Arrays.java:3513)
at java.base/java.util.Arrays.copyOf(Arrays.java:3482)
at java.base/java.util.ArrayList.grow(ArrayList.java:237)
at java.base/java.util.ArrayList.grow(ArrayList.java:244)
at java.base/java.util.ArrayList.add(ArrayList.java:483)
at java.base/java.util.ArrayList.add(ArrayList.java:496)
at generics/qa2.BigList.main(BigList.java:24)
Text
$ java -X
-Xmn<size> sets the initial and maximum size (in bytes) of the heap
for the young generation (nursery)
-Xms<size> set initial Java heap size
-Xmx<size> set maximum Java heap size
-Xnoclassgc disable class garbage collection
$ java -Xmx8g BigList
1024
1048576
1073741824
When do we use Records?
public record Customer(String name, String address) {}# Records
public class Customer {
private String name;
private String address;
public Customer(String name, String address) {
this.name = name;
this.address = address;
}
public String name() { return this.name; }
public String address() { return this.address; }
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(address, name);
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (this == obj)
return true;
if (obj == null)
return false;
if (getClass() != obj.getClass())
return false;
Customer other = (Customer) obj;
return Objects.equals(address, other.address) && Objects.equals(name, other.name);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Customer [name=" + name + ", address=" + address + "]";
}
}
menti.com 2335 3741
When do we use Records?
public record Customer(String name, String address) {}# Records
Customer2 customer = new Customer2("Stian", "Manchester");
System.out.println(customer);
System.out.println(customer.address());
System.out.println(customer.equals(new Customer2("Stian", "Manchester")));Customer2[name=Stian, address=Manchester]
Manchester
true
menti.com 2335 3741
When do we not use Records?
# Records
public record Customer(String name, String address) {}
public void stringName(String newName) {
this.name = newName;
// Compile error: The final field Customer2.name cannot be assigned
}
}menti.com 2335 3741
When do we not use Records?
# Records
public record Customer(String name, String address) {}
public void stringName(String newName) {
this.name = newName;
// Compile error: The final field Customer2.name cannot be assigned
}
}record Person(String name) {}
public record Customer2(String address) extends Person {}
// Syntax error on token "extends", implements expectedmenti.com 2335 3741
When do we not use Records?
# Records
public record Customer(String name, String address) {}
public void stringName(String newName) {
this.name = newName;
// Compile error: The final field Customer2.name cannot be assigned
}
}record Person(String name) {}
public record Customer2(String address) extends Person {}
// Syntax error on token "extends", implements expectedpublic record Customer3(String customerId, String name, String address) {
public Customer3 {
Objects.requireNonNull(customerId);
Objects.requireNonNull(name);
Objects.requireNonNull(address);
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object other) {
if (! (other instanceof Customer3)) {
return false;
}
Customer3 otherCustomer = (Customer3) other;
return customerId().equals(otherCustomer.customerId());
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return customerId().hashCode();
}
}
Where do we place the diamond operator?
# Generics
List<String> listA = new ArrayList<>();
// Implies:
List<String> listB = new ArrayList<String>();
// But not:
List<String> listC = new ArrayList();
// Type safety: The expression of type ArrayList needs unchecked
// conversion to conform to List<String>
List listD = new ArrayList<String>();
// Generics in constructor not reflected in type
List listE = new ArrayList();
// List is a raw type. References to generic type List<E>
// should be parameterized
List<String> listF = listE;
// Type safety: The expression of type List needs unchecked
// conversion to conform to List<String>
menti.com 2335 3741
Downcasting with generics
# Generics
ArrayList<String> myList = new ArrayList<>();
✅ myList.add("Hello");
✅ myList.set(0, "World");
✅ ensureCapacity(1024*1024);
List<String> myList2 = myList;
✅ myList2.set(0, "World");
🛑 ensureCapacity(1024*1024);
Collection<String> myList3 = new ArrayList<>();
✅ myList3.add("Hello");
🛑 myList3.set(0, "World");
Object myList4 = myList3;
🛑 myList3.add("Hello");
✅ System.out.println(myList3.toString());
What if I don't know type yet?
# Generics
public class ListFun<T> {
List<T> listA = new ArrayList<T>();
public static void main(String[] args) {
ListFun<String> strings = new ListFun<>();
ListFun<?> undecided = new ListFun<>();
ListFun badPractice = new ListFun();
// ListFun is a raw type. References to generic
// type ListFun<T> should be parameterized
}
}
Danger: Generics in generics
# Generics
public interface RentalProperty {
BigDecimal monthlyRate();
Optional<House> isPartOf();
}
public record House(BigDecimal monthlyRate, int floors) {
public Optional<House> isPartOf() {
return Optional.empty();
}
}
menti.com 2335 3741
Danger: Generics in generics
# Generics
public interface RentalProperty<T> {
BigDecimal monthlyRate();
Optional<T> isPartOf();
}
public record House(BigDecimal monthlyRate, int floors) implements RentalProperty {
public Optional<House> isPartOf() {
return Optional.empty();
}
}
public interface RentalProperty {
BigDecimal monthlyRate();
Optional<House> isPartOf();
}
public record House(BigDecimal monthlyRate, int floors) {
public Optional<House> isPartOf() {
return Optional.empty();
}
}
menti.com 2335 3741
Danger: Generics in generics
# Generics
public interface RentalProperty<T extends RentalProperty> {
BigDecimal monthlyRate();
Optional<T> isPartOf();
}
public record House(BigDecimal monthlyRate, int floors) implements RentalProperty {
public Optional<House> isPartOf() {
return Optional.empty();
}
}
public class Portfolio> {
private BigDecimal rentPercentage(RentalProperty rental) {
Optional<? extends RentalProperty> inBuilding = rental.isPartOf();
if (inBuilding.isEmpty()) {
return new BigDecimal("100.00");
} else {
RentalProperty house = inBuilding.get();
}
}
}menti.com 2335 3741
Streams
# Generics
private void printRentShare() {
for (RentalProperty rental : portfolio) {
BigDecimal share = rentPercentage1(rental);
System.out.print(share + "% ");
System.out.println(rental);
}
}
private void printRentShare2() {
stream()
.filter(rental -> rental.isPartOf().isPresent())
.map(this::rentPercentage)
.map(rate -> rate + "%")
.forEach(System.out::println);
}menti.com 2335 3741
Questions from Menti
Next week:
Week 9. Building GUIs with Java: Introduction to JavaFX item options